US Supreme Court: Judicial Review, Case Process & Influences
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What power does the U.S. Supreme Court have regarding acts of Congress?
The power to review acts of Congress and the executive branch and declare them invalid if they violate the Constitution.
What landmark case established the principle of judicial review?
Marbury v. Madison (1803).
What is the ruling of Marbury v. Madison regarding the Constitution?
The Constitution is the nation's highest law, and any act of Congress that violates it is invalid.
What are the implications of Marbury v. Madison?
1) The Supreme Court is the final word on the Constitution. 2) It can declare national, state, and local laws invalid if they violate the Constitution.
What percentage of laws passed by Congress have been struck down by the Supreme Court?
Less than 1%.
Who is the current Chief Justice of the United States?
John Roberts.
How many justices are currently on the Supreme Court?
Nine justices.
What is original jurisdiction in the context of the Supreme Court?
It refers to cases that can be heard directly by the Supreme Court, typically involving the balance of power between state and federal governments.
How many cases are appealed to the Supreme Court each year?
About 8,000 cases.
How many cases does the Supreme Court typically accept each year?
About 80 cases.
What is the 'cert pool' in the Supreme Court?
A system where law clerks screen cases petitioned to the Court and make recommendations to justices about which cases to take.
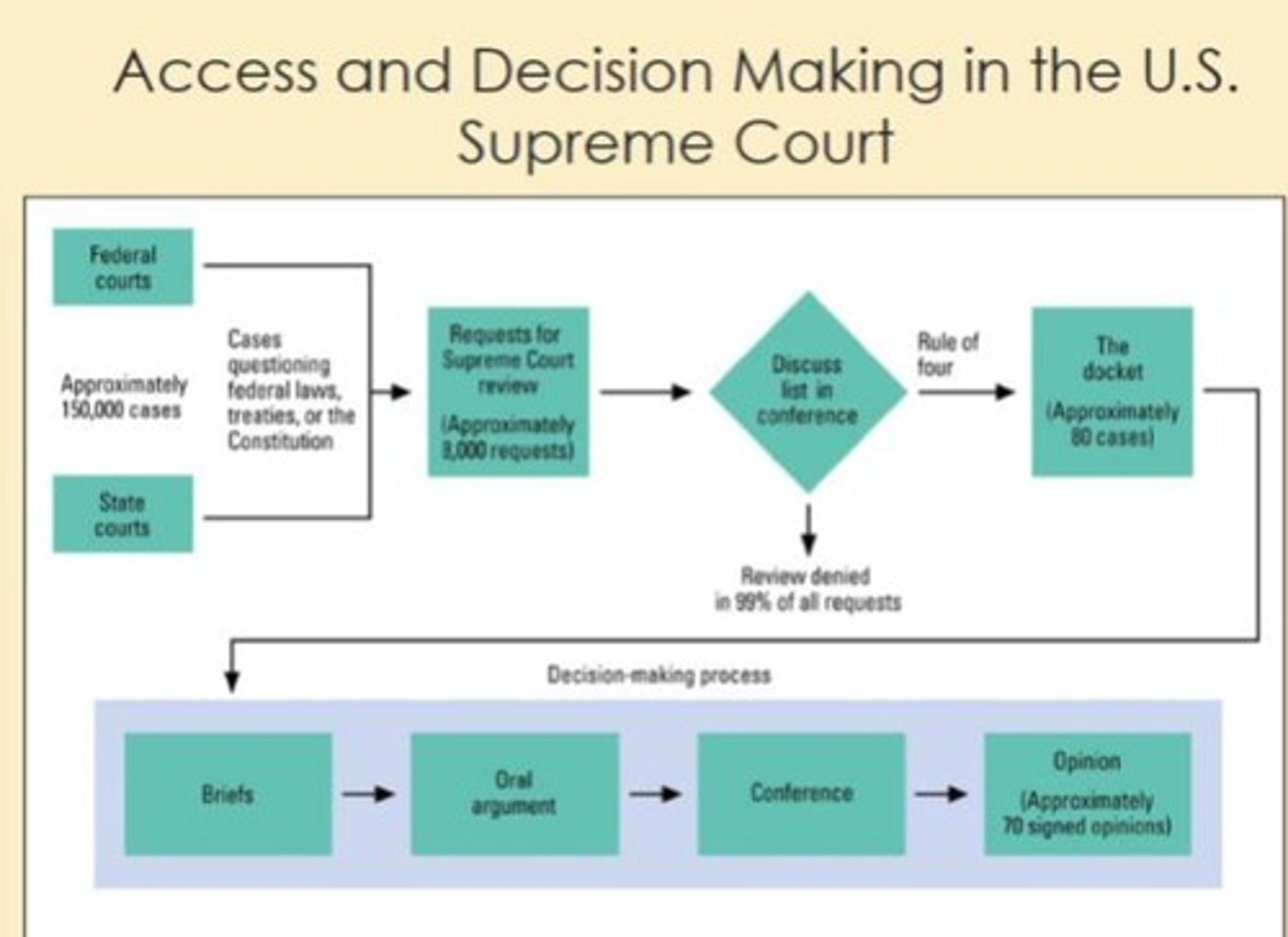
What is required for the Supreme Court to grant certiorari?
At least 4 justices must agree to hear the case.
What is the purpose of written briefs in Supreme Court cases?
To present formal arguments supporting each side of the case.
What are amicus briefs?
Briefs filed by individuals or groups not party to the suit but with an interest in the case.
What happens during oral arguments in the Supreme Court?
Each side has 30 minutes to present their case, and justices can ask questions.
What is a 'straw vote' in the context of Supreme Court conferences?
An unofficial vote taken by justices to gauge initial opinions on a case.
What types of opinions can be drafted by justices?
Majority opinion, dissenting opinion, and sometimes a concurring opinion.
What is the role of precedent in Supreme Court decisions?
It serves as a guiding principle based on previous court rulings, though the Court can overturn precedent.
What is the 'Attitudinal Model' in relation to justices' decisions?
It suggests that a judge's personal political beliefs and ideology influence their decisions.
What are the two main interpretations of the Constitution?
1) Strict Construction: Literal interpretation. 2) Living Constitution: Interpretation based on contemporary values.
What is judicial activism?
The belief that the Court should assert its interpretation of law, even if it overrules elected branches.
What is judicial restraint?
The belief that the Court's role is to interpret laws, not make them, and to defer to elected branches.
How does public opinion relate to Supreme Court decisions?
Supreme Court decisions are generally consistent with public opinion, but about one-third go against the majority opinion.
What checks exist on the Supreme Court's power?
Constitutional amendments, Congress can make new laws, and the Court relies on state and local governments for implementation.