Radiology Exam 2
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
abdomen imaging
x-ray- pain, acute series, gas pattern, organs
CT- trauma, evaluate multiple organ systems simultaneously
US- gallbladder and biliary tree, female pelvis, AAA screening, POCUS trauma assessment
MRI- difficult diagnoses
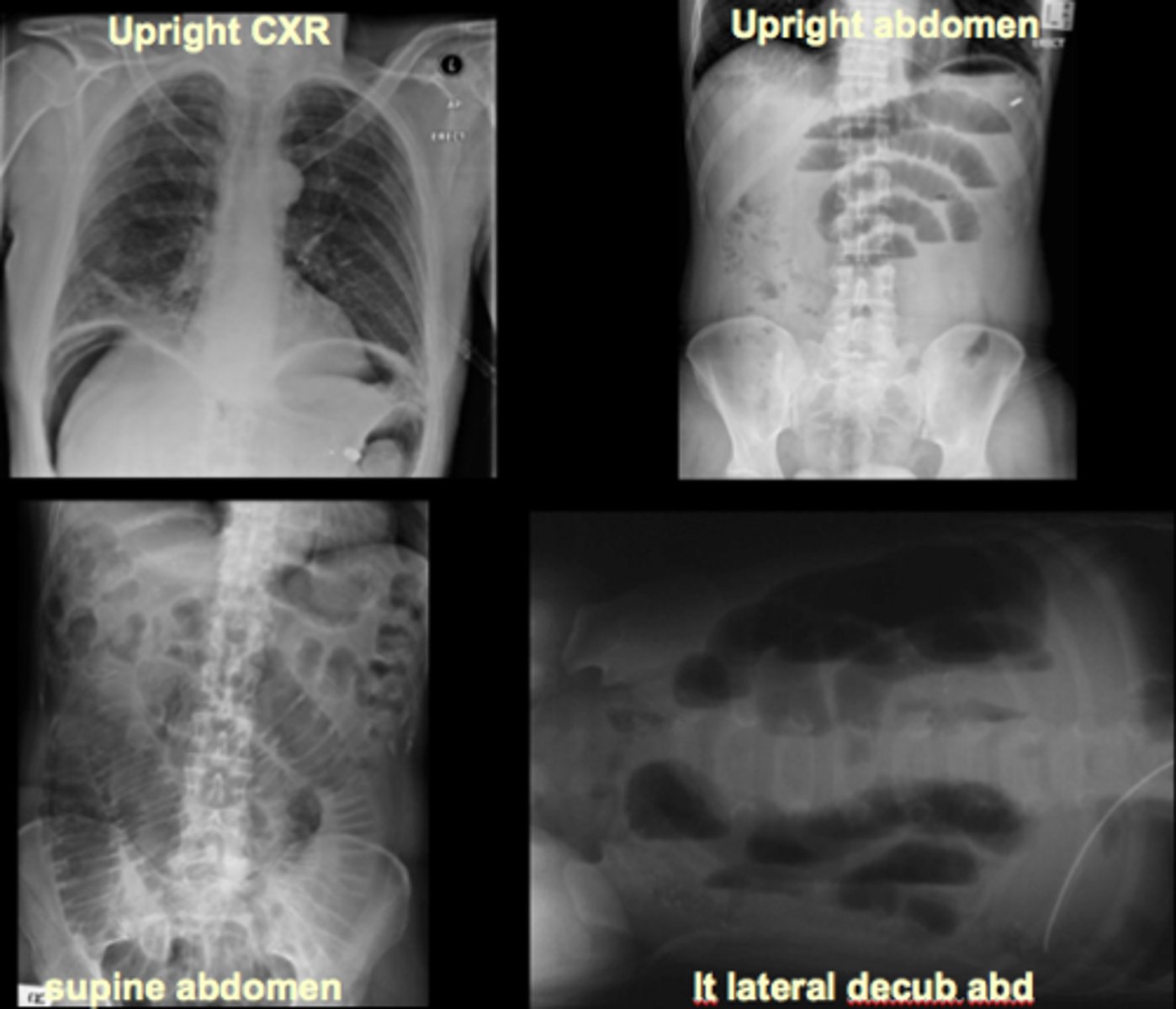
acute abdominal series
supine abdomen/KUB/scout - bowel gas pattern, calcifications, masses
upright abdomen - free air, air-fluid levels
upright chest - free air, pneumonia, pleural effusions
normal gas patterns
air in stomach, 2-3 loops of air in non-dilated small bowel, air in rectosigmoid, no free air in diaphram, liver displaces gas, no fluid or dilation of colon
colon
normally distended bowel loops, air fills lumen completely, haustra visible
small intestine
located centrally, valvulae markings extend across lumen from one wall to another
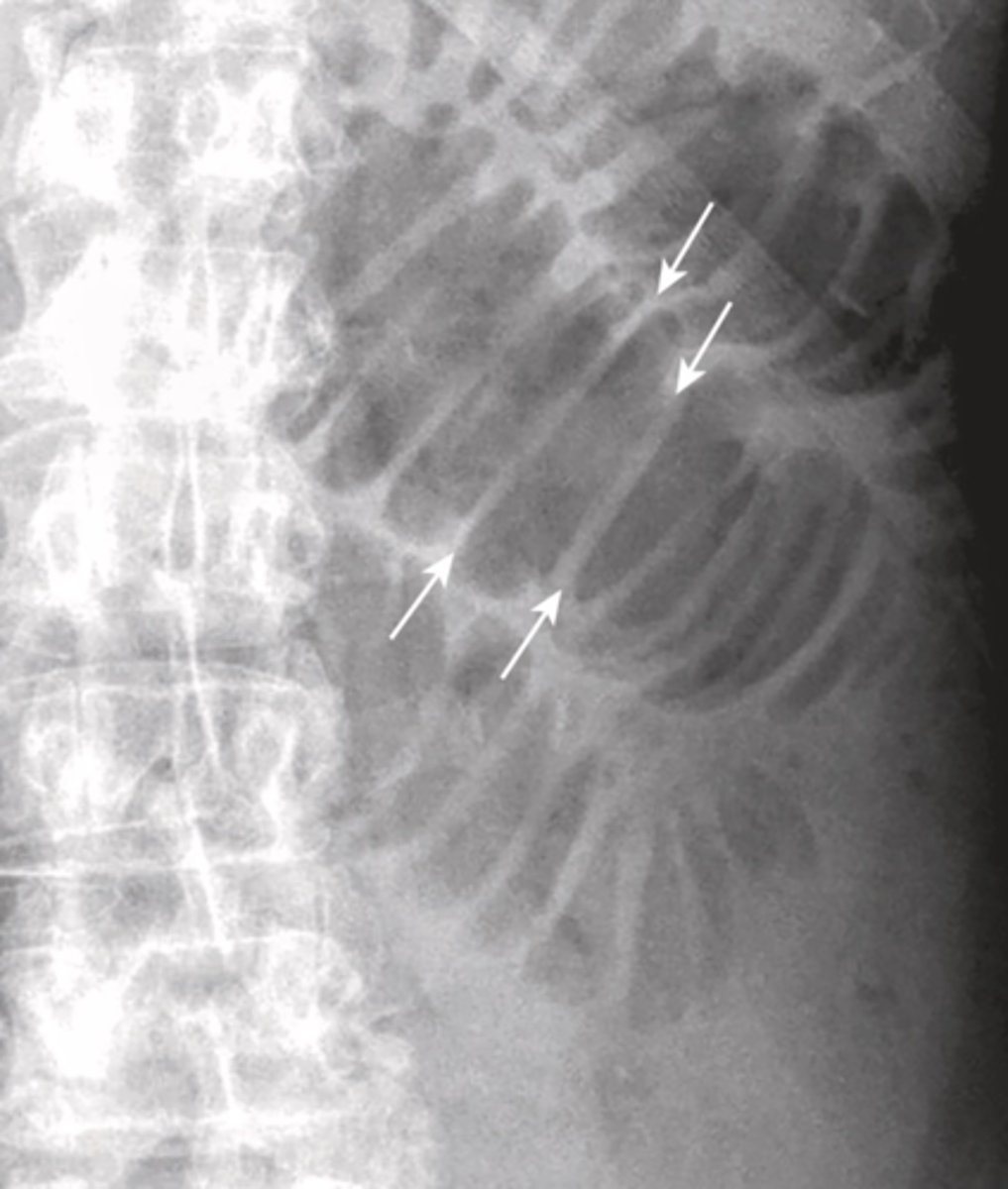
extraluminal air
air outside bowel lumen, can be intraperitoneal, extraperitoneal, in bowel wall (pneumatosis intestinalis), in biliary system (pneumobilia)
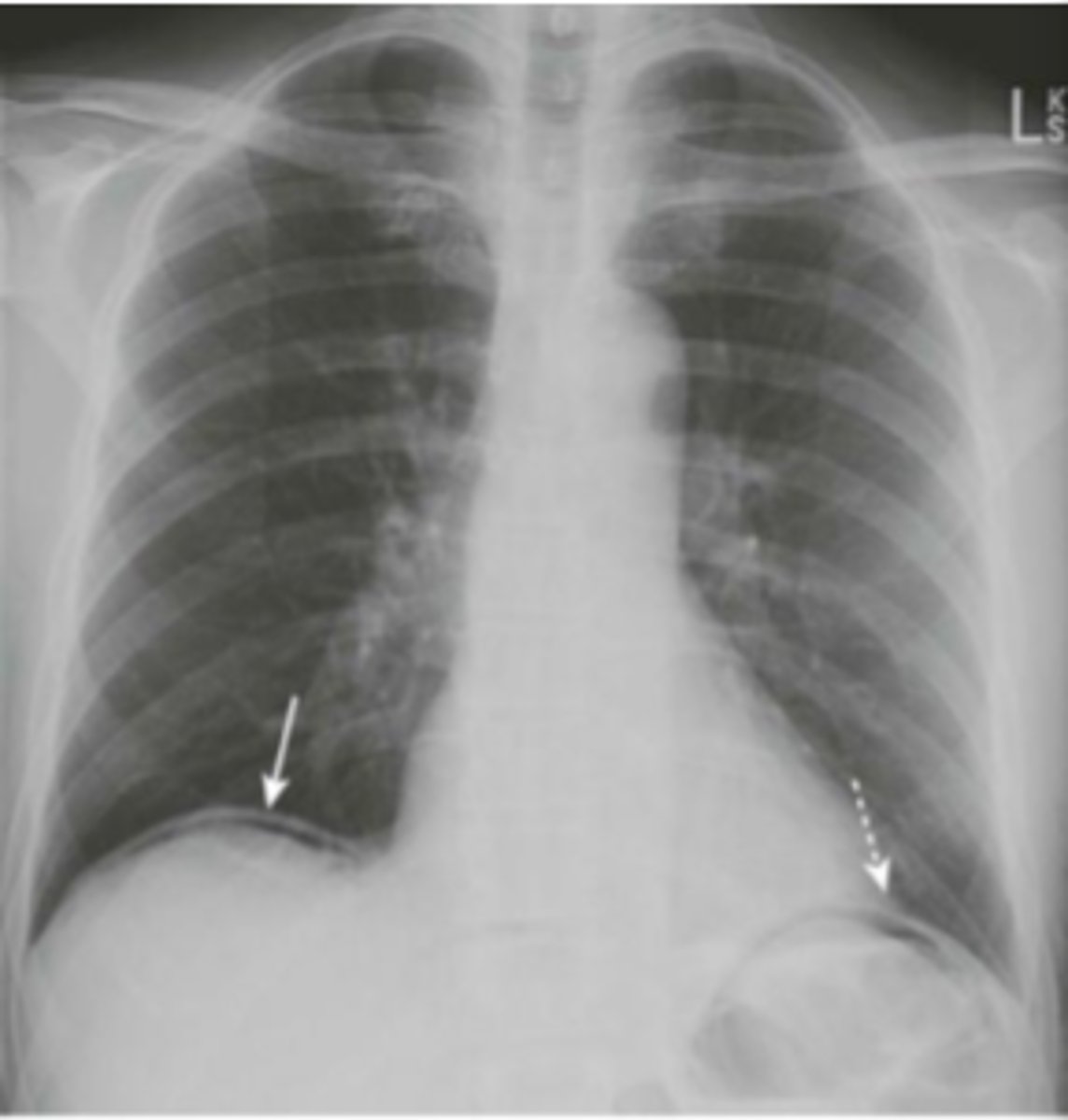
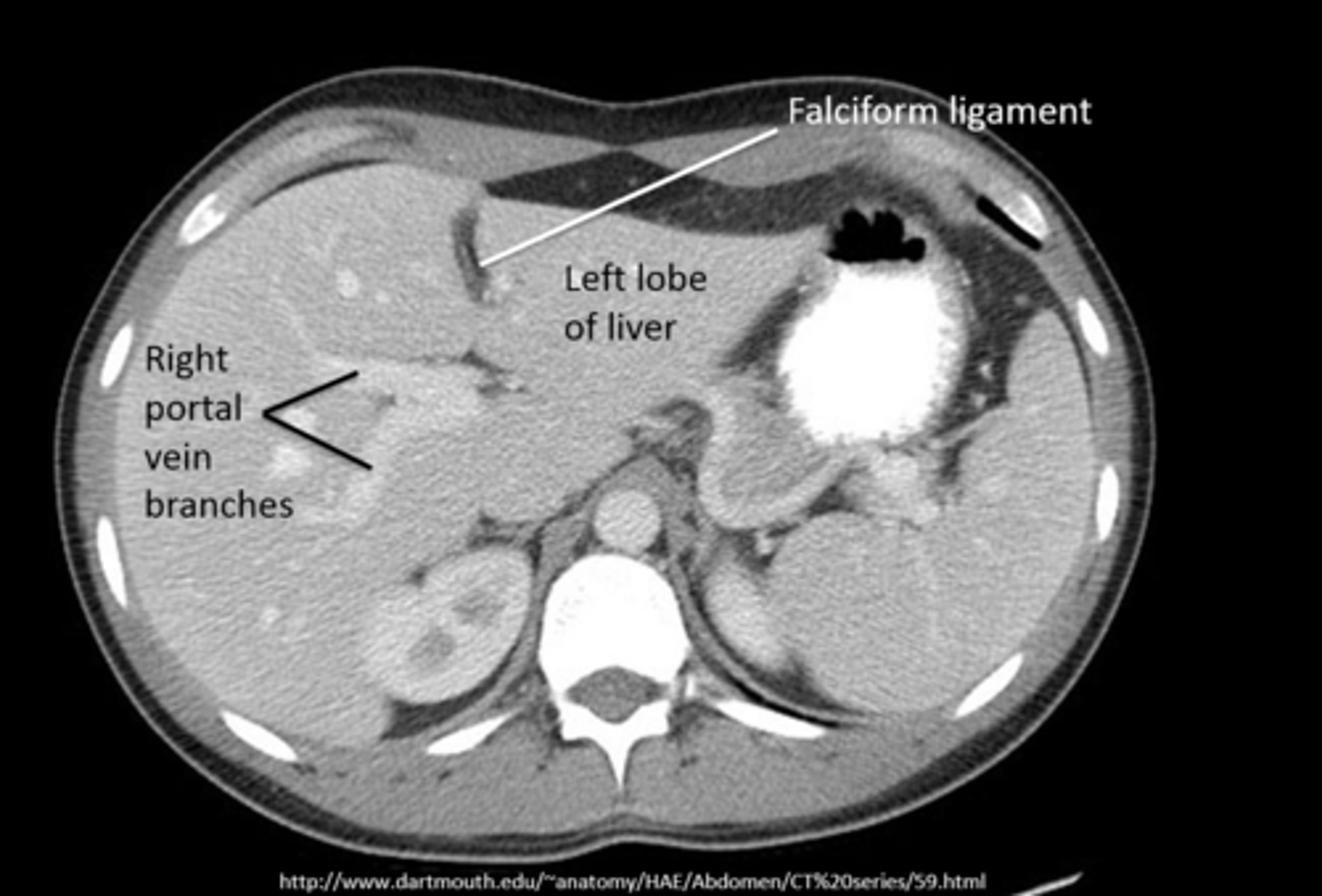
intraperitoneal air (pneumoperitoneum)
air in peritoneal cavity, caused by rupture of an air-containing loop of bowel, trauma, or abdominal surgery (5-7 days post op)
1. air beneath diaphragm
2. rigler sign- visualization of both sides of bowel wall
3. visualization of falciform ligament
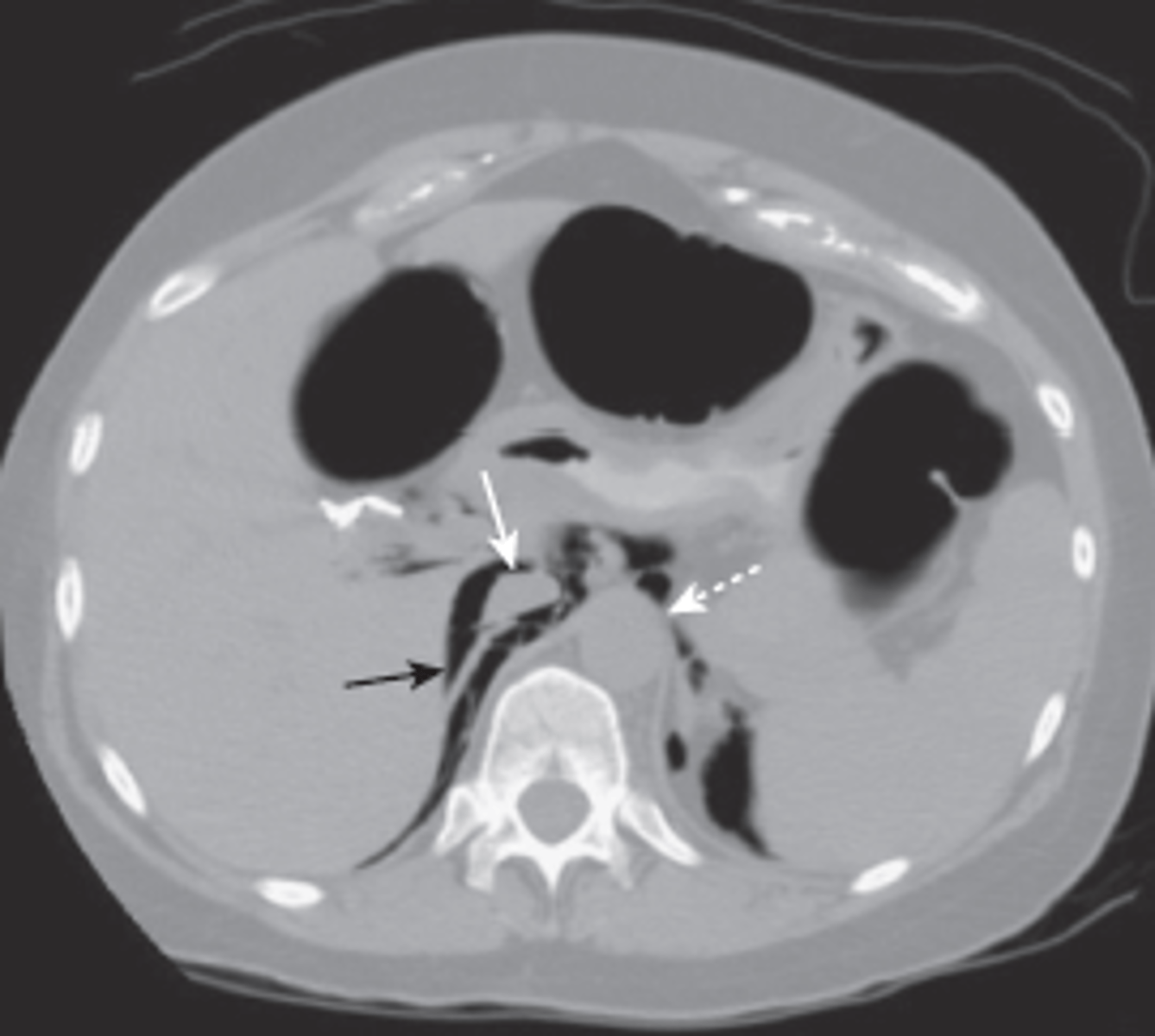
extraperitoneal air
air outside peritoneal cavity, same causes as intraperitoneal air
mostly seen on CT
streaky, linear appearance outlining extraperionteal structures, mottled blotchy appearance, relatively fixed position
hepatomegaly
enlarged liver, displacement of all bowel from RUQ down to iliac crest and across midline
splenomegaly
enlarged spleen, projects well below 12th posterior rib
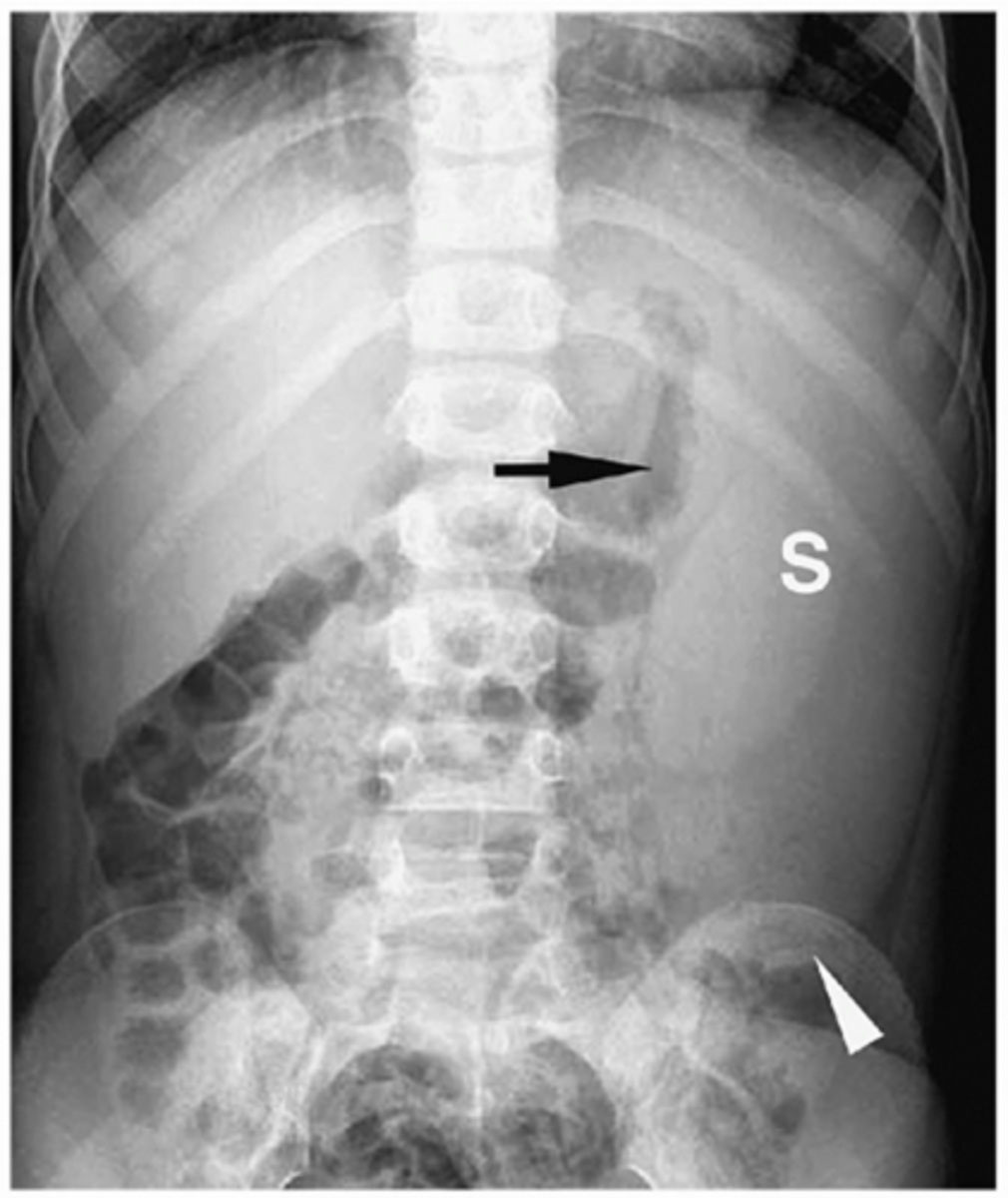
enlarged kidney
extremely enlarged organ or large masses, large cyst compressing and displacing other organs
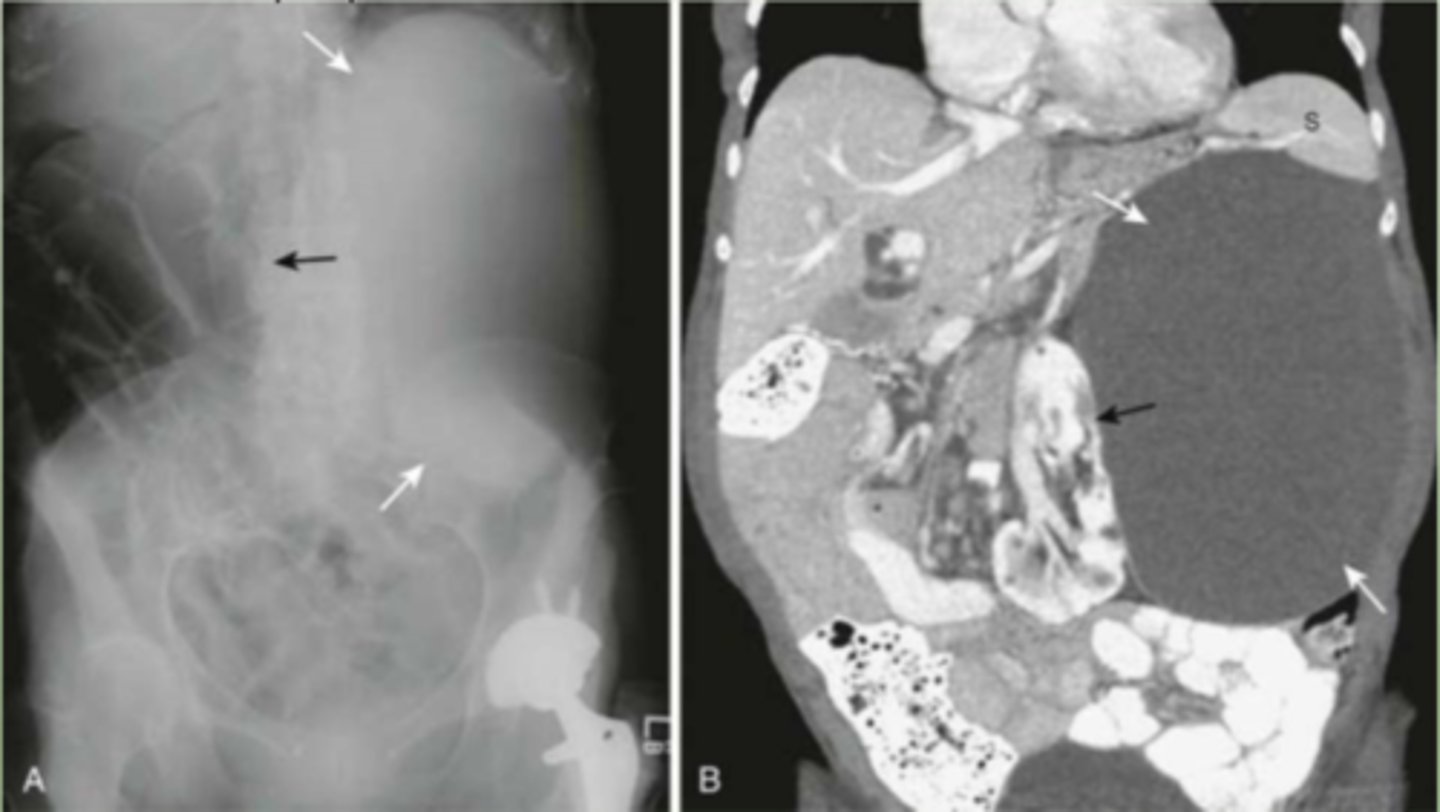
enlarged bladder
usually appears at soft tissue mass, displacing bowel
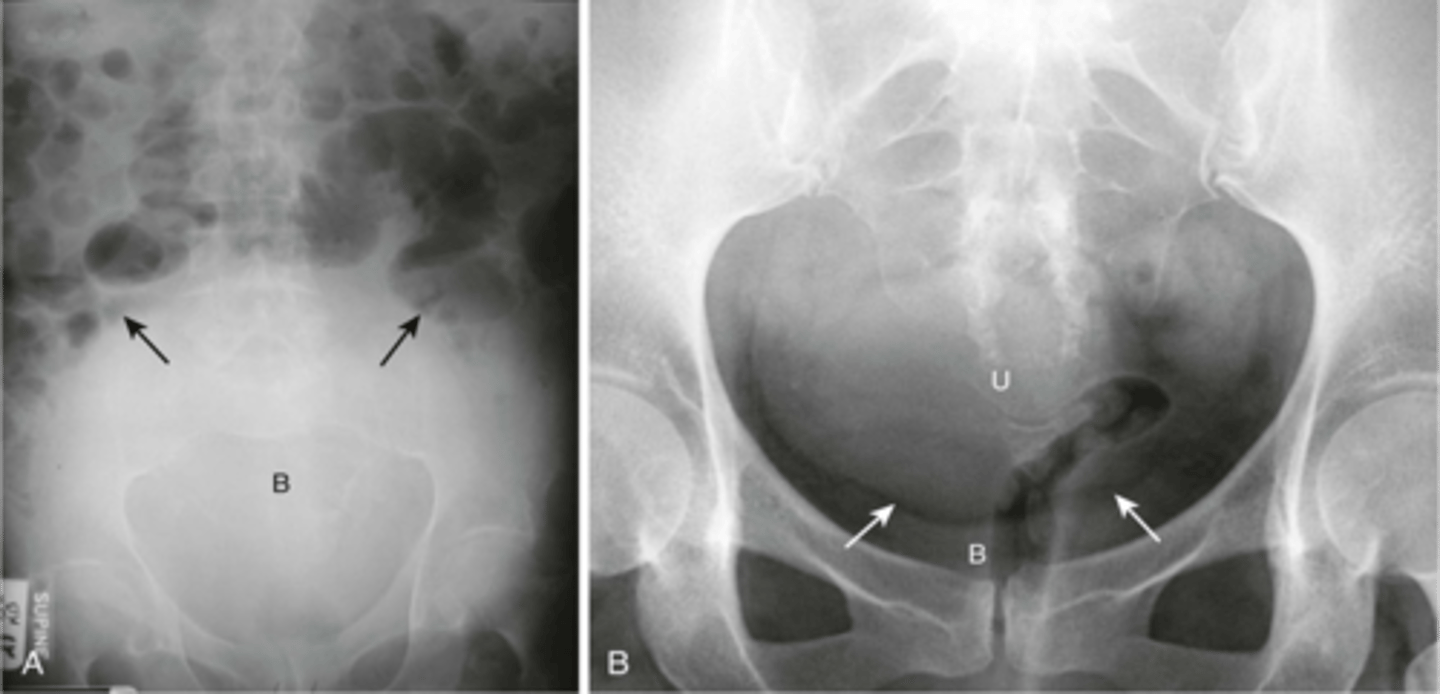
rim-like calcification
calcification of the wall of a hollow organ
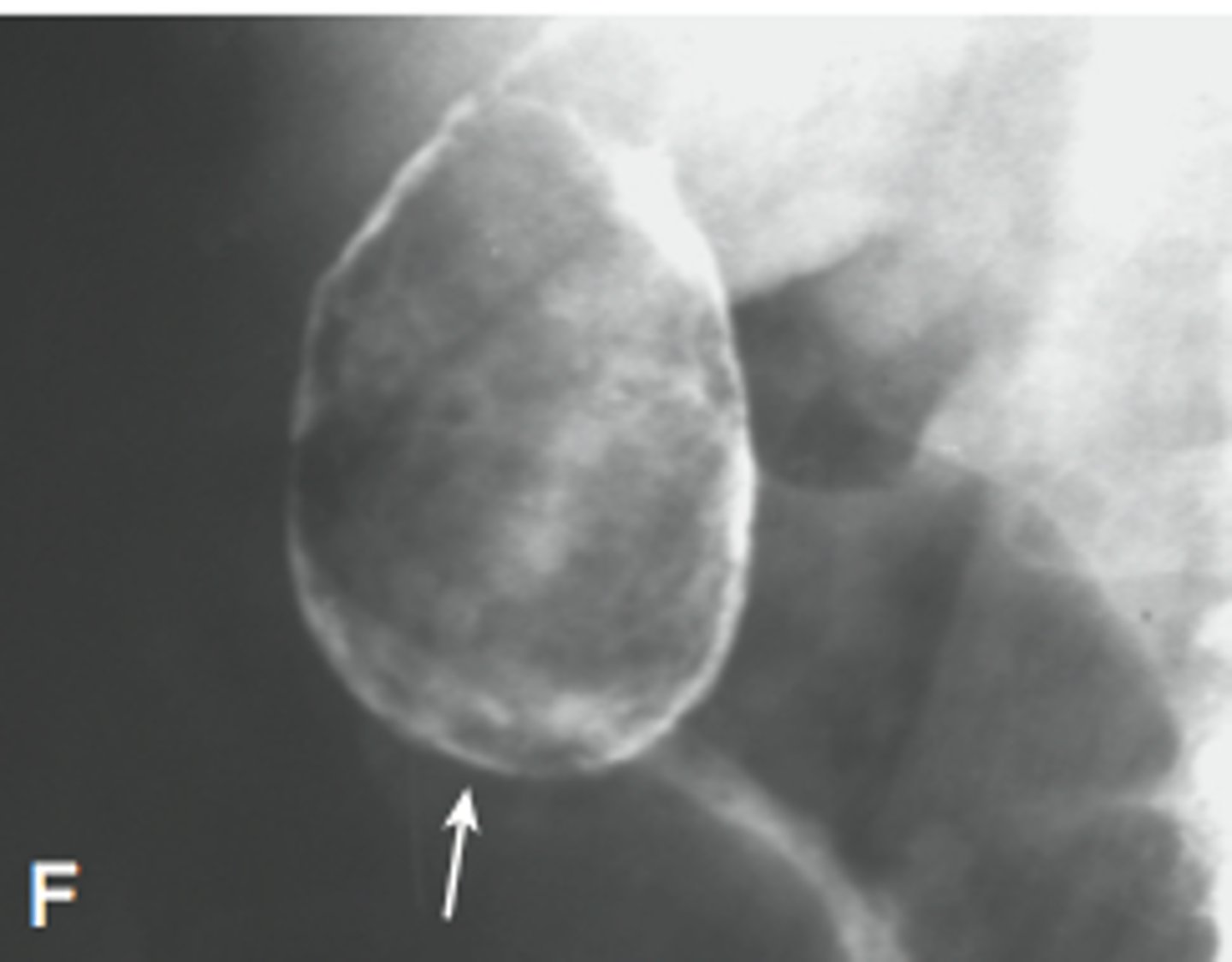
linear/track-like calcifications
calcification in the walls of tubular structures
ex. arteries, ureters, fallopian tubes, vas deferens
walls of veins do not calcify
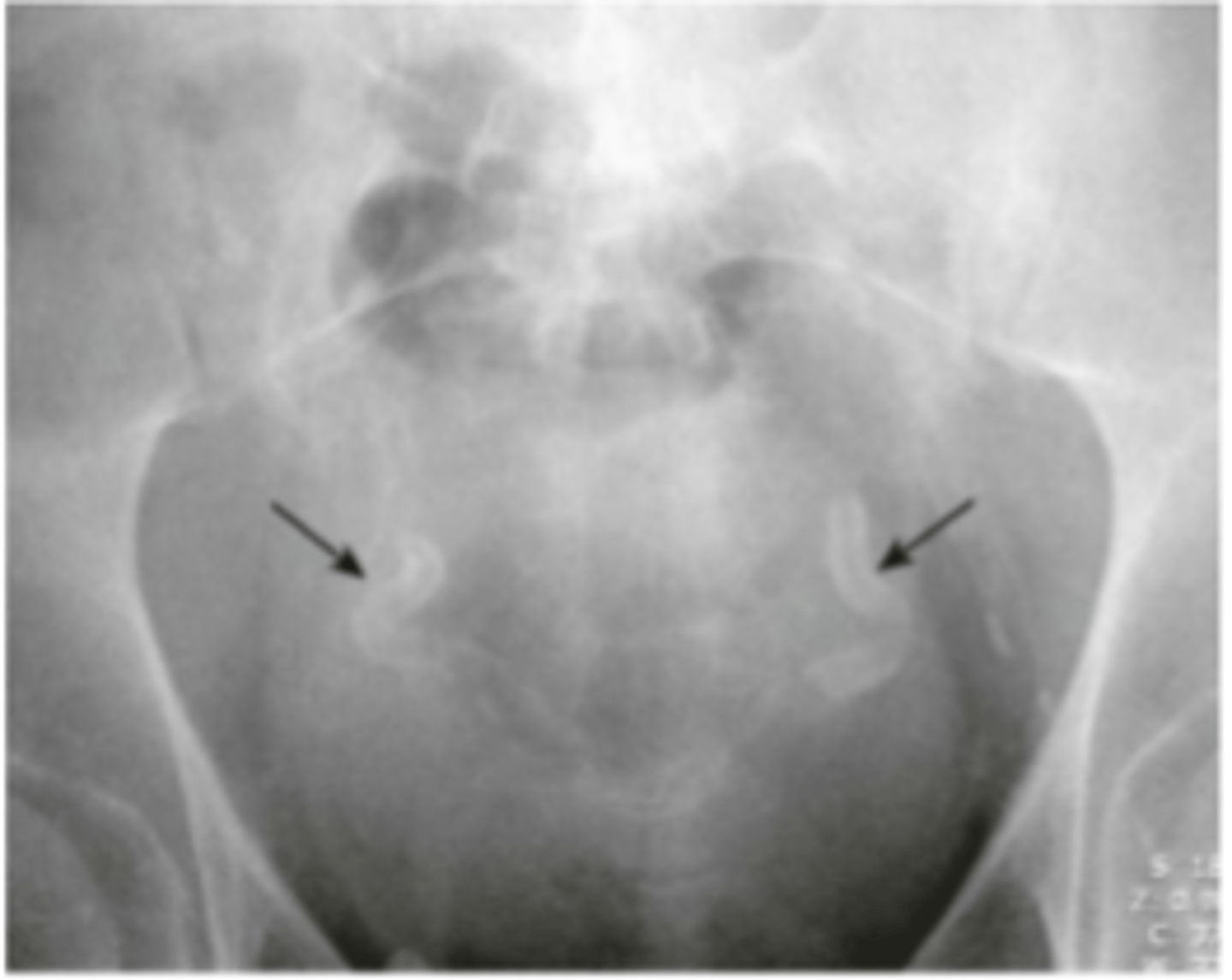
phleboliths
small blood clots in a vein that calcify over time, usually incidental finding, lucent centers
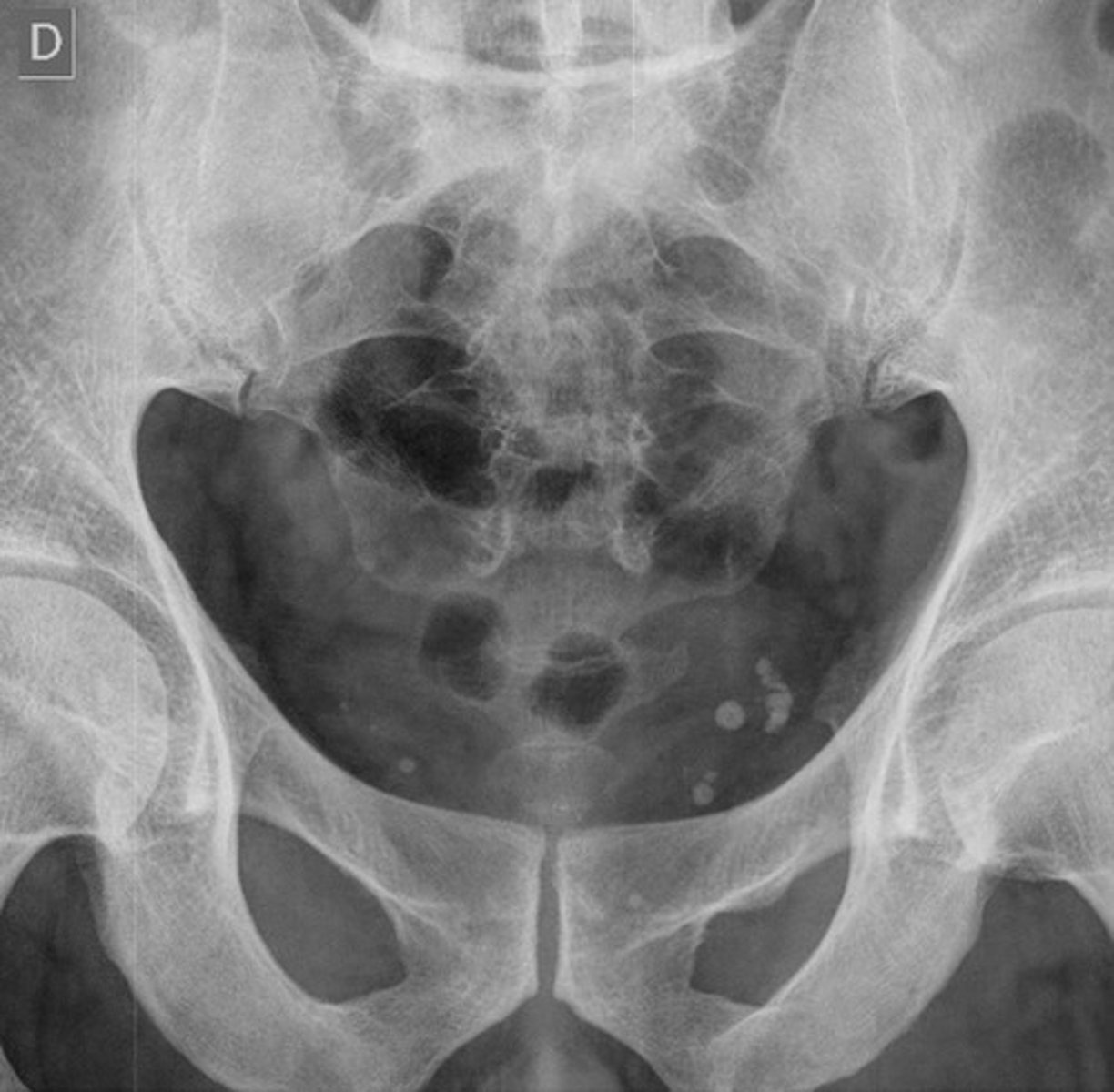
lamellar/laminar calcifications
calcification that forms inside a hollow (usually fluid-containing) lumen
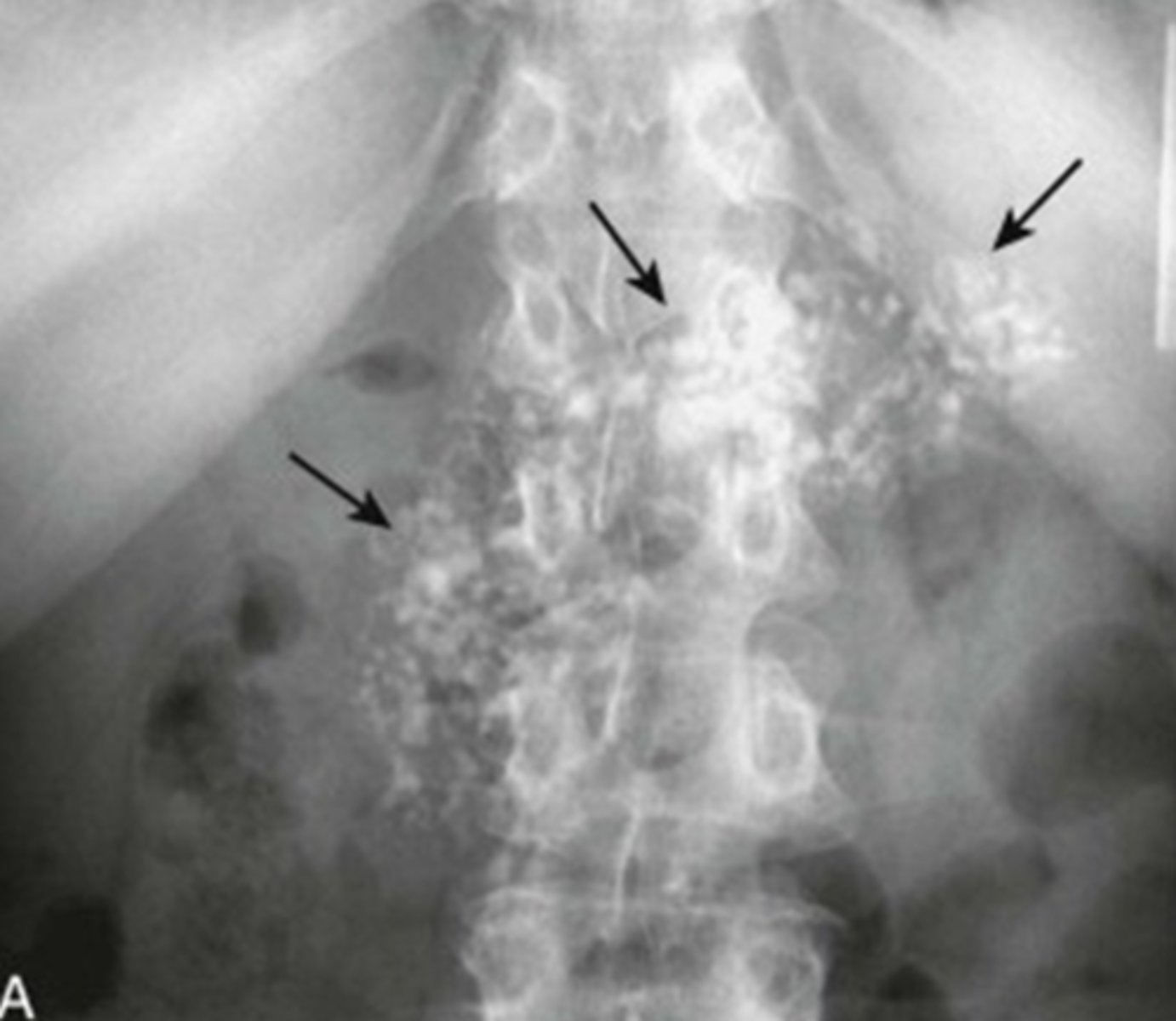
cloudlike amorphous/popcorn calcification
calcification inside a solid organ or tumor
esophagus
best assessed by upper endoscopy, barium swallow, or gastrofin swallow
Z line- sometimes visible, junction between mucosa of esophagus and stomach
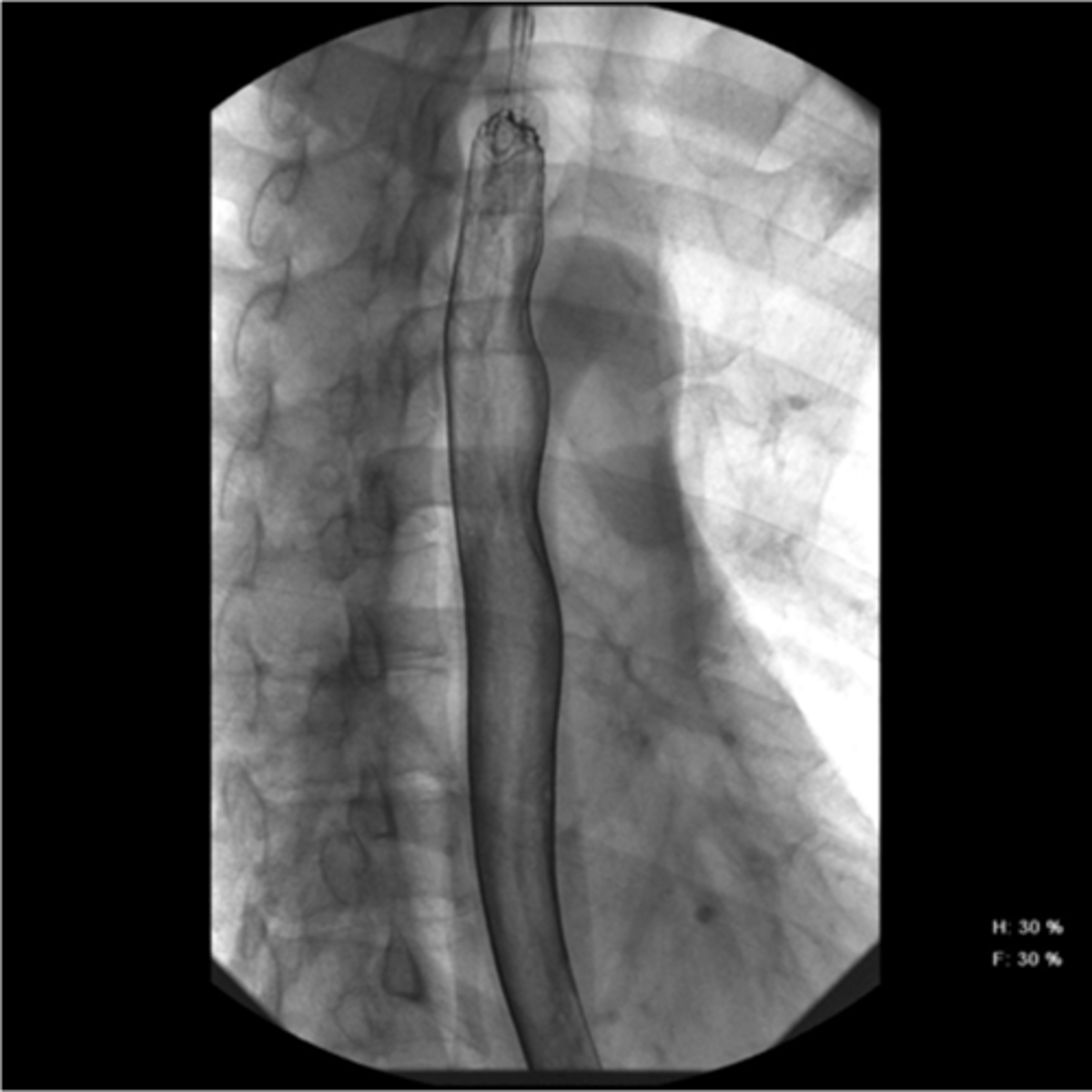
Zenker diverticulum
abnormal "pouch", food can get caught causing dysphagia
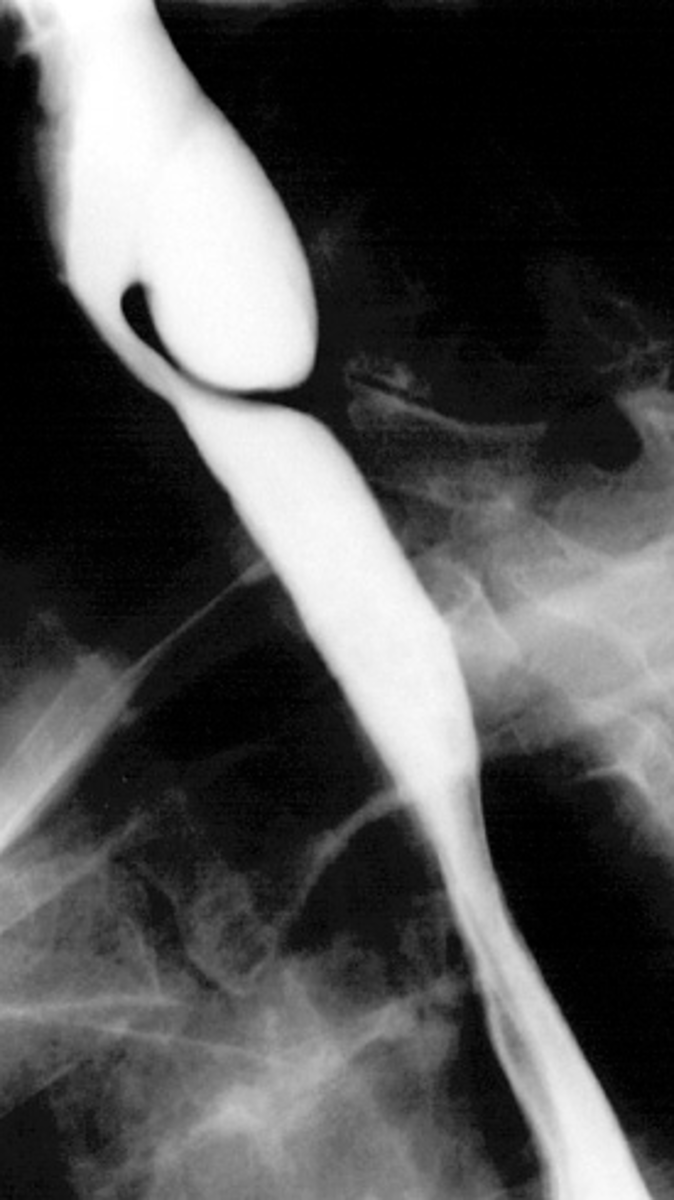
esophageal strictures
narrowing of the esophagus
superior- scarring from suicide attempts, lye or corrosive material swallowed, smooth appearance
middle and inferior- scarring from GERD, neoplasm
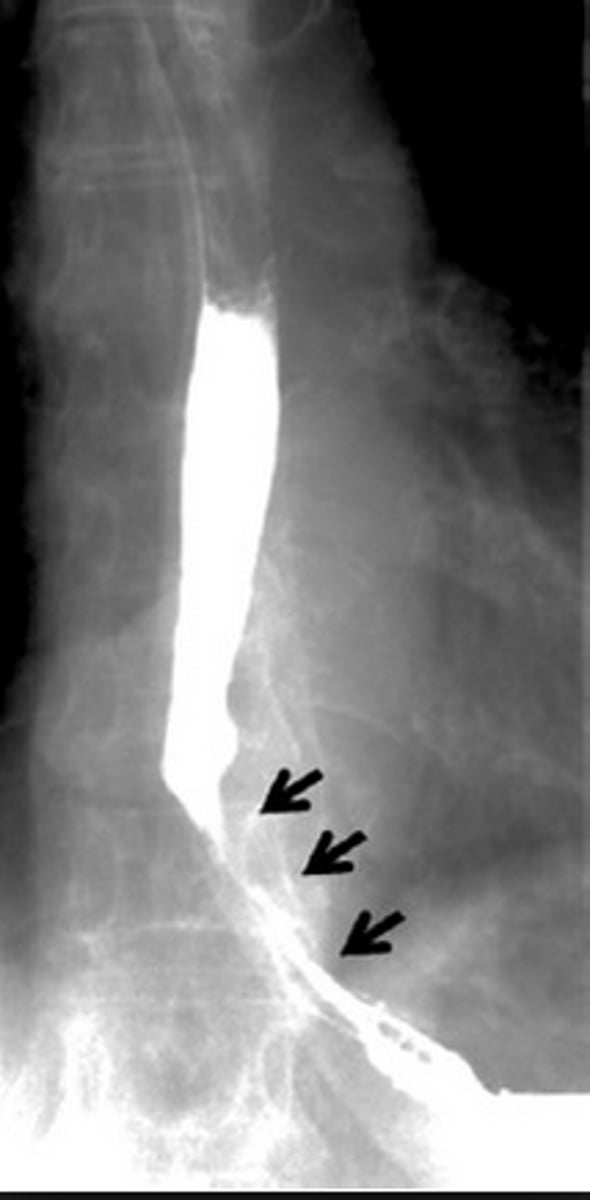
esophageal carcinoma
irregular column of barium entering stomach with peak like projections of barium -> concerning for malignancy
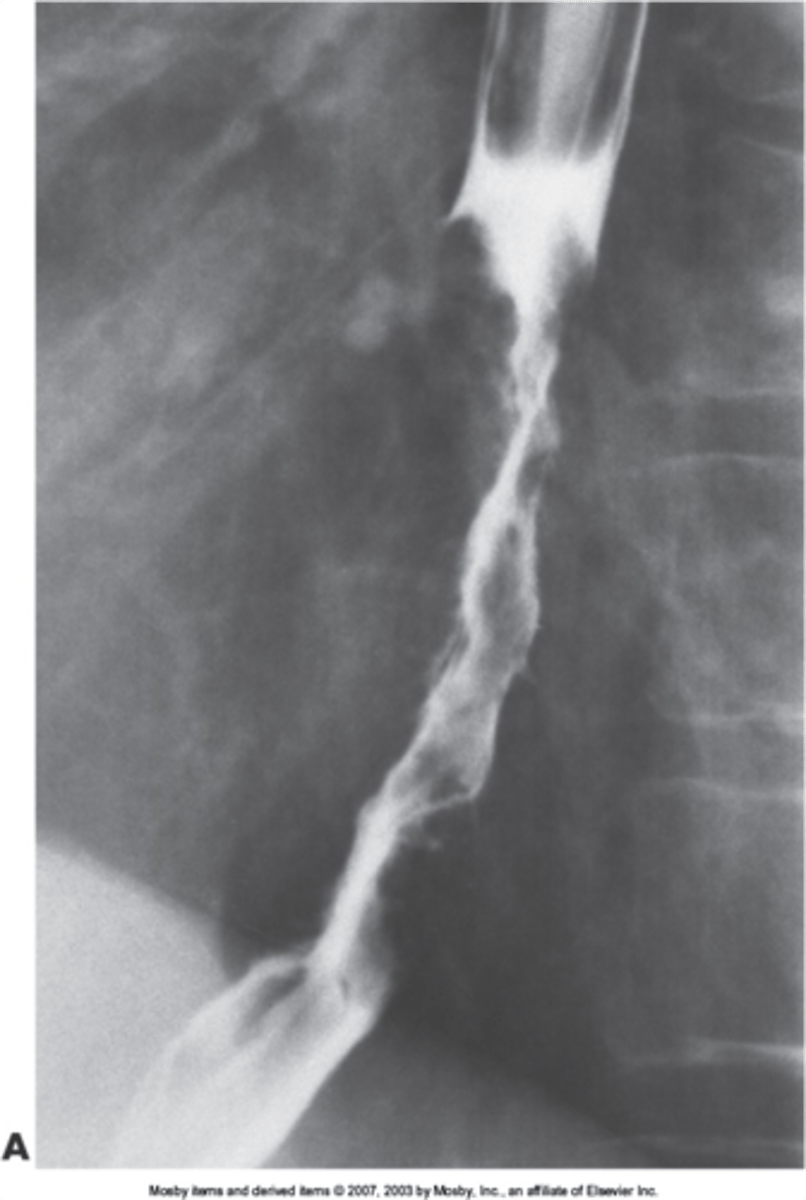
stomach
upper endoscopy is visualization of choice, abdominal CT imaging, barium upper GI no longer recommended
liver
xray- only shows organomegaly
CT- most common method for imaging
ultrasounds- detecting size and ascites
MRI- define tumors
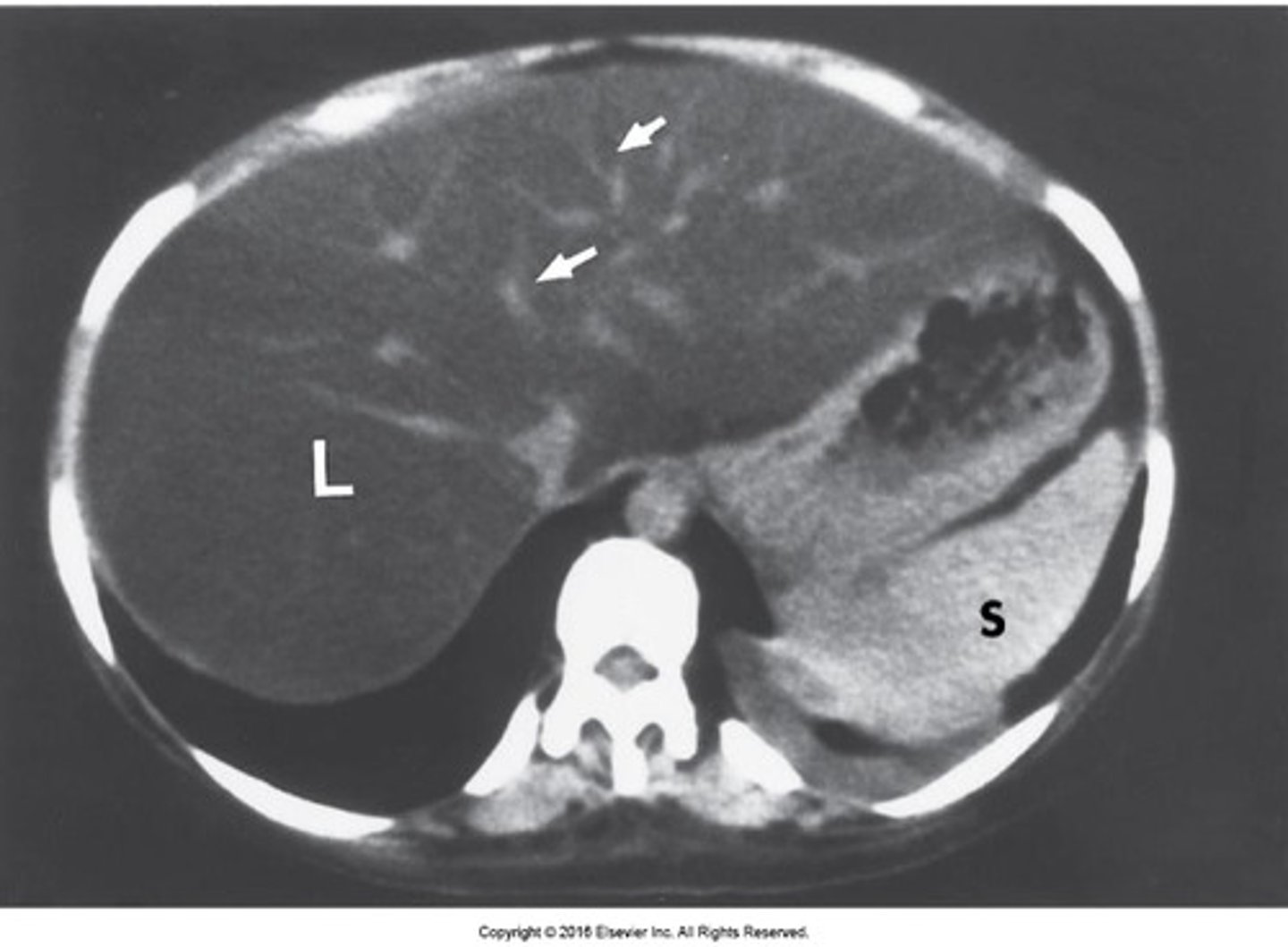
fatty liver
focal or diffuse fatty infiltration appears as less dense on CT
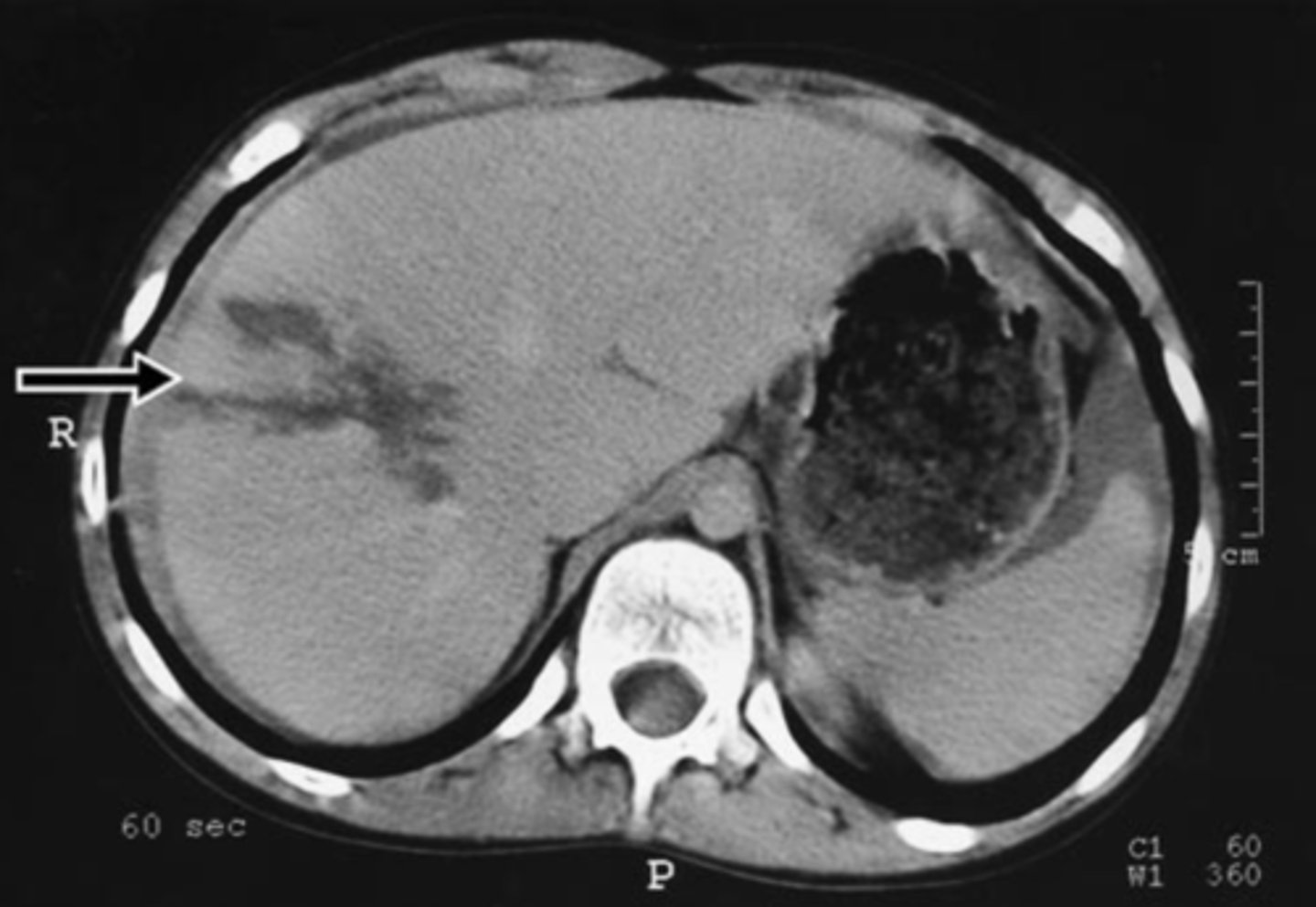
liver trauma
most injured intra-abdominal organ, lacerations and hemorrhages often seen
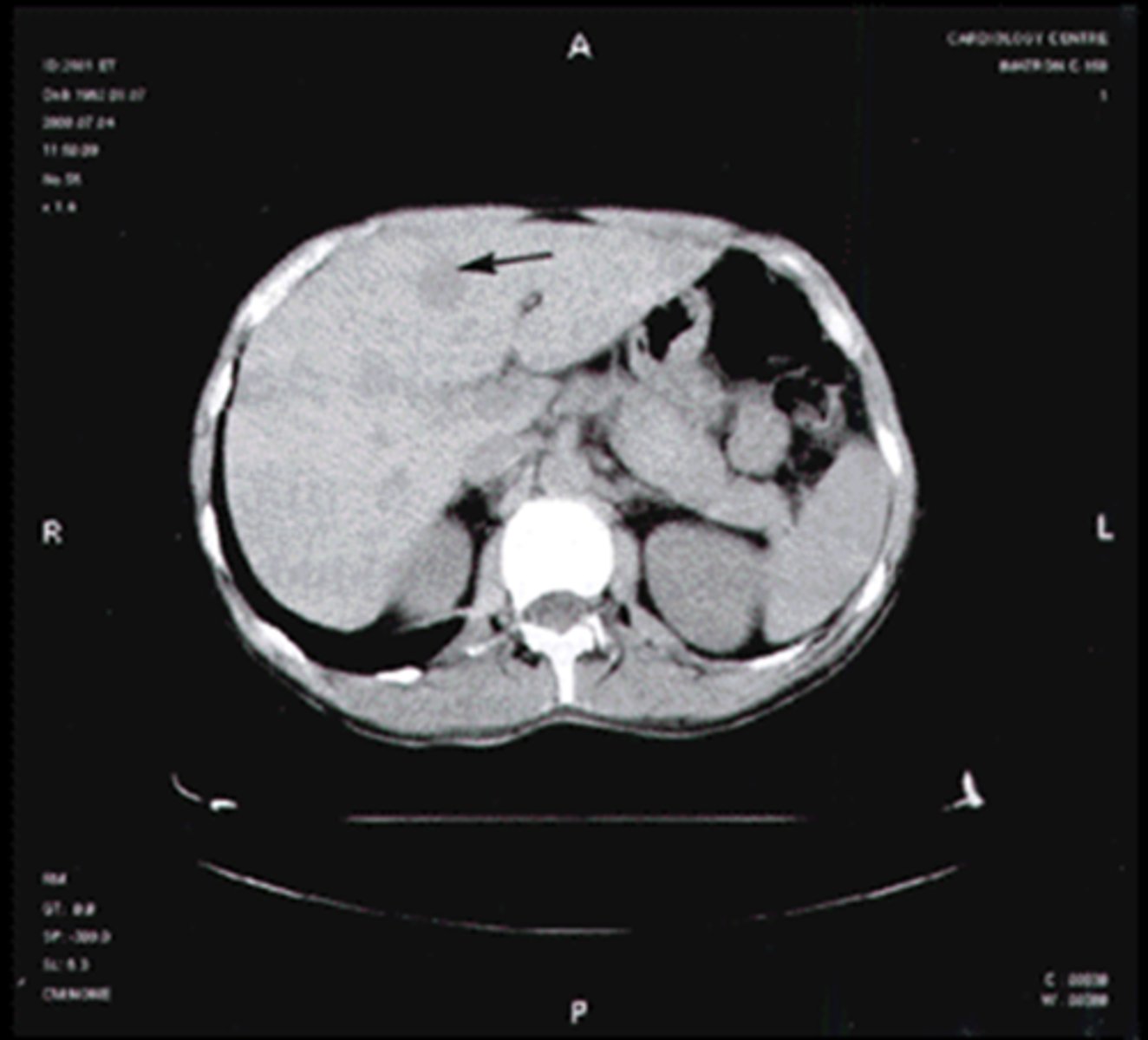
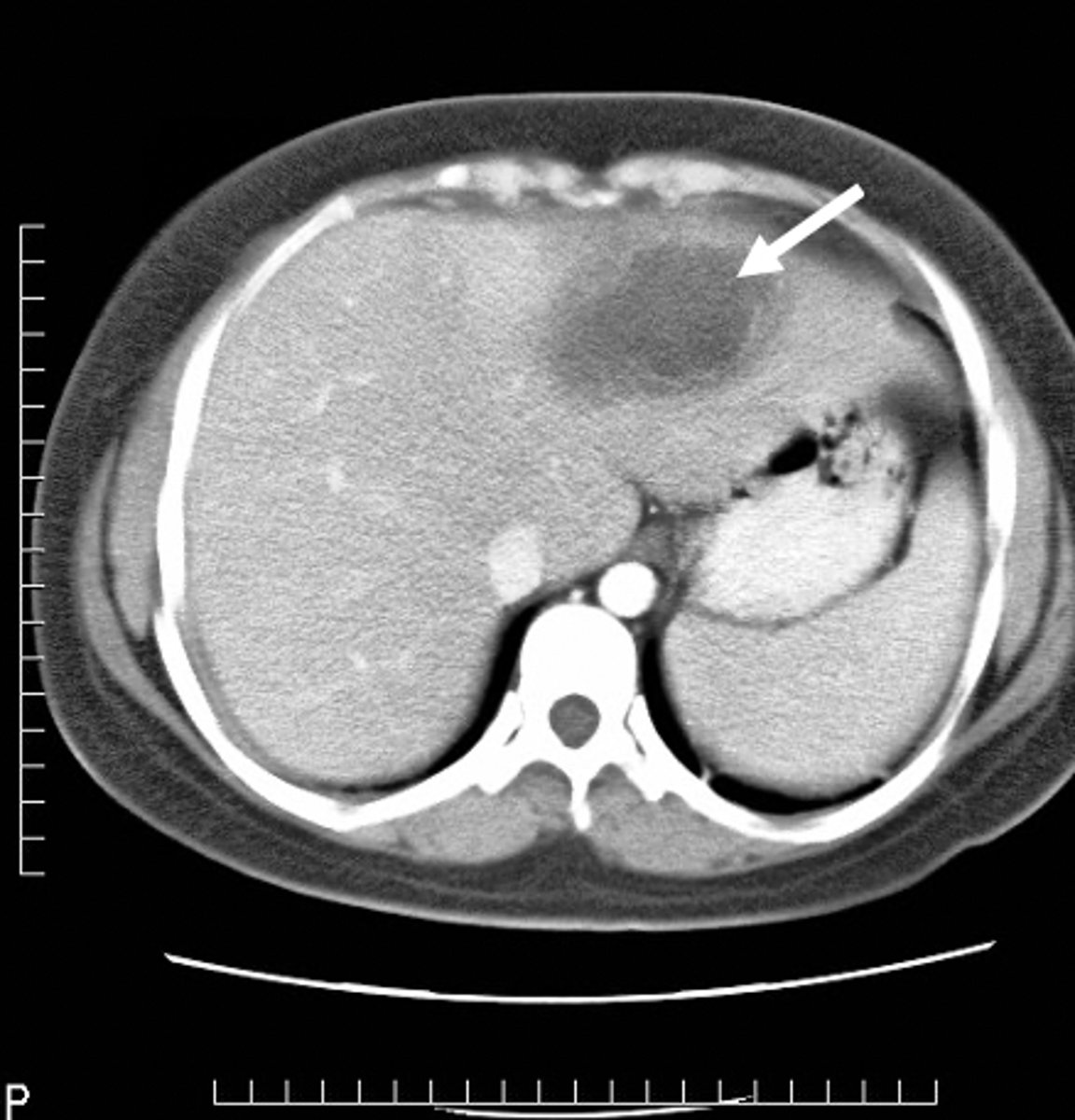
hemangioma
most common benign hepatic tumor, often found incidentally on US and CT, looks like normal liver with contrast
hepatoma
most common primary malignant hepatic tumor
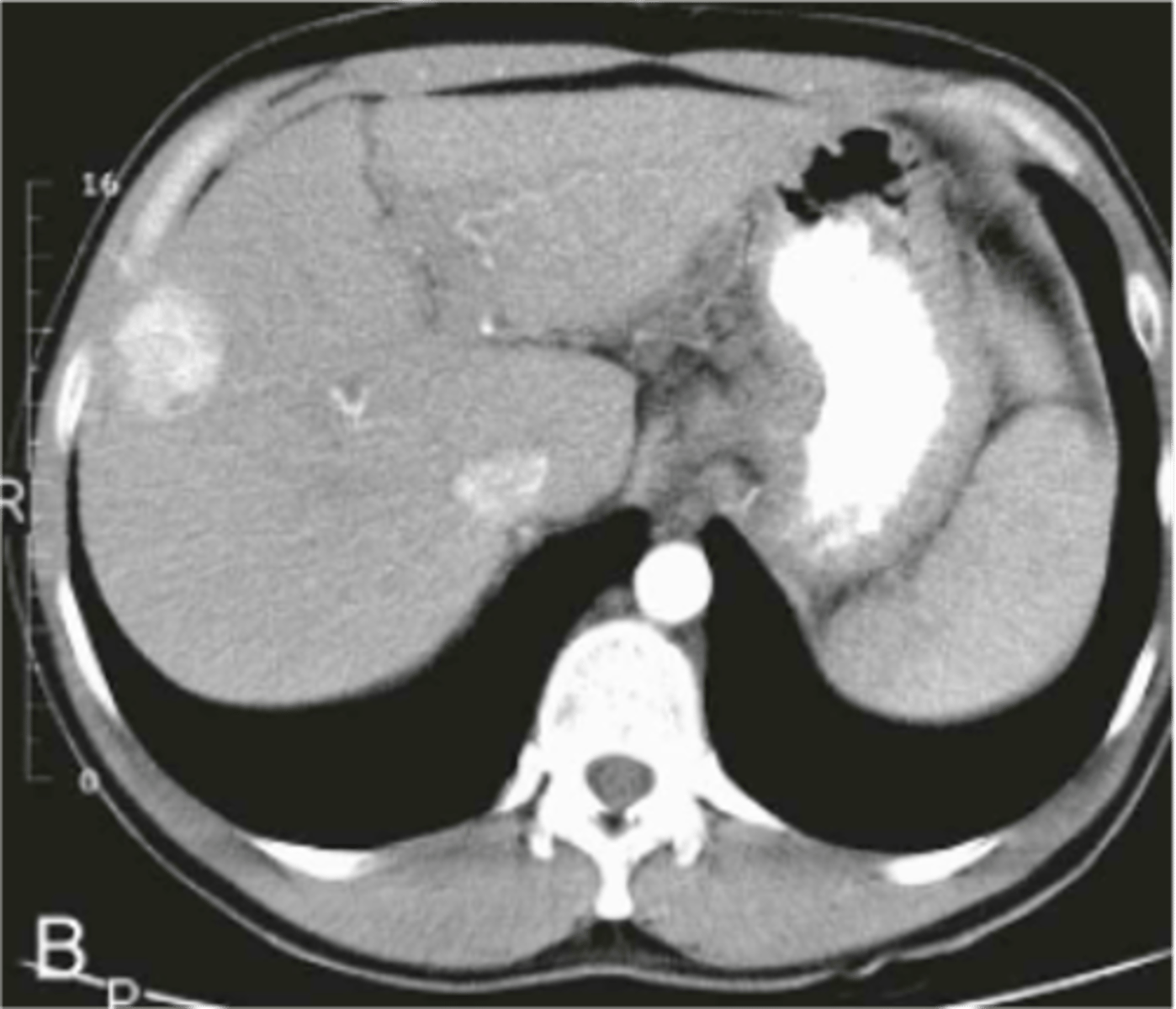
hepatic cysts
common, usually incidental findings, lower density than liver, clearly defineed
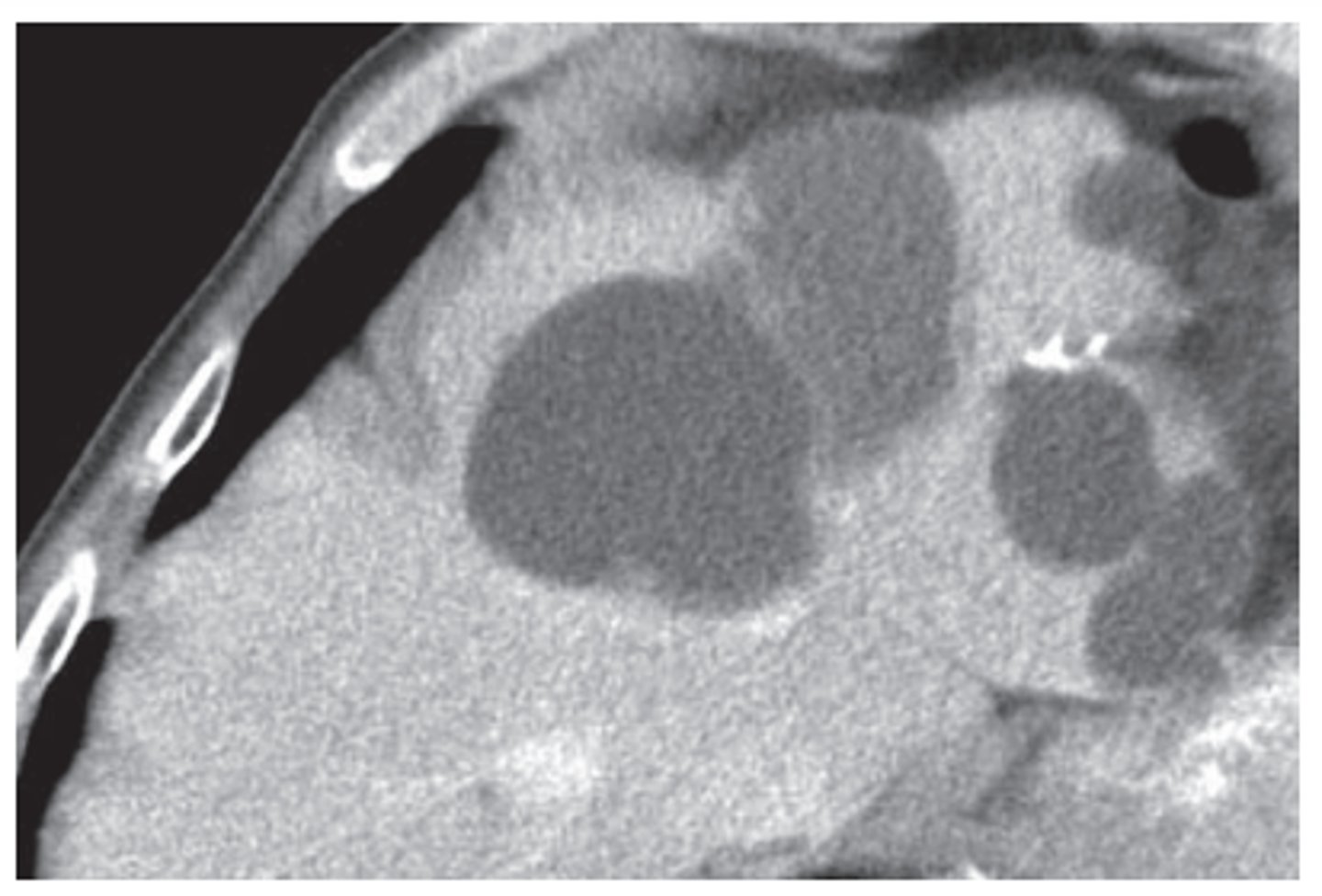
hepatic abscess
localized collection of pus, low density lesion
gallbladder and biliary tree
xray- radiopaque gallstones
US- diagnostic study of choice, abstain from food 6 hrs before
CT- less sensitive than US in detecting gallstones, good for difficult anatomy, masses, extent of disease
HIDA scan- nuclear medicine, visualizes flow of bile
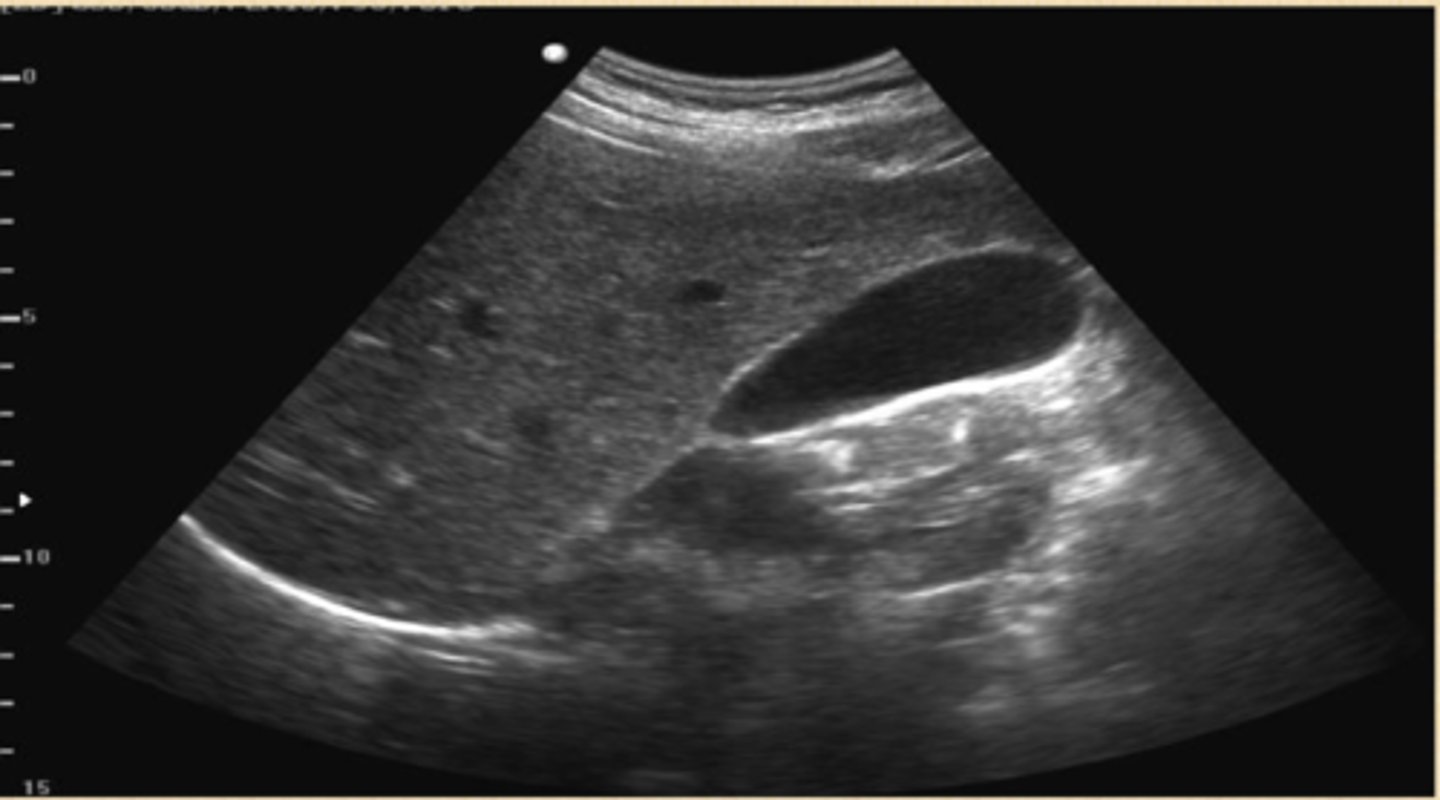
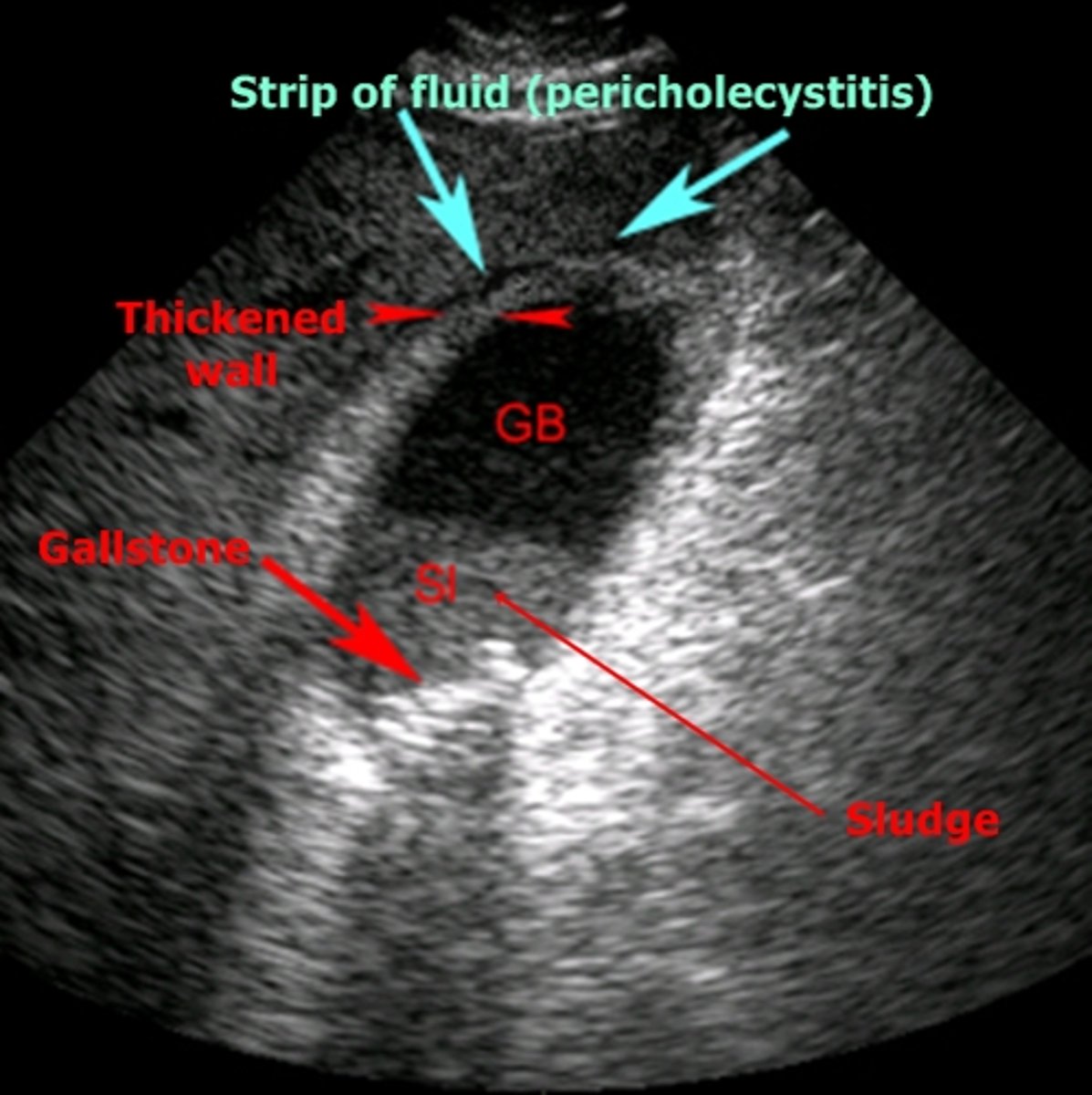
cholelithiasis
stones in the gallbladder, often asymptomatic, classic biliary pain characterized by infrequent episodes of steady severe pain in epigastrium or RUQ with radiation to R scapula
echogenic stones, posterior acoustic shadowing
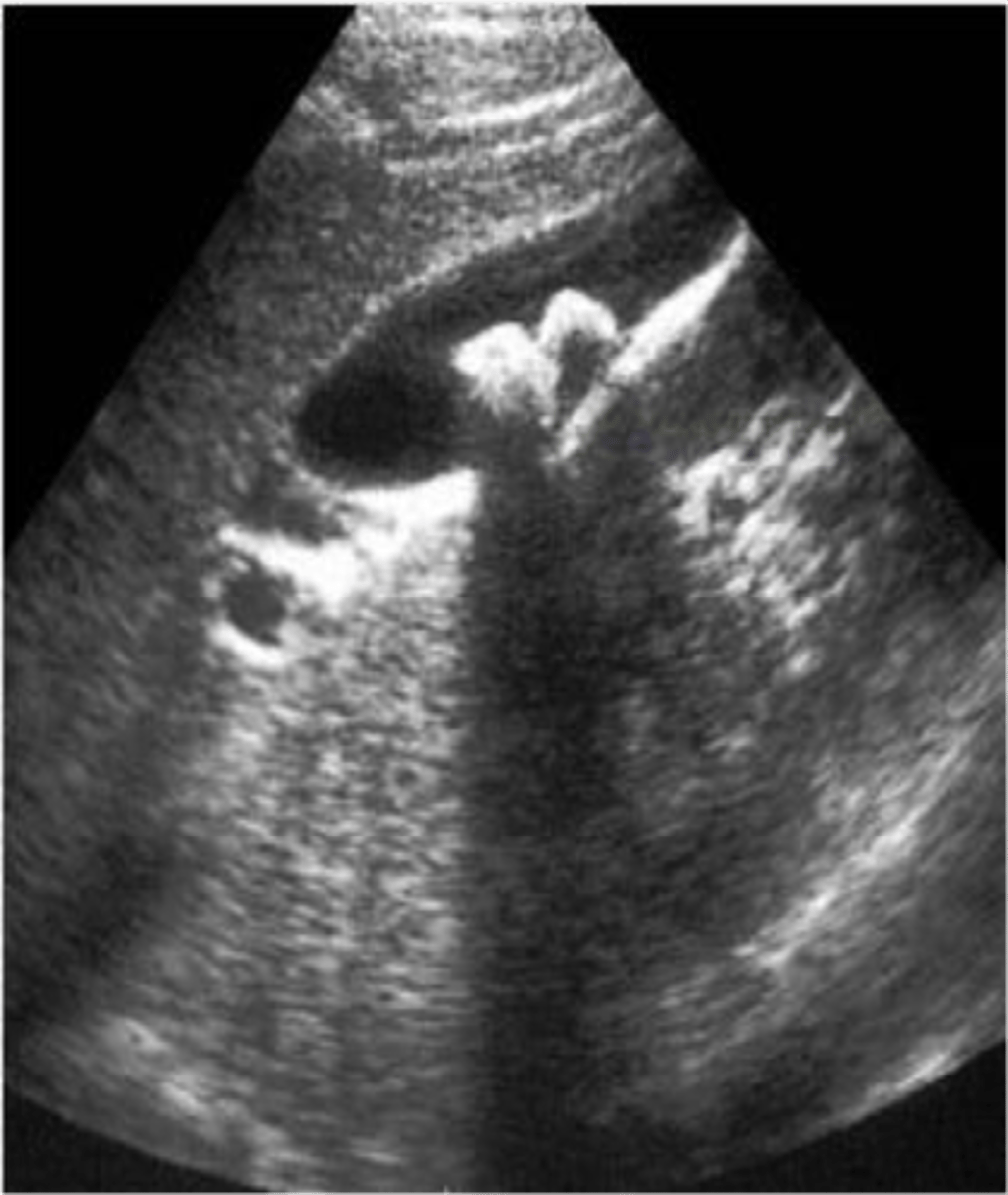
cholecystitis
inflammation of the gallbladder, usually caused by gallstone blocking outflow of bile through bile duct
-cystic duct most commonly obstructed
biliary sludge
aggregation that may contain cholesterol crystals, bilirubin, glycoprotein, often associated with biliary stasis
echogenic in gallbladder lumen, no acoustical shadowing
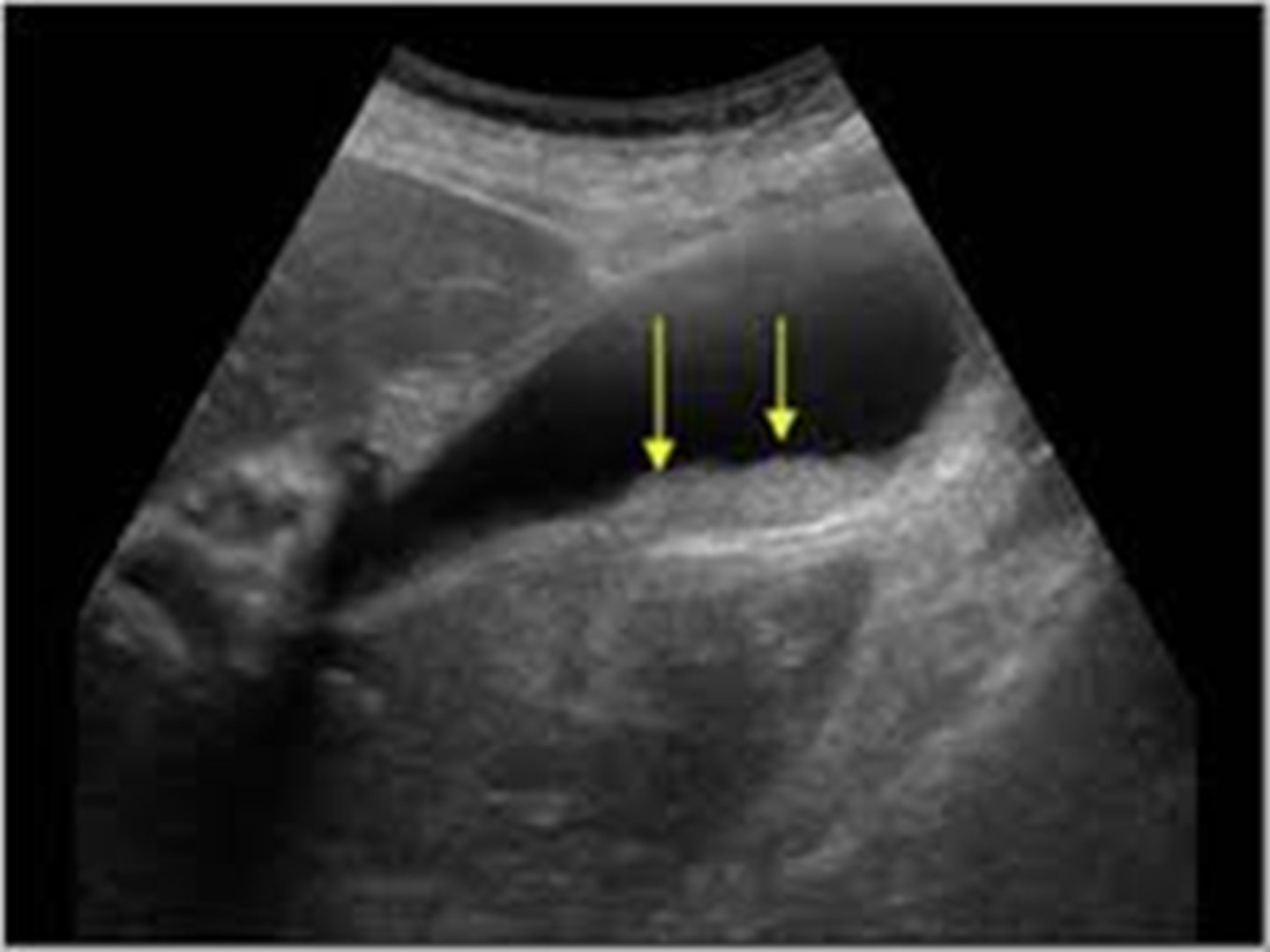
cholecystitis imaging
US- used most commonly, not best option
HIDA scan- useful for obstructed biliary duct, 96% sensitivity 90% specificity
MRI- 88% sensitivity 89% specificity
CT- may show perf or gangrene
pancreatitis
inflammation of pancreas, often related to biliary tract disease or alcohol intake
Sx: abrupt onset deep epigastric pain w/ radiation to back, N/V, sweating, weakness, abdominal tenderness and distention, fever
Labs: leukocytosis, increased serum amylase, increased serum lipase
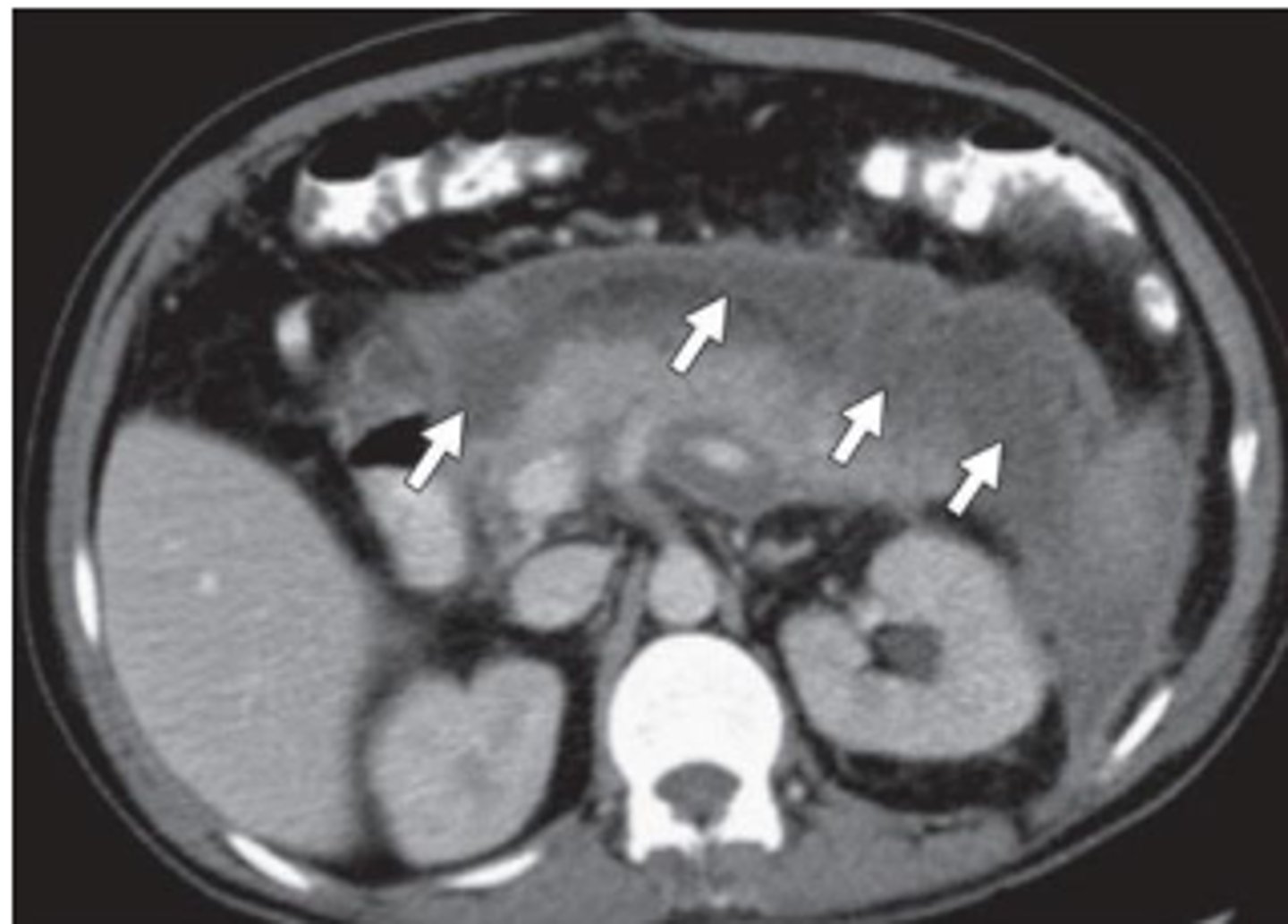
pancreas imaging
xray- may show calcified gallstones, localized ileus
US- not helpful in acute pancreatitis, may identify gallstones
CT- differentiating pancreatitis from other possibilities, enlarged pancreas
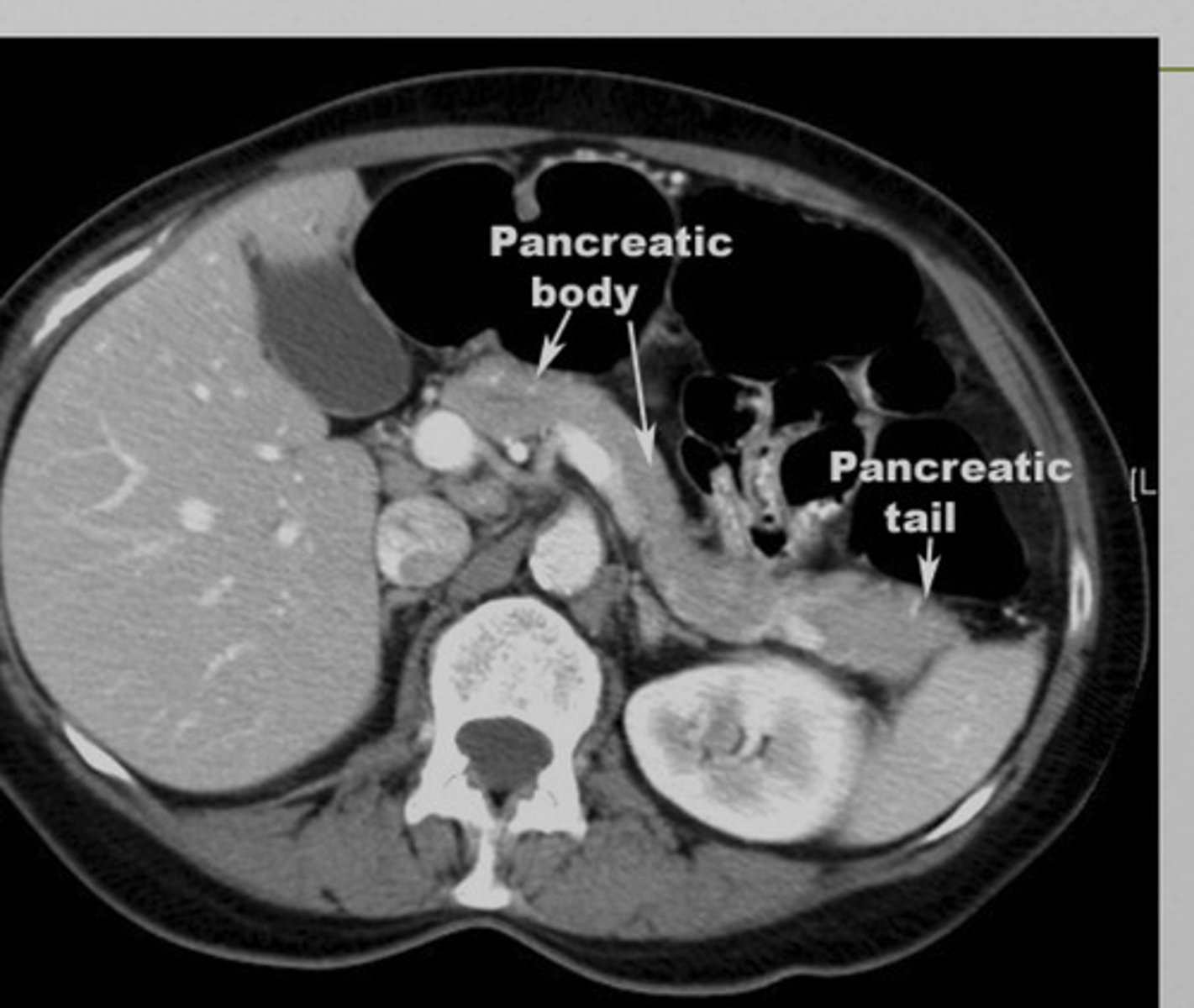
pancreatitis imaging
may appear enlarged and irregular, infiltration of peripancreatic fat, fluid surrounding
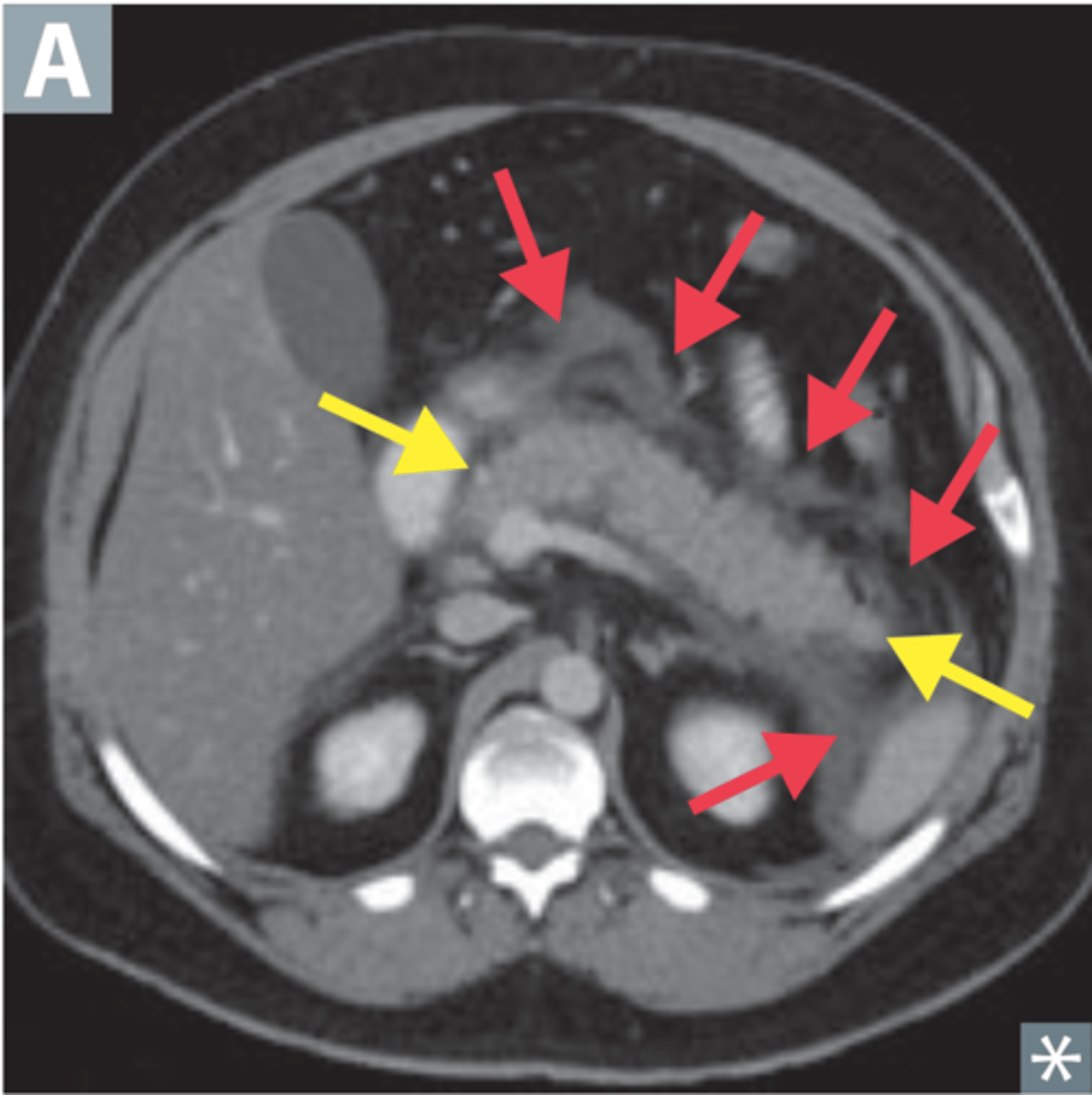
spleen
most highly vascular organ, most injured organ in blunt trauma
CT is diagnostic study of choice
Tx: mostly non-surgical
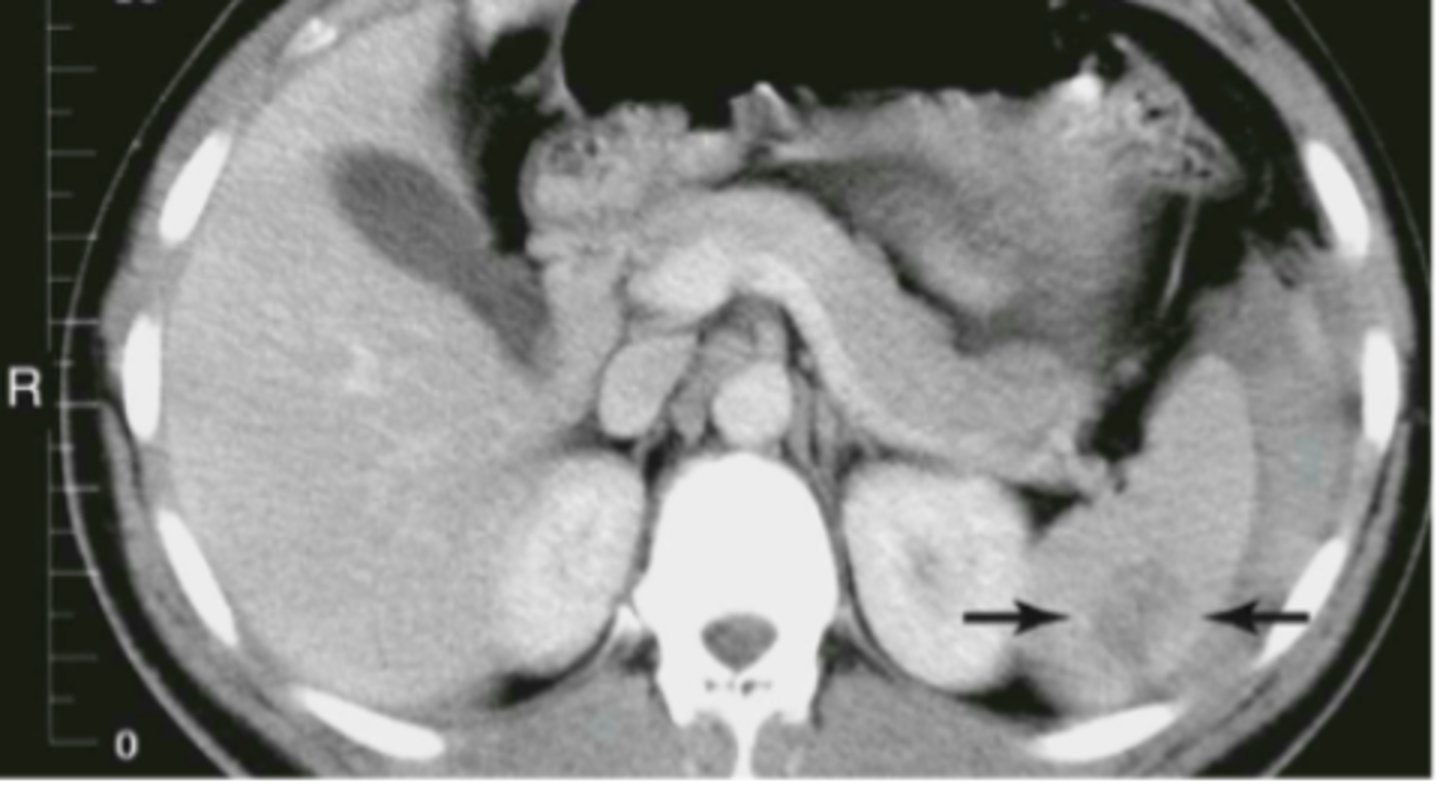
splenic laceration
hemorrhage and hematoma present, dark fluid is blood surrounding spleen
ileus
paralysis of smooth muscle of intestines, inability of intestinal wall to perform peristalsis, bowel sounds decreased or absent
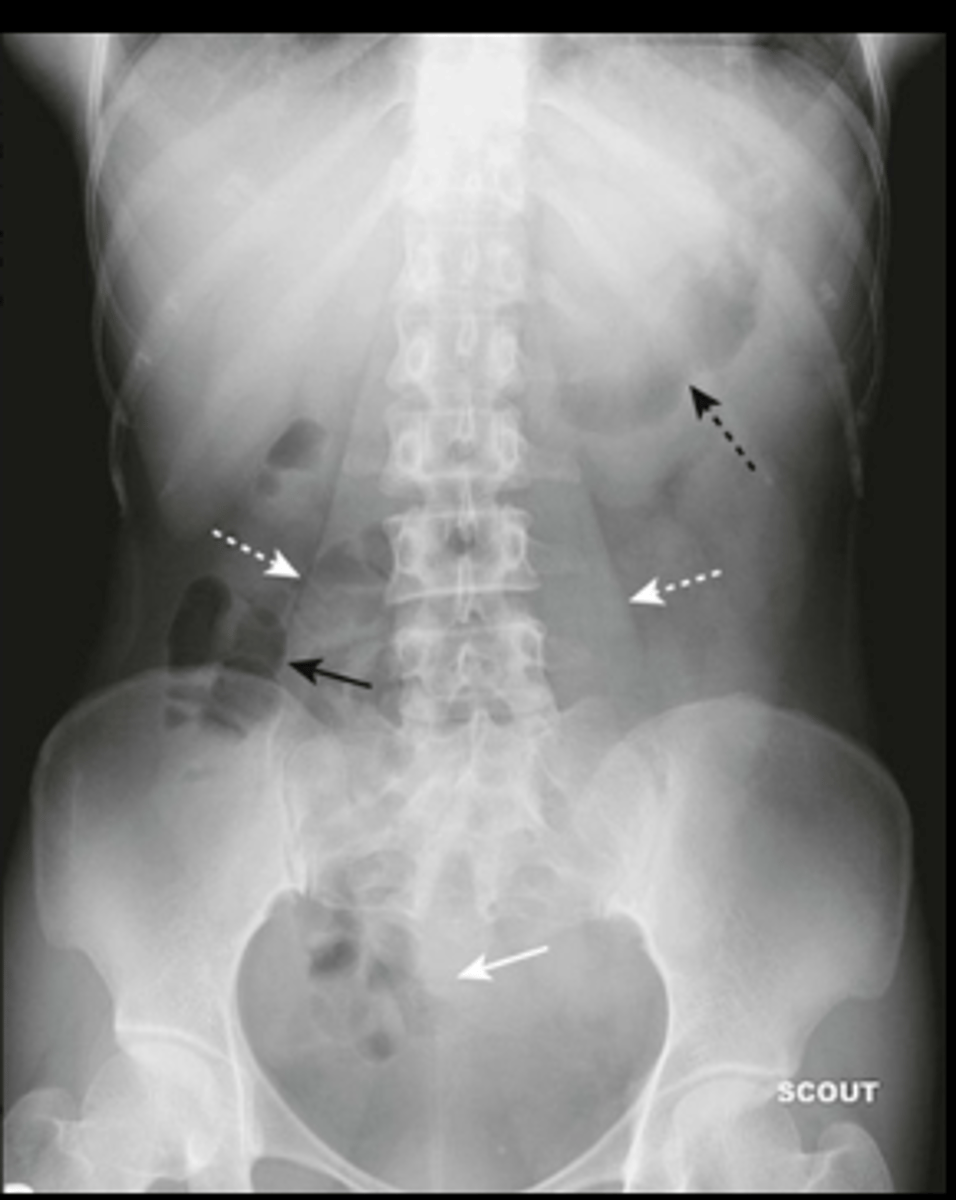
bowel obstruction
mechanical or functional obstruction of small intestine or colon
transition point- site of obstruction, high-pitched hyperactive bowel sounds
- bowel loops proximal to transition point dilate with air, secrete fluid
localized ileus
local irritation of 1 or more loops of a bowel secondary to inflammation of an adjacent visceral organ, "sentinel loops", loops lose normal fxn and become aperistaltic
CT scan shows cause
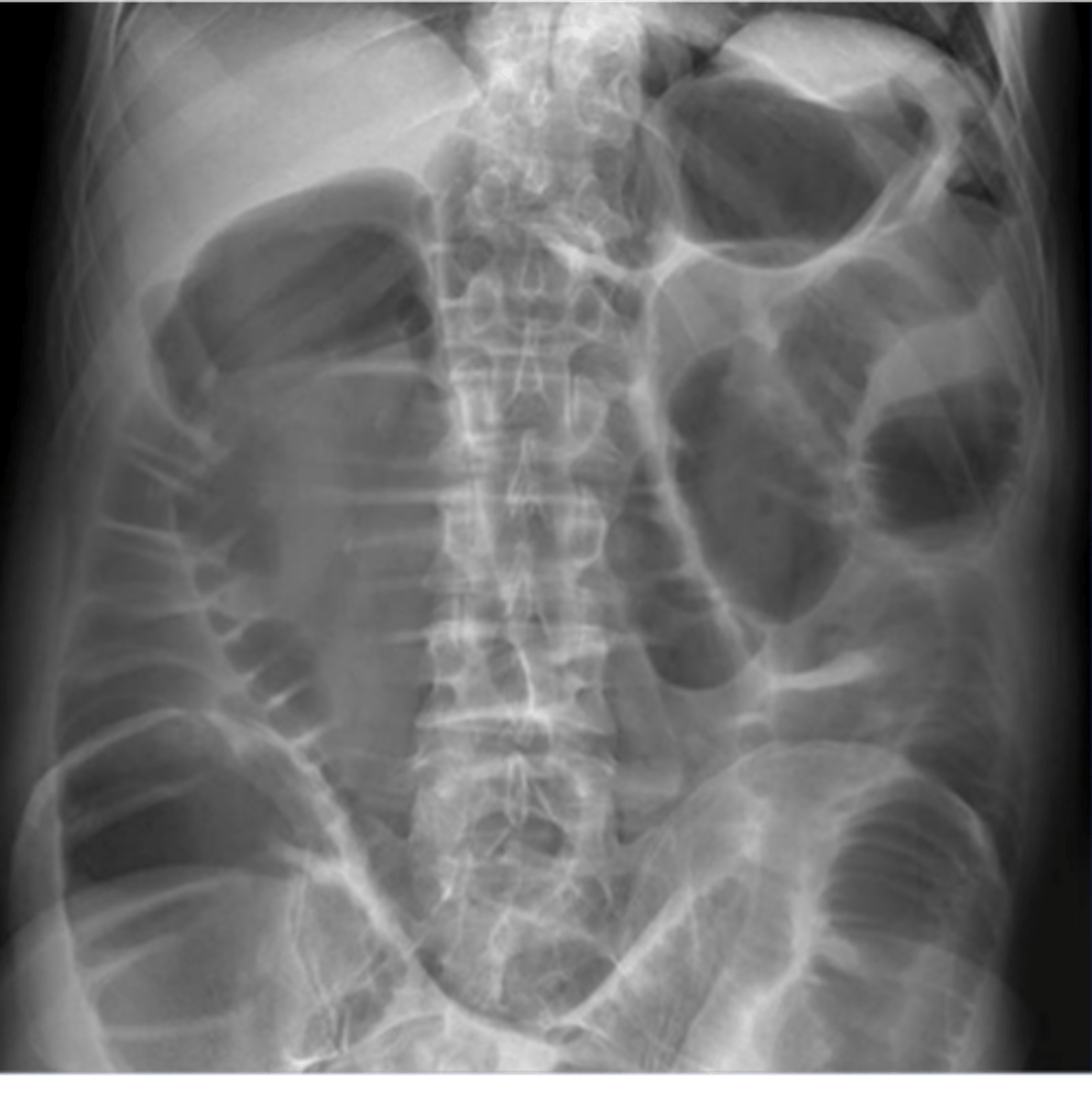
generalized adynamic ileus
entire bowel is aperistaltic, swallowed air dilates and fluid fills most loops of both small and large bowel
on imaging entire bowel is air-containing and dilated, air fluid levels, gas in rectum or sigmoid
bowel obstructions
small vs large bowel, causes differ based on bowel type
XRAY can be helpful
CT is most sensitive study for diagnosing site and cause
- oral contrast helps identify dilated loops -> do not use if large bowel obstruction suspected
- IV contrast helps detect complications of bowel obstruction
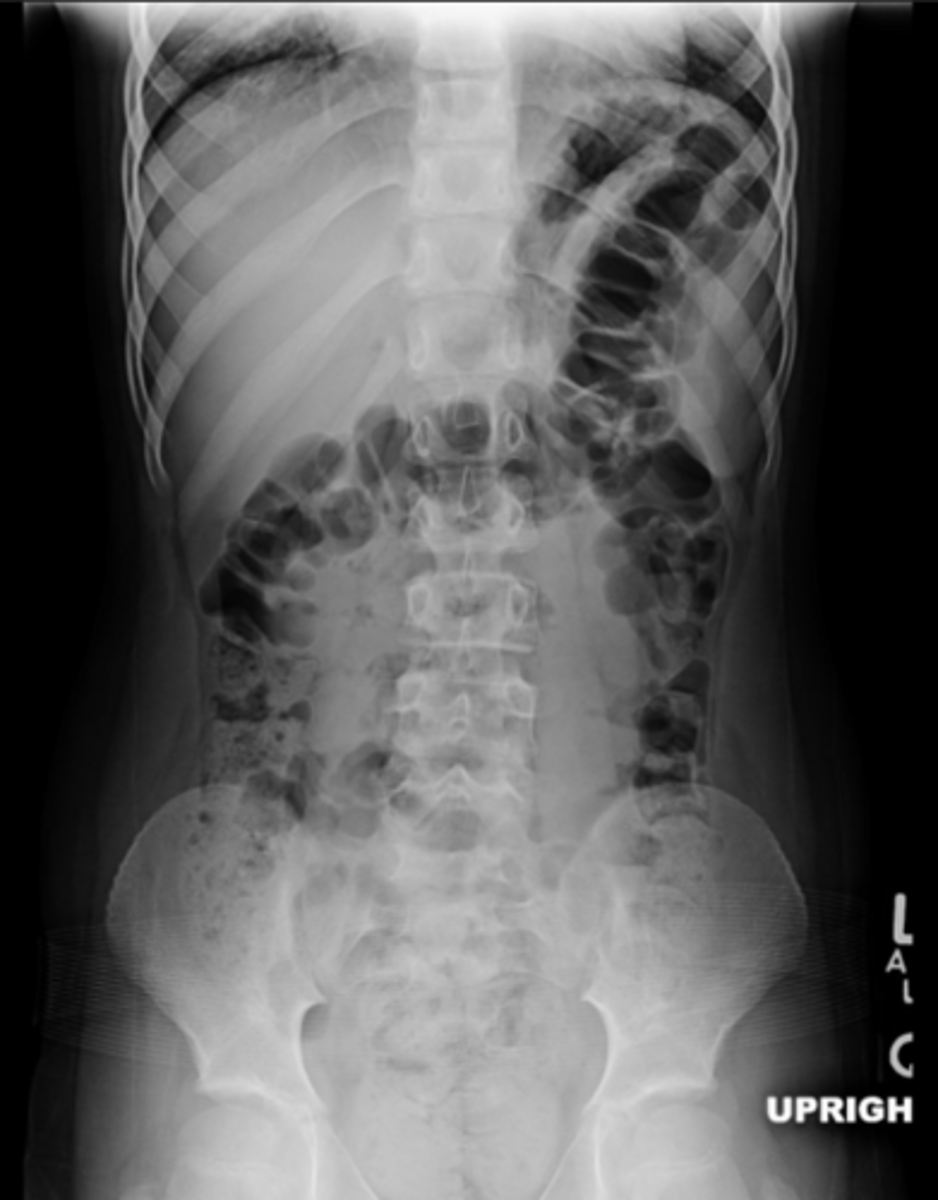
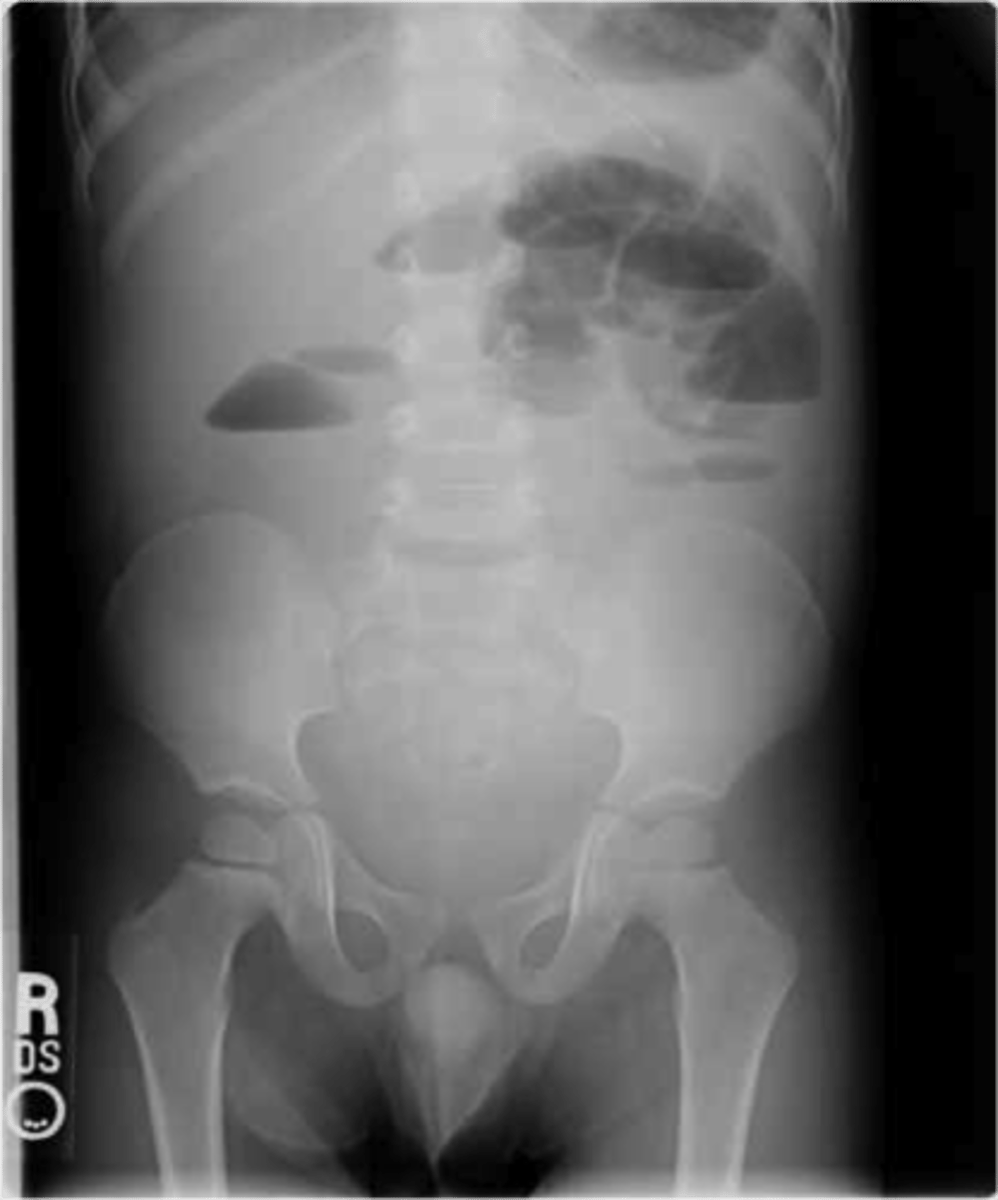
small bowel obstruction
lesion obstructs lumen, proximal to transition point bowel loops become dilated with air, distal to transition point bowel loops become decompressed, no air in rectosigmoid
causes: post-op adhesions, malignancy, hernia, gallstone ileus, intussusception, IBD
SBO imaging
X-Ray shows multiple dilated bowel loops, "step ladder appearance", no or little gas in colon/rectum
CT shows transition point, small-bowel feces sign (proximal to transition intestinal debris and fluid accumulate
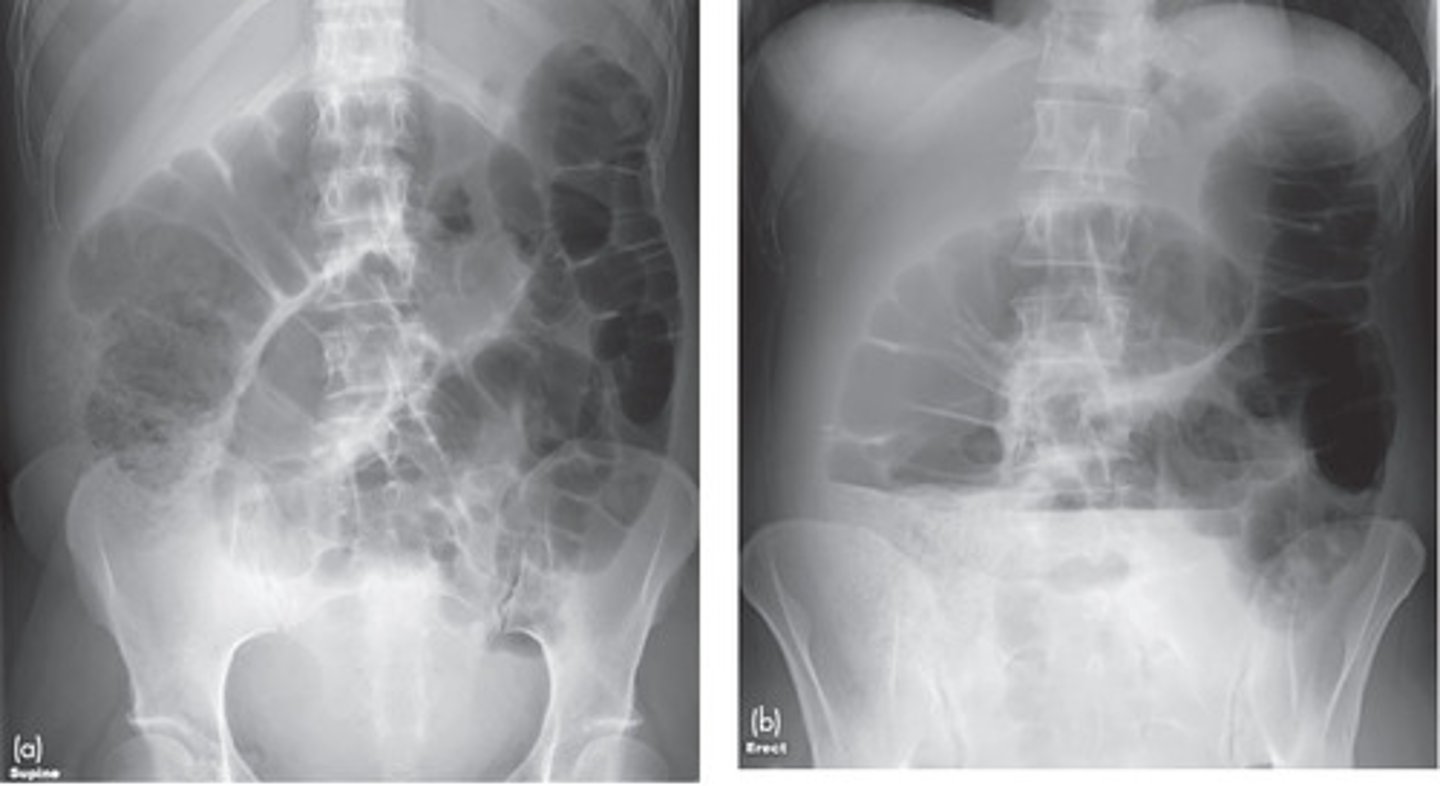
Large bowel obstruction
lesion obstructs lumen of the large bowel, proximal to transition point large bowel dilates, distal to transition point peristalsis continues, emptying colon
Causes: tumor, hernia, volvulus, diverticulitis, intussusception
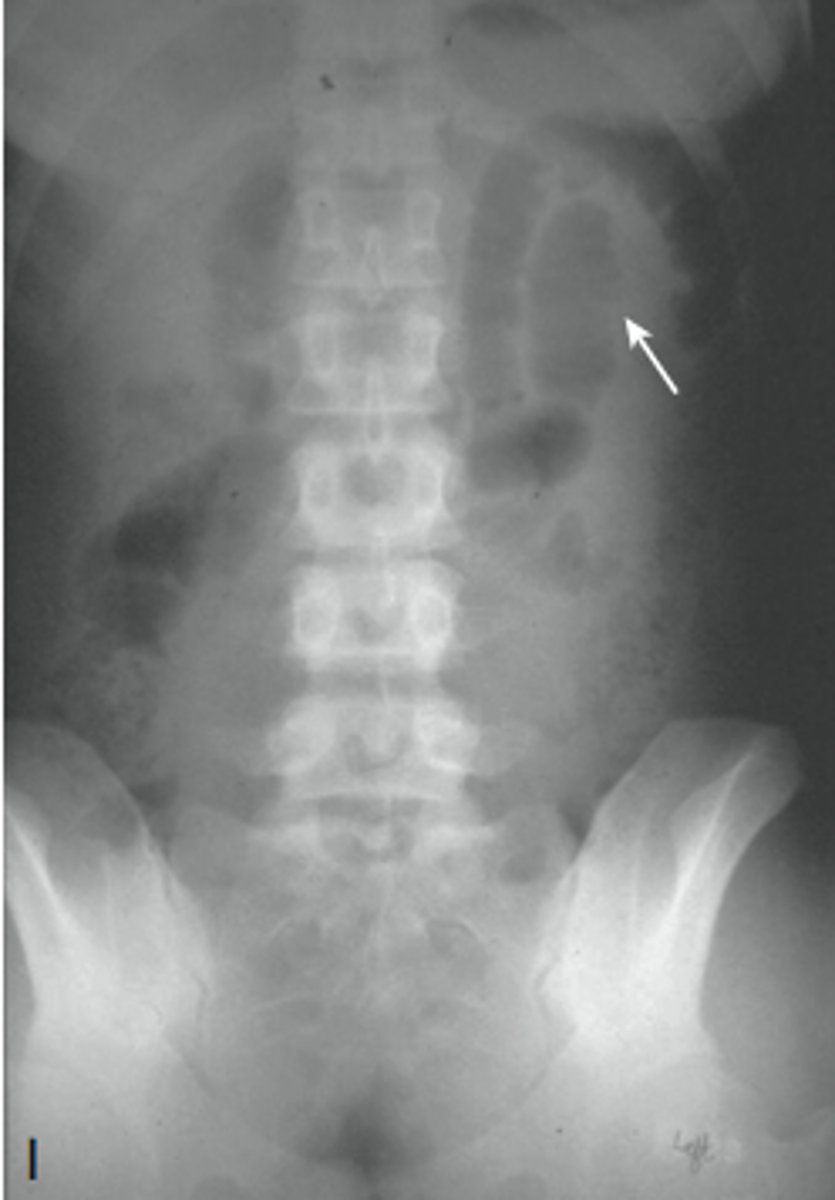
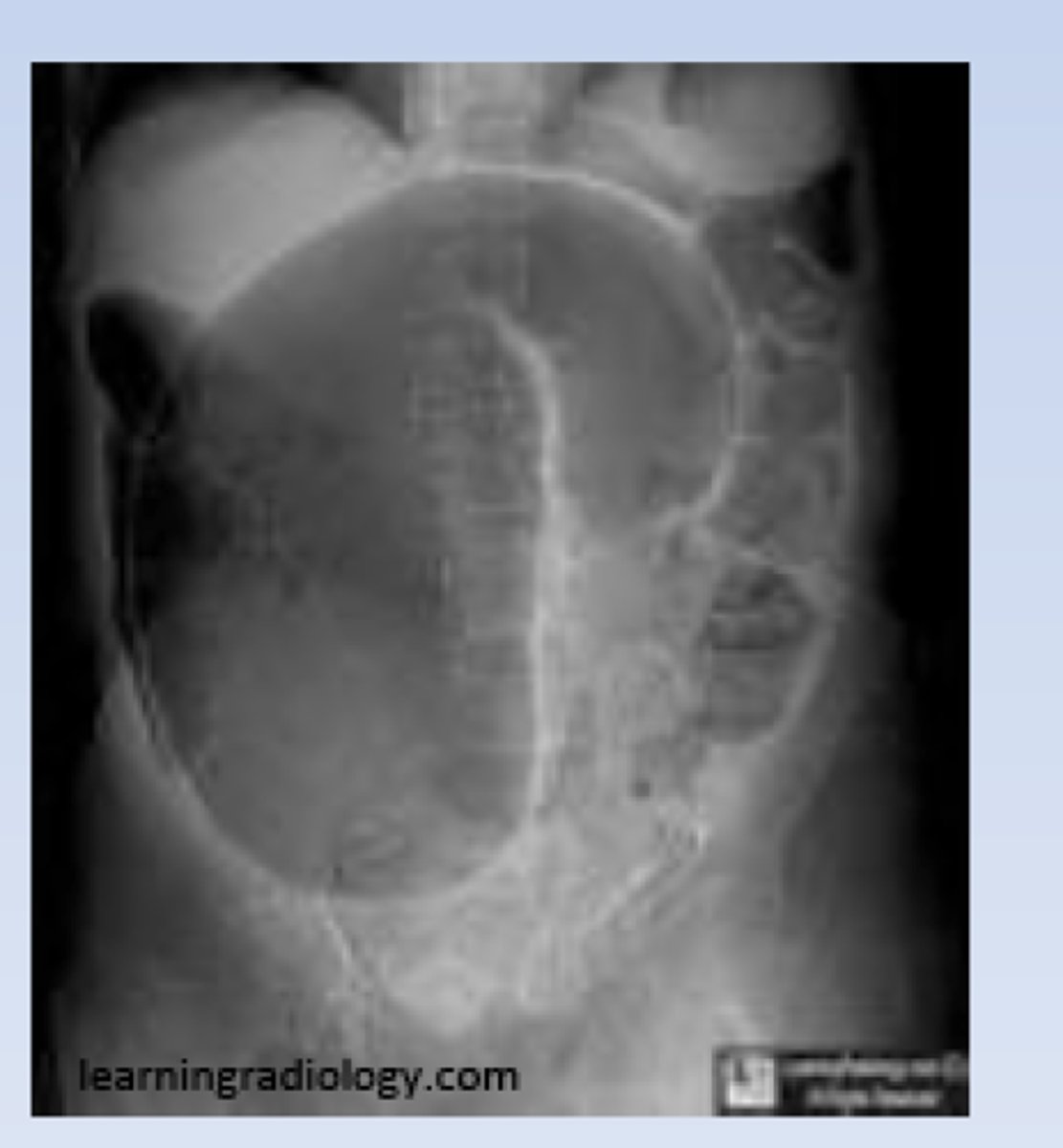
sigmoid volvulus
dilated sigmoid colon, air and stool in more proximal descending colon
can lead to strangulation (vascular compromise leading to infarction of bowel wall)
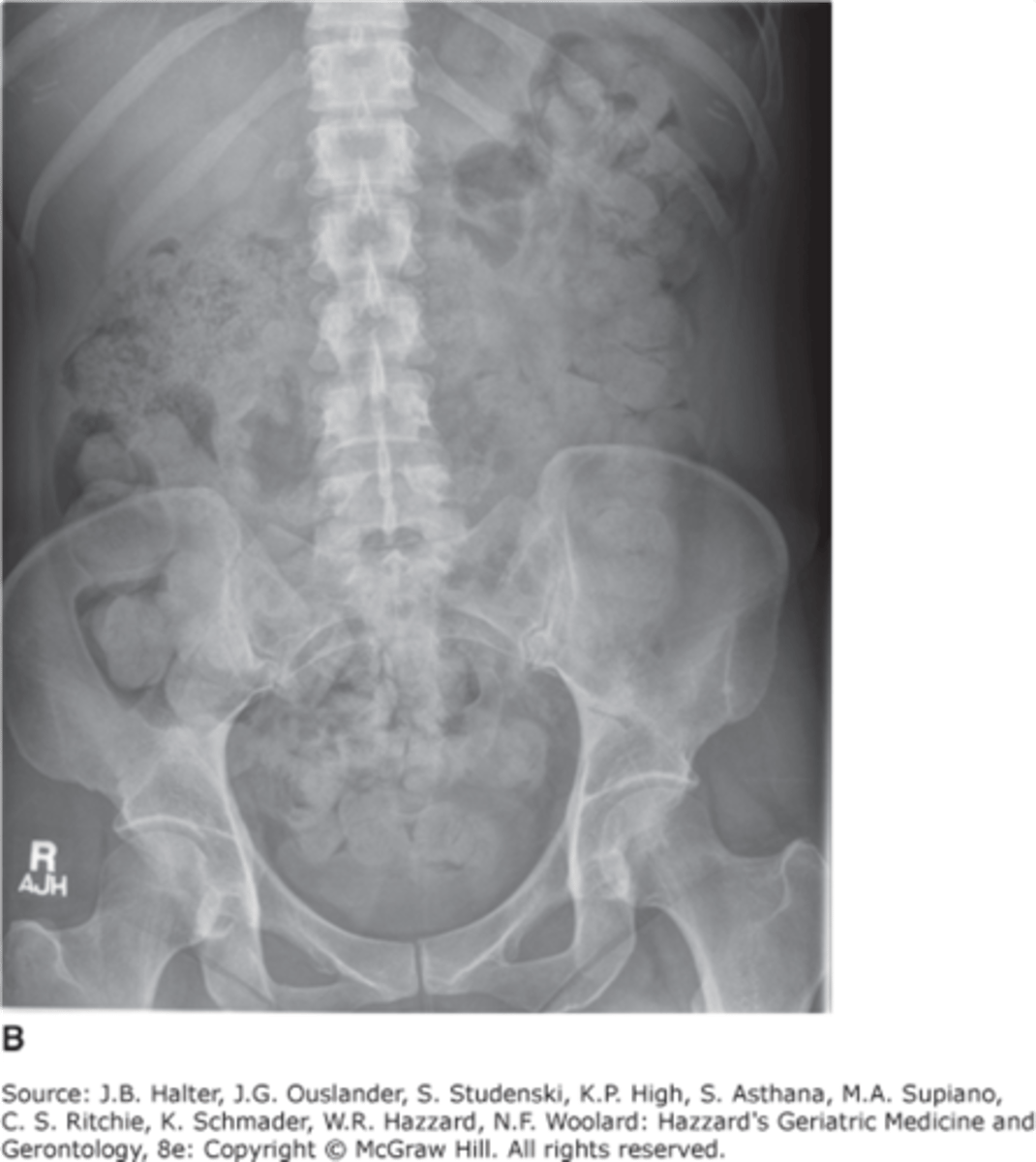
constipation
air in distal rectum, no bowel obstruction present
appendicitis
obstruction of appendix by a fecalith, inflammation, foreign body, or neoplasm -> leads to increased intraluminal pressure, venous congestion, infection and thrombosis of intramural vesses
S/Sx: vague pain, pain shift to RLQ, N/V, low fever
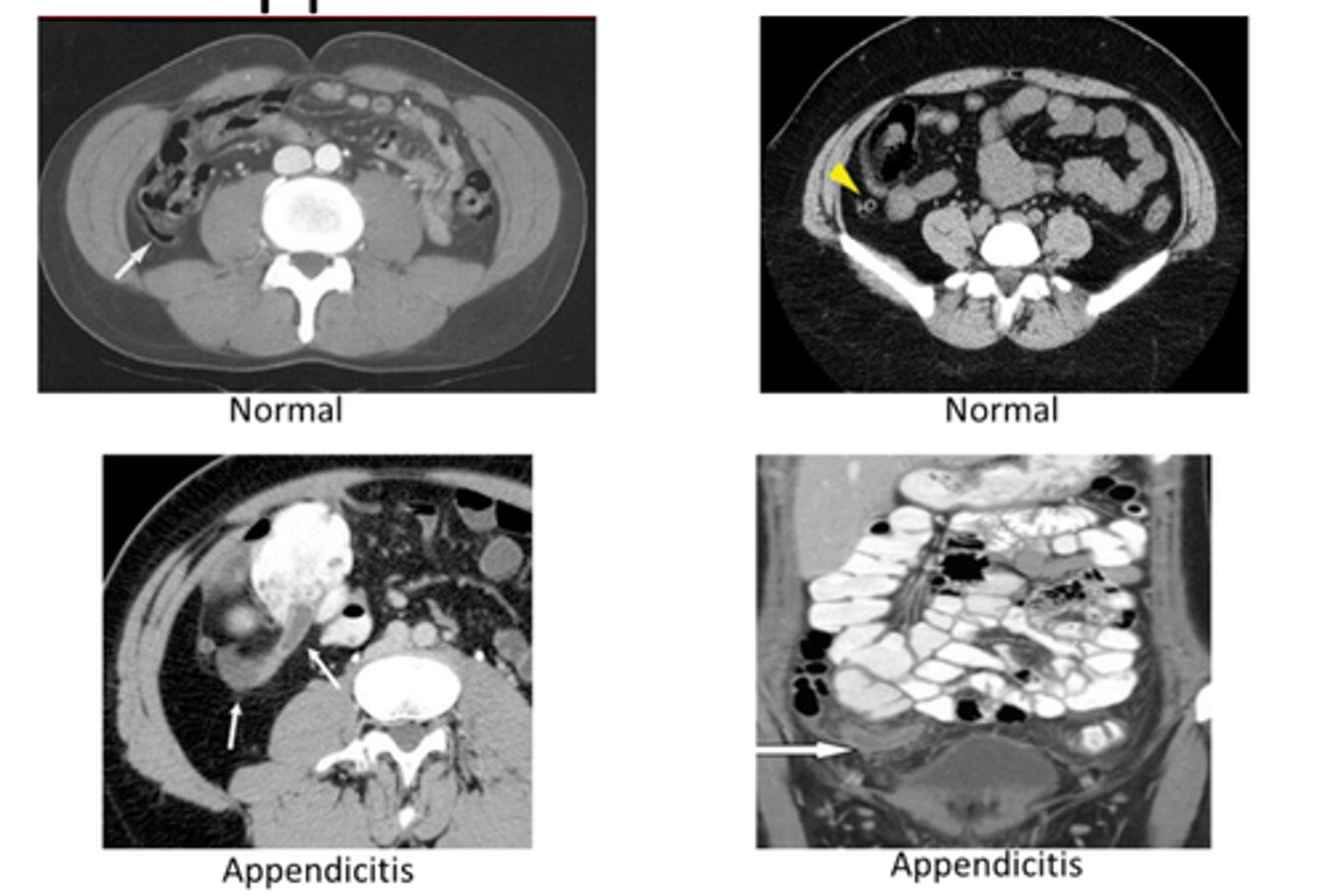
appendicitis imaging
CT- diagnostic study of choice in adults, dilated appendix that does not fill w oral contrast, periappendiceal inflammation, increased contrast enhancement of wall, perforation
US- diagnostic study of choice in pediatric pts
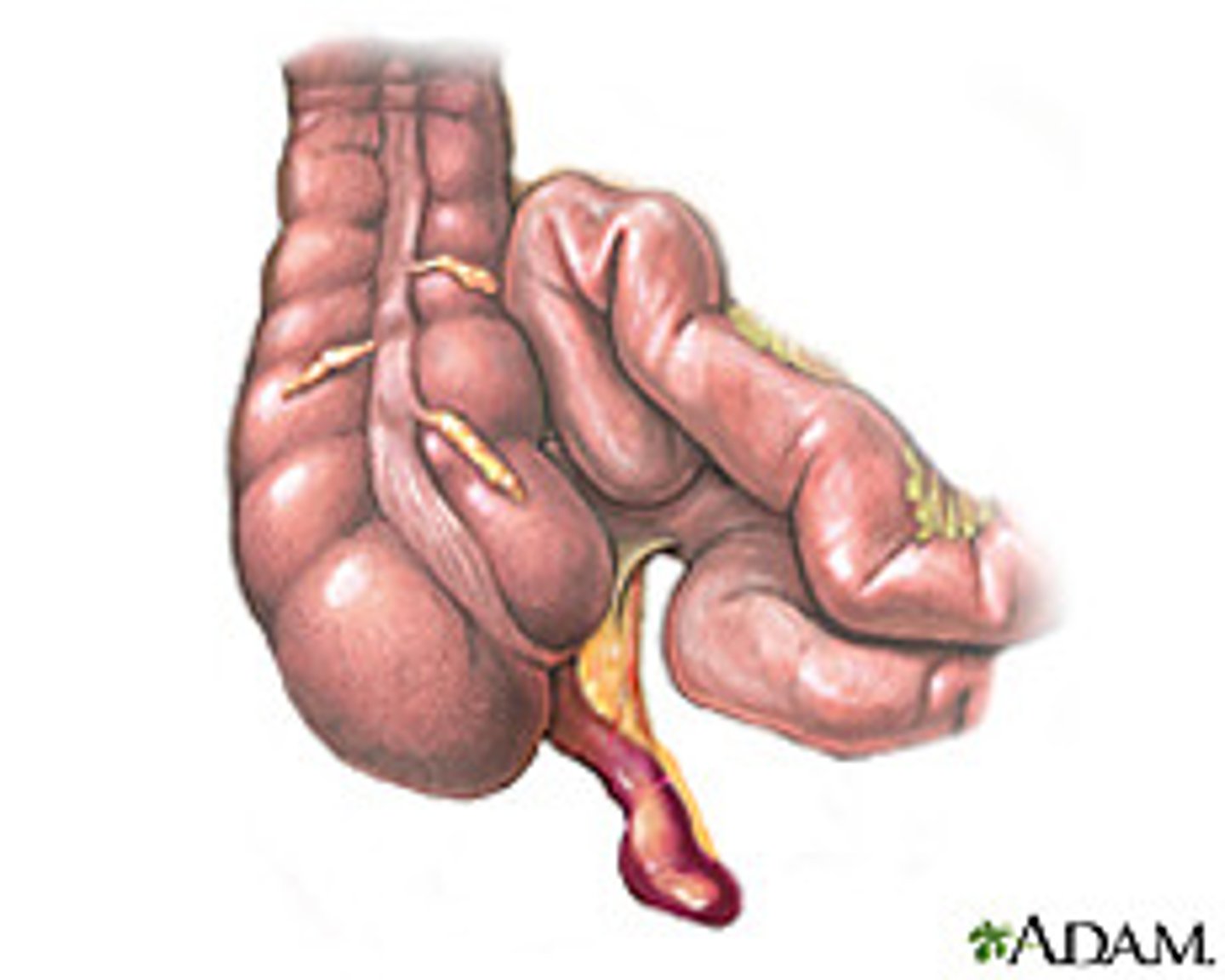
appendix
can be seen where it joins cecum, often not seen on CT
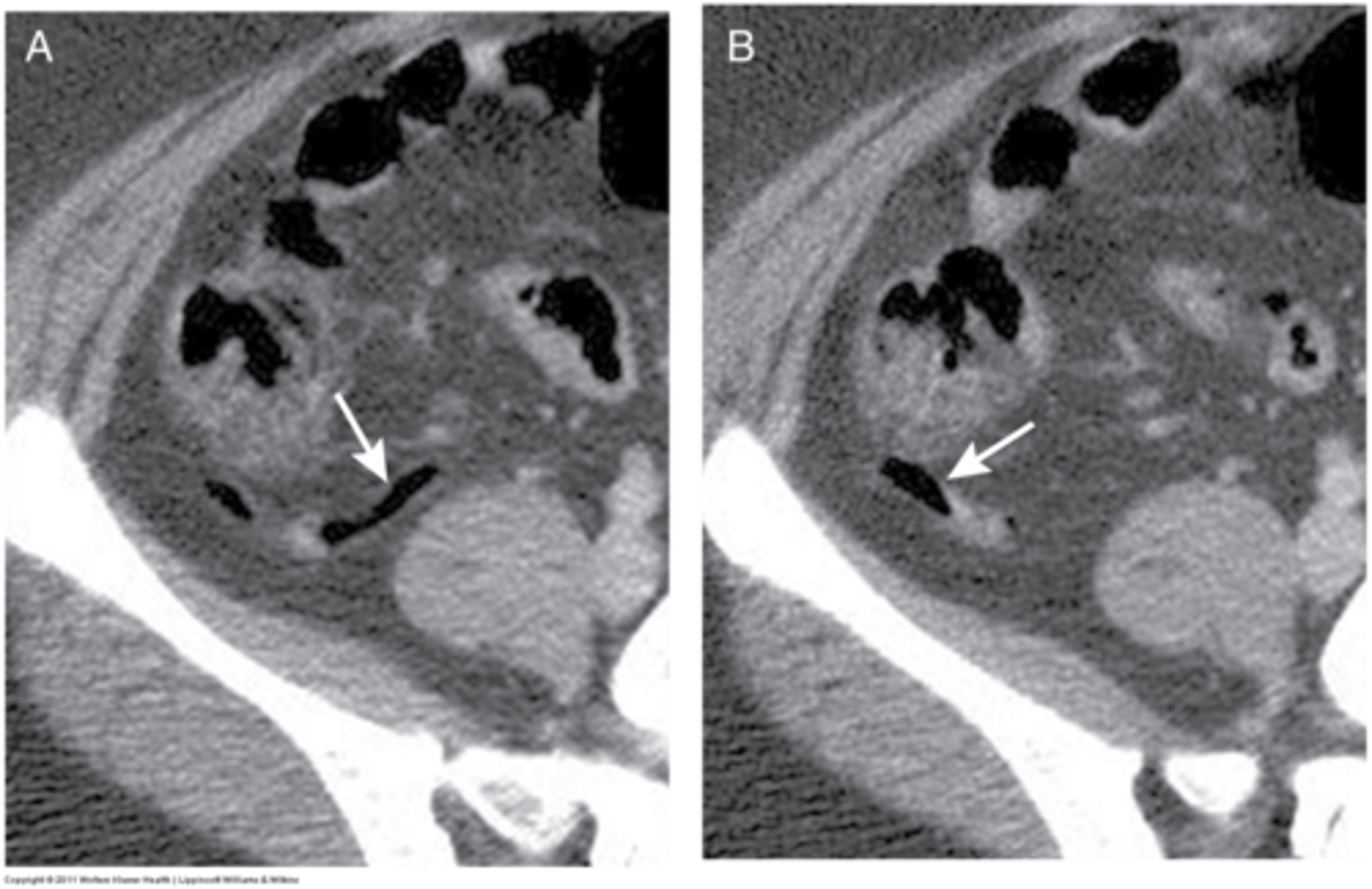
diverticulosis
outpouchings of colon, uncertain etiology, 90% pts asymptomatic, some pts have chronic constipation, abdominal pain, fluctuating bowel habits
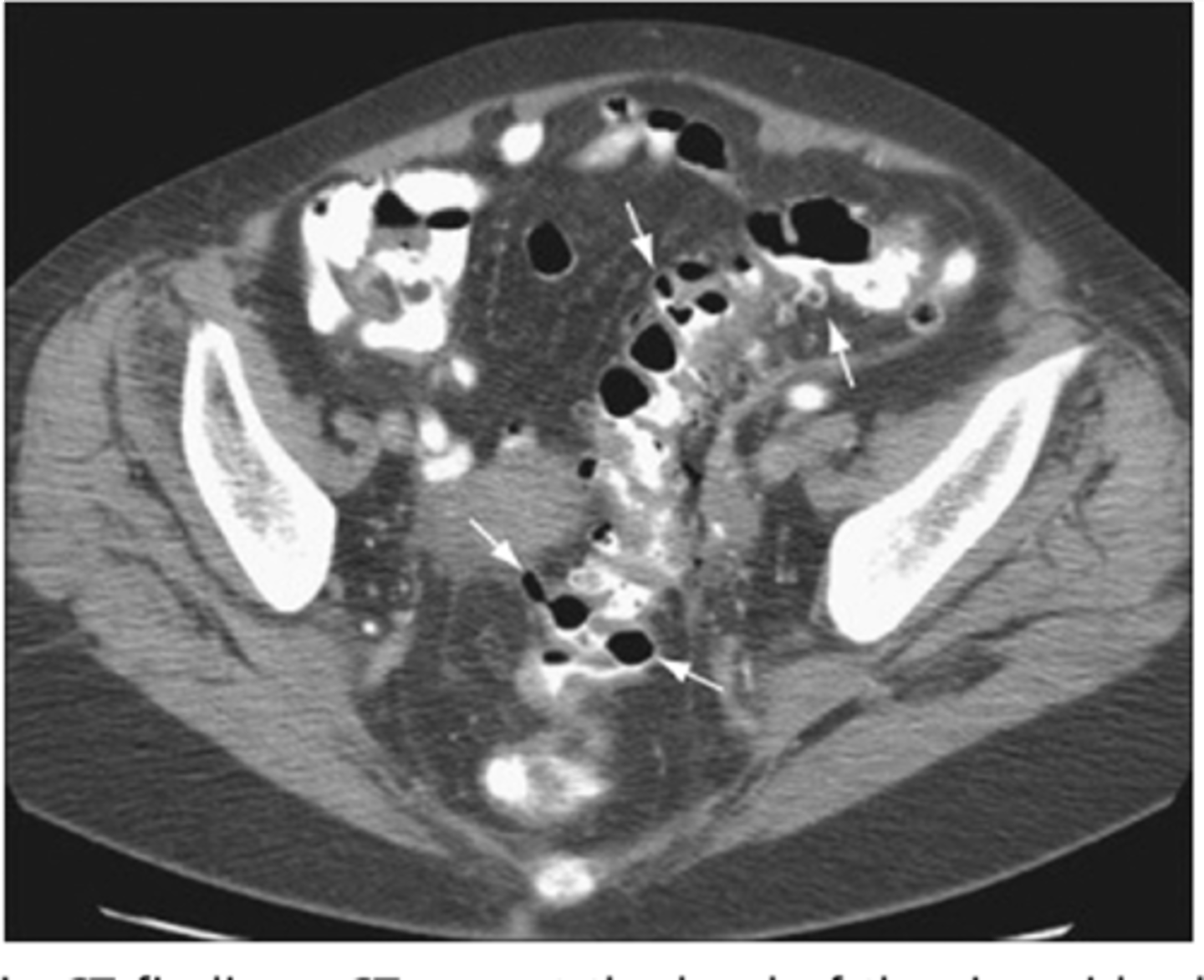
diverticulosis CT
air filled outpouchings of colon that represent diverticula
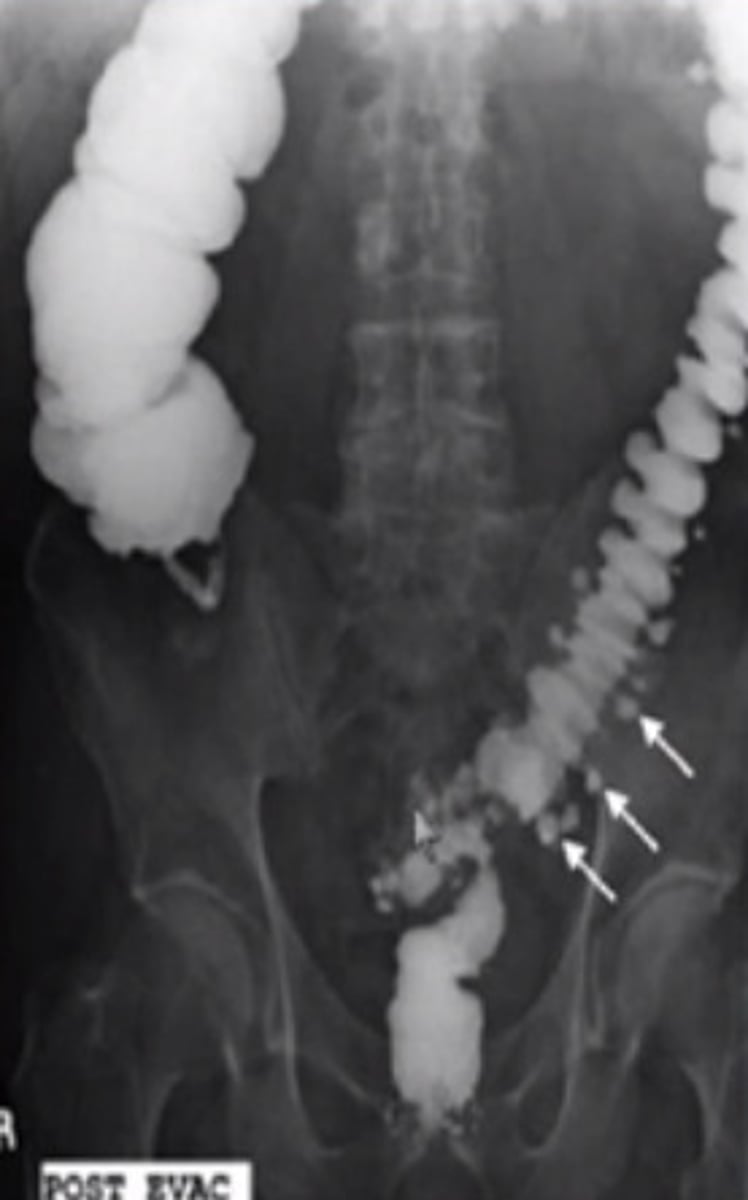
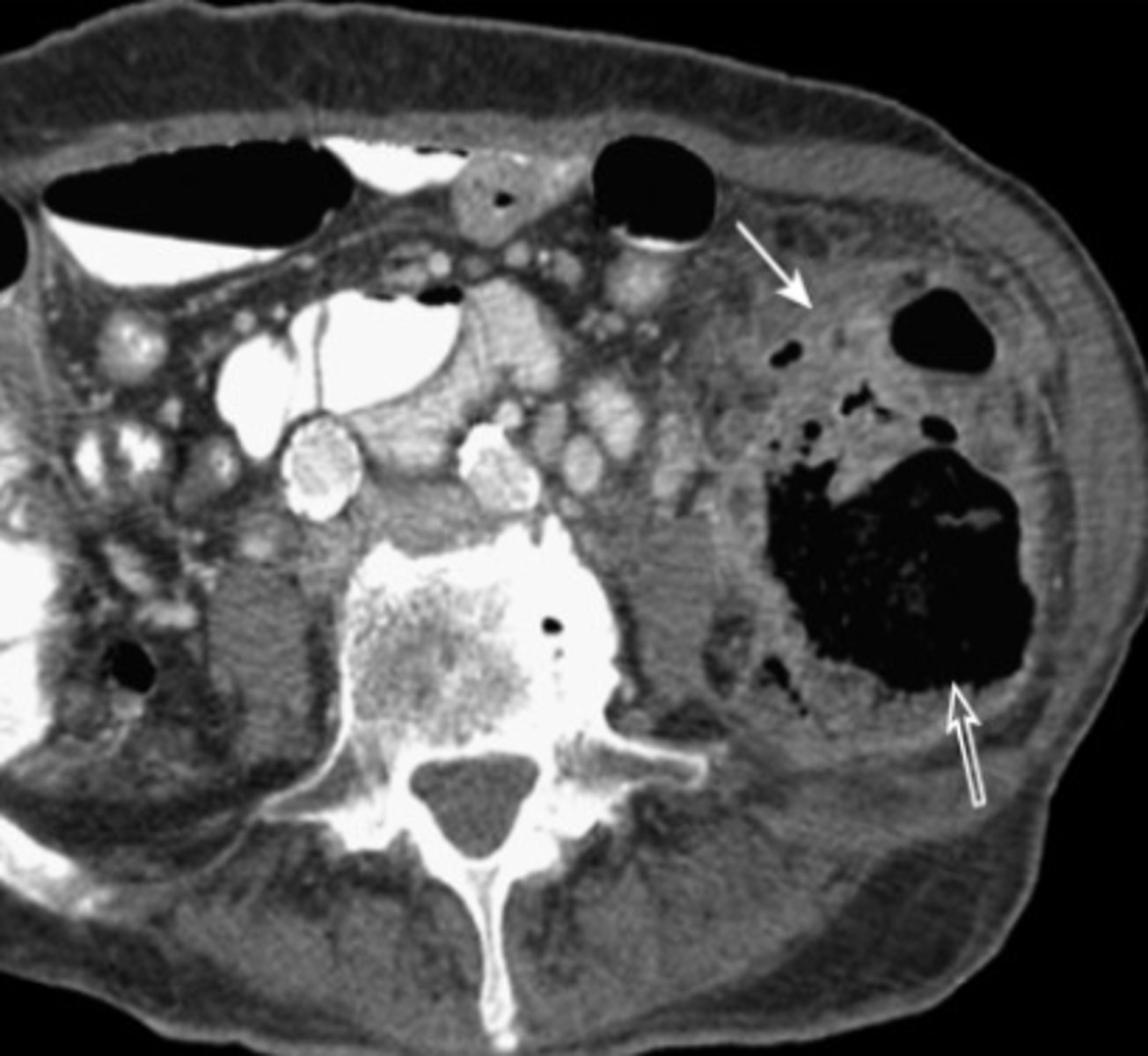
diverticulitis
macroscopic inflammation of a diverticulum, may lead to microperforation, abscess, or peritonitis
S/Sx: aching LLQ pain, N/V, constipation or loose stools
Abdominal CT + f/u Colonoscopy or CT colonography
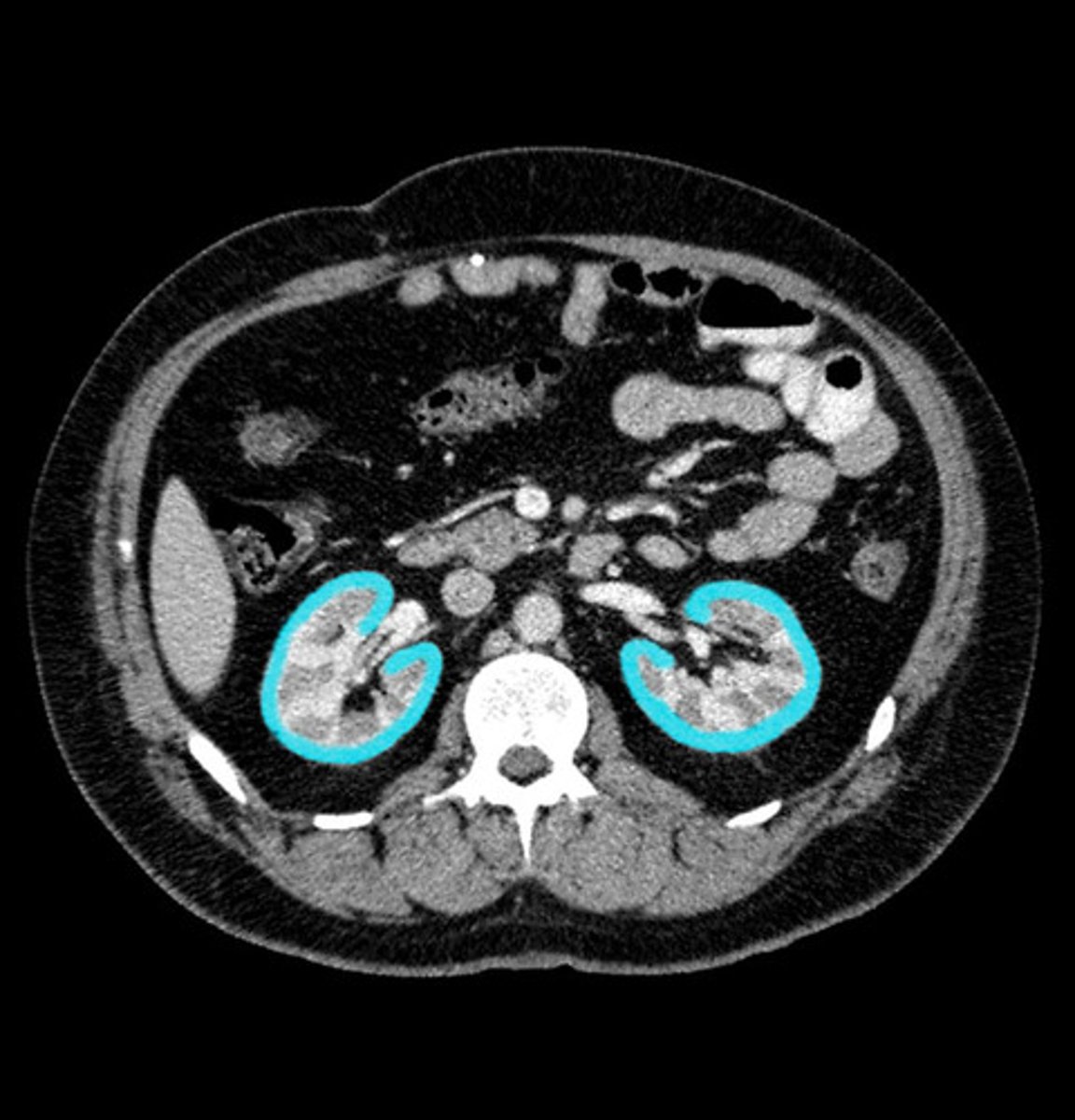
renal imaging
xray (IV pyelography)- mainly replaced by US and CT
US- size, symmetry, lesions, kidney stones, obstructions, hydronephrosis
CT- characterize US abnormalities, study of choice for nephrolithiasis, trauma
MRI- renal cell cancer, mass
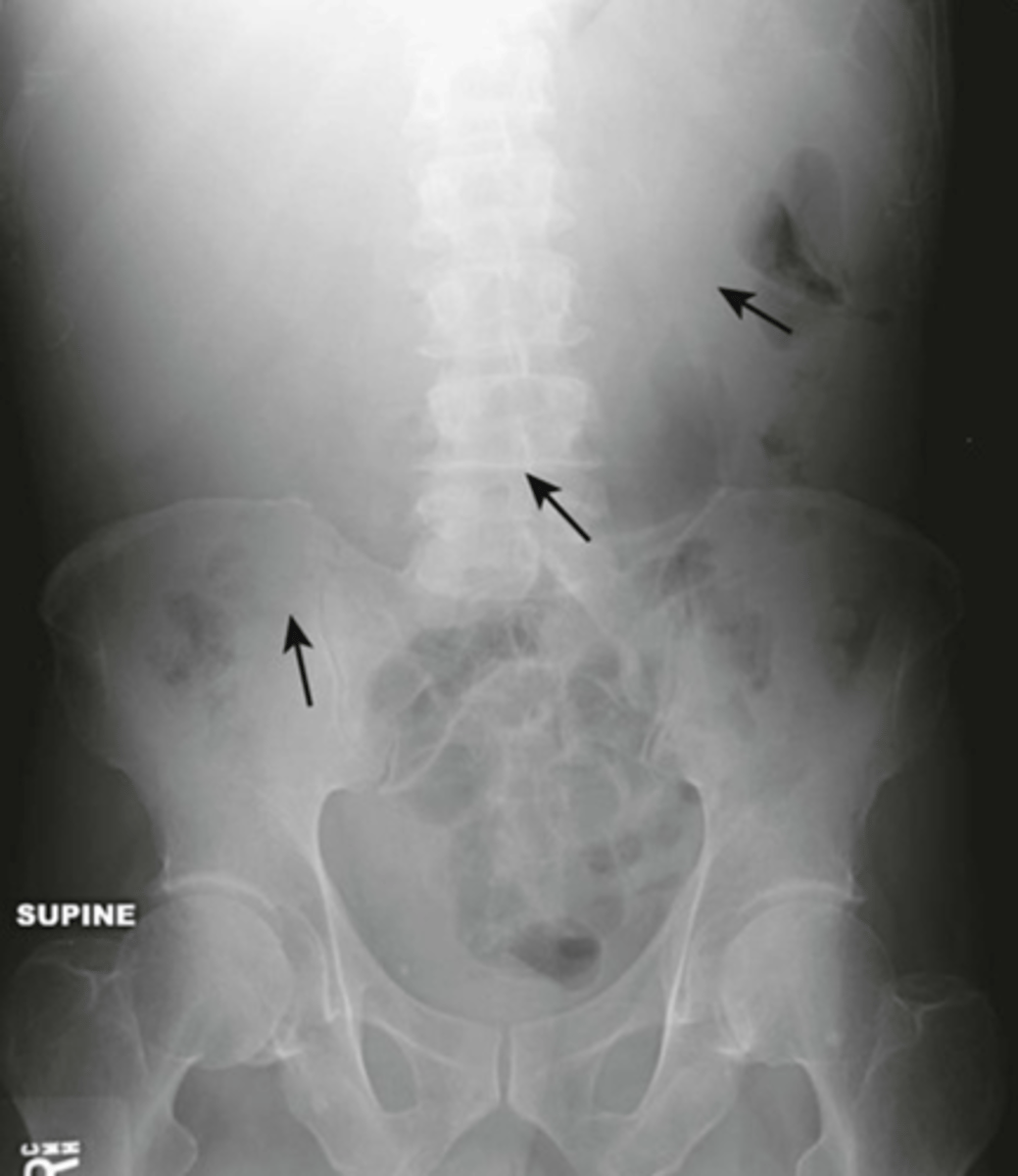
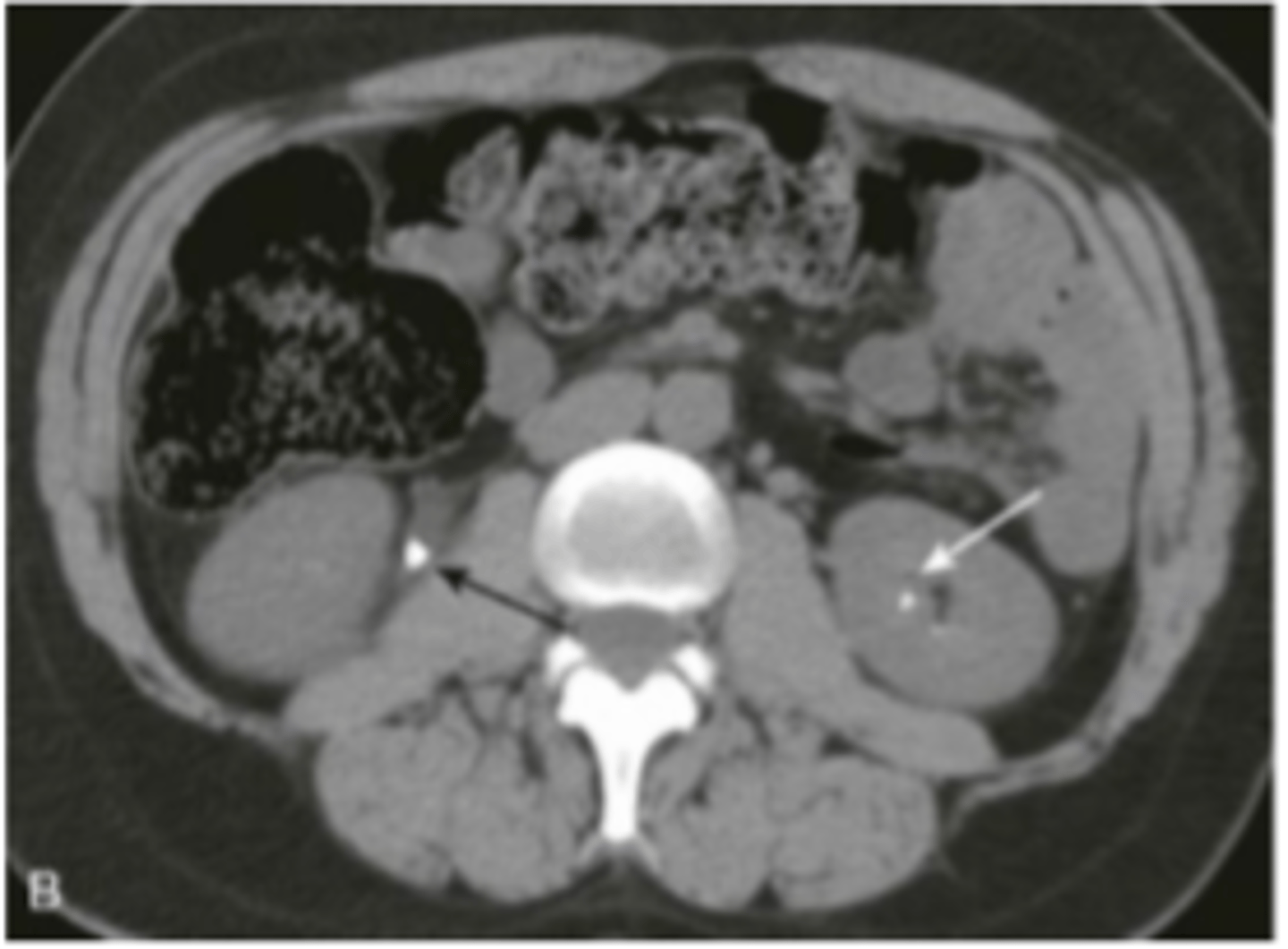
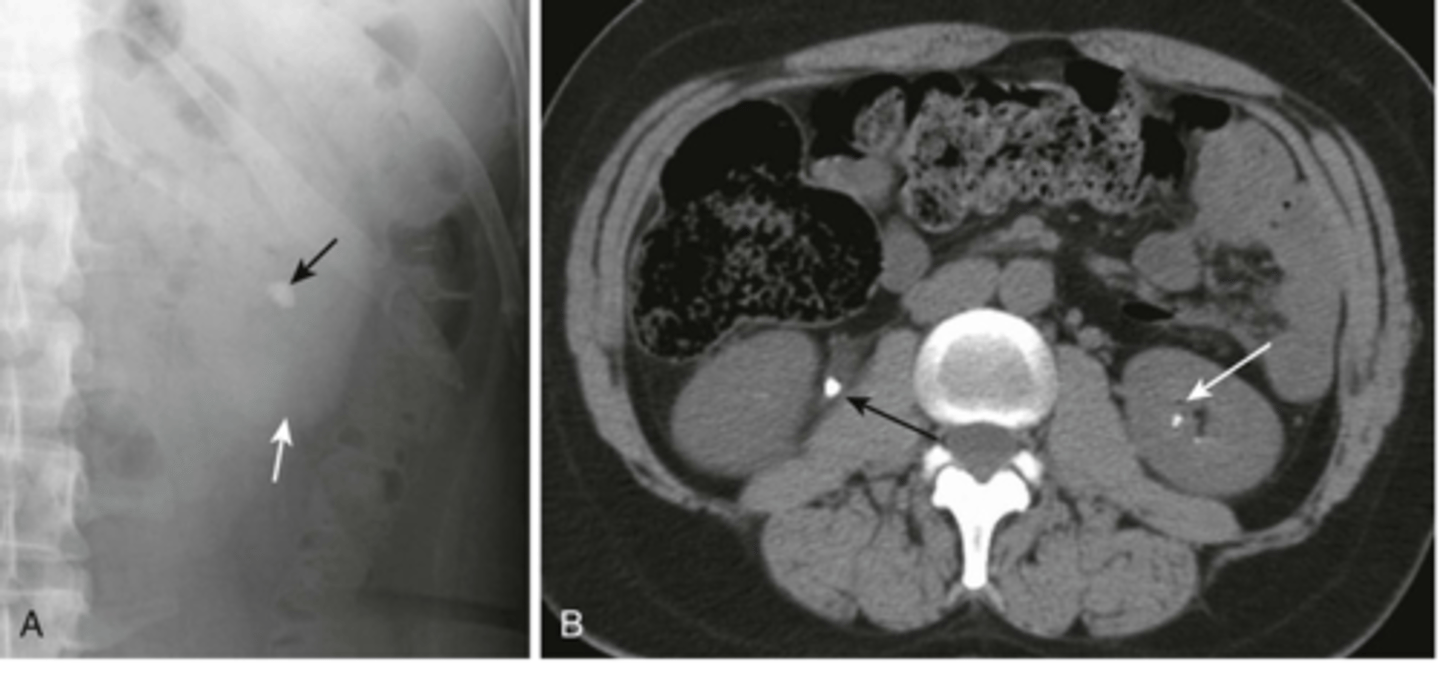
renal calculi
stone in R ureter, stone in L kidney
bladder imaging
X-ray- only enlargement
Ultrasound- asses wall thickness, tumors, stones, diverticula, estimate post-void volume
CT- characterize bladder cancer metastases and local disease
Cystoscopy- visualize bladder
scrotal ultrasound
1st line imaging for acute causes of scrotal pain, Color doppler US is used in assessment of suspected torsion
female pelvic organs
US- imaging study of choice in mass or pain, transabdominal or transvaginal
CT- assists in localizing masses and surrounding structures
uterine leiomyomas (fibrosis)
benign smooth muscle tumors of uterus that occur in up to 50% of women >30, usually asymptomatic, can cause pain, pelvic US is imaging study of choice
Ovarian ultrasound
US is imaging study of choice for evaluating ovaries, cysts/tumors/torsion/PID
pregnancy
US is safe and reliable means of visualizing fetus
exclude ectopic pregnancy, estimate age, determine viability, number of embryos, estimate amniotic fluid vol, detect abnormalities, placental and fetal positioning, guidance for invasive studies
MSK imaging
Xray- study of choice for initial testing and most injuries
CT- complex fractures, preop planning, eval of soft tissue infections/masses
MRI- study of choice for soft tissue pathology and injury
Nuclear medicine bone scan- study of choice for detecting skeletal metastases
Ultrasound- soft tissue injury eval
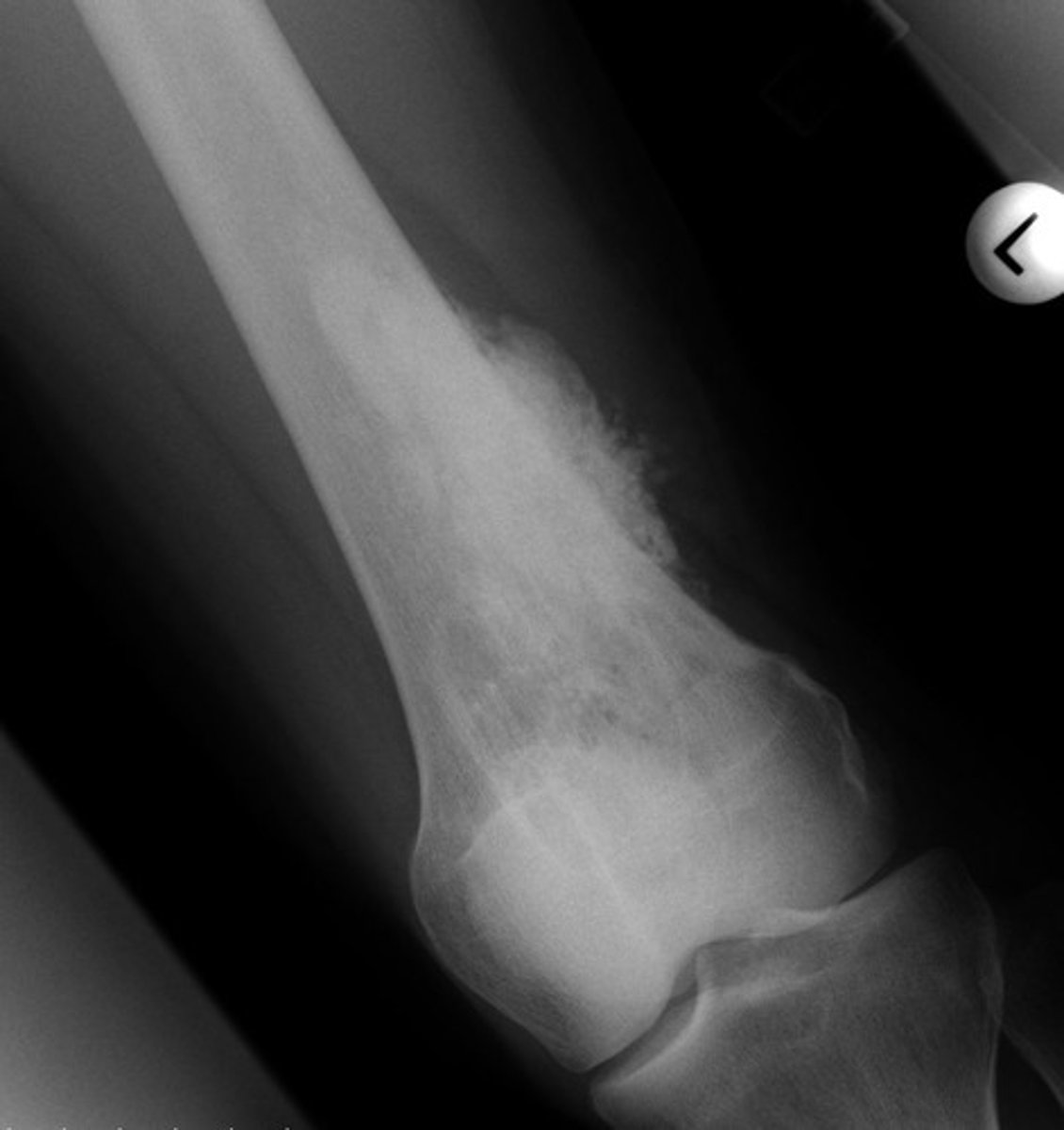
osteoblastic diseases
increase bone density, seen as opaqueness (sclerosis), abnormal cortico-medullary junction, possible pathological fractures of long bone
ex. osteosarcoma, osteoblastic metastatic disease, avascular necrosis of bone, paget disease
osteosarcoma
most common primary bone malignancy, adolescents, tumor arising from osteoblastic connective tissue
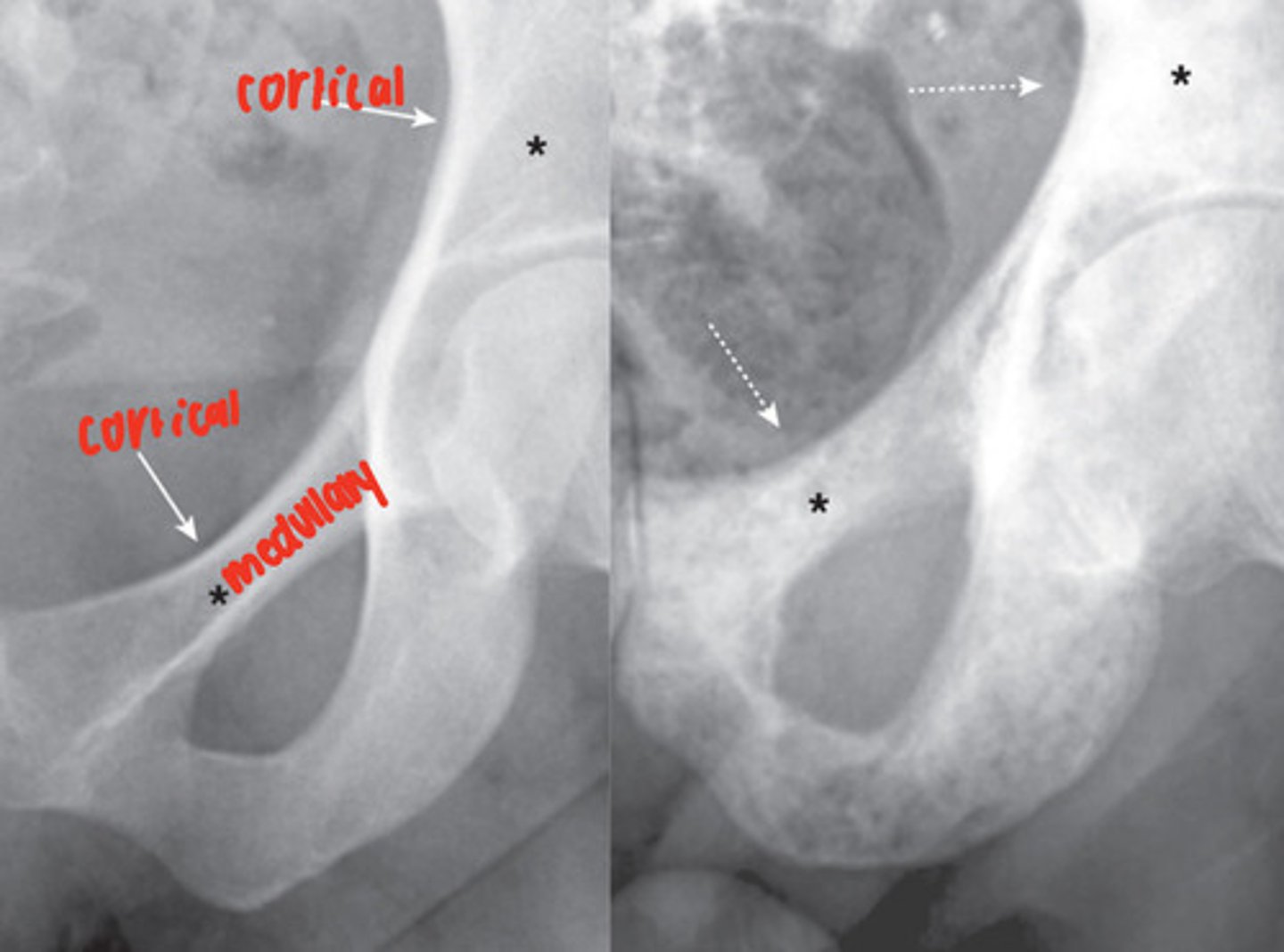
osteoblastic metastatic disease
malignancy that has spread into the bone, lesions most often seen in vertebrae, ribs, pelvis, humeri, femora
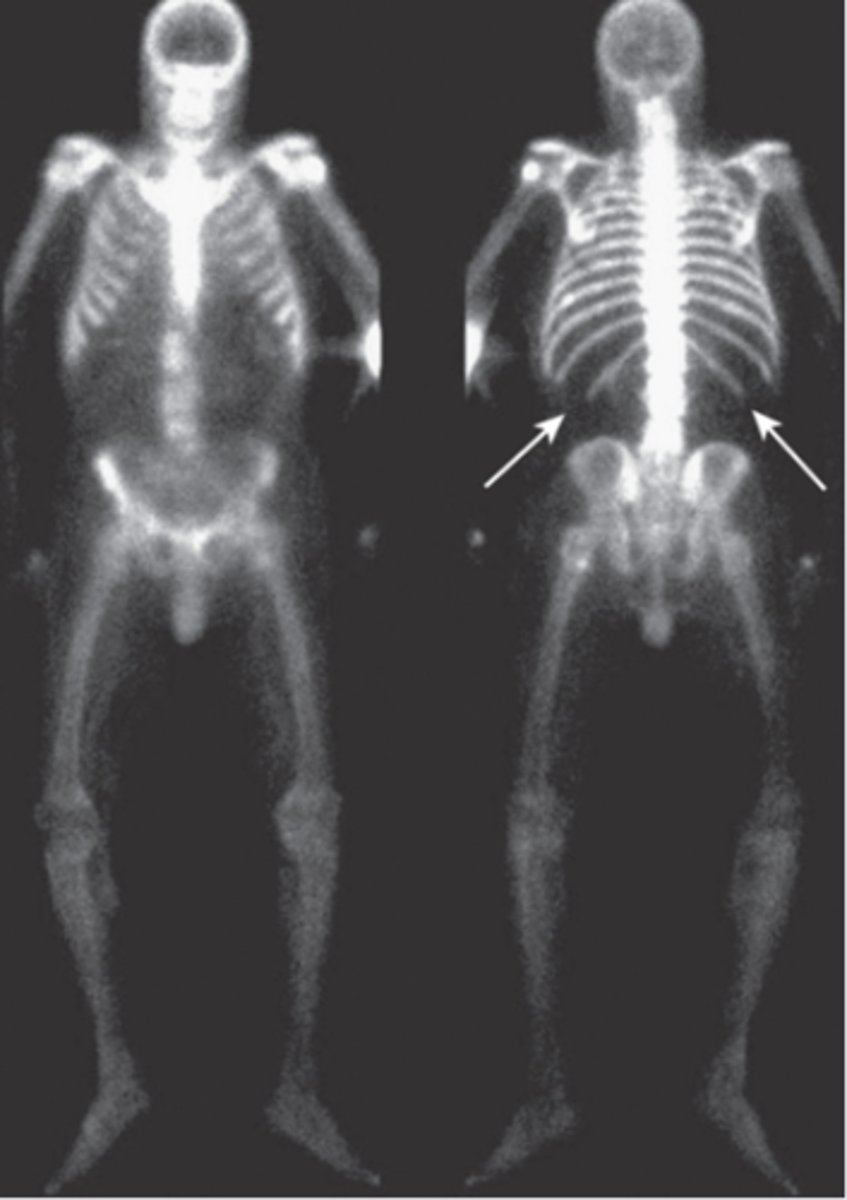
radionuclide bone scan
metastatic disease involving nearly every bone in the axial skeleton
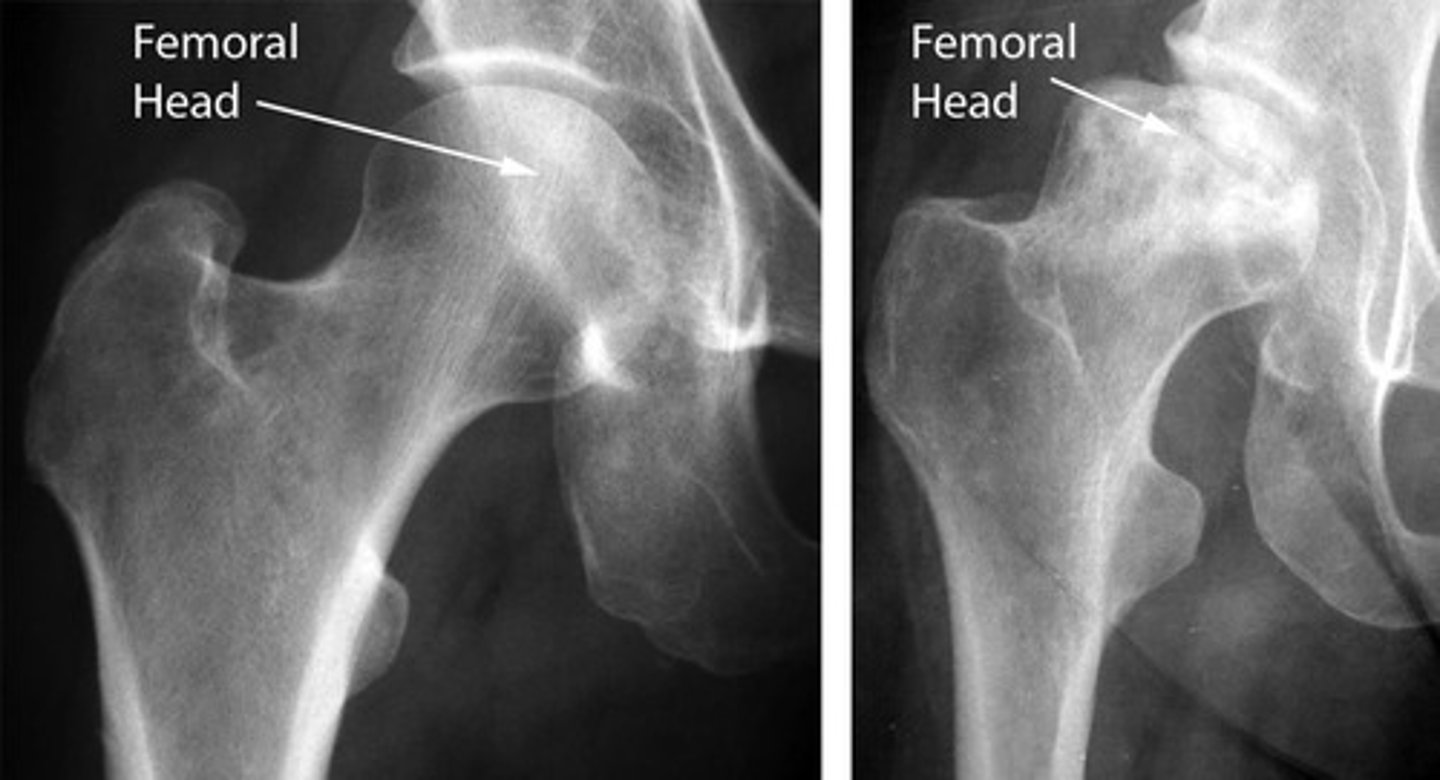
avascular necrosis
bone death due to lack of blood supply, often in proximal and distal femoral head, X-Ray is most used and MRI is most sensitive modality
caused by trauma, long term alcohol use, long term glucocorticoid use, sickle cell anemia, pediatric disorders
findings: devascularized bone becomes denser and more sclerotic
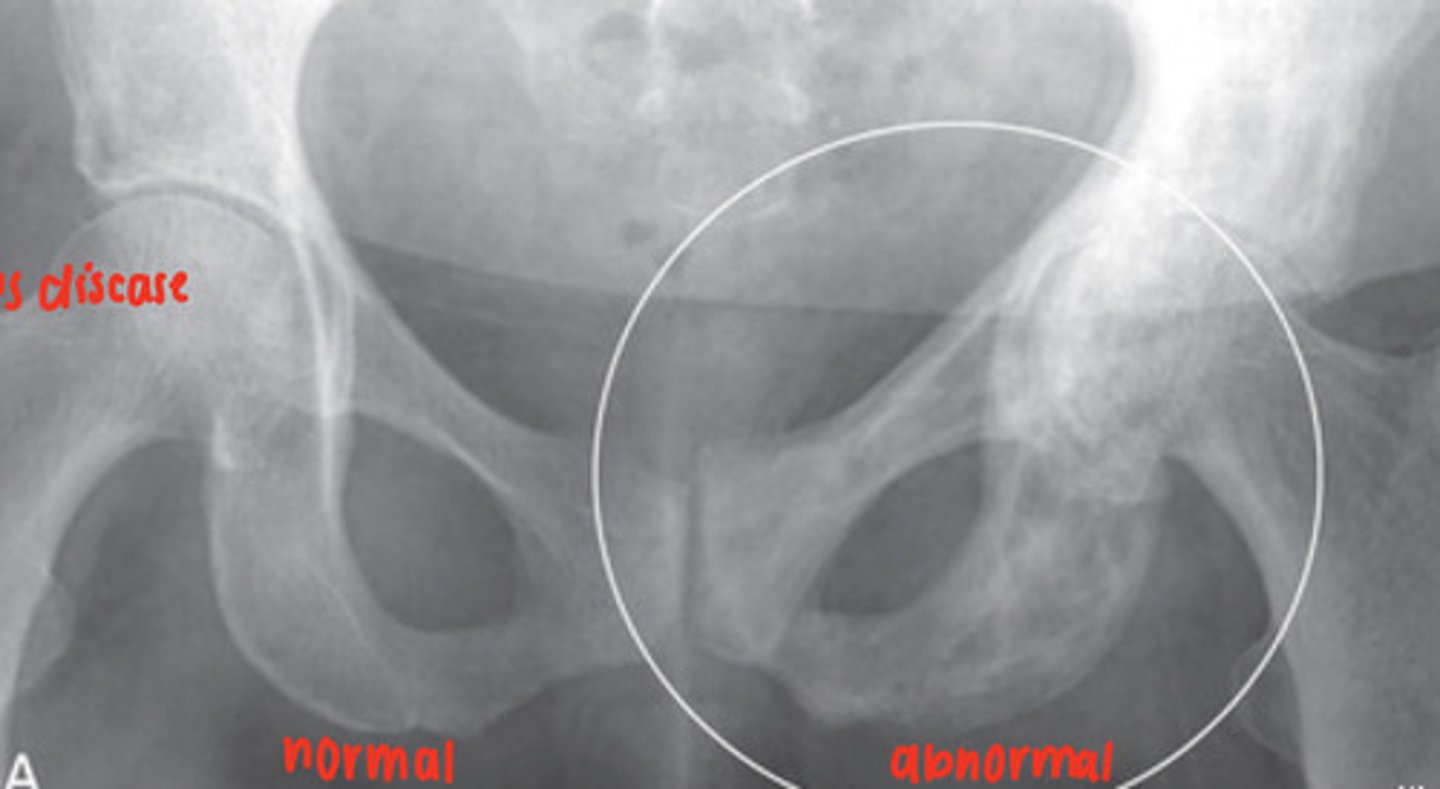
Paget's disease
focal disorder of bone metabolism, accelerated bone remodeling resulting in overgrowth, impairs integrity of affected bone, X-Ray and radionuclide bone scan
osteolytic diseases
decrease bone density, lower density of medullary cavity, accentuation of cortex, compression of vertebral bodies, pathologic fractures
ex. osteoporosis, hyperparathyroidism, osteolytic metastatic disease, multiple myeloma, osteomyelitis
osteoporosis
low bone mineral density, can be postmenopausal or aged related, risks include exogenous steroid administration/Cushing's disease, estrogen deficiency, inadequate physical activity, alcoholism
Dexa scan is imaging study of choice
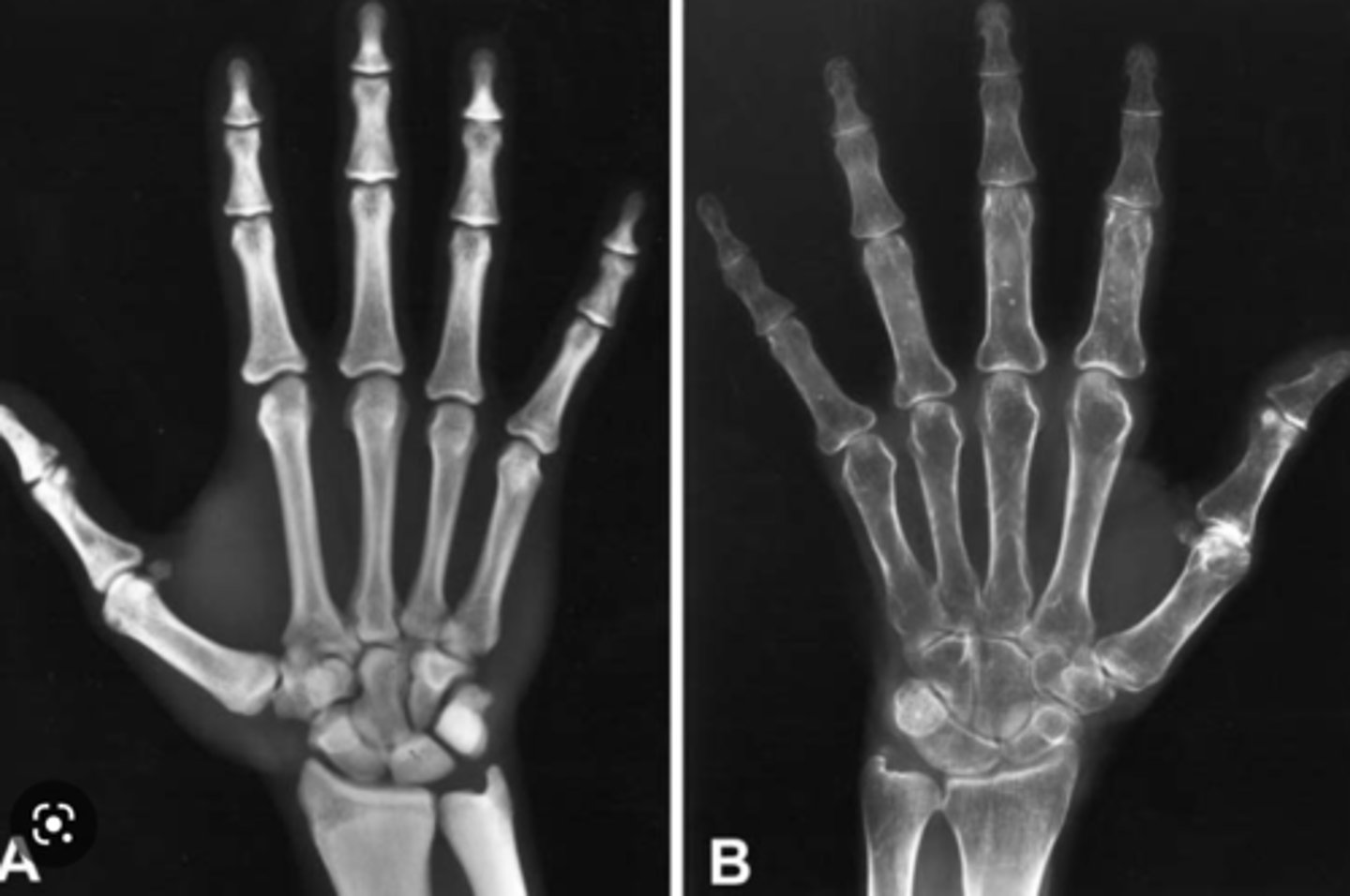
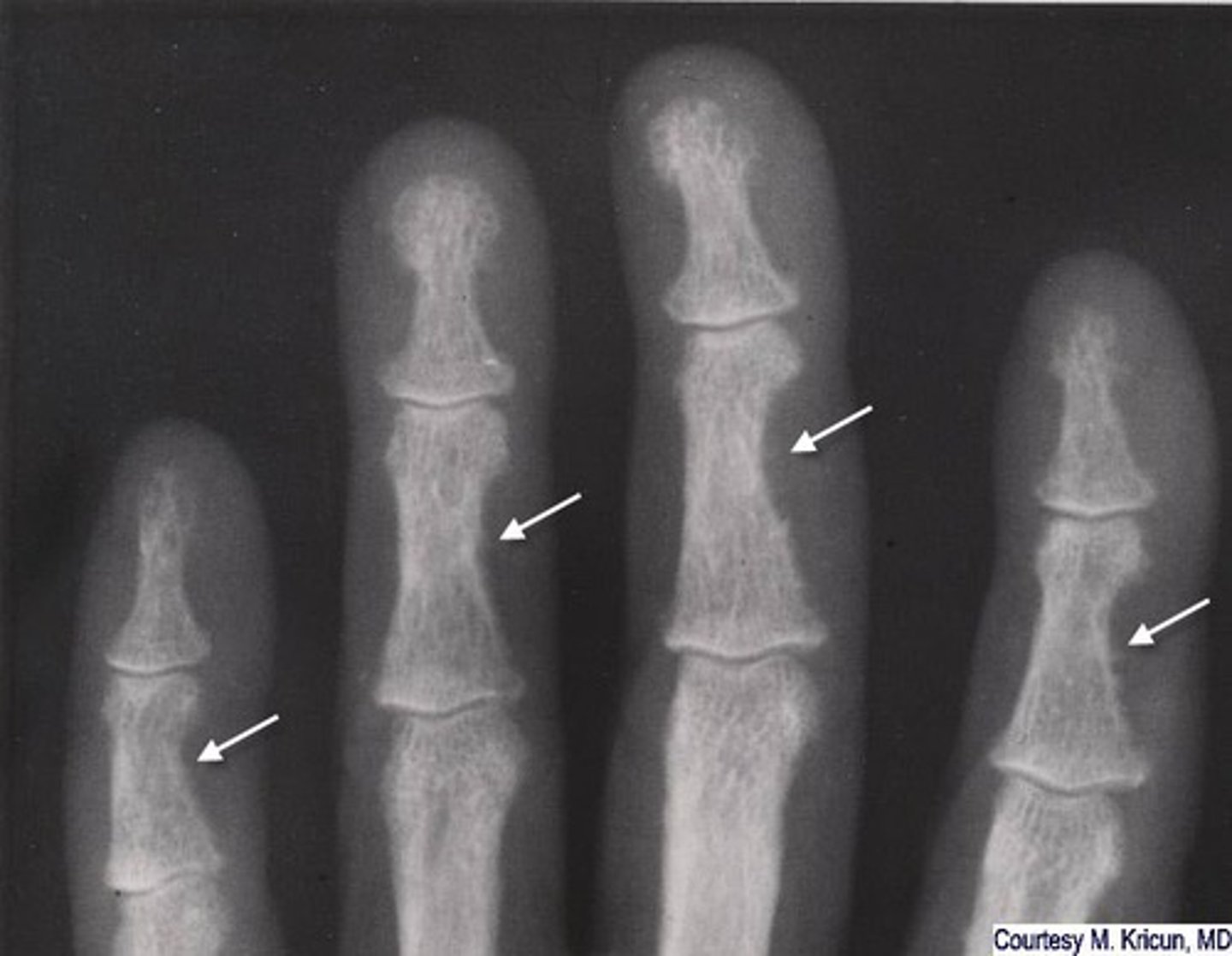
hyperparathyroidism
excessive secretion of PTH, stimulating osteoclastic activity, calcium removed from bone and deposited in bloodstream -> hypercalcemia
- decrease in bone density
- subperiosteal bone resorption of fingers
- erosion of distal clavicles
- well-circumscribed lytic lesions in long bones called brown tumors
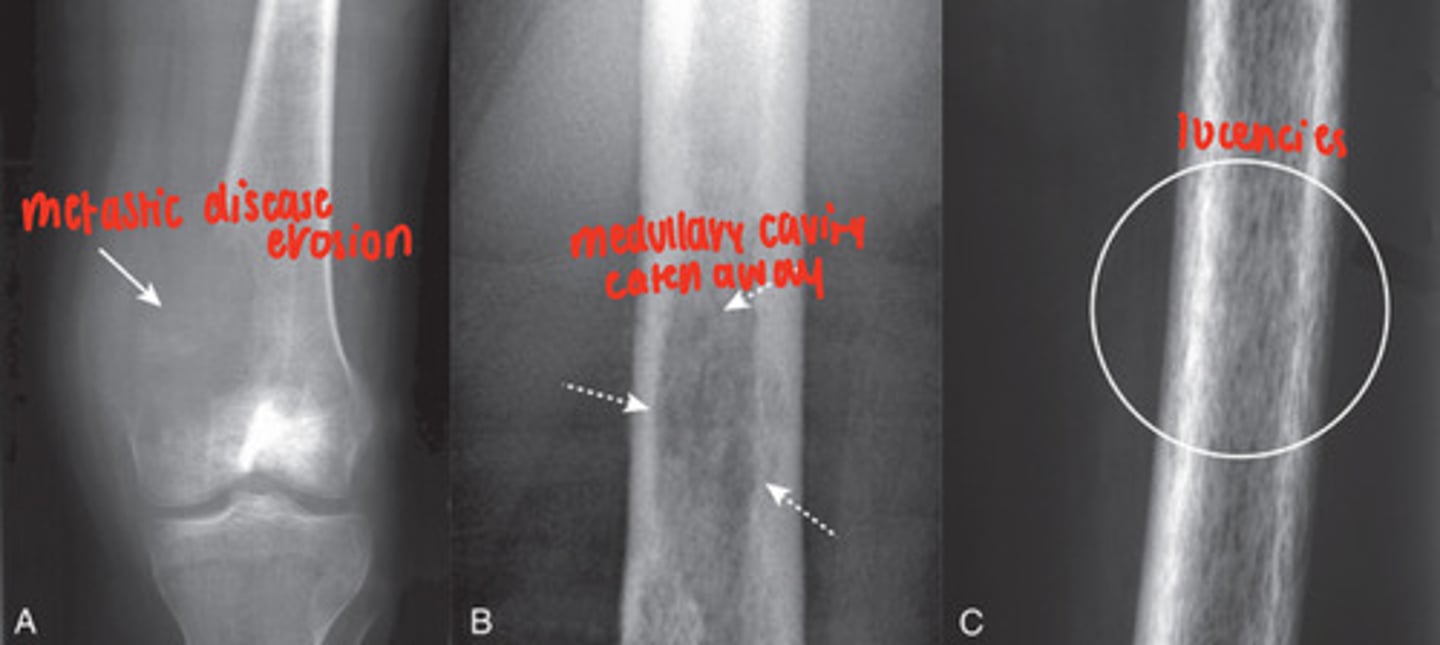
osteolytic metastatic disease
malignancy spread causes bone destruction, mainly medullary cavity but cortex can be involved
MRI- excellent at demonstrating status of the medullary cavity
- irregularly shaped, lucent bone lesions
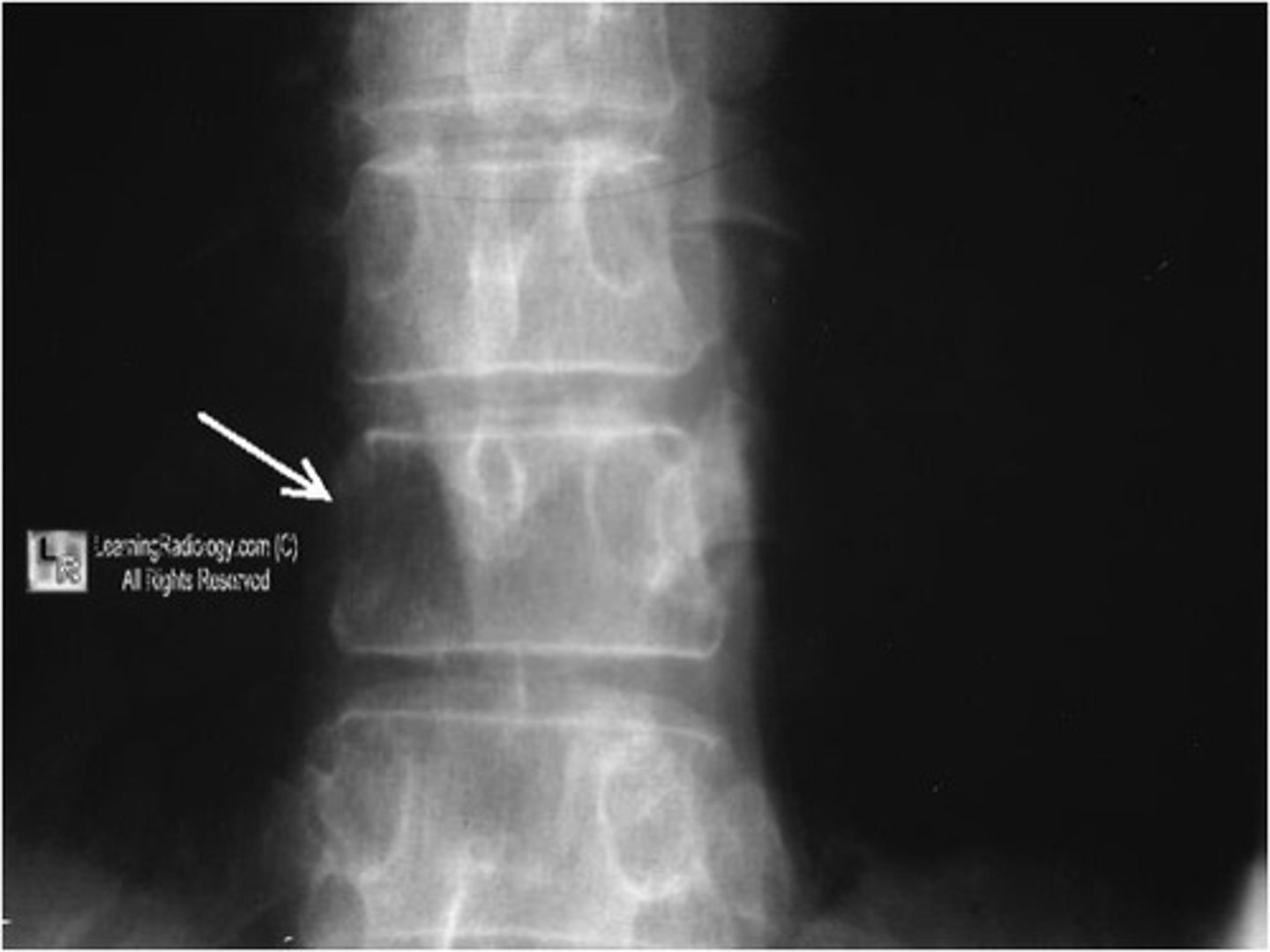
pedicle sign
osteolytic metastatic disease destroys pedicles because of their blood supply
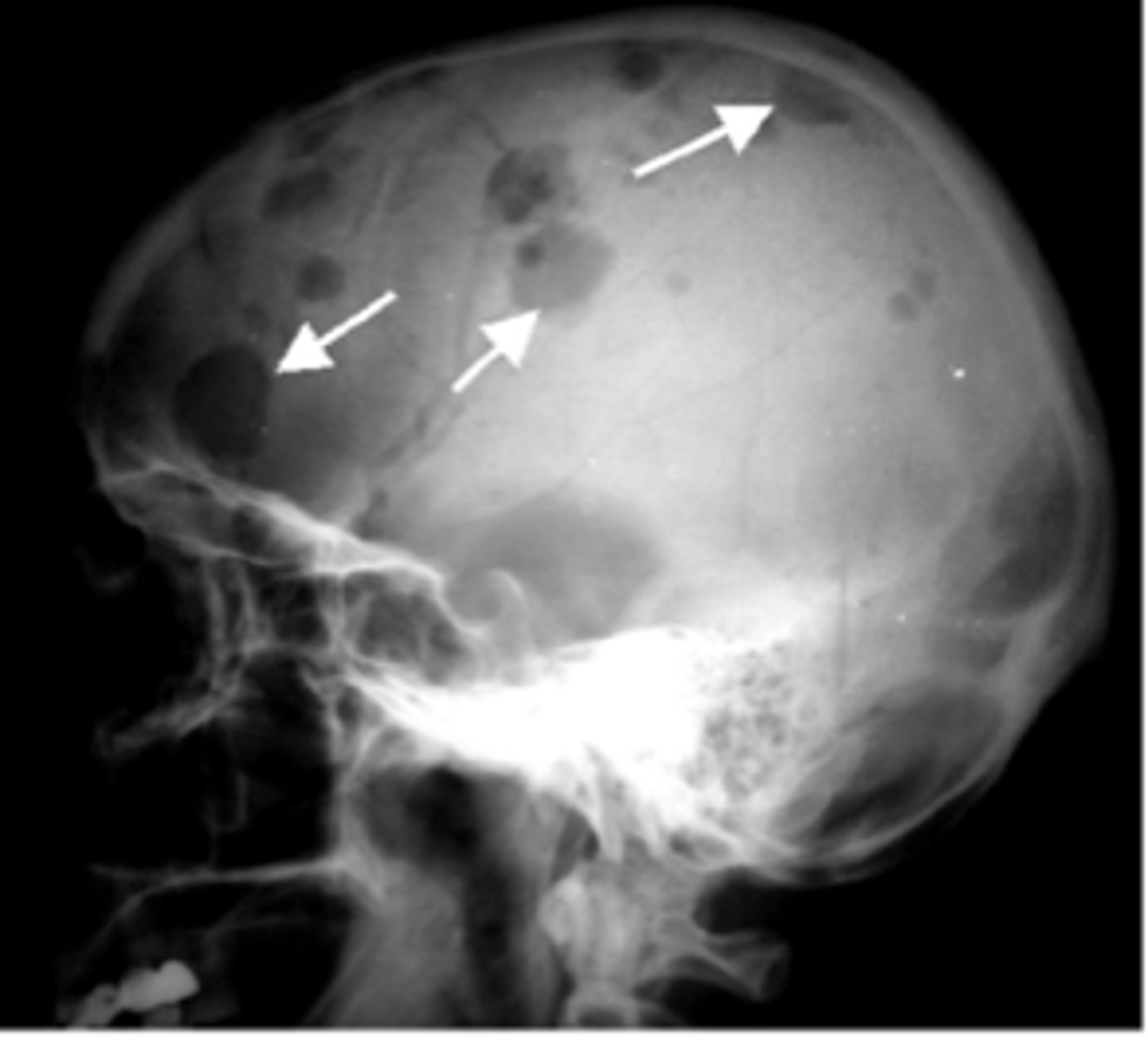
multiple myeloma
malignancy of bone in adults
solitary plasmacytoma- often seen as a soap-bubbly, expansile lesion in spine or pelvis
punched out lytic lesions- throughout axial and proximal appendicular skeleton
osteomyelitis
focal destruction of bone by blood-borne infectious agent (s. aureus)
xray- initial study, can take up to 10 days to display first findings
MRI- most widely used
radionuclide bone scan- higher sensitivity than MRI of approx 95%
- focal cortical bone destruction
- periosteal new bone formation
- soft tissue swelling and focal osteoporosis
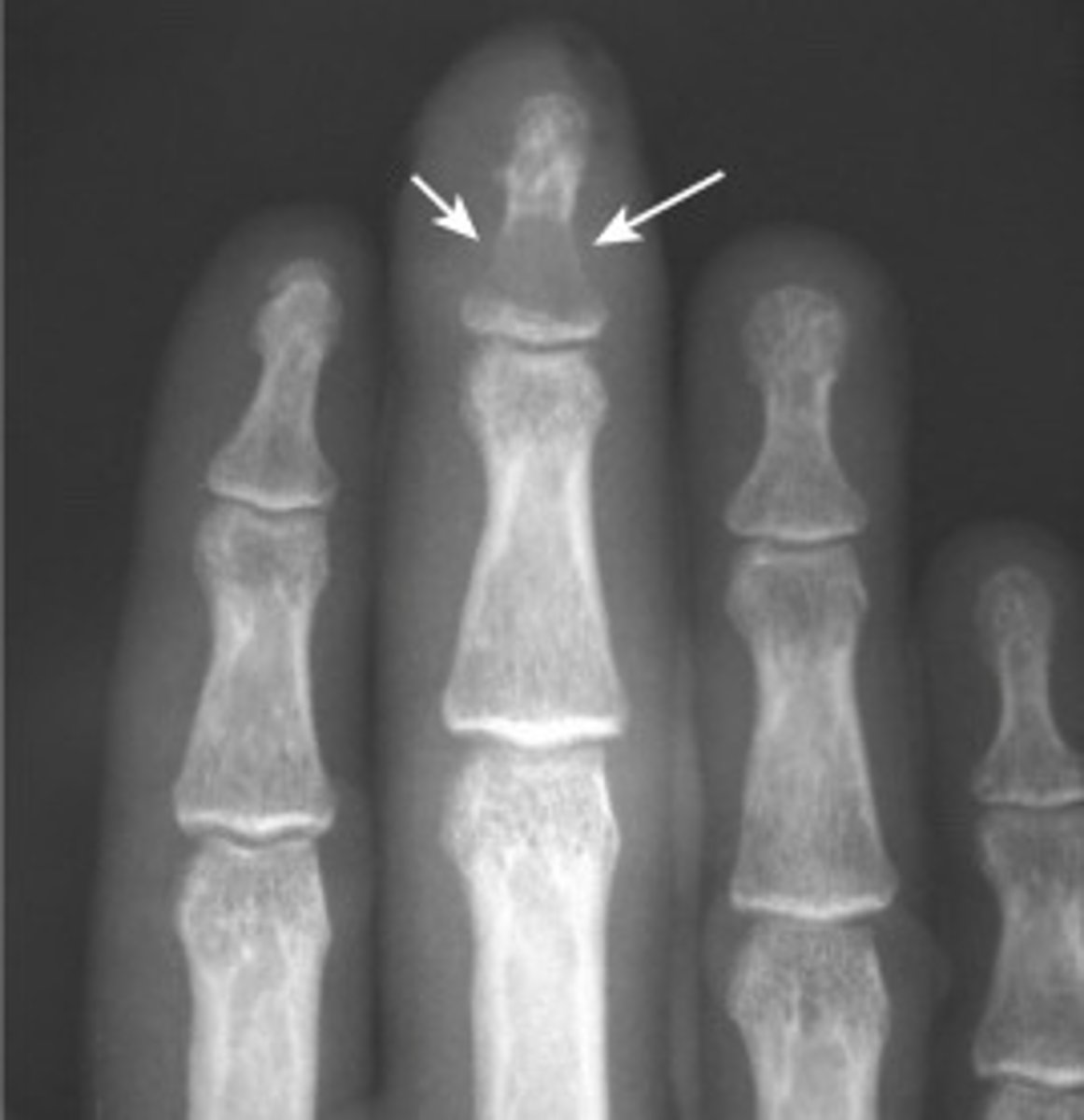
osteomyelitis MRI
infection of the bone and intervertebral discs
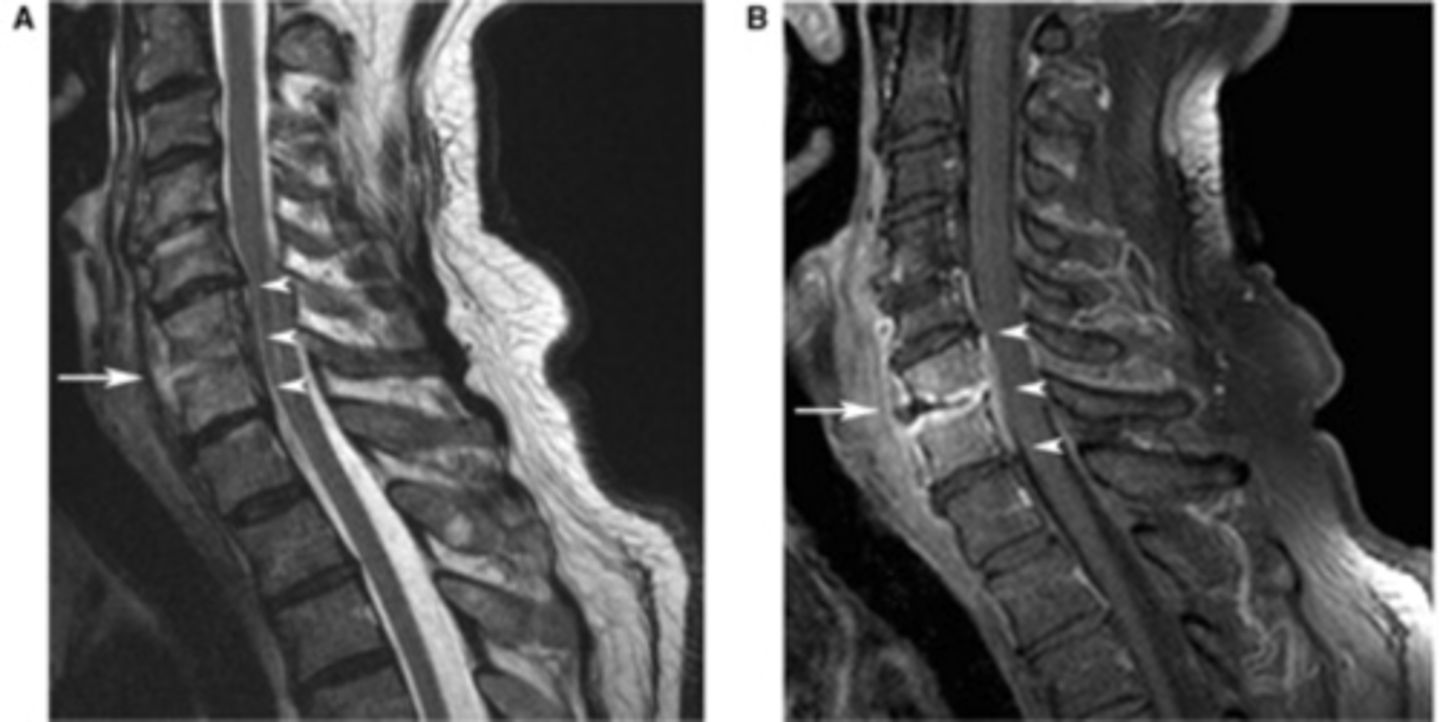
athritis
disease that affects a joint and bones on either side of the joint, joint space narrowing
conventional radiograph -> first study of choice
hypertrophic arthritis
bone formation at the site of involved joint
primary osteoarthritis- mechanical stress
secondary arthritis- trauma/infections/etc..
charcot arthopathy
- osteophyte formations
- subchondral sclerosis
- subchondral cysts
- narrowing of joint space
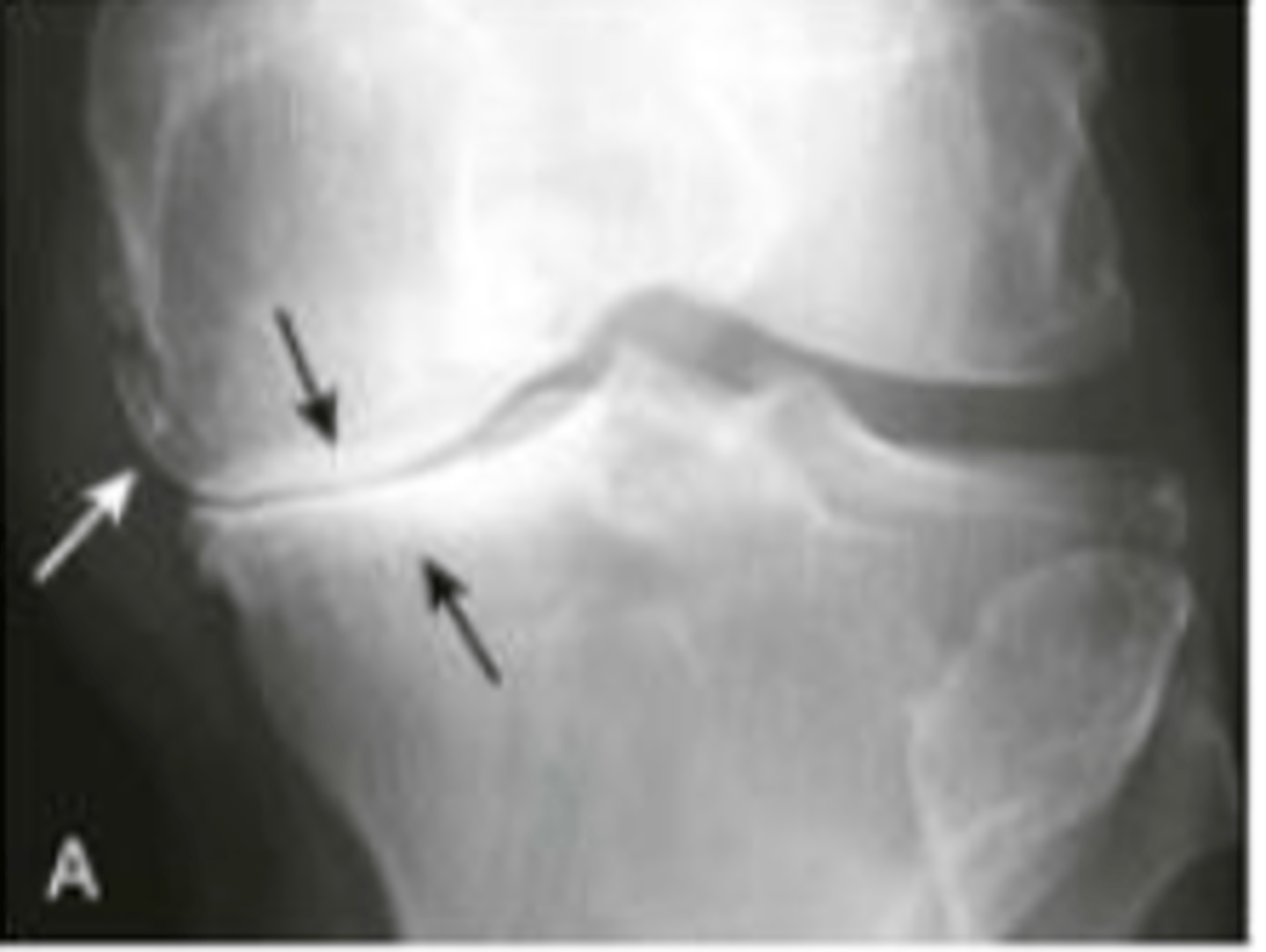
osteoarthritis
subchondral sclerosis, joint narrowing, osteophytes
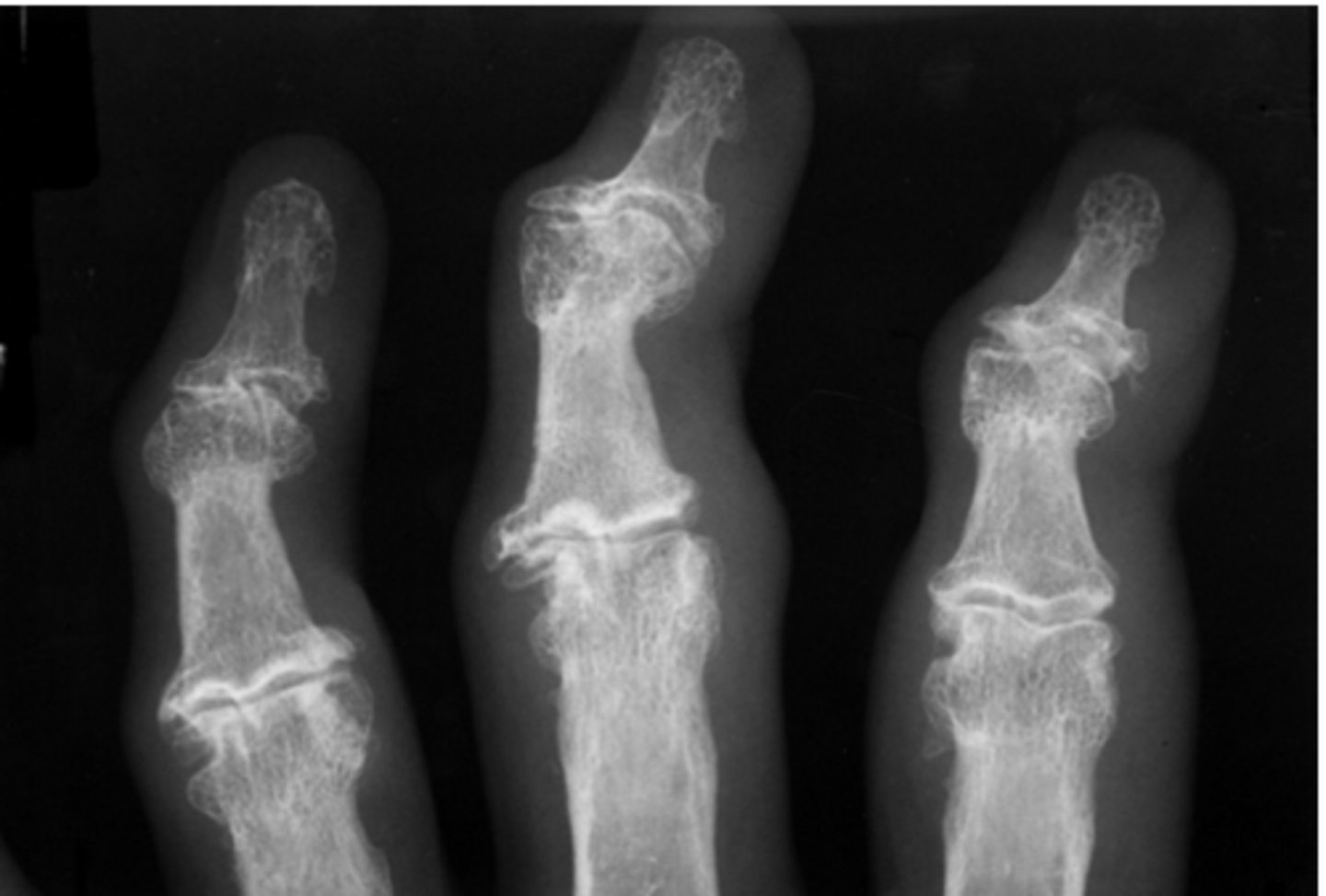
secondary osteoarthritis
joint space barely visible , subchondral sclerosis, phleboliths, cysts
erosive arthritis
inflammation and growth of abnormal tissue between the bones of a joint (pannus formation), lytic lesions near joint, pannus acts like a mass of growing and enlarging synovial tissue
rheumatoid arthiritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis
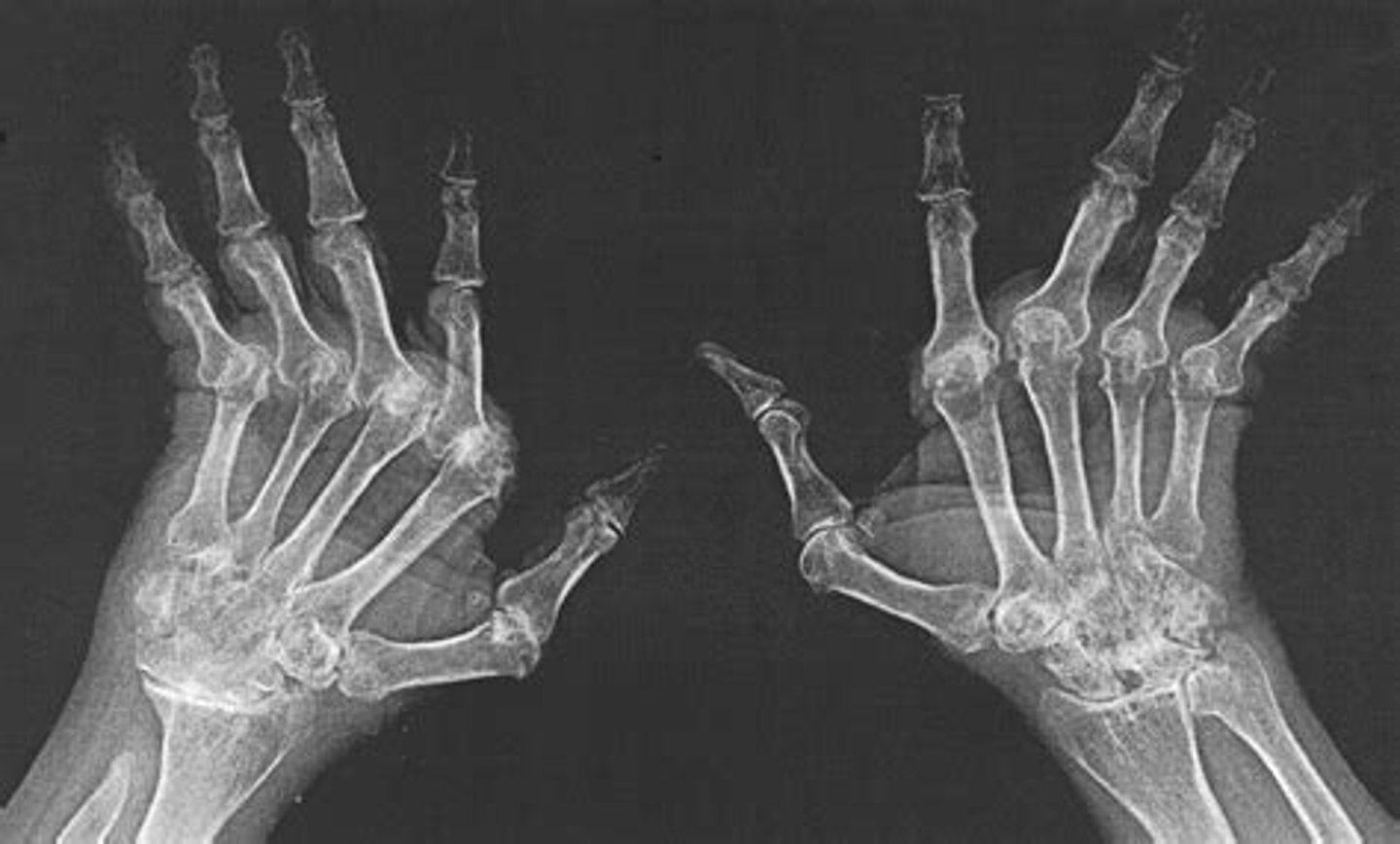
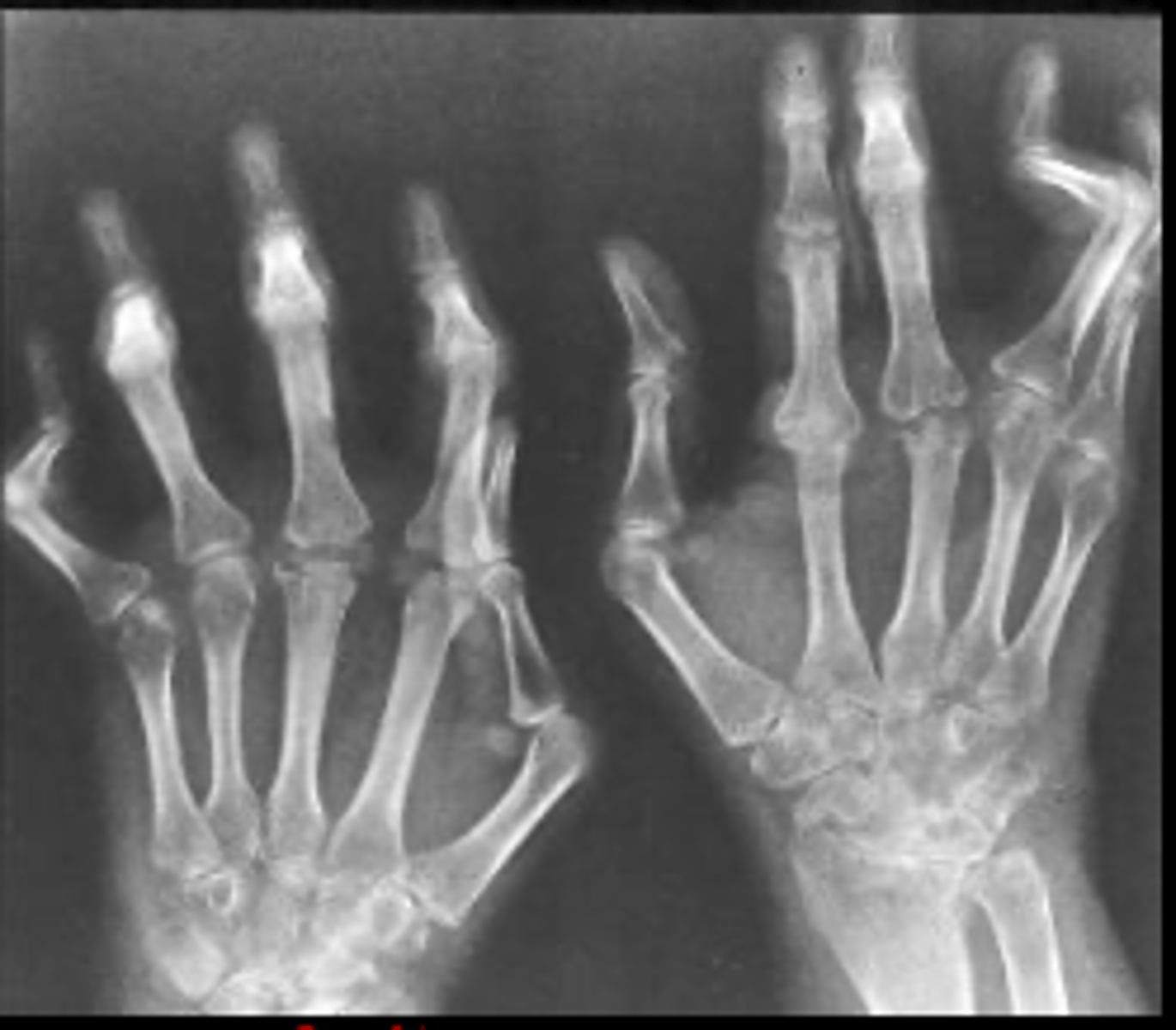
rheumatoid arthritis
autoimmune and inflammatory arthritis. located in proximal joints of hands and wrists, usually B/L
hands- erosions, ulnar deviation of fingers at MCPs, subluxation of MCPs, swan-neck and boutonniere deformities
wrist- erosions
larger joints usually show no erosions
swan-neck deformity
hyperextension of PIP and flexion of DIP, characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis
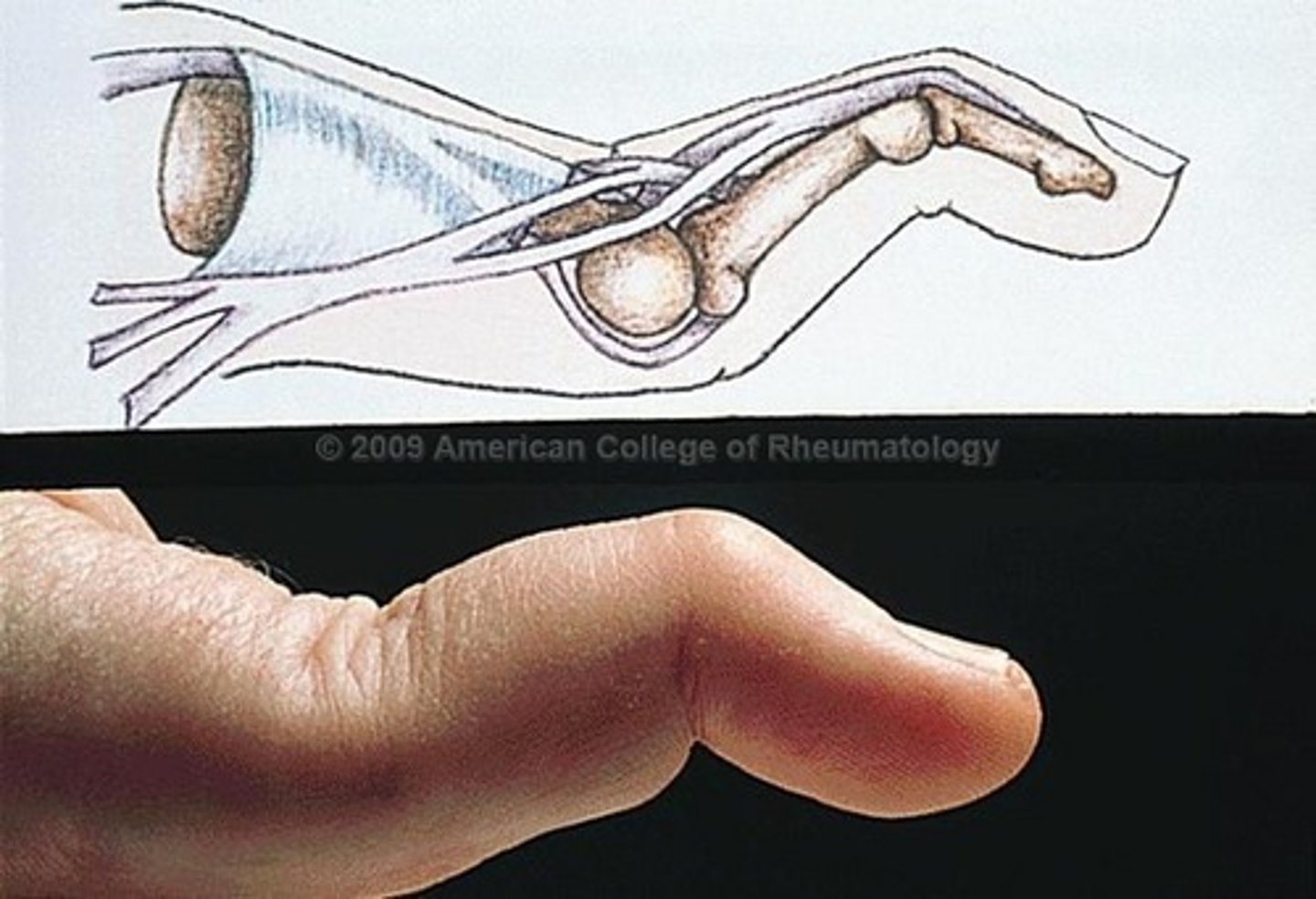
Boutonniere deformity
flexion contracture of a PIP joint, extension of a DIP joint, characteristic of rheumatoid arthritis
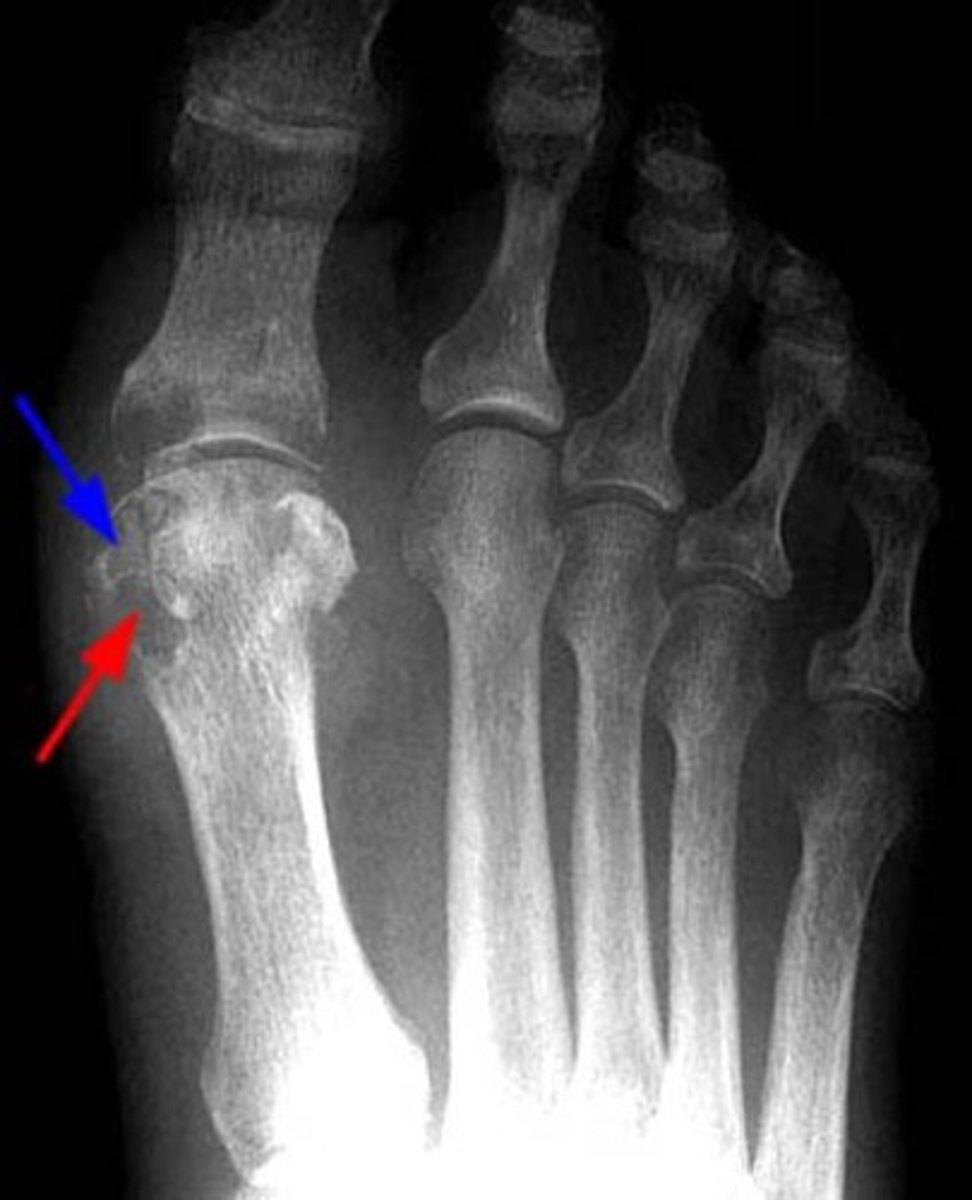
gout
inflammatory changes incited by deposition of calcium urate crystals in joint, most commonly metatarsal-phalangeal joint of great toe
- sharply marginated erosion w sclerotic border "rat bites"
- joint space narrowing
- tophi- collections of urate crystals
- olecranon bursitis
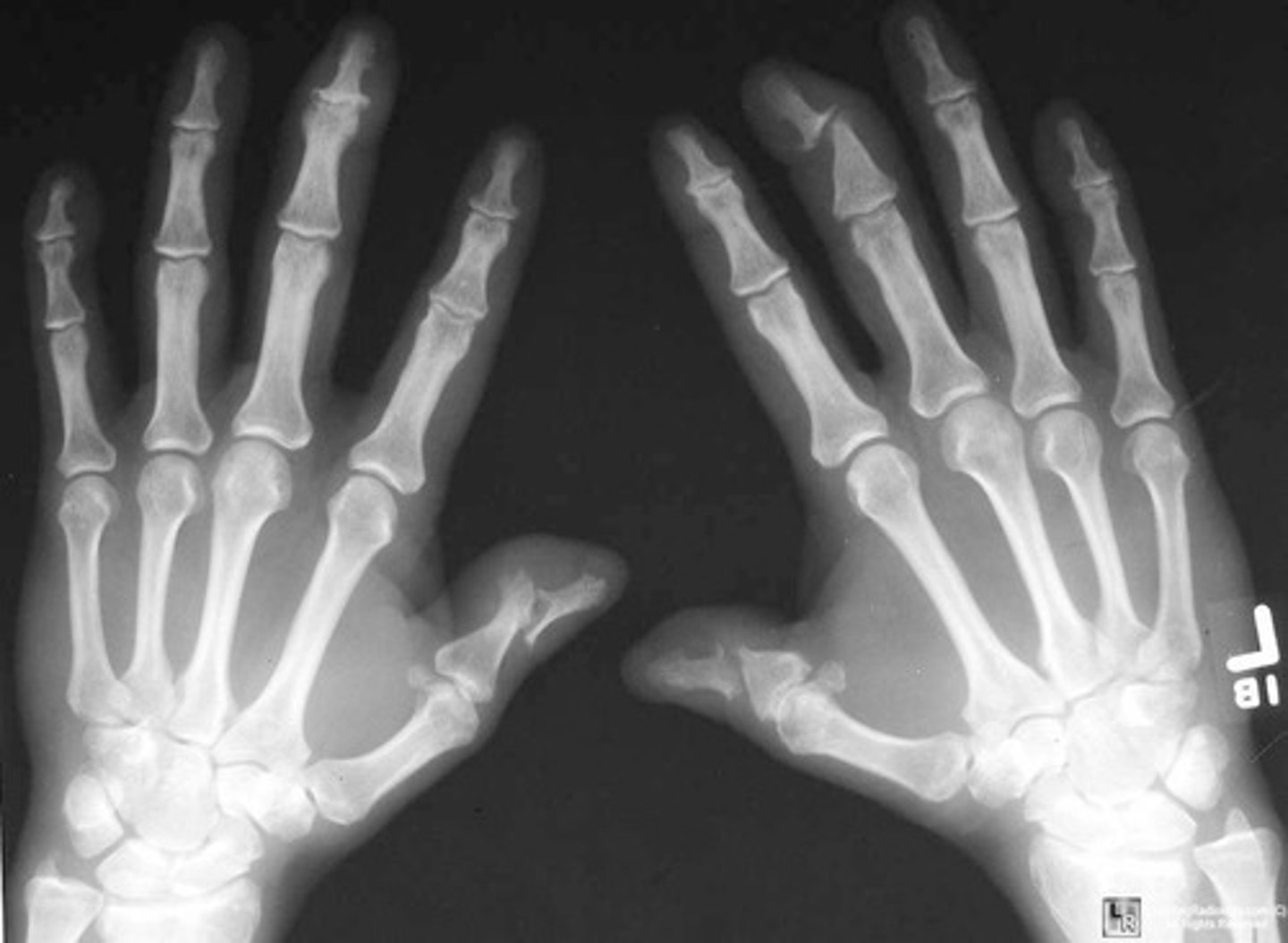
psoriatic arthritis
inflammatory arthritis associated with psoriasis, skin and nail changes along with joint changes, hands and feet usually
- juxtaarticular erosions
- enthesophytes -> bony proliferation at sites of tendon insertions
- pencil in cup deformity
- absence of osteoporosis
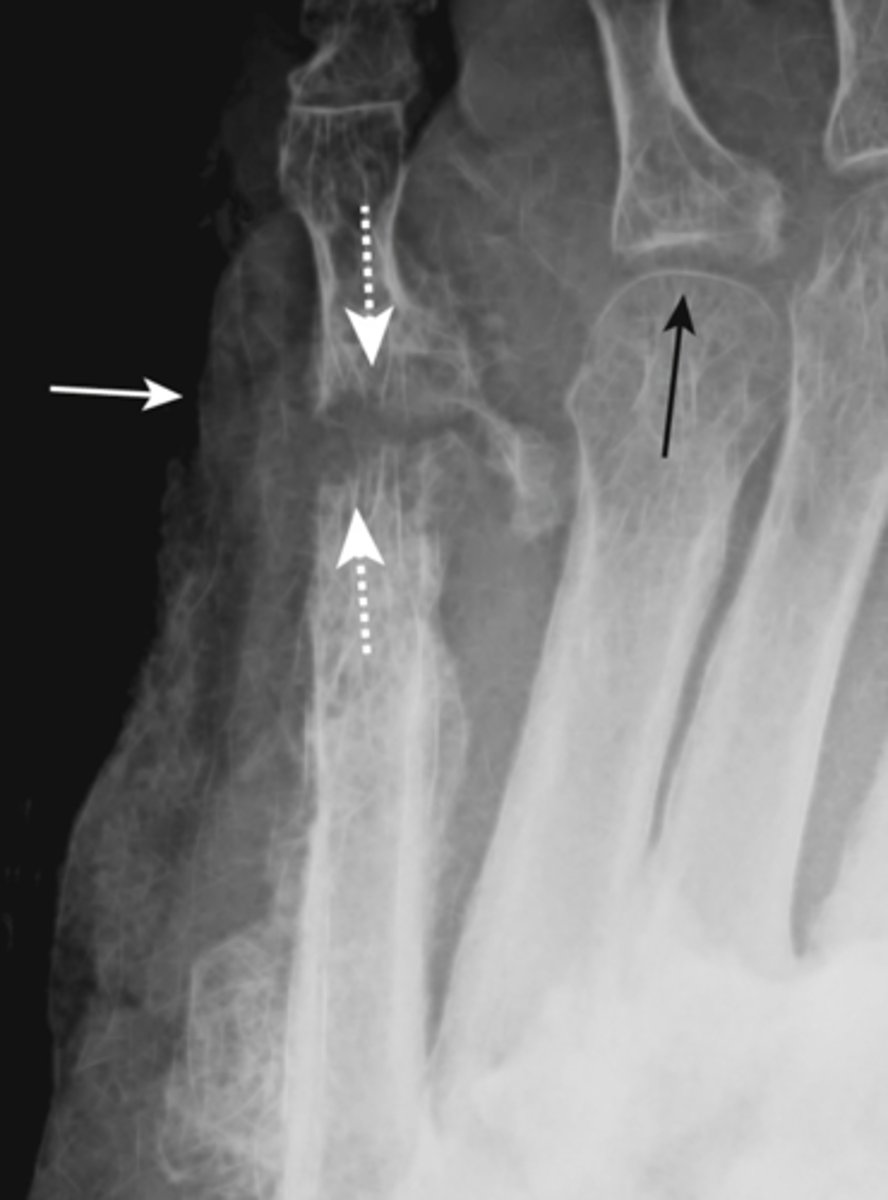
septic arthritis
synovial membrane infection from a wound infection or from direct contiguous extension from osteomyelitis adjacent to joint
- rapid destruction of articular cartilage
- usually monoarticular
- associated soft tissue swelling
- osteopenia from hyperemia of inflammation
spine imaging
xray- initially ordered
nuclear medicine bone scan- metastases
MRI- study of choice for spinal cord, intervertebral discs, compression of spinal nerves
CT- best for bony abnormalities, MRI contraindicated, non contrast for trauma
canadian C-spine rule
safely rule out cervical spine injury (CSI) in alert, stable trauma patients without the need to obtain radiographic images, more sensitive and specific than NEXUS, CT usually performed
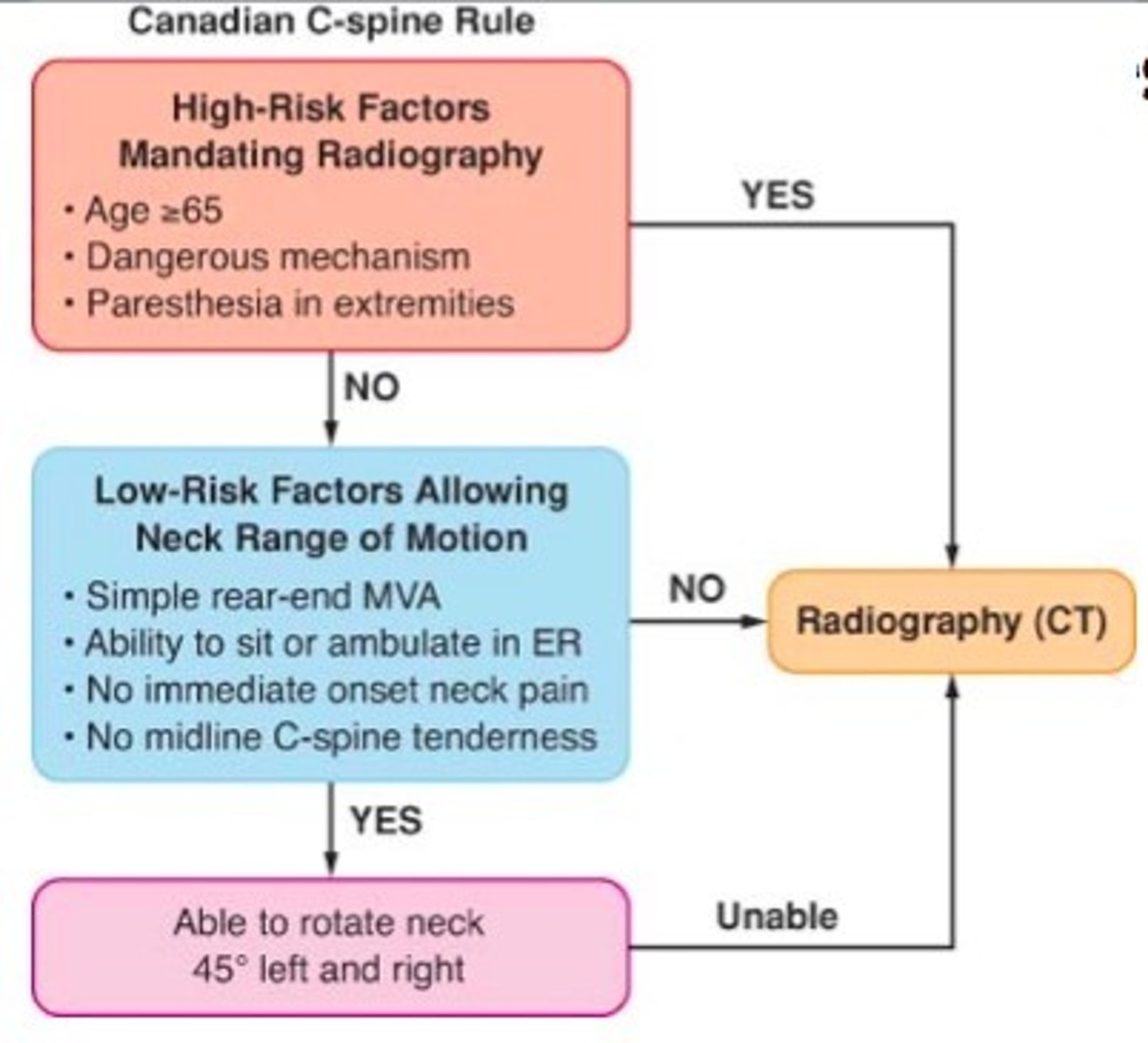
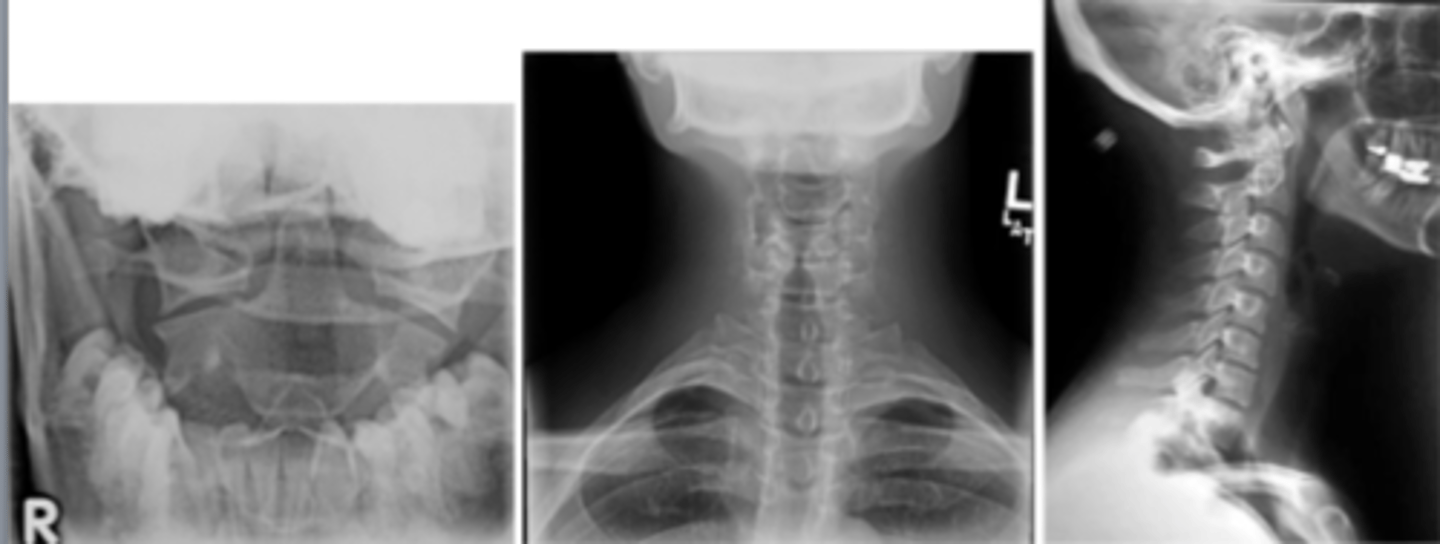
cervical spine imaging
immobilize neck with C-collar
xray- lateral, spinal fracture/subluxation
CT- usually performed rather than xray, fractures
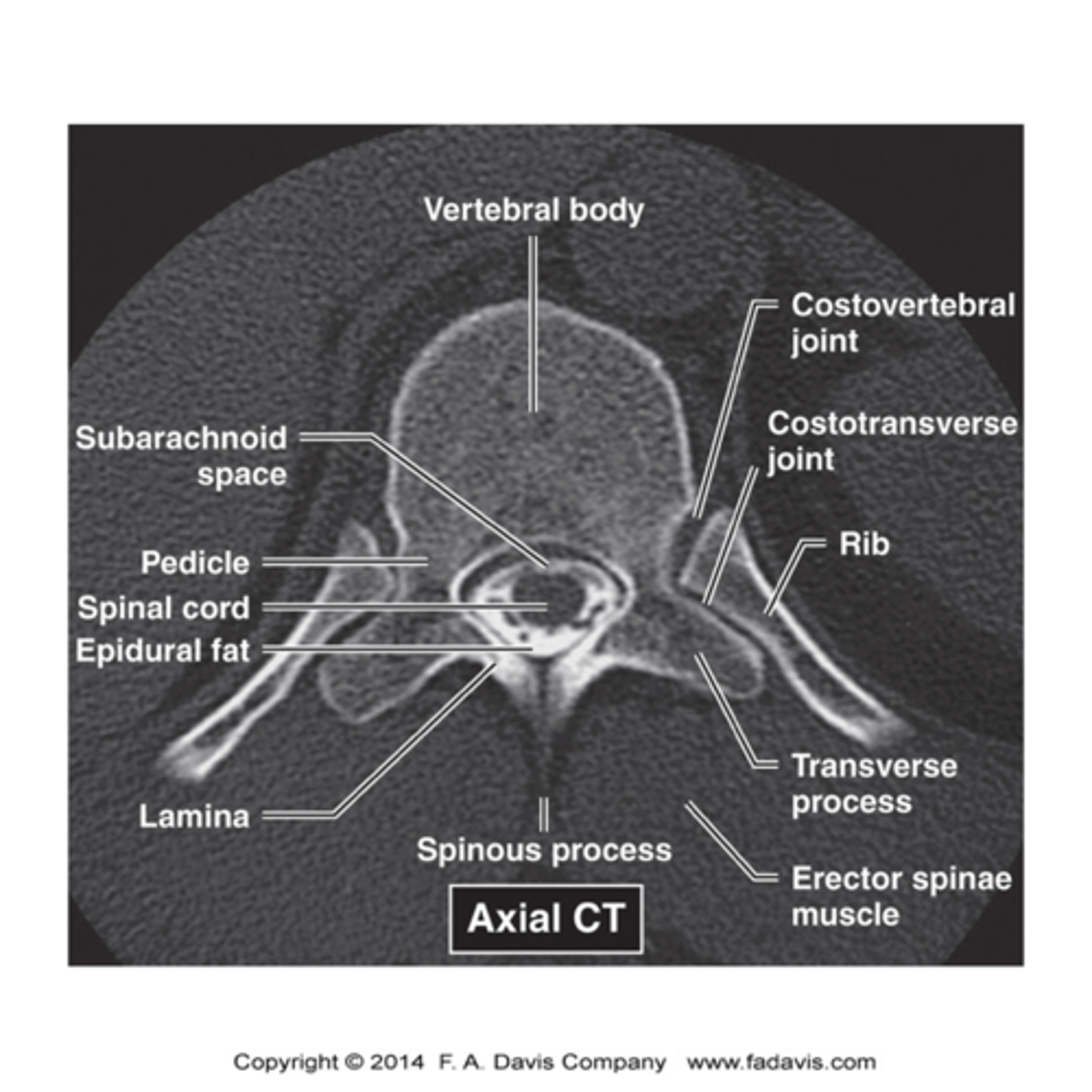
P.A.C.T.S.
AP spine view, look for:
pedicles: no erosion
alignment
count vertebral bodies
transverse processes
sacrum and SI joints
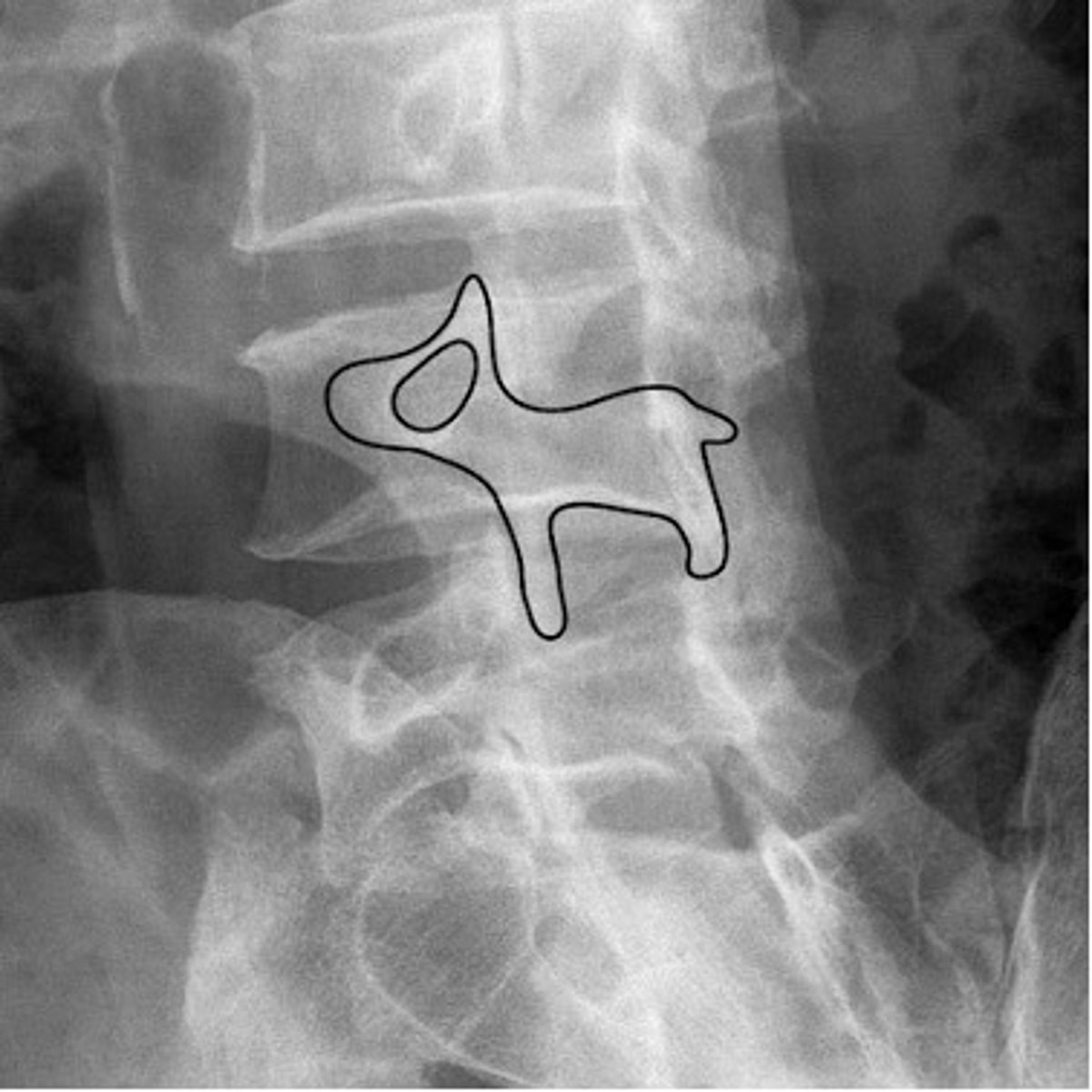
scottie dog
nose- transverse process
eye- pedicle
ear- superior articular facet
front leg- inferior articular facet
neck- pars interarticularis
degenerative disk disease
progressive loss of height of the intervertebral disk space
- disk space narrowing
- vertebral body changes
- vacuum disk phenomenon- appearance of air density in disk space
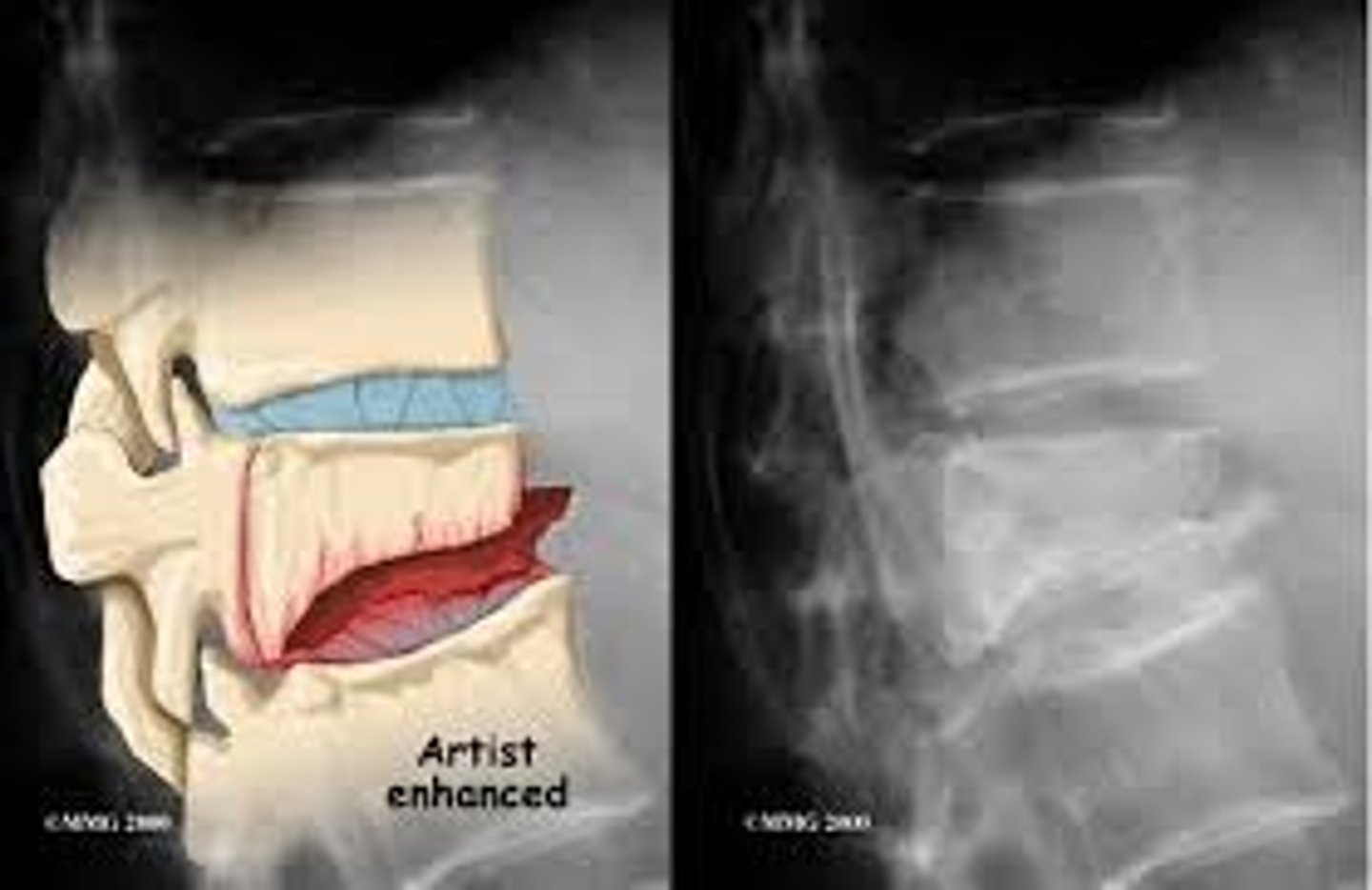
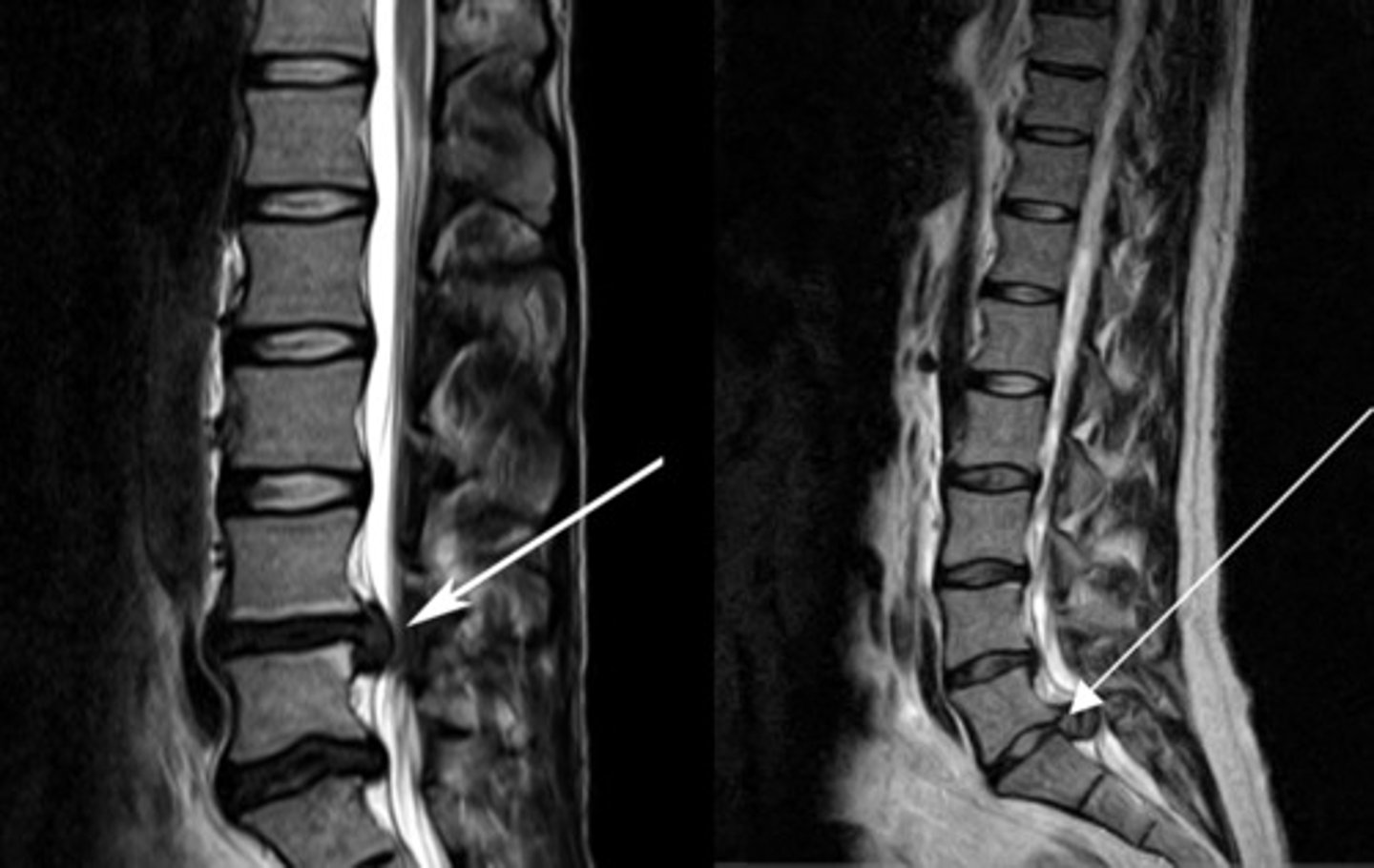
herniated disks
degeneration of outer annular fibers, caused by acute compression of nerve root
MRI is study of choice
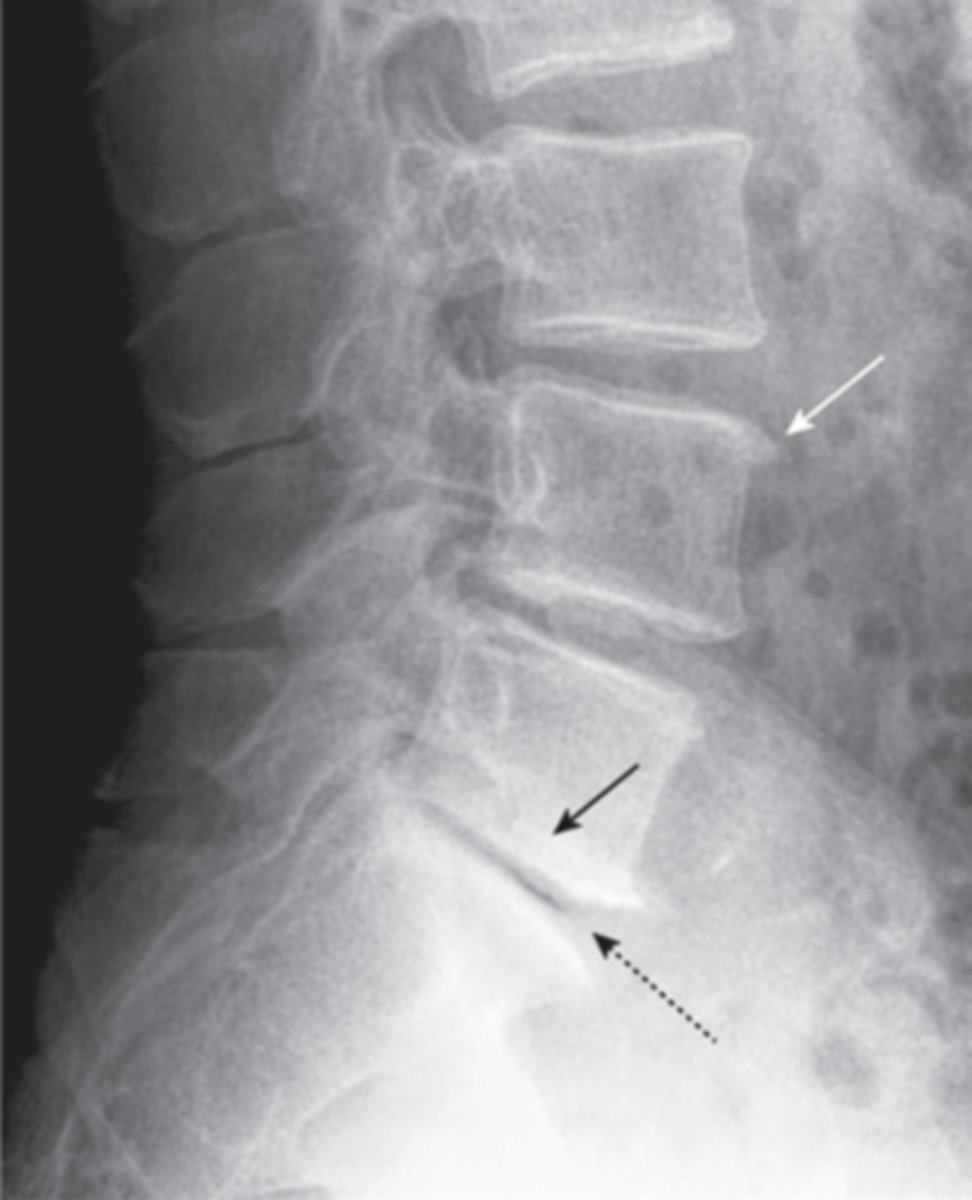
compression fractures
collapse of vertebrae, usually secondary to osteoporosis, no neuro deficit, wedge-shaped deformity
CT- best at identifying
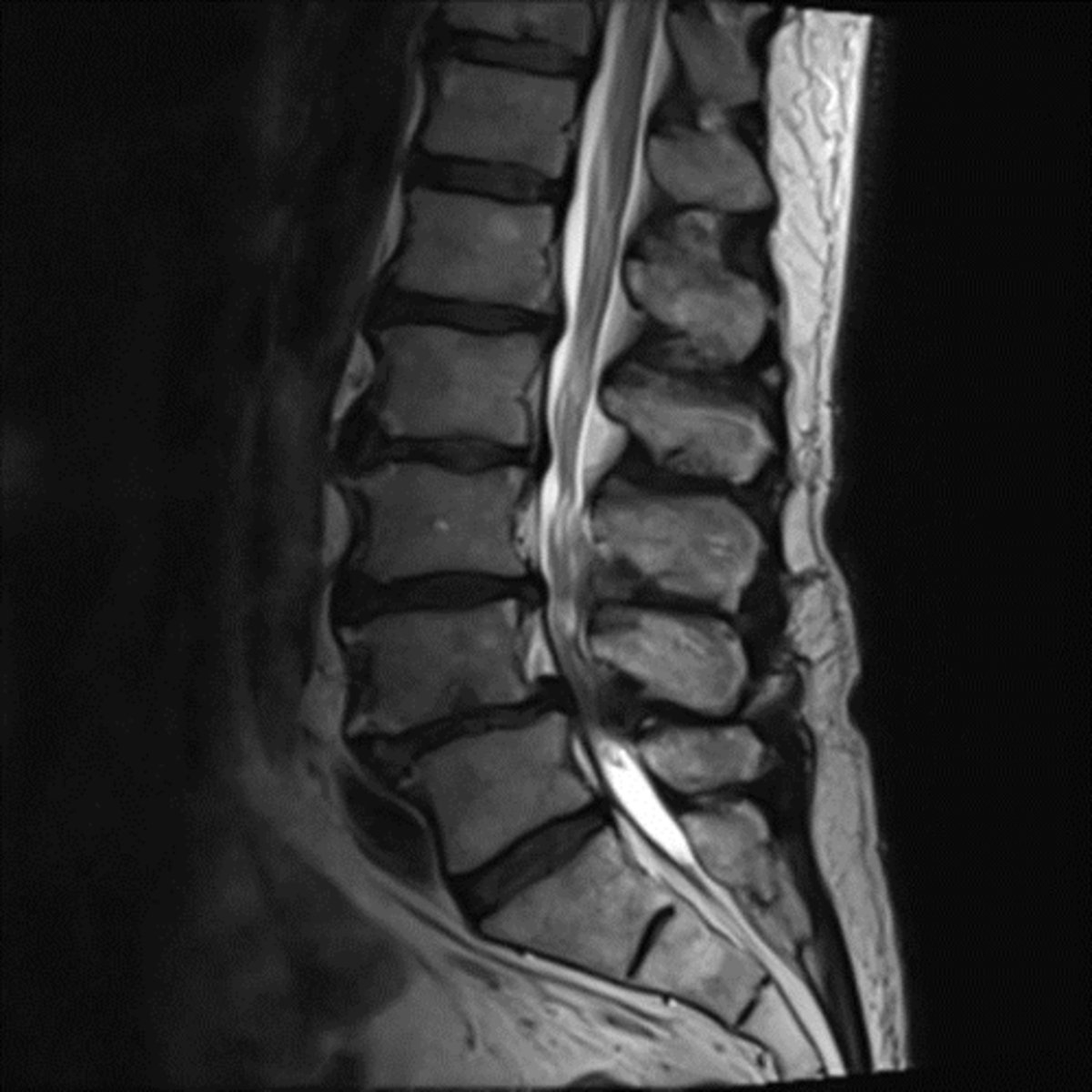
spinal stenosis
narrowing of the spinal canal or neural foramina, caused by soft tissue and bony abnormalities, congenital or acquired
MRI is study of choice
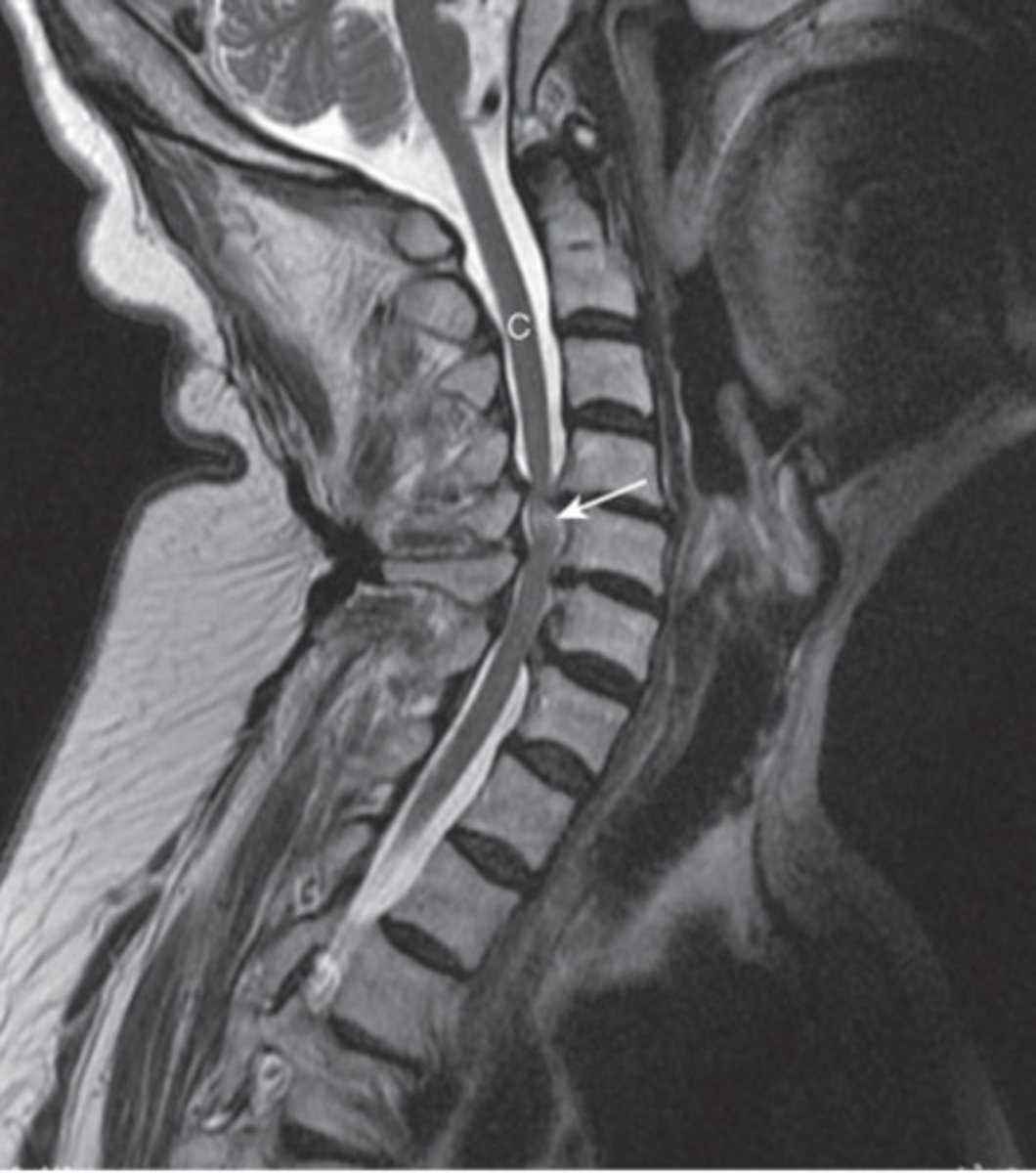
cauda equina syndrome
injury or herniated disk compresses cauda equina nerve roots, back pain, weakness, saddle anesthesia, incontinence
Tx- emergency surgical decompression
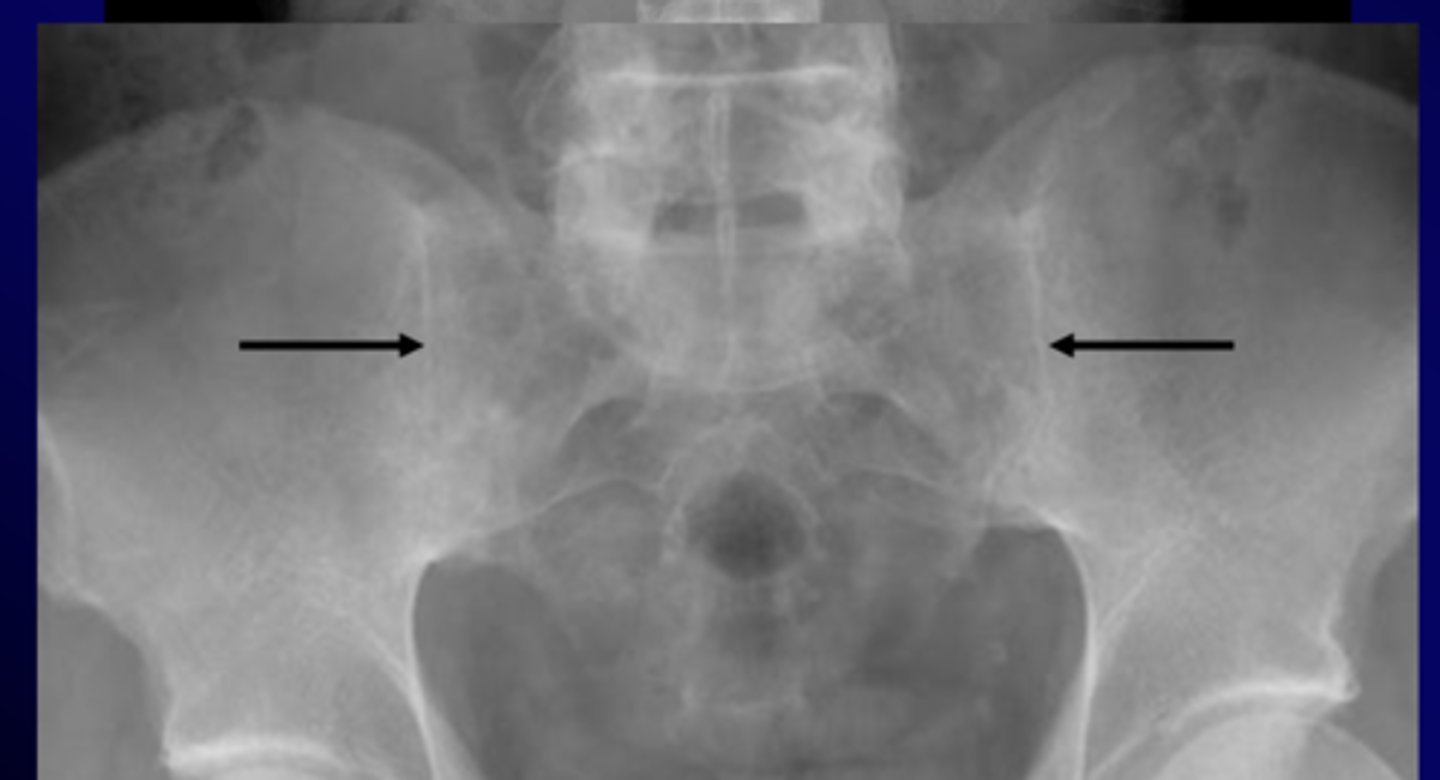
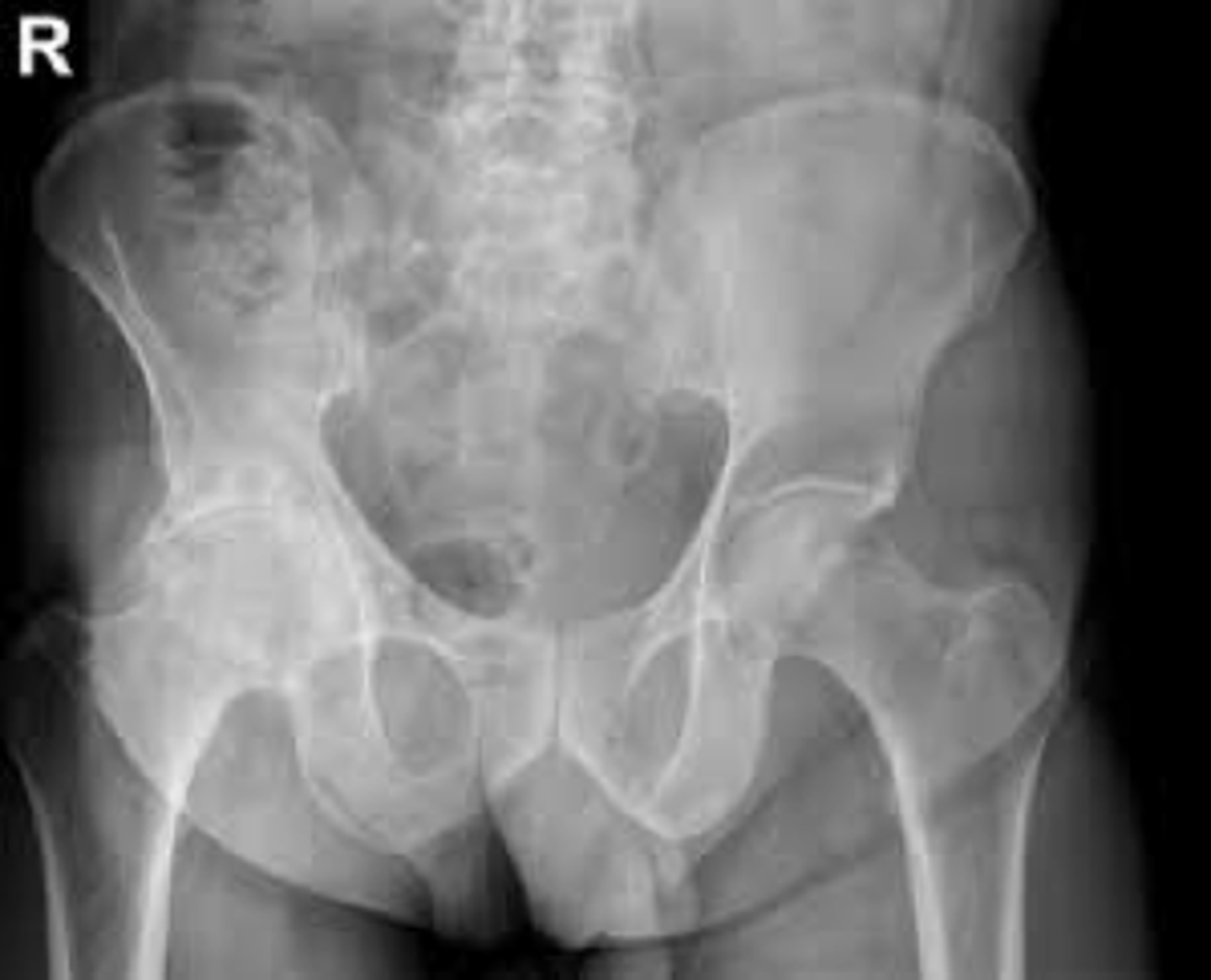
ankylosing spondylitis
chronic and progressive arthritis characterized by inflammation and eventual fusion of sacroiliac and spinal facet joints, involvement of paravertebral soft tissues, more common in young males
xray
- sacroiliitis: bony fusion or ankylosis of sacrum and ilium
- bamboo spine: ossification of outer fibers of annulus fibrosis