7B anxiety-panic disorder مقالي 🛑
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Panic disorder is an anxiety disorder characterized by:
Extreme and frequent unexpected panic attacks
Attacks may be:
with no apparent cause
Or triggered by a specific event or situation
What is Panic Disorder?
At least one of the following for ≥ (more or equal) 1 month:
Persistent fear of having another attack
Worry about the consequences of the attack
Behavioral changes related to the attacks
What conditions must be present for diagnosing Panic Disorder over one month?
Repeated intense episodes of extreme anxiety
Duration:
Usually 10 minutes
May be 1–5 minutes
May exceed 10 minutes
Attacks may:
Wax and wane for hours
Occur as rolling attacks
Severity and symptoms vary between patients
What are the general signs and course of Panic Disorder? + duration + it’s rhythm?
Rapid heart rate
Sweating
Nausea
Dizziness
Trembling
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Chills
Numbness
What are the Physical Symptoms of Panic Attacks?
Fear of losing control or going crazy
Fear of dying or having a heart attack
Feeling detached from reality
What are the Psychological Symptoms of Panic Attacks?
They often feel as if:
They are having a heart attack
They are about to die
How do patients describe a panic attack?
Avoidance of certain places or situations
Use of safety behaviors for reassurance
What are the Behavioral Symptoms of Panic Disorder?
Continuous avoidance of feared situations and objects
↳This avoidance may gradually develop into phobias
How can Panic Disorder lead to Phobias?
Persistent worry about future panic attacks
Impairment in daily functioning
What psychological distress occurs in Panic Disorder?
Recurring and unexpected panic attacks
For at least one month
What is meant by Duration and Frequency?
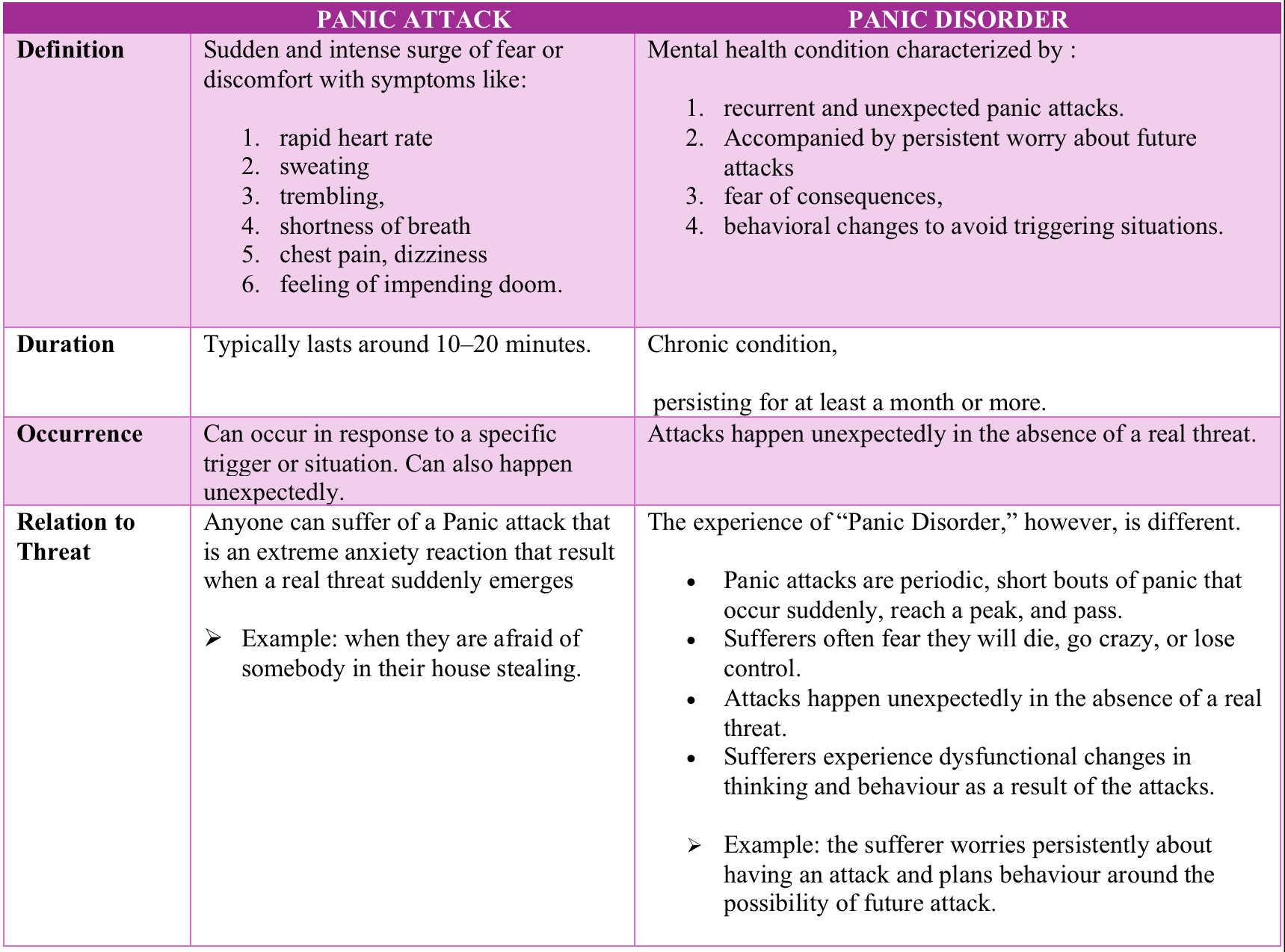
What is the Difference between Panic Attack & Panic Disorder?
Recurrent unexpected panic attacks
Peak within minutes
With 4 or more of the following:
Palpitations
Sweating
Trembling
Shortness of breath
Choking
Chest pain
Nausea
Dizziness
Chills or heat sensations
Paresthesia
Derealization or depersonalization
Fear of losing control
Fear of dying
What is DSM Criterion A of panic disorder?
At least one attack followed by one of:
Persistent worry about new attacks or their consequences
Maladaptive behavioral changes (avoidance)
for month or more
What is DSM Criterion B?
not attributed to the physiological effects of a substance
Substance use
Medication
Medical condition (e.g., hyperthyroidism, cardiopulmonary disorders)
What is DSM Criterion C?
Not better explained by another disorder:
SAD
Specific phobia
OCD
PTSD
SepAD
What is DSM Criterion D?
Hyperthyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Temporal-lobe epilepsy
Asthma
Cardiac arrhythmias
Excess caffeine and stimulants
What diseases mimic Panic Disorder?
Usually begins before age 25
May occur in the mid-30s
Saudi females: 1.9%
Saudi males: 1.3%
KSA overall prevalence: 1.6%
What is the age onset of panic disorder and its prevalence of ?
Family history
Smoking
Psychological stress
History of child abuse
What are the risk factors of Panic Disorder?
Biological
Pharmacological
Chronic illness (comorbidity > 90%)
Cognitive
What are the main perspectives explaining(causes) of Panic Disorder?
Runs in families
Twin studies: higher concordance in identical twins
First-degree relatives: 40% risk
▶ Neurochemical imbalance:
GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid)
Cortisol
Serotonin
Hyperexcitable neural circuitry in the brain
What explains Panic Disorder biologically?
Stimulants
Caffeine
Amphetamine
Alcohol
Some medications
Psychosomatic drug phobias
What substances can trigger Panic Disorder?
Alcohol withdrawal
Benzodiazepine withdrawal
Both may cause rebound panic attacks
What is the effect of substance withdrawal?
Major life transitions
Stimulus generalization
Learned helplessness
Maintained by negative reinforcement
Excessive threat focus
What are the cognitive causes of Panic Disorder?
Test/preformance anxiety
Poor academic performance
School avoidance
Public speaking stress
Why does Panic Disorder appear in school?
Schizophrenia
OCD
Specific phobias
Social phobia
Agoraphobia
What psychiatric disorders are comorbid with Panic Disorder?
Heart disease
Hyperthyroidism
Drug use
What is the differential diagnosis of Panic Disorder?
Life restriction
Job and housing limitation
Avoidance of driving and shopping
One-third become housebound
Development of agoraphobia
What are the outcomes of untreated Panic Disorder?
Decrease frequency of attacks
Decrease intensity of attacks
Decrease anticipatory anxiety
Decrease phobic avoidance
What are the goals of treatment?
A psychiatrist
psychologist, or a mental health care provider.
Who should monitor all patients with PD?
Psychiatric care.
What type of care is shown to be the most effective and low cost for patients with PD?
Higher efficacy
Lower cost
Lower dropout rate
Lower relapse rate
12–16 weekly sessions
Focus on symptom recreation and response modification
Why is CBT the treatment of choice?
A thought
A situation
A heartbeat change
What can act as triggers?
Separate panic from the trigger
Increase trigger awareness
What are the CBT therapy goals?
Gradual exposure
Desensitization
Relaxation techniques
Respiratory training:
to control hyperventilation during panic attacks
Controlled breathing
Triggers can be created such as:
Light-headedness
Blurred vision
Dizziness
What does behavioral therapy include in anxiety and panic disorder?
Benzodiazepines (short-term)
SSRIs (long-term)
Used with psychotherapy
What medications are used?
First follow-up in 2 weeks
Start SSRIs at lowest dose
Assess suicide risk
Treat substance use
Refer to cardiologist if needed
What is the follow-up plan?
Dangerous behavior
Suicidal or homicidal ideation
Intoxication or withdrawal
Inability to follow outpatient care
Medical instability
When is hospitalization (inpatient) required?
Major life stress
Loss of loved ones
Requires restarting:
CBT
SSRIs
Tricyclics if SSRIs fail
Why does relapse occur?
65% achieve remission within 6 months
CAD risk nearly doubled
Panic can induce myocardial ischemia
Combined CBT + medication effective in >85% of cases
What is the prognosis of Panic Disorder?