Pharmacology Fundamentals
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch. 1-3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Steps in the nursing process
Assessment
Analysis
Planning
Nursing interventions/implementation
Evaluation
Subjective:
Based on personal feelings, opinions, or experiences (e.g., “I feel tired”).
Objective:
Based on measurable facts or direct observations (e.g., “Heart rate is 80 bpm”).
The 5 steps of the nursing process are:
Assessment – Gather information about the patient.
Diagnosis – Identify the patient’s problems.
Planning – Set goals and plan care.
Implementation – Carry out the care plan.
Evaluation – Check if goals were met and adjust care.
Drugs in high demand (4)
• Obesity and Diabetes drugs
• Cancer drugs
• Neurologic drugs
• Immunologic drugs
New drugs needed.. (3)
• Antibiotics
• Pain-relievers
• Anti-depressants/anxiety
Drug Development Process (5)
Discovery and development
Preclinical research
Clinical development
FDA review
Post-market monitoring
FDA-approved Medications
• Promotes safety and protects public health
• Regulates new medication research and development
• All FDA-approved drugs have been tested and deemed safe
• Some FDA-approved drugs have been later recalled
Principles of ethics (know definitions as well) (4)
Autonomy – Respect patient’s choices
Beneficence – Do good for the patient
Nonmaleficence – Do no harm
Justice – Treat patients fairly
ANA Code of Ethics
“Was developed as a guide for carrying out nursing responsibilities in a manner consistent with quality in nursing care and the ethical obligations of the profession.”
• Adopted in 1950
• Revised in 2015
The Nurse’s role in clinical research (4)
• Responsible for patient safety
• Responsible for integrity of research protocol
• Avoid bias
• Protect special populations (children, marginalized groups)
Over-the-Counter Drugs
• Found to be safe and appropriate for use without direct supervision of health care provider
• Available without a prescription
• In 2002, FDA standardized OTC labeling
• Provide consumers with better information
• Describes benefits and risks with OTC drugs
• Nurse’s role
• Be aware of OTC drugs and their implications (interactions, side effects)
Pharmacokinetics & processes (4)
drug movement through the body and what the body does to the drug
• Processes include absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion (ADME)
Pharmacodynamics & phases (3)
“drug power”
• What the drug does to the body as drug moves throughout the body
• Primary effect
• Desirable response
• Secondary effect
• Desirable or undesirable
Phase involves: receptor binding, postreceptor effects, chemical reactions
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption
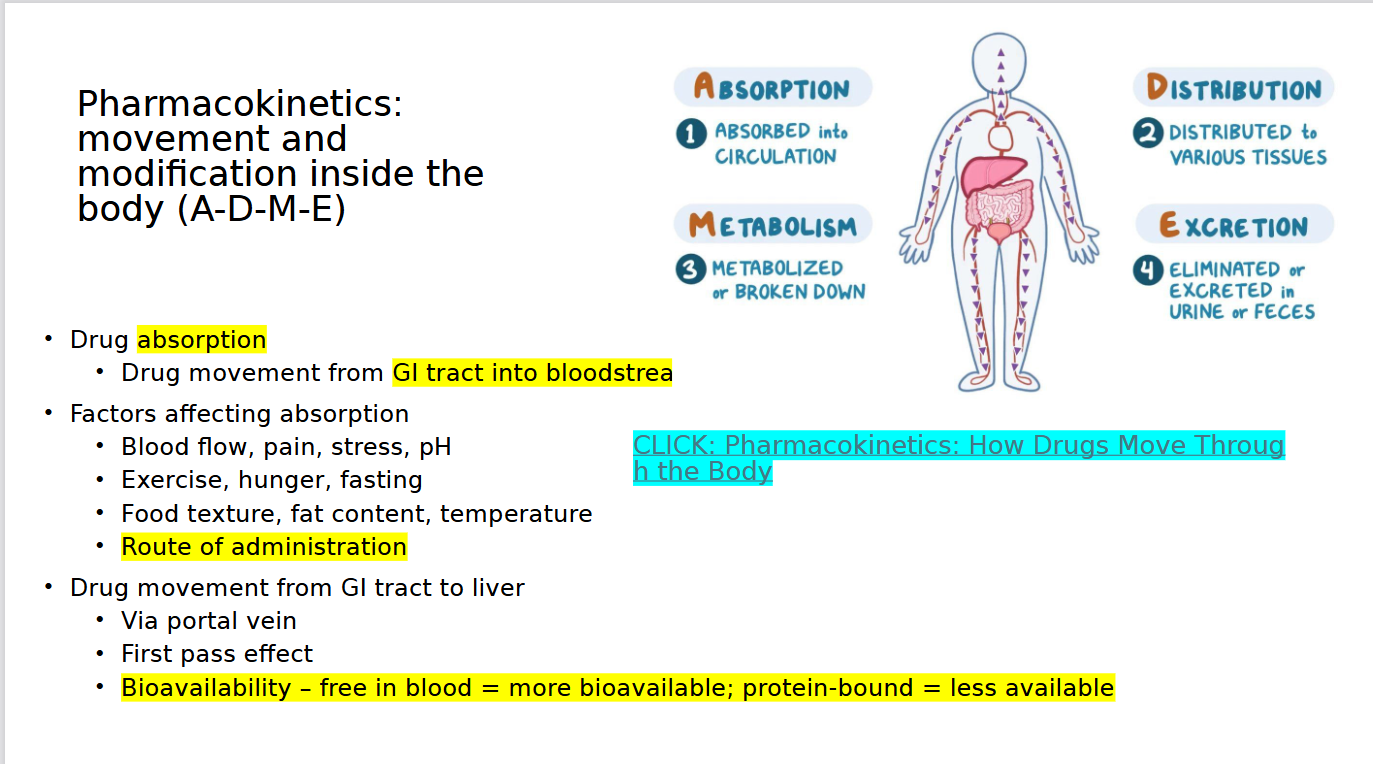
Pharmacokinetics: metabolism (biotransformation)
• Process of body chemically changing drug into a form to be excreted
• First pass effect
• Half-life (t½)
• Steady state
• Loading dose
• Protein-bound vs free
bioavailability
The amount of a drug that actually reaches the bloodstream and can have an effect.
First pass effect
When a drug is broken down by the liver before it reaches the bloodstream, reducing its effectiveness.
Protein-bound vs free
Protein-bound: Drug attached to proteins in the blood → inactive.
Free: Drug not attached → active and can work in the body.
Drug Half Life
The time it takes for half of a drug to be removed from the body.
Pharmacokinetics: Drug excretion (elimination) (6)
• **Kidneys
• **Liver (bile)
• Lungs
• Saliva
• Sweat
• Breast milk
Pharmacodynamics: Drug response relationship
Body’s physiologic response to changes in drug
concentration at site of action
Pharmacodynamics: Potency
• Amount of drug needed to elicit specific physiologic response
Pharmacodynamics: Maximal efficacy
• Point which increasing a drug’s dosage no longer
increases desired therapeutic response
Pharmacodynamics: Therapeutic index
• Relationship between therapeutic dose and toxic dose
Pharmacodynamics: Onset
Time it takes for drug to reach minimum effective concentration
Pharmacodynamics: Peak
Highest drug concentration in blood
(risk of toxicity)
Pharmacodynamics: Duration
Length of time drug exerts a therapeutic effect
Pharmacodynamics: Trough
Lowest concentration before next dose
(risk of ineffectiveness)
Pharmacodynamics: Mechanisms of drug action
• Stimulation
• Depression
• Irritation
• Replacement
• Cytotoxic action
• Antimicrobial action
• Modification of immune status
Pharmacodynamics: Agonists
• Activate receptors
• Produce desired response
Pharmacodynamics: Partial Agonists
• Elicit only moderate activity when binding to receptors
• Prevent receptor activation by other drugs
Pharmacodynamics: Antagonists
• Prevent receptor activation
• Block response
Cholinergic receptors and where are they located
Receptors that respond to acetylcholine (ACh).
bladder, heart, blood vessels, stomach, bronchi, and eyes
Epinephrine affects three different receptors: what are they
alpha1, beta1, and beta2.
Alpha1:
Constricts blood vessels → raises blood pressure.
Alpha2:
Reduces norepinephrine → lowers blood pressure.
Beta1:
Increases heart rate and heart strength.
Beta2:
Relaxes lungs and other smooth muscles → opens airways.
Side effects
• Secondary drug effects
Adverse reactions
• Mild to severe
• Unintentional, unexpected
• Undesirable effects
Drug toxicity
• Drug level exceeds therapeutic range
Tolerance:
When the body responds less to a drug over time, so a higher dose is needed to get the same effect.
Medication Safety and Prevention: Common hazards
• Drug interactions
• Overdose
• Allergic reactions
Medication Safety and Prevention: Preventive strategies
• Medication reconciliation
• Barcoding systems
• Double-checking high-alert meds
7 Rights of Medication Administration:
Right patient – confirm who will get the med.
Right medication – check the correct medication.
Right dose – verify the correct amount.
Right route – give by the correct method (oral, IV, etc.).
Right time – give at the correct time/frequency.
Right documentation – record administration accurately
Right reason – ensure the drug is given for the correct purpose.