Lecture 11: Wound Healing and Surgical Inflammation
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
surgery =
creation of a wound
disruption of tissue homeostasis —> inflammation
normal surgical inflammation is
acute
mild-moderate
dependent on procedure and body system
local
short duration
reduced with primary wound closure
and self-limited
abnormal surgical inflammation
prolonged (chronic)
severe
signs of infection
systemic signs
underlying pathology
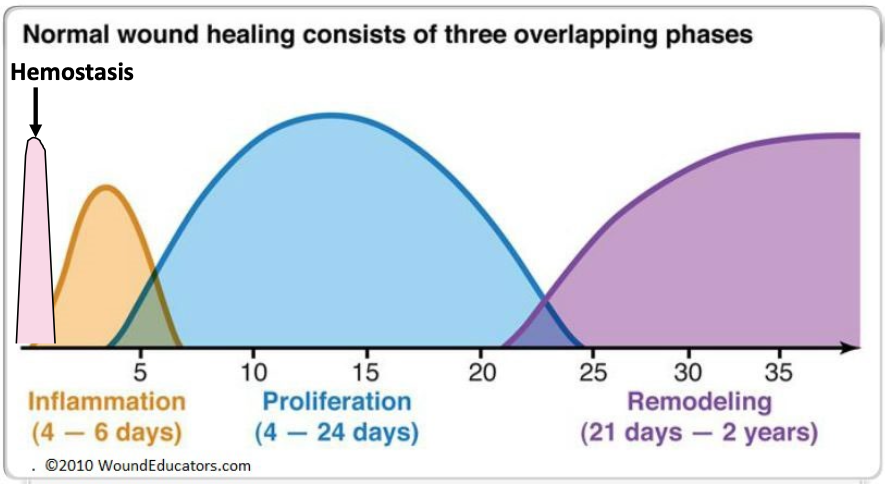
phases of wound healing
what is the body’s goal during bleeding?
hemostasis, to stop bleeding while maintaining perfusion
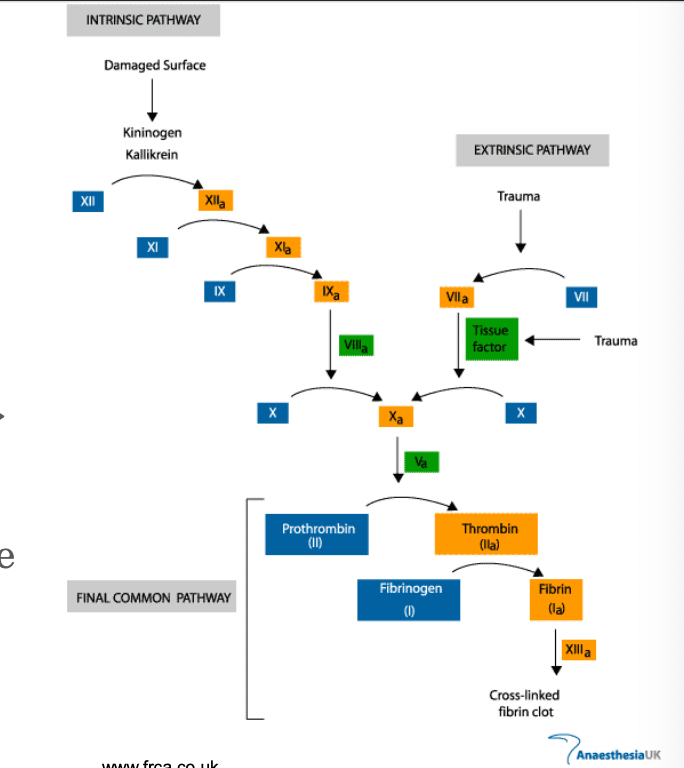
Hemostasis involves:
endothelial cell disruption
immediate vasoconstriction
exposure of vWF —> platelet activation and aggregation
coagulation cascade
hemostasis —> inflammation, how?
endothelial cells release vasodilators —> vasodilation
—> increased blood flow )- redness & heat
mediated by: histamine, NO, LTs, PGs, complement
hemostasis —> inflammation
post-capillary venule leakiness
increases inflammatory cell and inflammatory mediator infiltration
protein leakage
hemostasis —> inflammation
protein leakage
decreased osmotic pressure
increased blood viscosity
increased interstitial pressure
= edema formation (swelling)
edema
facilitates delivery of soluble factors and cells
PAIN & loss of function
vascular congestion
fluid loss to edema
hemoconcentration
reduced velocity of blood flow
inflammation is also called:
debridement phase
2 phases of debridement phase
early —> neutrophil recruitment
late —> monocyte transformation
functions of inflammation:
prepares the body for next phases of wound healing
removes dead tissue and foreign material
severity of truama —> intensity of inflammation —>
extent of scar tissue formed
leukocytes during inflammation are recruited from:
from circulation by chemoattractants (from coagulation)
initiate: Rolling, Activation, Tight Adhesion, and Transmigration of cells through microvascular endothelium
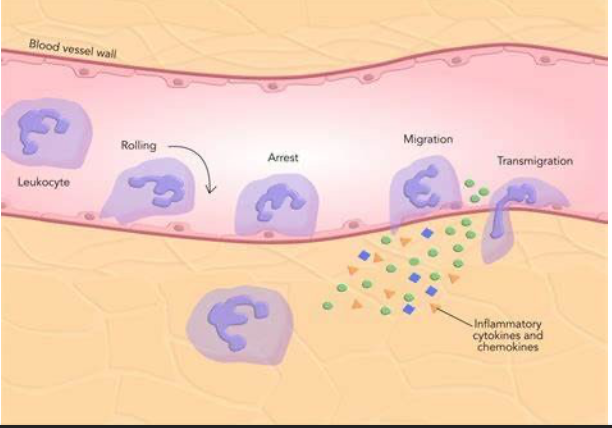
neutrophil diapedesis is encouraged by what during inflammation?
increased capillary permeability
diapedesis:
the passage of blood cells through intact capillary walls
when do neutrophils join the party during inflammation?
1-2 days after injury
neutrophil jobs
they are the first line of defense against contaminated wounds
they destroy debris
they phagocytose bacteria
the latter 2 jobs process ends when wound is cleaned up
what ends the early phase of inflammation?
when neutrophils destroy debris and phagocytose bacteria
macrophages during inflammation, how do they get there?
monocytes migrate from vasculature and become macrophages
what do macrophages do?
pro-inflammatory functions
stimulate proliferation of dermal, endodermal, and epithelial tissues
help with remodeling phase
macs jobs help to orchestrate all the phases of wound healing!
how do we reach resolution of inflammation?
each of the pathways needs to be halted or reversed
apoptosis of cells
doesn’t always work!
can lead to chronic, suppurative inflammation and a non-healing wound
excessive granulation tissue (proud flesh in horses)
which phase of wound healing is the most easily manipulated by clinicians?
the inflammatory phase
what can clinicians do to modulate the inflammatory phase?
1) proper surgical debridement
2) good hemostasis
3) adequate drainage
4) medications
NSAID's
Steroids
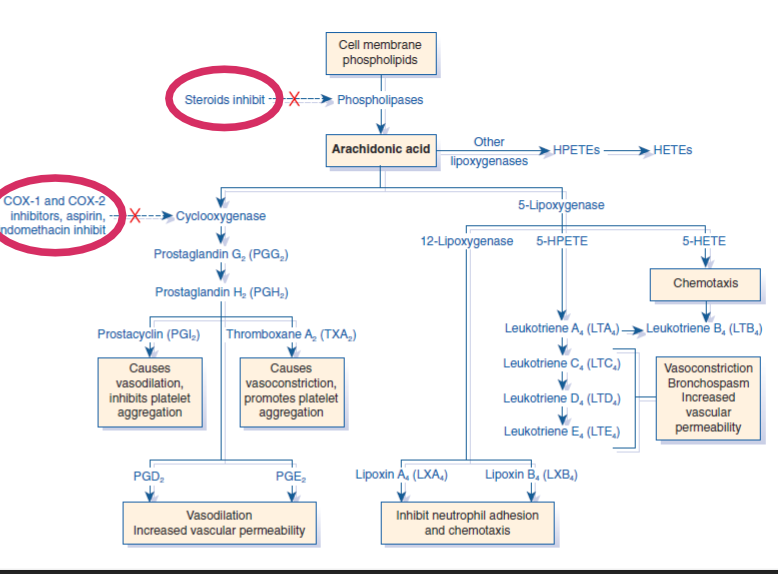
how do steroids and COX 1 and 2 inhibitor affect inflammation
proliferation phase includes
fibroplasia
necessary for other processes
angiogenesis
epithelialization
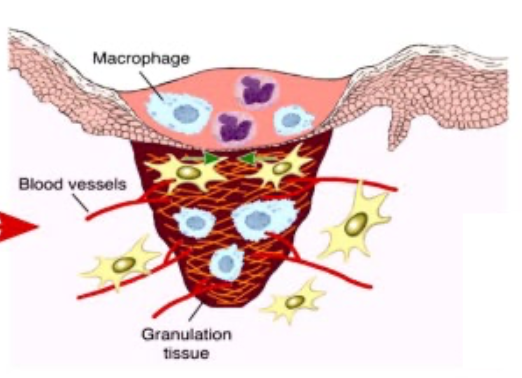
fibroplasia, what is it?
formation of granulation tissue by fibroblasts
scaffold
temporary barrier infection
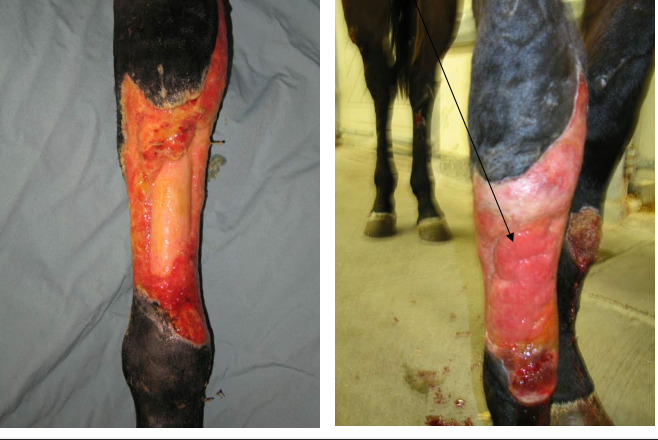
granulation tissue
fibroplasia is made by 3 elements:
1) macrophages - debride, produce cytokines and growth factors that stimulate angiogenesis and fibroplasia
2) fibroblasts - proliferate and make new extracellular matrix
3) blood vessels - carry O2 and nutrients for cell metabolism and growth
when do you start to see granulation tissue?
around day 5!
fibroplasia in detail
fibroblasts are directed by macrophages via cytokines and growth factors
produce ECM - initially more type III collagen (immature)
later more type I collagen (mature)
time of increasing wound strength with fibroplasia:
rapid gain 7 - 14 days
corresponds to time of suture removal
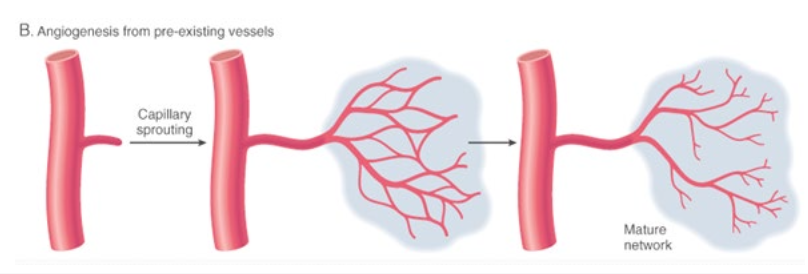
angiogenesis is:
the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing vessels
what is angiogenesis regulated by:
macrophages and endothelium
VEGF
other misc. angiogenesis growth factors
increases tissue hypoxia —> increases vessel ingrowth
what happens during epithelialization and how fast does it happen?
epithelium covers wound
reform barrier of infection
centripetal
0.1 - 0.2 mm/day
what happens during maturation?
continued epithelialization
thickening of epidermis
wound contraction
fibroblasts differentiate into myofibroblasts under influence of GF and cytokines
myofibroblasts contain a-smooth muscle actin
what happens during remodeling?
converstion of granulation tissue into scar tissue
what is involved in remodeling?
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)
collagenases
gelatinases
stromelysins
these are the demolition team!
how long does remodeling take?
up to 1 - 2 years, depending on size of wound
what is good about remodeling?
progressive increase in tensile strength of wound
when does healing stop?
when wound edges meet
ideal
when tension surrounding skin > force of myofibroblasts
not ideal
reduced #s of myofibroblasts
not ideal
granulation tissue is proliferative
epithelial cells can’t climb!!!
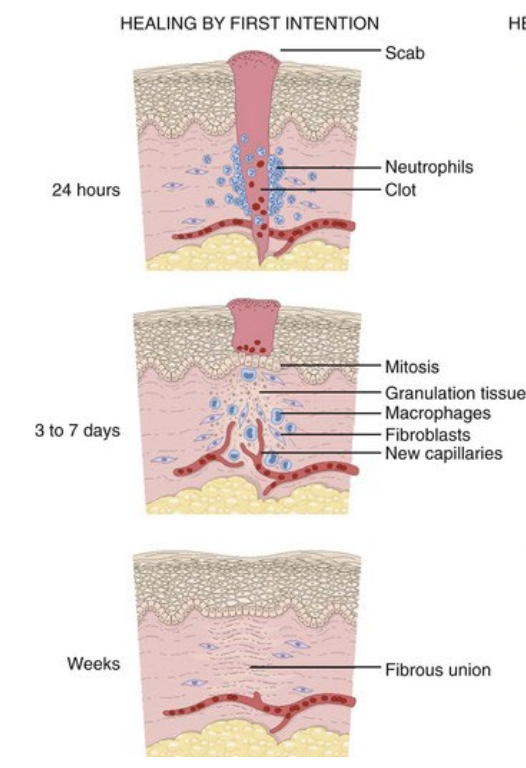
healing by first intention
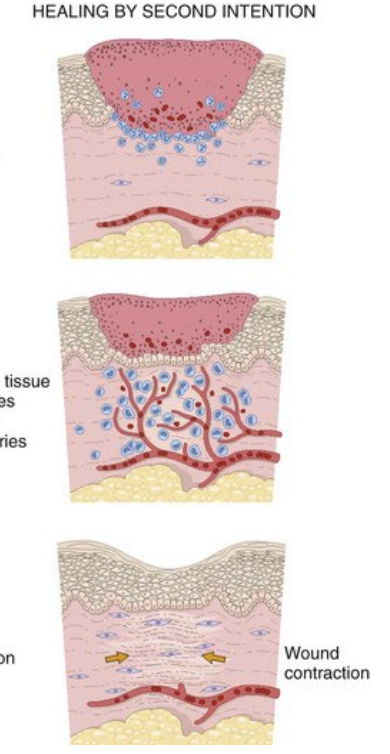
healing by second intention
dysfunction in the inflammatory response - shock
“the rude unhinging of the machinery of life” Samuel D Gross, 1872
cascade of events that begins when cells/tissue are O2 deprived from inadequate perfusion
can lead to SIRS and MOD
will discuss. ore 3rd year…
SIRS
Systemic Inflammatory Response Syndrome
causes of SIRS
normal?
many causes - one syndrome
infectious
non-infectious
generally considered excessive response
“cytokine storm”
leukocyte dysfunction
delayed resolution of inflammation
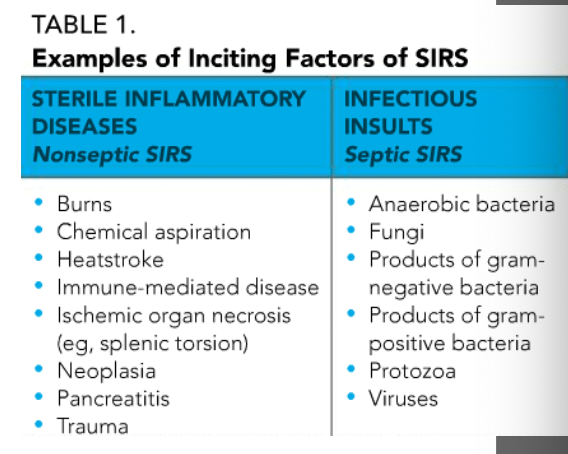
examples of inciting factors of SIRS
Clinical definition of SIRS
must meet any 2 with underlying pathologic cause:
hyper- or hyothermia
tachycardia
tachypnea
leukocytosis or leukopenia
depression
neutrophils ± left shift
hyperthemia (fever), what’s going on behind the scenes?
IL-1, IL-6, TNF-a, PGE2
act on hypothalamus
increases body’s thermostat —> fever
hypothermia can lead to
shock
hypoperfusion
central blood sequestration
BAD sign
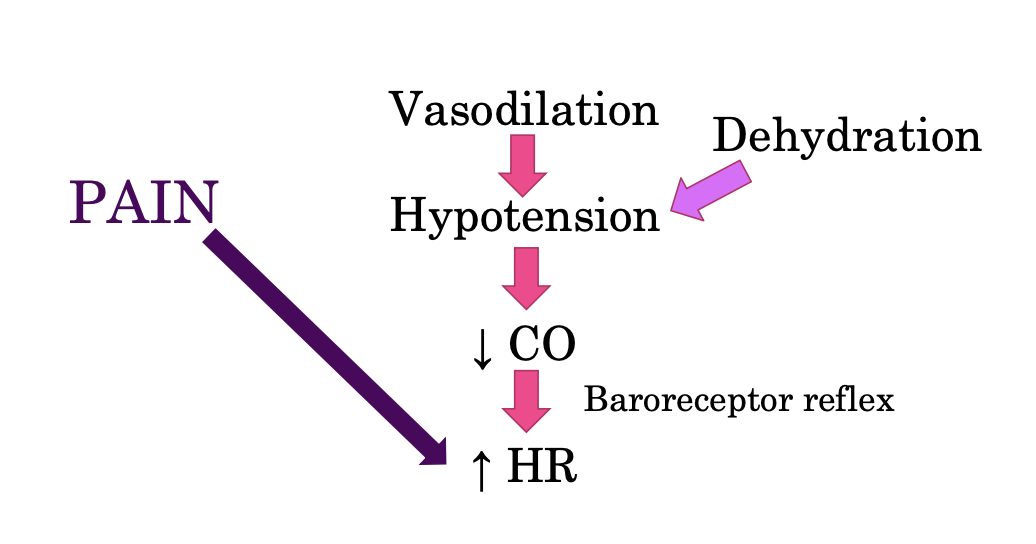
mechanism behind tachycardia
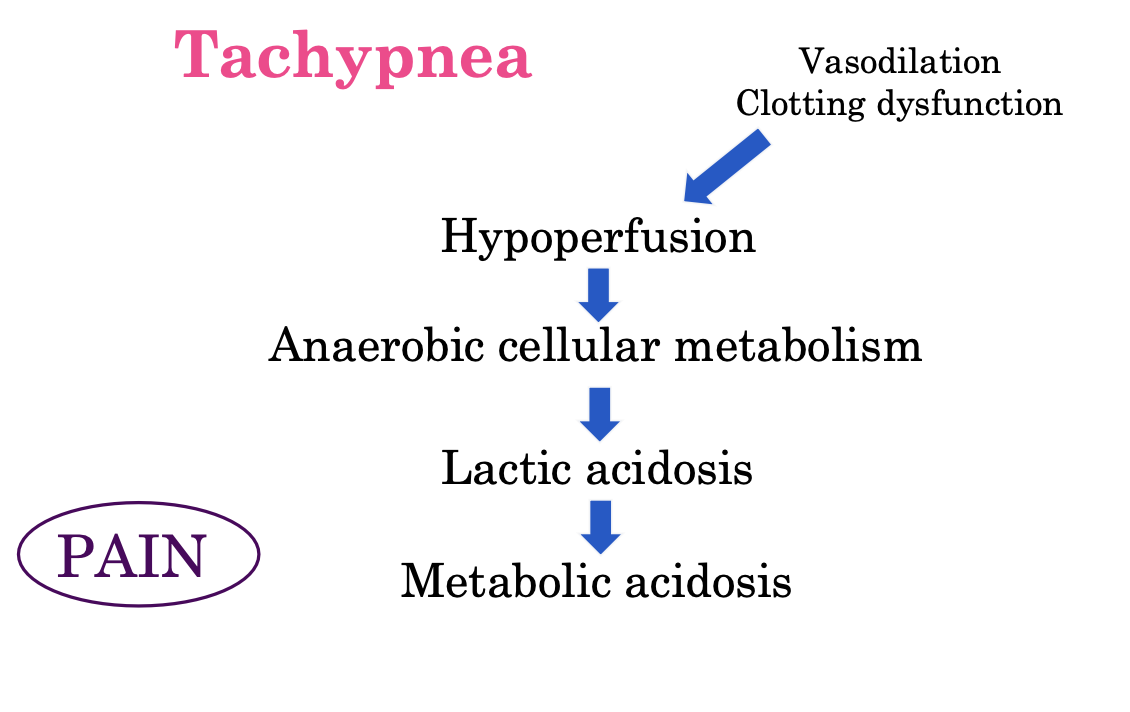
mechanism behind tachypnea
CBC alterations during shock
primarily from change in neutrophils
1st: leukopenia (<48 hours)
initial - endothelial “stickiness”
increased use
2nd: leukocytosis (>48 hours)
release from sequestered areas
bone marrow, spleen
3rd: left shift (variable)
immature neutrophils
supply < demand
mechanisms behind depression
cytokines
eicosanoids
what happens during the stress response?
IL-1 and TNF-a —> increases Adrenocorticotropic
REDUCE*** healing
anti-inflammatory
reduce activity/production of growth factors
stress leukograpm is:
variable by species
due to endogenous (or exogenous) corticosteroids
neutrophilia (usually mature, no bands)
lymphopenia
monocytosis - more common in dogs
eosinopenia
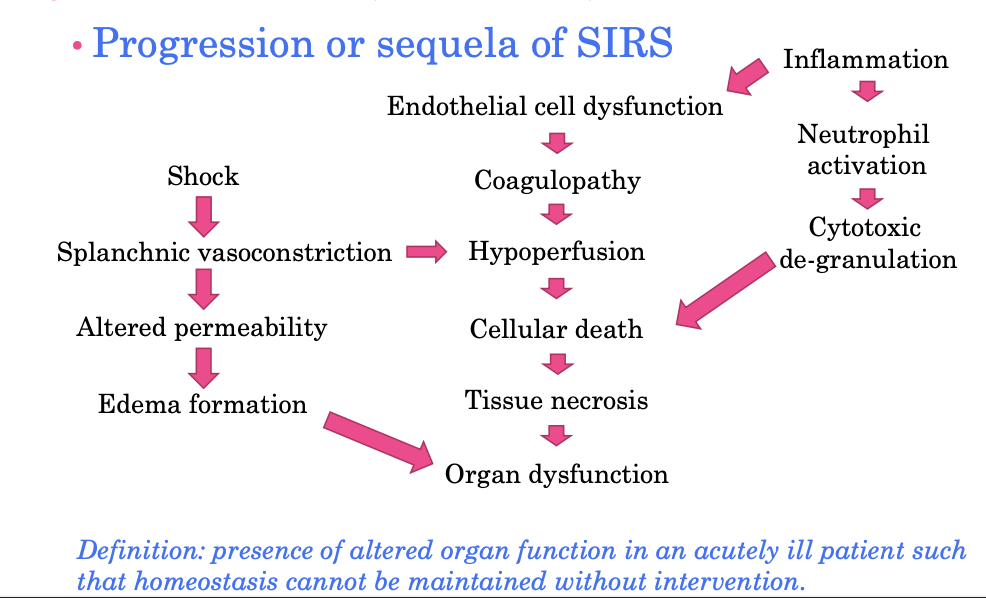
Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (FYI) MODS
progression or sequela of SIRS