Alkanes and Alkenes
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Hydrocarbons
compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only.
crude oil (petroleum)
complex mixture of hydrocarbons, in which molecules have carbon atoms in chains.
Fractional distillation
when substances in crude oil are separated into hydrocarbons through evaporation.
Fractions
Substances that can be tapped off.
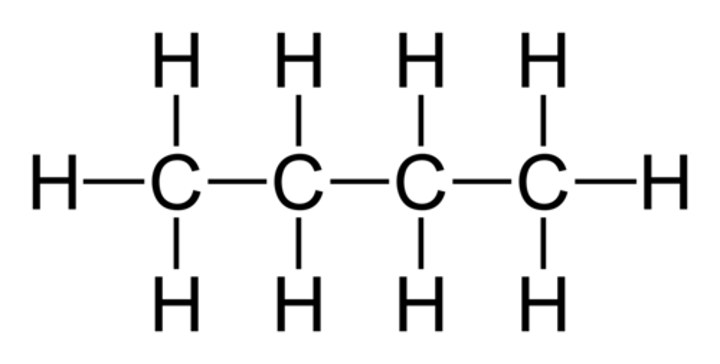
Alkanes
Saturated hydrocarbons, with carbon single bonds.
Displayed formula
The formula of the structure of a substance.
MONKEYS EAT PEANUT BUTTER
A part of a homologous series of alkanes, represented by the same general formula, consisting of methane, ethane, propane, butane and pentane etc, etc
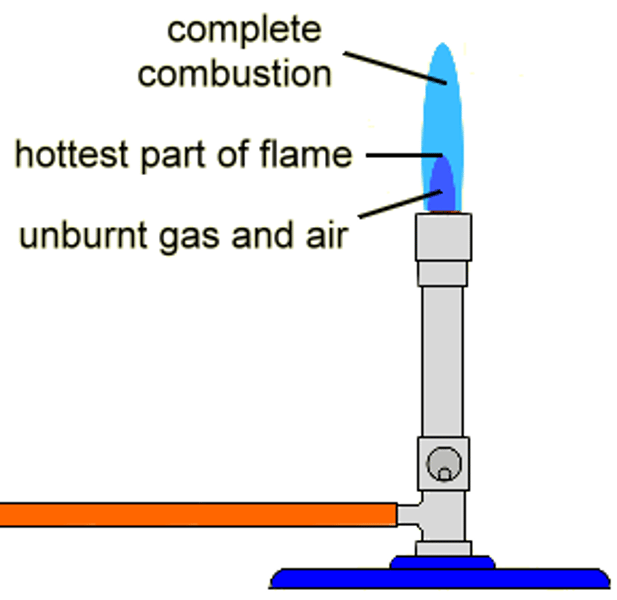
Complete combustion
alkane + hydrogen → carbon dioxide + water
Occurs when oxygen is abundant and results in gas burning with a clean blue fame.
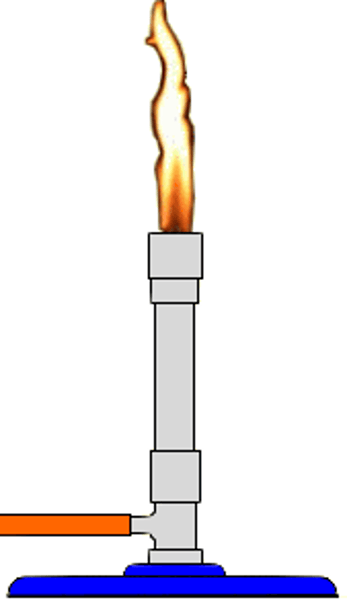
Incomplete combustion
alkane + oxygen → carbon monoxide + carbon dioxide + water
Occurs when oxygen is limited.
Alkenes
Unsaturated hydrocarbons, with chains of carbons atoms, bonded to each other with carbon double bonds, surrounded by hydrogen atoms.
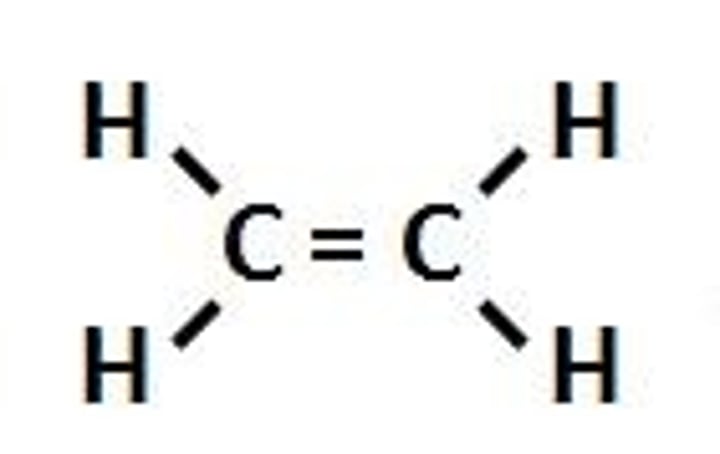
Addition reaction
Where 2 or more molecules combine to create a larger product ex. when halogens react with alkenes and the double bond is broken.
Saturated
a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon single bonds is....
Unsaturated
a hydrocarbon with C=C double bonds is....
Carbon monoxide
It can bind to one's haemoglobin and limit the blood's ability to carry oxygen, turning blood pink.
Soot
produced by incomplete combustion, causes global dimming, solid carbon particles.
Sulfur dioxide
Most fuels contain a small amount of sulfur, which combust in air to form.....
Acid rain
caused by sulfur dioxide dissolving in water.
Methane
CH4
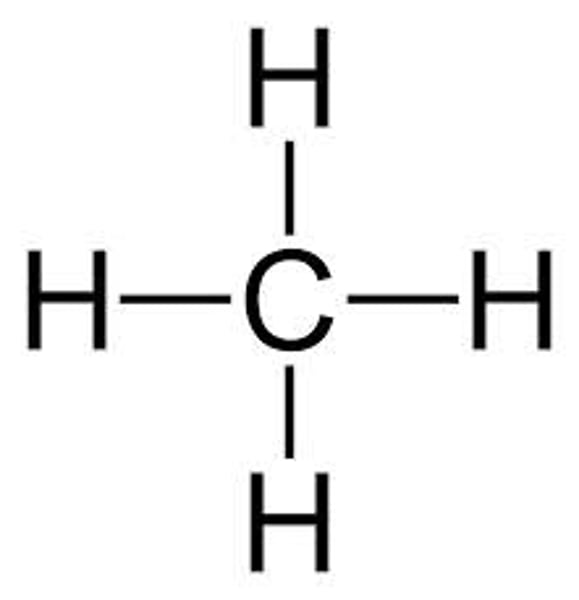
Nitrogen monoxide
created when the two elements: nitrogen and oxygen combine in air and is released when fuels are burned in engines. It is a pollutant.
Nitrogen dioxide
created the nitrogen monoxide combines with oxygen in air to form...... It is a pollutant.
Ethane
C2H6
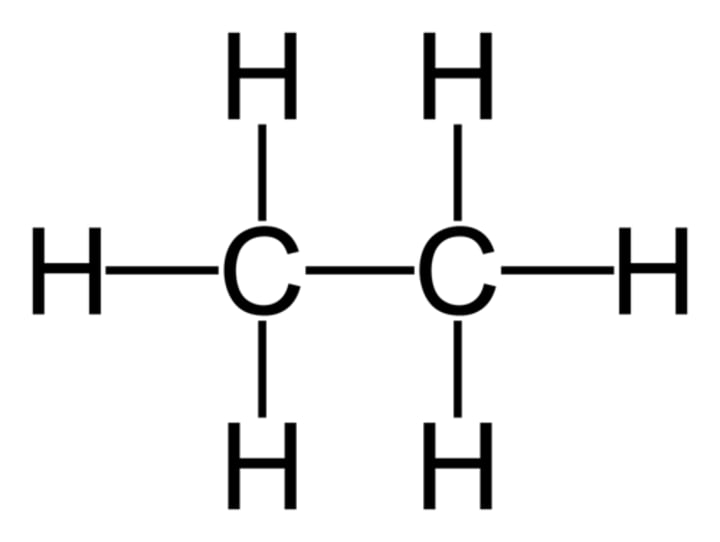
Propane
C3H8
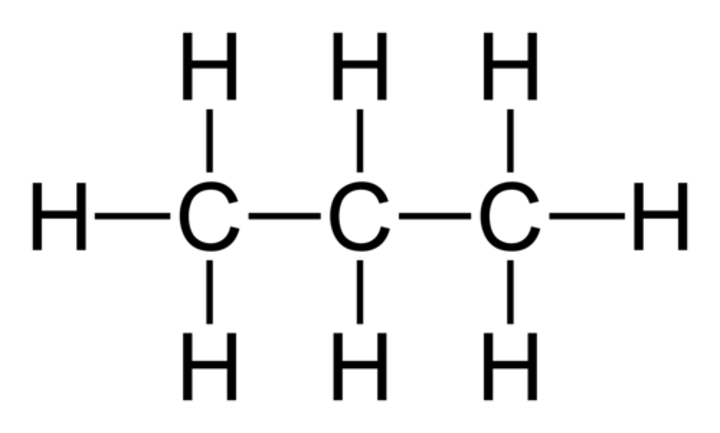
Butane
C4H10
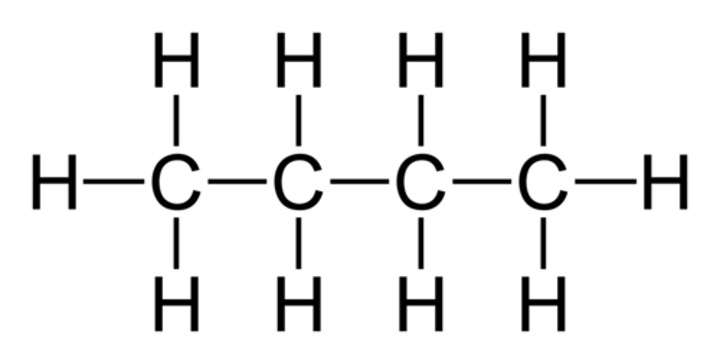
Ethene
C2H4
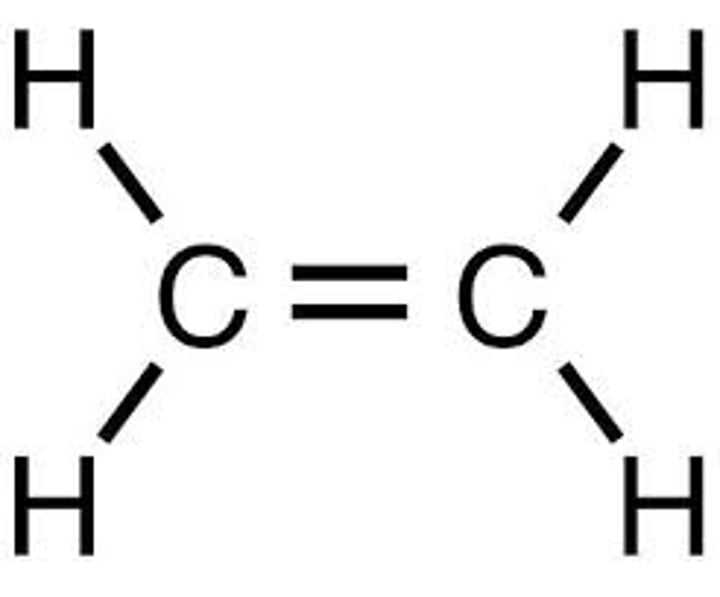
Propene
C3H6
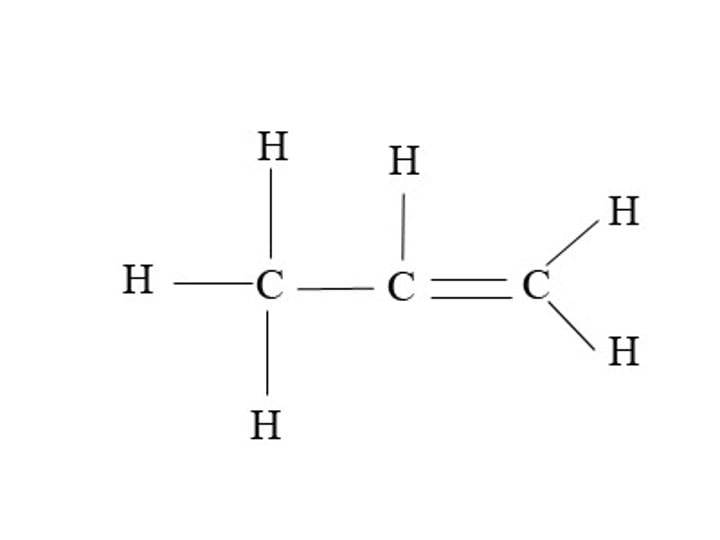
Butene
C4H8
Cracking
Breaking up large hydrocarbons into smaller ones using heat.
Viscous
The longer the hydrocarbon the more......
CnH2n
The general formula for alkenes is...
Cn2n+2
The general formula for alkanes is...
goes colourless
When shook with bromine water alkenes (unsaturated).....the bromine water
stays orange
When shook with bromine water the alkanes (saturated) ..... the bromine water
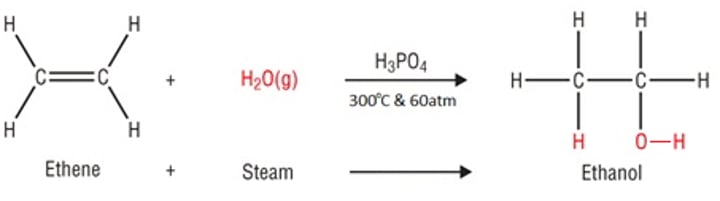
Ethanol
Addition reaction of ethene and water produces _____
Alkane
Addition reaction of alkene and hydrogen produces ____
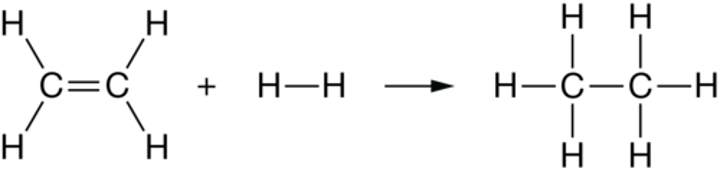
Viscosity
resistance to flow (thickness of liquid)

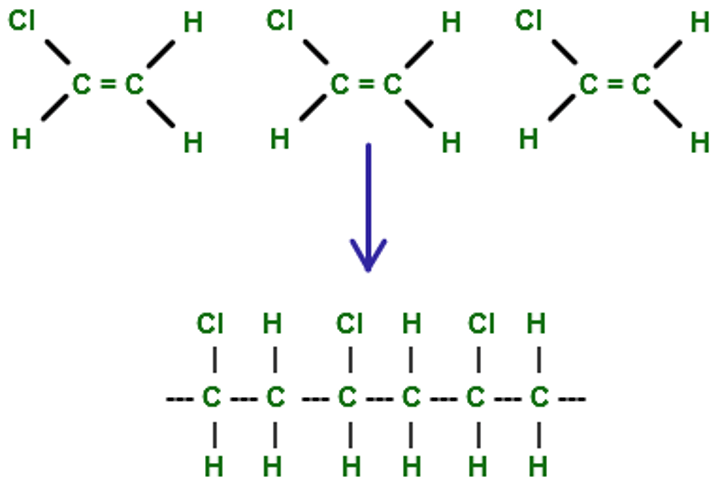
Polymer
A long molecule consisting of many similar or identical monomers linked together.
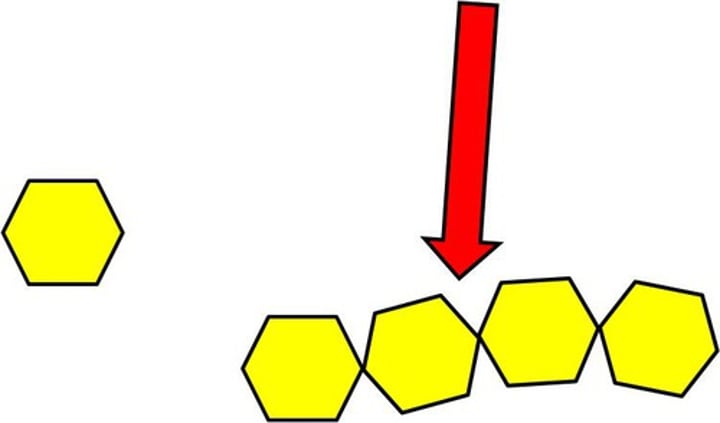
addition polymerisation
a type of polymerisation in which the monomers simply add together to form the polymer, with no other products
Why do we need cracking?
Because the long hydrocarbon molecules are not so useful
Homologous series
having the same chemical reactions and properties.
neighbouring compounds differ by 1 carbon and 2 hydrogen.
Thermal decomposition
Breaking up using heat
Monomer
small molecule that bonds with other small molecules to form a larger molecule (polymer)
Repeating unit
the part of the polymer which gets repeated to make a complete polymer chain
Empirical formula
simplest ratio of atom in a compound