Lab Final Exam - ALL Terms
1/971
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
972 Terms
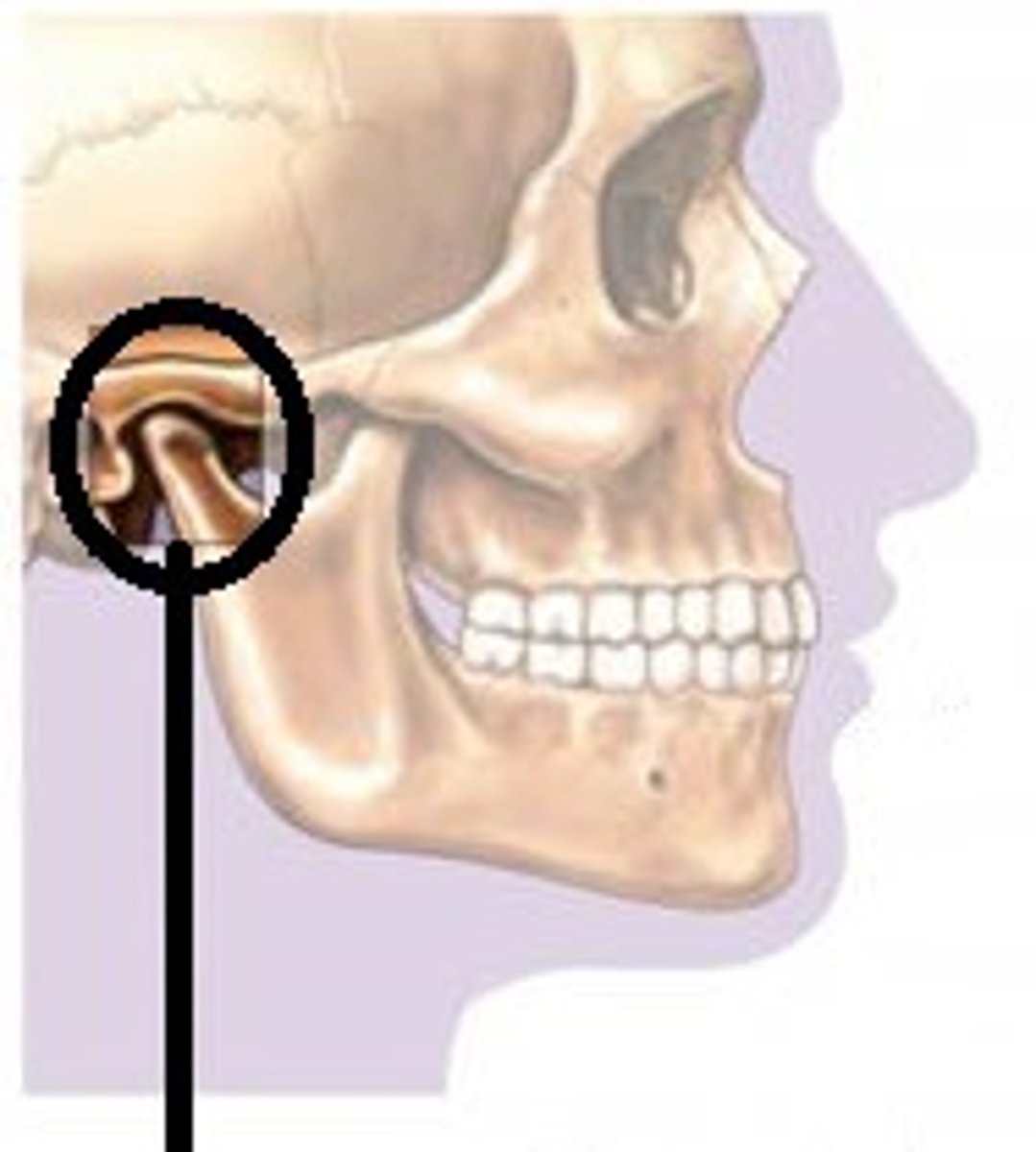
temporomandibular joint
- articulation of the condylar process of the mandible with the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits elevation/depression of the mandible (opening/closing the jaw)
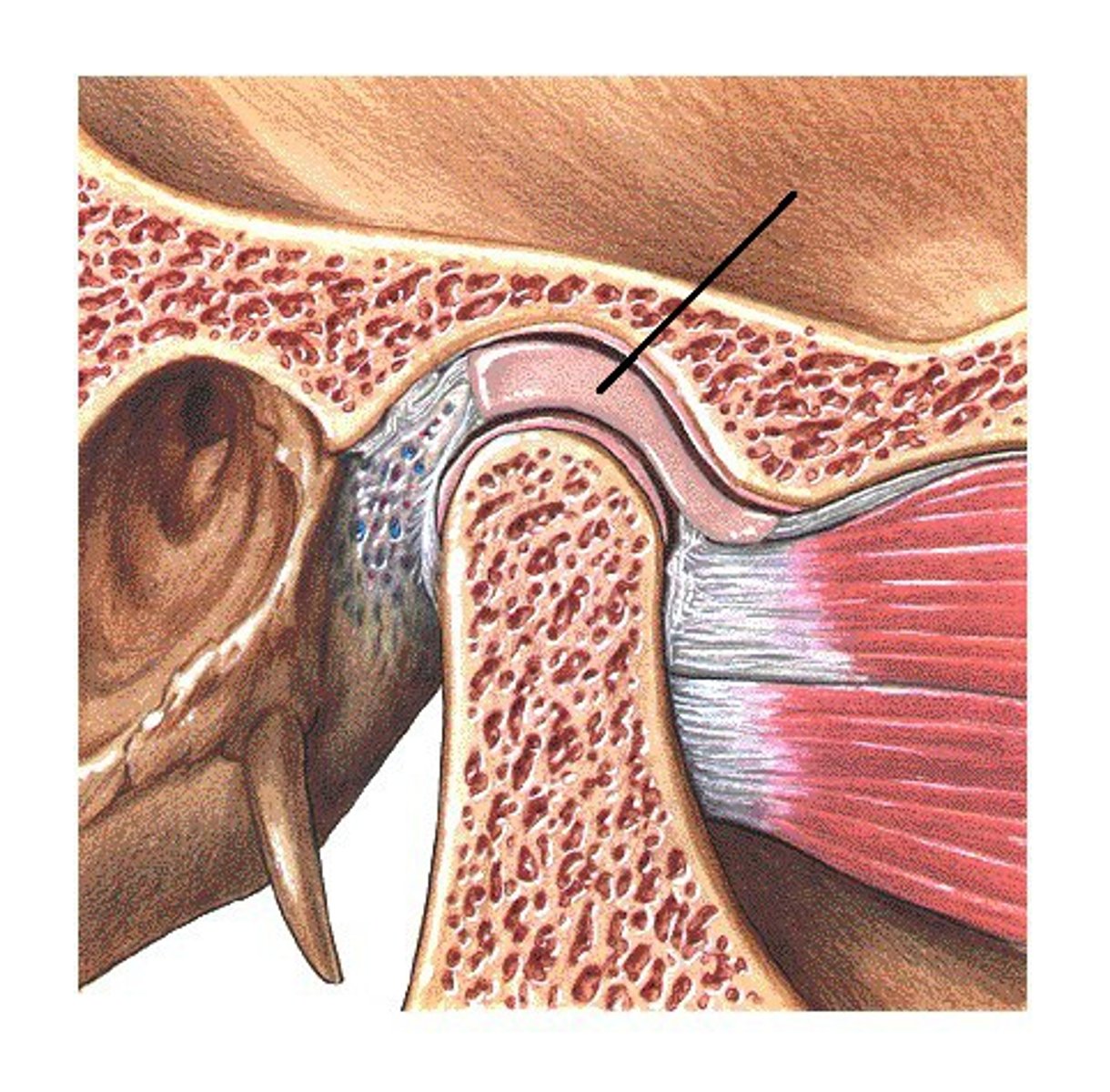
articular disc
- fibrocartilage disk between the condylar process of the mandible and the mandibular fossa of the temporal bone
- separates the TMJ into two joint cavities
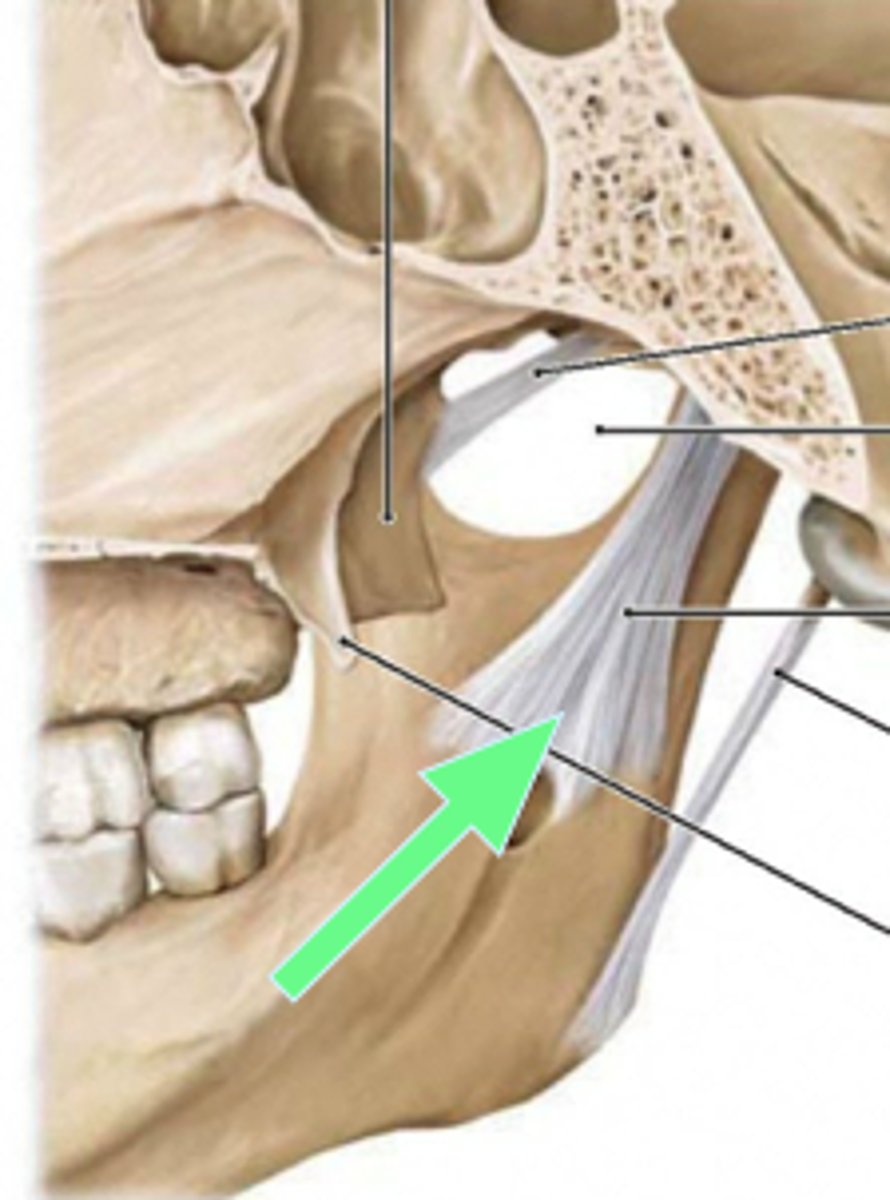
stylomandibular ligament
- ligament running from the styloid process to the angle of the mandible
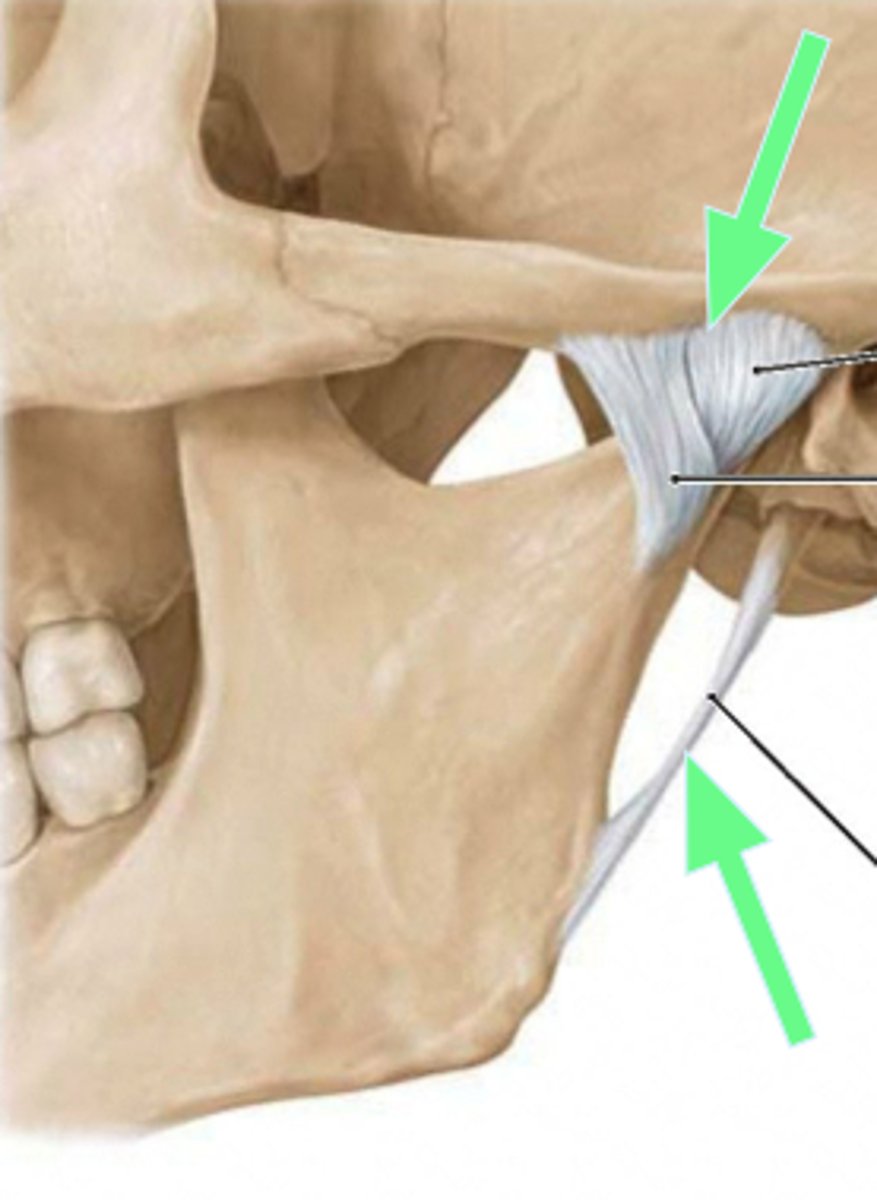
sphenomandibular ligament
ligament running from the sphenoid bone to the ramus of the mandible
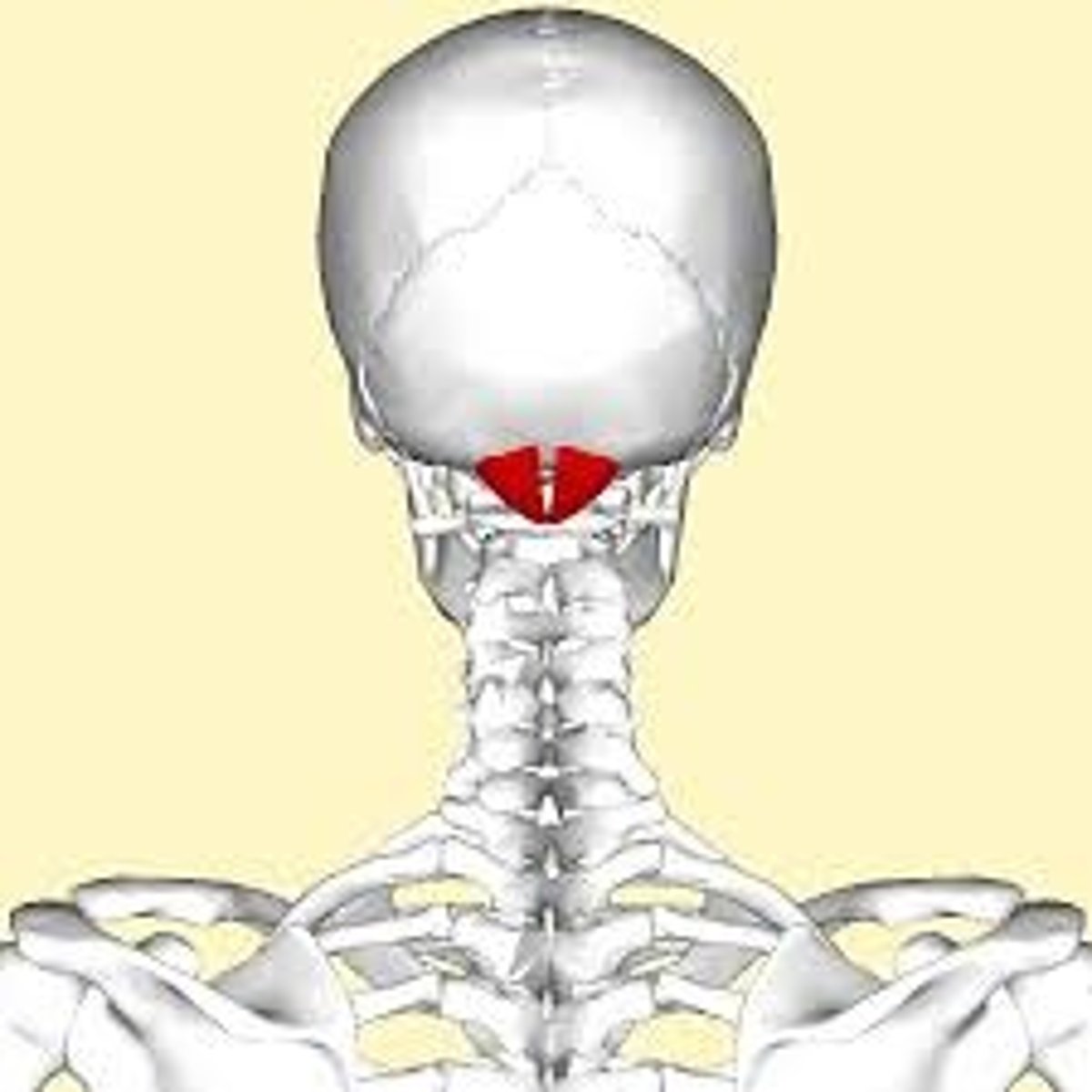
atlanto-occipital joint
- articulates of the atlas (C1) with the occipital condyles of the skull
- condyloid type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the neck (nodding head yes)
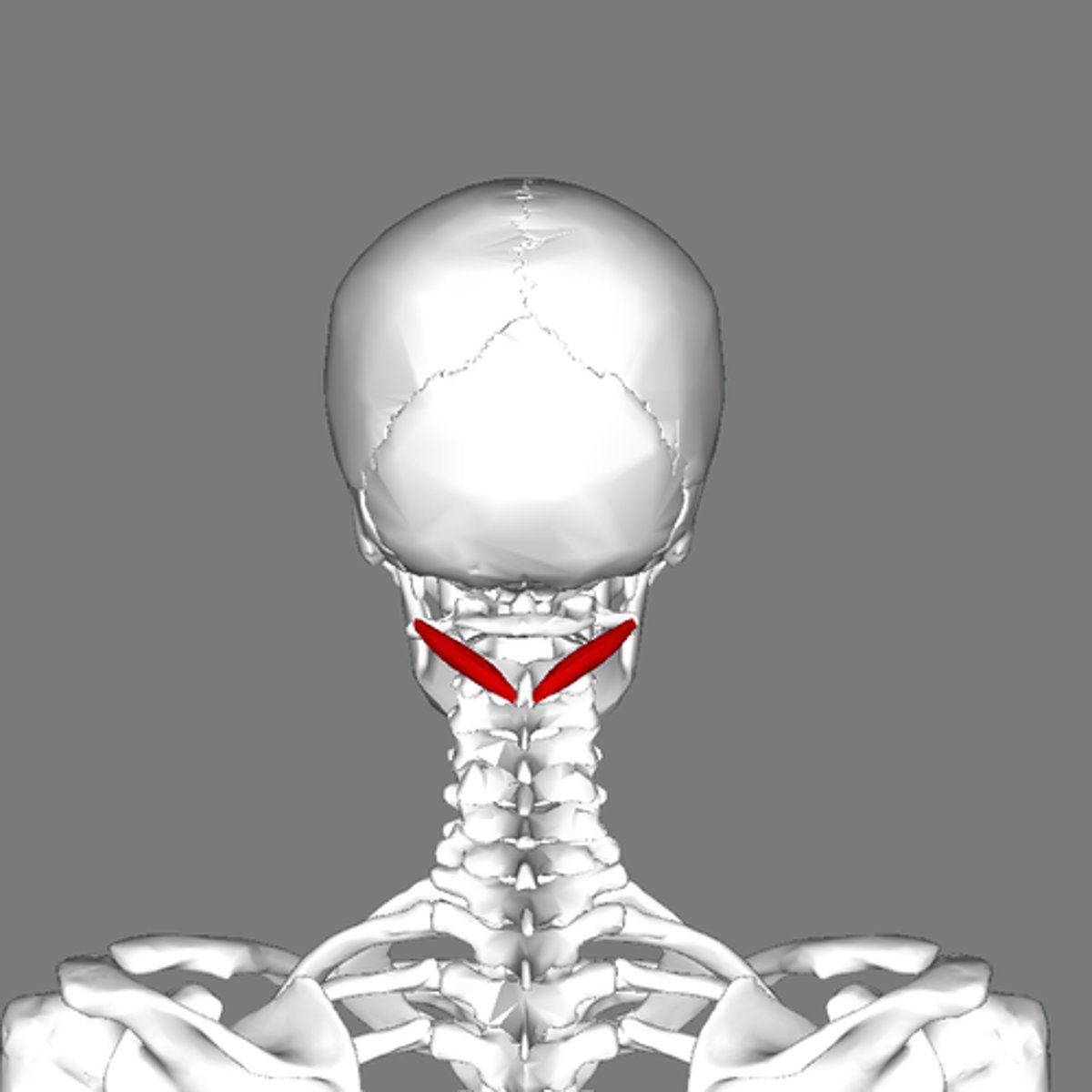
atlanto-axial joint
- articulation of the atlas (C1) with the dens of the axis (C2)
- pivot type of synovial joint
- permits rotation of the neck (turning head no)
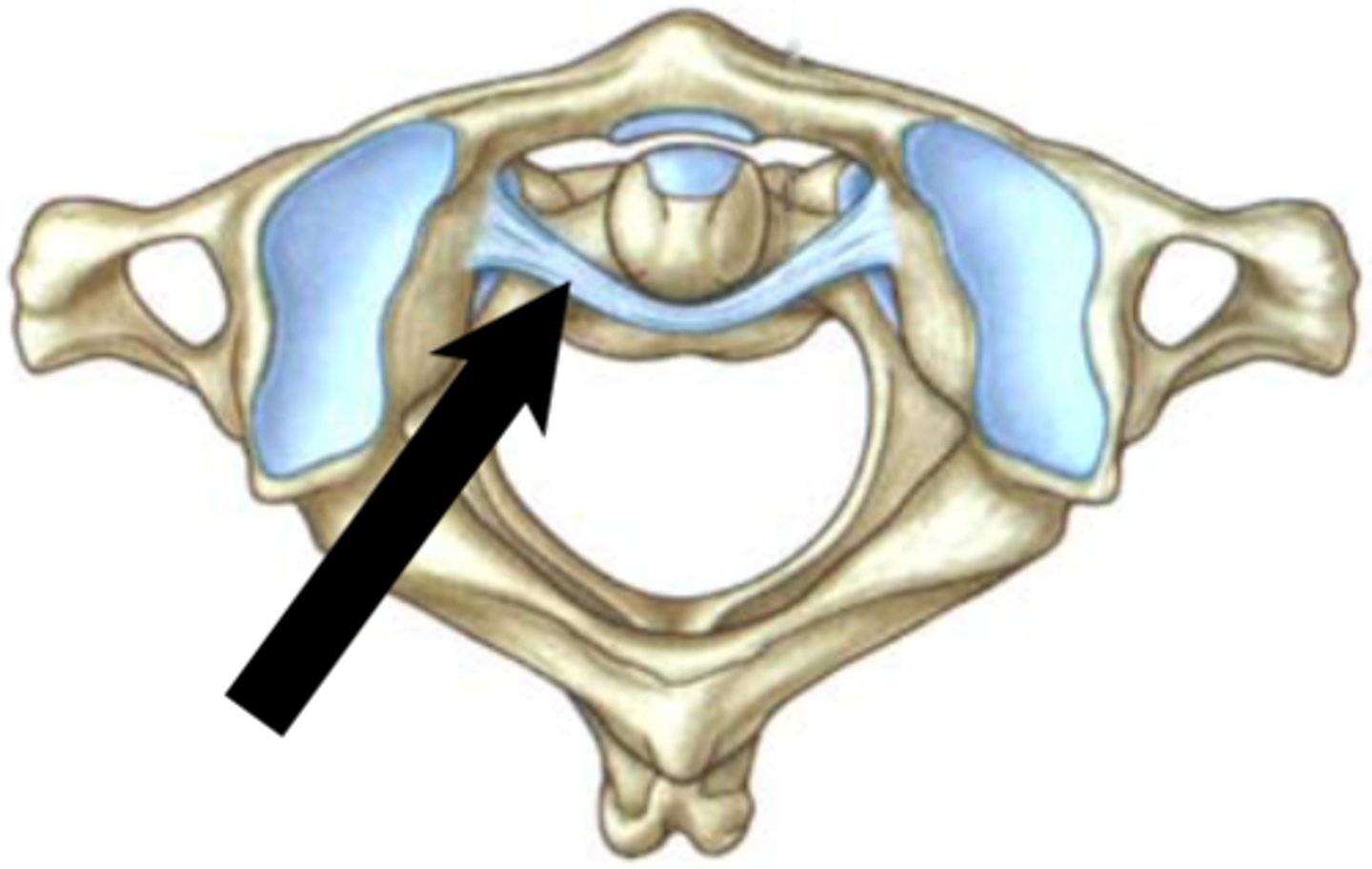
transverse ligament of atlas
- ligament arching across the ring of the atlas along the posterior aspect of the dens
- holds the dens in place against the atlas
supraspinous ligament
- ligament running along the tips of adjacent spinous processes
- rope-like ligament along the vertebral column
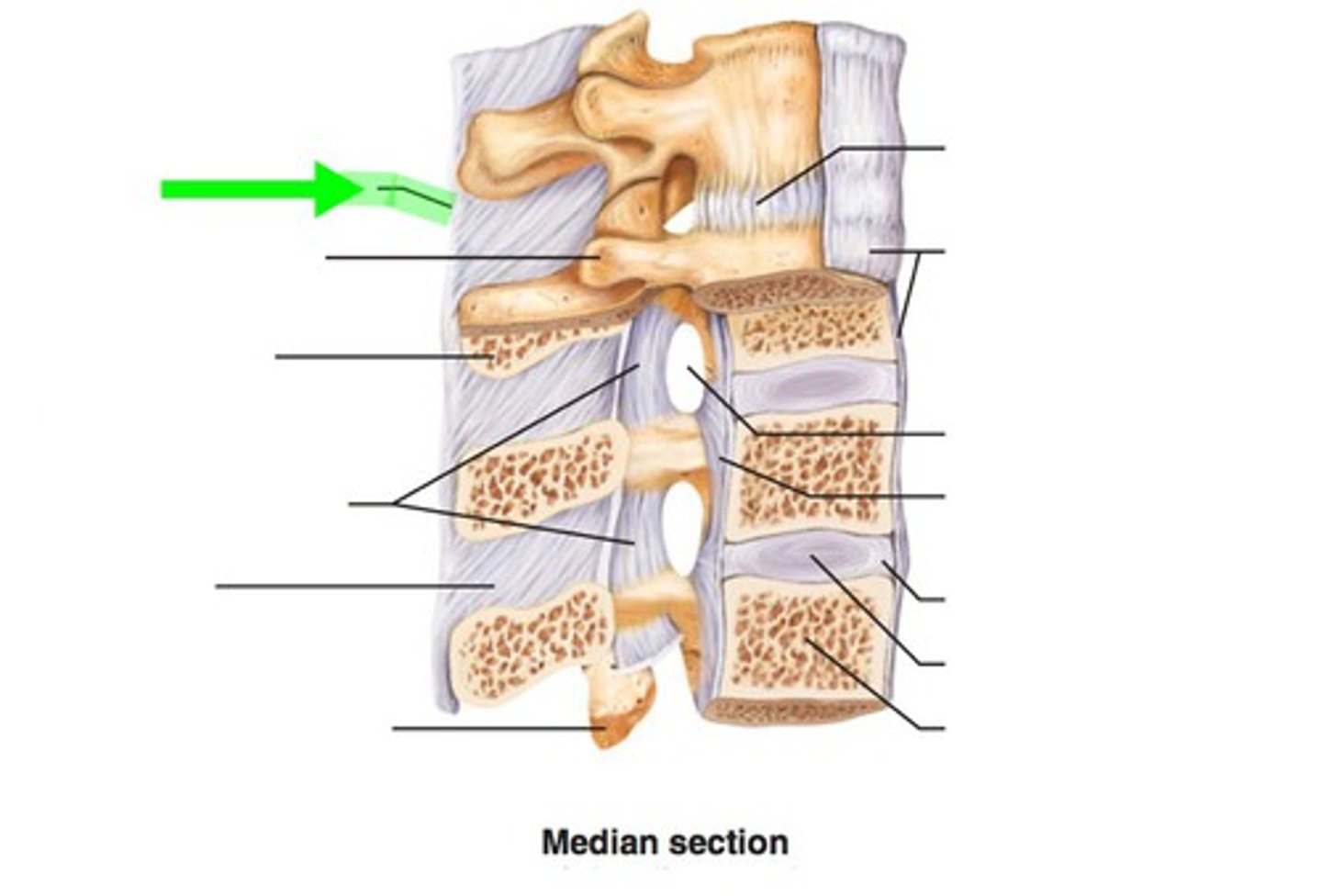
ligamentum flavum
- ligament running from the lamina of one vertebrae to the lamina of an adjacent vertebrae
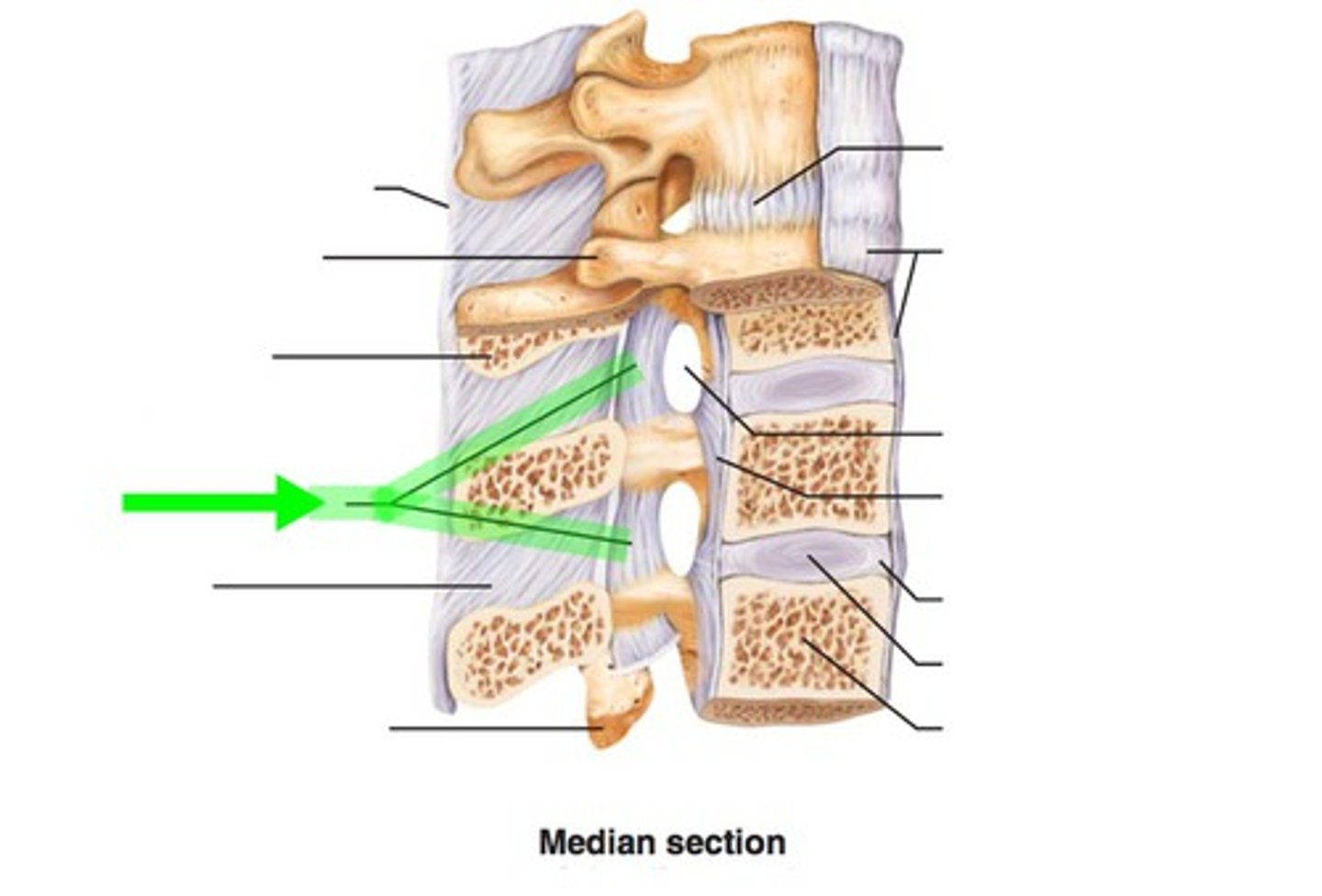
posterior longitudinal ligament
- ligament running vertically along the posterior aspect of the vertebral bodies
- runs all the way down the vertebral column INSIDE the vertebral canal
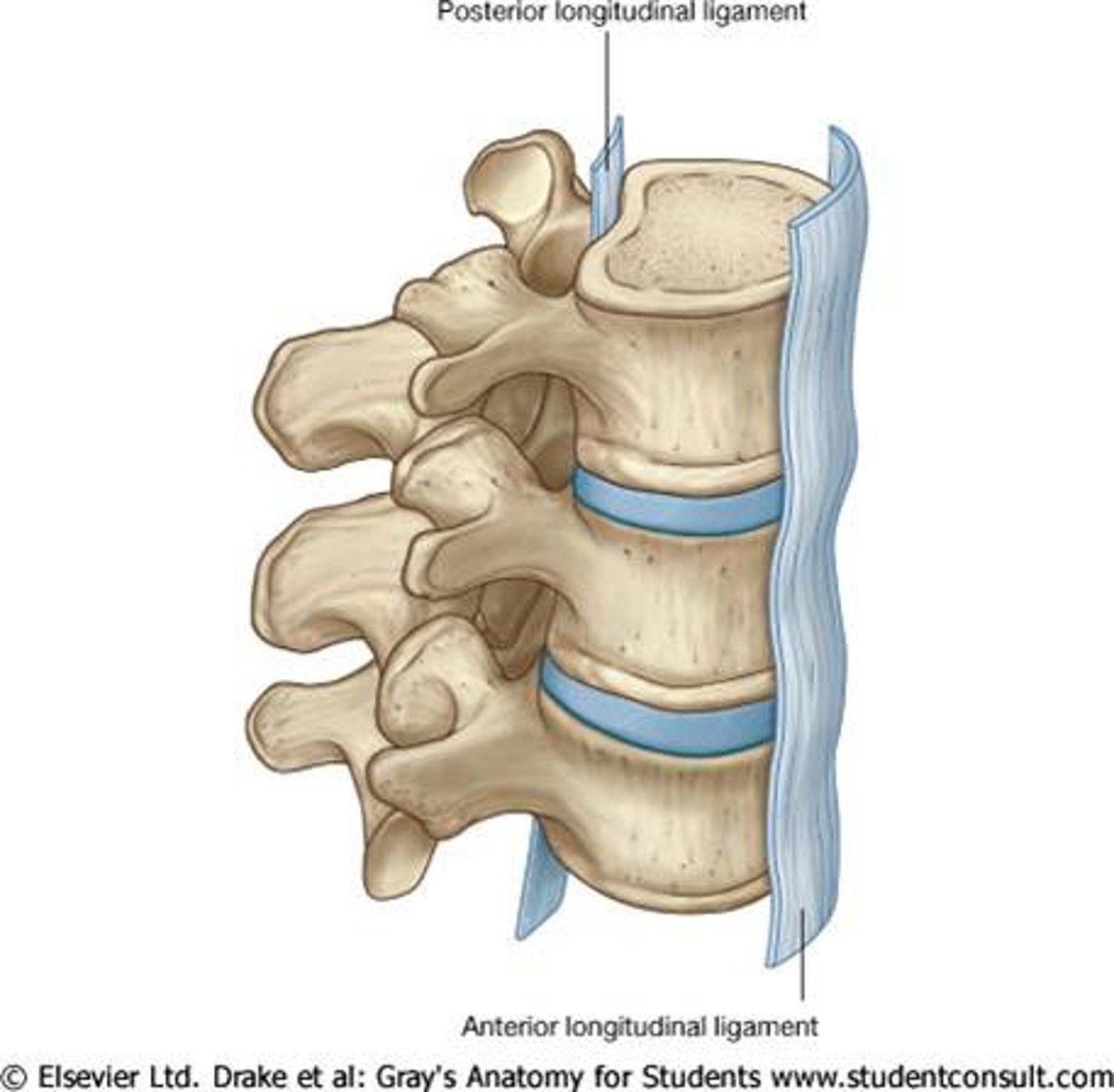
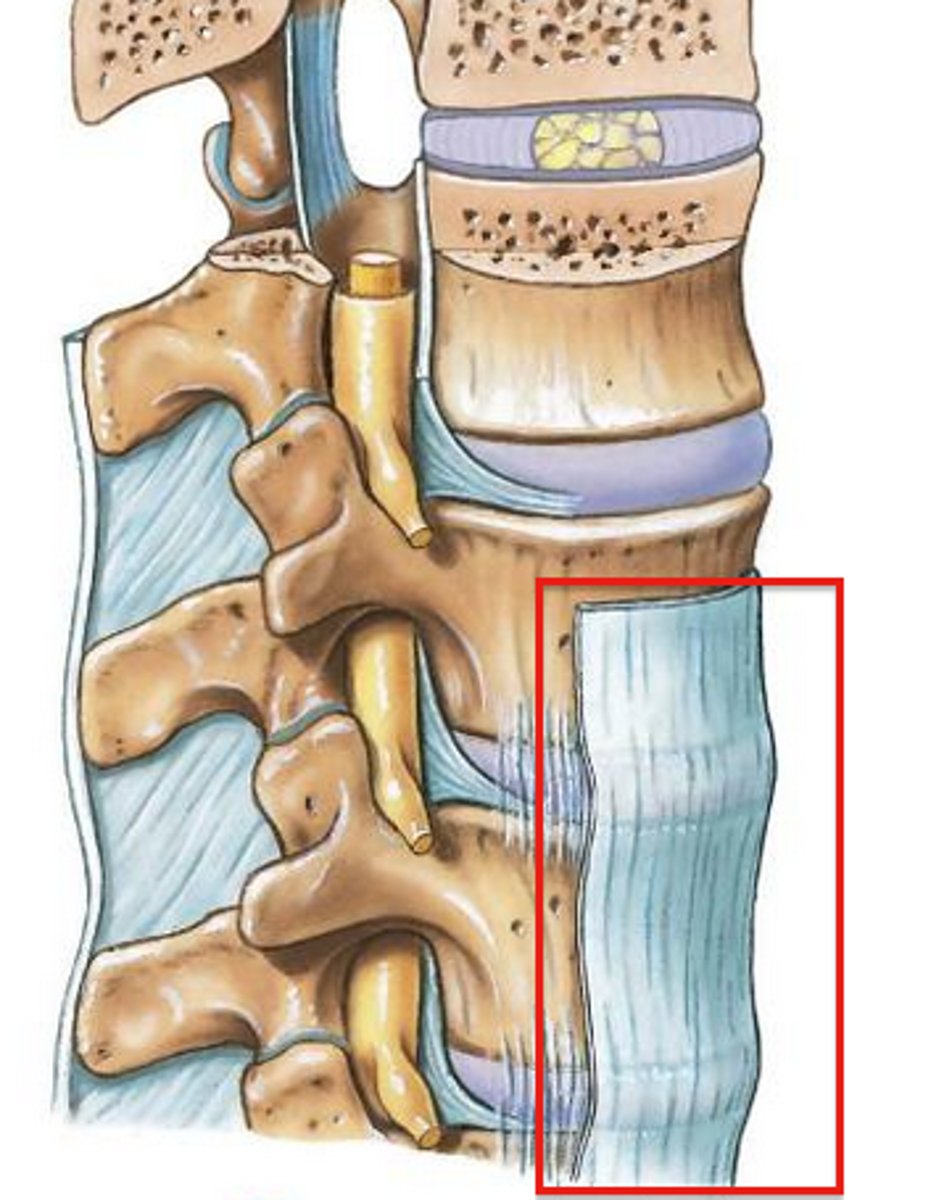
anterior longitudinal ligament
- ligament running vertically along the posterior aspect of the vertebral bodies
- runs all the way down the vertebral column OUTSIDE of the vertebral canal
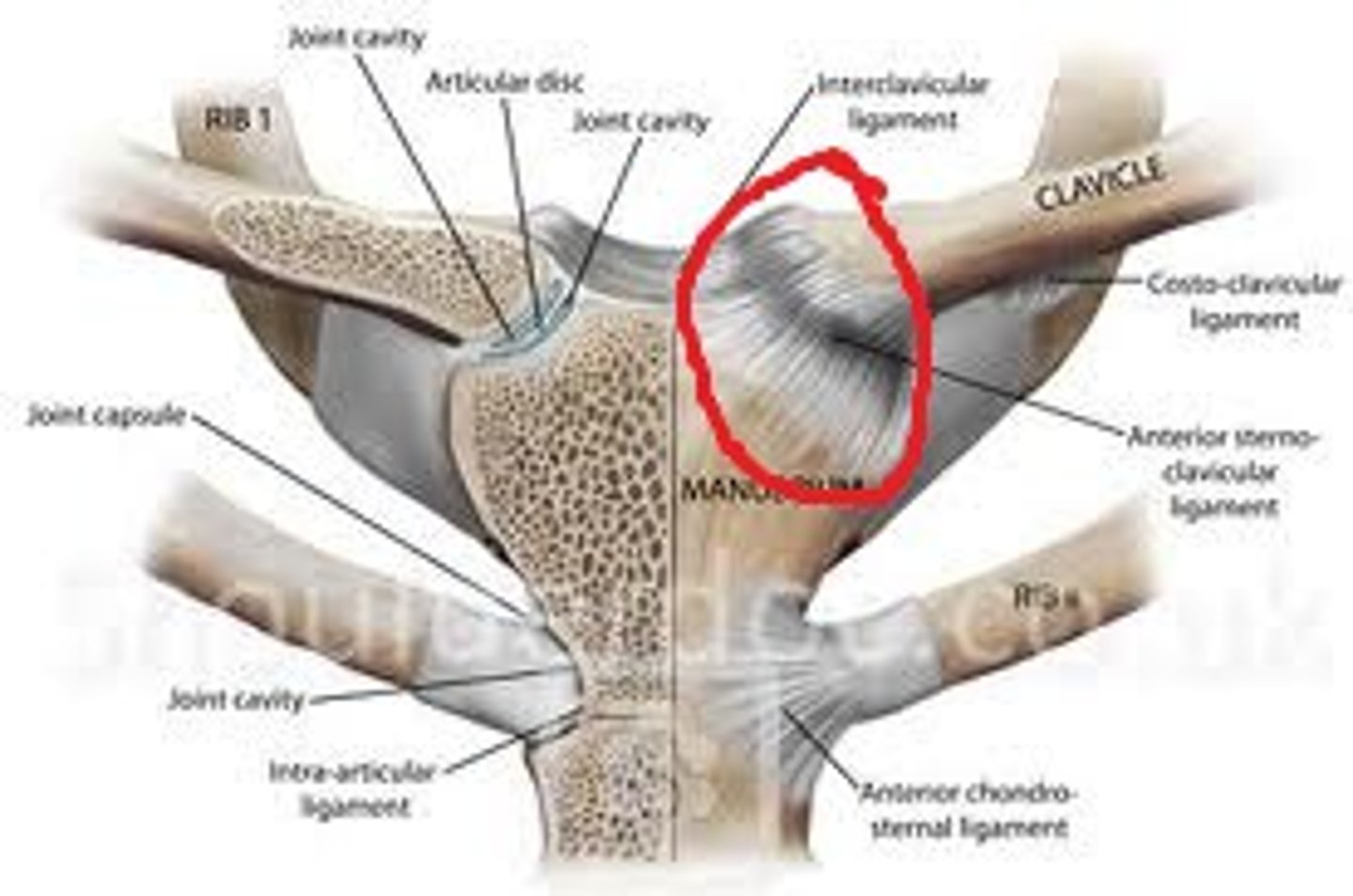
sternoclavicular joint
- articulation of the medial end of the clavicle with the manubrium (clavicular notch) of the sternum
- saddle type of synovial joint
- helps of permit elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, and upward/downward rotation of the scapula
glenohumeral joint
- articulation of the head of the humerus with the glenoid cavity of the scapula
- ball-and-socket type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and internal/external rotation of the shoulder
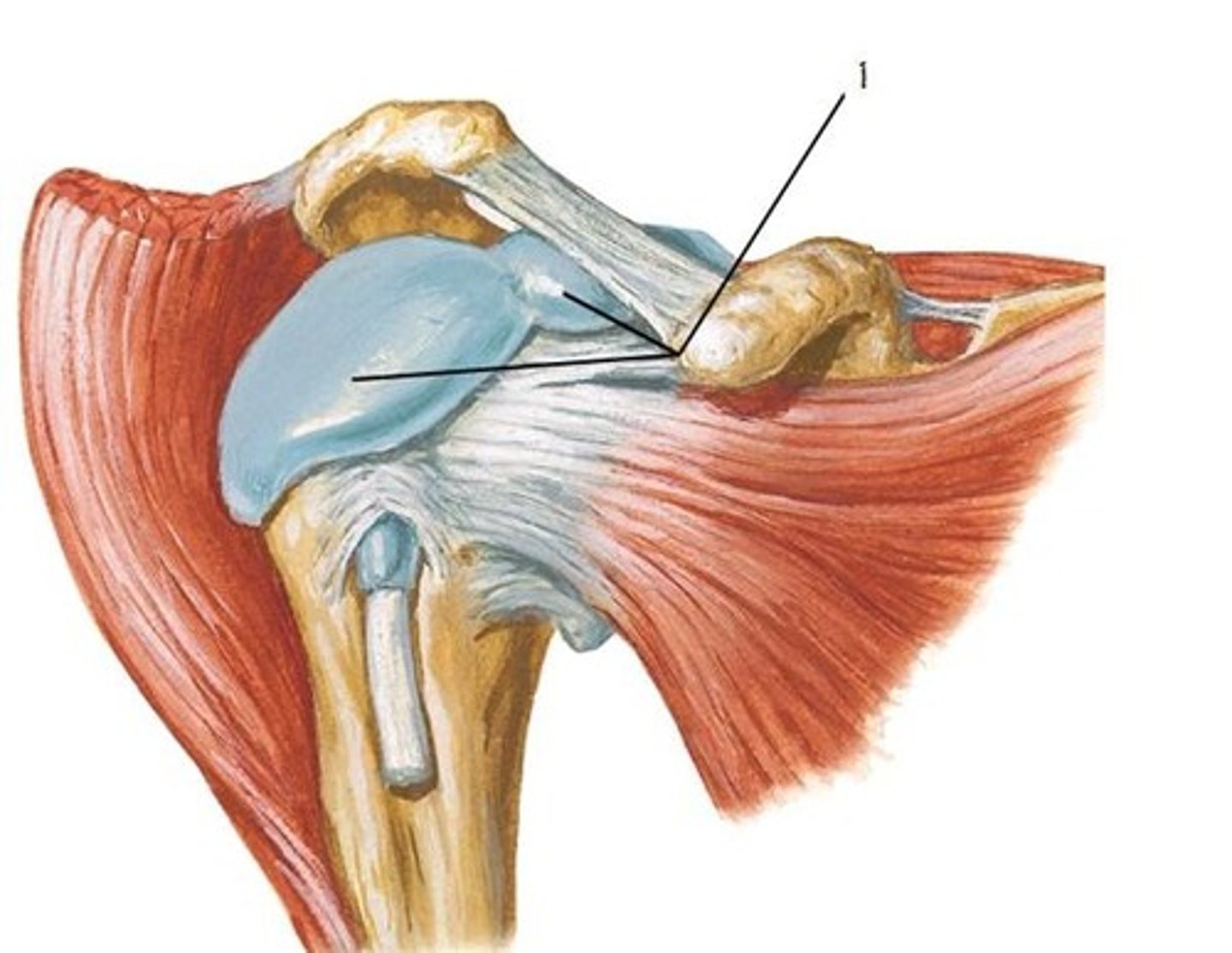
subacromial bursa
- located inferior to the acromion, coracoacromial ligament, and deltoid muscle, and superior to the glenohumeral joint capsule
- below (sub-) the deltoid
- a bursa is a sac-like cavity containing synovial fluid located in areas of friction to prevent abrasion
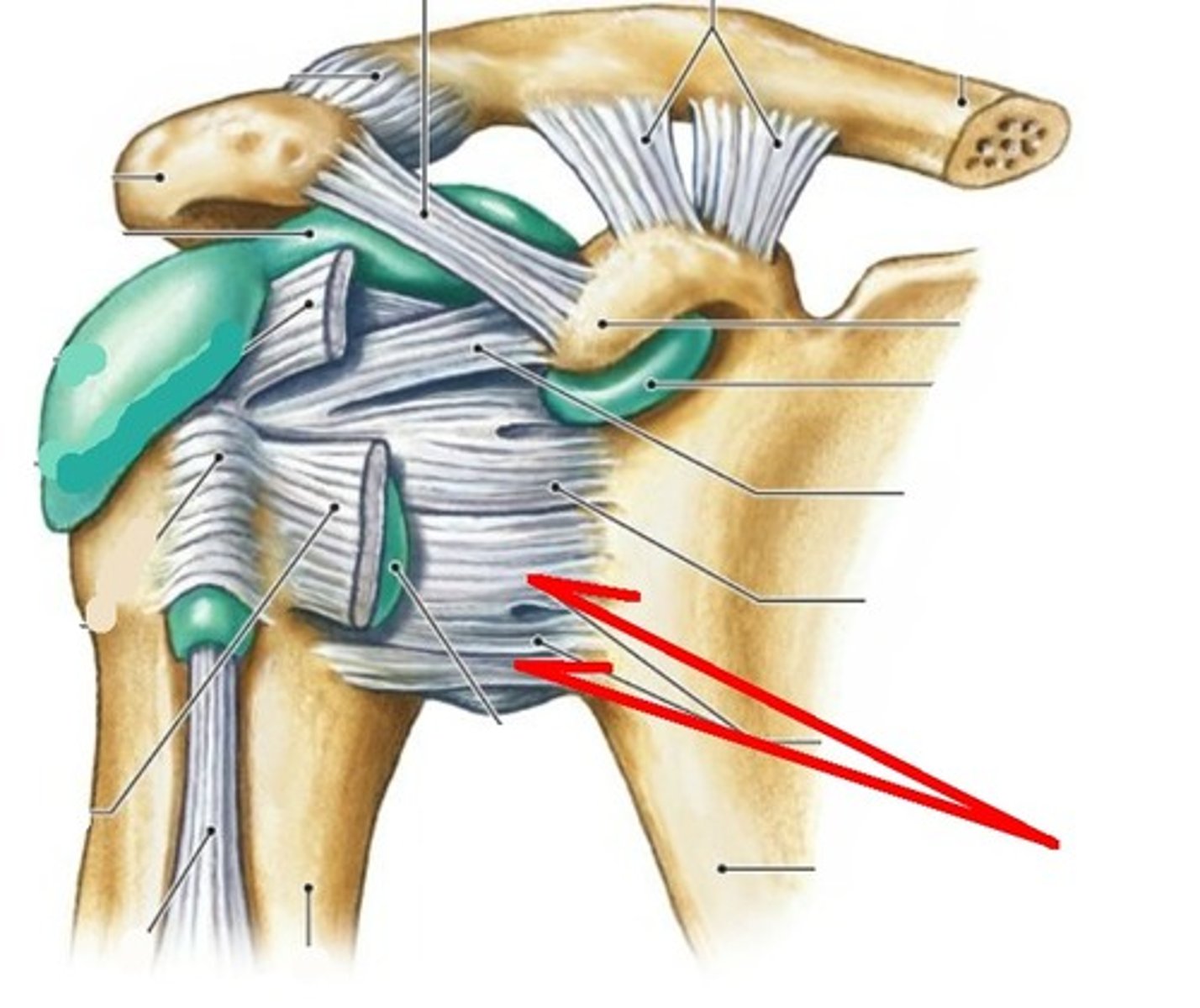
glenohumeral ligament
- ligament running from the glenoid vanity of the scapula to the head of the humerus
- has a superior, middle, and inferior part that blend with the genoid labrum
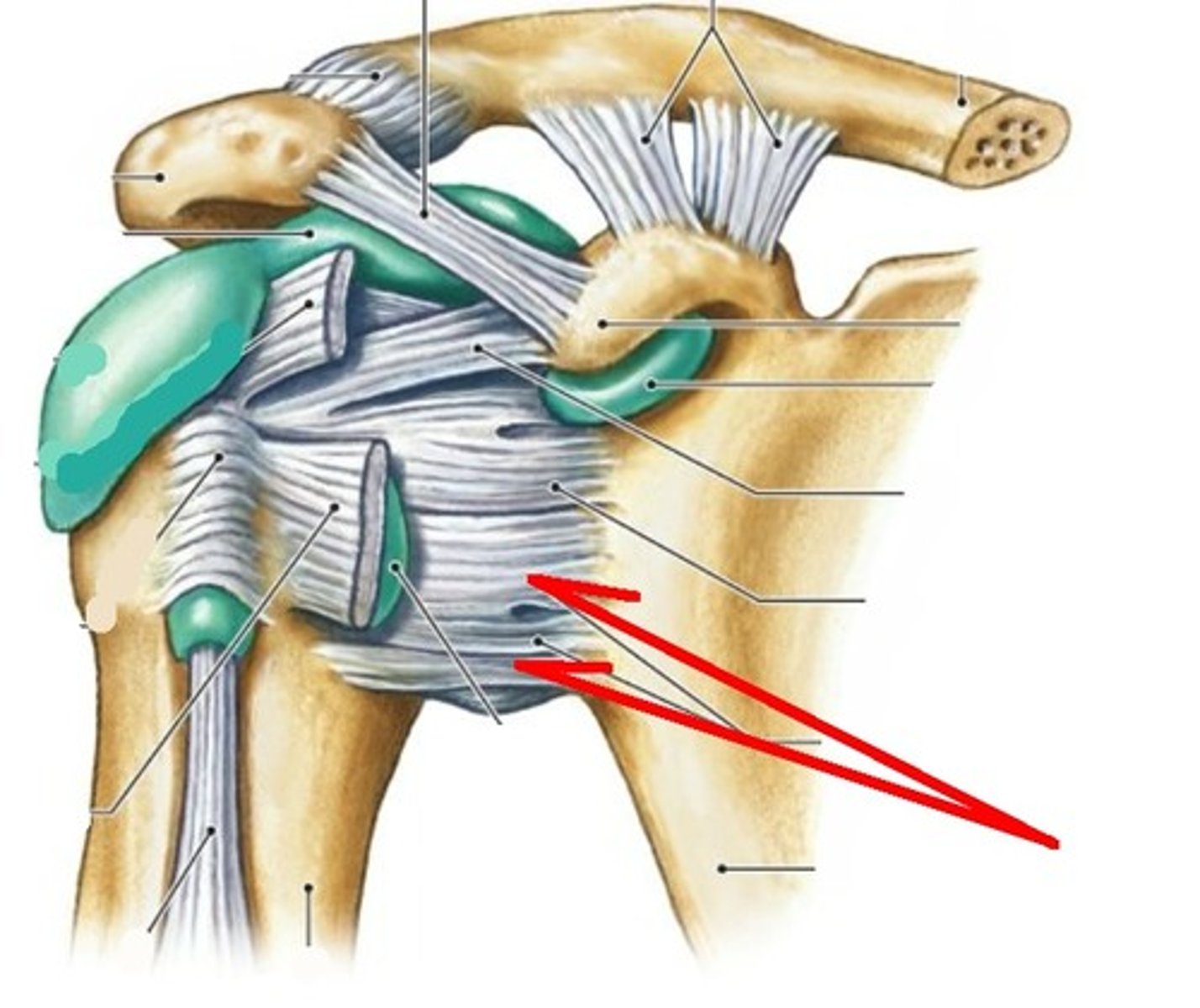
coracohumeral ligament
- ligament running from the coracoid process of the scapula to the greater tubercle of the humerus
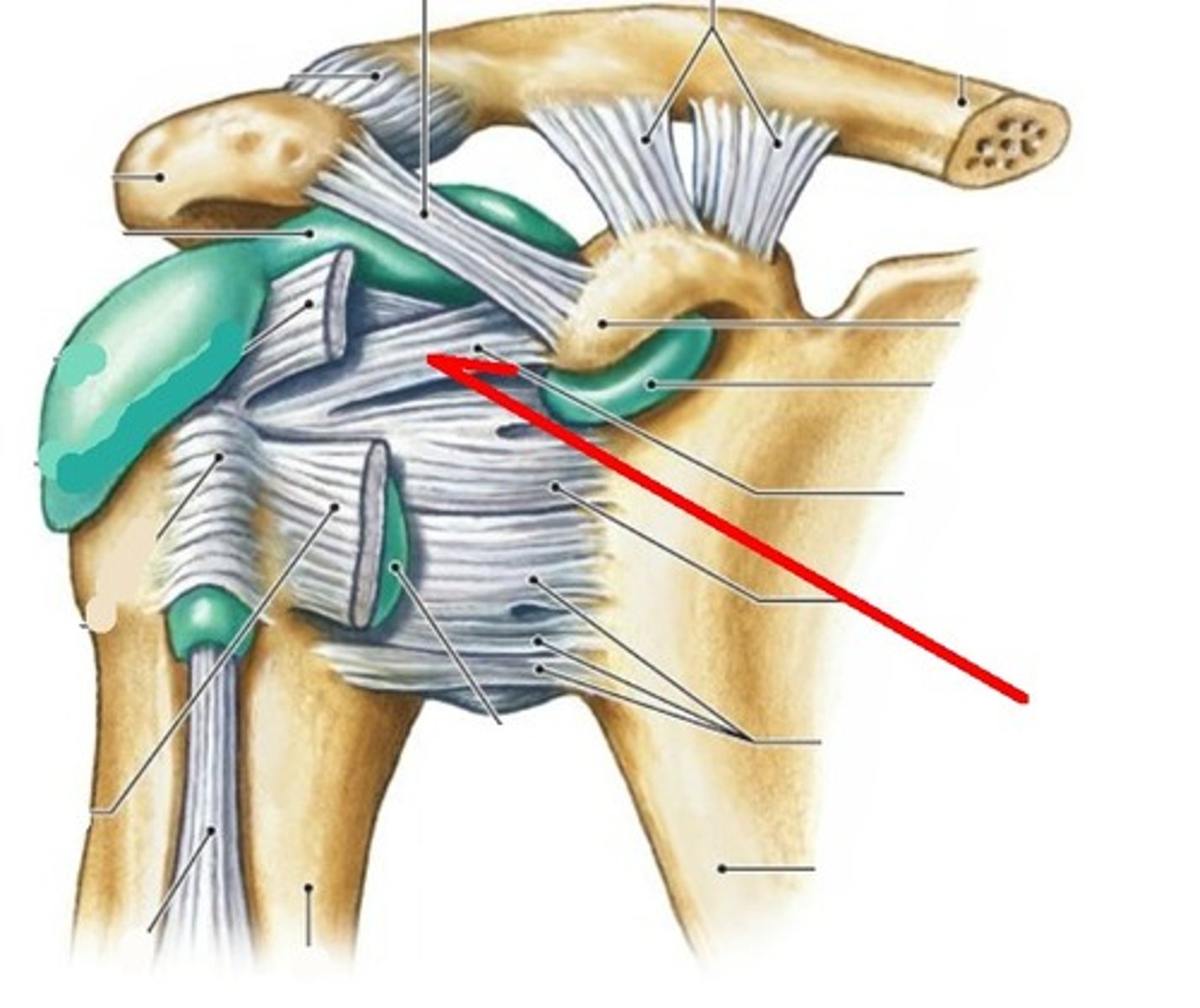
coracoacromial ligament
- ligament running from the coracoid process to the acromium of the scapula
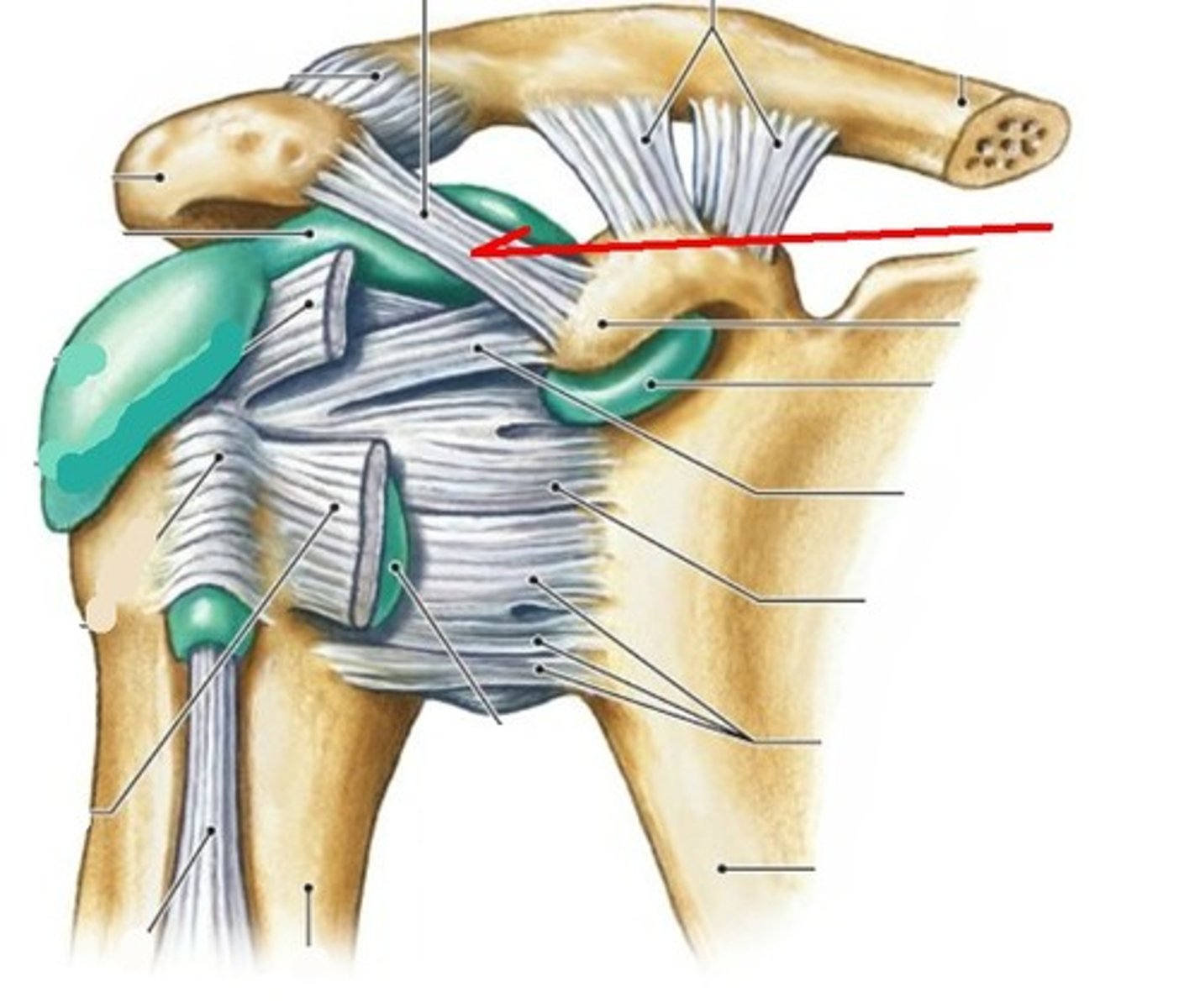
transverse humeral ligament
- ligament running from the greater to the lesser tubercle of the humerus
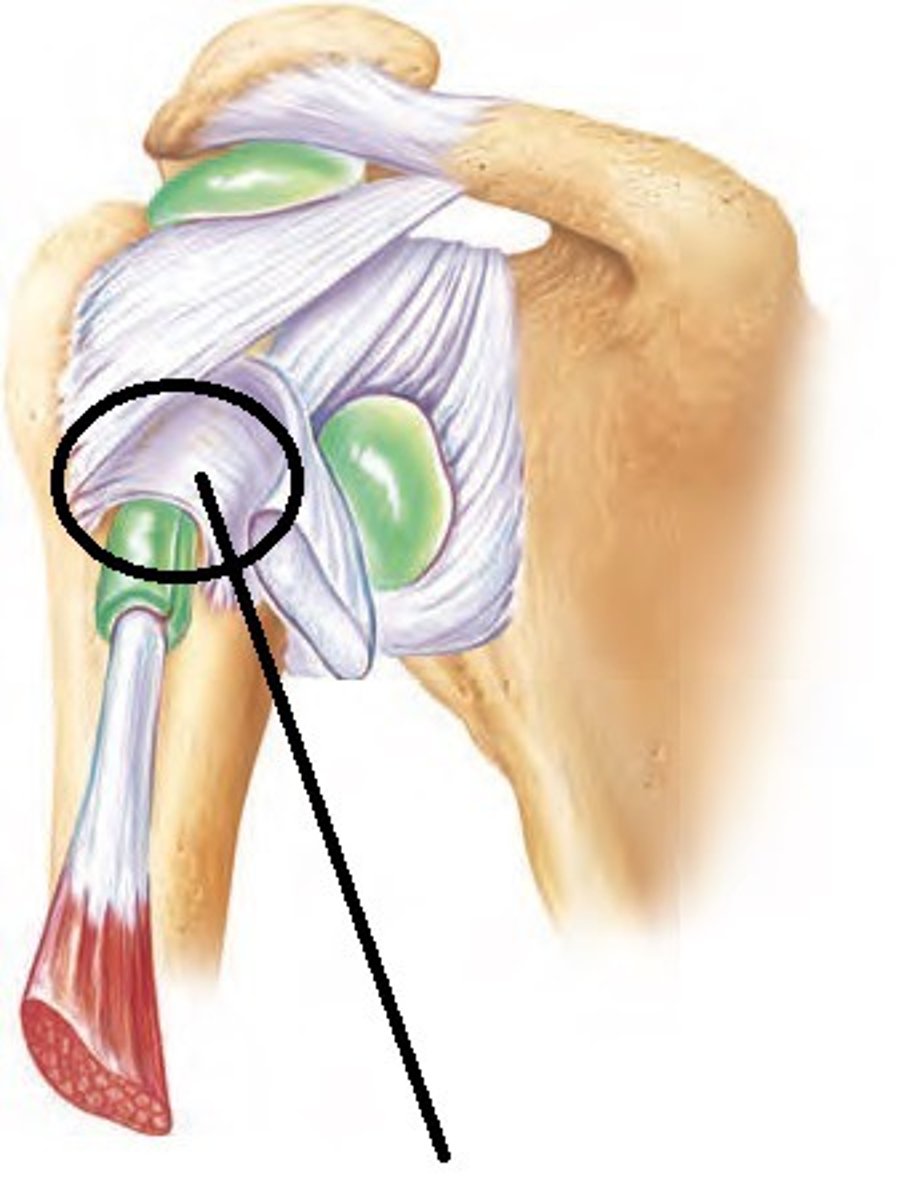
acromioclavicular joint
- articulation of the acromial end of the clavicle with the acrimony of the scapula
- plane type of synovial joint
- helps to permit elevation/depression, protraction/retraction, and upward/downward rotation of the scapula
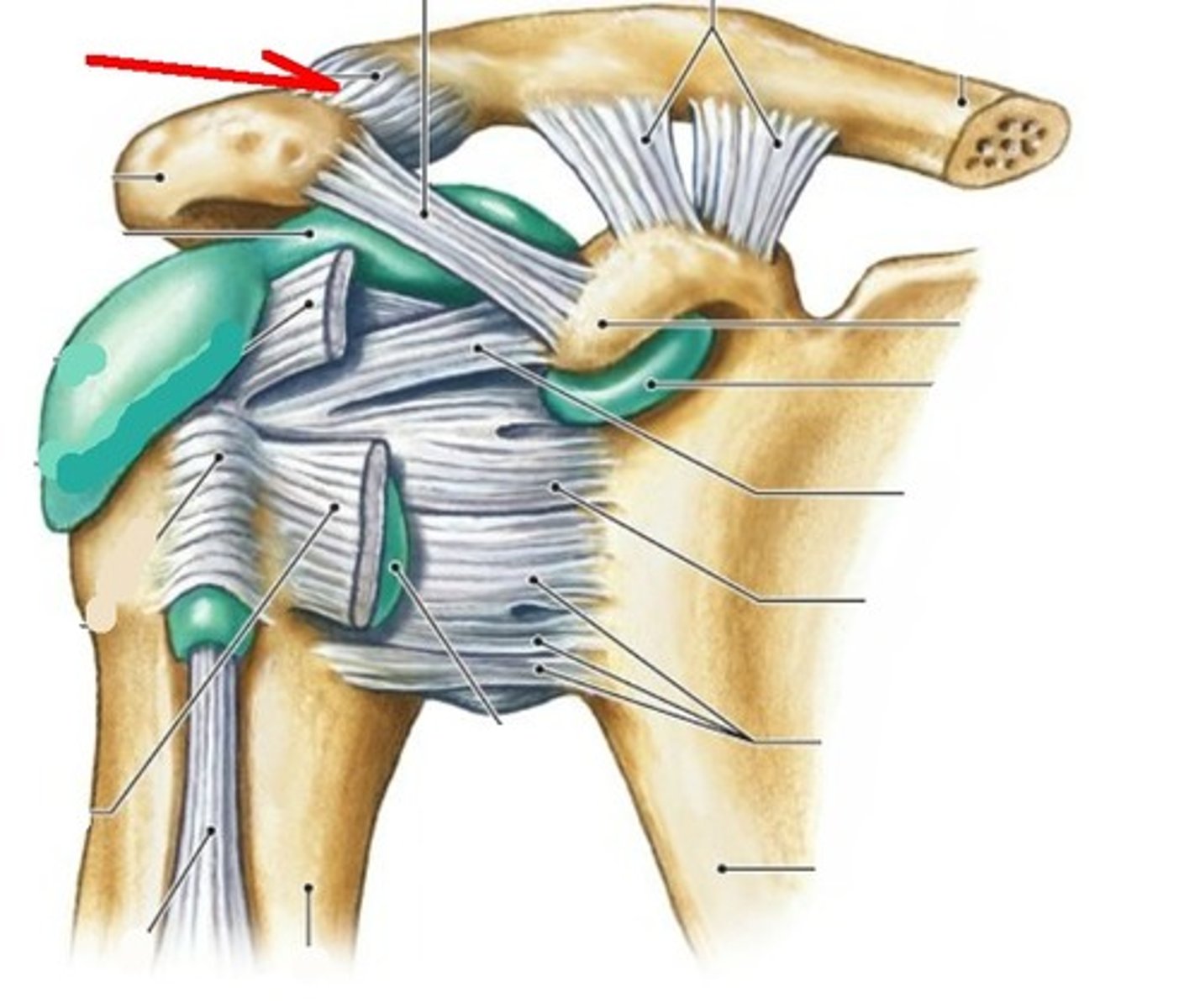
acromioclavicular ligament
- ligament running from the acromion of the scapular to the lateral end of the clavicle
- dislocation of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is known as "shoulder separation"
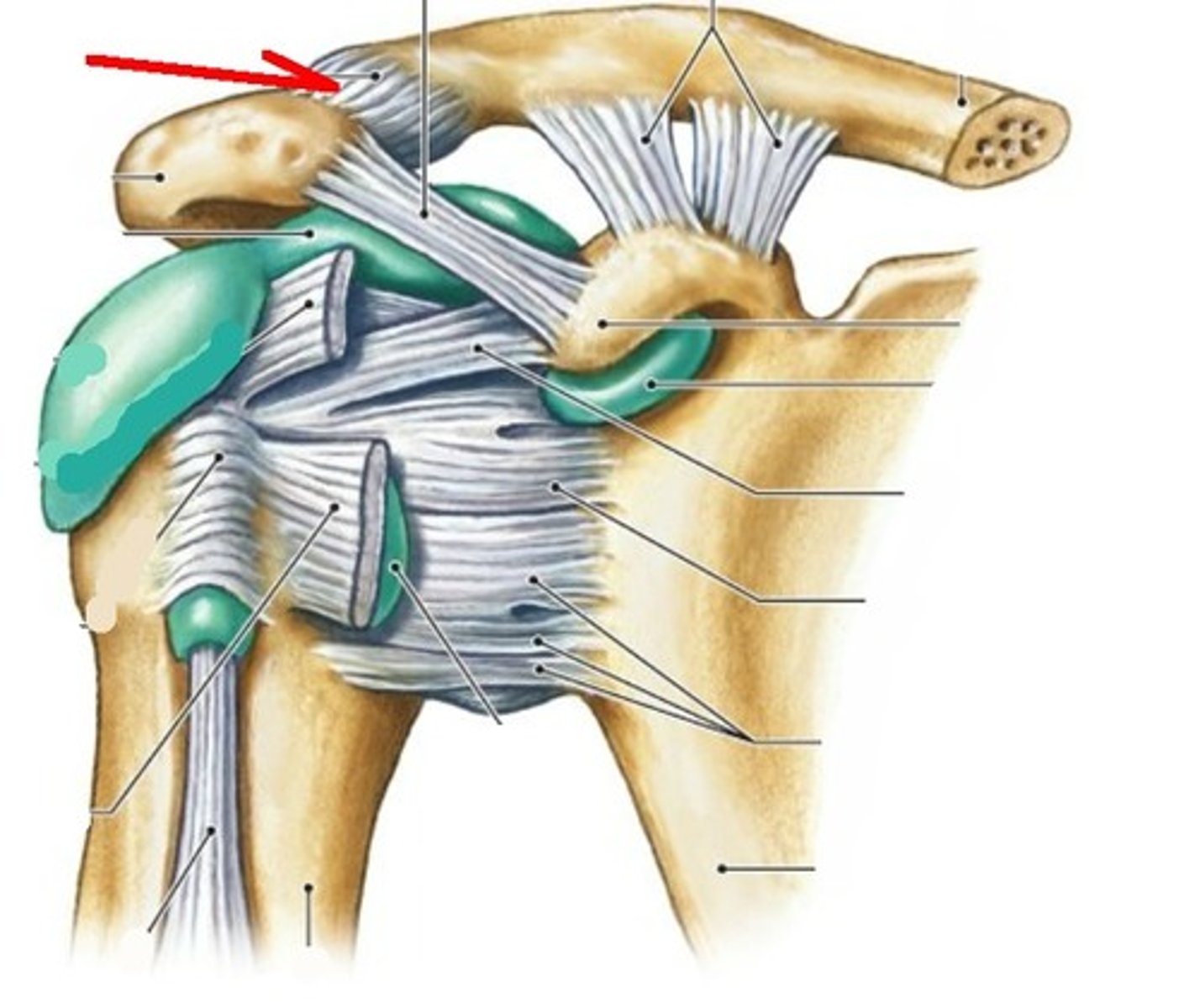
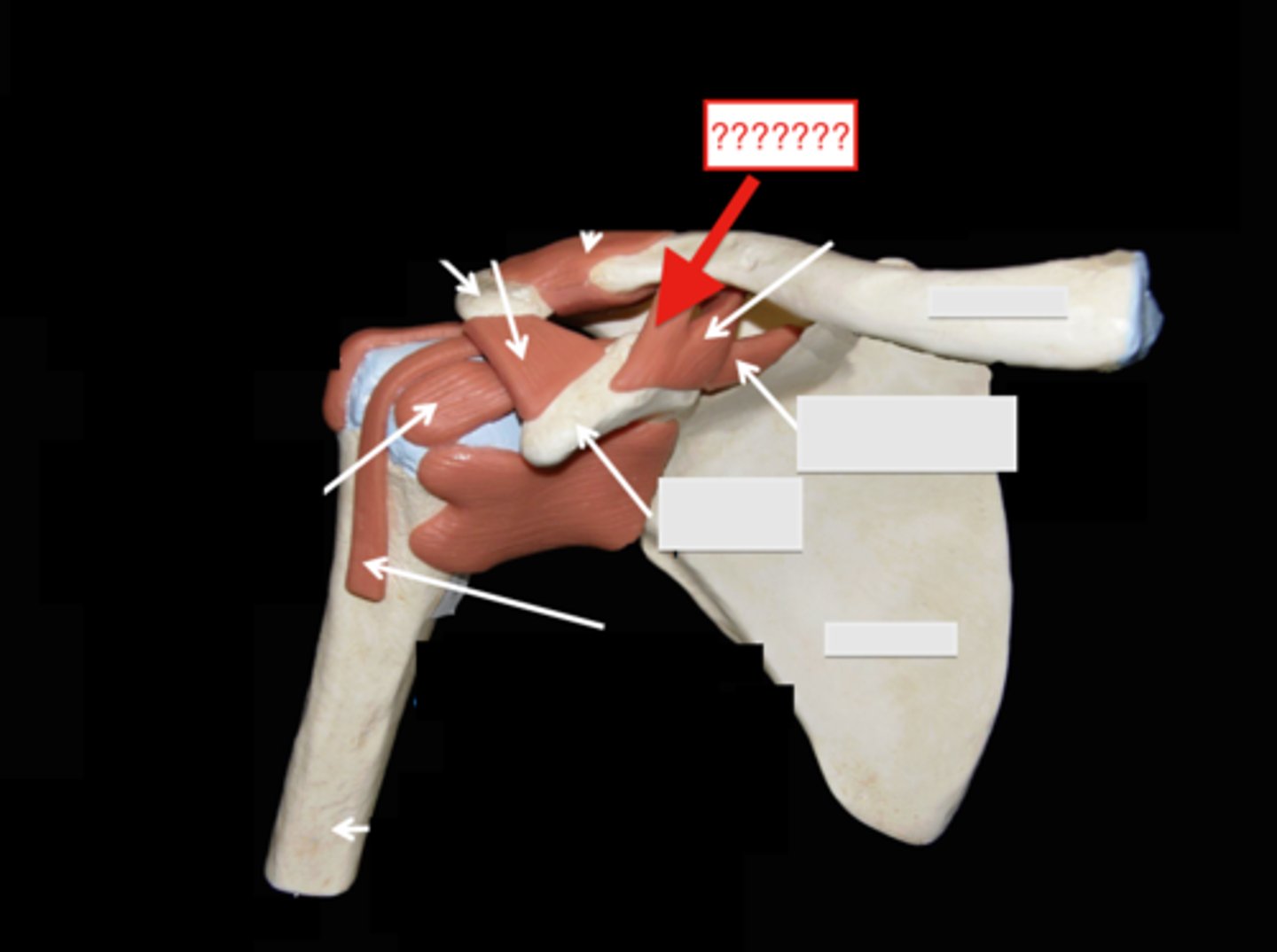
conoid ligament
- ligament running from the coracoid process of the scapula to the conoid tubercle of the clavicle
- one of the two ligaments that makes up the coracoclavicular ligament
- medial to the trapezoid ligament
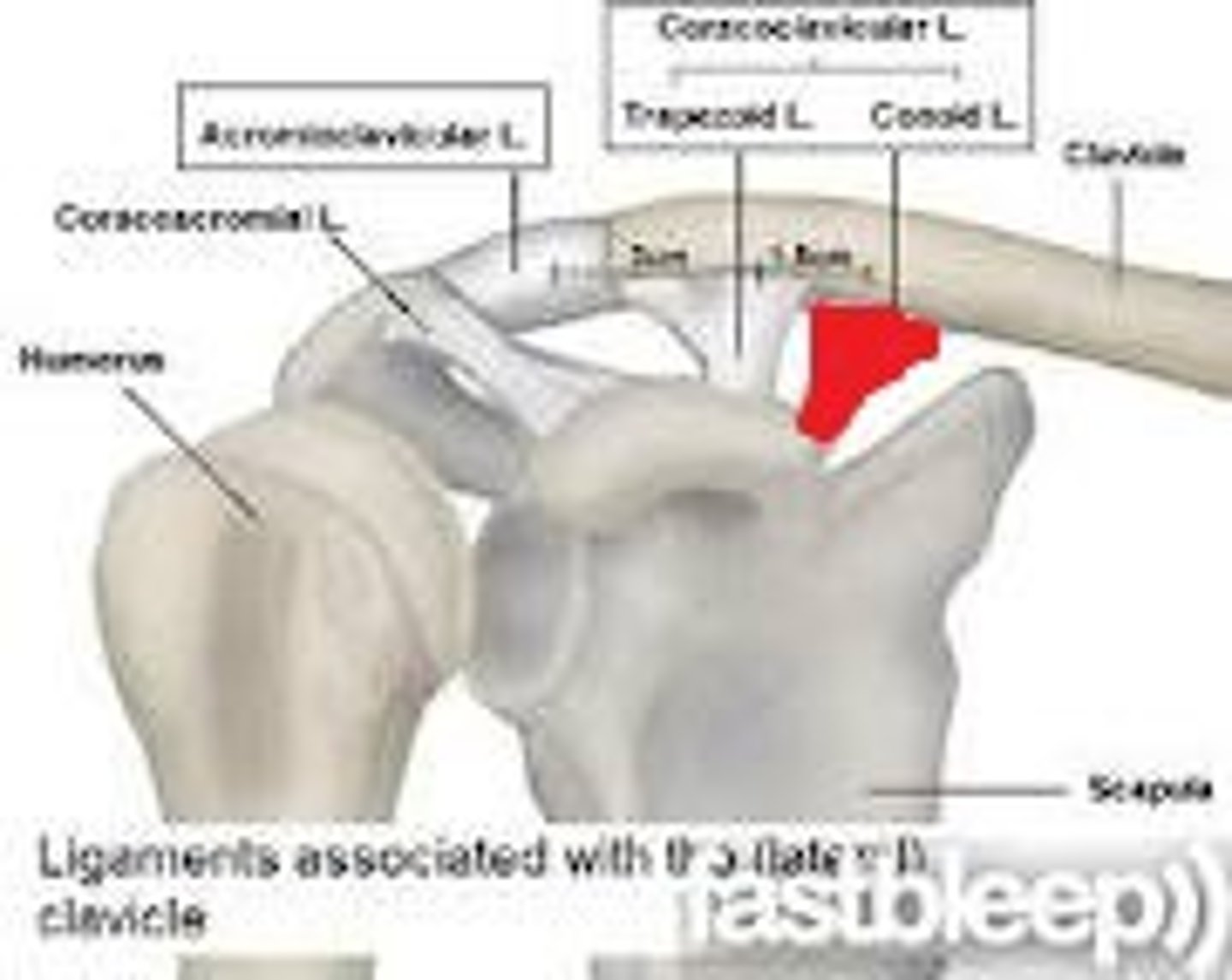
trapezoid ligament
- ligament running from the coracoid process of the scapula to the inferior surface of the clavicle
- one of the two ligaments that make. up the coracoclavicular ligament
- lateral to the conoid ligament
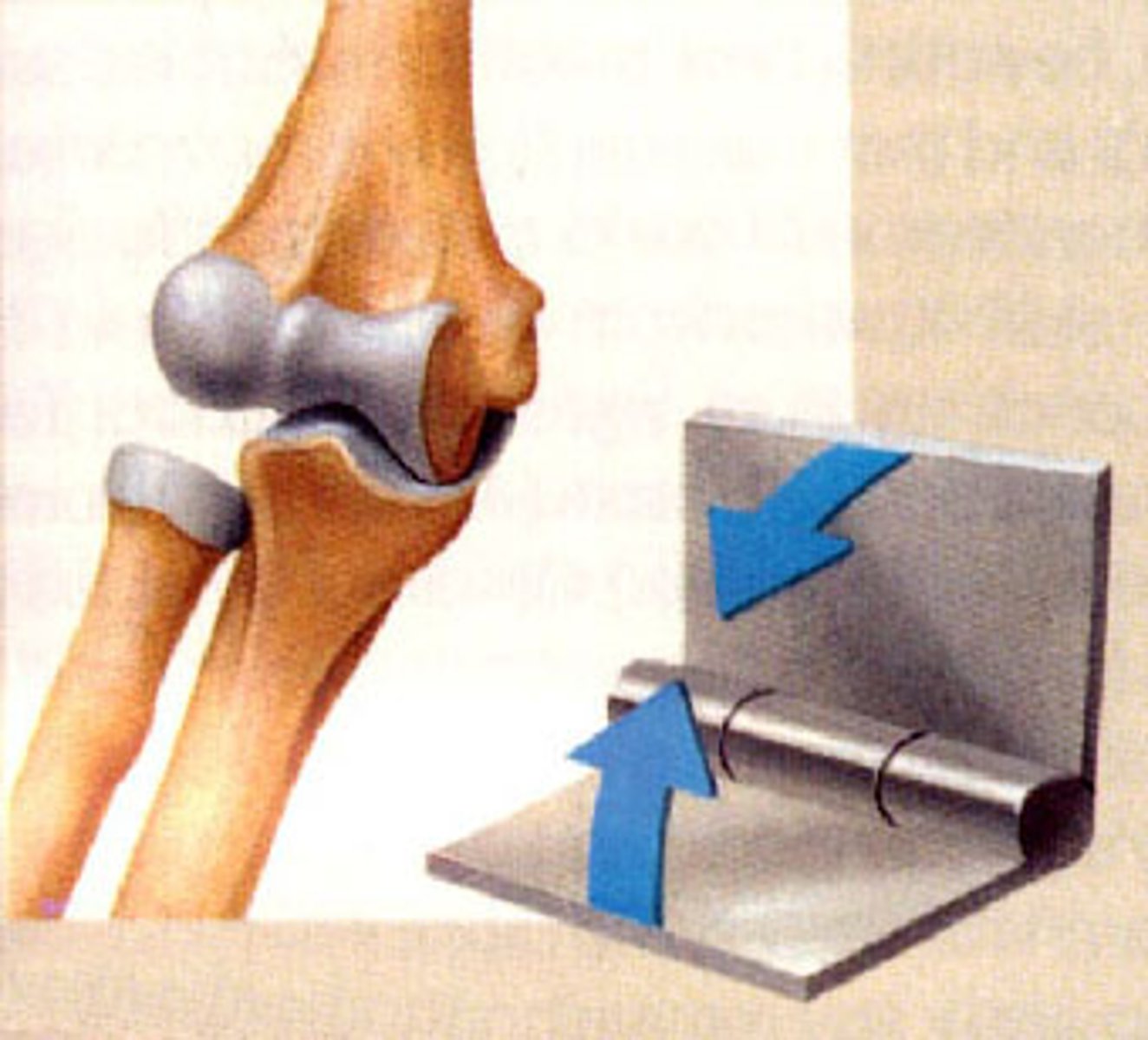
elbow joint
- articulations of the trochlea of the humerus with he trochlear notch, and the capitulum of the humerus with the head of the radius
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the elbow
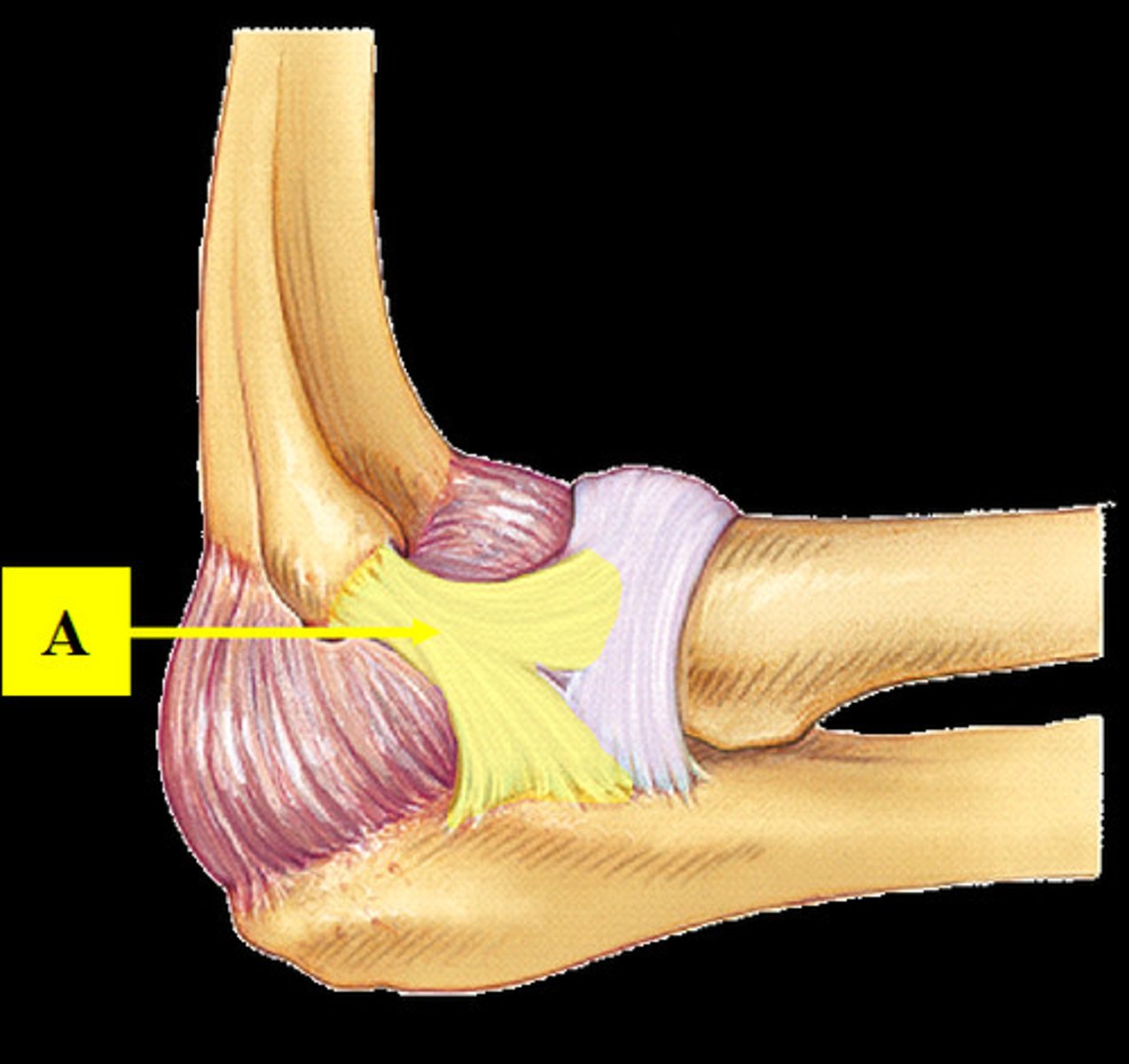
ulnar collateral ligament of elbow
- ligament running from the medical epicondyle of the humerus to the coronoid process and olecranon of the ulna
- broad, triangular ligamentous band on the medial side of the elbow
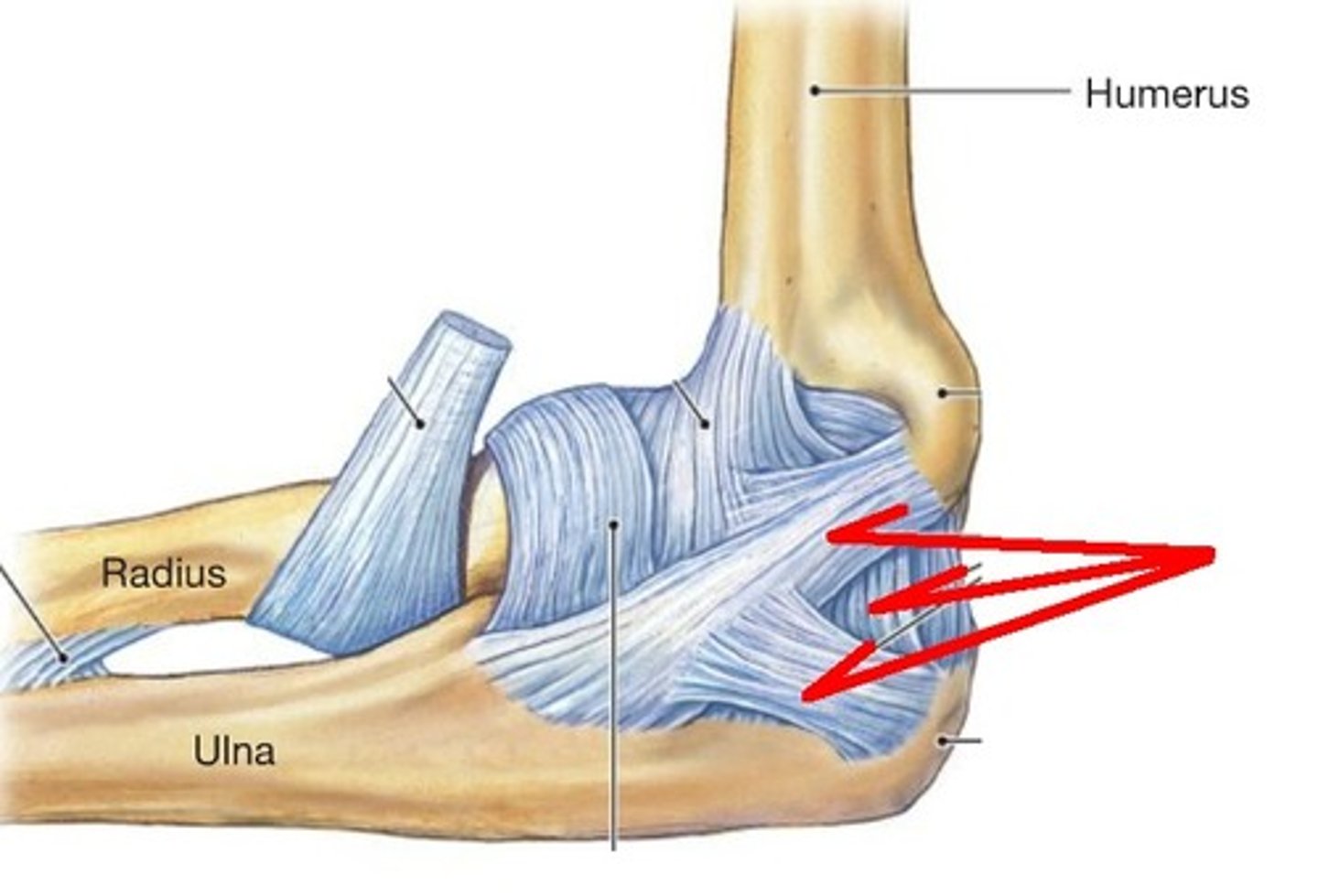
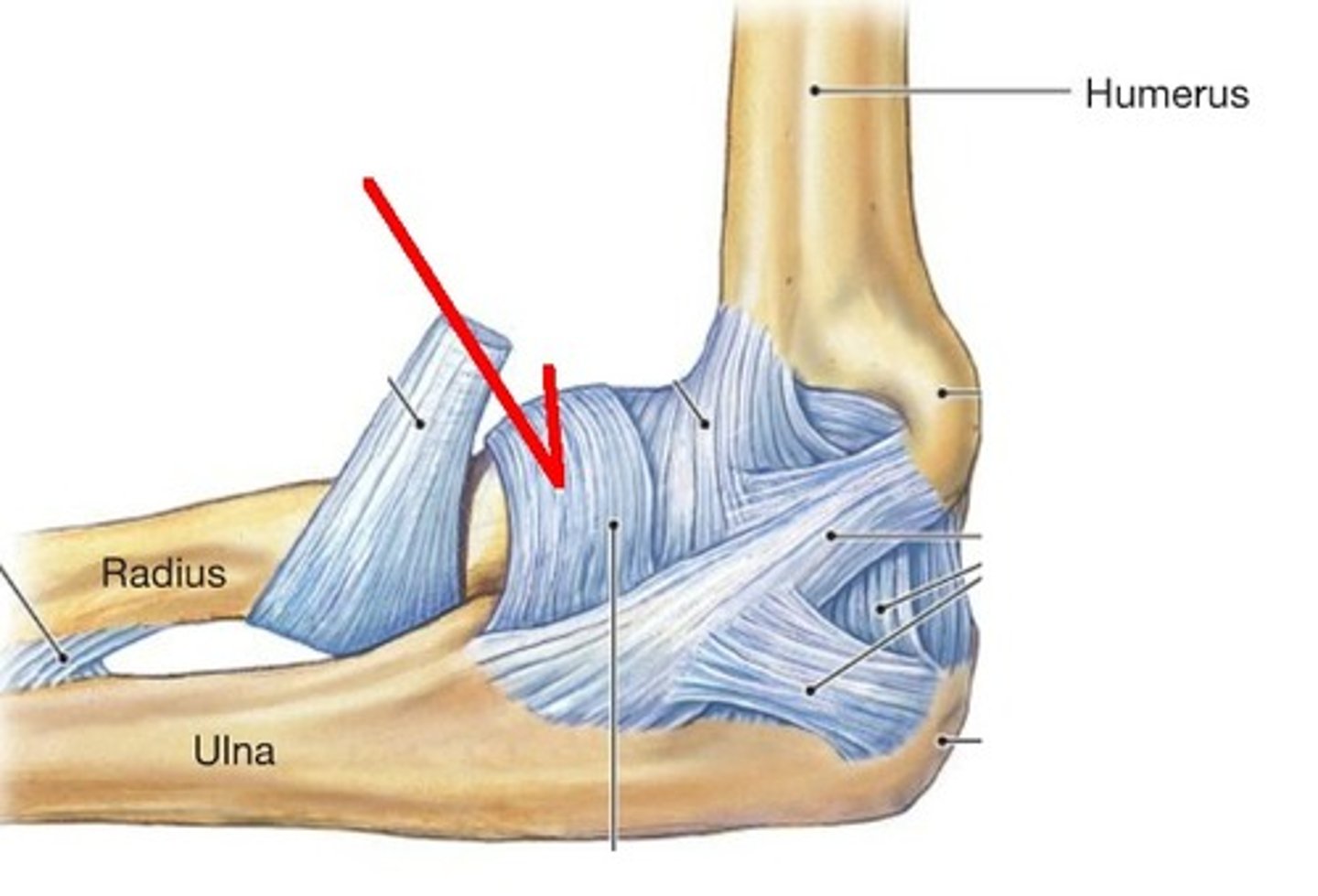
radial collateral ligament of elbow
- ligament running from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus to the annular ligament of the radius
- broad, triangular ligamentous band on the lateral side of the elbow
annular ligament
- ligament running from the anterior to posterior aspect of ulna surrounding the head of the radius
- encircles the head of the radius like a "sling" to hold the radius in the radial notch of the ulna
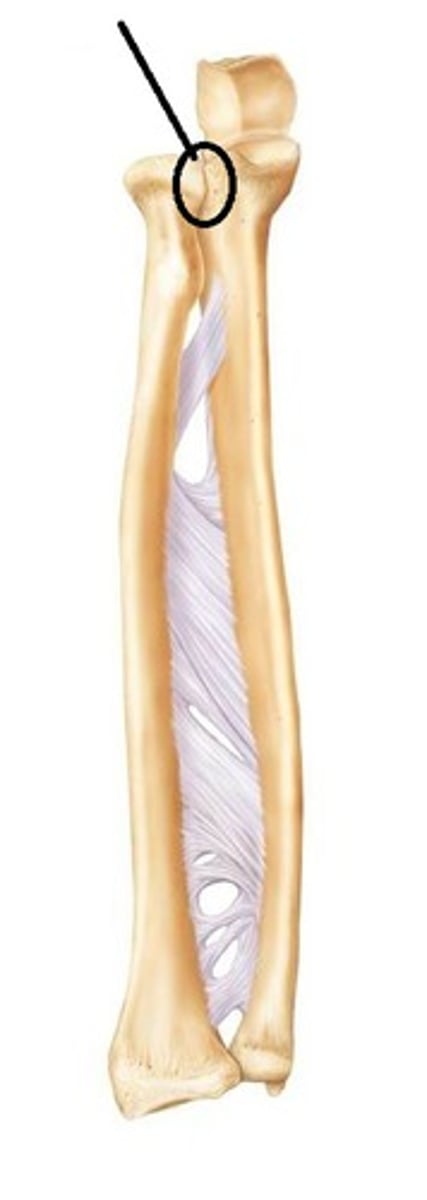
proximal radioulnar joint
- articulation of the head of the radius with the radial notch of the ulna
- pivot type of synovial joint
- permits pronation/supination of the forearm

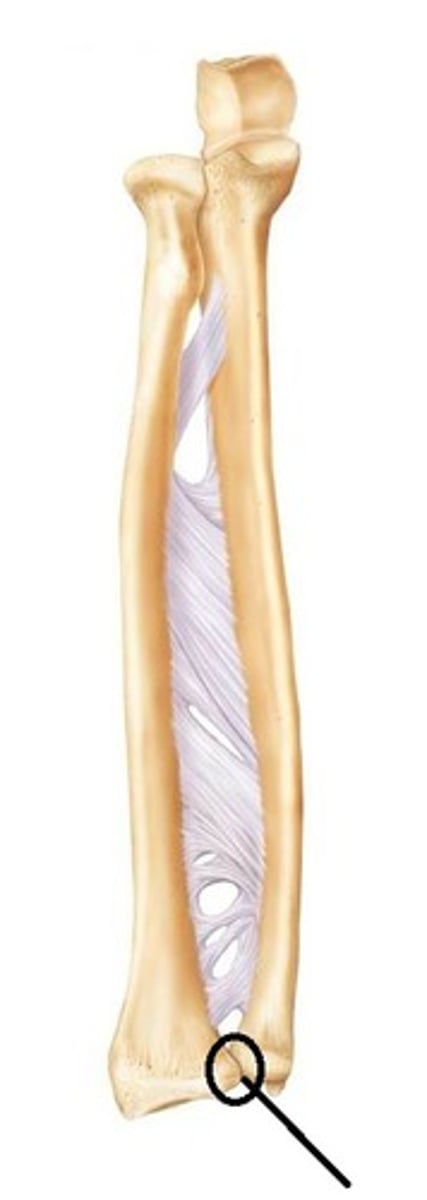
distal radioulnar joint
- articulation of the head of the ulna with the ulnar notch of the radius
- pivot type of synovial joint
- permits pronation/supination of the forearm

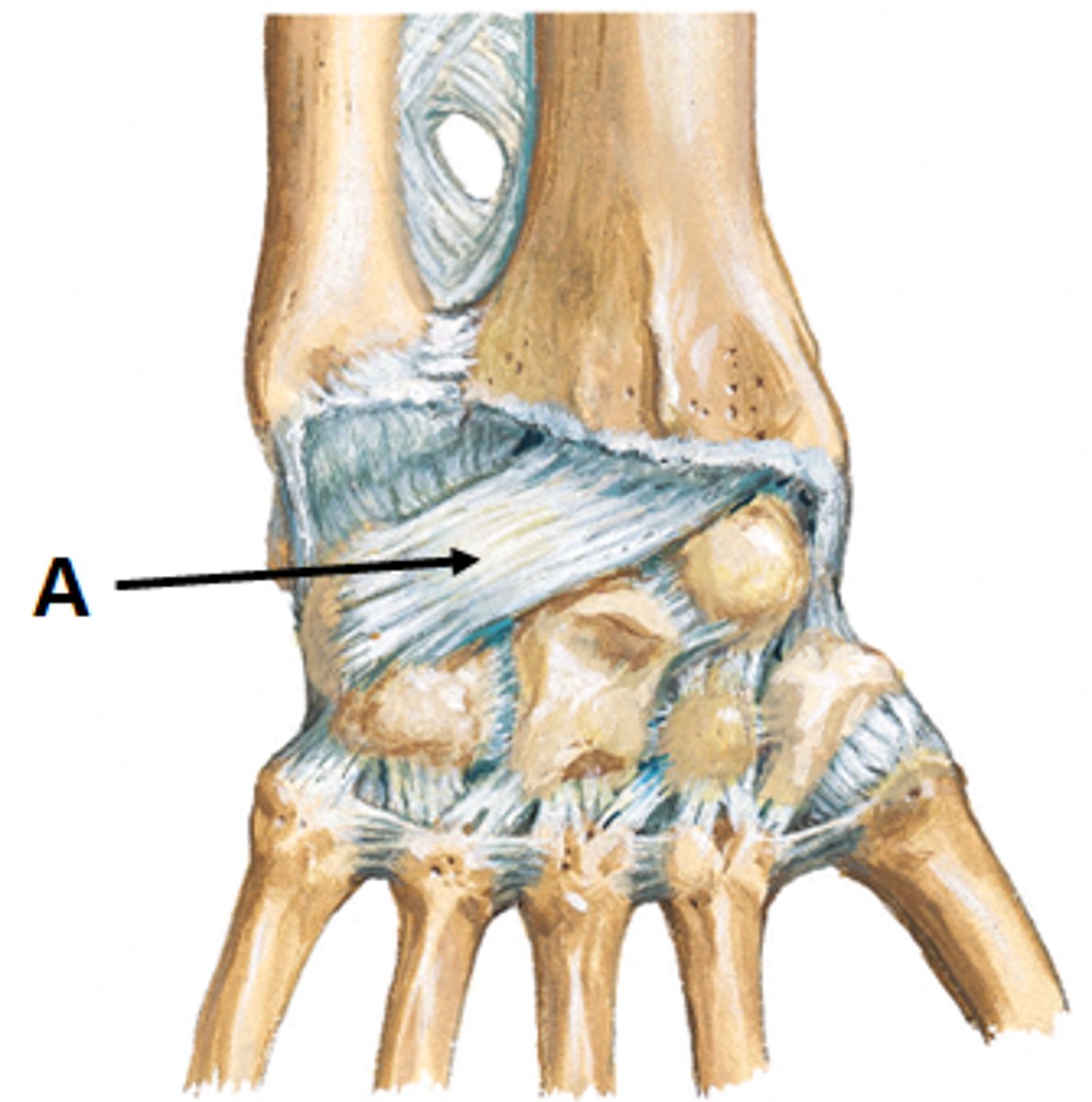
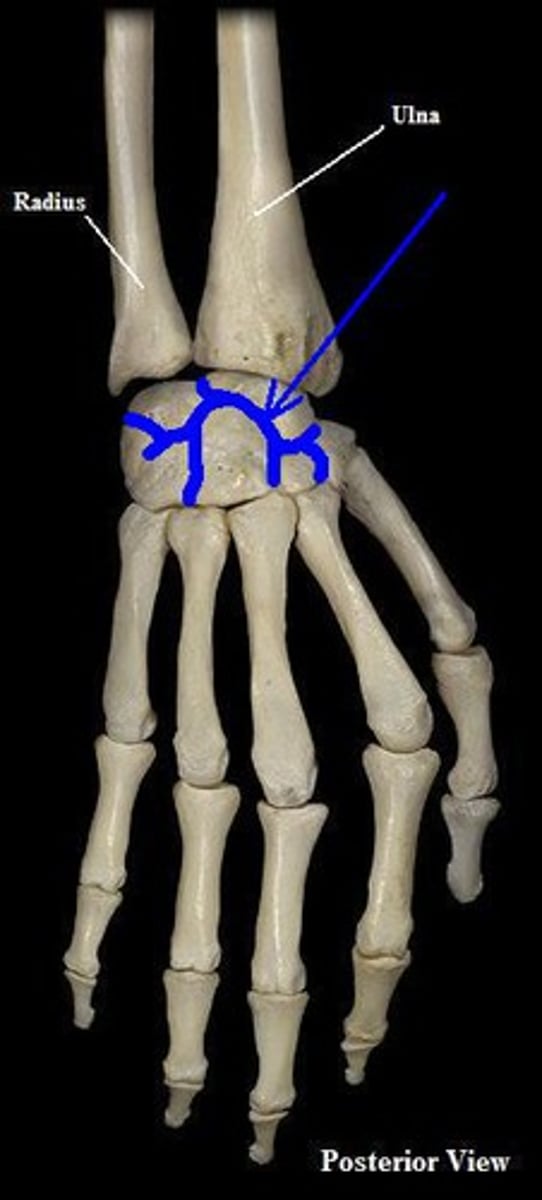
radiocarpal joint
- articulation of the distal radius with the proximal row of carpal bones
- condyloid type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension and radial/ulnar deviation of the wrist
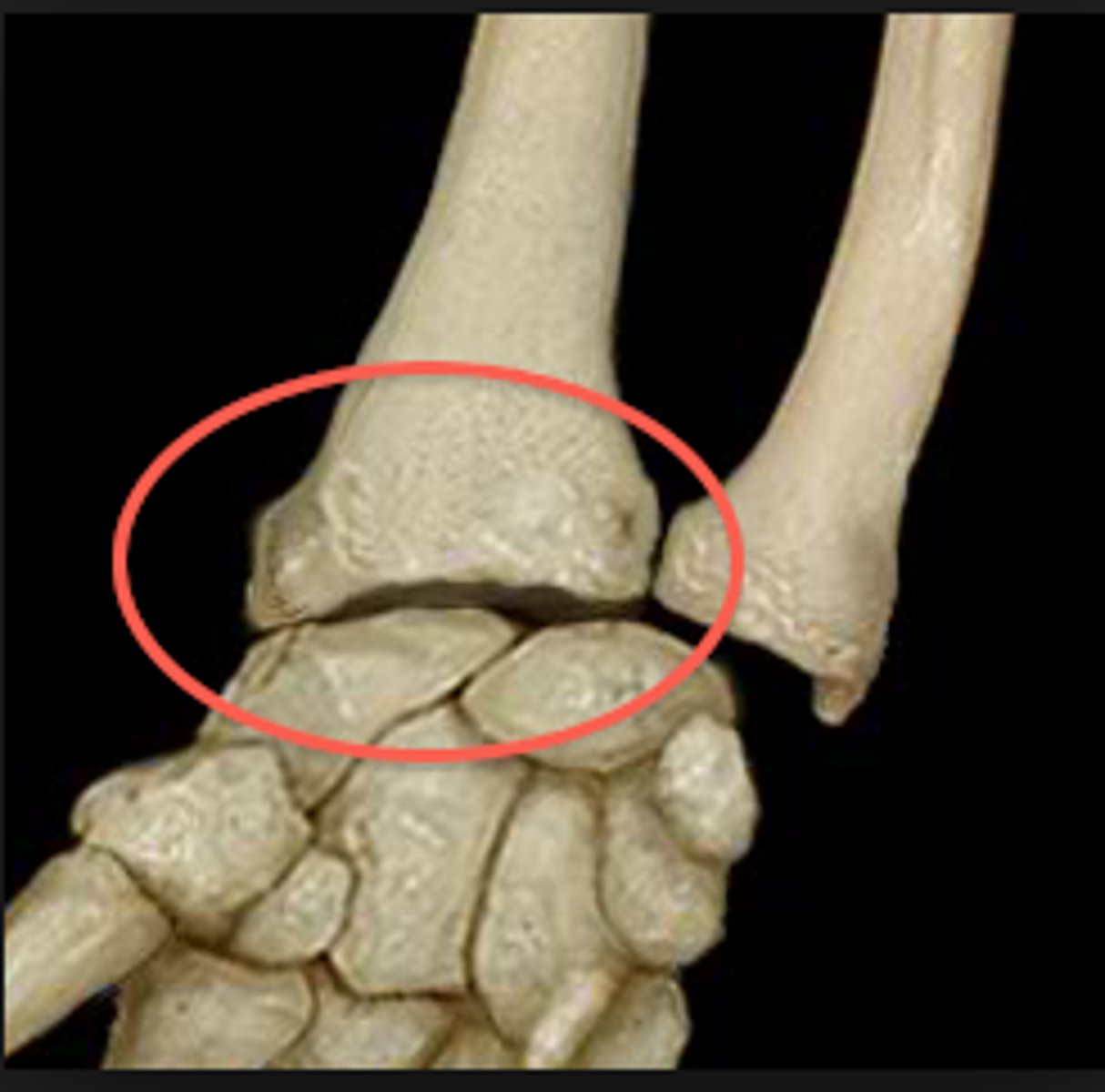
ulnar collateral ligament of wrist
- ligament running from the styloid process of the ulna to the medial surface of the triquetrum
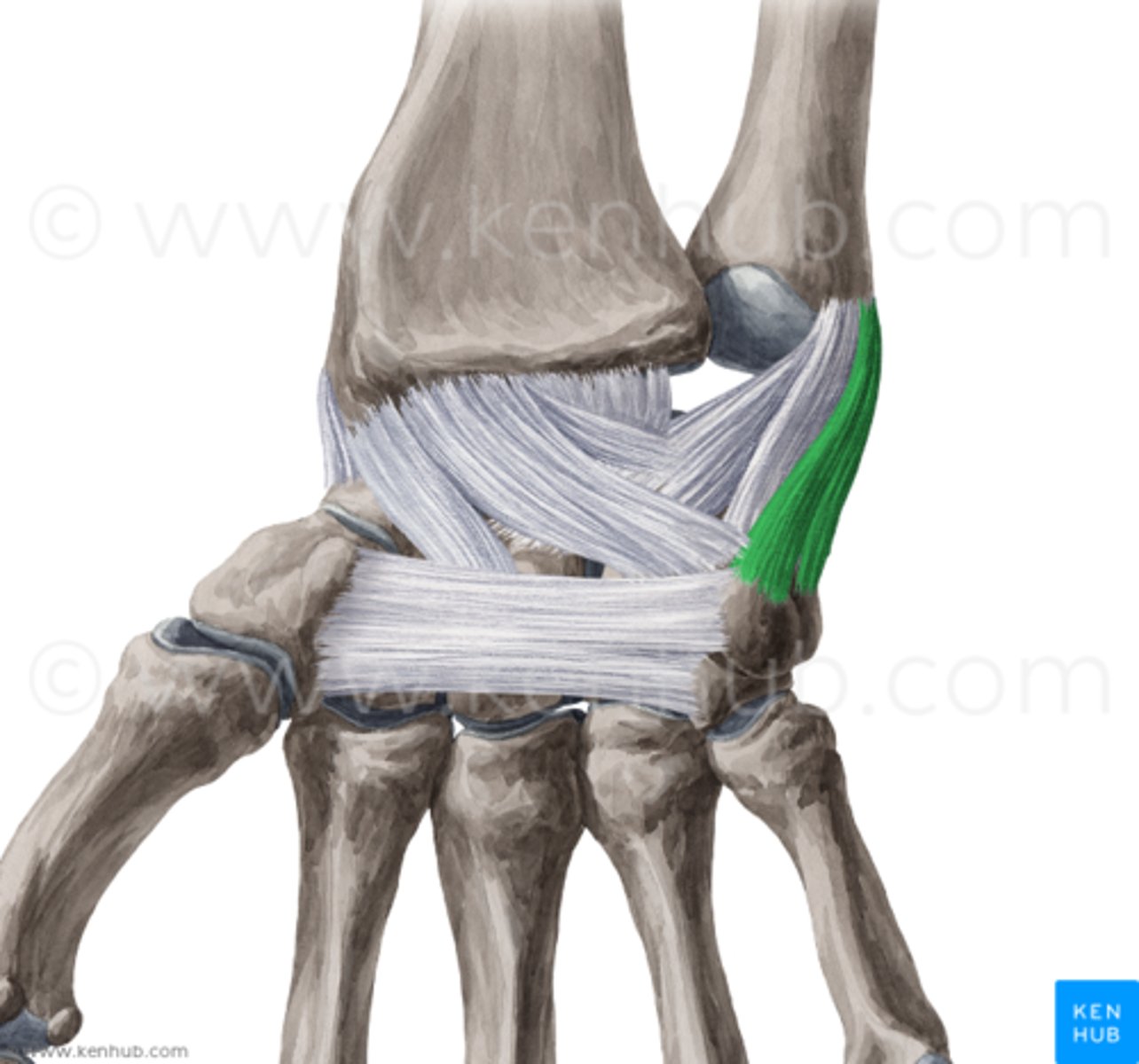
radial collateral ligament of wrist
- ligament running from the styloid process of the radius to the lateral surface of the scaphoid
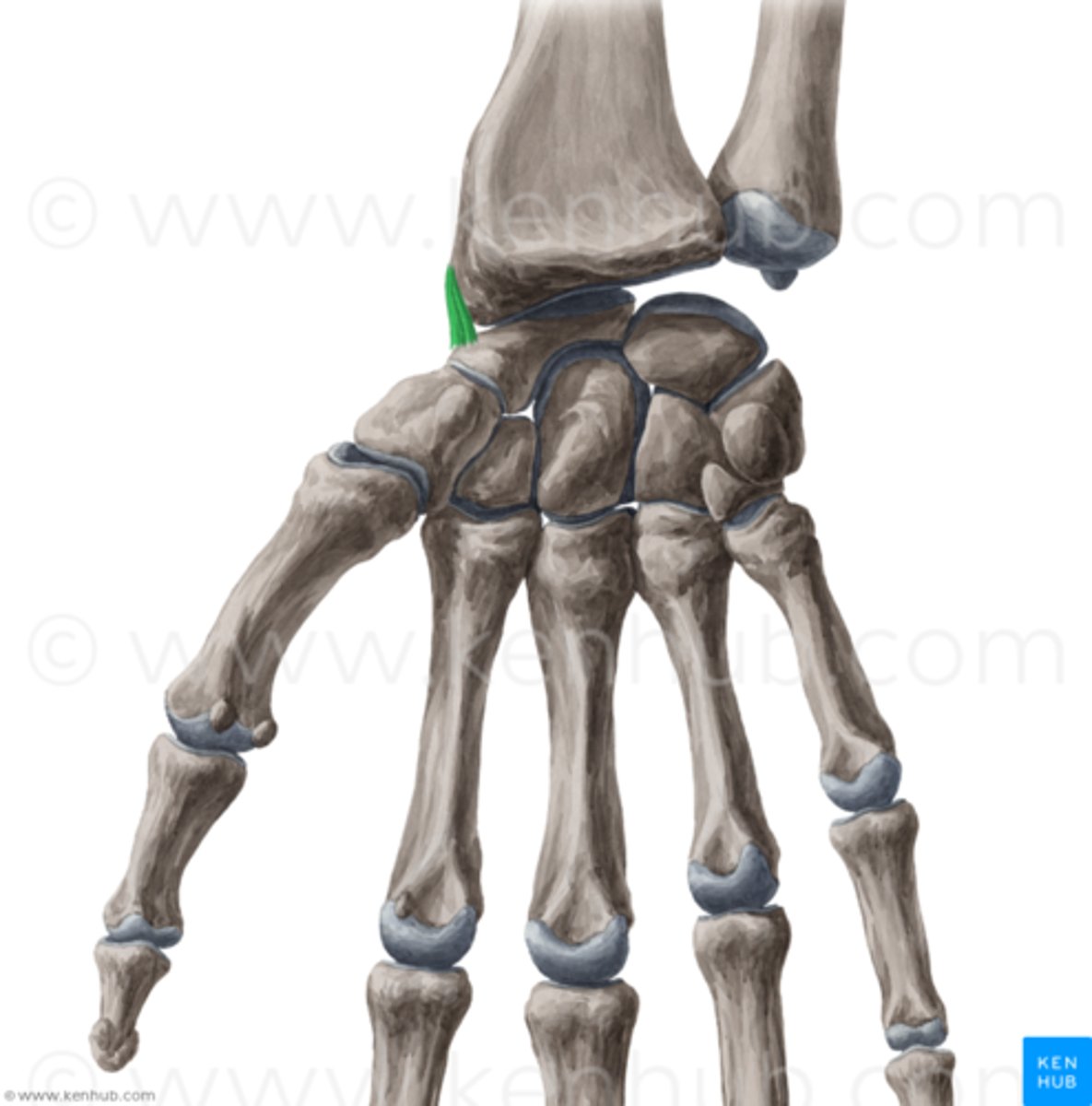
palmar radiocarpal ligament
- ligament running from the anterior surface of the distal radius to the anterior surface of the carpal bones
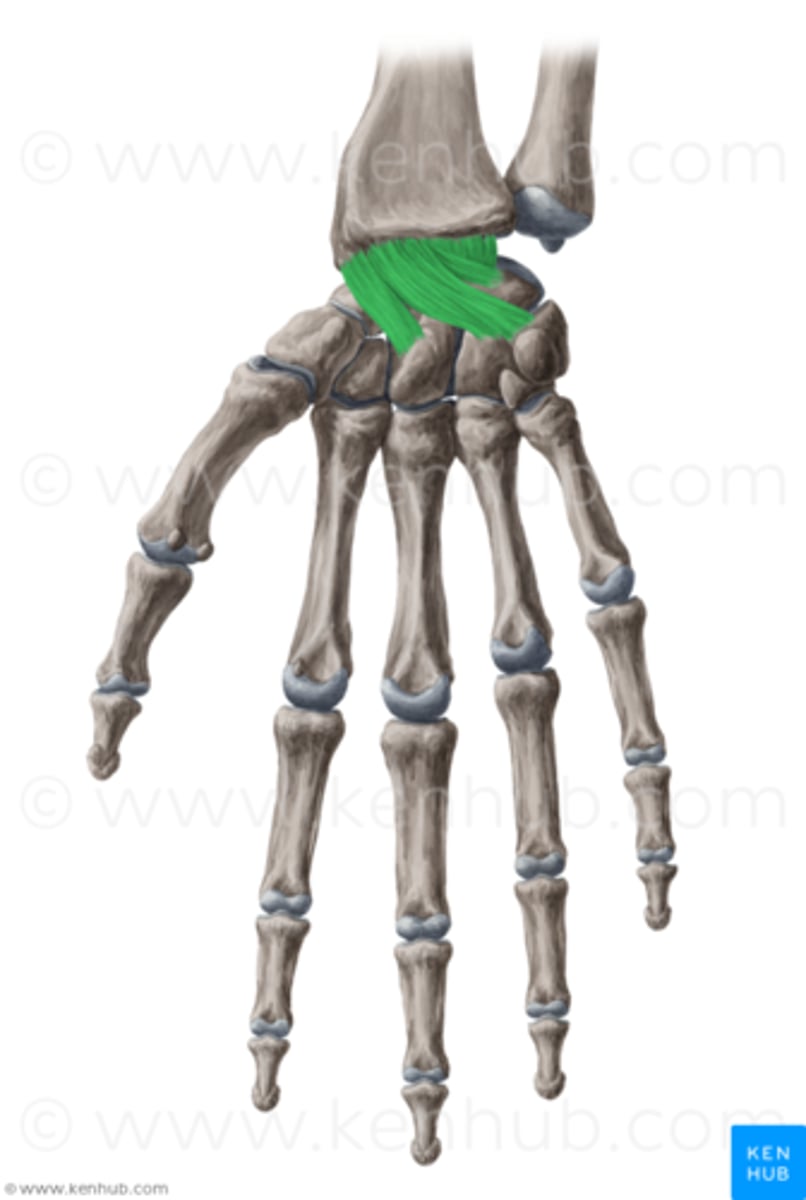
dorsal radiocarpal ligament
- ligament running from the posterior surface of the distal radius to the posterior surface of the carpal bones
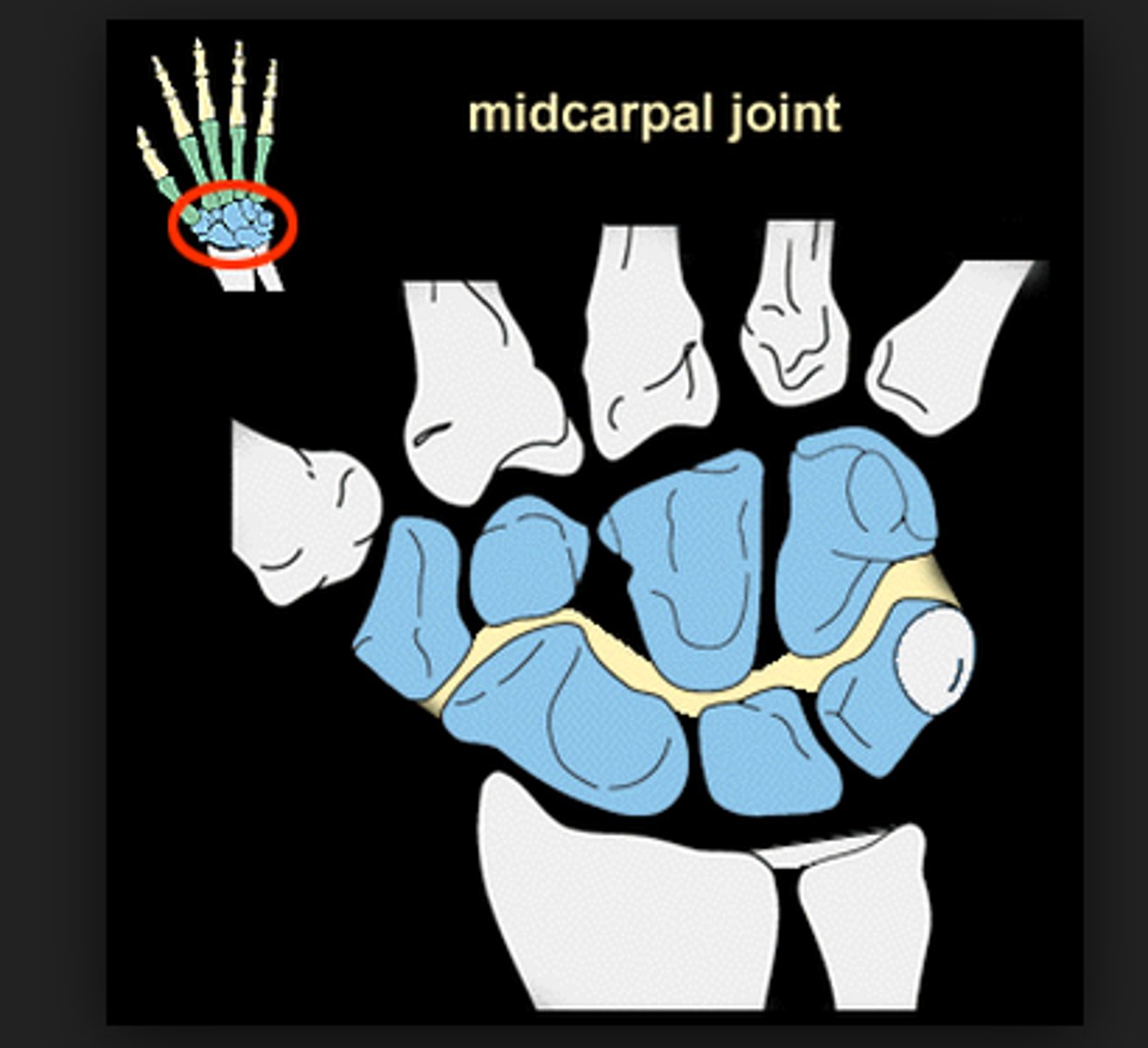
midcarpal joints
- articulation of the proximal row of carpal bones with the distal row of carpal bones
- condyloid type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of radial/ulnar deviation of the wrist
intercarpal joints
- articulation of the carpal bones with adjacent carpal bones in the same row
- plane type of synovial joint
- permits gliding movements of the carpal bones
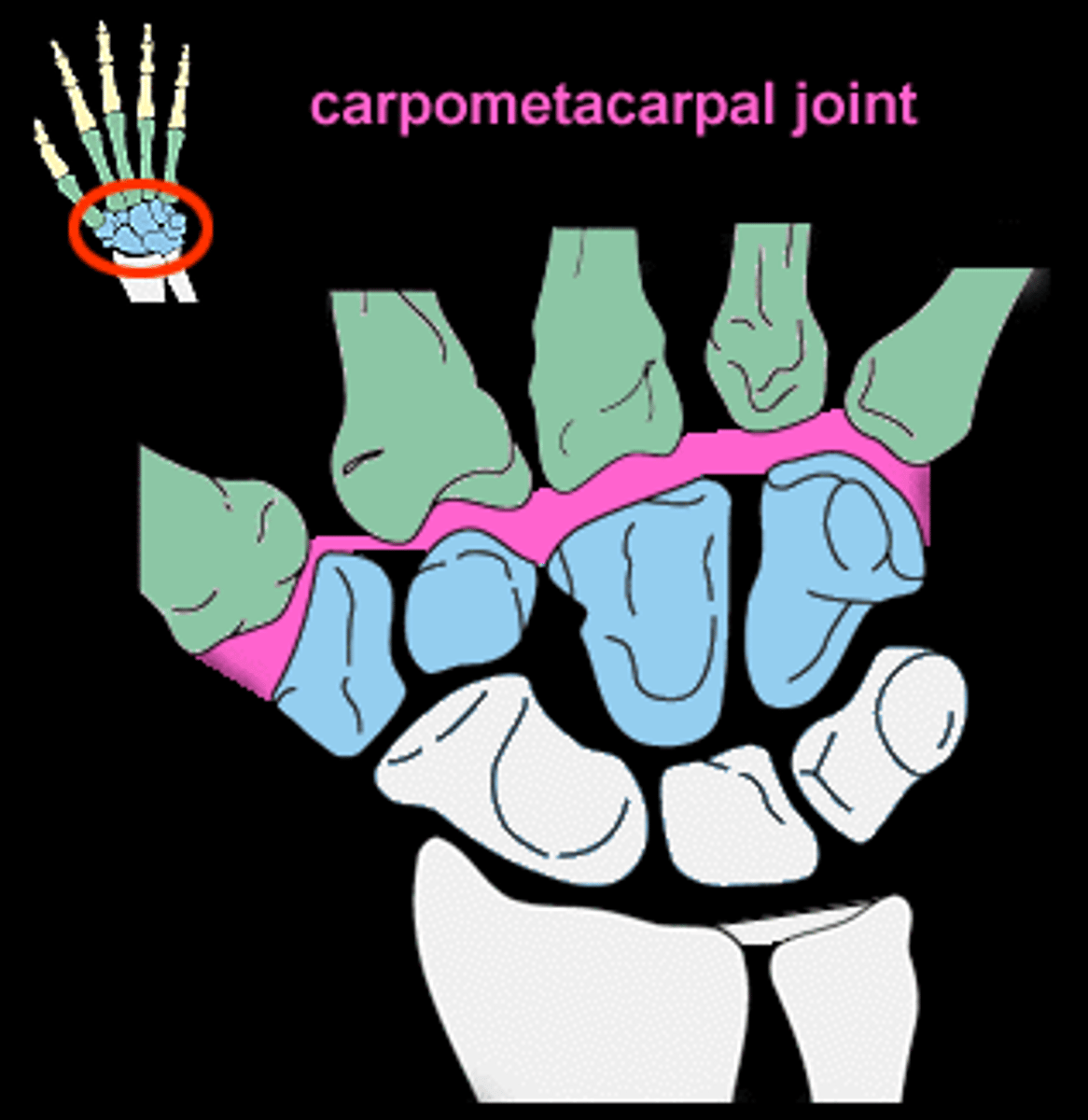
carpometacarpal joints
- articulation of the distal row of carpal bones with metacarpals
- plane type of synovial joint (digits 2-5) and saddle type of synovial joint (digit 1)
- permits little movement (digits 2-5) and flexion/extension and abduction/adduction (digit 1)
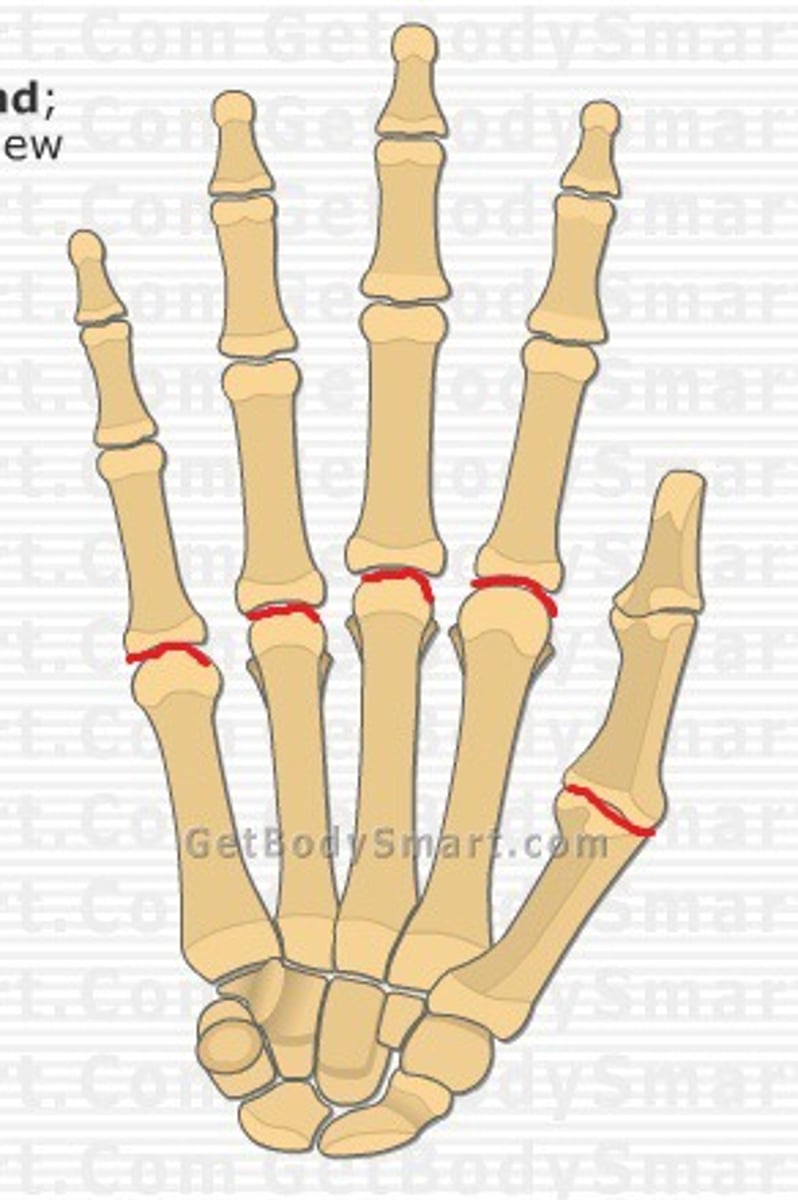
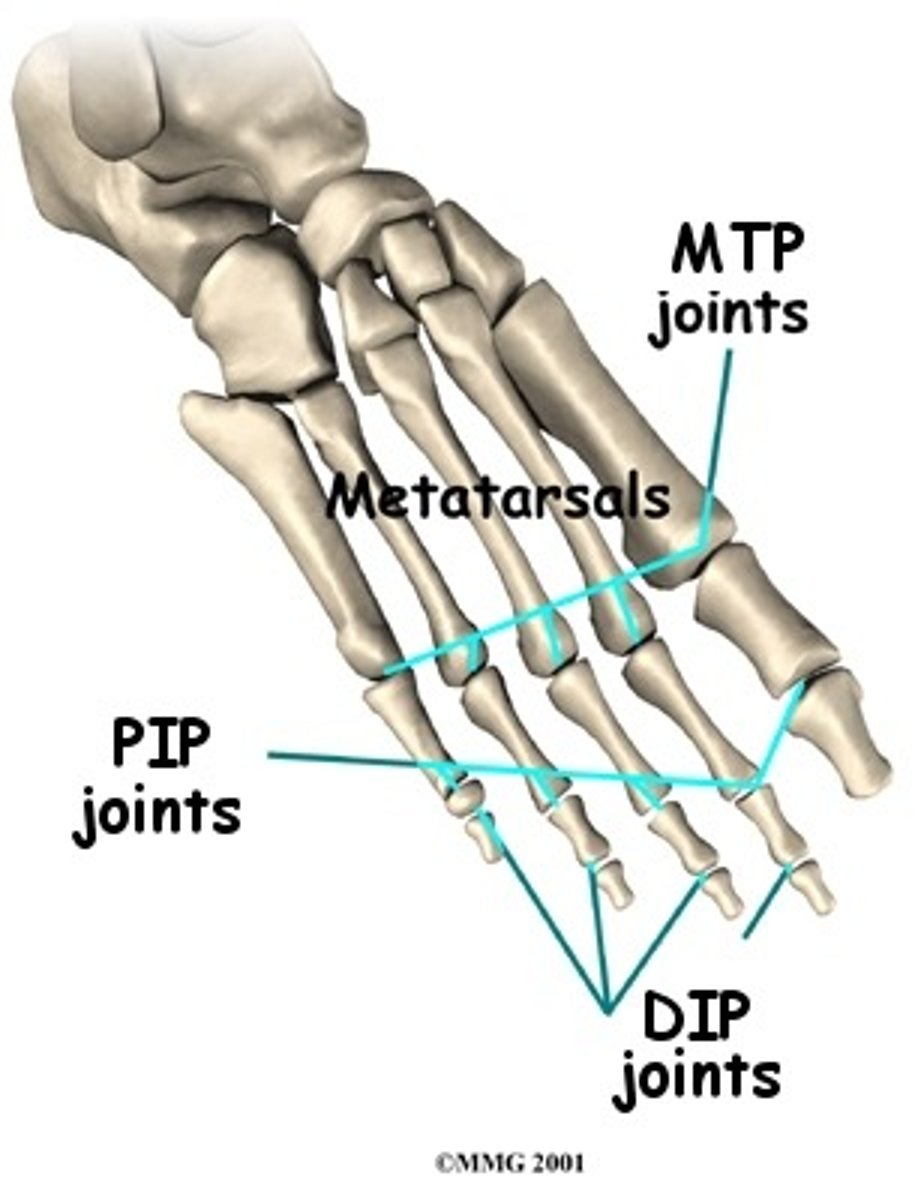
metacarpophalangeal joints
- articulation of the metacarpals with the proximal phalanges
- condyloid type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension and abduction/adduction (digits 2-5) and flexion/extension (digit 1)
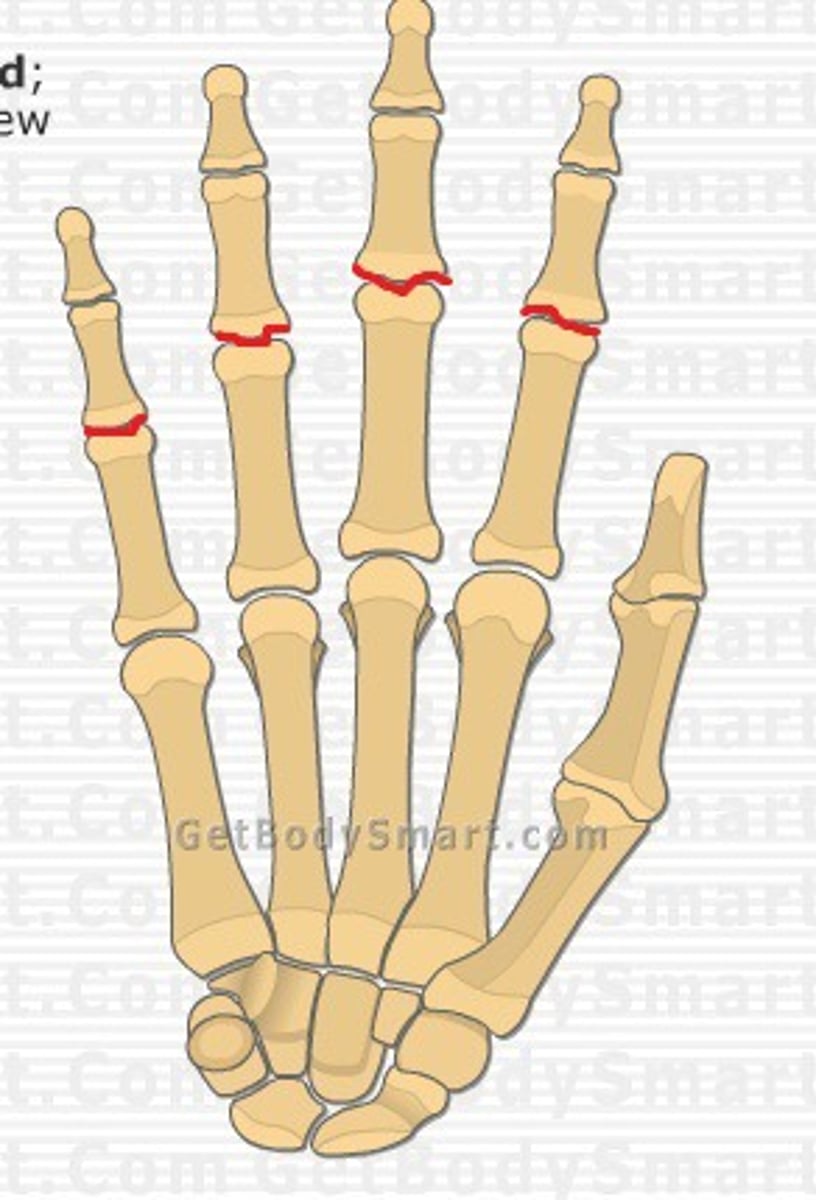
proximal interphalangeal joints of hand
- articulation of the proximal phalanges with the middle phalanges
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the digits
- only present in digits 2-5
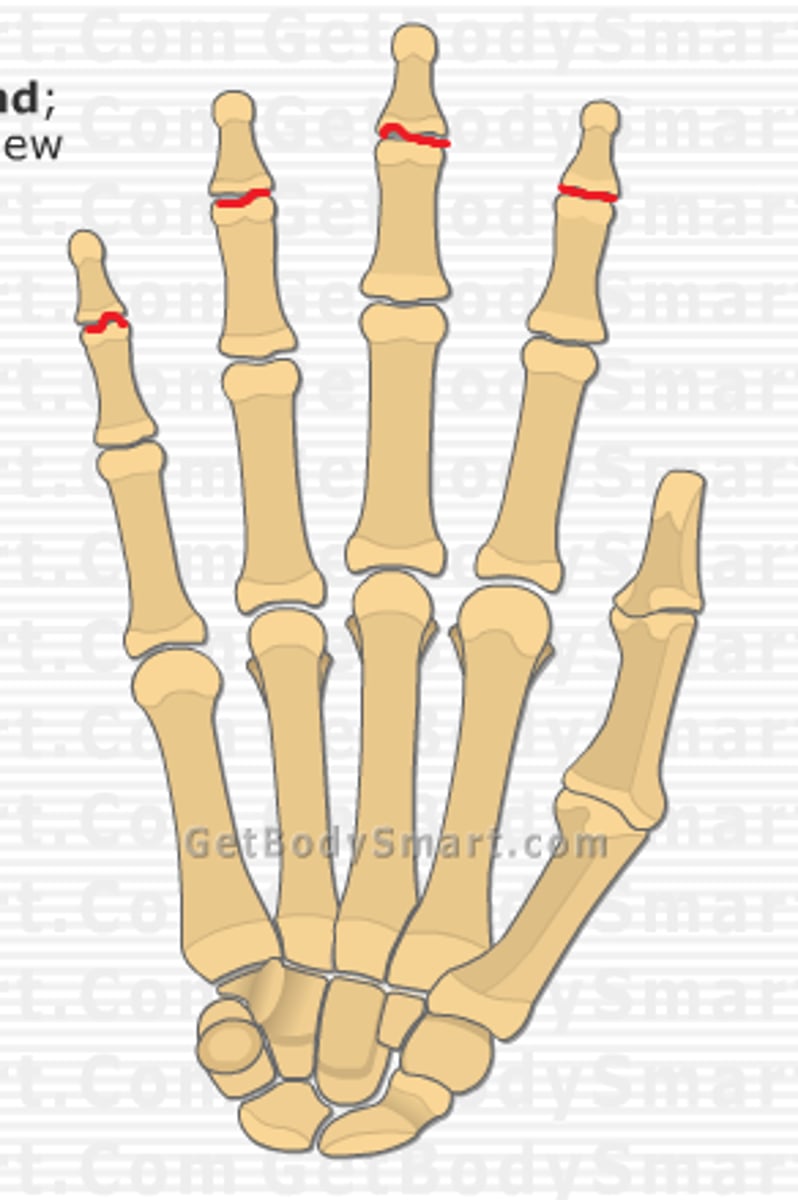
distal interphalangeal joints of hand
- articulation of the middle phalanges with the distal phalanges
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the digits
- digit 1 only has an interphalangeal joint
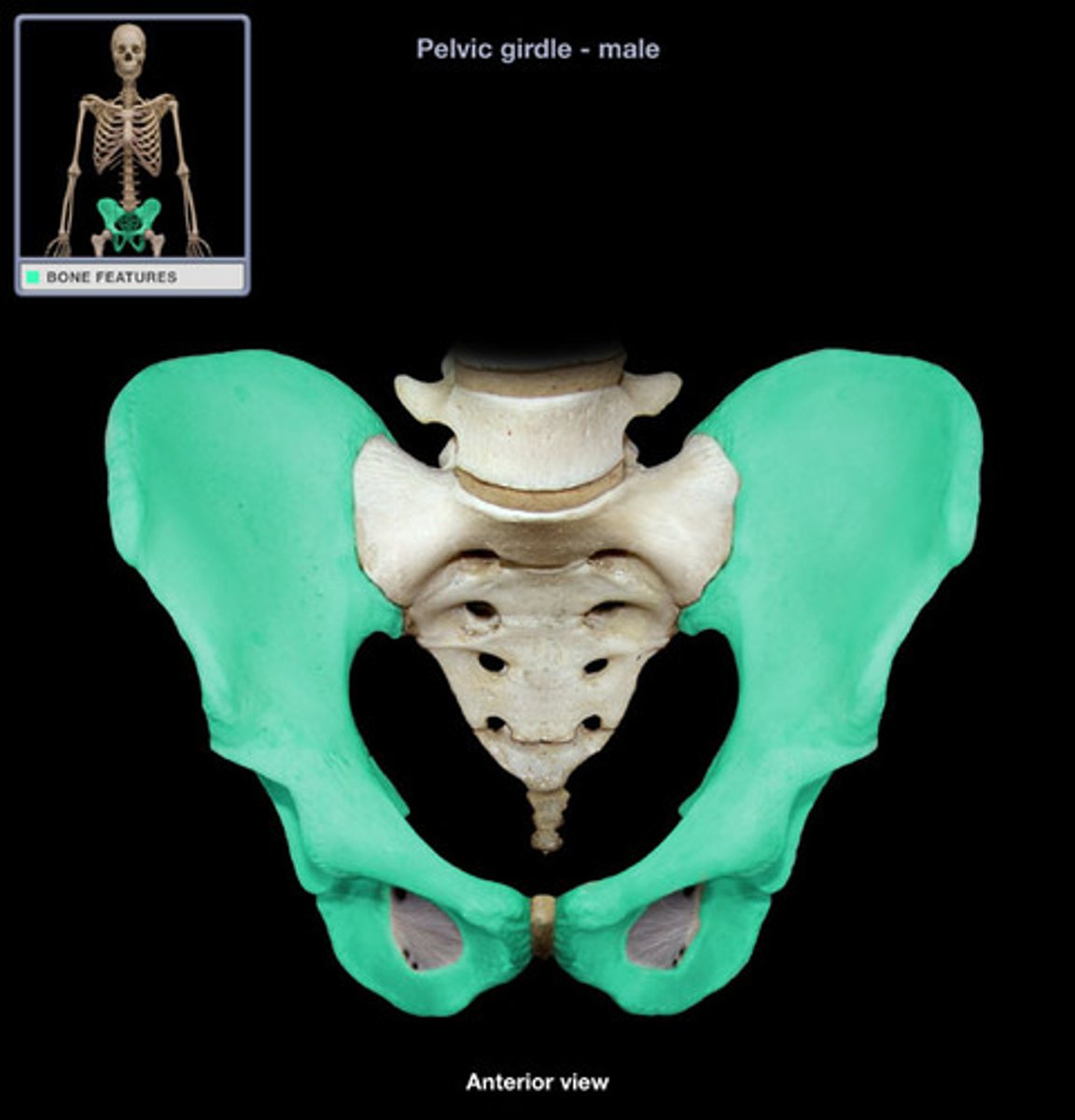
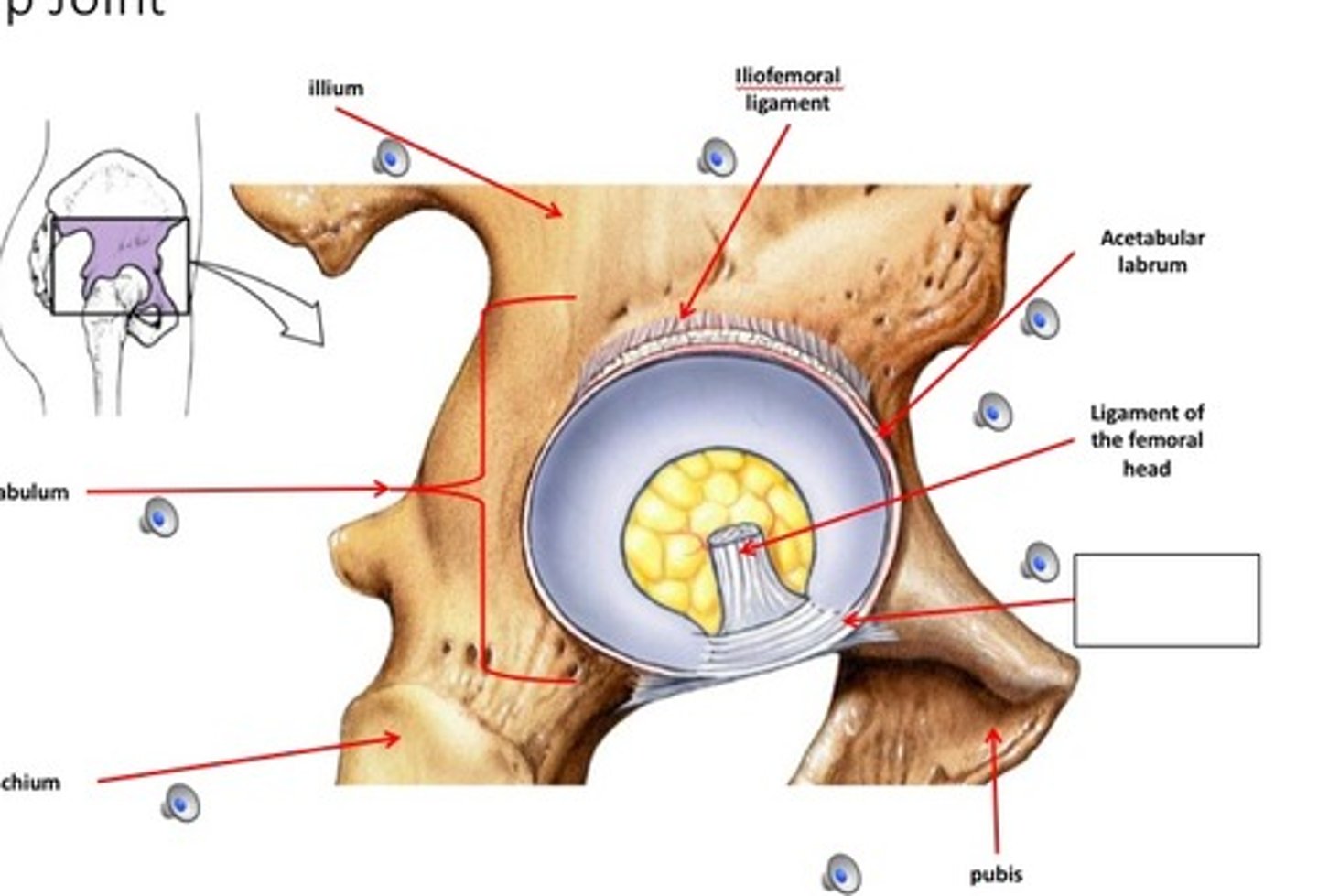
hip joint
- articulation of the head of the femur with the acetabulum of the coral bone
- ball-and-socket type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension, abduction/adduction, and internal/external rotation of the hip
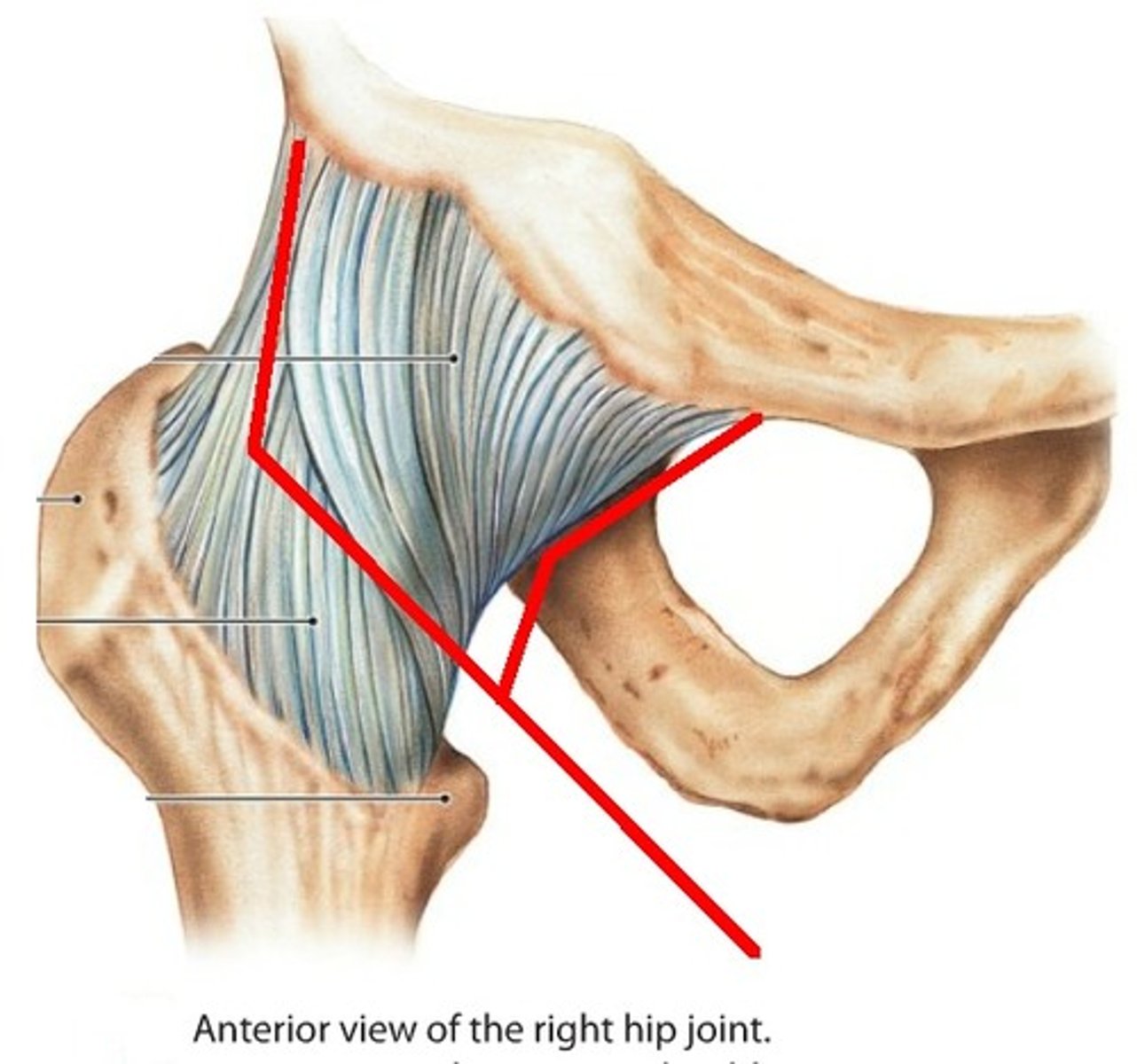
iliofemoral ligament
- ligament running from the ilium to the head of the femur
- Y-shaped ligament
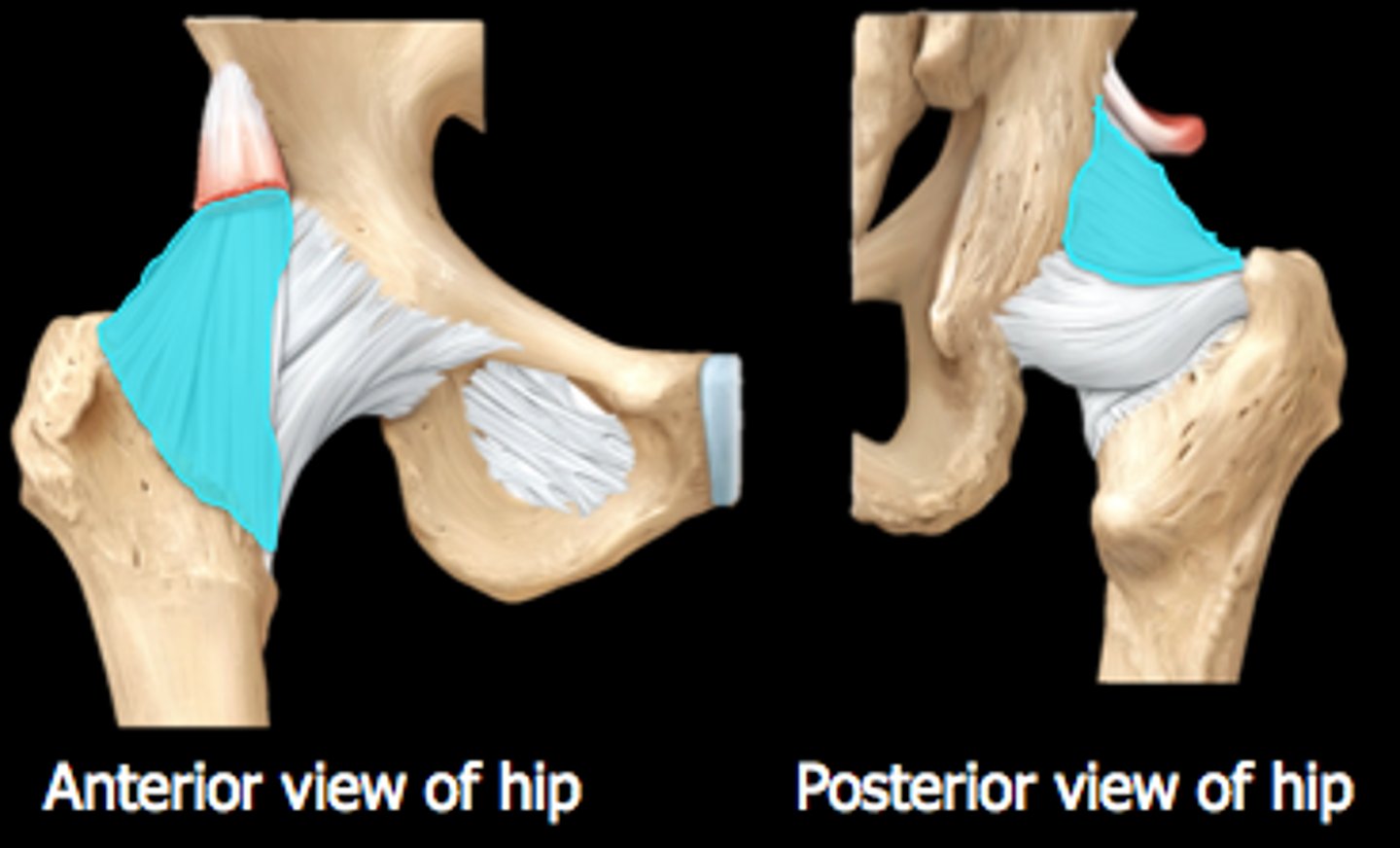
ischiofemoral ligament
- ligament running from the ischium to the head of the femur
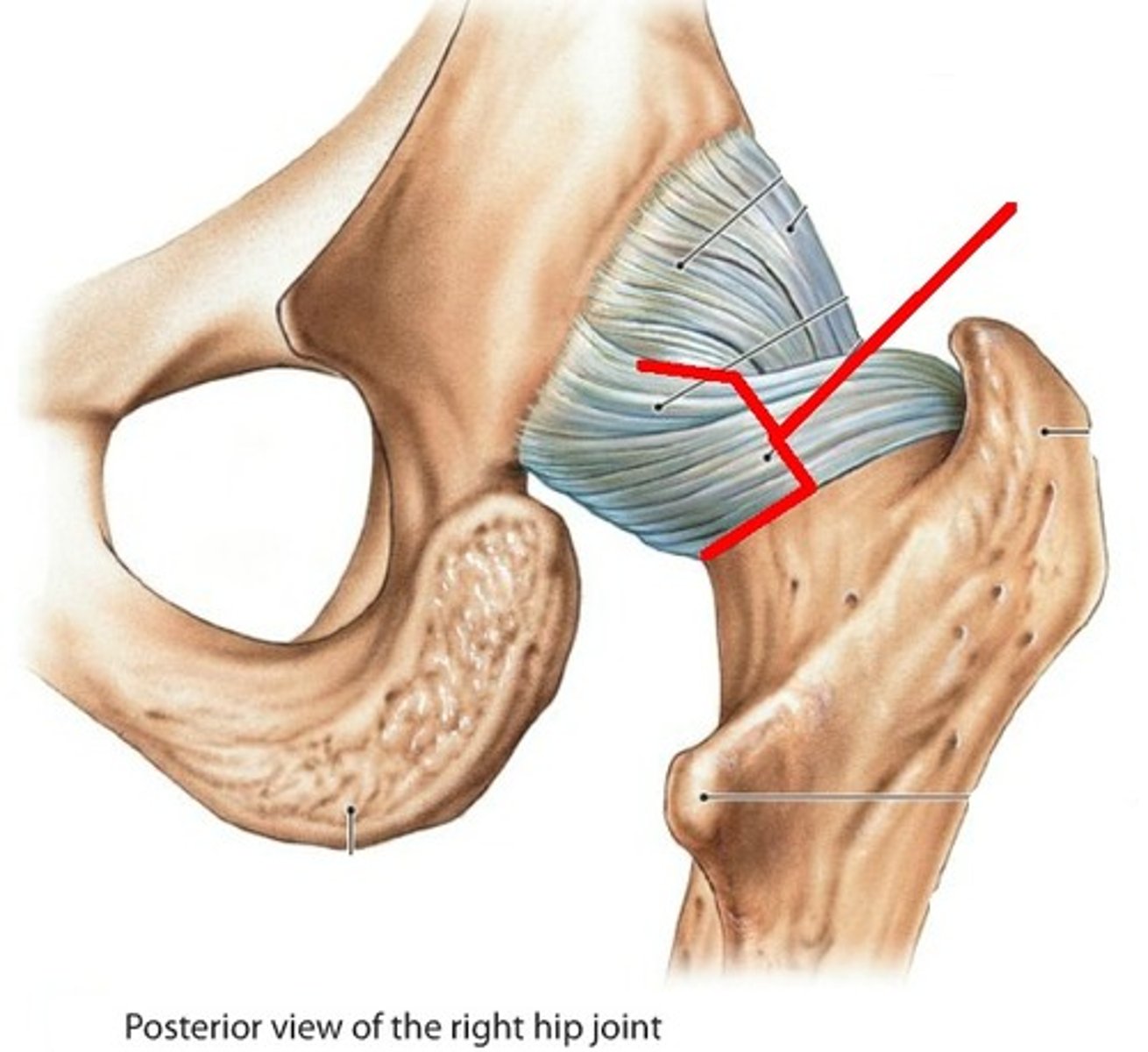
pubofemoral ligament
- ligament running from the pubic to the head of the femur
- blends with the iliofemoral ligament
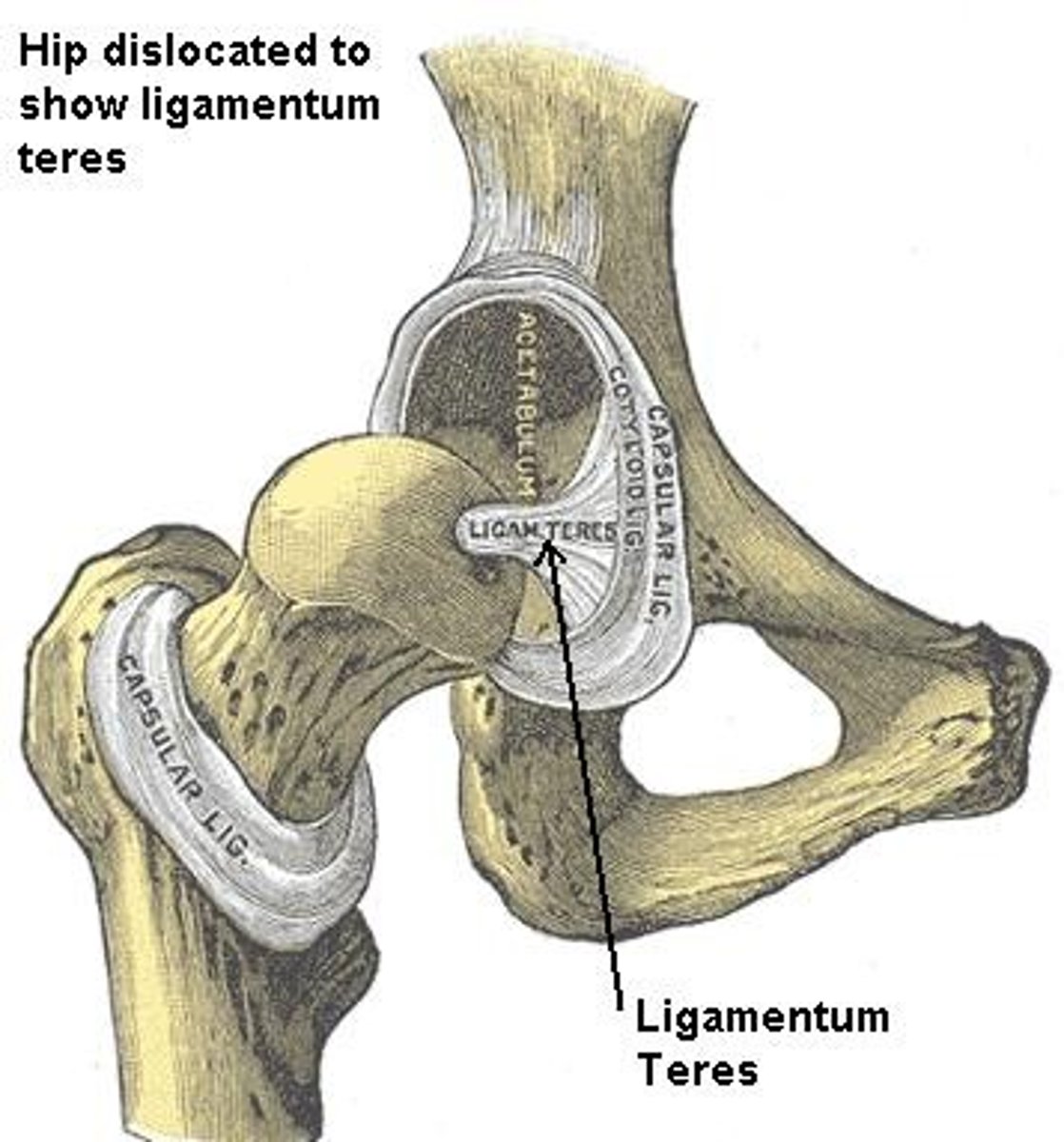
ligament of the femoral head
- ligament running from the head of the femur to the acetabular notch
acetabular labrum
- fibrocartilaginous ring lining the wall of the acetabulum
- increases surface area and decreases joint stress
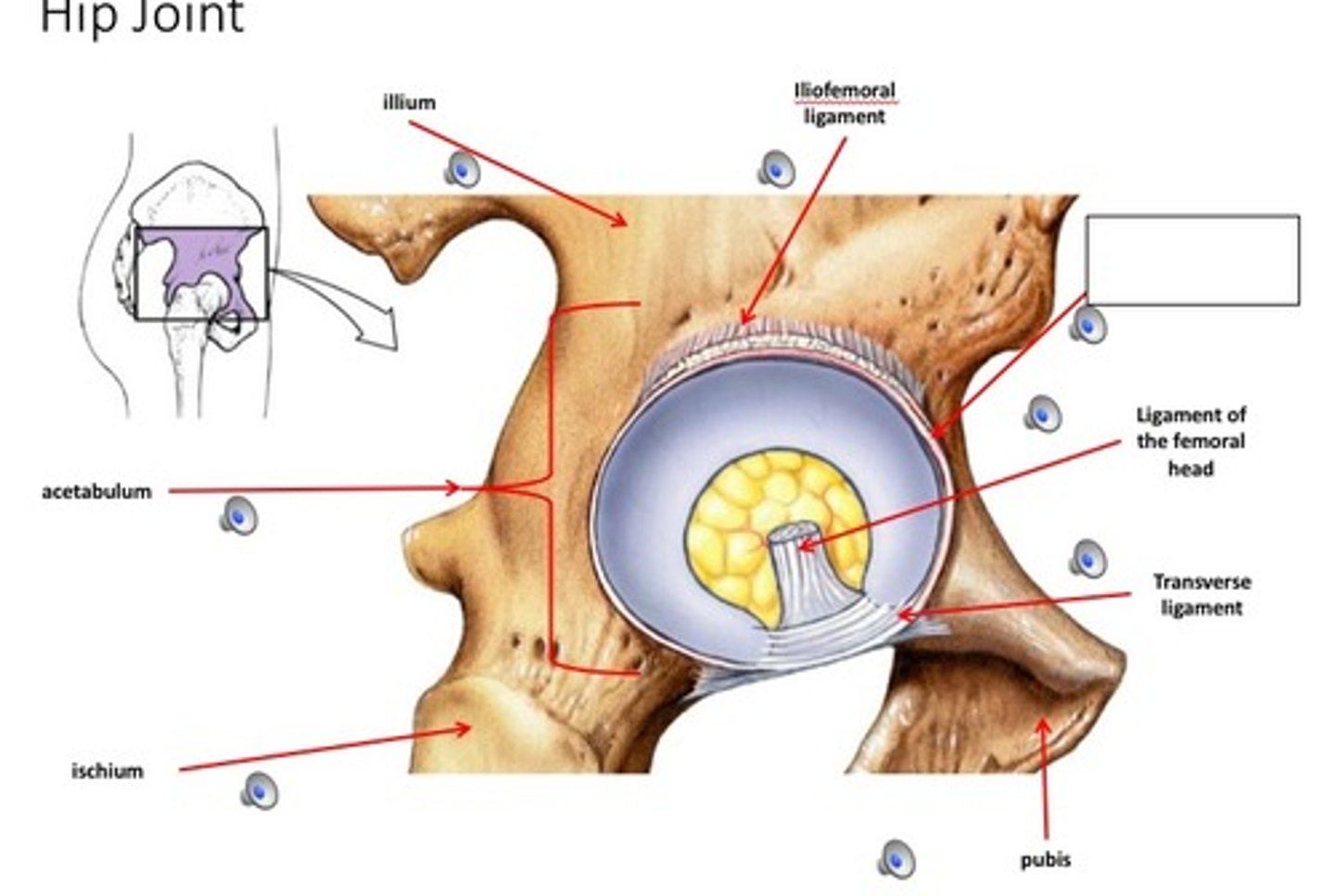
transverse ligament of the hip
- ligament running across the acetabular notch
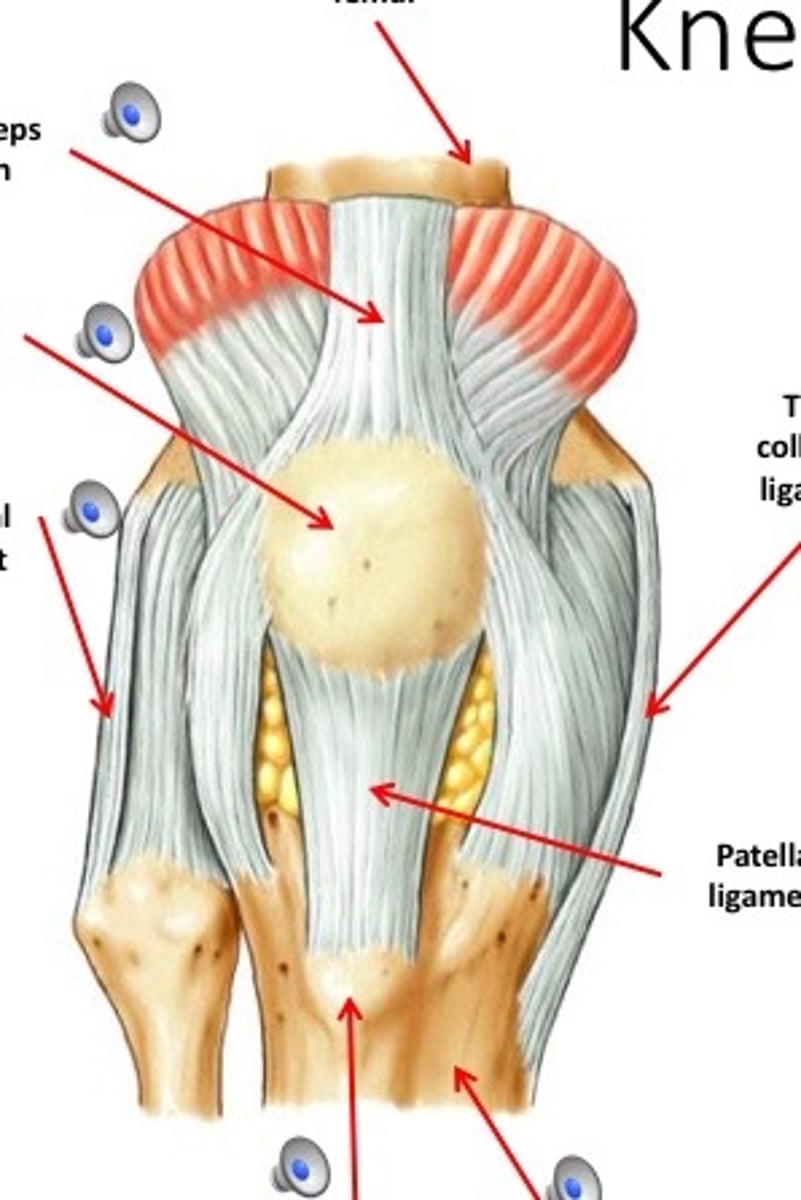
knee joint
- articulation of the medial/lateral femoral condyles with the medial/lateral tibial condyles
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the knee
tibial (medial) collateral ligament
- ligament running from the medial epicondyle of the femur to the medial condyle of the tibia
- flat, band-like capsular ligament
- weaker Thant he fibular collateral ligament
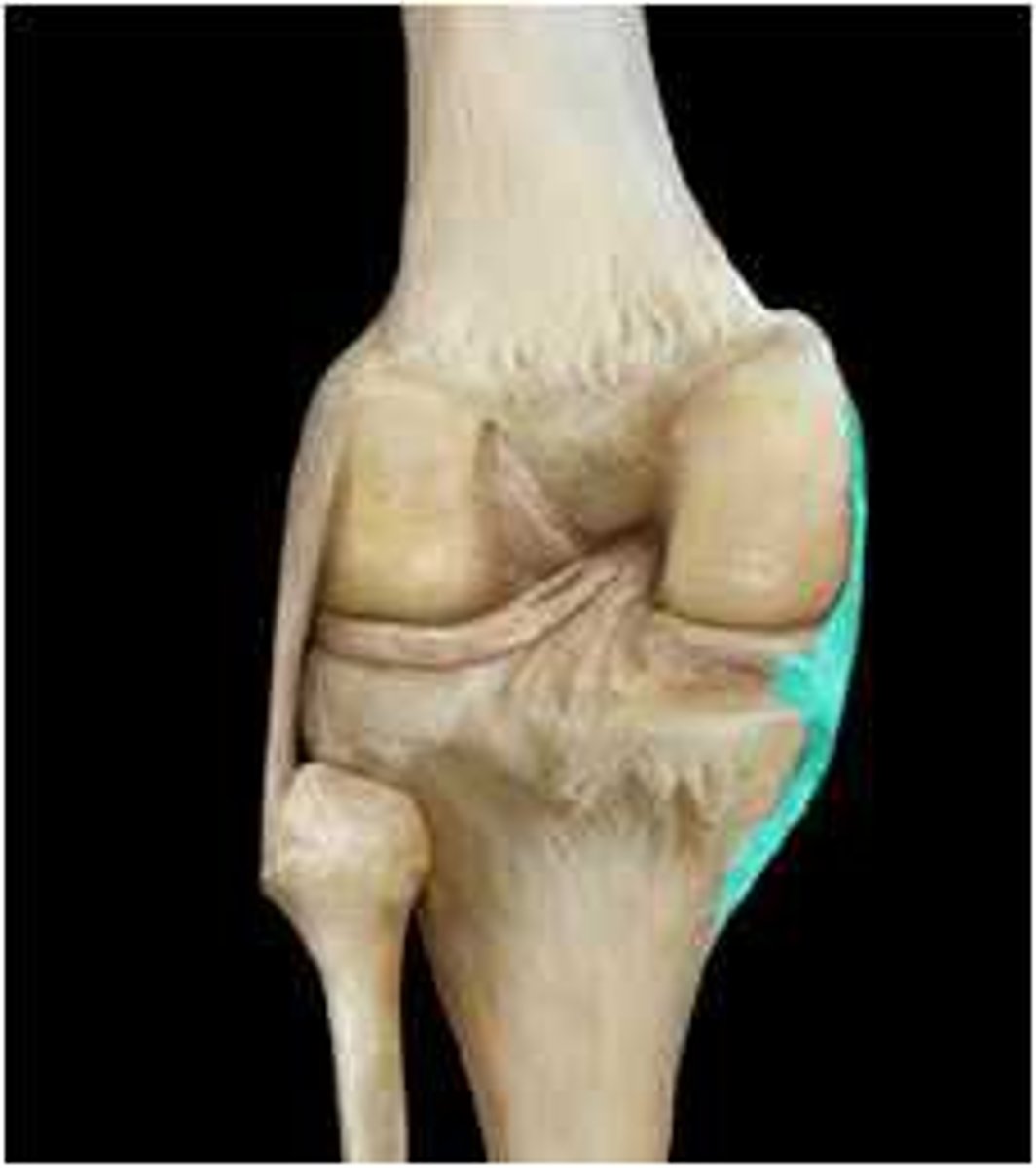
fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
- ligament running from the lateral epicondyle of the femur to the head of the fibula
- cord-like extracapsular ligament
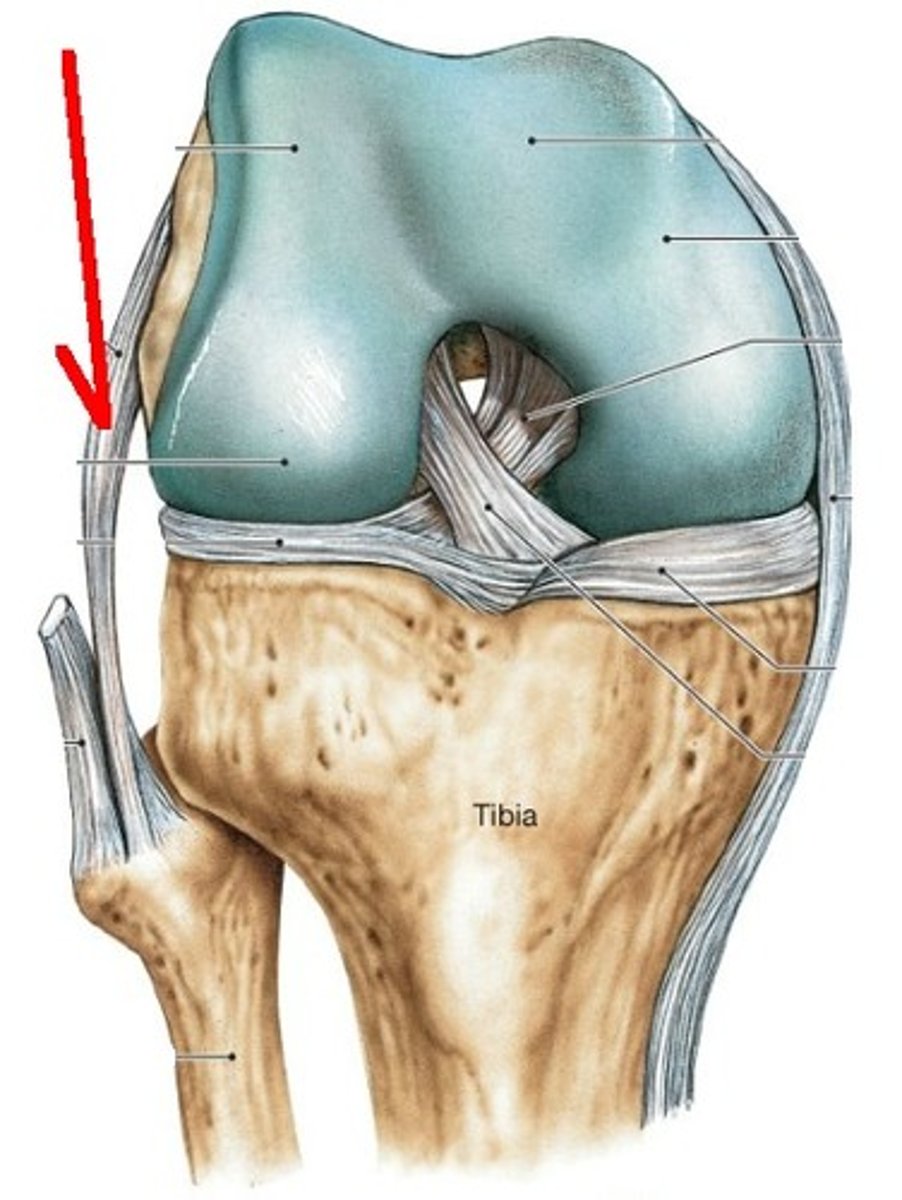
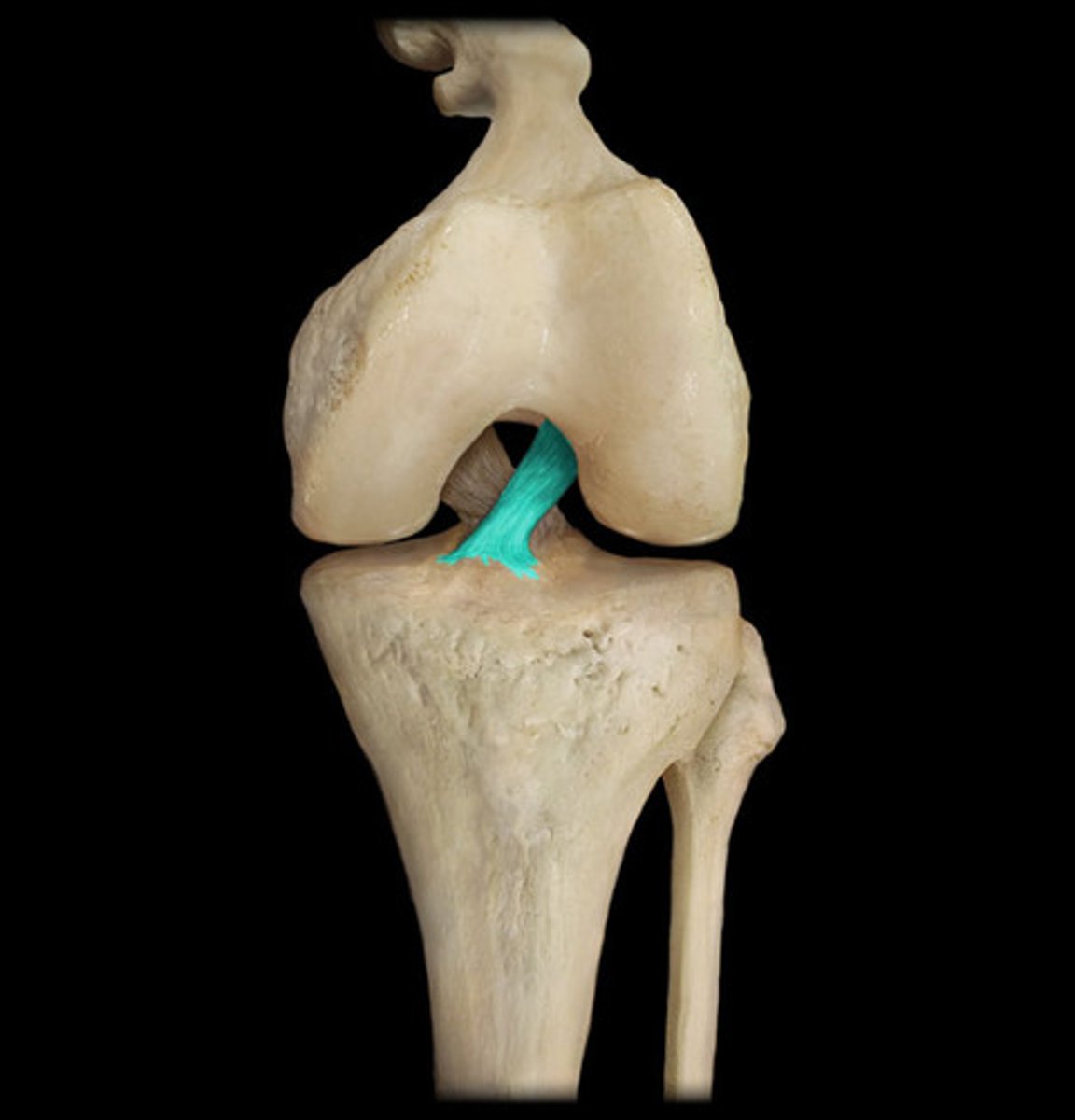
anterior cruciate ligament
- ligament running from the anterior aspect of the intercondylar area of the tibia to the medal aspect of the lateral femoral condyle
- prevents posterior displacement of the femur on the tibia and hyperextension of the knee joint
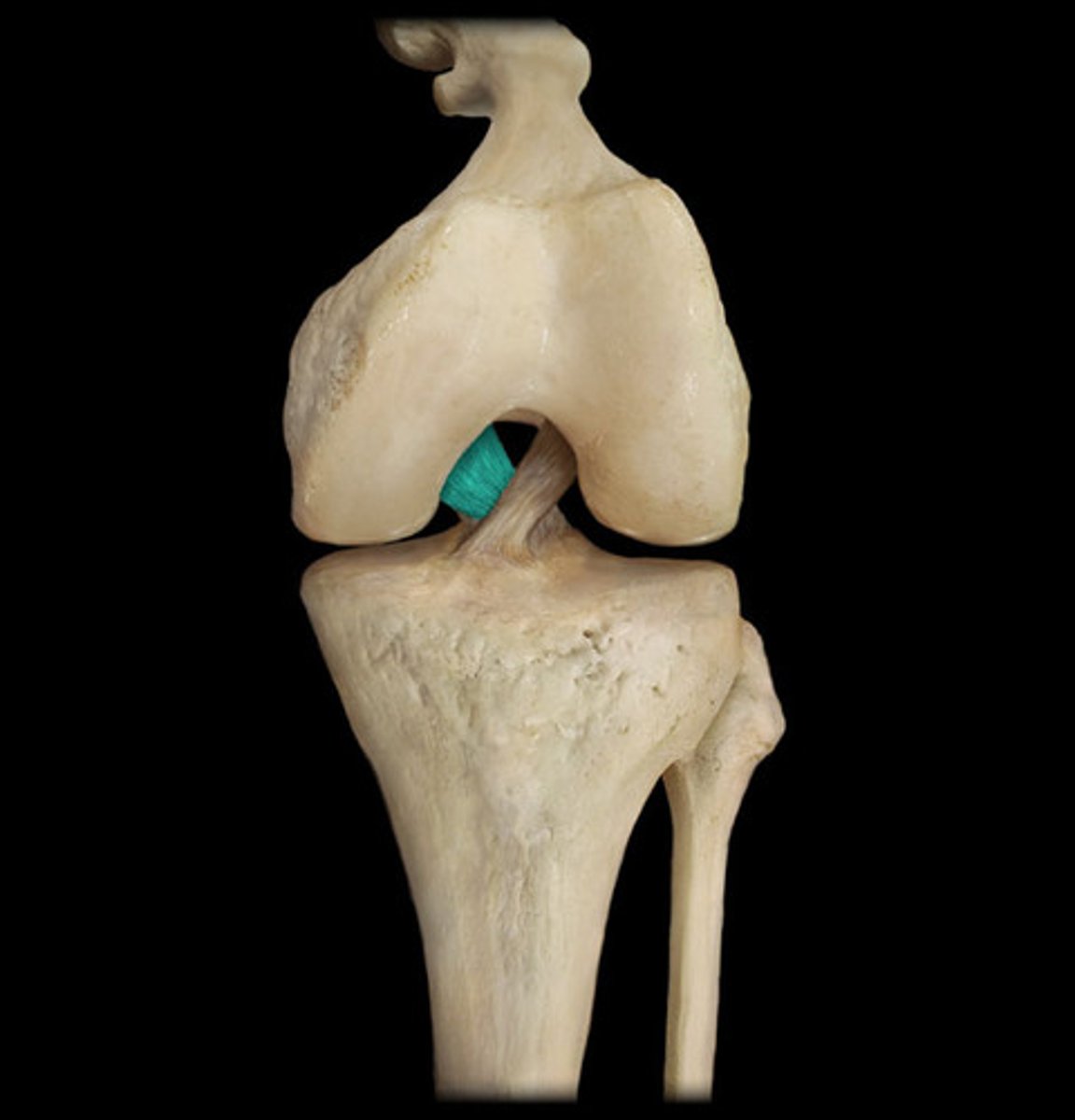
posterior cruciate ligament
- ligament running from the posterior aspect of the intercondylar area of the tibia to the lateral surface of the medial femoral condyle
- prevents anterior displacement of the femur on the tibia and hyperextension of the knee cap
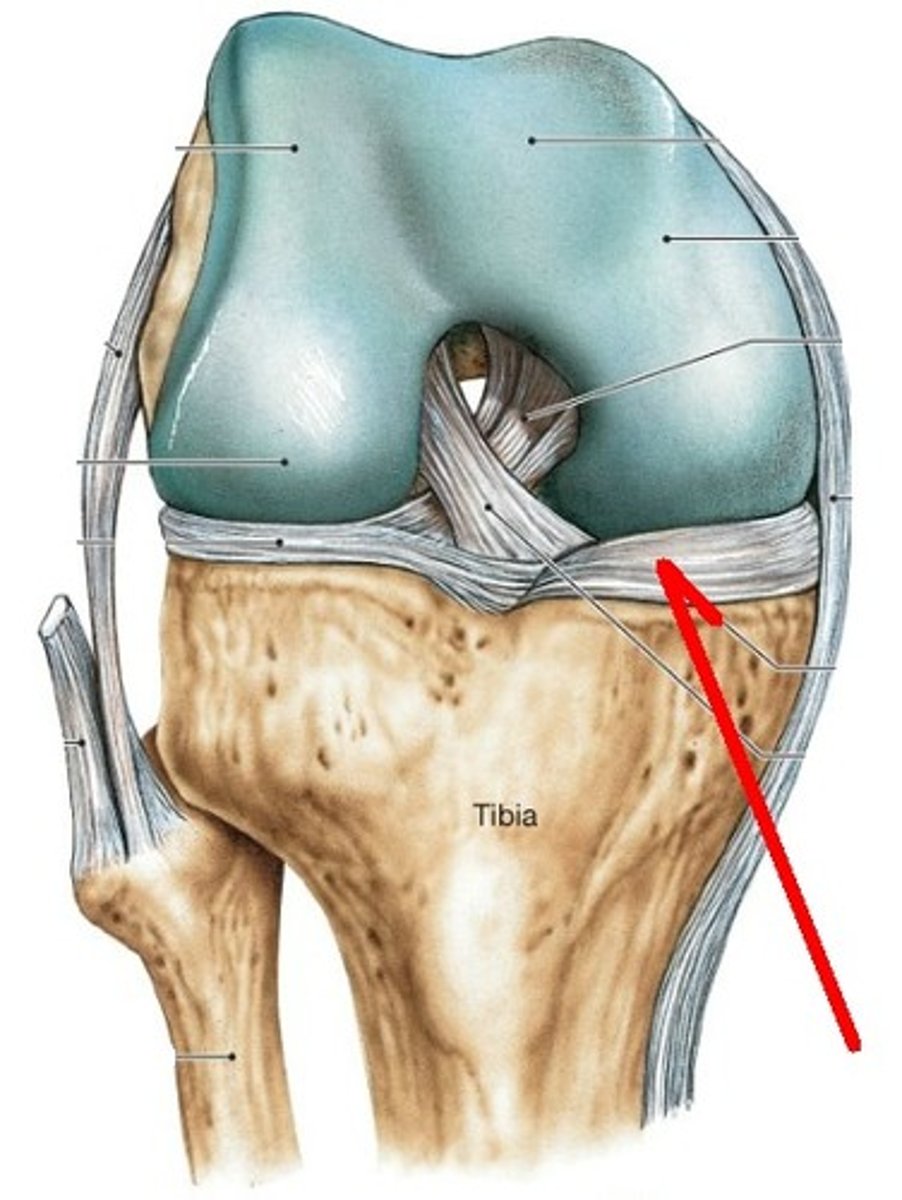
medial meniscus
- semicircular cartilage on the superior surface of the medial tibial condyle
- commonly injured with the lateral force to the knee
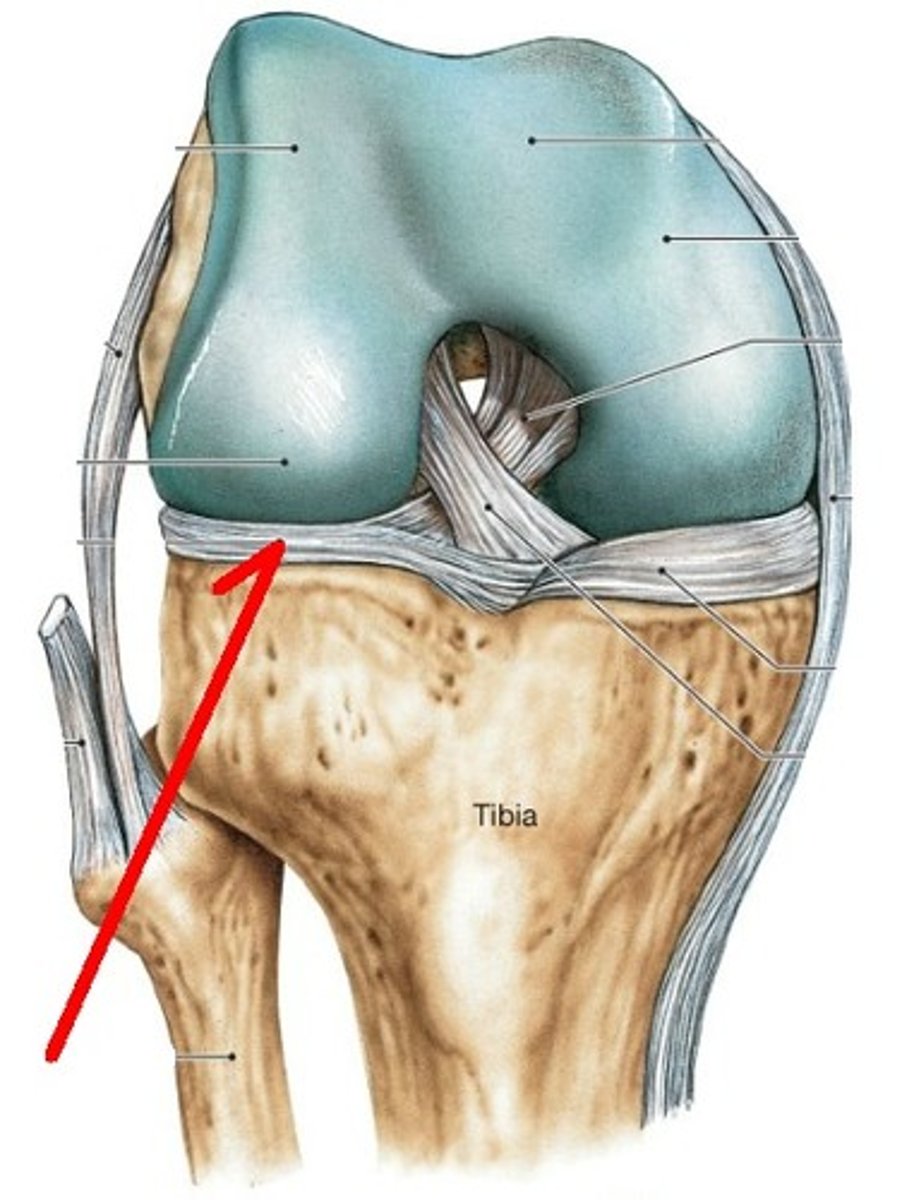
lateral meniscus
- semicircular cartilage on the superior surface of the lateral tibial condyle
- acts as a "shock absorber" for the knee joint
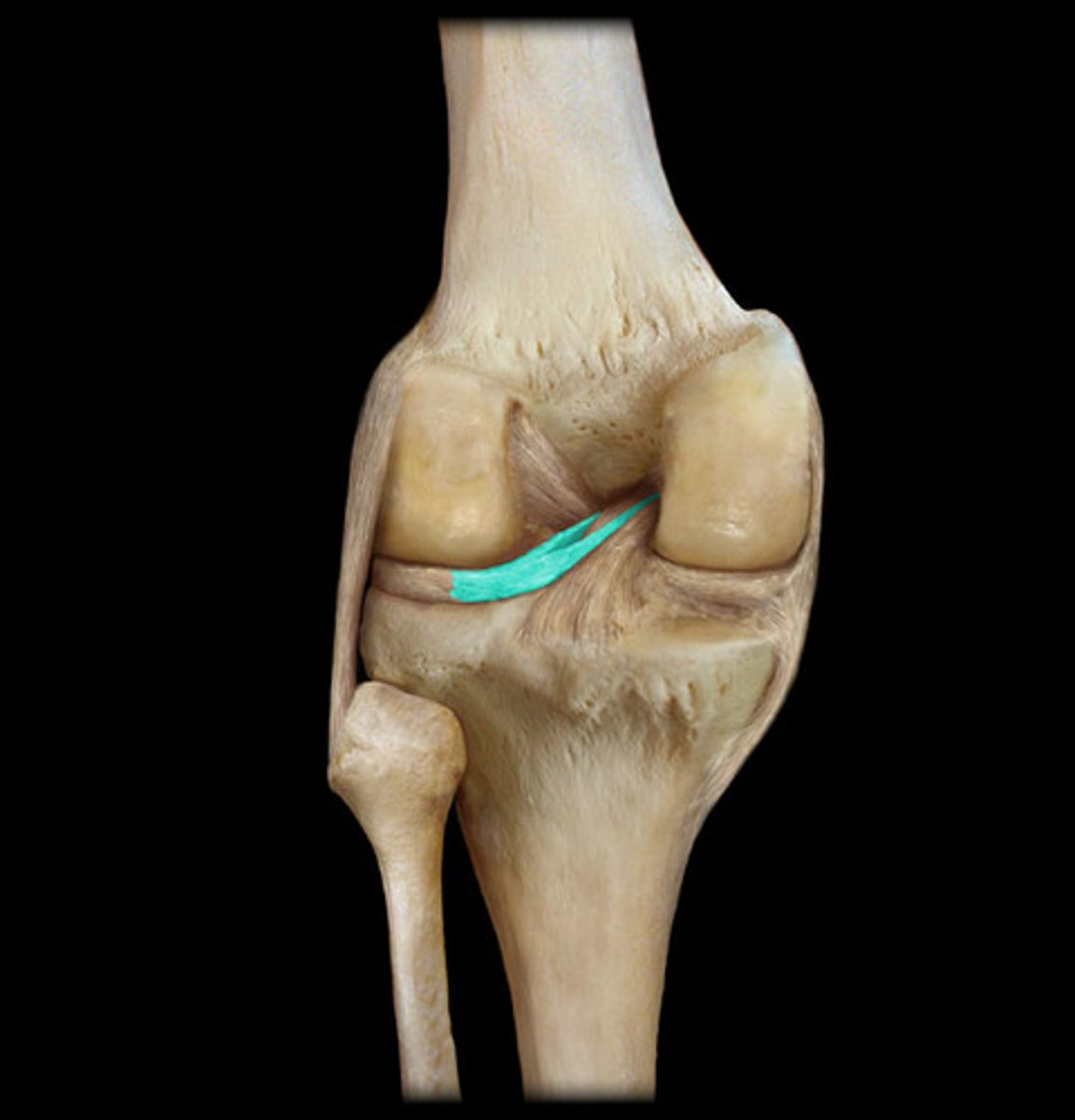
posterior meniscofemoral ligament
- ligament between the lateral meniscus and medial condyle of the femur
- fibrous band on the posterior knee
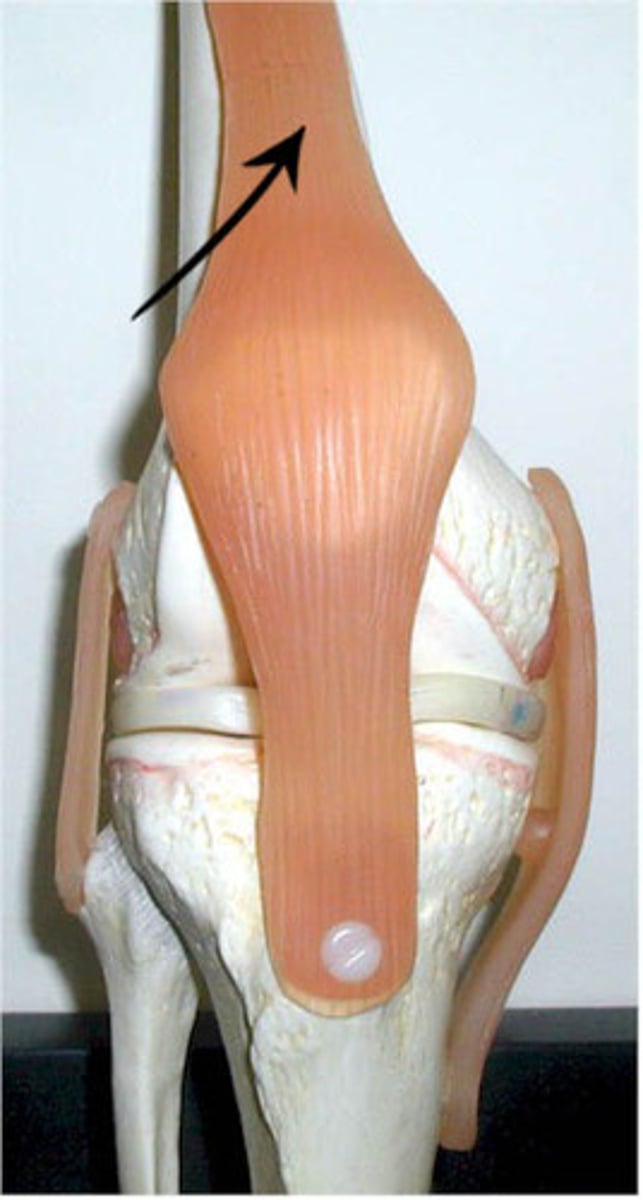
quadriceps tendon
- connecting the quadriceps muscles to the patella
- common insertion of the four quadriceps muscles
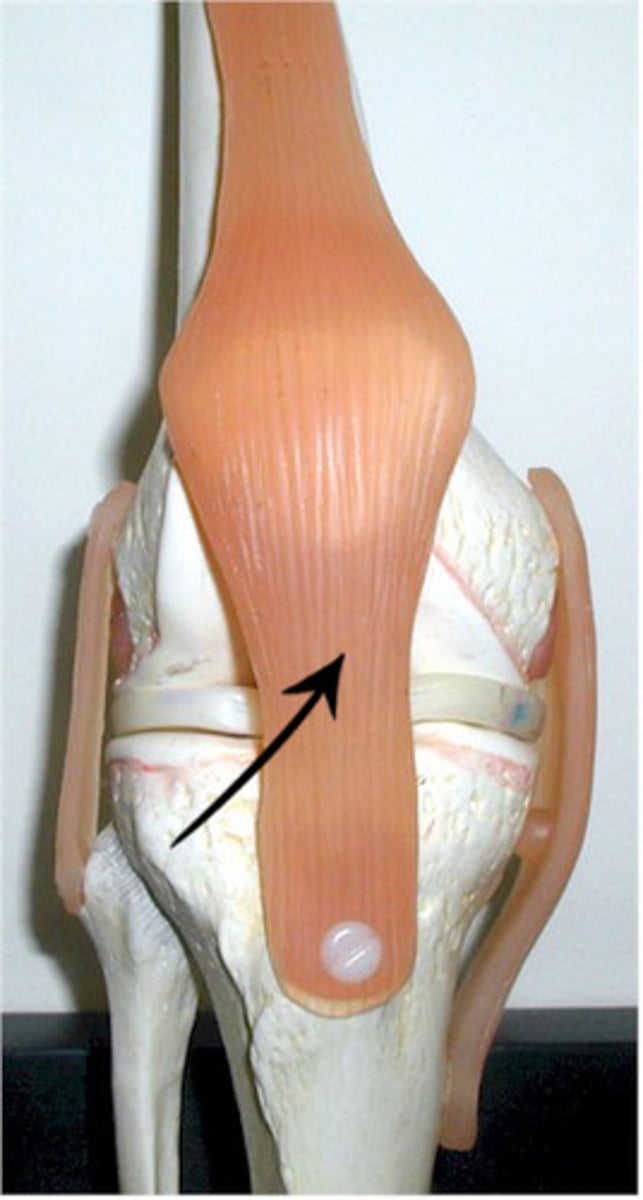
patellar ligament
- ligament between the patella and tibial tuberosity
- distal continuation of the quadriceps tendon
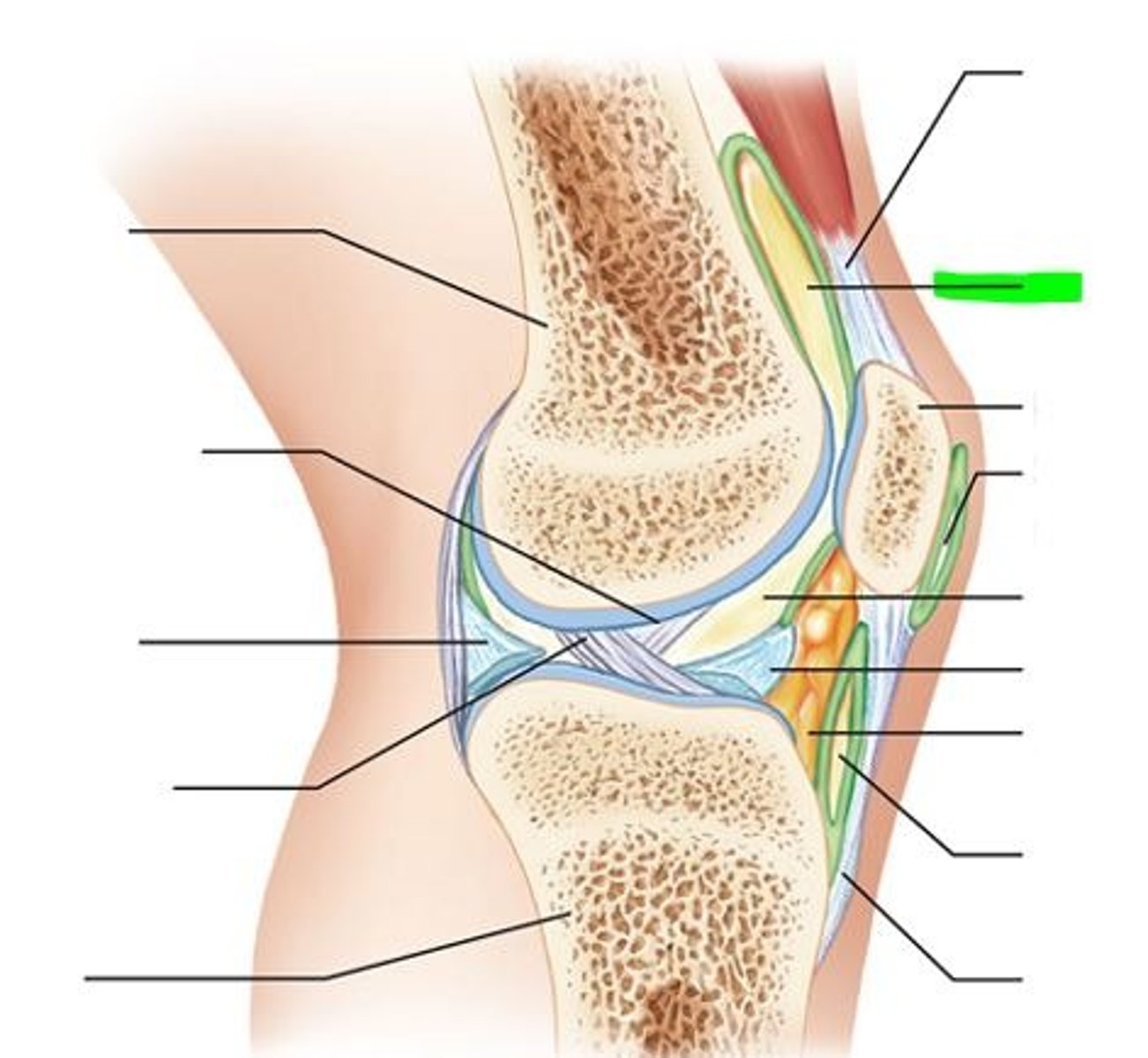
suprapatellar bursa
- large bursa between the anterior surface of the femur and the quadriceps tendon
- allows for movement of the quadriceps tendon
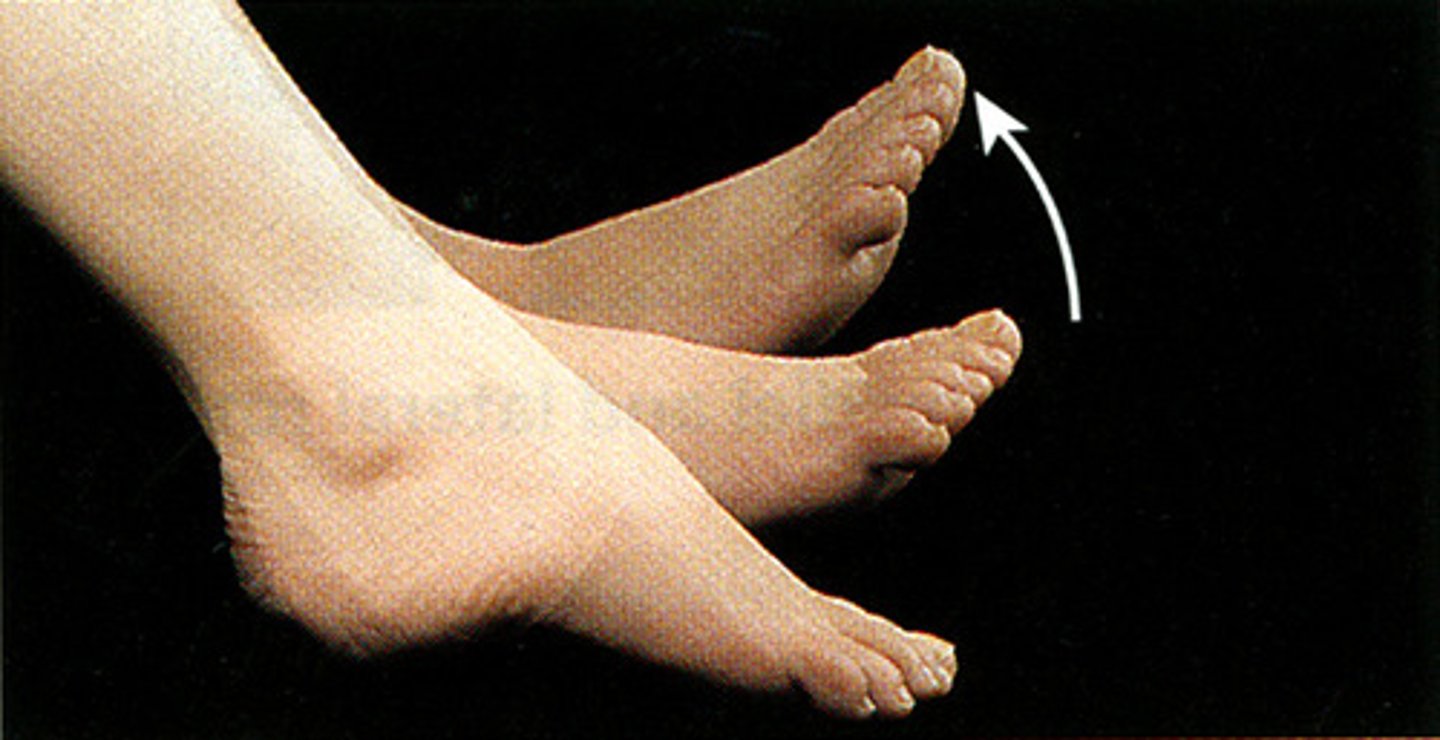
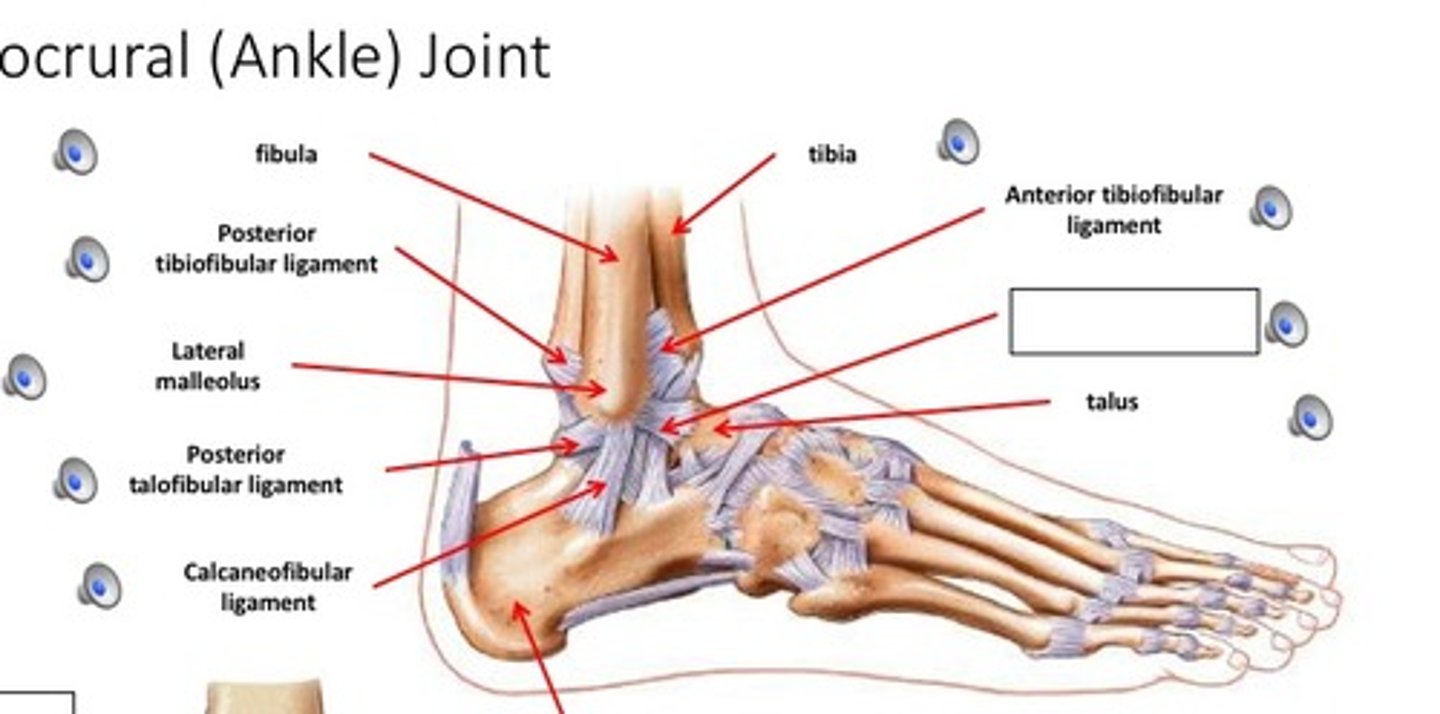
ankle joint
- articulation of the distal ends of the tibia and fibula with the superior surface of the talus
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits plantarflexion/dorsoflexinon of the ankle
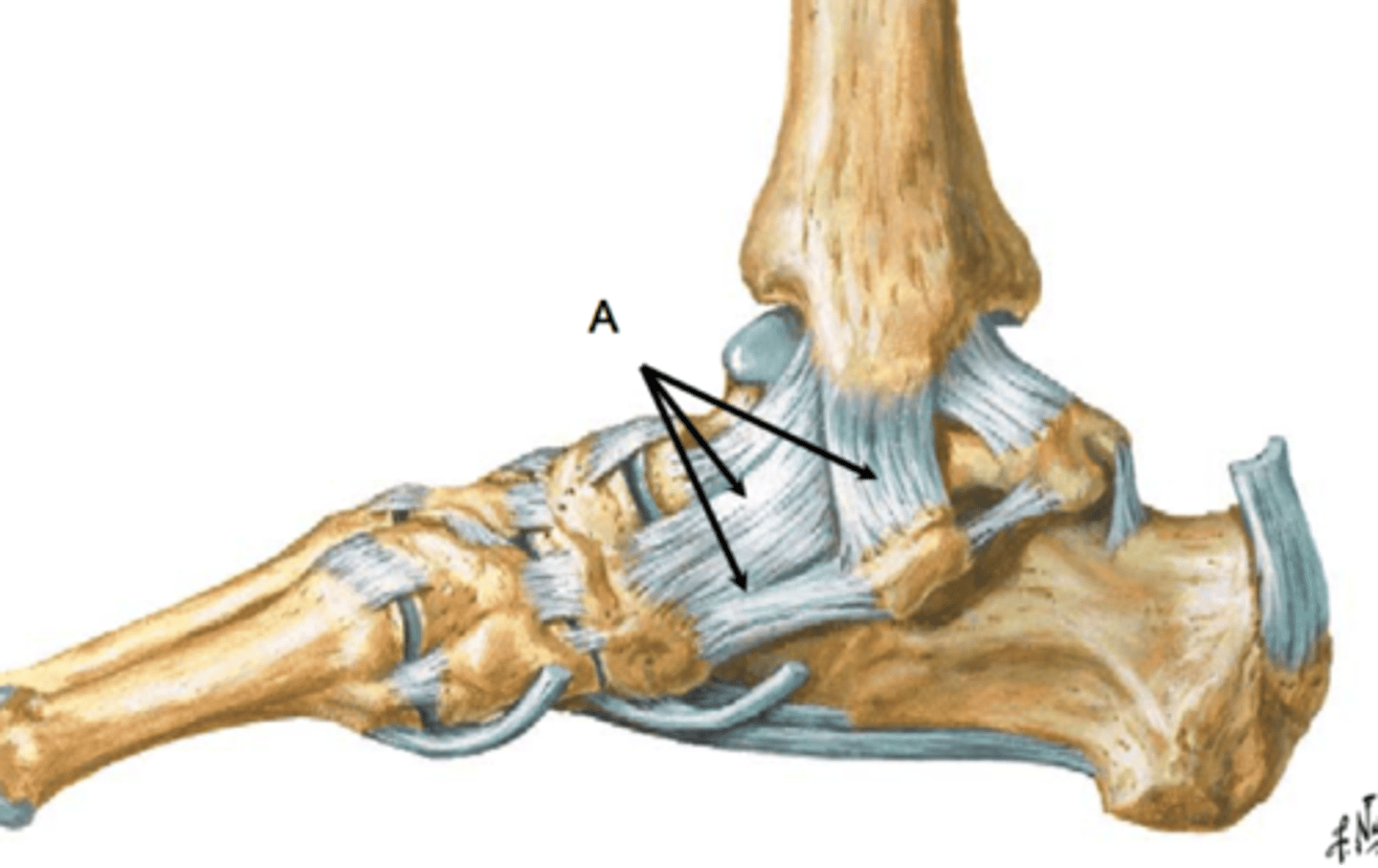
deltoid ligament
- fan-shaped ligament running from the medial malleolus of the tibia to the talus, navicular, and calcaneus
- broad, medial, extra capsular ligament of the ankle
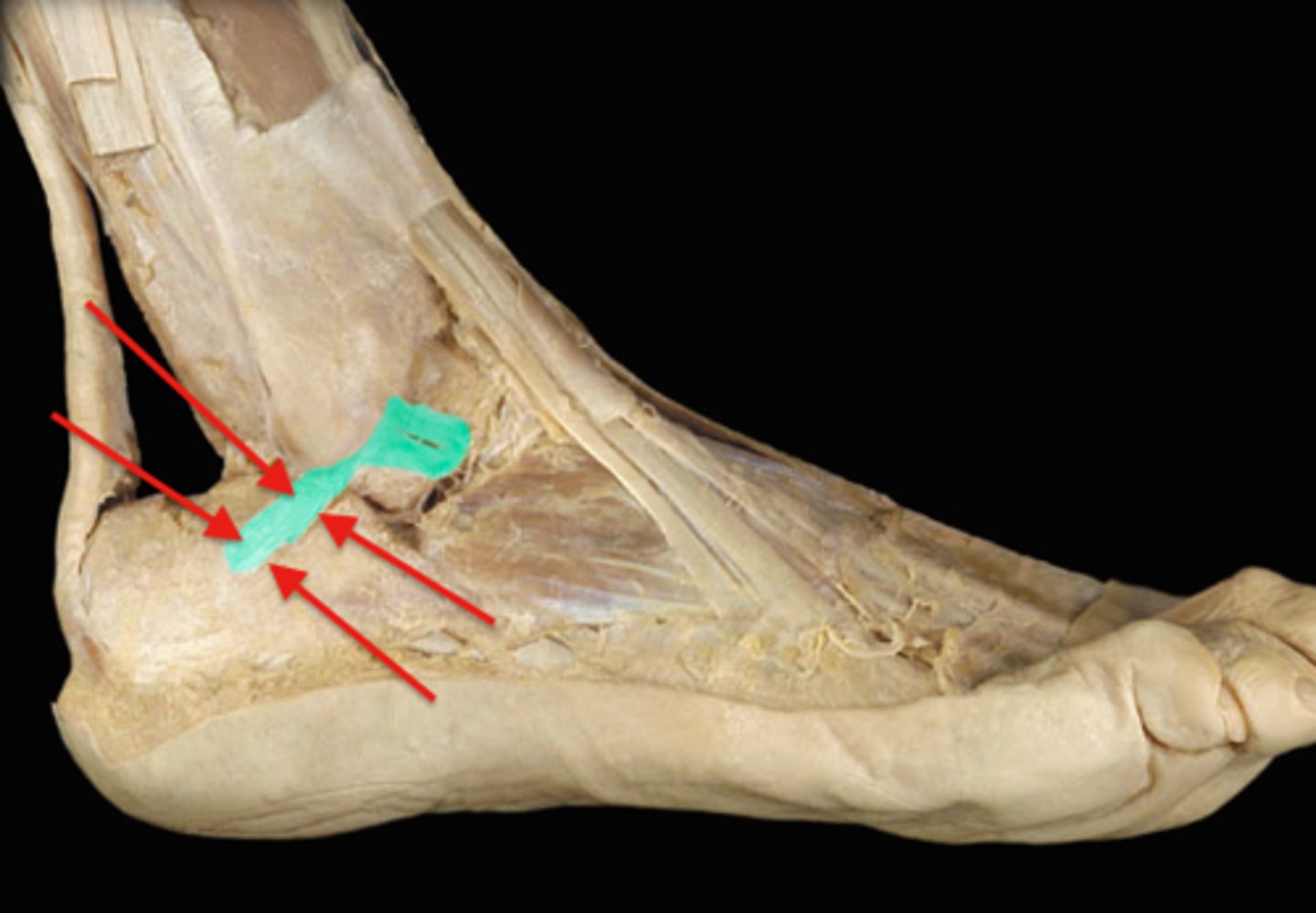
calcaneofibular ligament
- ligament running from the lateral surface of the calcaneus to the lateral malleolus of the fibula
- smaller, lateral extra capsular ligament of the ankle
- covered by the fibulas longs and braves tendons
posterior talofibular ligament
- ligament running from the posterior aspect of the talus to the fibula
- horizontal band between the posterior talus and fibula
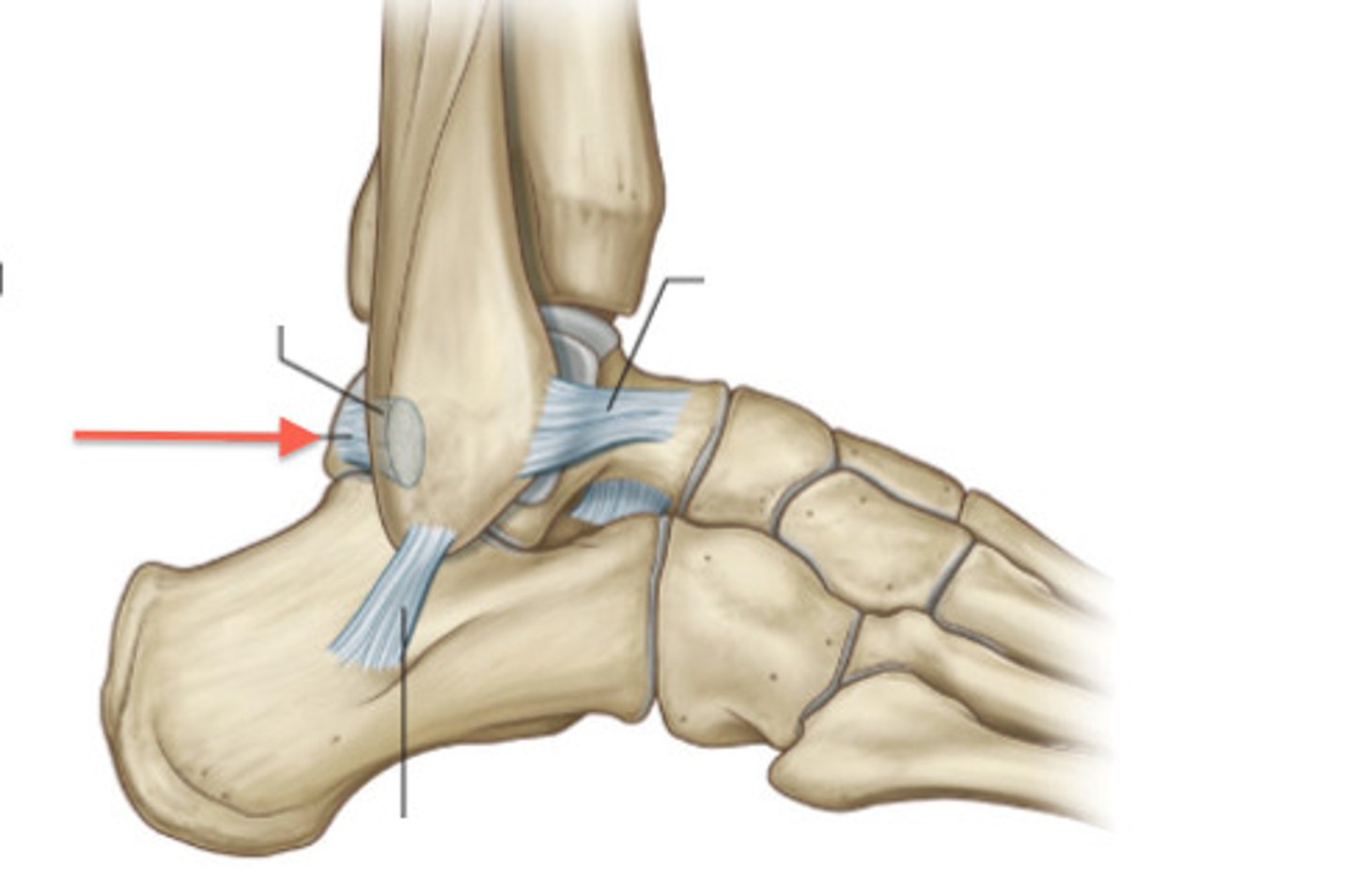
anterior talofibular ligament
- ligament running from the anterior aspect of the talus to the fibula
- horizontal band between the anterior talus and fibula
- most commonly injured ligament in a sprained ankle
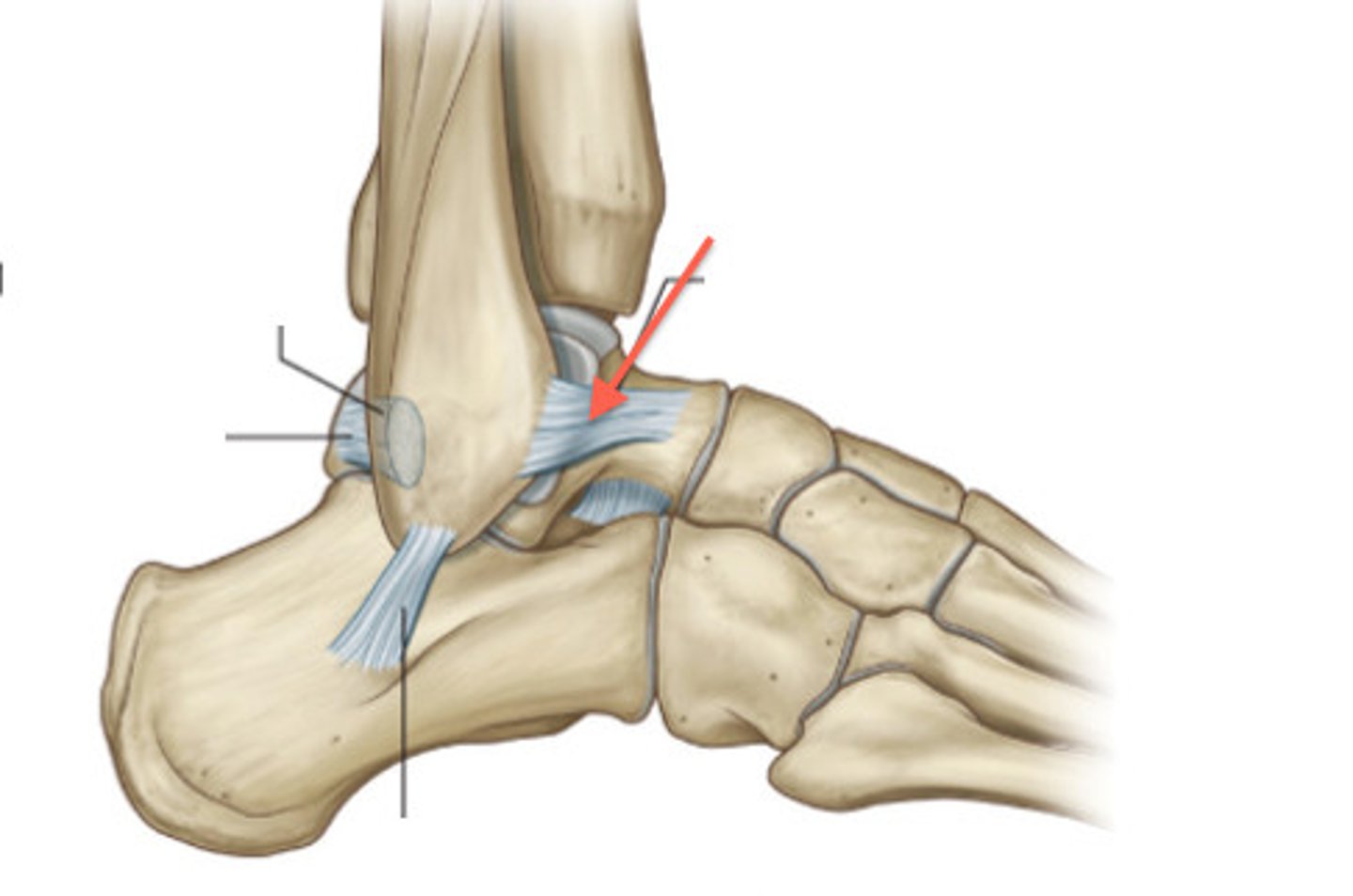
posterior tibiofibular ligament
- ligament running between the posterior aspects of the tibia and fibula
- thick, triangular band extending obliquely between the posterior tibia and fibula
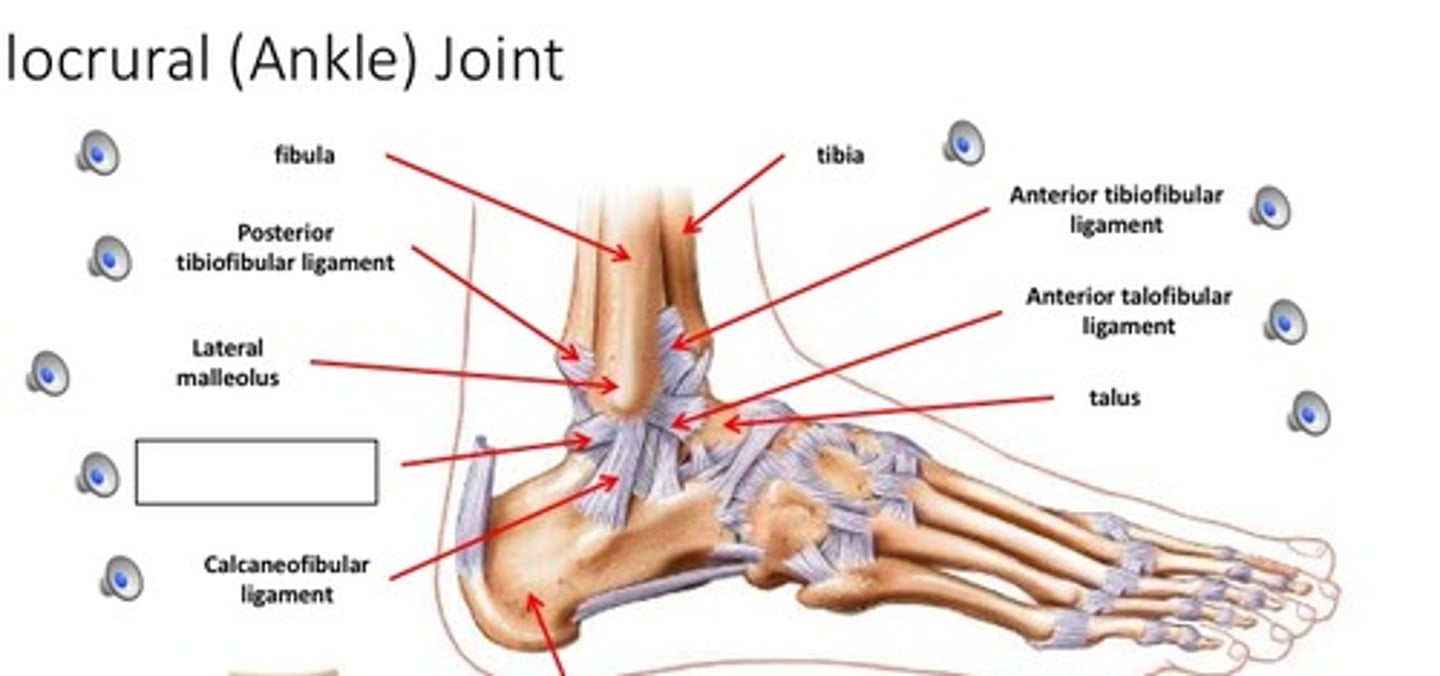
anterior tibiofibular ligament
- ligament running between the anterior aspects of the tibia and fibula
- thick, triangular band extending obliquely between the anterior tibia and fibula
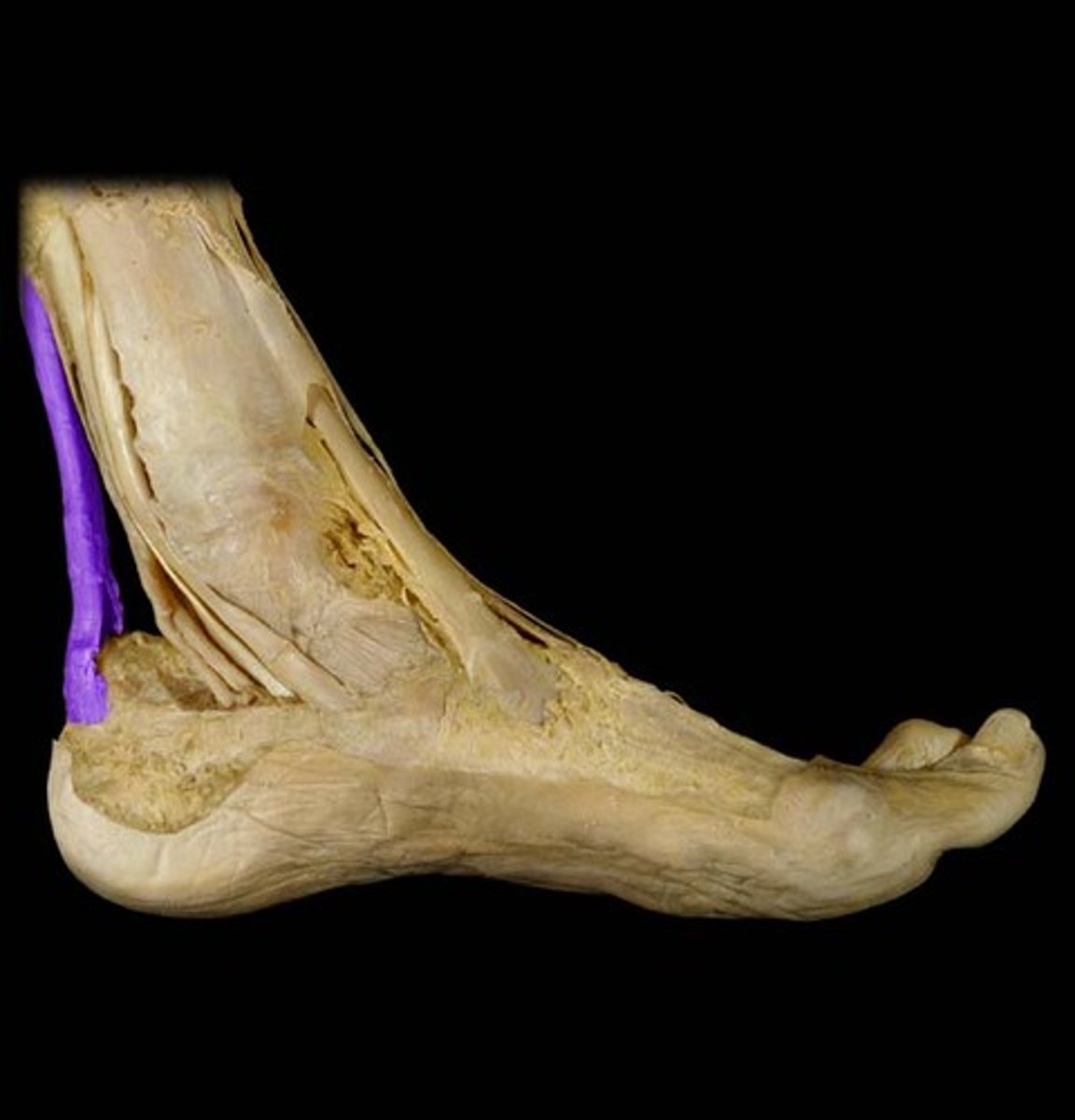
calcaneal tendon
- connecting the gastrocnemius and soles muscles to the calcaneus
- also known as the "achilles" tendon
- strongest tendon of the body
subtalar joint
- articulation of the inferior surface of the talus with the superior surface of the calcaneus
- plane type of synovial joint
- permits inversion/eversion of the foot
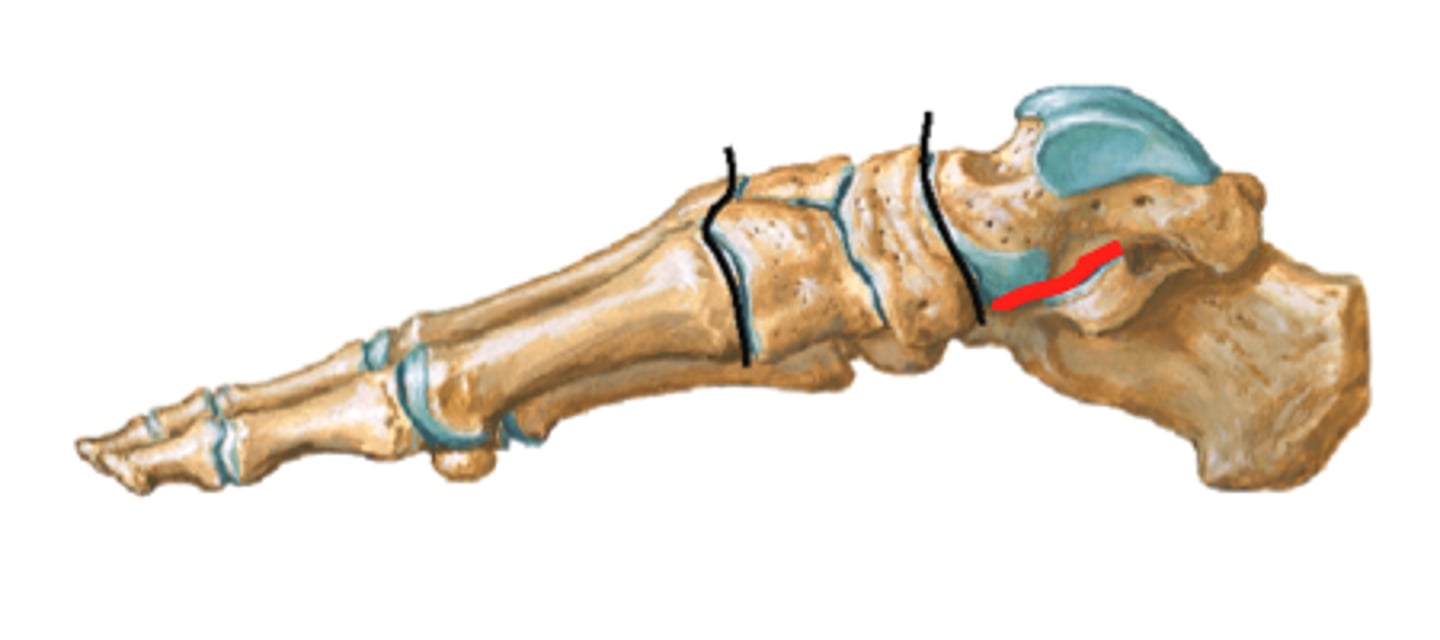
tarsometatarsal joints
- articulations of the tarsal bones with the metatarsals
- plane type of synovial joint
- permits gliding movements of the tarsal bones
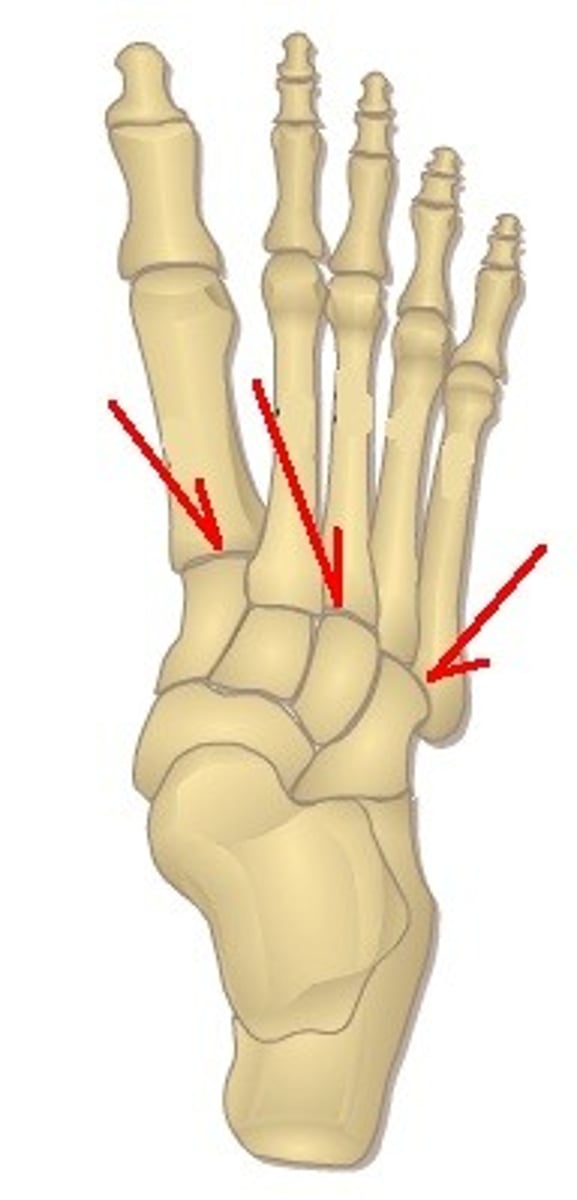
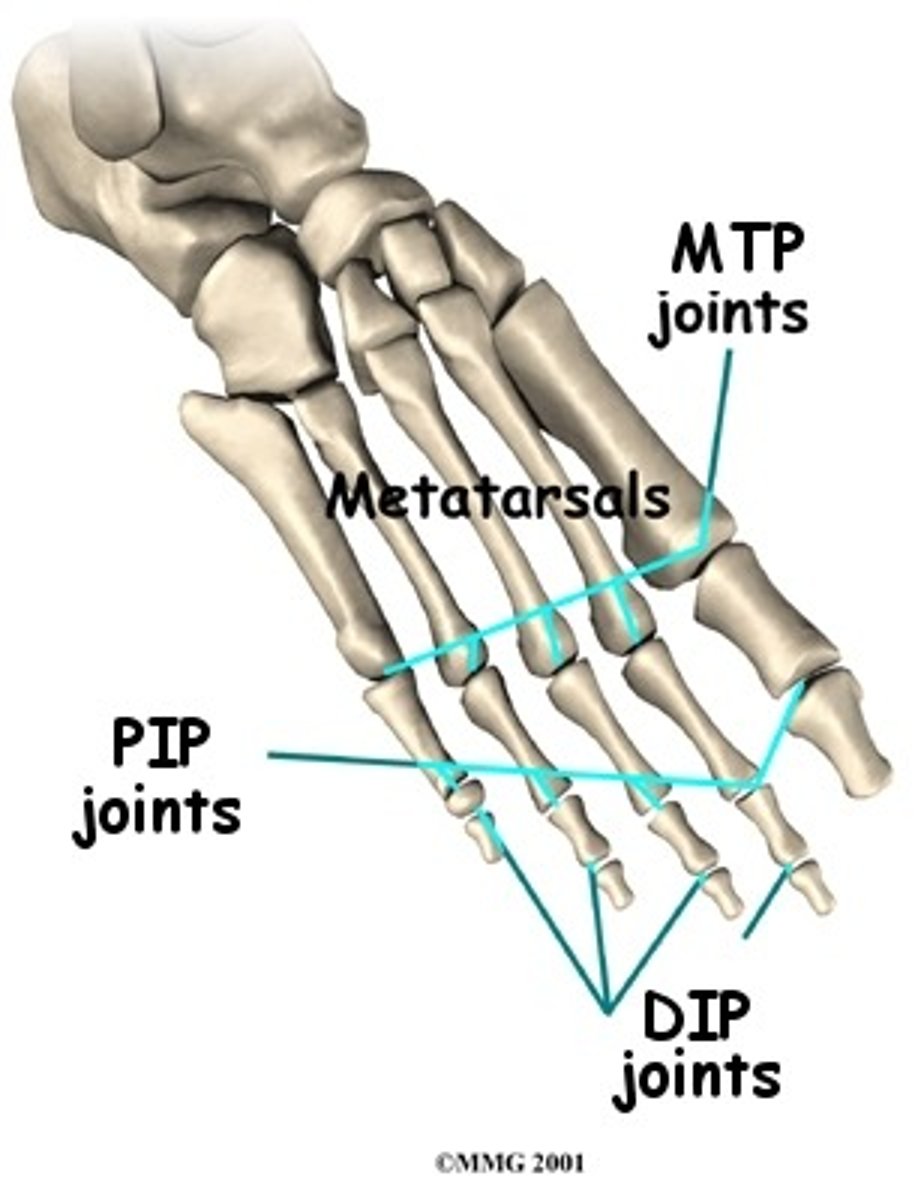
metatarsophalangeal joint
- articulation of the metatarsals with the proximal phalanges
- condyloid type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension and abduction/adduction of the digits
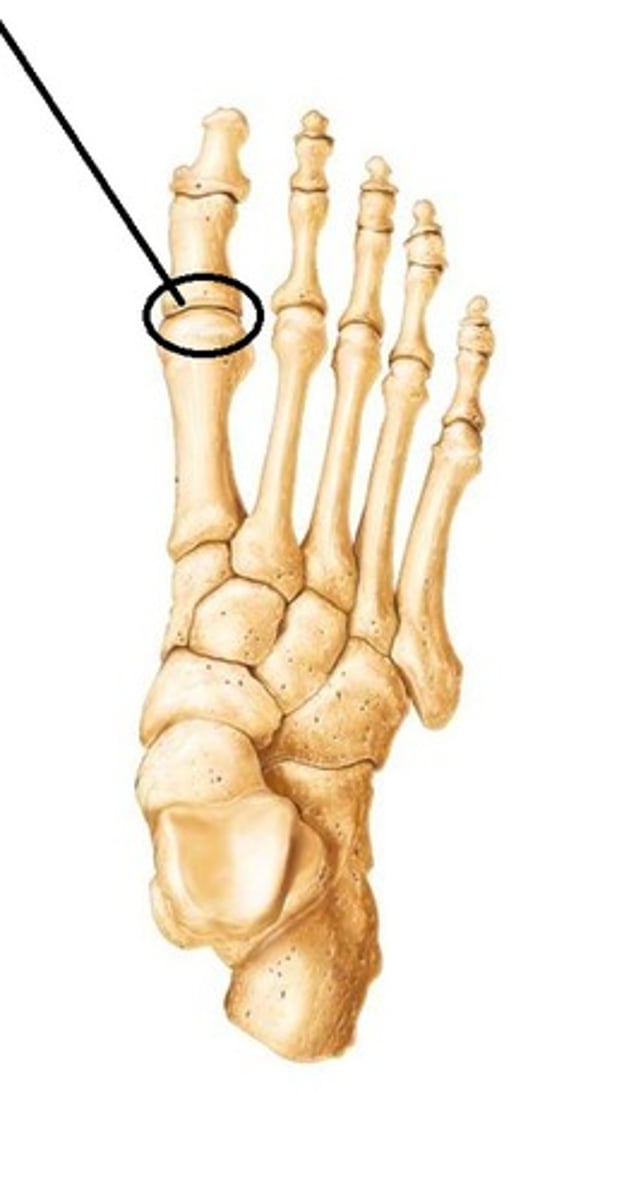
proximal interphalangeal joints of foot
- articulation of the proximal phalanges with the middle phalanges
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the digits
- only present in digits 2-5
distal interphalangeal joints of foot
- articulation of the middle phalanges with the distal phalanges
- hinge type of synovial joint
- permits flexion/extension of the digits
- digit 1 only has an interphalangeal joint
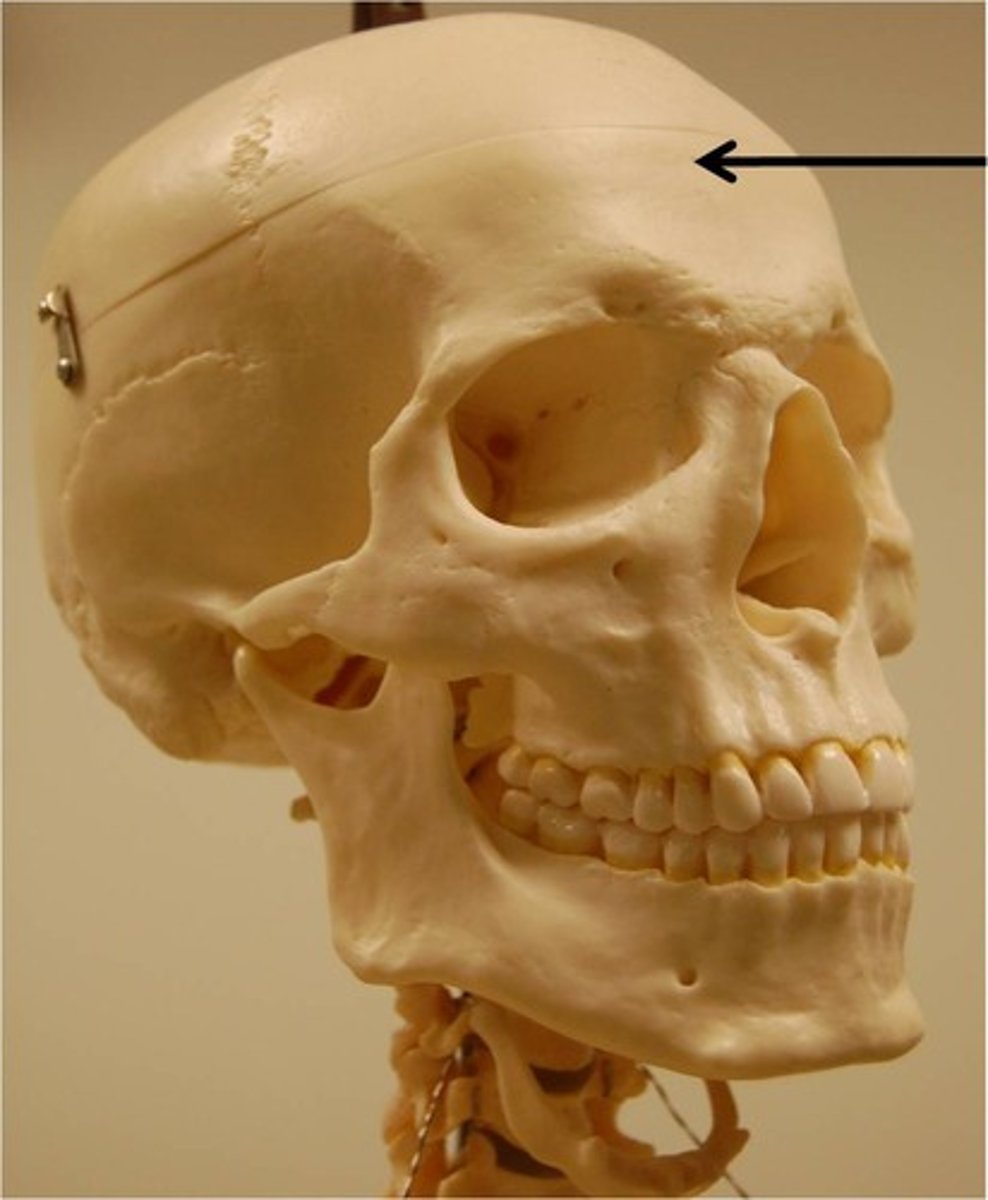
Frontal bone
Name the bone
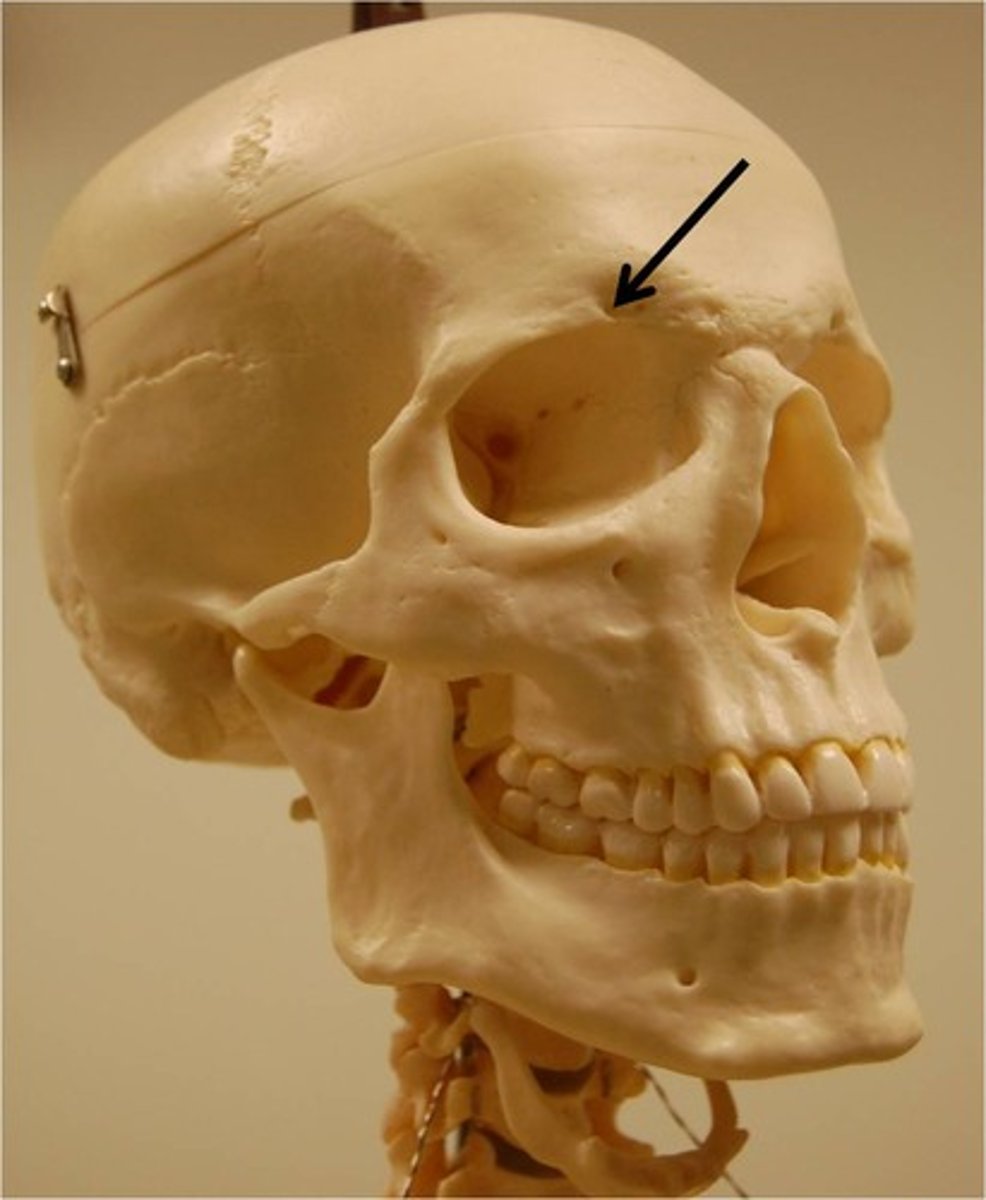
Supraorbital foramen
Name the small space
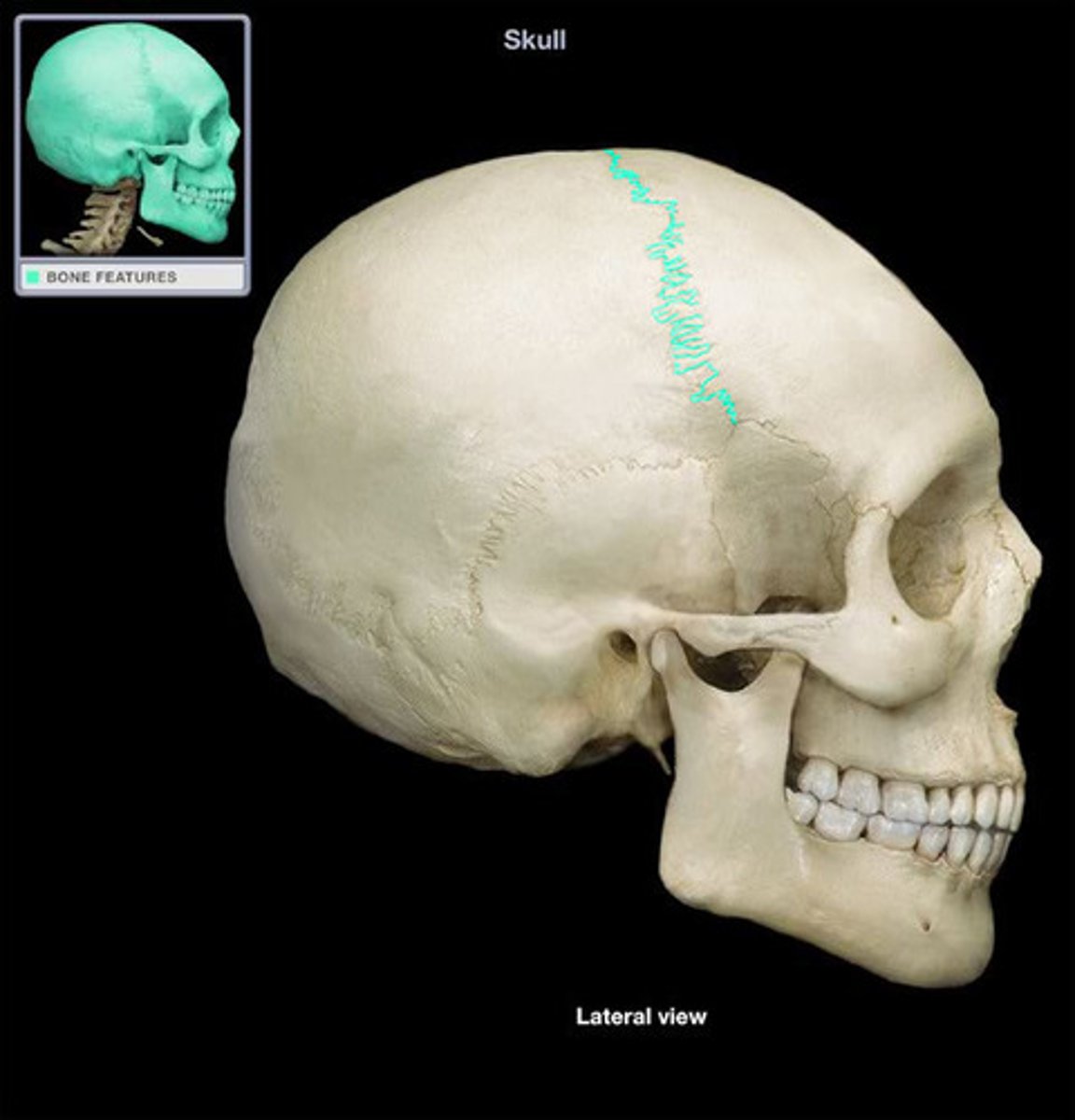
Coronal suture
Name the structure
Parietal bones
Name the bones
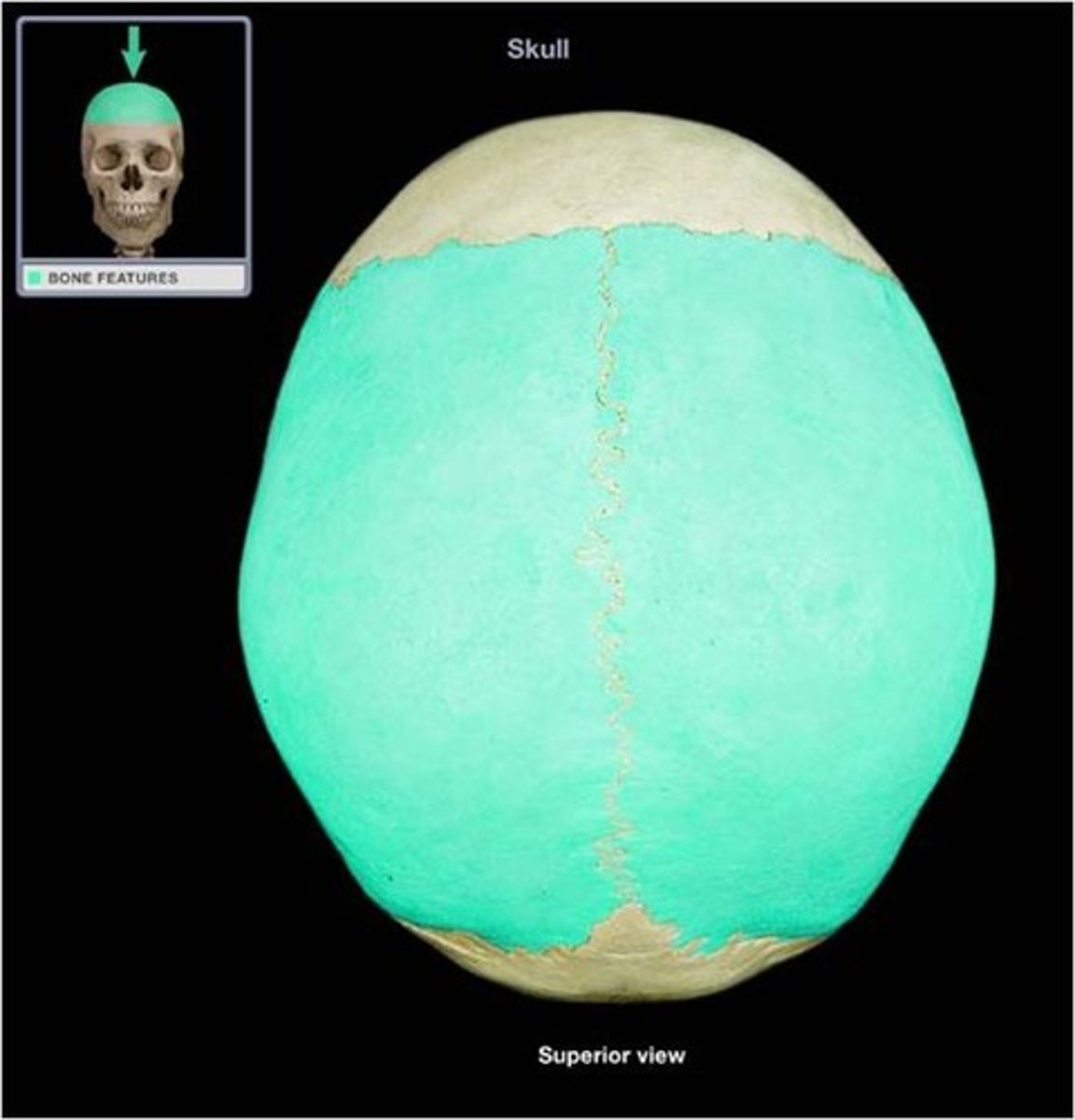
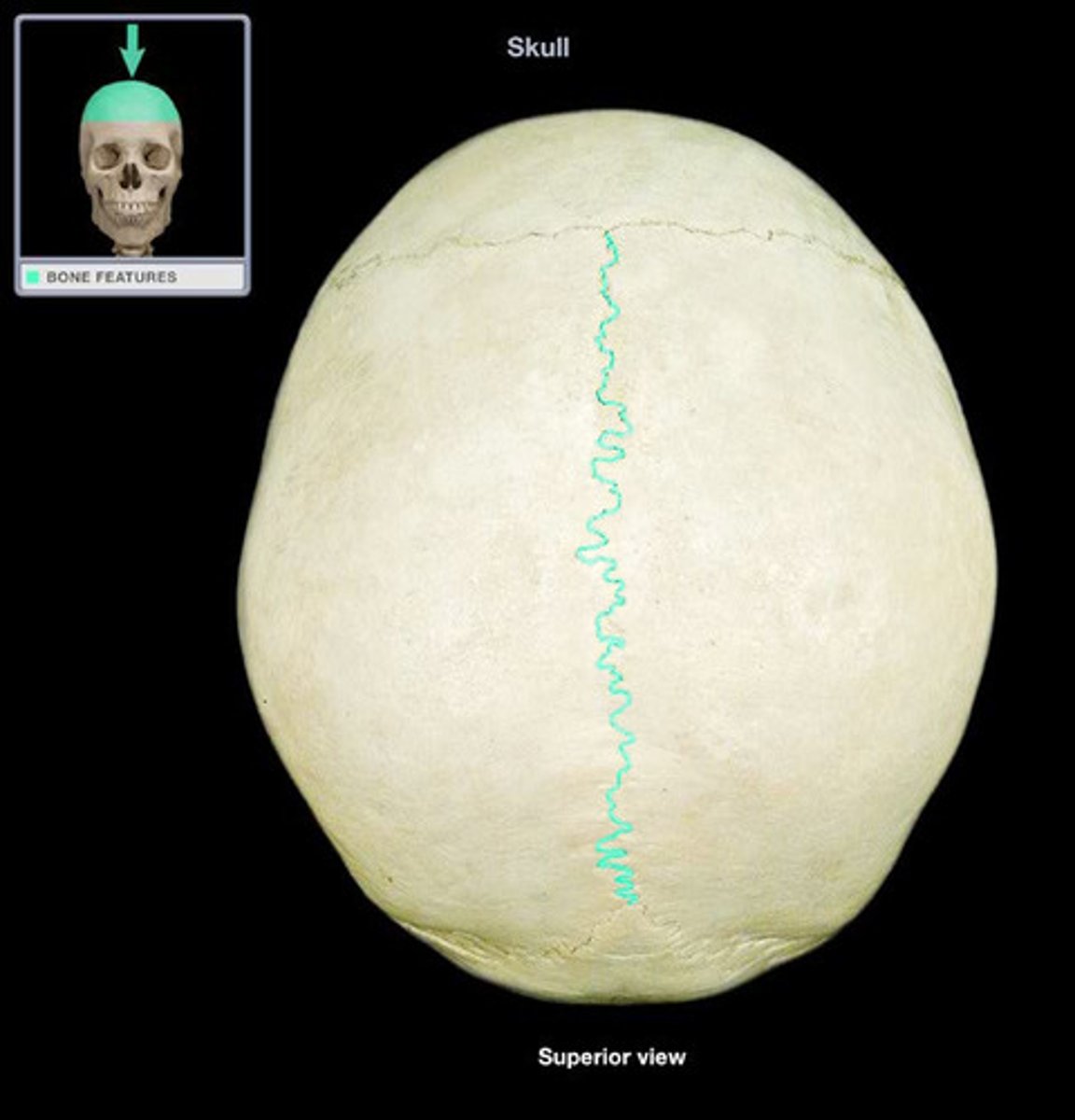
Sagittal suture
Name the structure
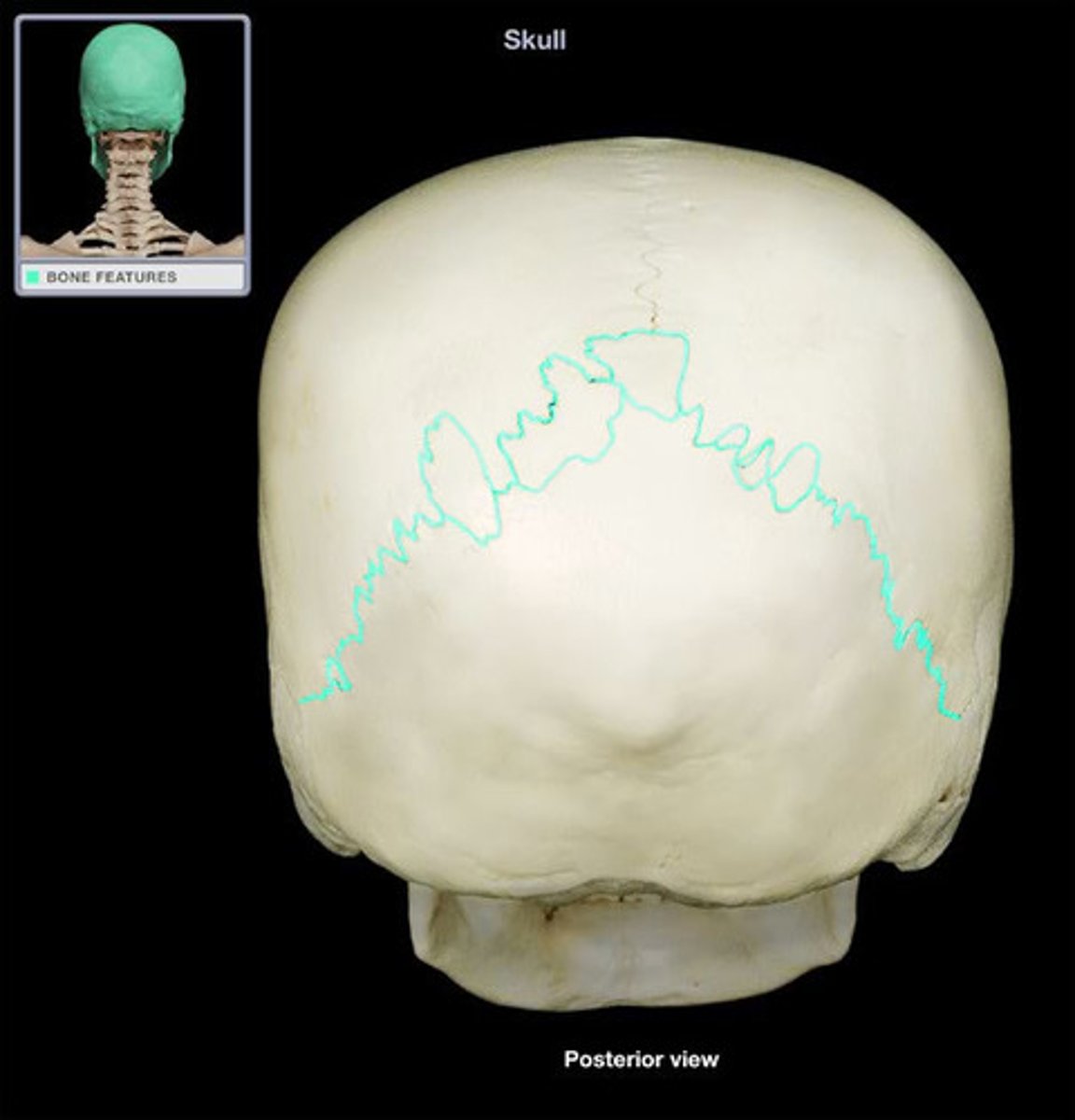
Lambdoid suture
Name the structure
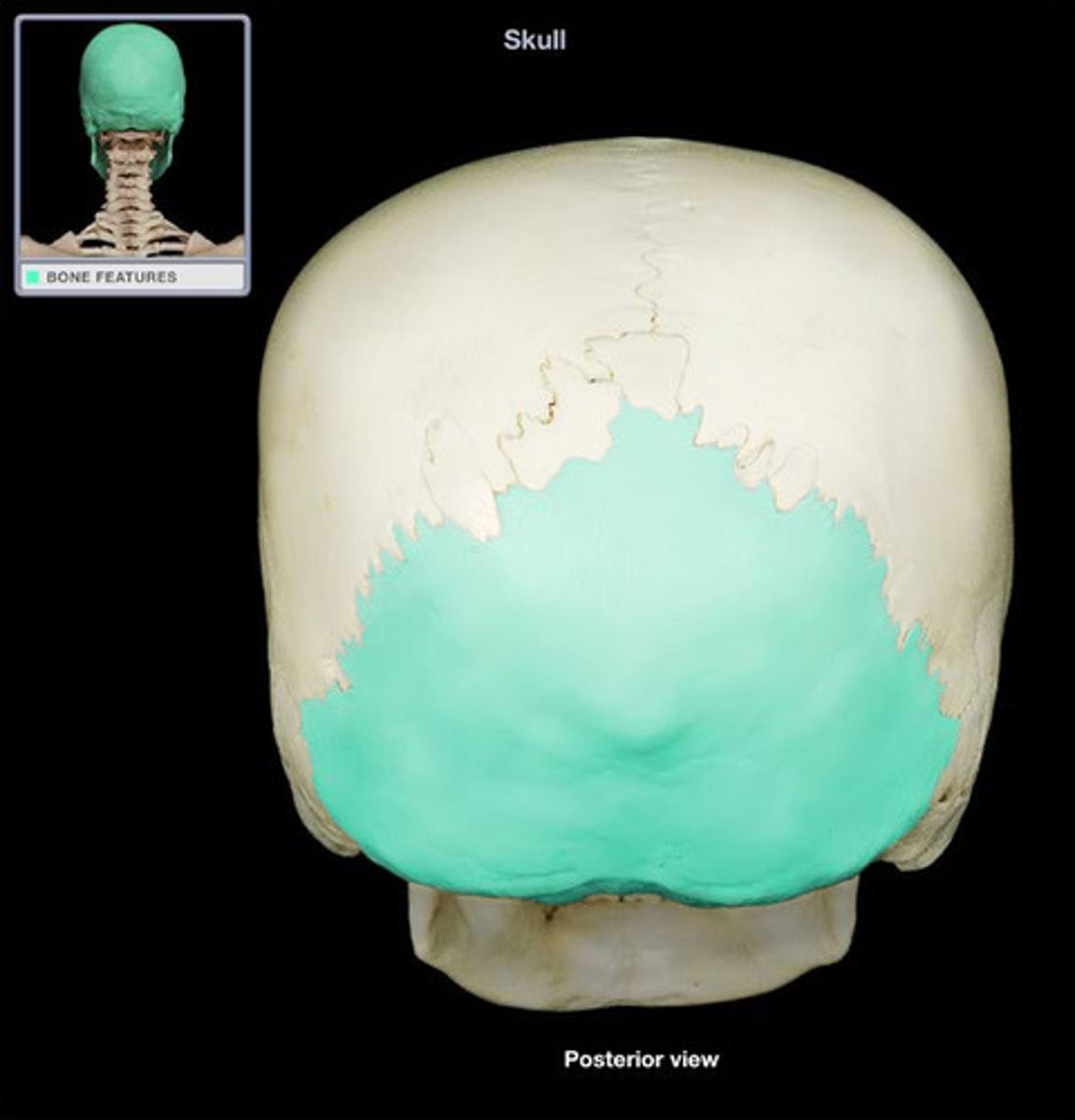
Occipital bone
Name the bone
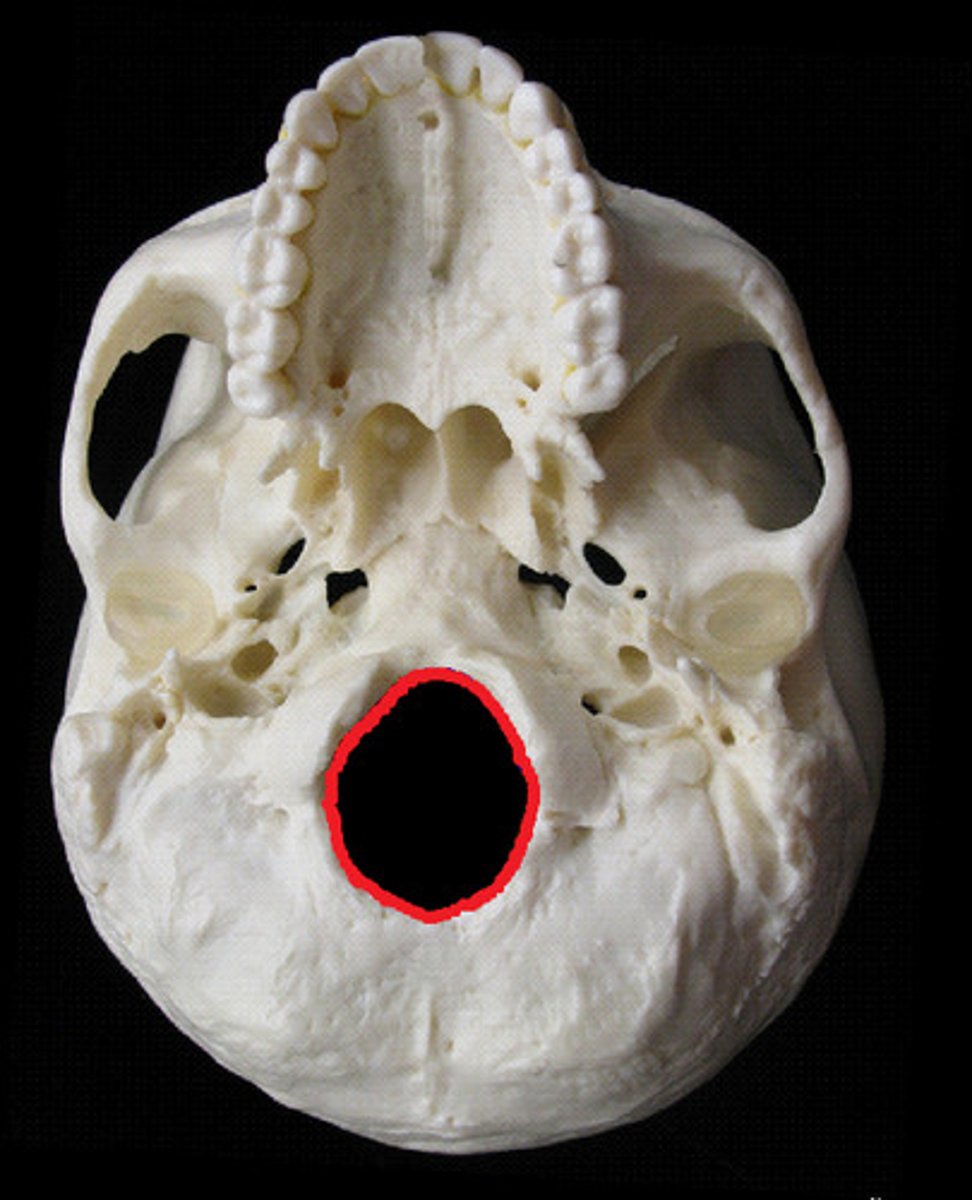
Foramen magnum
Name the space
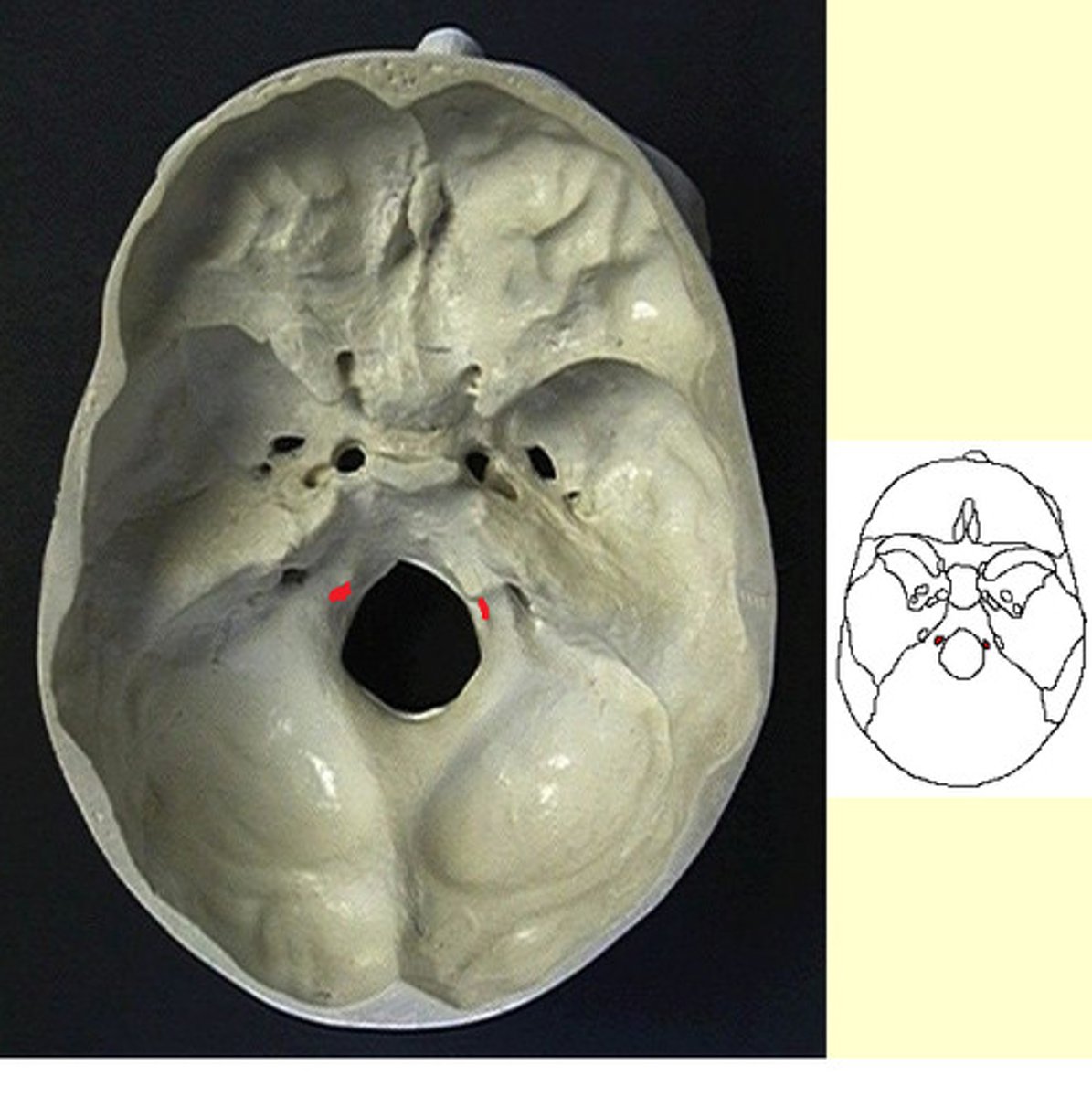
Hypoglossal canal
Name the space
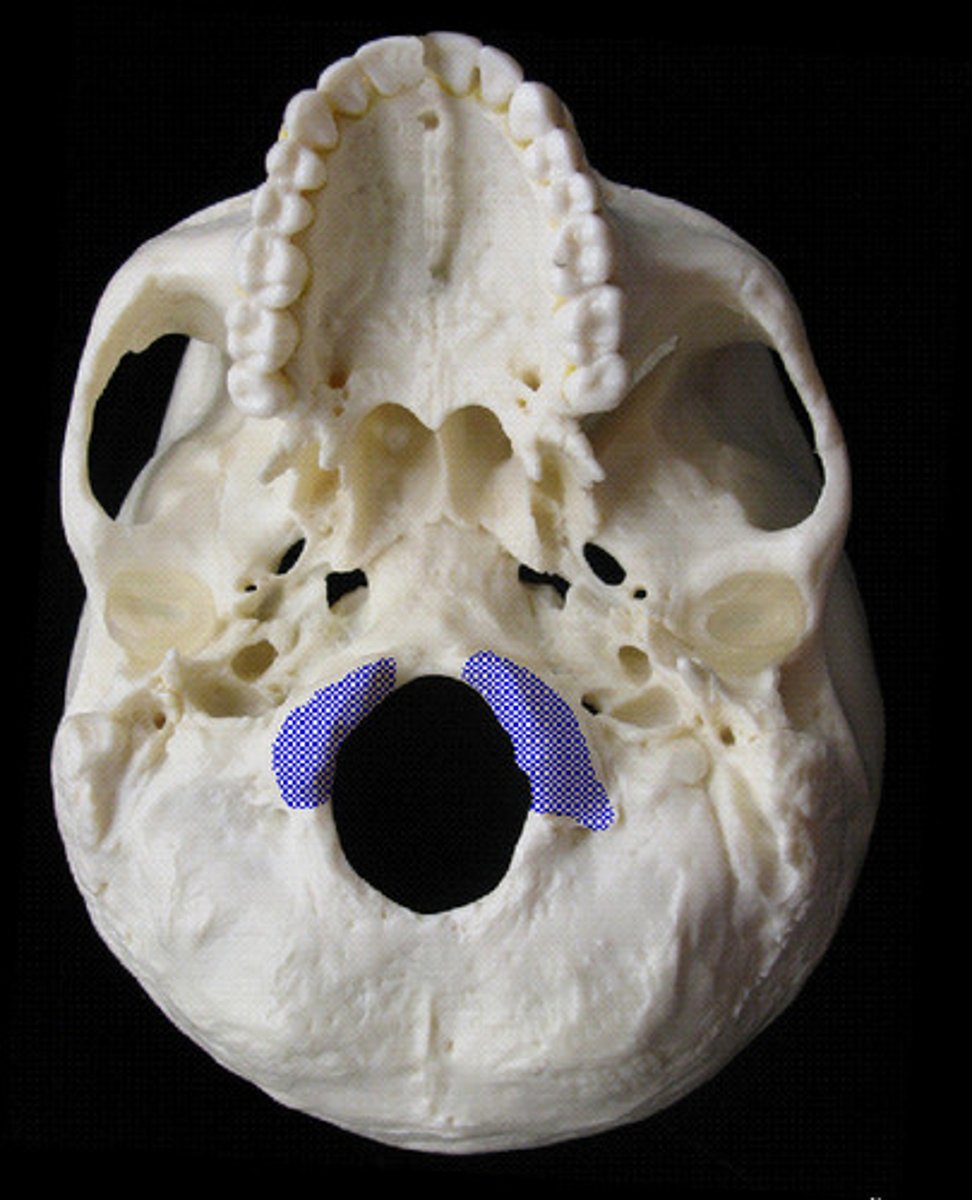
Occipital condyles
Name the structures
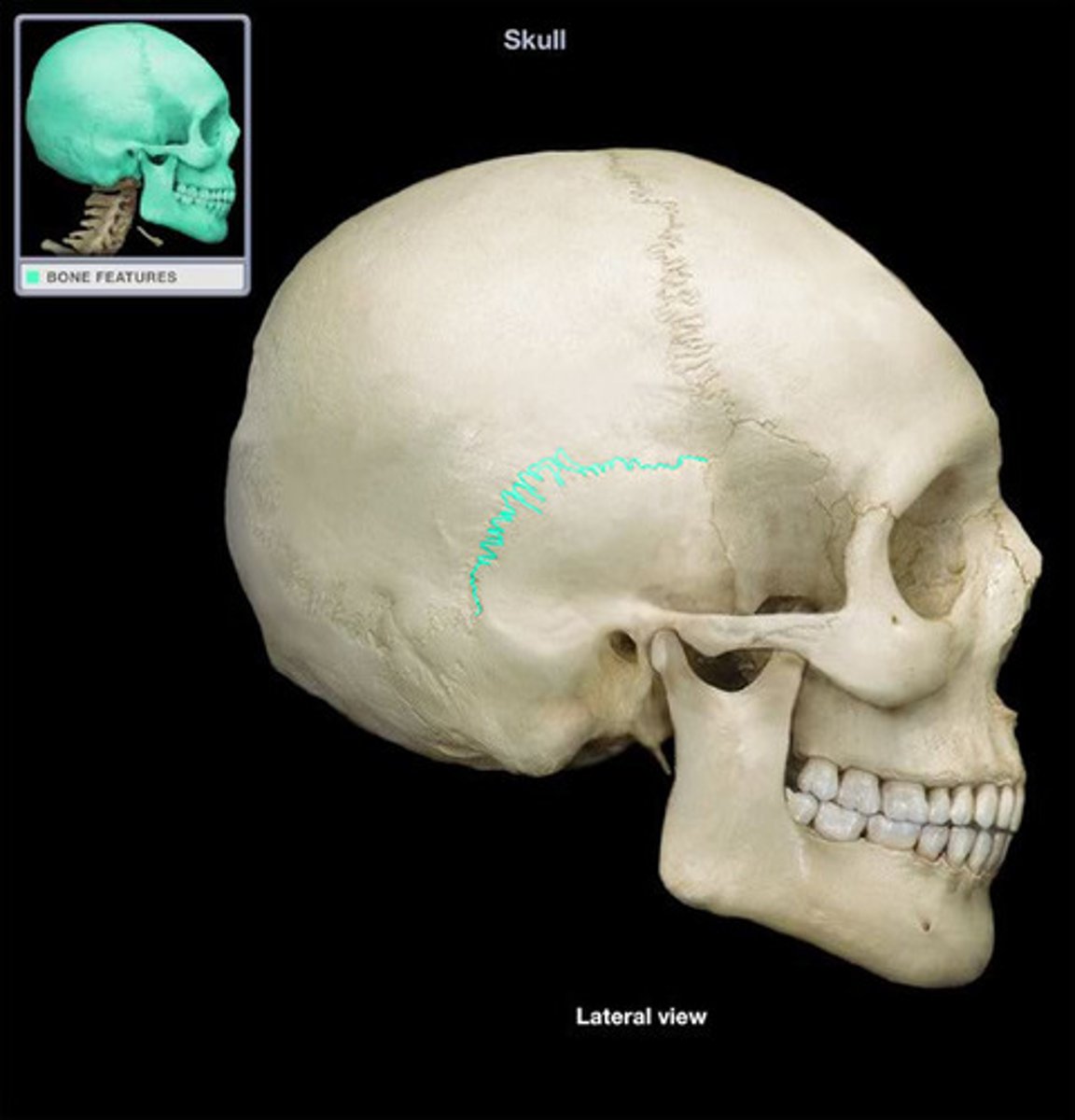
Squamous suture
Name the structure
Temporal bones
Name the bones
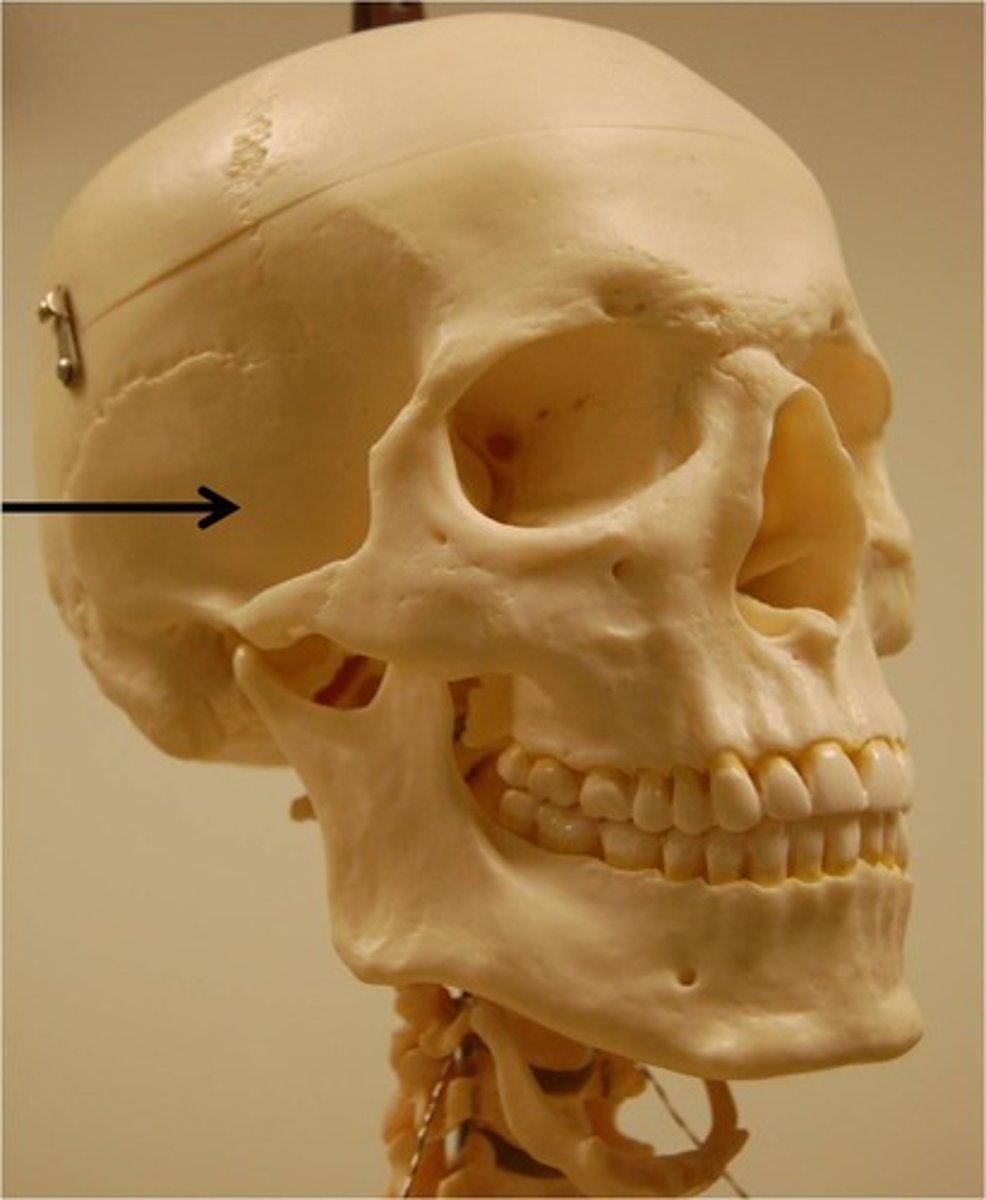
Mastoid process
Name the structure
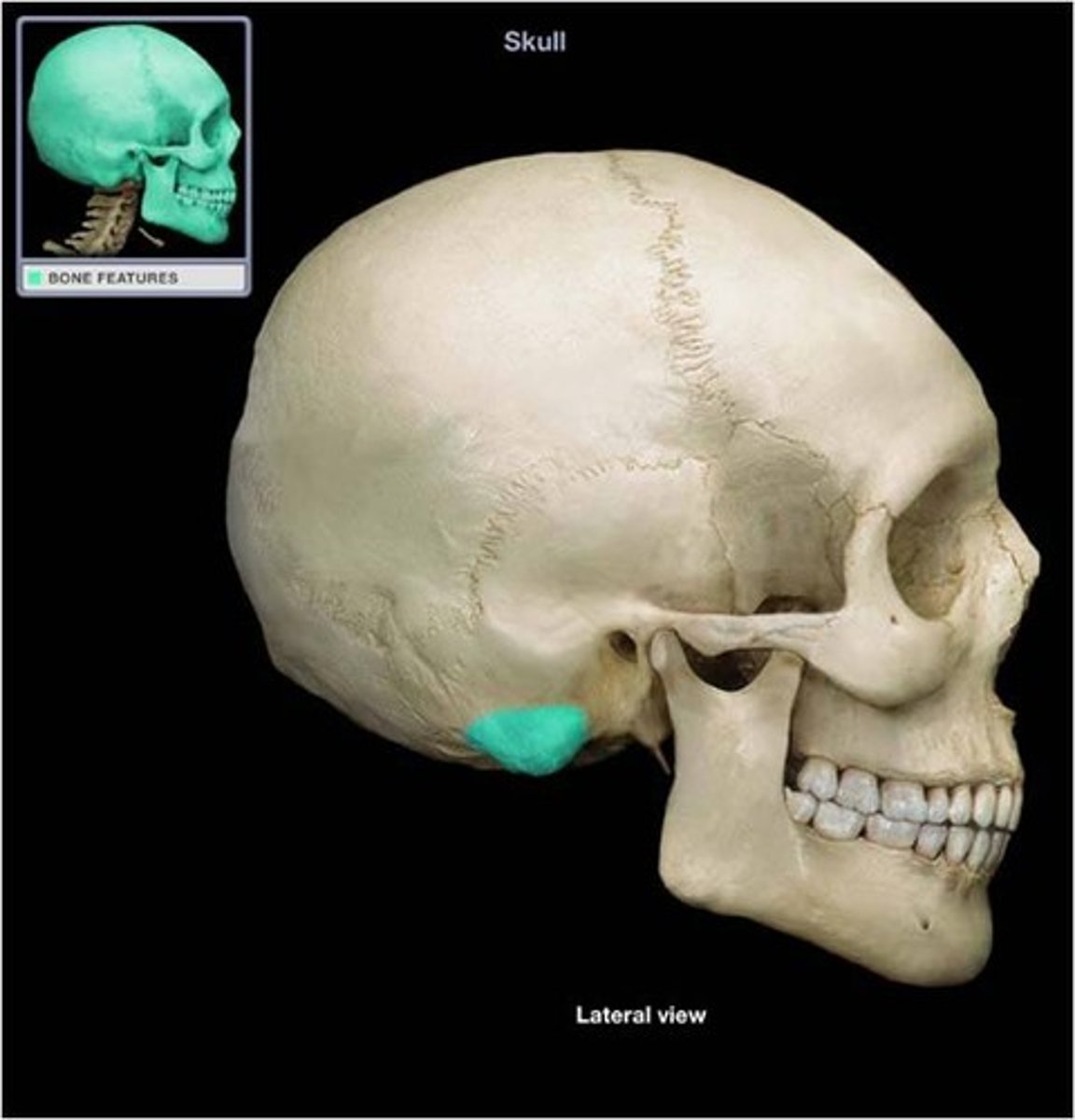
External auditory meatus
Name the space
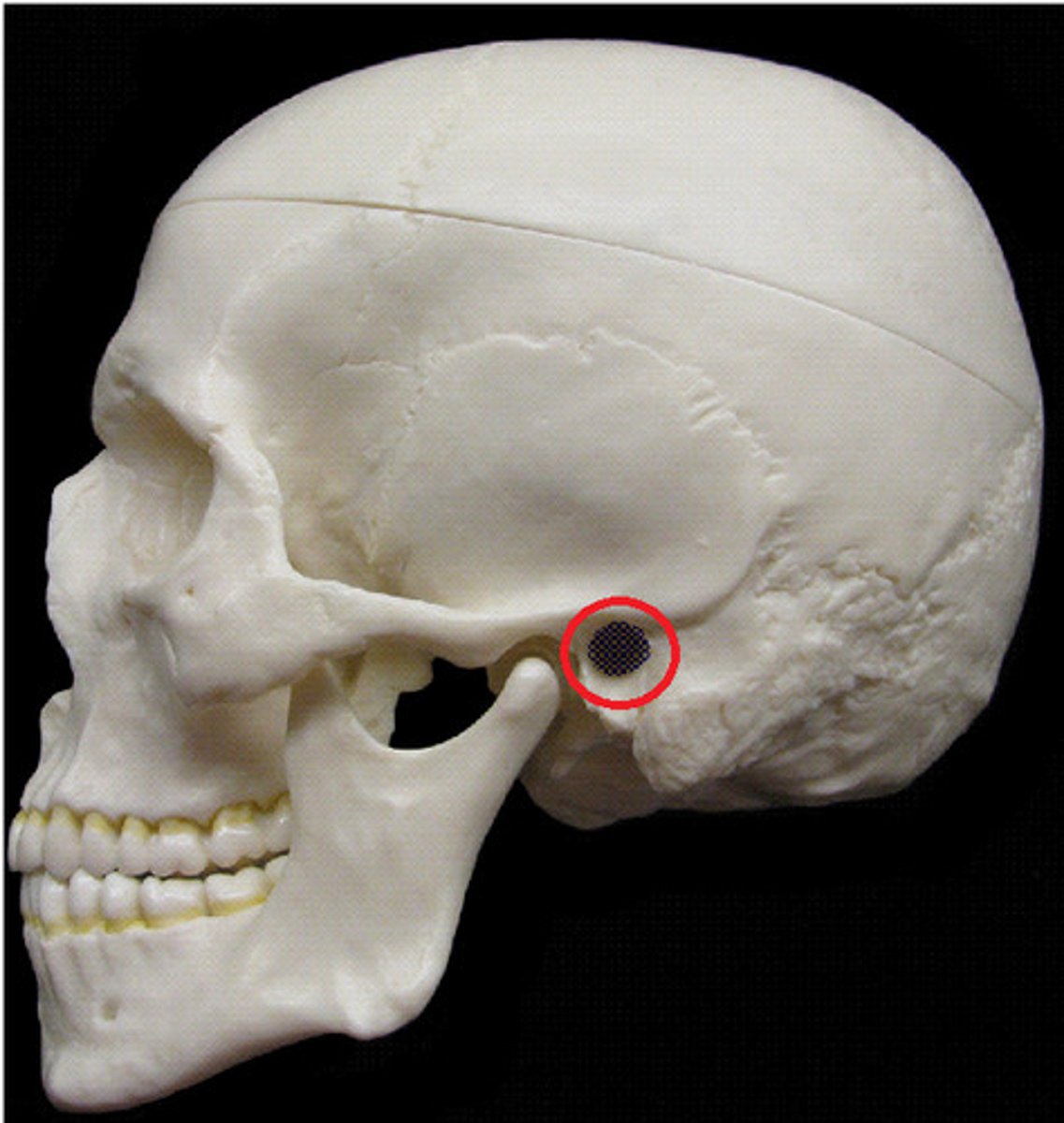
Internal auditory meatus
Name the space
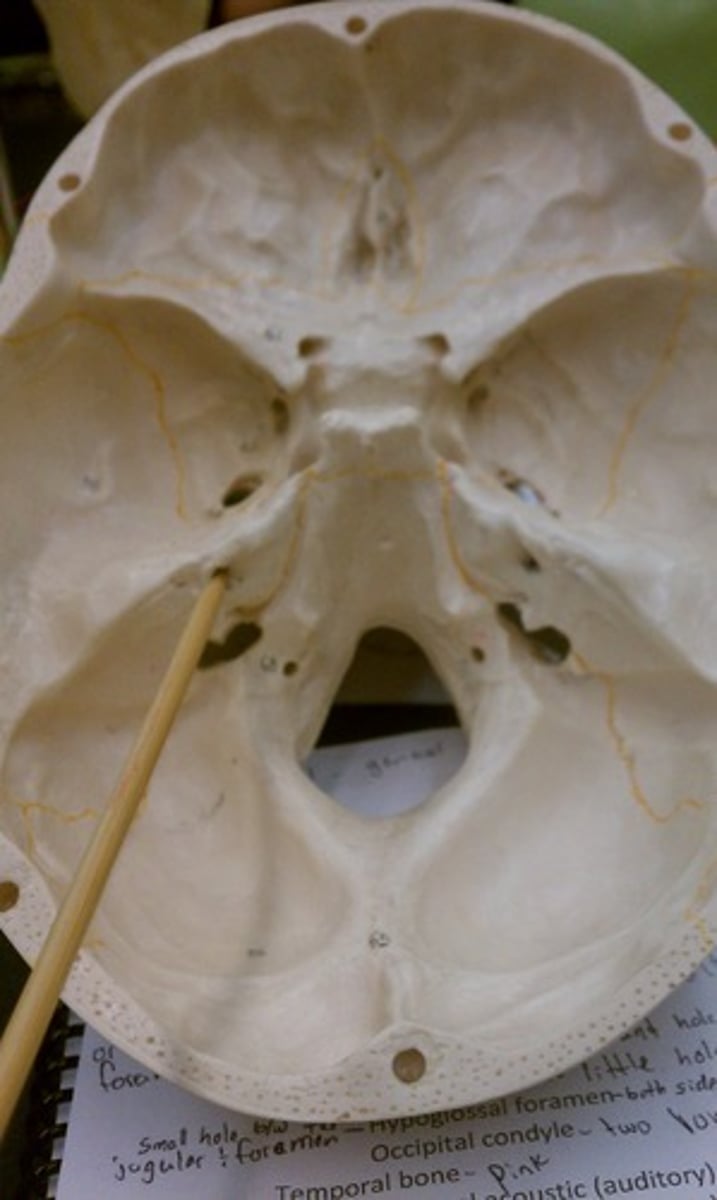
Mandibular fossa
Name the space
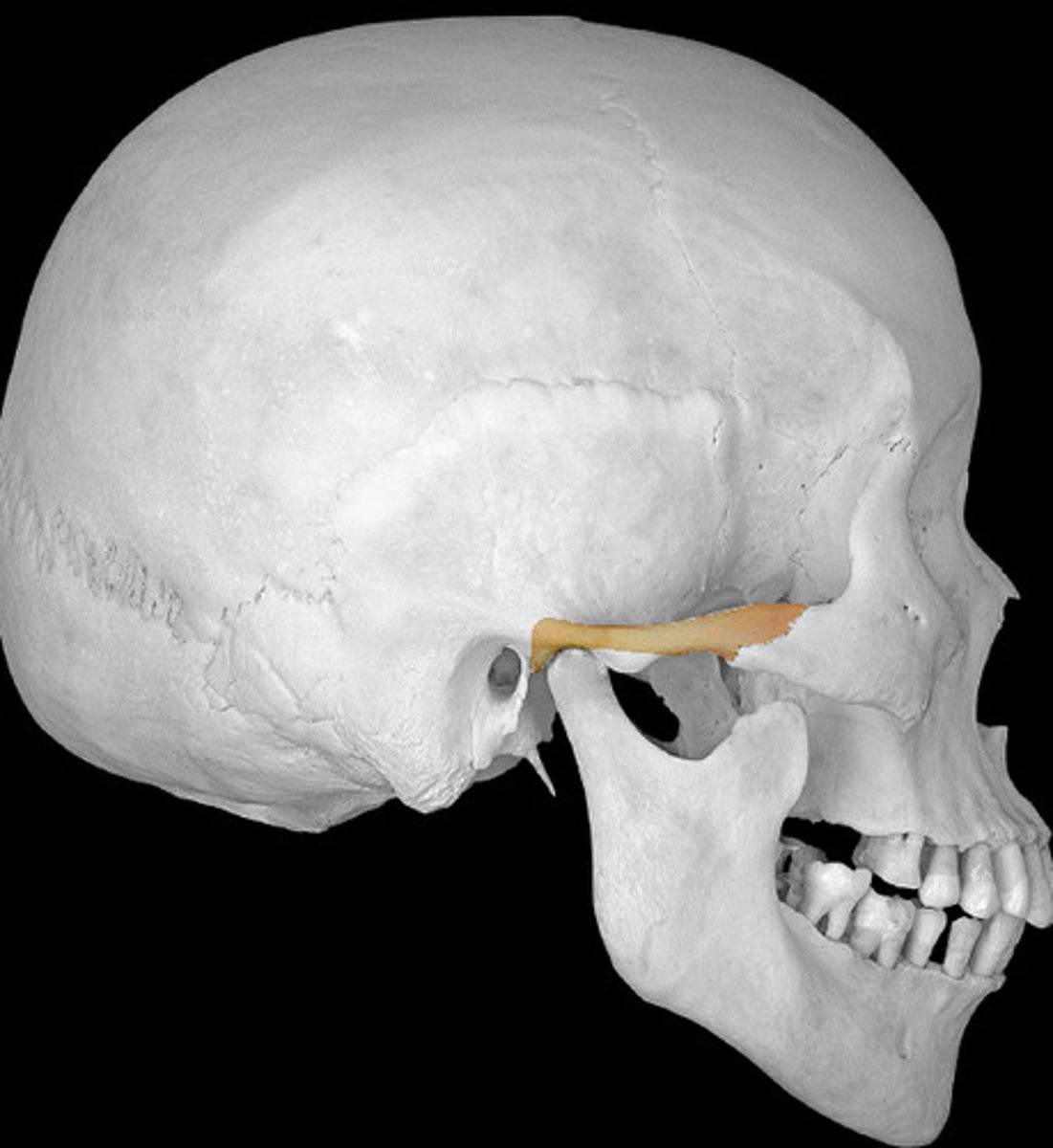
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone
Name the structure
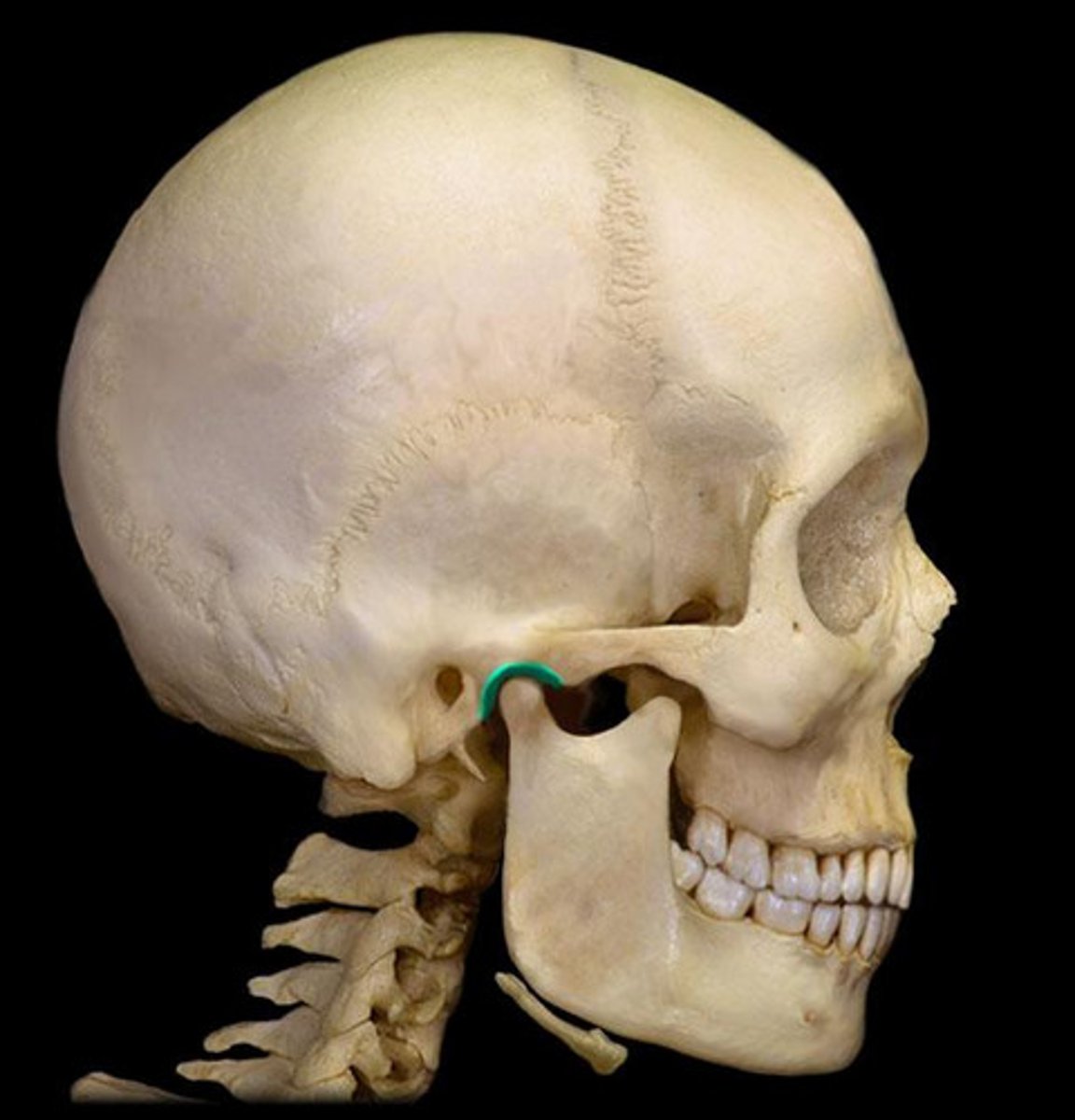
Styloid process
Name the structure
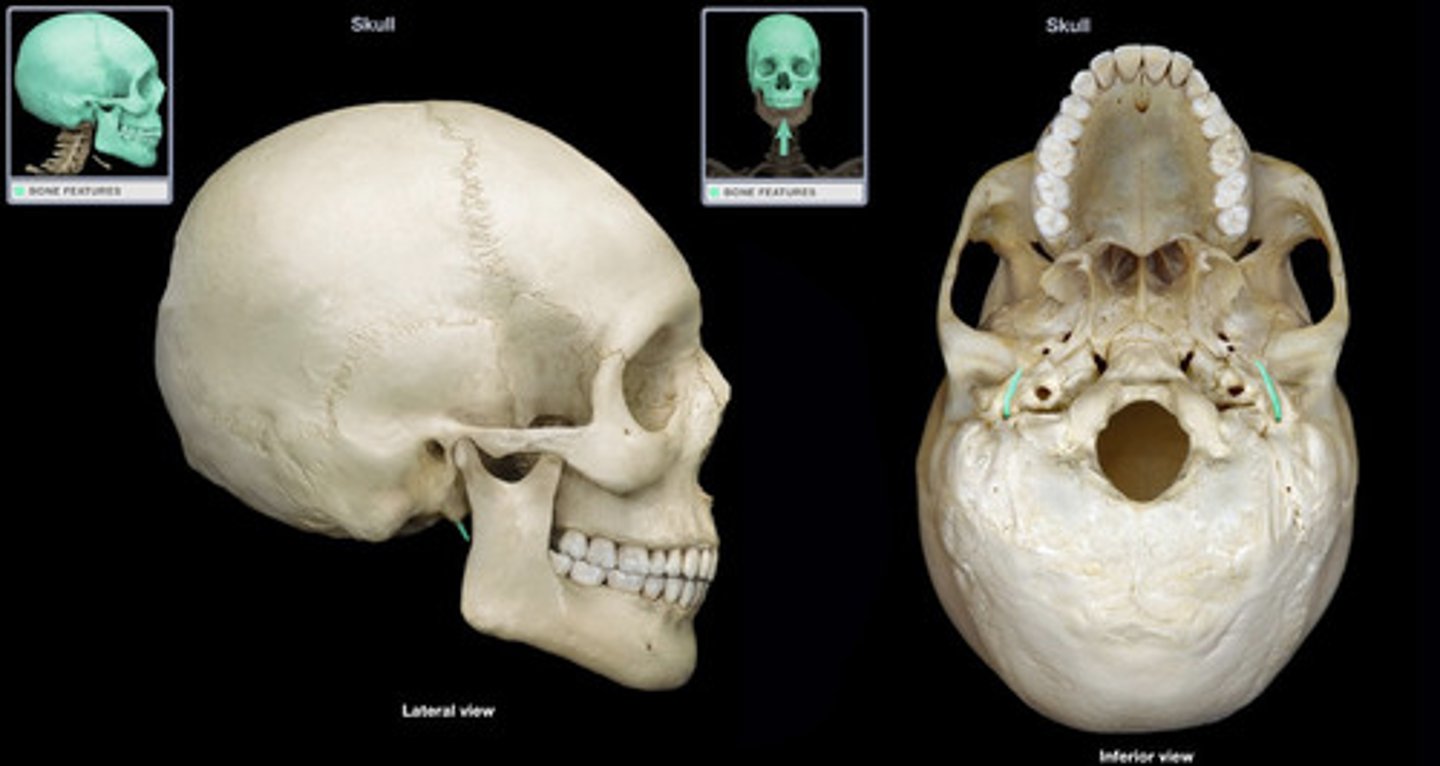
Carotid canal
Name the space
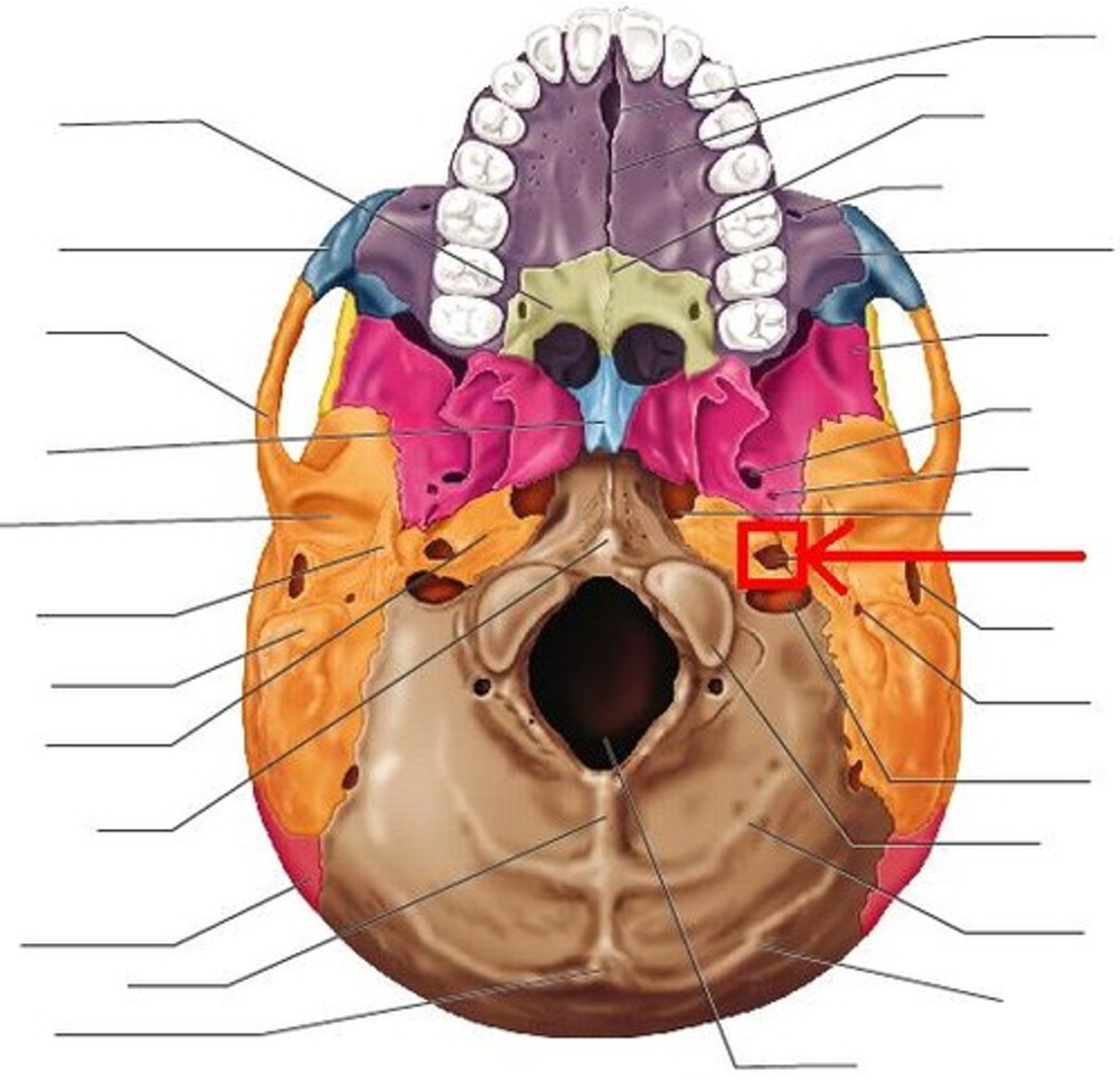
Jugular foramen
Name the space
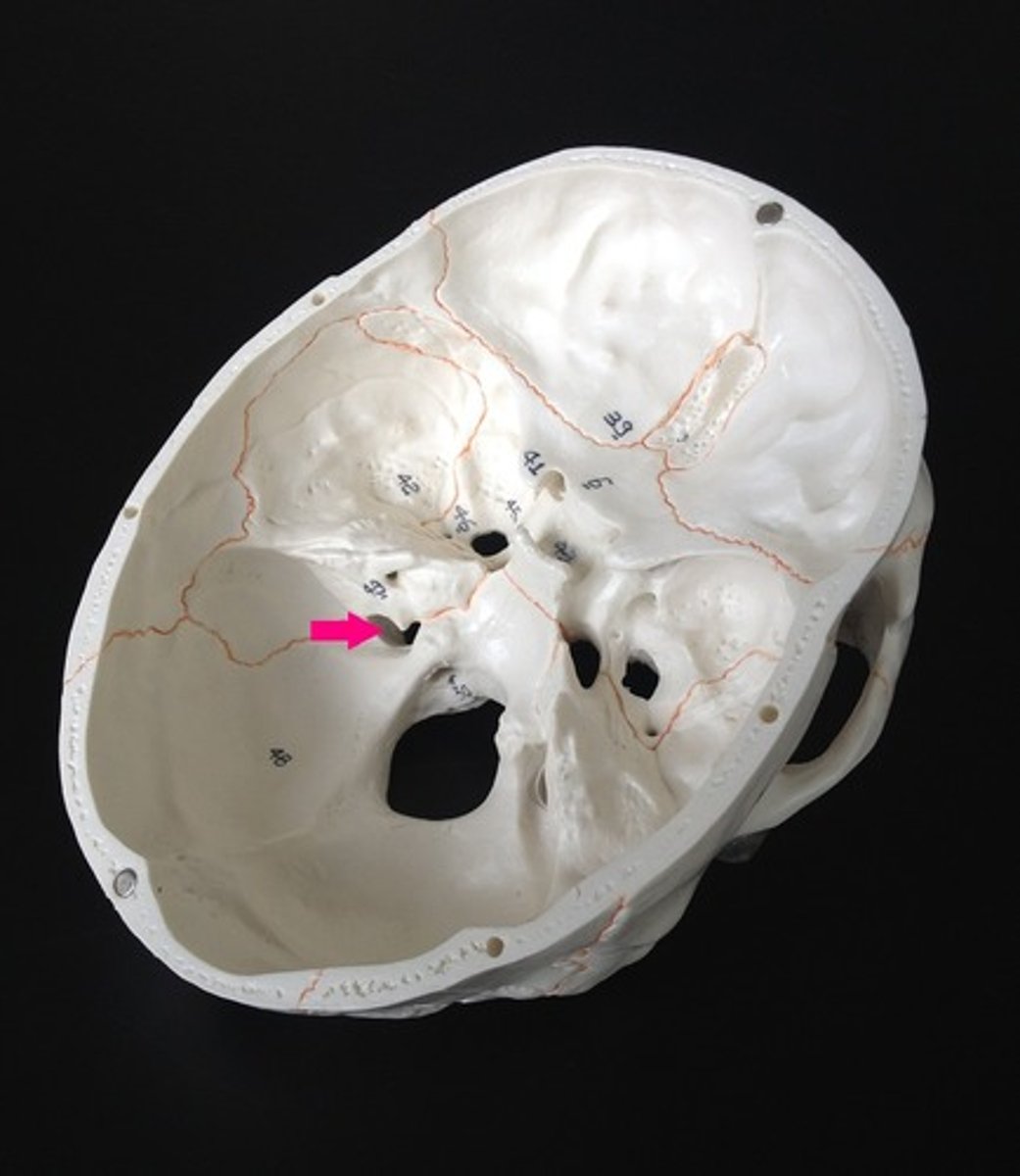
Foramen lacerum
Name the space
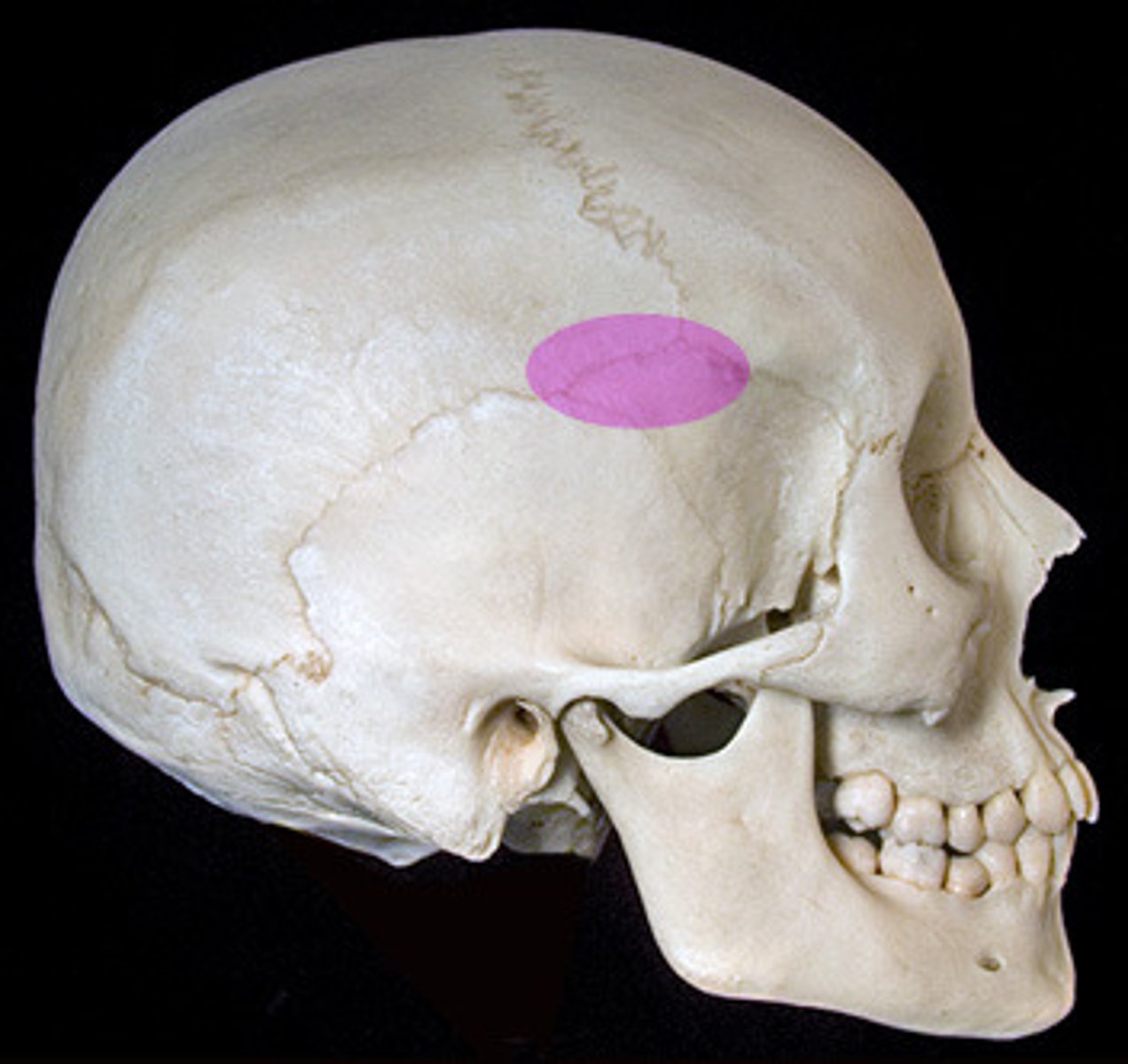
Pterion
Name the structure
Sphenoid bone
Name the bone
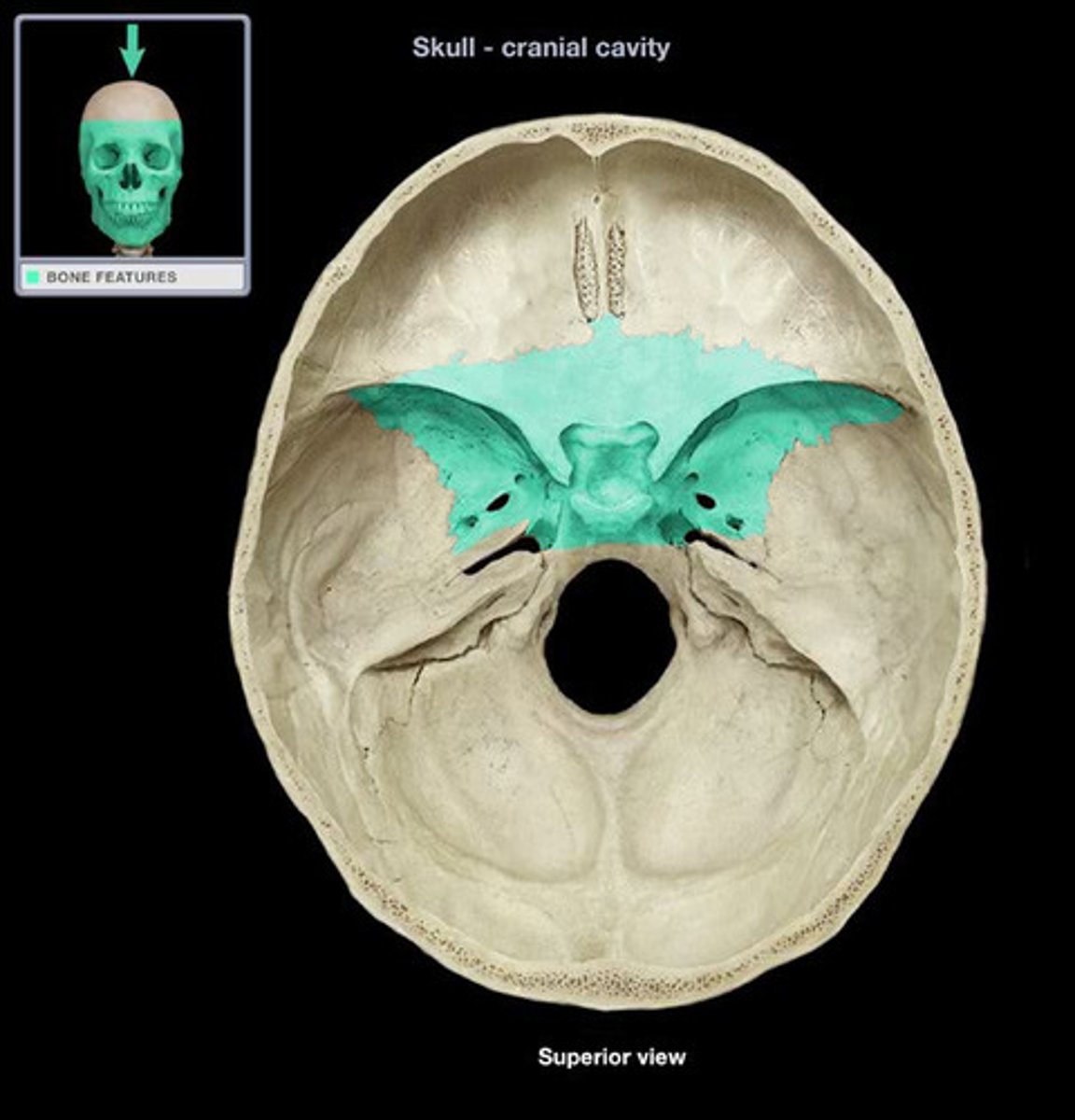
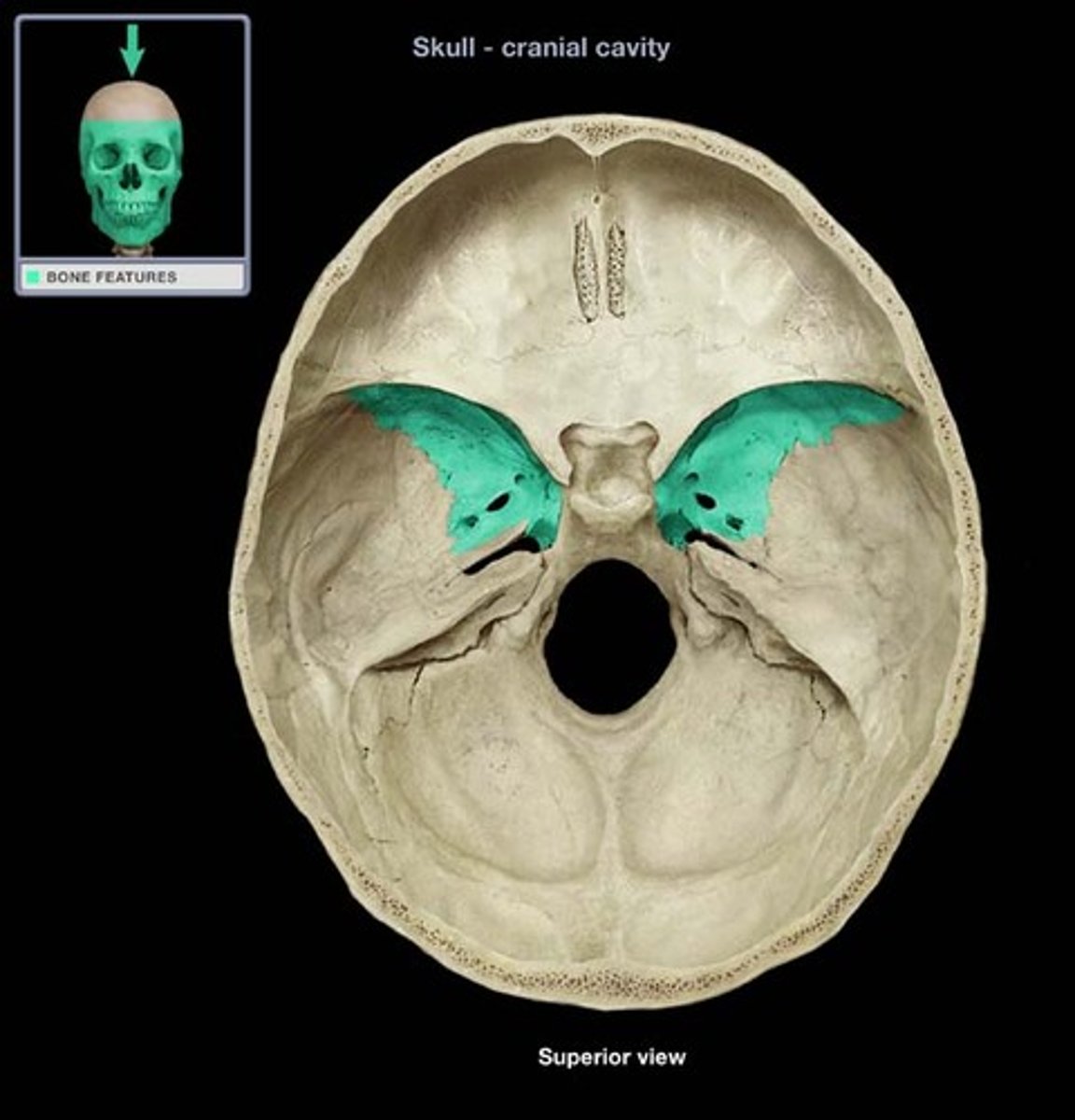
Greater wings of sphenoid bone
Name the specific portion of bone
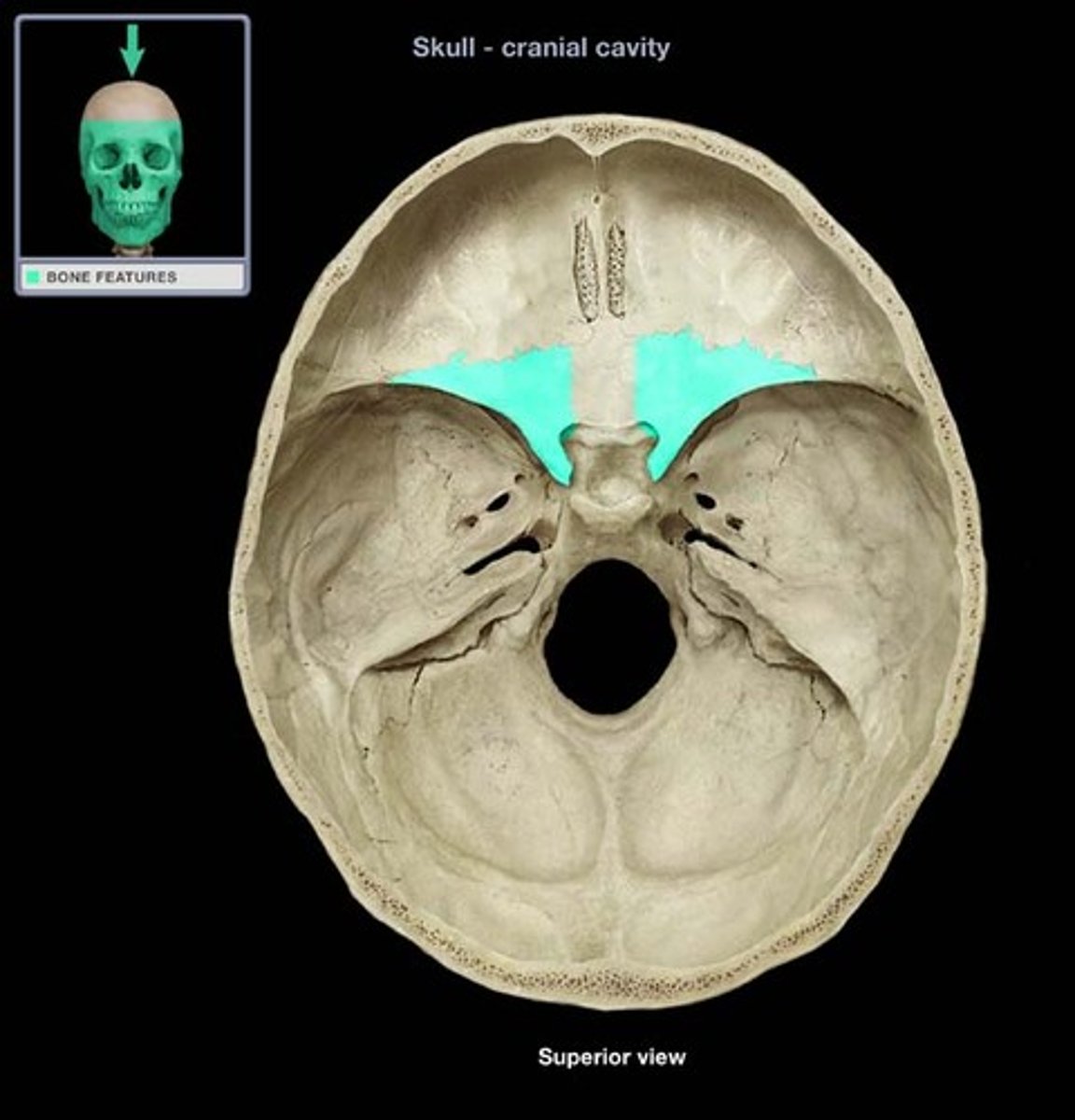
Lesser wings of sphenoid bone
Name the specific portion of bone
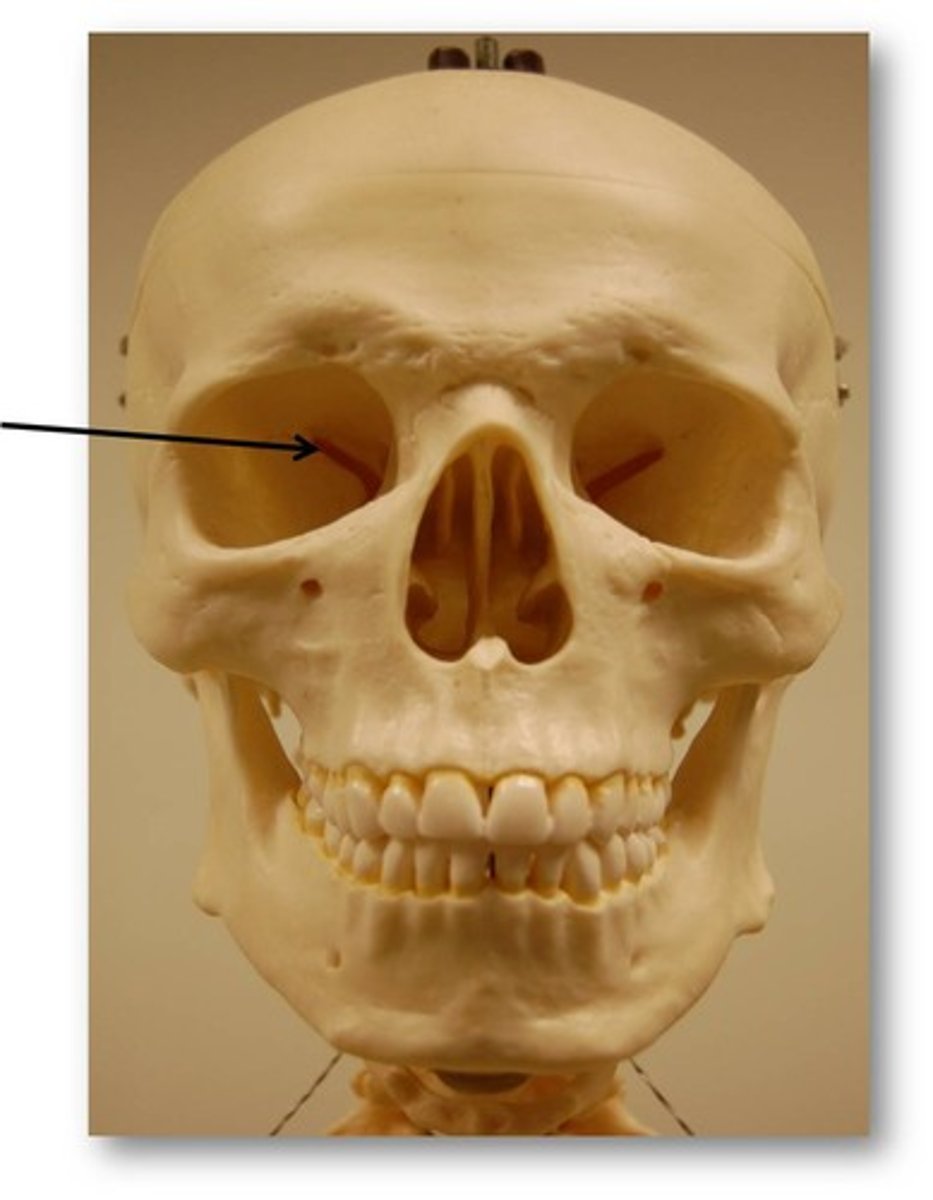
Superior orbital fissure
Name the space
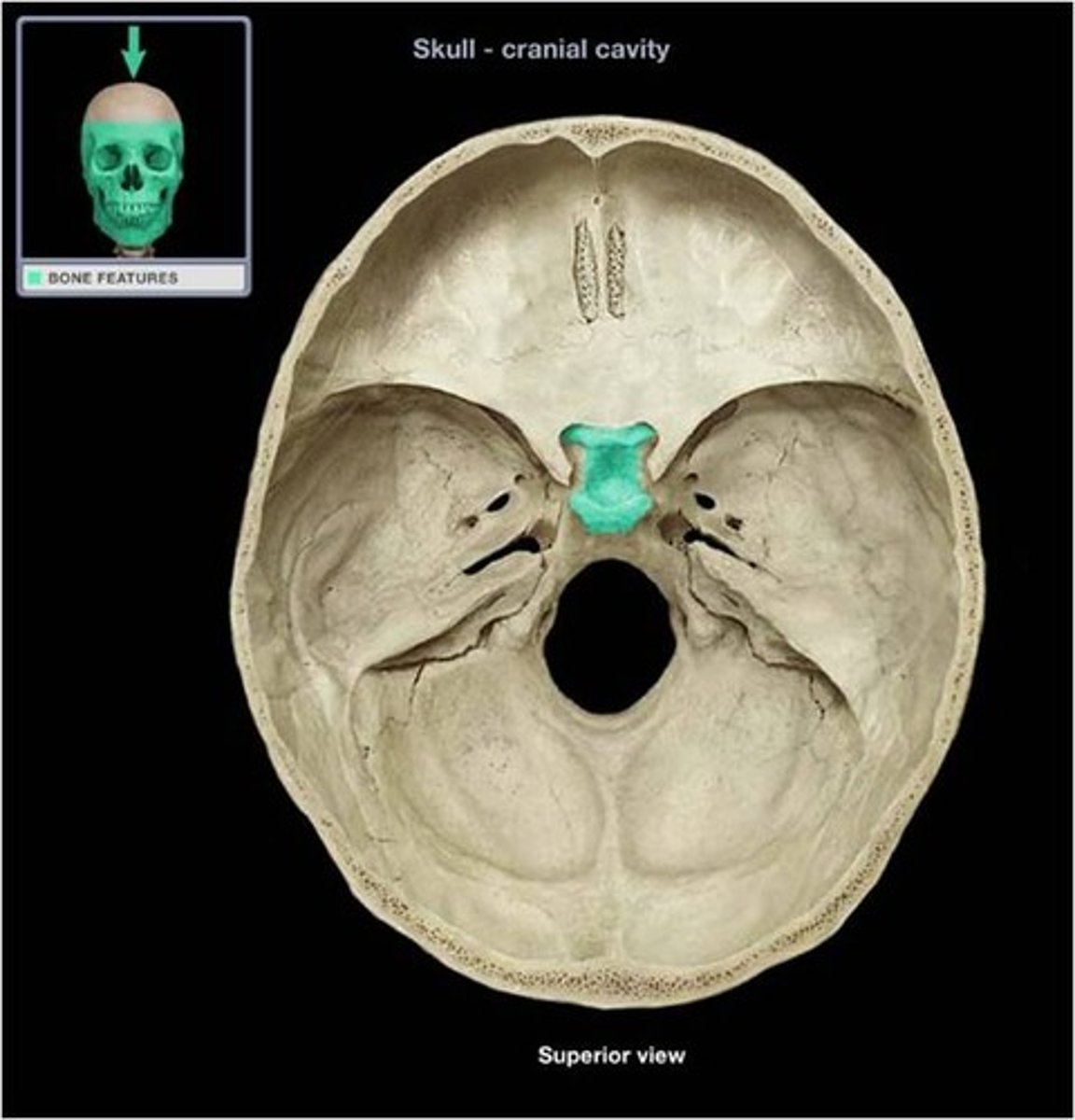
Sella turcica
Name the structure
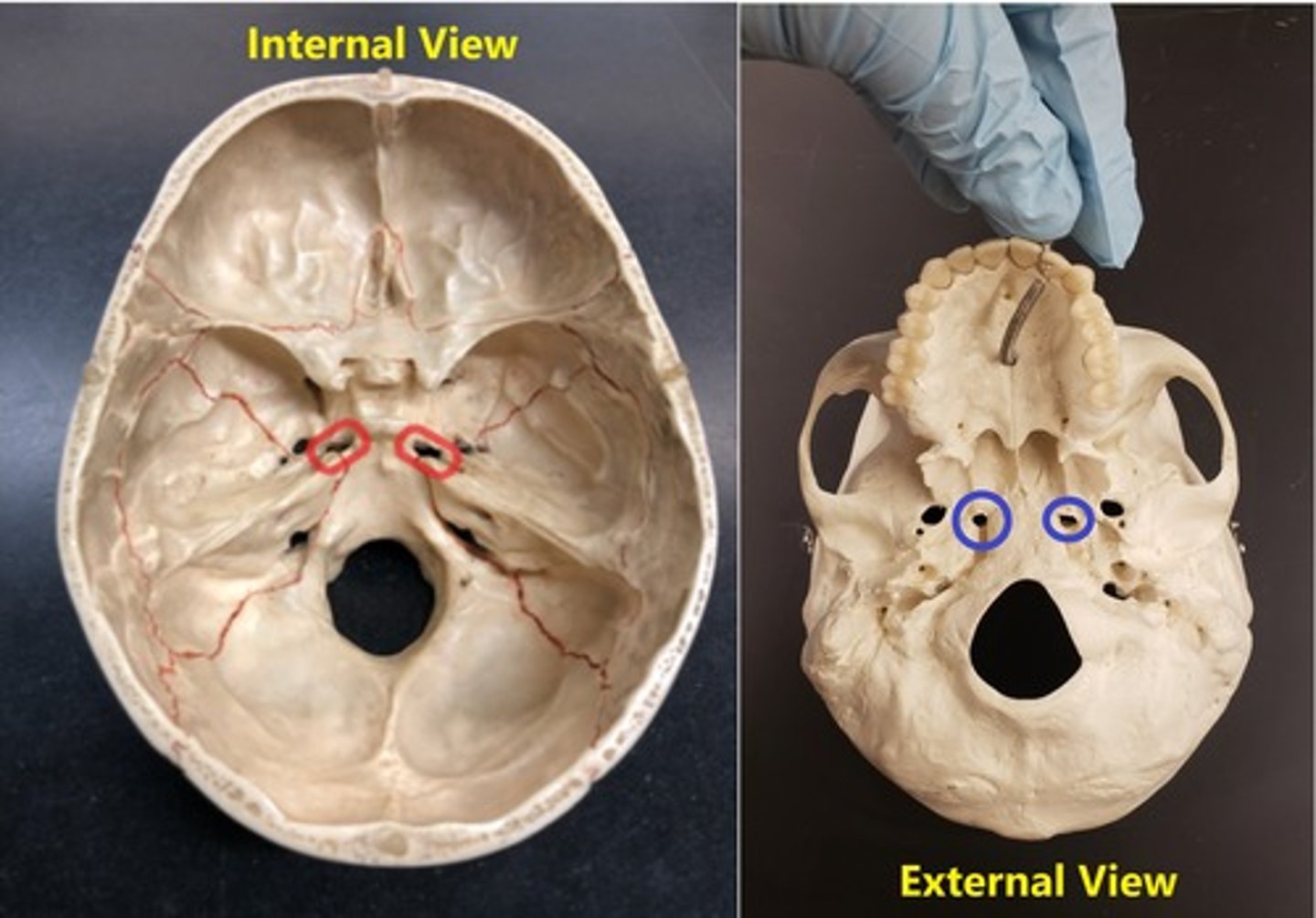
Optic foramen
Name the space
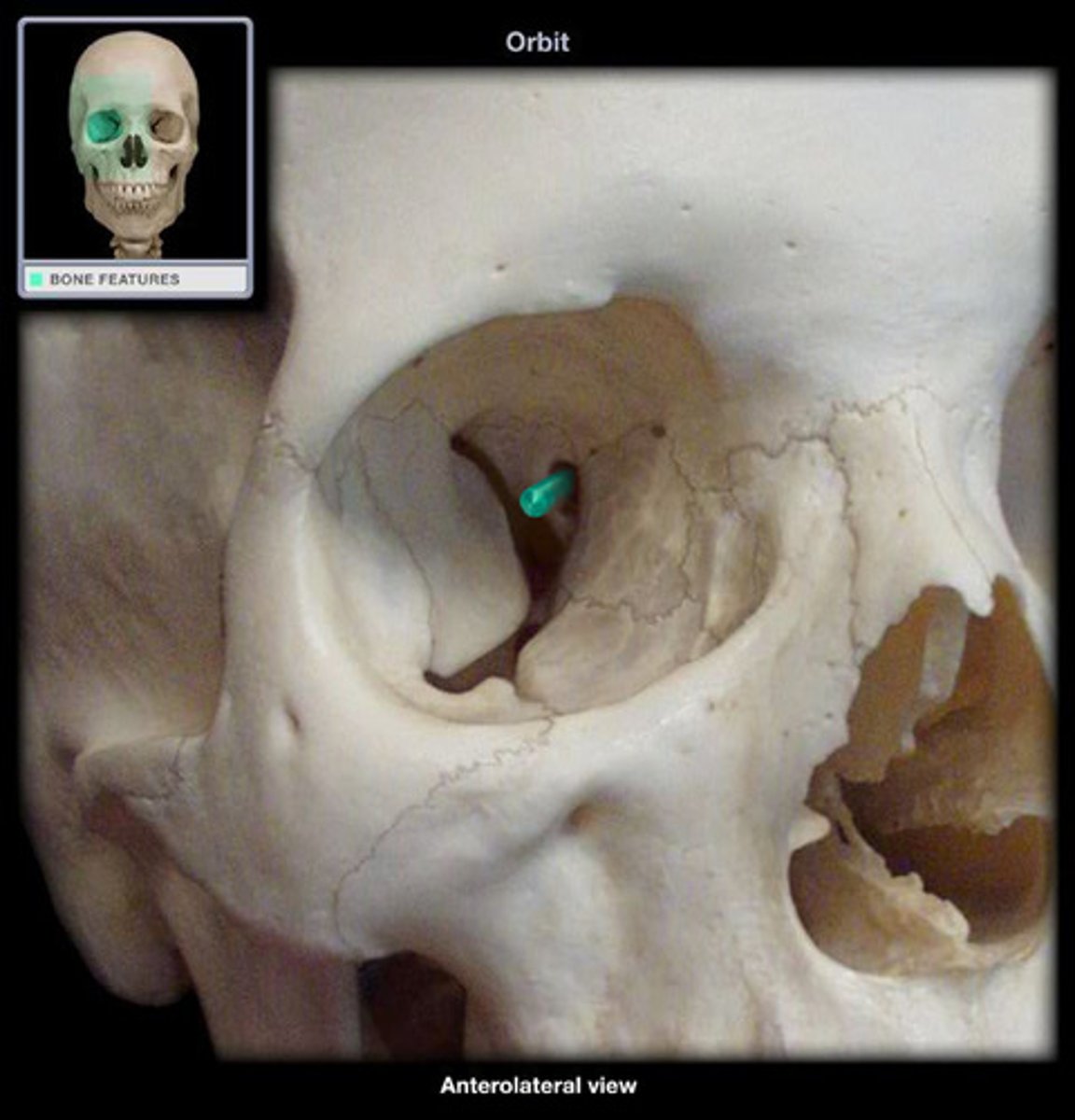
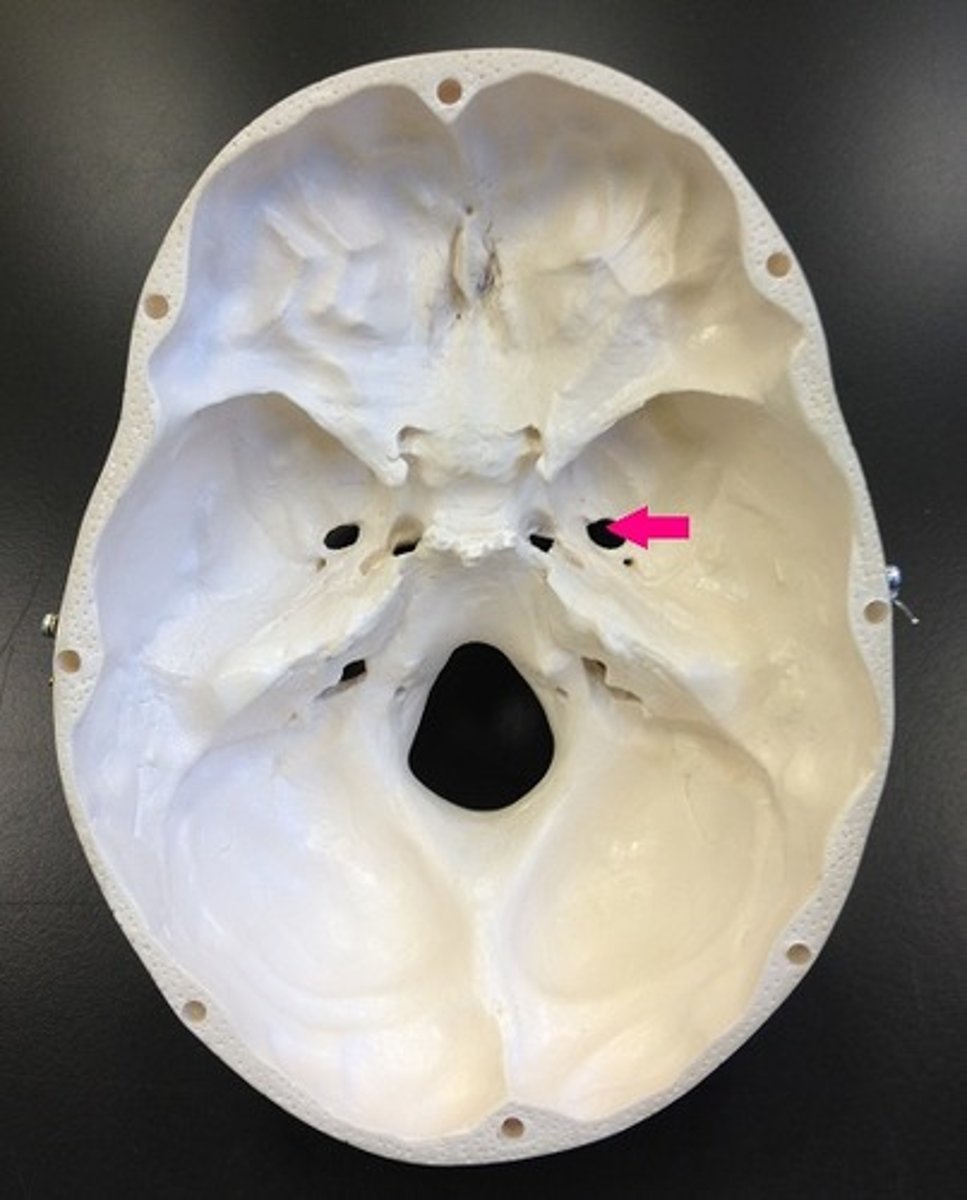
Foramen rotundum
Name the space
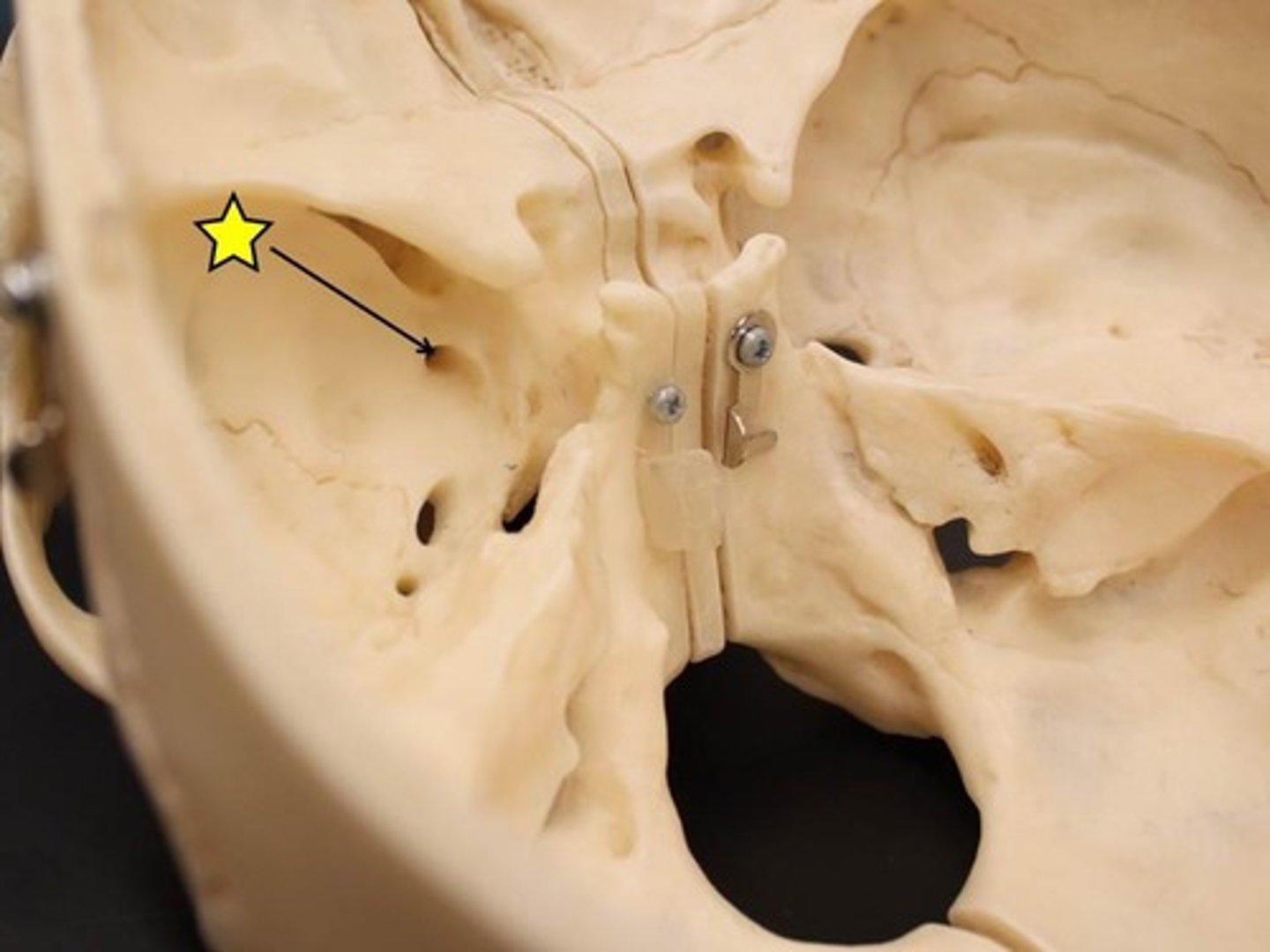
Foramen ovale
Name the space