Unit 1 - AP Macro
1/33
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Scarcity
we have unlimited wants but limited resources
Because of scarcity choices need to be made
trade-offs + opportunity cost
Consumer Goods
Direct consumption (pizza)
Capital Goods
Indirect Consumption (cheese, knives, bowl)
Factors of Production
Land, Labor, Capital (Human +Physical), Entrepreneurship
Physical Capital
Any human-made resource that is used to create other goods and services.
Human Capital
Any skills or knowledge gained by a worker through education and experience.
Productivity
A measure of efficiency that shows the number of outputs per unit of input.
Price vs Cost
Amount buyer pays for product vs Amount seller pays to make good
Constant Opportunity Cost
Resources are easily adaptable for producing either good. (pizzas and calzones)
3 shifters of PPC
1. Change in resource quantity or quality
2. Change in Technology
3. Change in Trade (allows more consumption)
Per Unit Opportunity Cost
Opportunity Cost / Units Gained
Absolute Advantage
The producer that can produce the most output OR requires the least amount of inputs (resources).
Comparative Advantage
The producer with the lowest opportunity cost.
Output Questions
OOO= Output: Other goes Over
Input Questions
IOU = Other goes Under
Demand
The different quantities of goods that consumers are willing and able to buy at different prices.
Demand Shifters
Change in Disposable Income (DI) Spendable income after taxes and debts are paid
Change in spending (domestic/foreign)
Change in interest rates
Change in population
Change in preferences
Prices don’t shift demand unless price of another good changes.
Substitutes are goods used in place of one another. (coke + pepsi)
Complements are two goods that are bought and used together. (hot dogs + buns)
Supply
The different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices.
Law of Supply
DIRECT (or positive) relationship between price and quantity
Supply Shifters
Prices/Availability of inputs (resources)
Number of Sellers
Technology
Government Action: Laws, Taxes & Subsidies
Expectations of Future Profit
Surplus or Shortage in a Free Market
Prices automatically move towards equilibrium; surplus: producers will lower prices shortage: producers will raise prices
Price Ceiling
Maximum legal price a seller can charge for a product.
Goal: Make affordable by keeping price from reaching Eq.
Result: Shortage —> Black Markets (demand is higher than the quantity)
Price Floor
Minimum legal price a seller can sell a product.
Goal: Keep price high by keeping price from falling to Eq.
price control
Price ceilings and price floors result in a misallocation of resources
Circular Flow Model
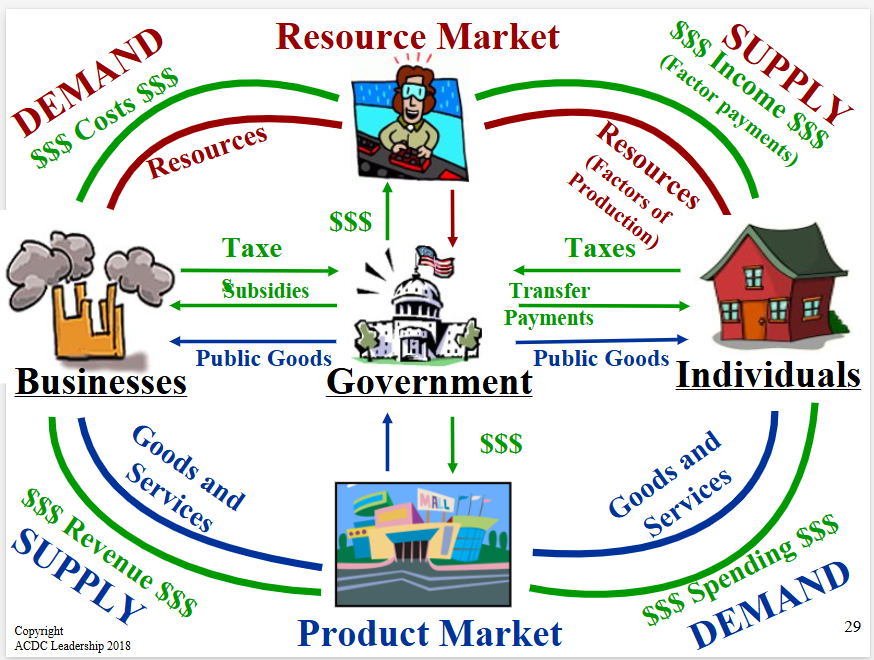
(CFM) The Product Market
The “place” where goods and services produced by businesses are sold to households.
(CFM) The Resource (Factor) Market
The “place” where resources (land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship) are sold to businesses.
Private Sector
Part of the economy that is run by individuals and businesses.
Public Sector
Part of the economy that is controlled by the government.
Factor Payments
Payment for the factors of production, namely: rent, wages, interest, and profit.
Transfer Payments
When the government redistributes income (ex: welfare, social security)
Subsidies
Government payments to businesses.