Lecture 1: Overview of Hazards
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
What are some hazards that pose a risk to humans and the environment?
nuclear meltdowns
Toxic gas release
Oil spills
Ozone depletion
Acid rain
Infrastructure failure
Shipwrecks
Airplane crashes
What are the 3 main processes natural hazards can arise from?
Internal forces within the Earth
External forces on Earth’s surface
Gravitational attraction
Internal forces within the earth - driven by what? Example?
Driven by the internal energy of the Earth
Example: Plate tectonics
External forces on earth’s surface - driven by what? Example?
driven by the sun’s energy
example: atmospheric effects
Gravitational attraction - driven by what? Example?
driven by the force of gravity
example: downslope movement
Hazard:
A process that poses a potential threat to people or the environment
Risk:
The probability of an event occurring multiplied by the impact on people or the environment
probability x impact
Disaster:
A brief event that causes great property damage or loss of life
- The carrying out of a hazard
Catastrophe:
A massive disaster
Hazards that are more likely to be catastrophic:
tsunamis
earthquakes
volcanoes
hurricanes
floods
Hazards that are less likely to be catastrophic:
landslides
avalanches
wildfires
tornadoes
What is the impact of a hazard?
Both its magnitude (energy released) and frequency
What is the Magnitude-Frequency Concept?
There is an inverse relationship between magnitude and frequency
3 components of the Geologic Cycle
Tectonic cycle
Rock cycle
Hydrologic cycle
What is the tectonic cycle?
the creation, movement, and destruction of tectonic plates
What are tectonic plates ?
Large blocks of the Earth’s crust that form its outer shell
How many tectonic plates are there?
14
7 big plates - 7 continents
7 small plates in between continents
where is new land formed?
mid ocean ridges
where is land destroyed?
subduction zones
What energy drives the tectonic cycle?
Earth’s internal energy
Earth’s internal structure
Core (inner, outer)
Mantle
Asthenosphere (upper mantle)
Lithosphere
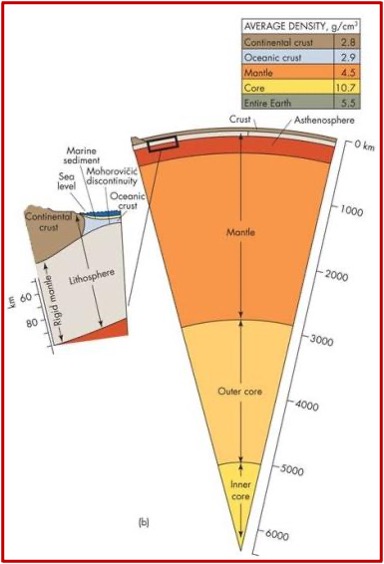
Inner core:
extremely hot and solid
Asthenosphere (upper mantle)
composed of hot magma with some flow
Lithosphere:
a thin and brittle crust
What is the crust?
Forms the upper part of the lithosphere and is broken into fragments (plates)
2 types of crusts:
Oceanic: dense, thin (avg 7km thick)
Continental: relatively buoyant, thick (avg 30 km thick)
What causes the movement of plates?
Convection currents within the mantle
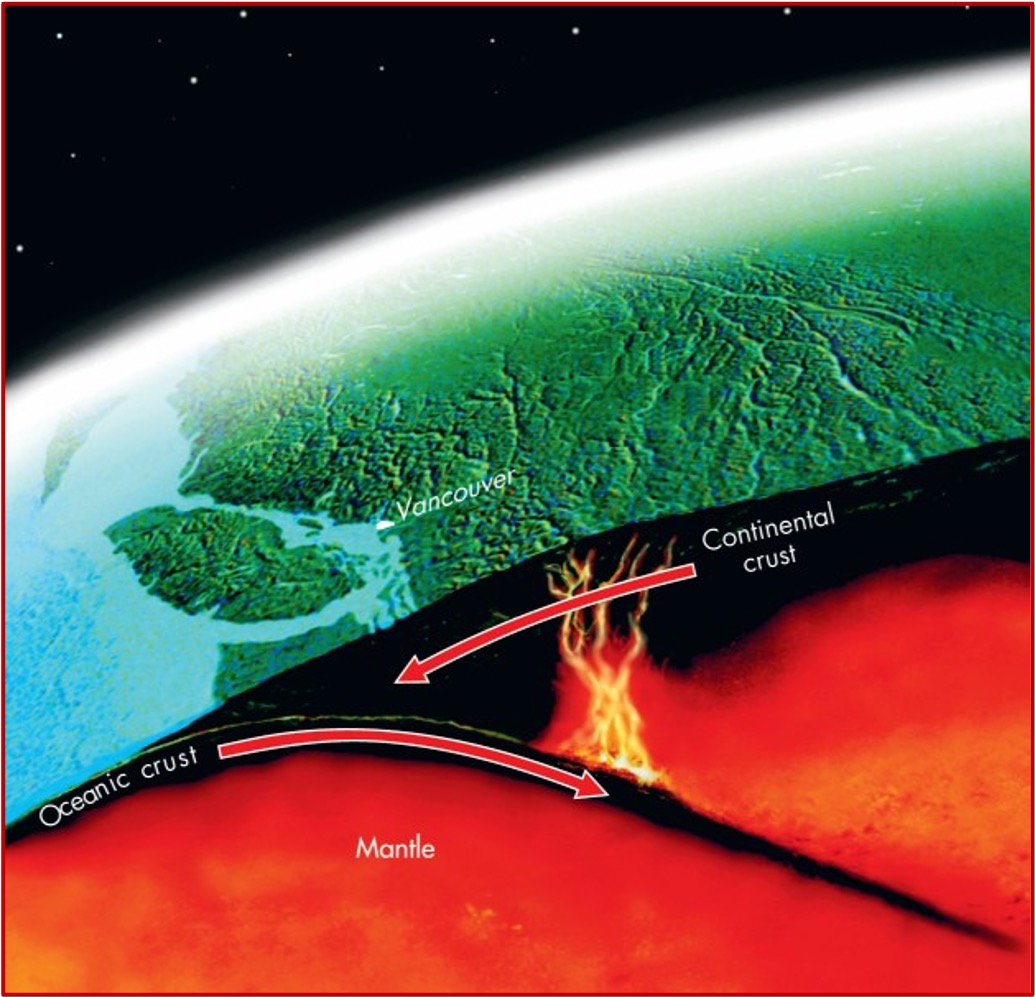
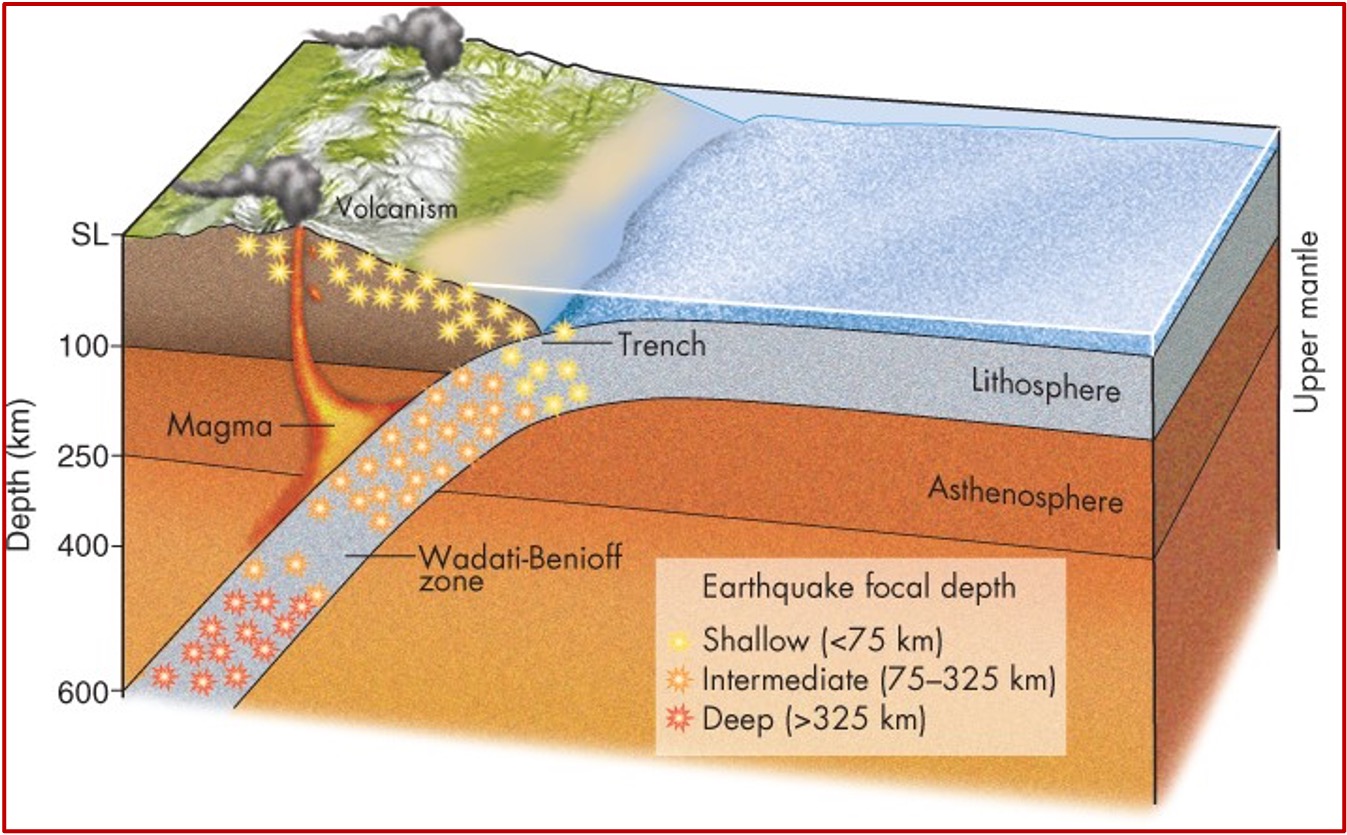
Subduction Zone (image)
Do plate boundaries match up with the boundaries of continents or oceans?
No
3 types of plate boundaries
Divergent
Convergent
Transform
Plate boundaries (map)
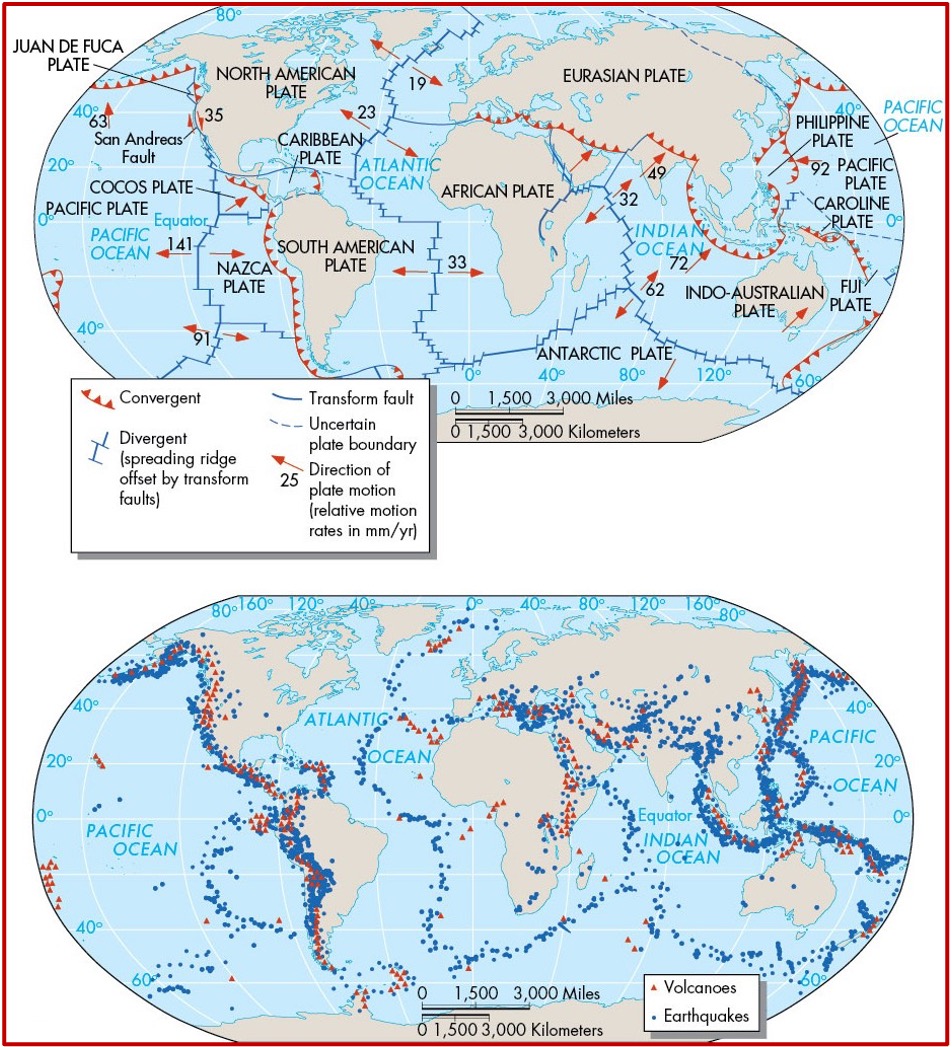
What are some evidence for Pangaea?
Current mountain ranges
fossils
What are Divergent Plate Boundaries?
At these boundaries, plates move away from each other (diverge)
new land gets created
results in seafloor spreading
oceanic ridges form
Example: the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
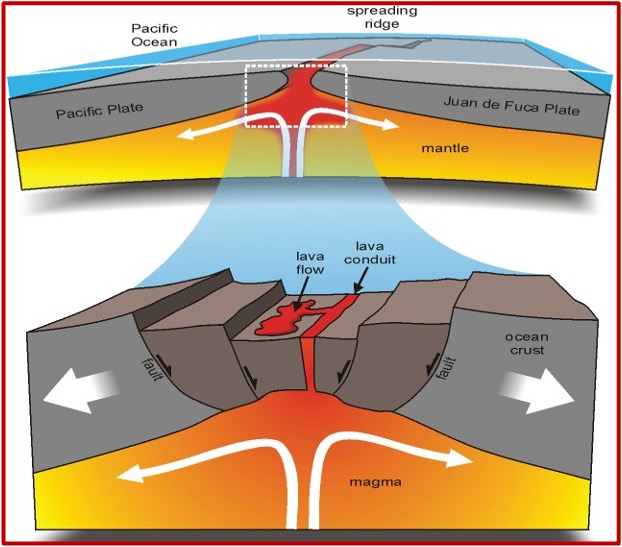
Is the Atlantic Ocean getting wider or narrower?
(hint, its a divergent plate boundary)
Wider
What are Convergent Plate Boundaries?
At these boundaries, plates move toward each other
cause collisions - result in different things depending on the type of crusts involved
Collisions involving oceanic and continental crust result in what? (and what forms)
Subduction zones
dense ocean plates sink and melt
melted magma rises to form mountains and volcanoes
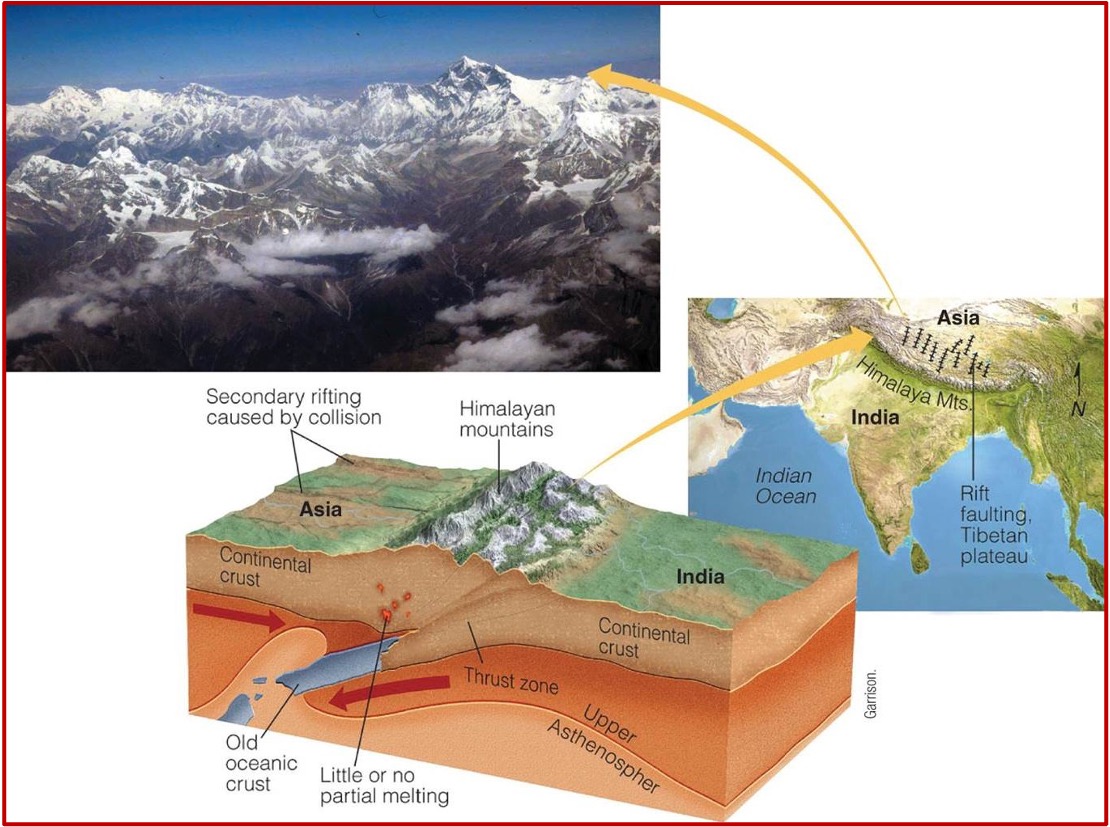
Collisions involving 2 continental plates results in what? (and what forms)
Collision boundaries
niether plate sinks
tall mountain tend to form
What is this image of?
Subduction zone
What is this image of?
Collision boundaries
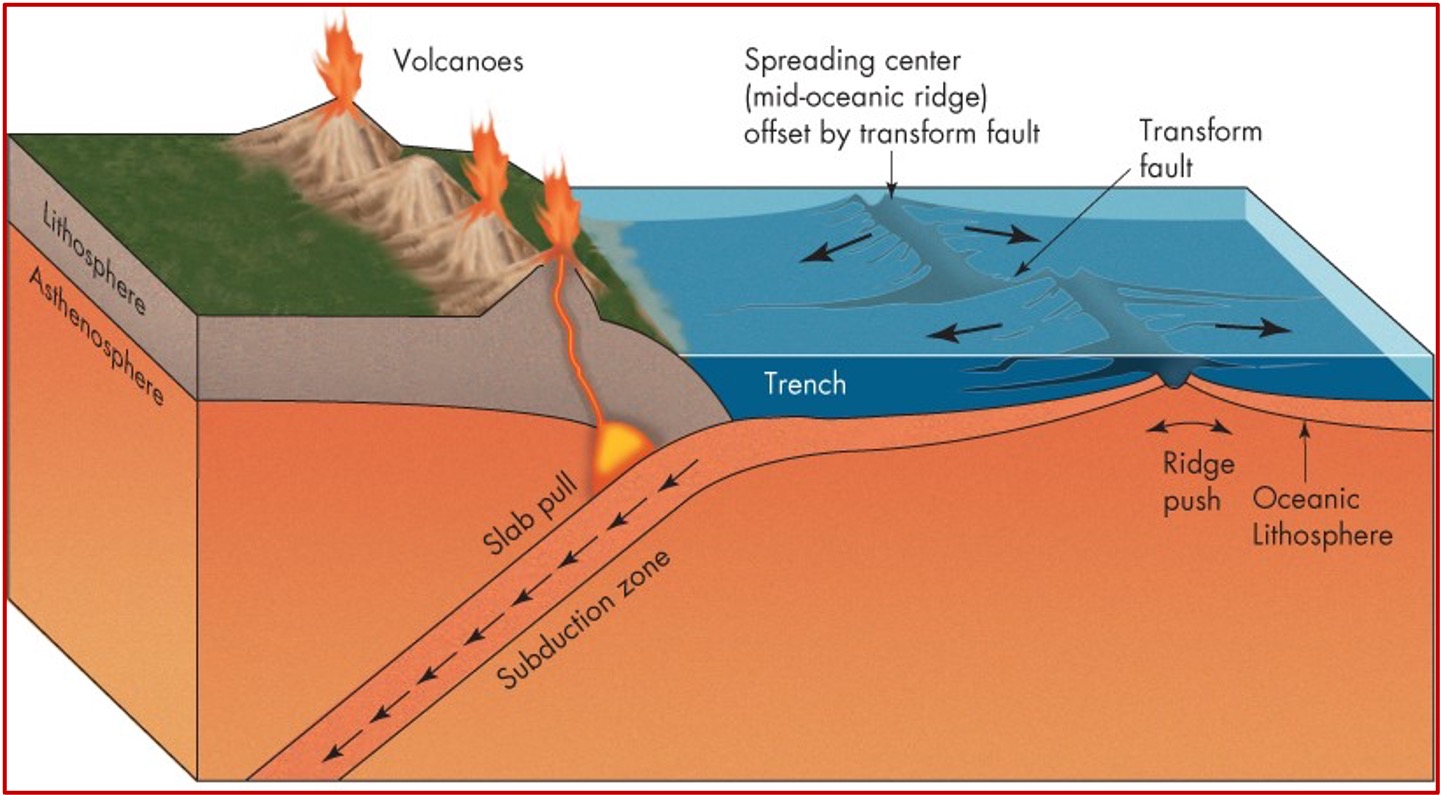
What are Transform Boundaries?
At these boundaries, plates slide horizontally past each other
the zone along which the movement occurs is called a transform fault
most of these faults are located beneath oceans, but some occur on continents
Example: San Andreas Fault
Plate boundaries summary image
What are Hot Spots?
Spots where magma rises from the mantle, where the currents are strong enough to pull magma up
found away from plate boundaries
magma erupting at surface results in the formation of volcanoes
Example: strings on islands (Hawaiian Islands)
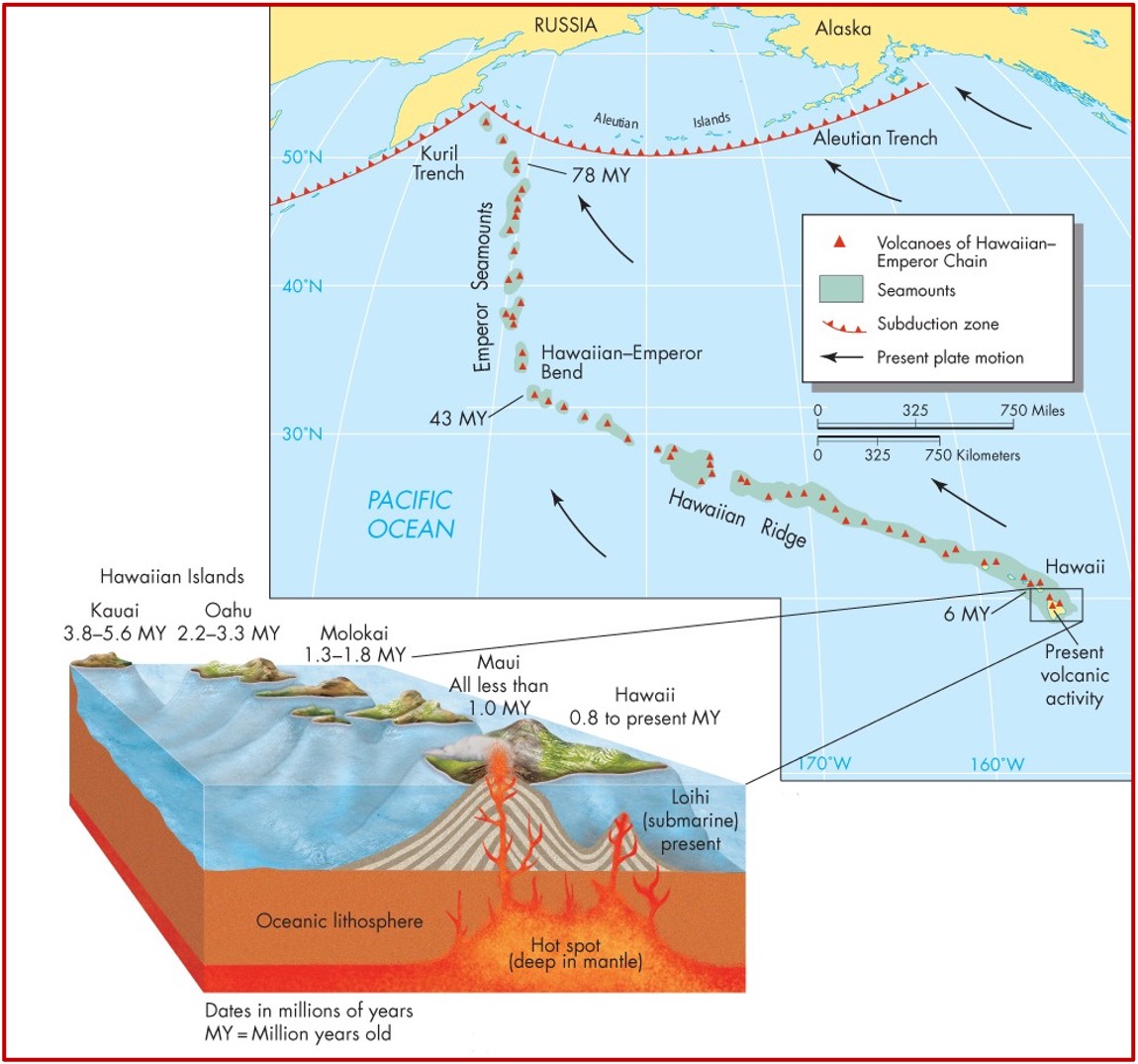
What is this image of?
Hot spots
What is a rock?
An aggregate of one or more minerals
What are the 3 different rock types?
Igneous
Sedimentary
Metamorphic
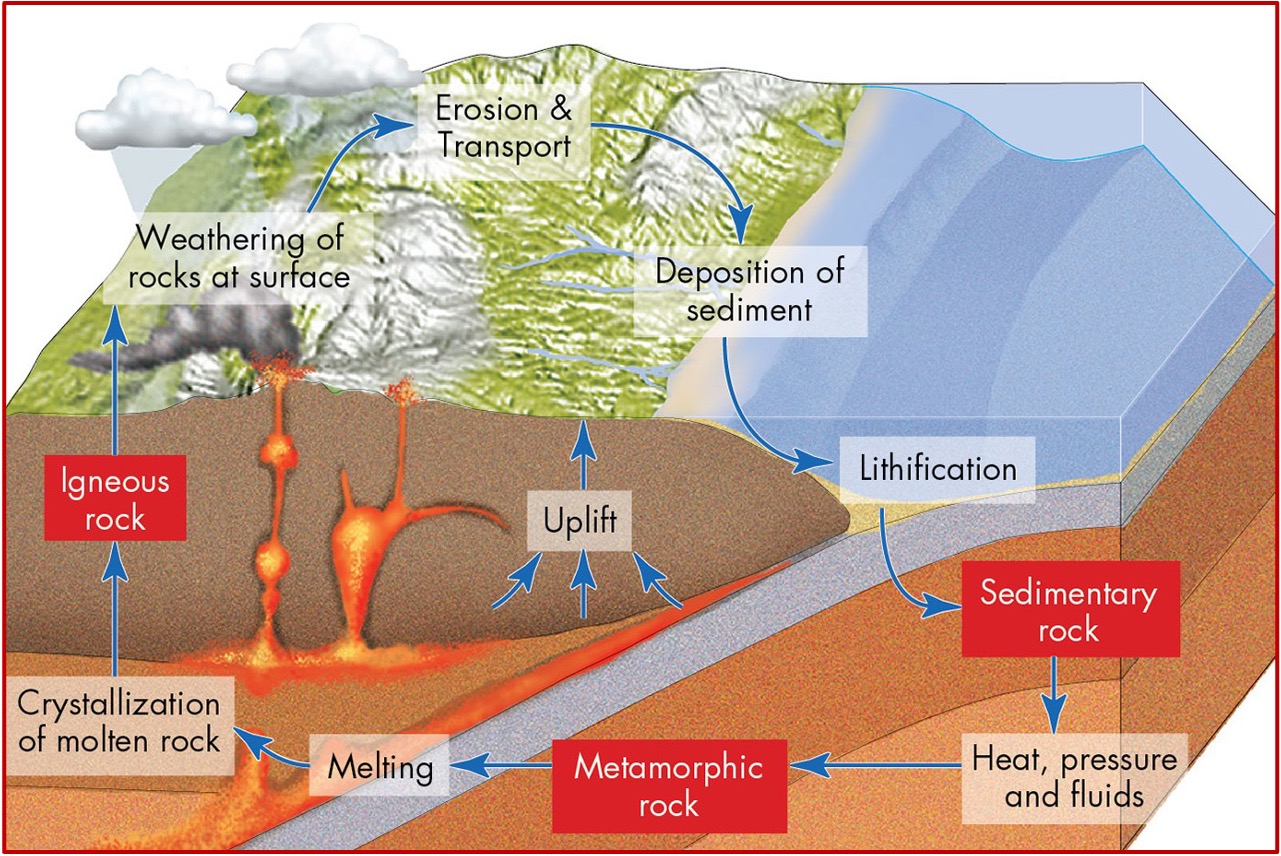
The Rock Cycle
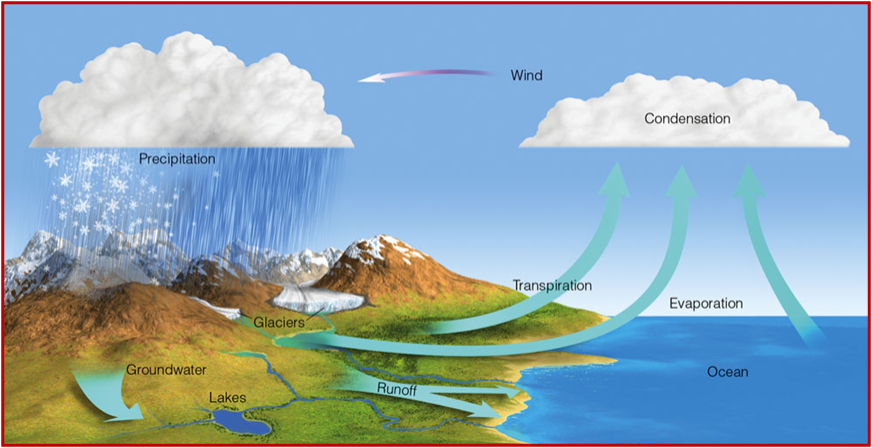
What is the Hydrologic Cycle?
The movement and exchange of water among the land, atmosphere, and oceans by changes in state
water cycle
solar energy drives the movement of water
What is the residence time of a water molecule?
Ranges from days (in the atmosphere) to thousands of years (in the ocean)
The Hydrologic Cycle
What are the 5 major course themes?
Hazards can be understood through scientific investigation and analysis
An understanding of hazardous processes is needed to evaluate risk
Hazards are linked to each other and the environment
Population growth and socio-economic changes are increasing the risk from hazards
The consequences of hazards can be reduced
Theme 1: Hazards can be understood
Scientists observe a hazardous event and form a possible explanation for the cause
From this explanations, a hypothesis is formed
Data are then collected to test the hypothesis
Knowing the cause allows for the identification of where hazards may occur
Knowledge of past events aids in predicting future events
Are hazards natural processes?
These events are natural forces; they only become hazardous when they disrupt human activity or the environment
These processes are not within our control. We cannot prevent them; we can only respond to them
The best solution to mitigate loss is preparation
What is a prediction?
a specific time, date, location, and magnitude of the event
only some hazards can be preducted
What is a forecast?
a range of probability for the event
many hazards can be forecasted
What is risk?
Risk = (probability of event) x (consequences)
What are consequences?
damage to people, property, the environment, the economy
impacts
What is acceptable risk?
The amount of risk that an individual is willing to take
The frequency of an event plays a role in determining acceptable risk
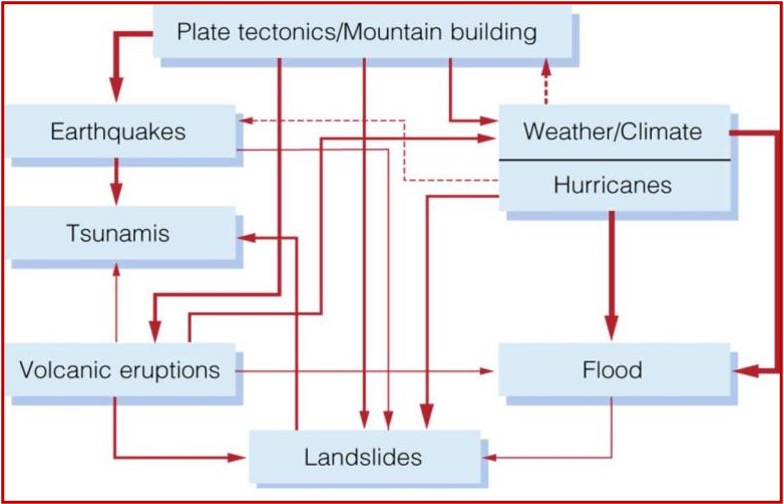
What are 2 examples of how hazards are linked? (theme 3)
Earthquakes may cause tsunamis and landslides
Hurricanes may cause tornadoes and flooding
Theme 3: Hazards are linked (image)
Theme 4: The increasing risk of hazards
Concentration of human population creates greater loss of life in a disaster
Population growth is putting greater demand on Earth’s resources
Rapid population growth is currently occurring in most developing countries
Many people live in areas that are prone to hazards
Explain the human footprint and how it is increasing the risk of hazards
The risks associated with hazards change as human development expands
Examples:
Neighborhoods extend onto hillsides and floodplains
Urbanization alters drainage and slopes
Agriculture, forestry, and mining can increase erosion
In Canada, property damage from hazards is increasing but deaths from hazards are decreasing (because of better planning and warning).
Socio-economic factors of disaster (developed vs developing countries)
Economic losses from disasters are much higher in developed countries
Deaths from disasters are much higher in developing countries
Direct effects vs Indirect effects
Direct effects: deaths, injuries, displacement of people, damage to property
Indirect effects: crop failure, starvation, emotional distress, loss of employment
Reactive approaches to hazards:
recovery
search and rescue
providing food
water
shelter
rebuilding
Proactive approaches to hazards
Adjustment through:
lang-use planning
building codes
insurance
evacuation planning
disaster preparedness
artificial control
What are benefits of hazardous events called?
Natural service functions
Examples of natural service functions:
Flooding provides nutrients for the soil
Landslides form natural dams that create lakes
Volcanic eruptions create new land
Climate change & natual hazards
Global climate change is currently the most crucial environmental issue facing the Earth
As climate changes, the frequency of some natural processes will increase.
The sea level rise from melting ice sheets will cause more coastal erosion and flooding
Warmer oceans will cause for frequent hurricanes
Which mountain chain is the result of an ocean-continent subduction zone?
The Andes