Topic 12: Acids and bases strength
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are examples of strong acids?
HCl, H2SO4 and HNO3
What is the definition of a strong acid?
Completely transfer their protons to aqueous solution (completely ionises/dissociates)
All H+ ions are released
What type of conjugate base does a strong acid have?
A weak conjugate base
What are examples of weak acids?
Most carboxylic acids
What is the definition of a weak acid?
Partially dissociate into ions in aqueous solution.
What type of conjugate base does a weak acid have?
Strong conjugate base
What is a monoprotic acid and how many mols of H+ ions does it produce for one mol of the monoprotic acid?
Monoprotic acid: acid which only contains 1 H in its molecular formula
1 mol of monoprotic acid produces 1 mol of H+ ions
What is a diprotic acid and how many mols of H+ ions does it produce for one mol of the diprotic acid?
Monoprotic acid: acid which only contains 2 H in its molecular formula
1 mol of dioprotic acid produces 2 mol of H+ ions
What are example of strong bases?
Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), barium hydroxide (Ba(OH)2
What is the definition of a strong base?
Dissociates/ionises almost completely in aqueous solution
What type of conjugate acid will the strong base have?
Weak acid
What are examples of weak bases?
Ammonia (NH3)
What is the definition of a weak base?
Partially react with water to give ions in aqueous solution.
What type of acids and bases have reactions which are not in equilibrium?
Strong acids and bases as they dissociate entirely.
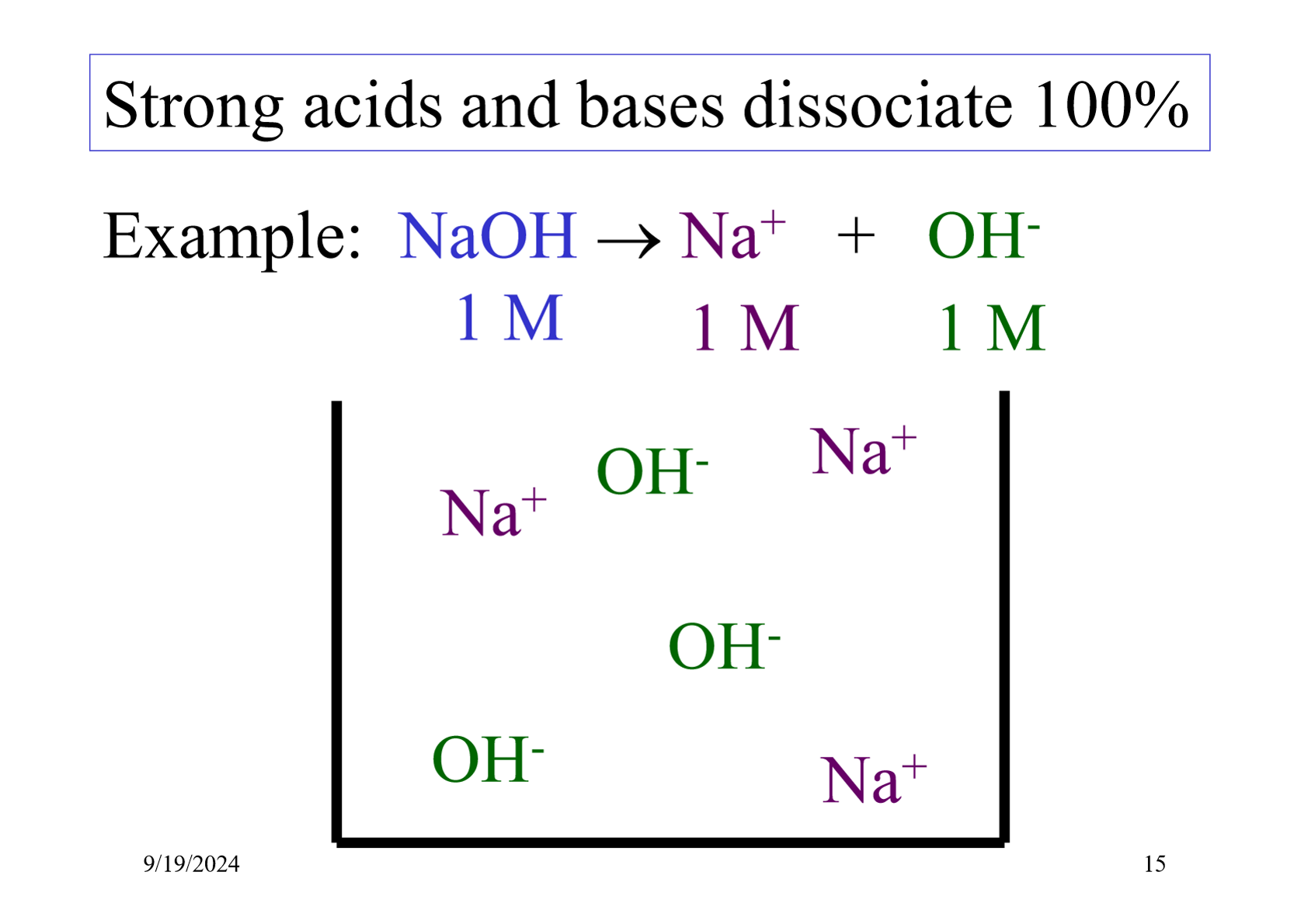
What type of acids and bases have reactions which are in equilibrium?
Weak acids and bases
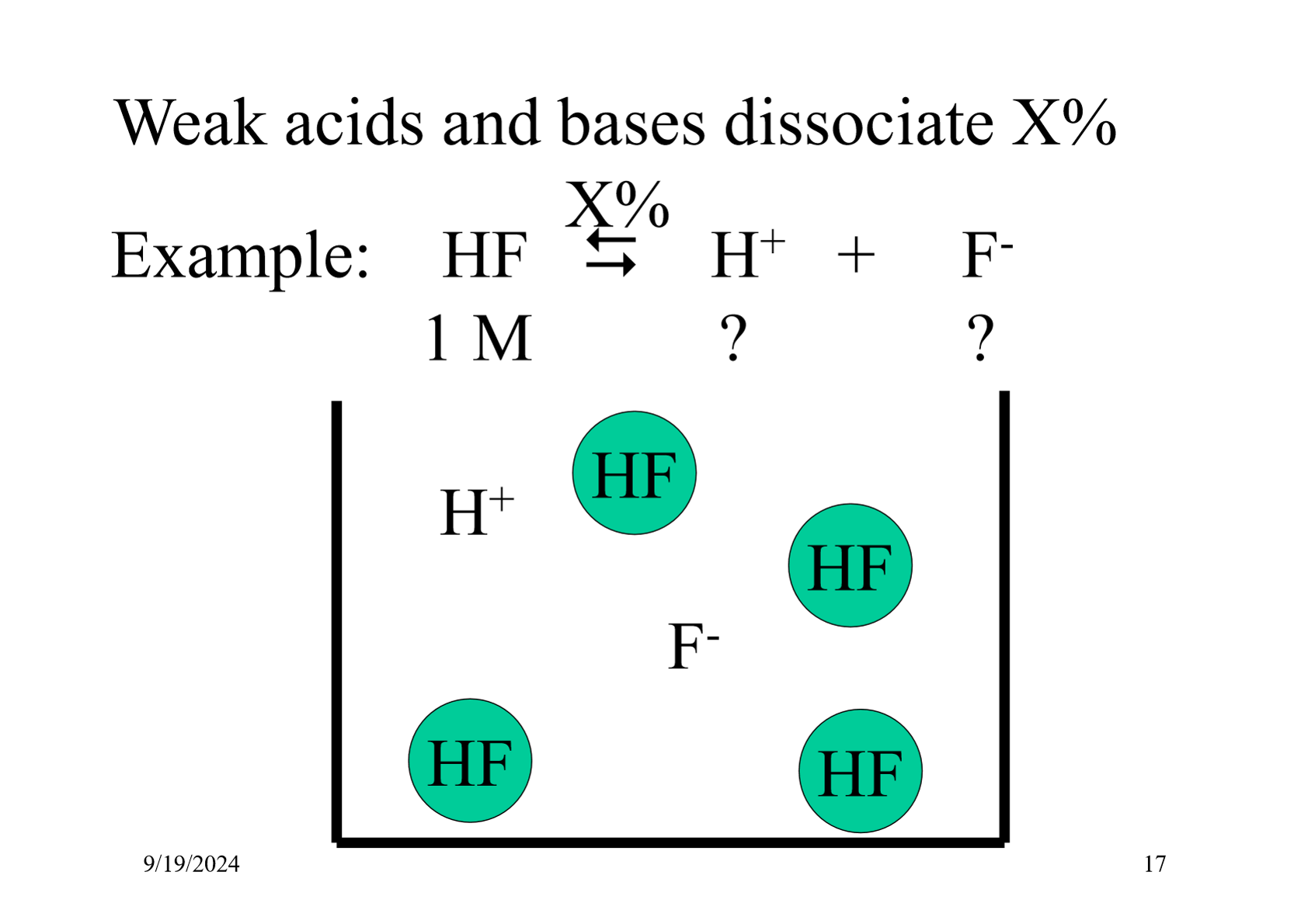
Why do weaker acids have a lower enthalpy change of neutralisation?
