Short run and long run agreagate supply
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Short-run agreagate supply (SRAS) increase
Is the current supply given a firms capital expenditure on fixed assets.
The SRAS curve is upward sloping because of two assumptions of producers in the economy:
All firms aim to maximise profits
In the short run, the cost of producing extra units of output increases as firms produce more
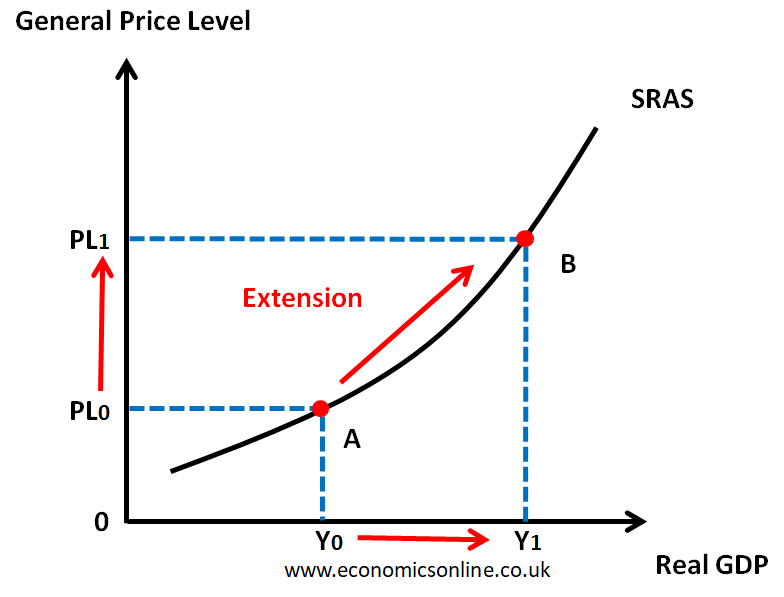
Increase in SRAS
In the short run all the factor of production are fixed. Therefore to increase SRAS you can’t increase the amount of factors of production, you have to utilise the factors of production you already have more. For example increasing productivity.
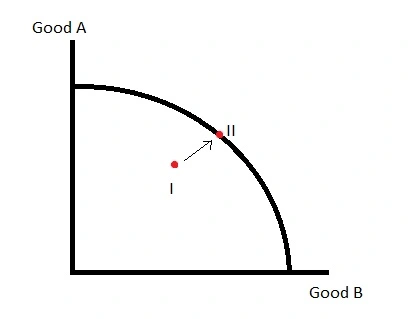
This can be shown on a PPF curve by a shift of a point from inside the curve, to on the curve
Long run aggregate supply (LRAS) increase
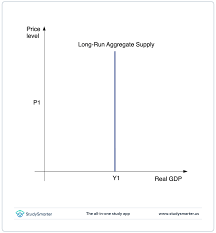
LRAS- An economies output, assuming full utilisation of all factors of production and flexible prices.
LRAS is a straight vertical line because in the long term wages and prices are fully flexible, so a change in price level won’t change output.
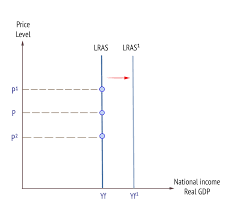
Increase in LRAS
As LRAS is the theoretical maximum level of production with the current quantity factors of production, an increase it is caused by increasing the amount of factors of production in an economy.
This is shown on the diagram by a rightward shift in the LRAS curve.
Determinants of SRAS
Factors that can cause an increase in SRAS:
A fall in firm’s cost of production
A fall in unit labour cost
A reduction in indirect taxes
An increase in subsidies
Technological advancement
Determinants of LRAS
The factors which effect the level of LRAS:
The level of technology
The quantity of the factor of production
The mobility of the factors of production
The productivity of the factors of production
The level of entrepreneurship
Economic incentives
Institutional structures of the economy