TRANSITIONS IN POLYMERS
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
give some examples of natural polymers
collagen
silk
DNA
protein
natural rubber
give examples of everyday polymers
polystyrene
polyamide
low density polyethylene
give examples of aspects of dentistry that uses polymers
prosthodontics: denture bases and teeth, soft liners, custom trays, temporary restoratives
operative dentistry: dentine bonding agents, sealants, veneers
orthodontics: brackets, spacers, bracket bonding resins/ cements
endodontics: root canal sealants, rubber dams
equipment: mixing bowls, spatulas, protective eyewear
state advantages of dental resins
mechanically strong
physically stable
easily manipulated
excellent aesthetic qualities
chemically stable - in the mouth and in storage
biocompatible
reasonable cost
where are acrylic resins often used in dentistry
denture base material
what is another name for acrylic resins
PMMA
when was PMMA introduced
1936
what type of polymer is PMMA
thermoplastic amorphous polymer
what are advantages of PMMA
acceptable cost of material and processing method
good mechanical properties - rigidity, strength, wear resistance
biocompatible - tasteless, odourless, non-toxic, non-irritating, resistance to microbial colonisation
suitable manipulation/ processing properties - easy to mix, shapable, simple to process and cure
aesthetic properties - translucency and transparency
what are problems with PMMA
colour stability
shrinking problems
adhesion problems
how can the shrinking problems of PMMA be resolved
adding MMA (methyl methacrylate)
when were room temperature polymerising methacrylates introduced
1940
when were self curing dimethacrylates reinforced by a ceramic particle ‘filler’
late 1950s
when were PMMA resins replaced by more durable monomers such as bisGMA
1940
define polymer
polymer: a large, chain-like molecule made up of monomers
what type of bonds are the monomers in a polymer joined by
covalent bonds
diagram showing polymer classification
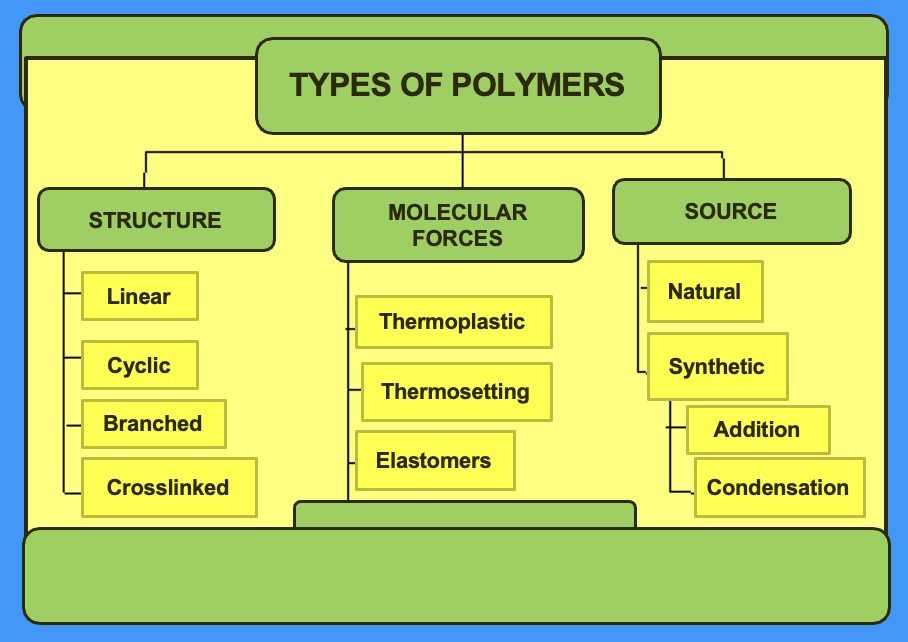
what do the physical properties of polymers depend on
how their molecules are arranged i.e. polymer structure
the strength of the forces between these molecules i.e. intermolecular forces
in a polymer, where are intermolecular forces present
weak intermolecular attract individual polymer chains together
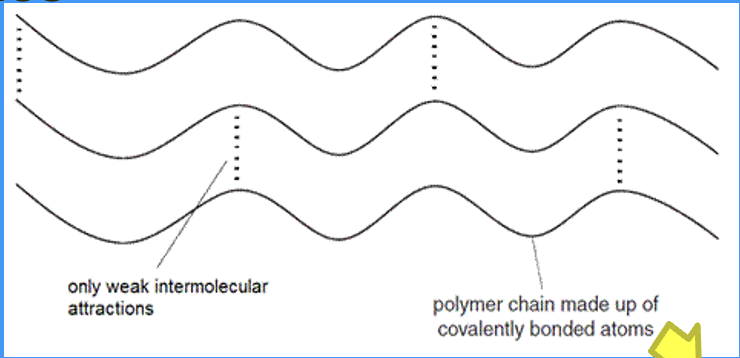
when can covalent bonds join individual polymer chains together
in cross linking, covalent bonds can join individual polymer chains together
what factors do the strength and flexibility of the polymer depend on
chain length
side groups
branching
cross-linking
outline the factors influencing strength and flexibility of the polymer
chain length: generally, the longer the chains the stronger the polymer
side groups: intramolecular forces e.g. hydrogen bonding give stronger attraction between polymer chains
branching: straight, unbranched chains can pack together more closely than highly branched chains
» polymers with higher density, more crystalline and therefore stronger
cross-linking: if polymer chains are linked together by covalent bonds, the polymer is harder and more difficult to melt
define crystallinity
crystallinity: the degree of structural order
diagram showing amorphous and crystalline structures
lines = chains of polymers
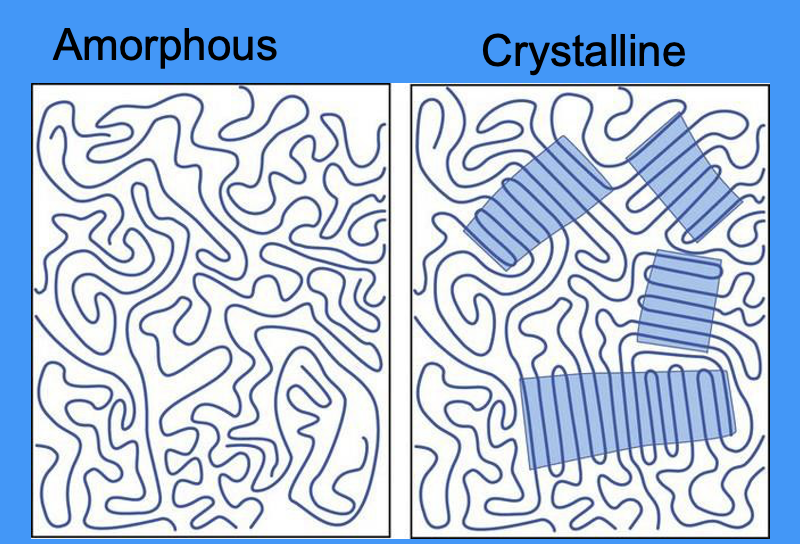
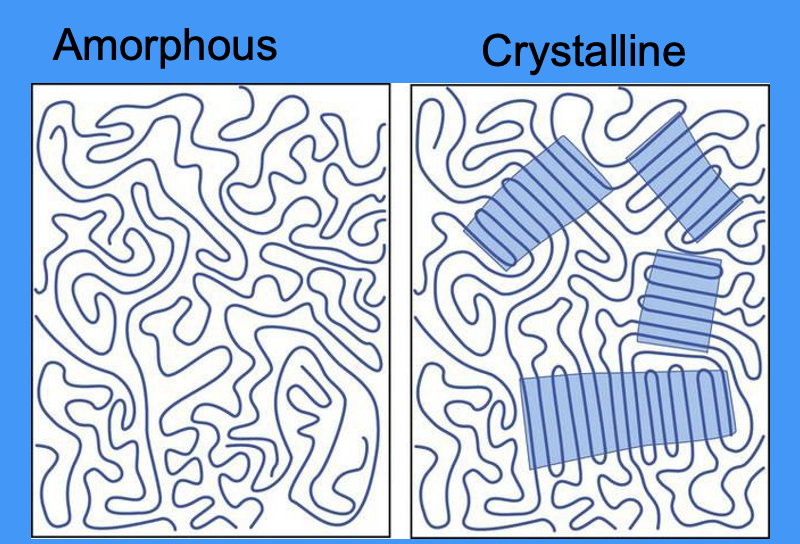
what do the highlighted areas in the crystalline diagram represent
crystal-like ordered structure of randomly packed polymer chains
give examples of amorphous polymers
acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS)
atactic polystyrene
polycarbonate
polyisoprene
polybutadiene
give examples of crystalline polymers
nylon
crystalline PET (CPET)
syndiotactic polystyrene
Kevlar and Nomex
polyketones
what polymer properties does crystallisation affect
optical properties
mechanical properties
thermal properties
chemical properties
outline thermoplastic polymers
linear/ branches structures
flow when heated and can be reshaped upon heating
easily moulded and extruded into films
give an example of a thermoplastic polymer
polypropylene
outline thermosetting polymers
crosslinked structures
cannot be reshaped upon heating
hard and durable
give an example of a thermosetting polymer
epoxy resin
outline elastomers
rubbery polymers
can be stretched easily
return to their original dimensions when the applied stress is released
give an example of an elastomer
natural rubber
what is Tg
Tg: glass transition temperature
the temperature at which the polymer chains begin to flow past each other
the polymer is soft, rubbery and easy to handle but NOT melted
graph showing Tg
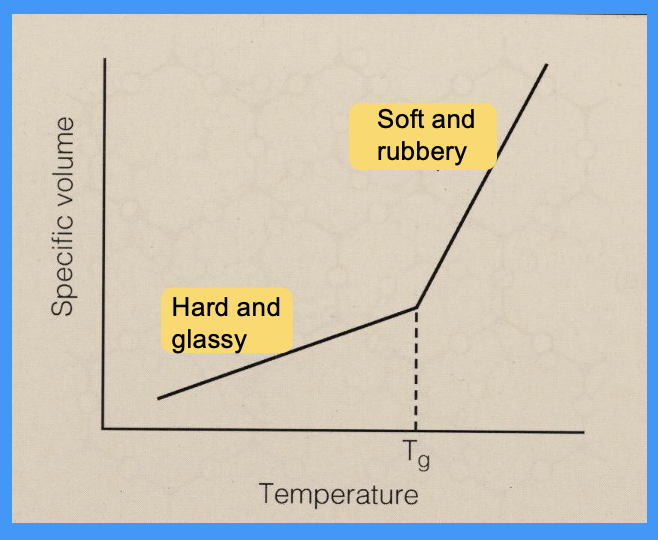
is Tg higher or lower than the melting temperature
Tg is always lower than the melting temperature (Tm)
the ______ the secondary bonds the _____ the Tg
the weaker the secondary bonds the lower the Tg
define polymerisation
polymerisation: the chemical reaction in which monomers of a low molecular weight are converted into chains of polymers with a high molecular weight
monomer molecules are bonded by covalent bonds
what are the types of polymerisation
addition
condensation
define addition polymerisation
addition polymerisation: occurs when a reaction between two molecules produces a larger molecule without the elimination of a smaller molecule
what are the steps of addition polymerisation
activation
initiation
propagation
termination
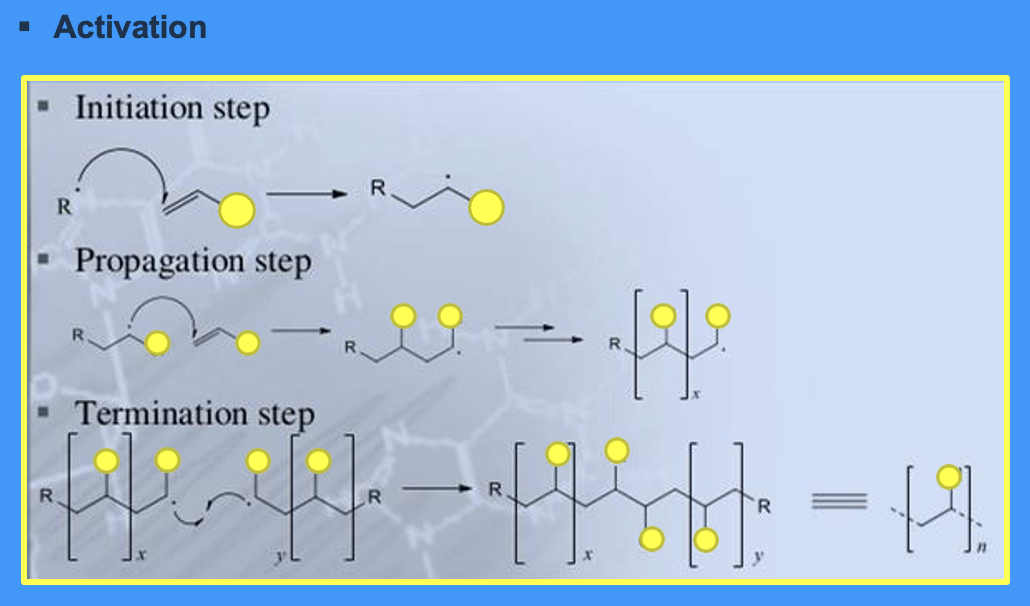
what are the common activators in the activation stage
heat
chemical compounds e.g. tertiary amines
light

what initiates polymerisation
free radical (a molecule with only one free electron) created by the activator
what occurs in the propagation stage
reaction of an active chain with a monomer
what occurs in the termination stage
2 radicals join to make a big polymer
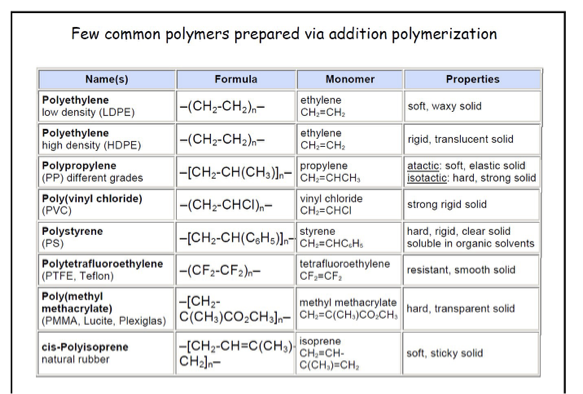
table showing common polymers prepared via addition polymerisation
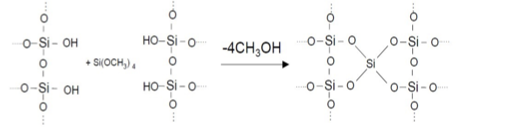
define condensation polymerisation
condensation polymerisation: occurs when a reaction between two molecules produces a larger molecule with the elimination of a smaller molecule
diagram showing example of condensation polymerisation
what is a copolymer
copolymer: two different types of monomers from different polymers are joined chemically in the same polymer chain, creating a new molecule
more noticeable in mechanical properties
what is a blend
mixing polymers prior to moulding
polymers generally miscible
» achieve moderate changes in mechanical properties
e.g. PLA + PCL
what is a plasticiser
small molecule added to the polymer that reduces attraction forces between polymer chains
» big effect in mechanical properties
lowers Tg and elastic modulus so good for brittle polymers
give an example of a composite
glass reinforced polymer
define resin-based composite
resin-based composite: highly crosslinked resin reinforced by a dispersion of amorphous silica or organic resin filler particles and/ or fibres bonded to the polymer matrix by a coupling agent