Biol 145 - Plant Science - Week 3
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
Cells produced by stem what become what?
Meristems; shoot system with branches and leaves
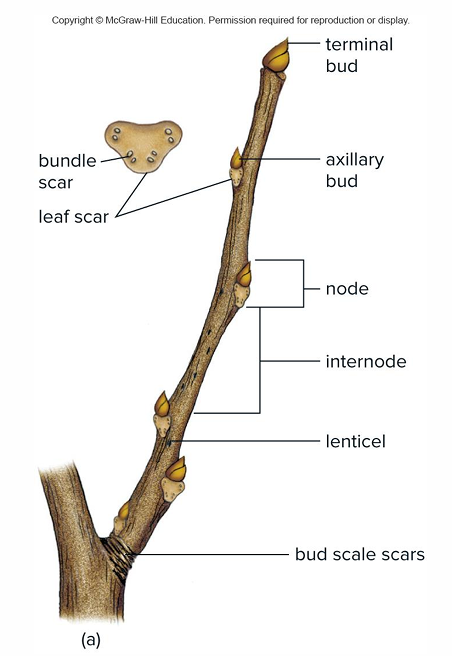
Node definition
Area of stem where leaves are attached
Node Alternate or spiral looks like?

Node opposite - attached at pairs. Looks like?

Node whorled- In groups of three or more. Looks like?

Internode
Stem region between nodes
Axil
Angle between petiole and stem
Axillary bud located?
Axil
Bud scales protect?
Buds
Axillary bud located in axil will become?
Branches or flowers
Terminal bud is at?
Twig tip
Stipules
Paired, often leaflike appendages at base of leaf

Deciduous tree and shrubs (lose all leaves annually)
After leaves fall, have dormant axillary buds with leaf scars below
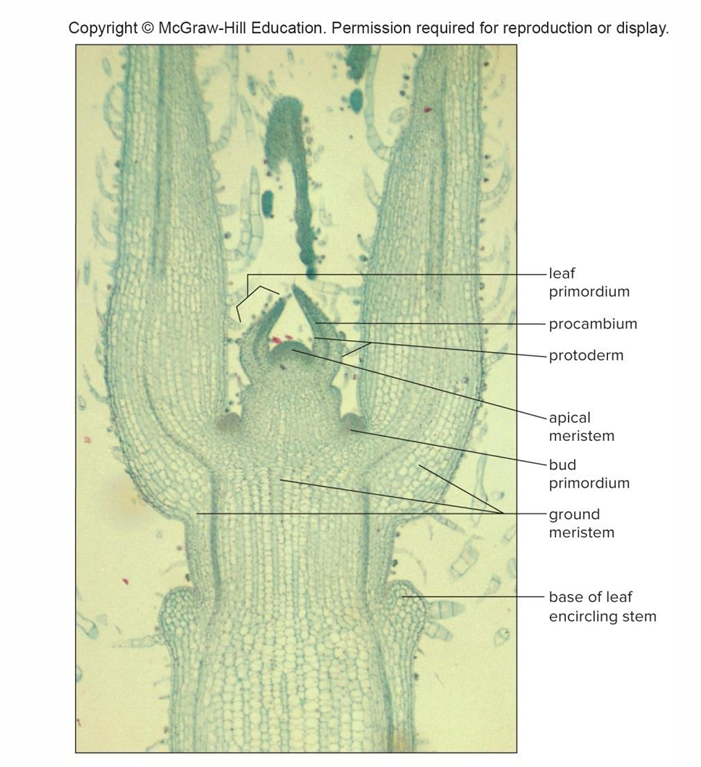
Apical meristem at stem tip
Contributes increase in stem length, dormant before growing season, and protected by bud scales and leaf primordia
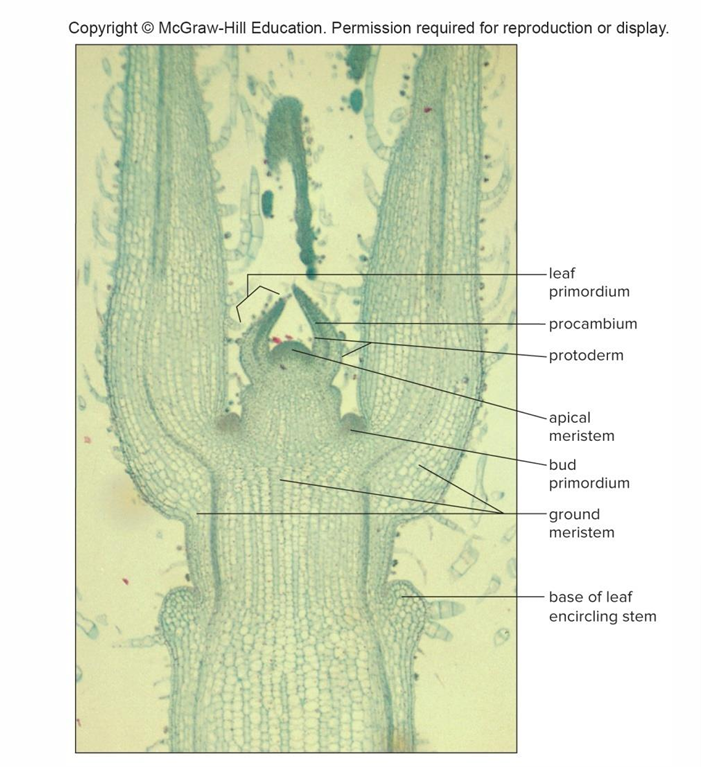
Leaf primordia
Tiny embryonic leaves that develop into mature leaves
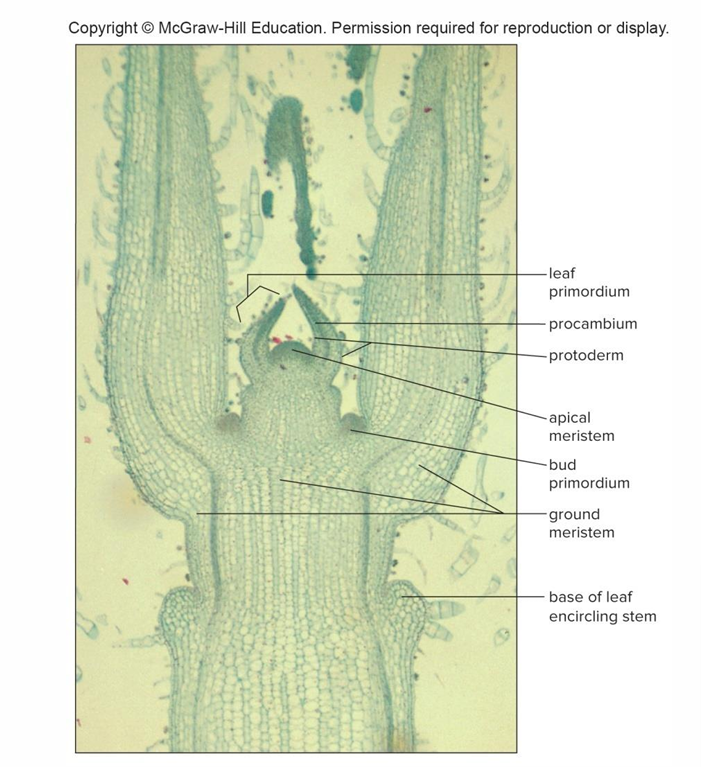
Apical meristem cells form 3 primary meristems: Protoderm
Gives rise to epidermis
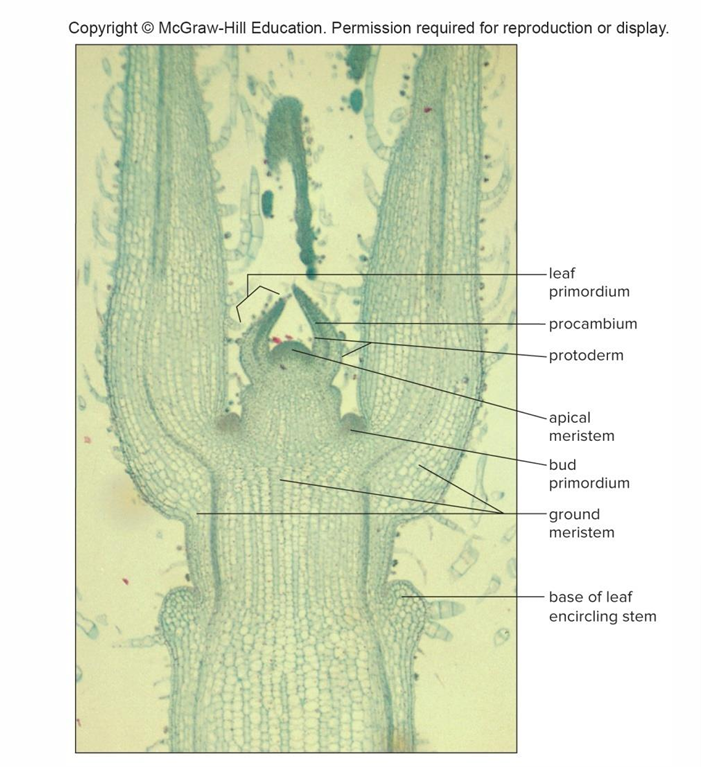
Apical meristem cells form 3 primary meristems: Procambium
Produces primary xylem and phloem
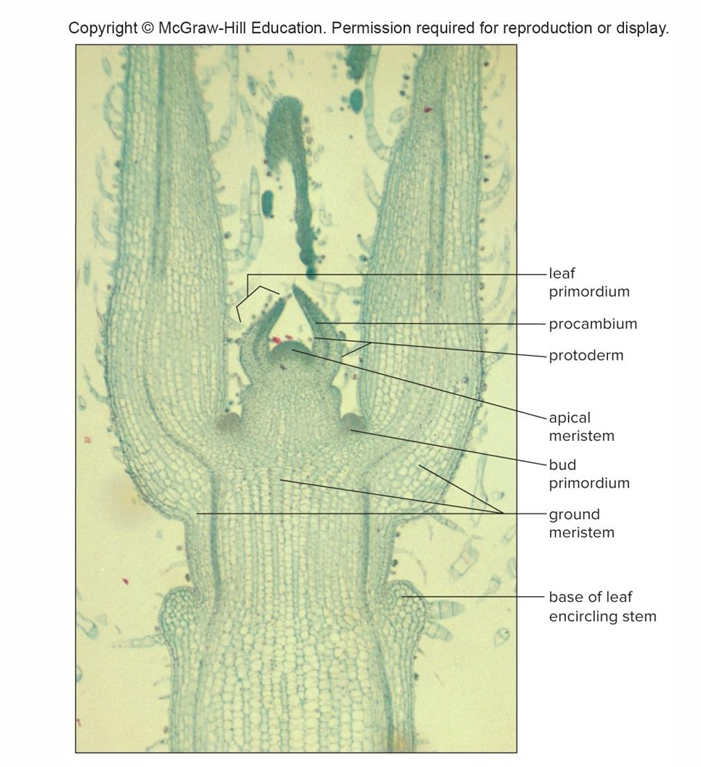
Apical meristem cells form 3 primary meristems: Ground meristem
Produces pith and cortex, both composed of parenchyma cells
Leaf primordia and bud primordia develop into mature leaves and buds
Traces branch off from cylinder of xylem and phloem, and enter leaf or bud
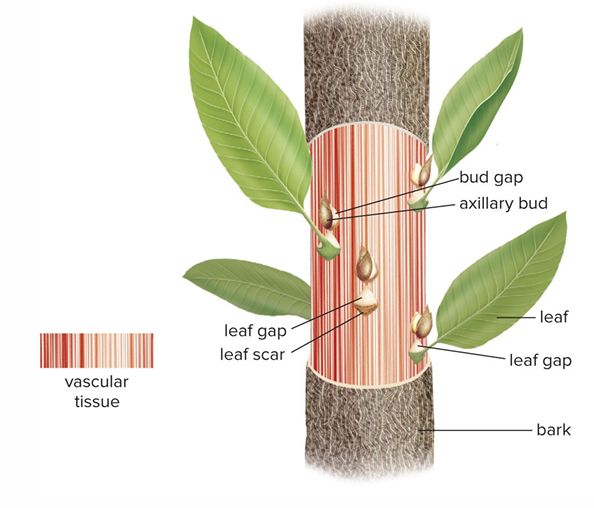
Trace means?
Strand of xylem and phloem
Narrow band of cells between the primary xylem and primary phloem may become?
Vascular cambium
Cells produced by the vascular cambium become components of?
Secondary xylem toward center and secondary phloem toward surface
In many plants cork cambium (phellogen) produces?
Cork cells with suberin and phelloderm cells. (waxy coating)
Cork cambium function?
Reduce water loss and to protect against injury
Lenticels
Parenchyma cells in cork for exchange of gases
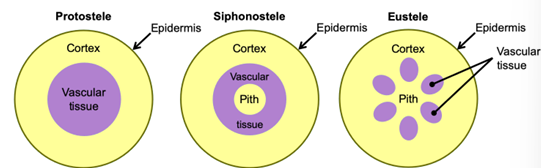
Stele
Central cylinder of primary xylem, primary phloem, and pith (if present)
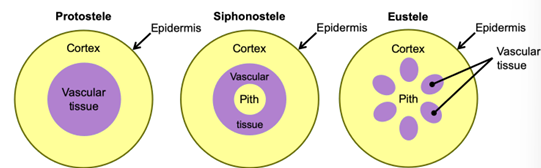
Protostele
Solid core, phloem surrounds xylem
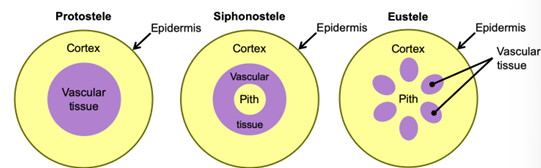
Siphonosteles
Tubular with pith in center
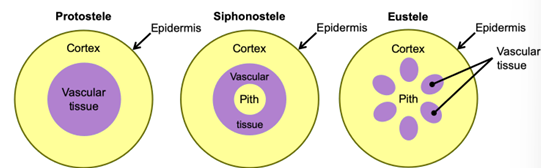
Eusteles
Discrete vascular bundles
Cotyledons
Seed leaves attached to embryonic stems (store food needed by young seedling)
Dicotyledons (dicots)
Flowering plants that develop from seeds having two cotyledons
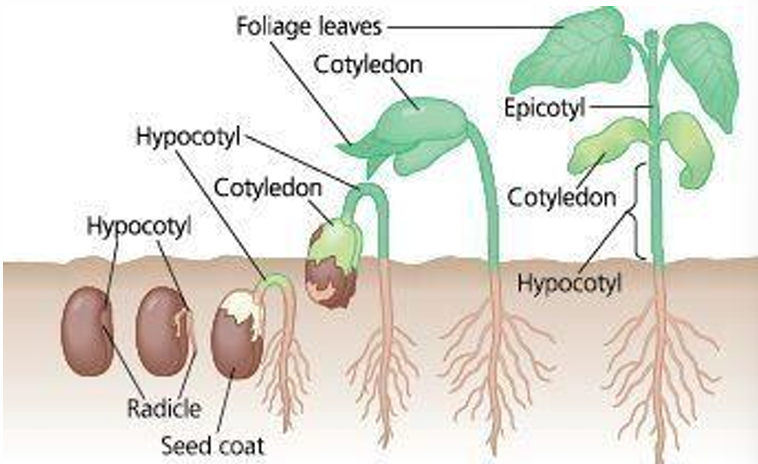
Monocotyledons (monocots)
Flowering plants that develop from seeds with a single
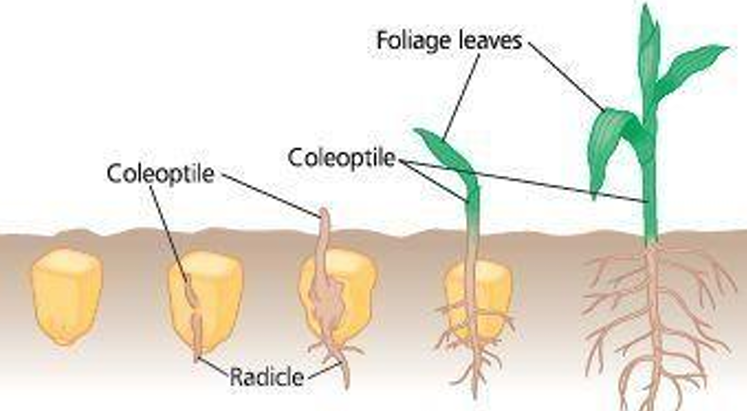
Herbaceous dicots have?
Discrete vascular bundles arranged in a cylinder
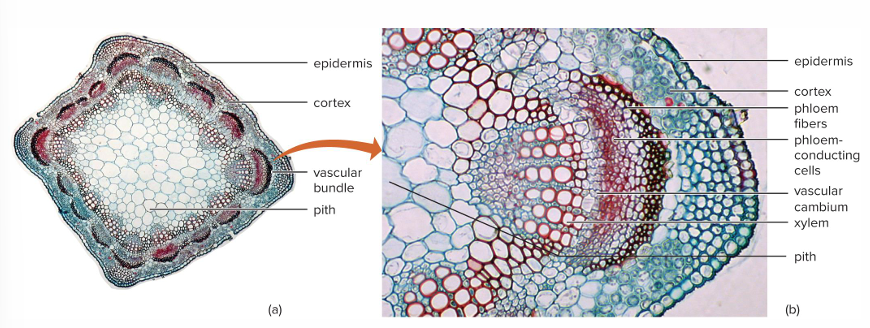
Vascular cambium arises between?
Primary xylem and primary phloem. Adds secondary xylem and secondary phloem
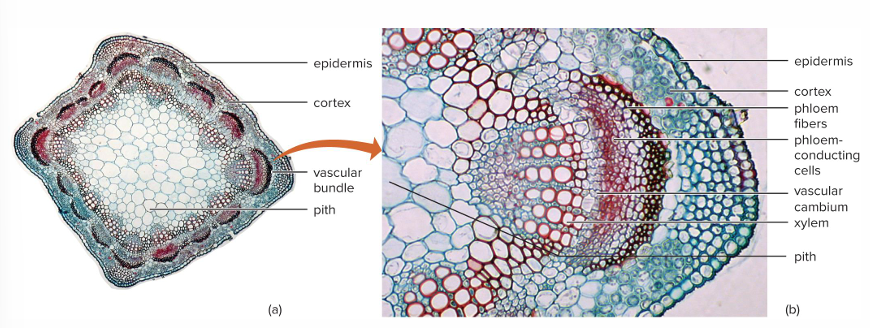
Wood =
Secondary xylem
After spring wood
Fewer, smaller vessel elements in proportion to tracheids and fibers
In spring wood
Relatively large vessel elements of secondary xylem produced
Xylem ray
Part of ray within xylem
Phloem ray
Part of ray through phloem
Softwood
Wood of conifers; no fibers or vessel elements
Hardwood
Wood of dicot trees; resin canals
Resin canals
Tube-like canals scattered throughout xylem and other tissues
Bark
Tissues outside vascular cambium, including secondary phloem. Mature bark may consist of alternating layers of crushed phloem and cork
Laticifers
Ducts found mostly in phloem that have latex secreting cells. Used to make rubber, gum, and morphine
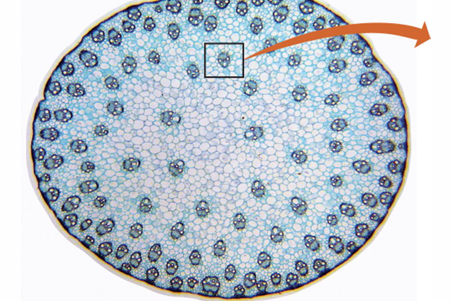
Monocots stems have neither a …
vascular cambium nor a cork cambium
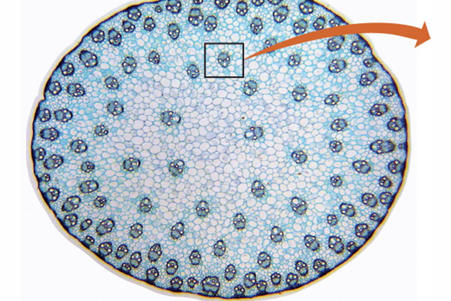
Monocot stems produce no…
Secondary vascular tissue or cork
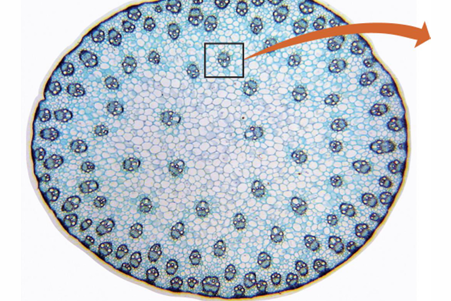
Monocot stems primary….
Xylem and phloem in discrete vascular bundles scattered throughout the stem
Monocot vascular bundle has?
Two large vessels with several small vessels. First formed xylem cells stretch and collapse.
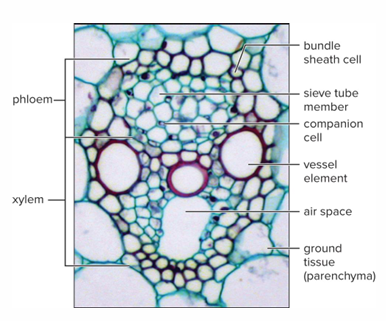
Monocot vascular bundle also has?
Leave irregularly shaped air space. Phloem consists of sieve tubes and companion cells
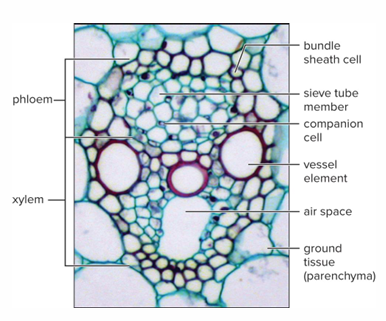
The monocot vascular bundle is surrounded by what?
Sheath of sclerenchyma cells
Rhizomes
Horizontal stems that grow below-ground and have long to short internodes. EX: irises, some grasses, ferns
Runners
Horizontal stems that grow above ground and have long internodes. EX: strawberry
Stolons
Produced beneath the surface of the ground and tend to grow in different directions. EX: potato
Tubers
Swollen, fleshy, underground stem. EX: potatoes(eyes of potato are)
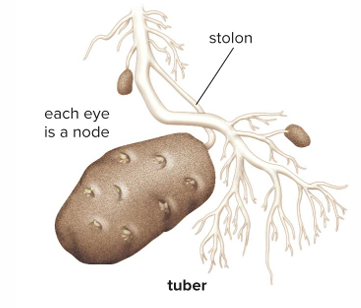
Bulbs
Large buds surrounded by numerous fleshy leaves, with a small stem at lower end. EX: onions, lilies, hyacinths, tulips
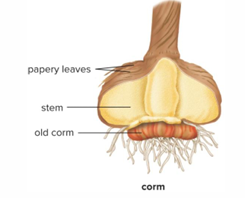
Corms
Resemble bulbs, but composed almost entirely of stem tissue, with papery leaves. EX: crocus and gladiolus
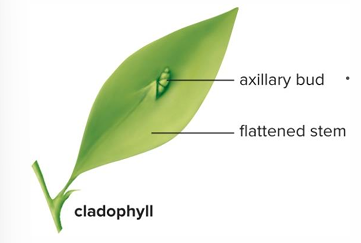
Cladophylls
Flattened leaf-like stems. EX: greenbriers, some orchids, prickly pear cactus
Flattened blade =
Lamina
Network of veins =
Vascular bundles
Simple leaves
Single blade
Compound leaves
Blade divided into leaflets
Pinnately compound leaves
Leaflets in pairs along rachis (petiole)
Bi-pinnately compound leaf
Leaflets subdivided

Palmately compound leaves
All leaflets attached at same points at the end of petiole
Photosynthesis
Trapping and storing of energy in sugar molecules that are constructed from water and carbon dioxide
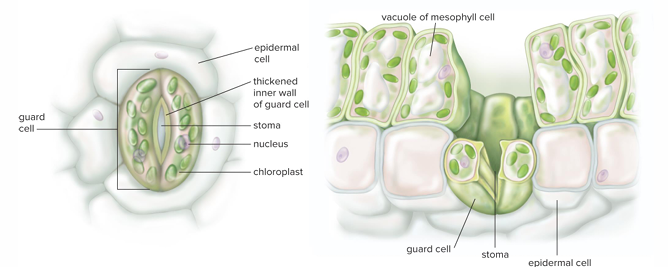
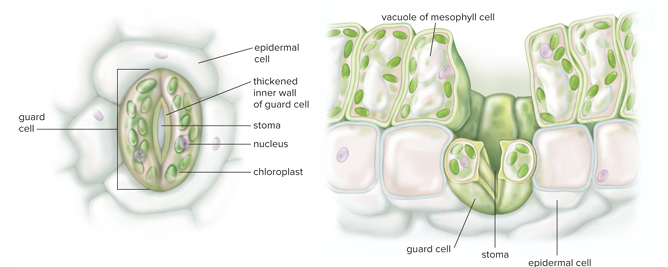
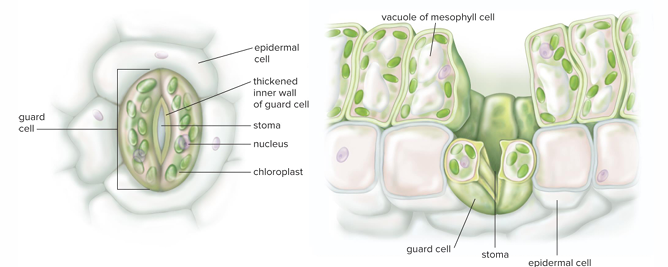
Stomata
Tiny pores on lower surfaces of leaves. Allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to diffuse out. Water vapor also escapes via stomata
Guard cells control what?
Water loss by opening or closing pores of stomatal apparatus
Guttation
Root pressure forces water out hydathodes at tip of leaf veins in some plants
Wastes is metabolic processes accumulate in leaves and…
Are disposed of when leaves are shed
Phyllotaxy
Arrangement of leaves on stem
Venation
Arrangement of veins in a leaf or leaflet blade
Pinnately veined leaves
Main midvein included within enlarged midrib

Secondary veins branch from?
Midvein
Palmately veined leaves
Several primary veins fan out from base of blase
Dicots - Primary veins divergent in various ways =
Nettled or reticulate venation
Dichotomous venation
Veins fork evenly and progressively form base of blade
Monocots - primary veins parallel =
Parallel venation
Epidermis
Single layer of cells covering the entire surface of the leaf
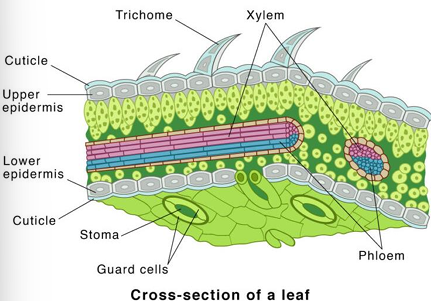
Epidermis is absent of
Chloroplasts
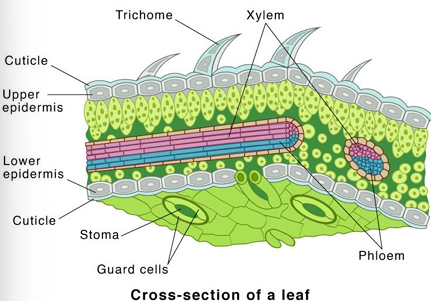
Epidermis is coated with
Cuticle (with cutin)
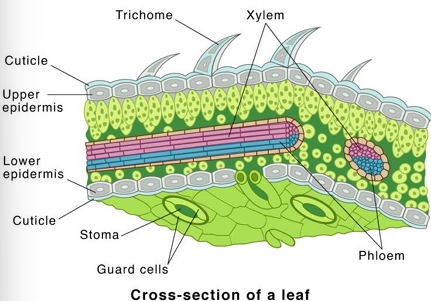
Lower epidermis typically has thinner layer of
Cutin and is perforated by numerous stomata
Guard cells originate from the same
Parent cell and contain chloroplasts
Inflate
Stomata open
Deflate
Stomata close
Stomata primary functions
Regulates gas exchange between leaf interior and atmosphere. Regulate evaporation of water (changes in amount of water in guard cells cause them to inflate or deflate)
Most photosynthesis takes place in the mesophyll between the two epidermal layers. Also known as the?
Palisade Mesophyll
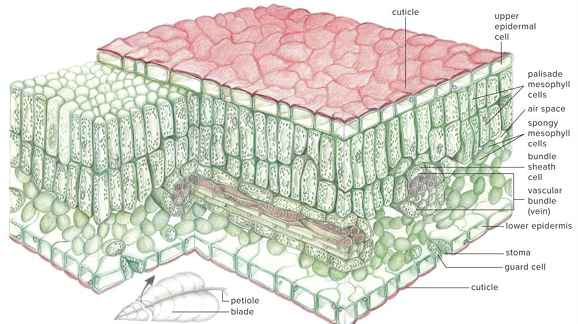
Spongy mesophyll
Compactly stacked, barrel-shaped parenchyma cells, commonly in two rows. Contains most of Leafs chloroplasts
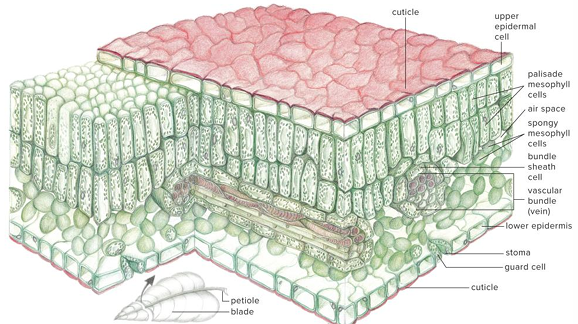
Veins (vascular bundles) are scattered throughout?
Mesophyll
Veins consist of
Xylem and phloem tissues surrounded by bundle sheath of thicker-walled parenchyma
Leaves reduce loss of water by
Thick, leathery leaves, fewer stomata or sunken stomata, succulent leaves or no leaves, and dense hairy coverings
Leaves of aquatic areas
Less xylem and phloem. Transpiration does not work here. Large air spaces. Mesophyll not differentiated into palisade and spongy layers
Tendrils
Leaves curl around rigid object creating support. EX: garden peas
Spines
Leaves that reduce leaf surface and water loss and protect plant. EX: cacti
Thorns
Arising IN the axils of leaves of woody plants
Prickles
Outgrowth from epidermis of cortex
Storage leaves
Succulent leaves. Have parenchyma cells with large vacuoles
Flower-pot leaves
Leaves develop urn-like pouches that become home of ant colonies. Ants provide soil adding nitrogenous waste

Window leaves
Leaves buried in ground, except exposed end. End transparent thick epidermis and transparent water storage cells underneath. Let’s light in without dried leaves

Reproductive leaves: walking fern
New plants at leaf tips
Reproductive leaves: air plant
Tiny plantlets along leaf margins