Unit 1: Kinematics
3.8(10)
Card Sorting
1/14
Last updated 5:47 AM on 4/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
1
New cards
Kinematics
the study of motion without considering the forces causing the motion.
2
New cards
Displacement
the change in position of an object. It is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
3
New cards
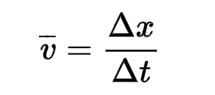
Velocity
the rate at which an object's displacement changes over time. It is a vector quantity.
4
New cards
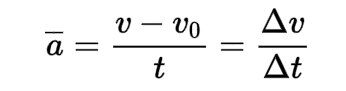
Acceleration
the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time. It is a vector quantity.
5
New cards
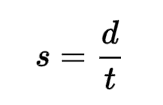
Speed
the rate at which an object travels over a distance. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it only has magnitude and no direction.
6
New cards
Scalar quantity
a quantity that has only magnitude and no direction, such as speed or mass.
7
New cards
Vector quantity
a quantity that has both magnitude and direction, such as velocity or force.
8
New cards
Position
the location of an object in space. It is often measured relative to a reference point.
9
New cards
Time
a dimension in which events occur in a sequence. It is often measured in seconds.
10
New cards
Distance
the total length traveled by an object, regardless of direction. It is a scalar quantity.
11
New cards
Displacement-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's displacement over time.
12
New cards
Velocity-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's velocity over time.
13
New cards
Acceleration-time graph
a graph that shows the change in an object's acceleration over time.
14
New cards
Uniform motion
when an object travels with a constant velocity (i.e. no acceleration).
15
New cards
Uniformly accelerated motion
when an object accelerates at a constant rate.