archeology final id's
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
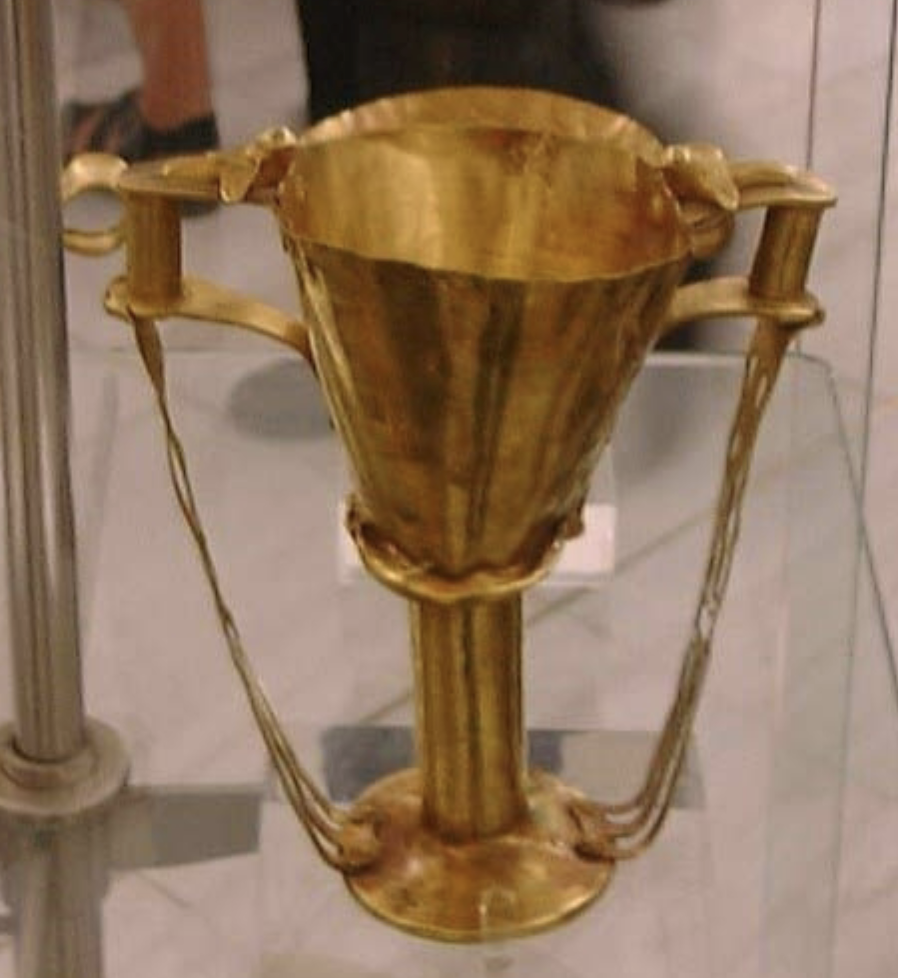

Nestor’s cup
WHEN: 16th century BC
WHERE: Mycenae
WHY: Homeric / heroic design & value
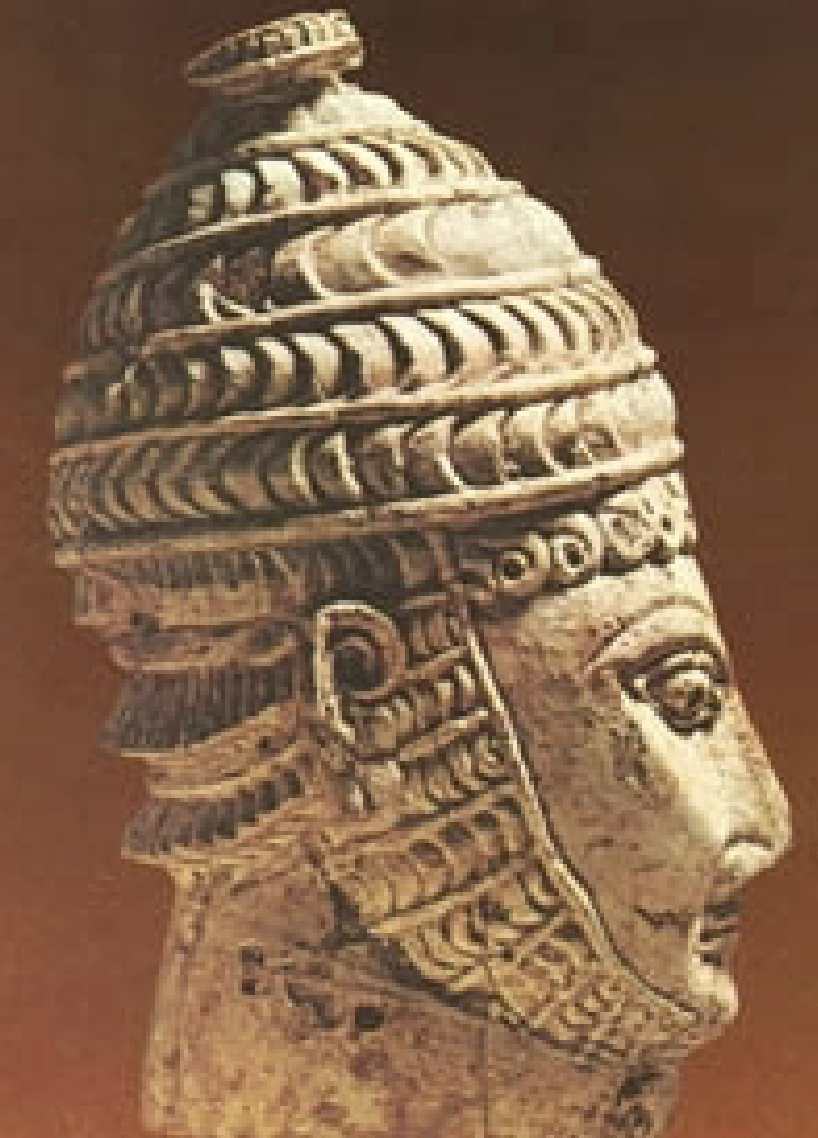

Boar’s tooth helmet
WHEN: 14th century BC
WHERE: Mycenae
WHY: Display of wealth & status (numerous boar teeth & use of silver) & connection to Homeric epics/tales of Bronze age heros
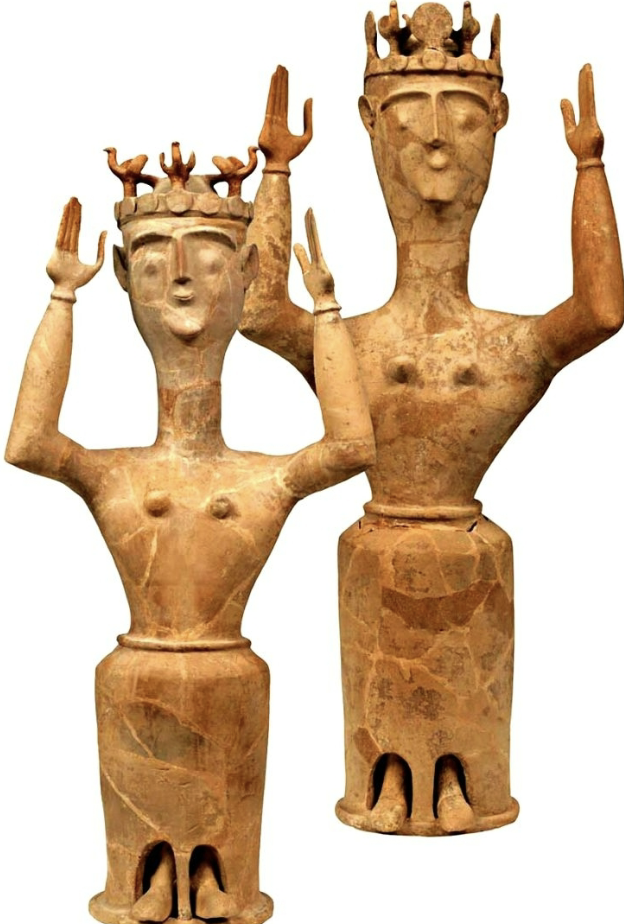

Goddess with upraised arms
WHEN: LM III (1300-1100BCE)
WHERE: Crete
WHY: Relates to matriarchal society / importance of women, nature, religion, fertility, nature, female goddesses, Aphrodite
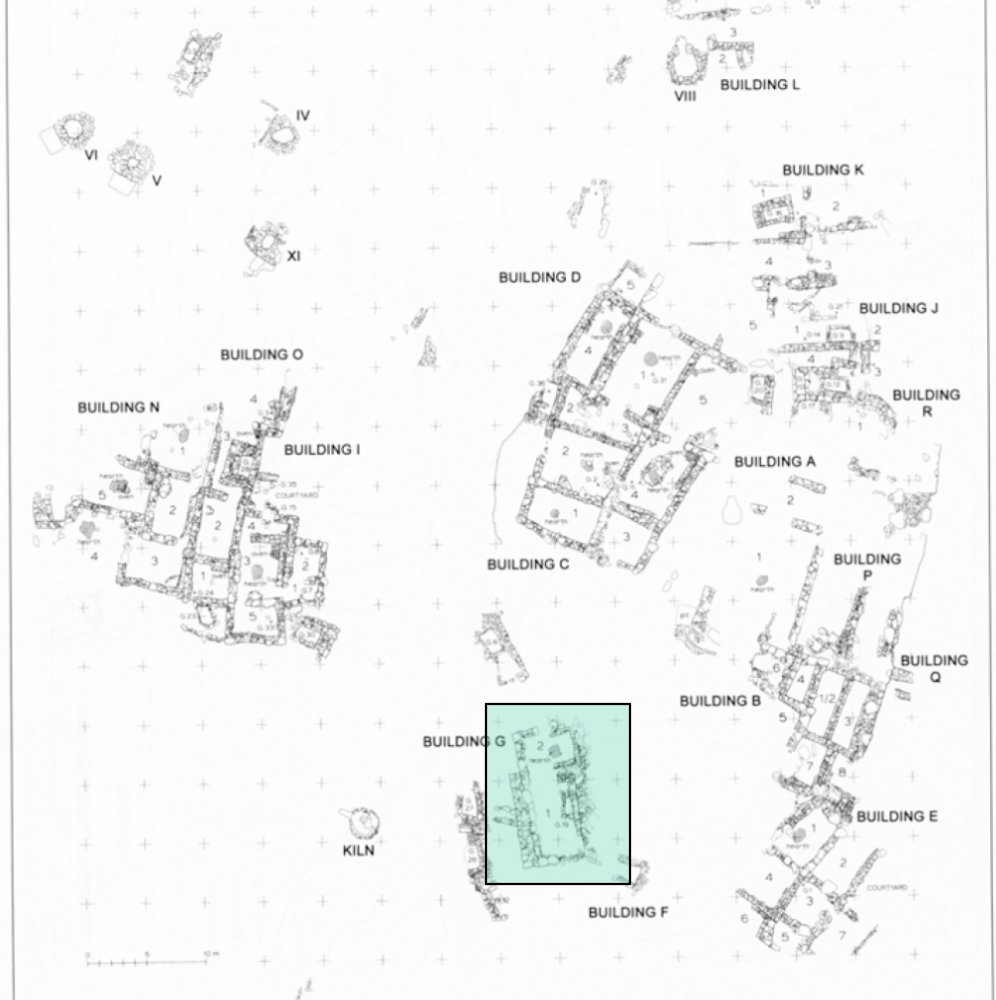
Kavousi Vronda
WHEN: LMIIIC
WHERE: Crete
WHY: showcases transition from Bronze age to Greek dark ages → insight on everyday life & domestic architecture. potentially seeking protection after collapse of palaces → death & religion through shrines & burials
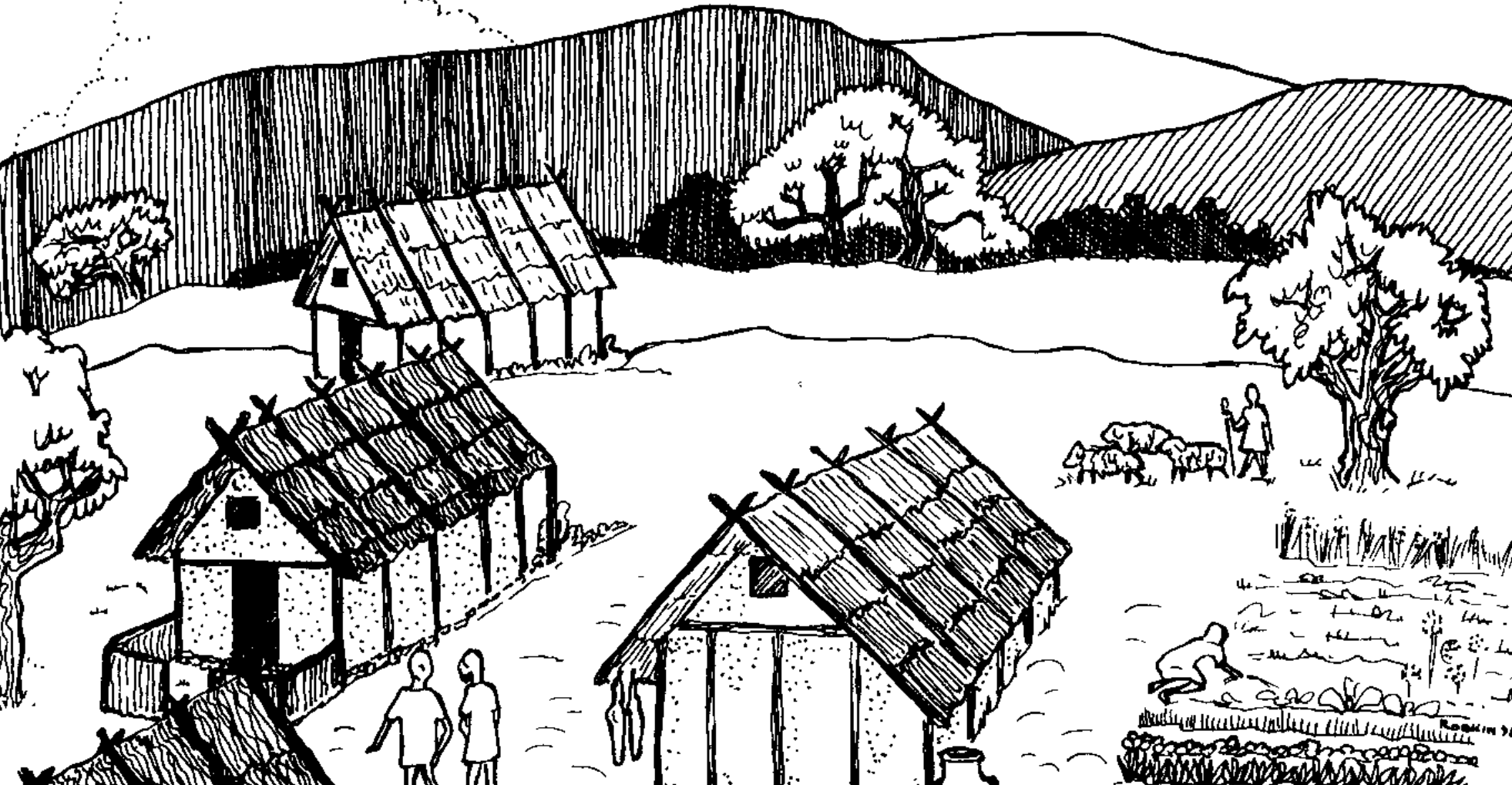

Greek Dark Age
WHEN: 1100-800
WHERE: Crete
WHY: period after the Bronze age: palaces are destroyed, Greece enters period of small villages w/ little populations, little art & primary focus on farming

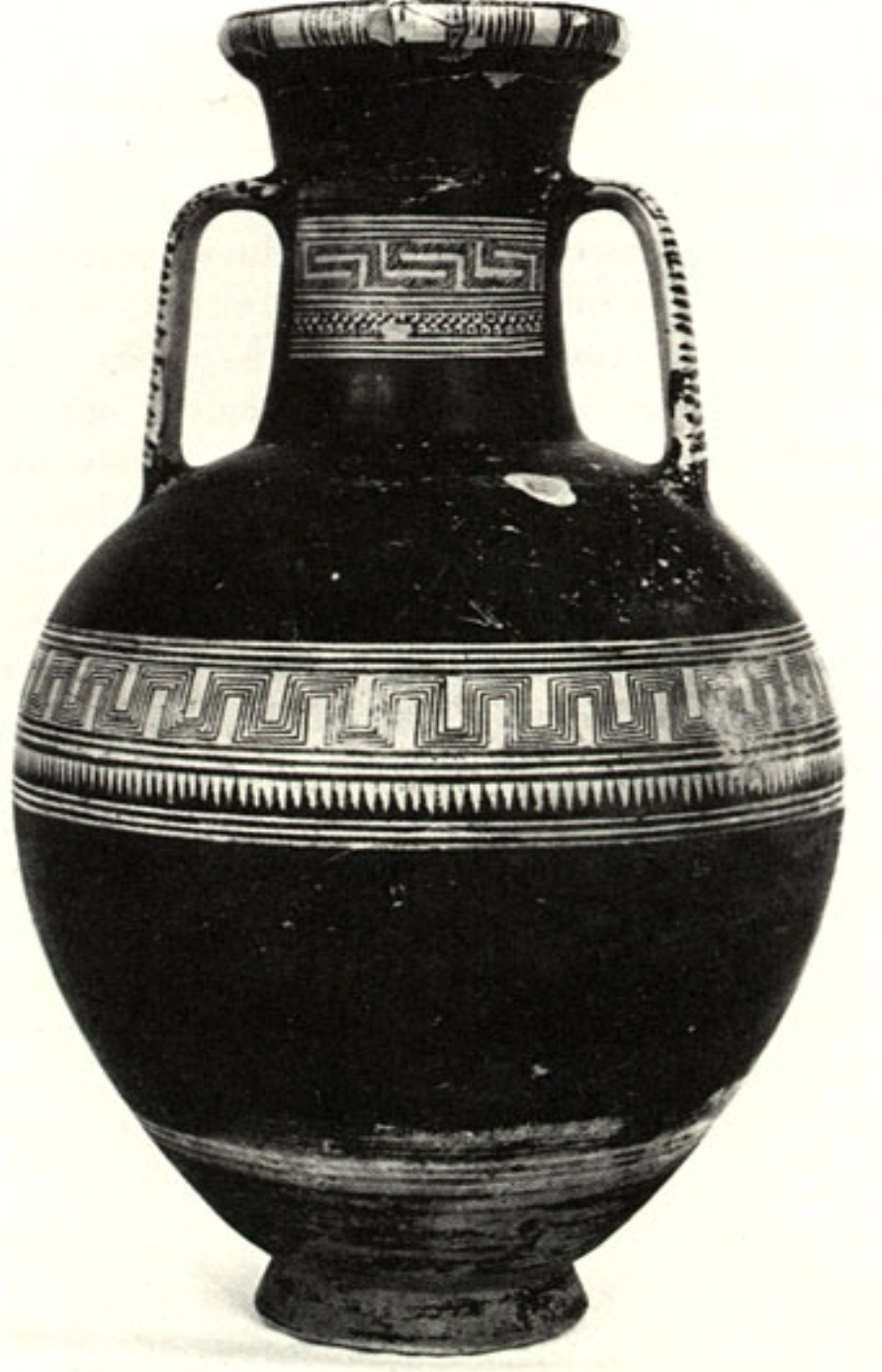
Proto-geometric pottery style
WHEN: 1100-800 BCE
WHERE: Athens/mainland Greece
WHY: during the “Dark Ages” representing new technological discoveries (fast spinning wheels) and setting the stage for more advanced artistic choices → transition from fall of Bronze ages to geometric period

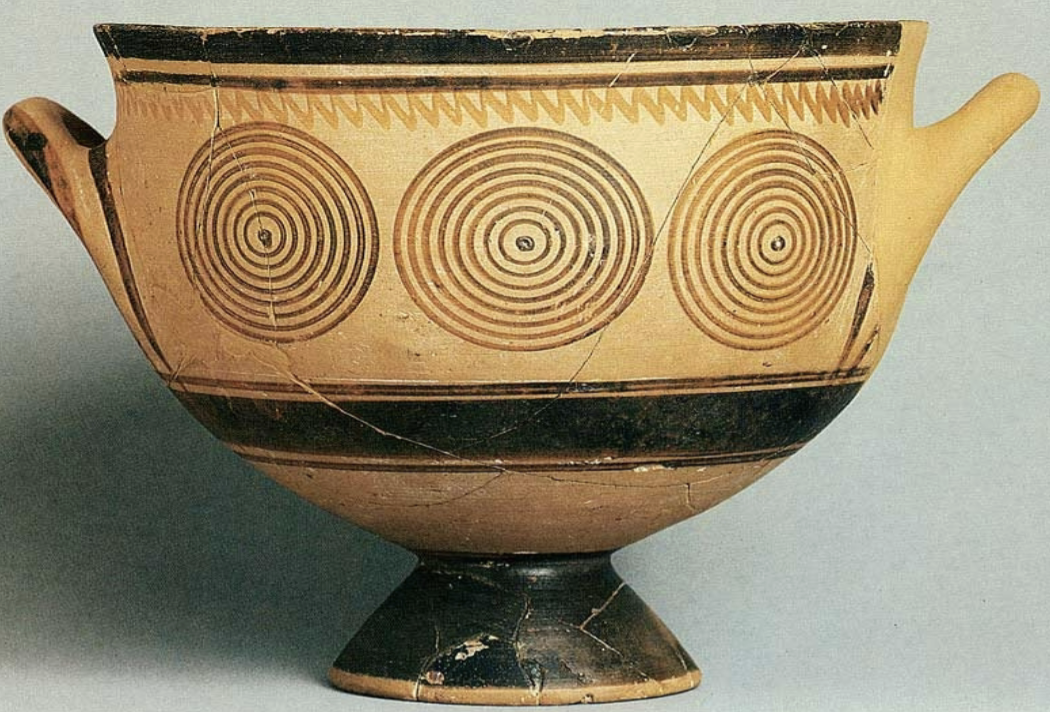
Geometric pottery style
WHEN: 800-700 BCE
WHERE: Athens/mainland Greece
WHY: Artistic shift from more abstract patterns to more complex pottery designs with improved technical skill

Warrior burials
WHEN: early-middle geometric period
WHERE: Athens
WHY: reflects social status & rituals → military importance, honoring of heroes & combat skills → potential reality of Homeric epics
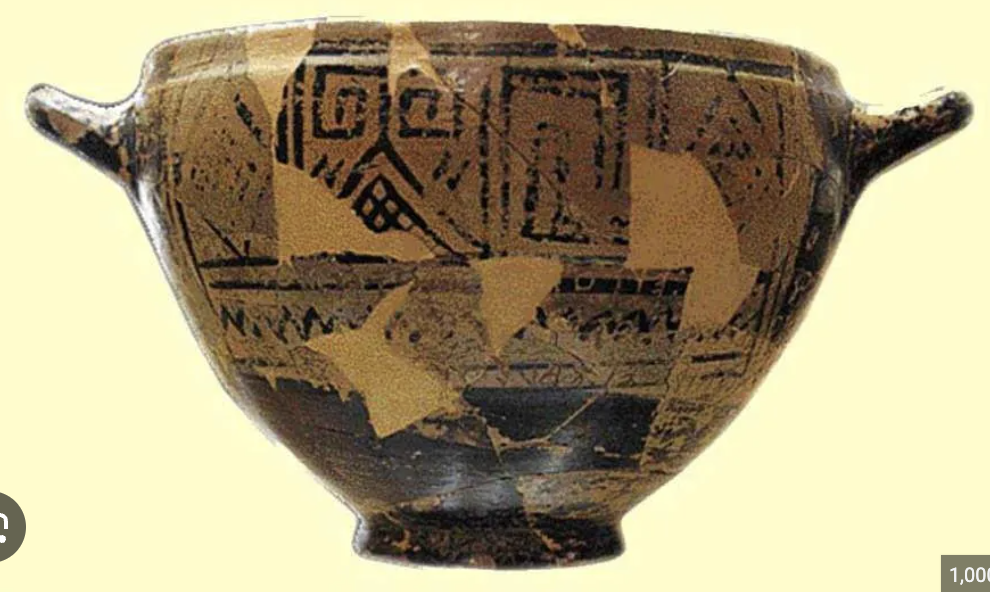

Cup of Nestor
WHEN: 750 BCE
WHERE: in a tomb on Ischia, Italy
WHY: One of the oldest known examples of the Greek alphabet, links to Homeric epics & religious significance
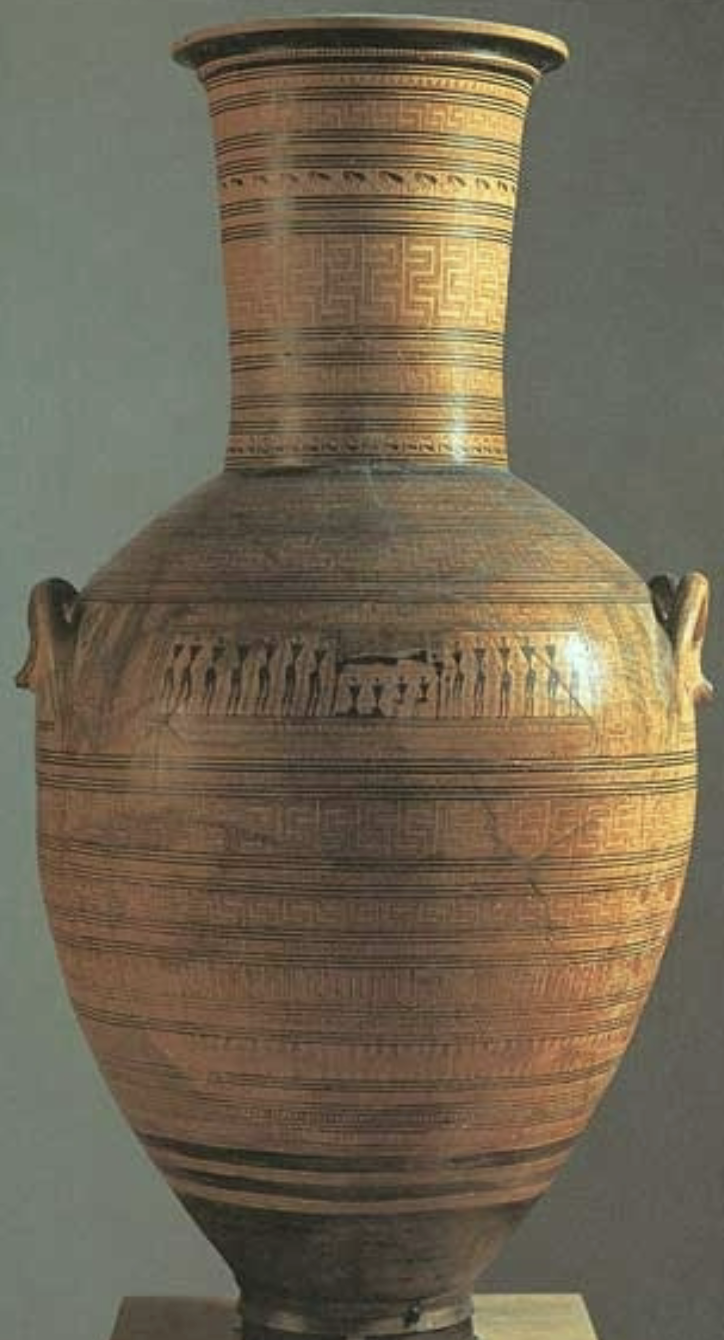

Dipylon pottery / late geometric
WHEN: 750 BCE
WHERE: Athens
WHY: artistic innovation w/ narrative storytelling & figures → symbolic grave marker: symbolism of death, mourning, high status, rituals
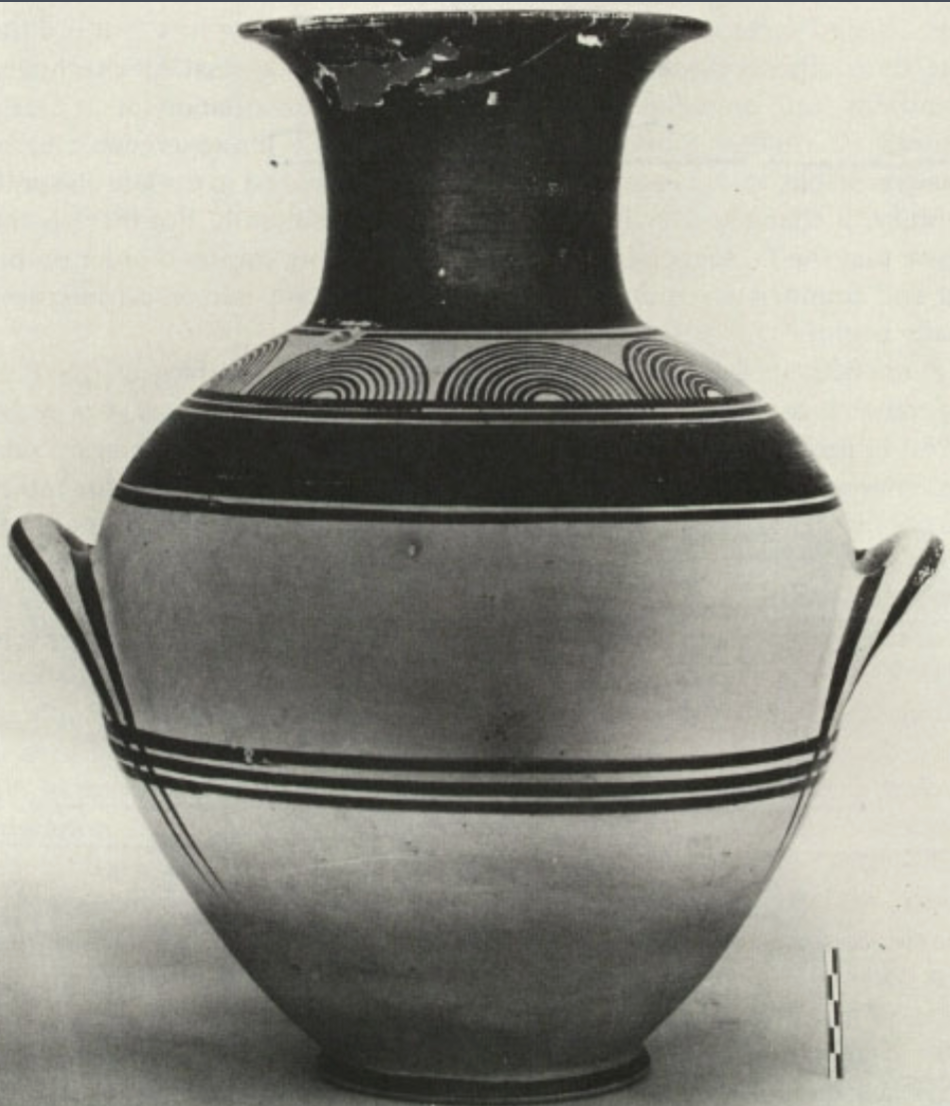

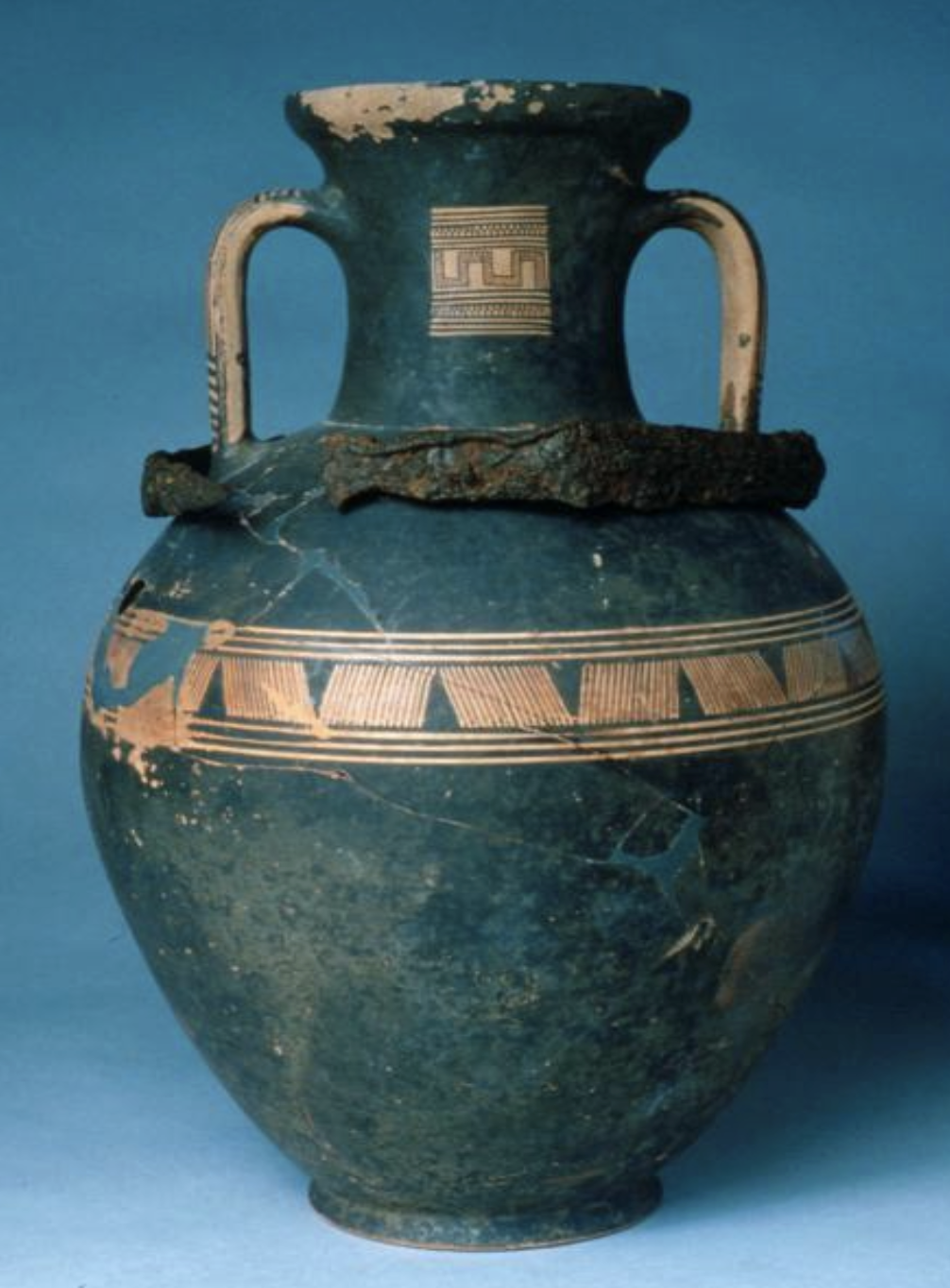
Water vessel ash urn
WHEN: geometric period (740-735BC)
WHERE: Athens
WHY: hints at societal structure, social roles, (religious) rituals → women’s ashes in water vessels & men’s ashes in wine vessels
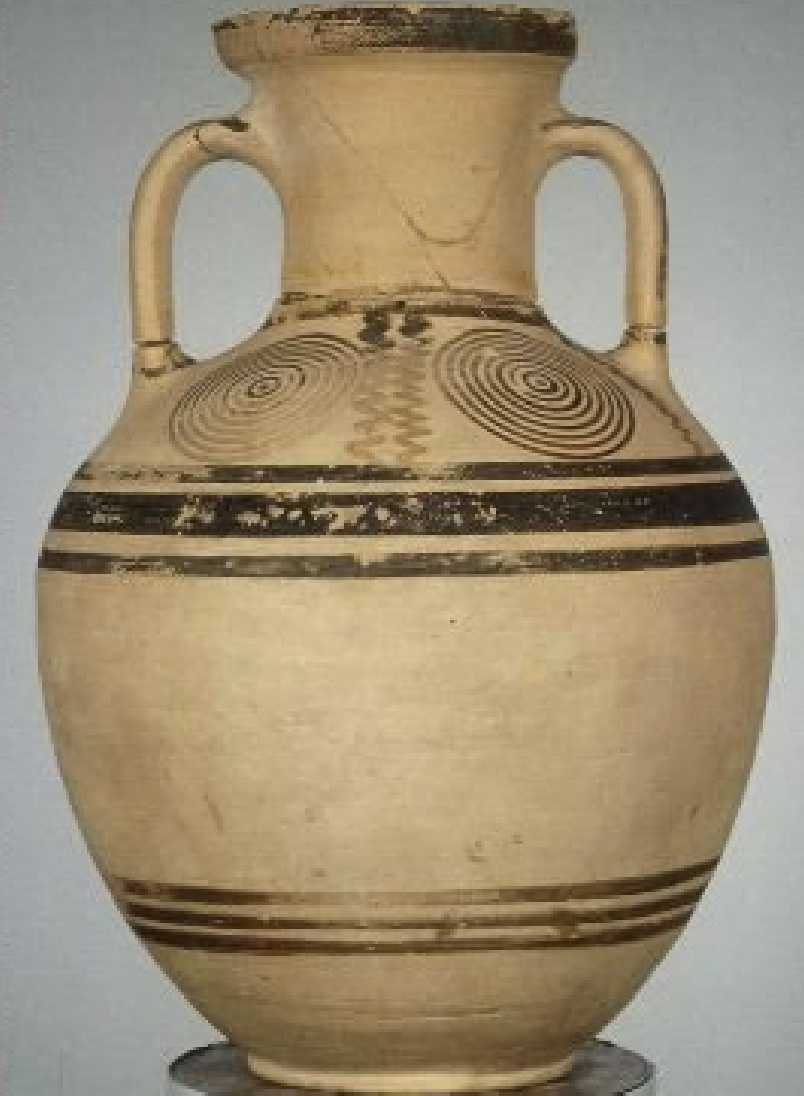

Wine vessel ash urn
WHEN: geometric period (740-735BC)
WHERE: Athens
WHY: hints at societal structure, social roles, (religious) rituals → women’s ashes in water vessels & men’s ashes in wine vessels
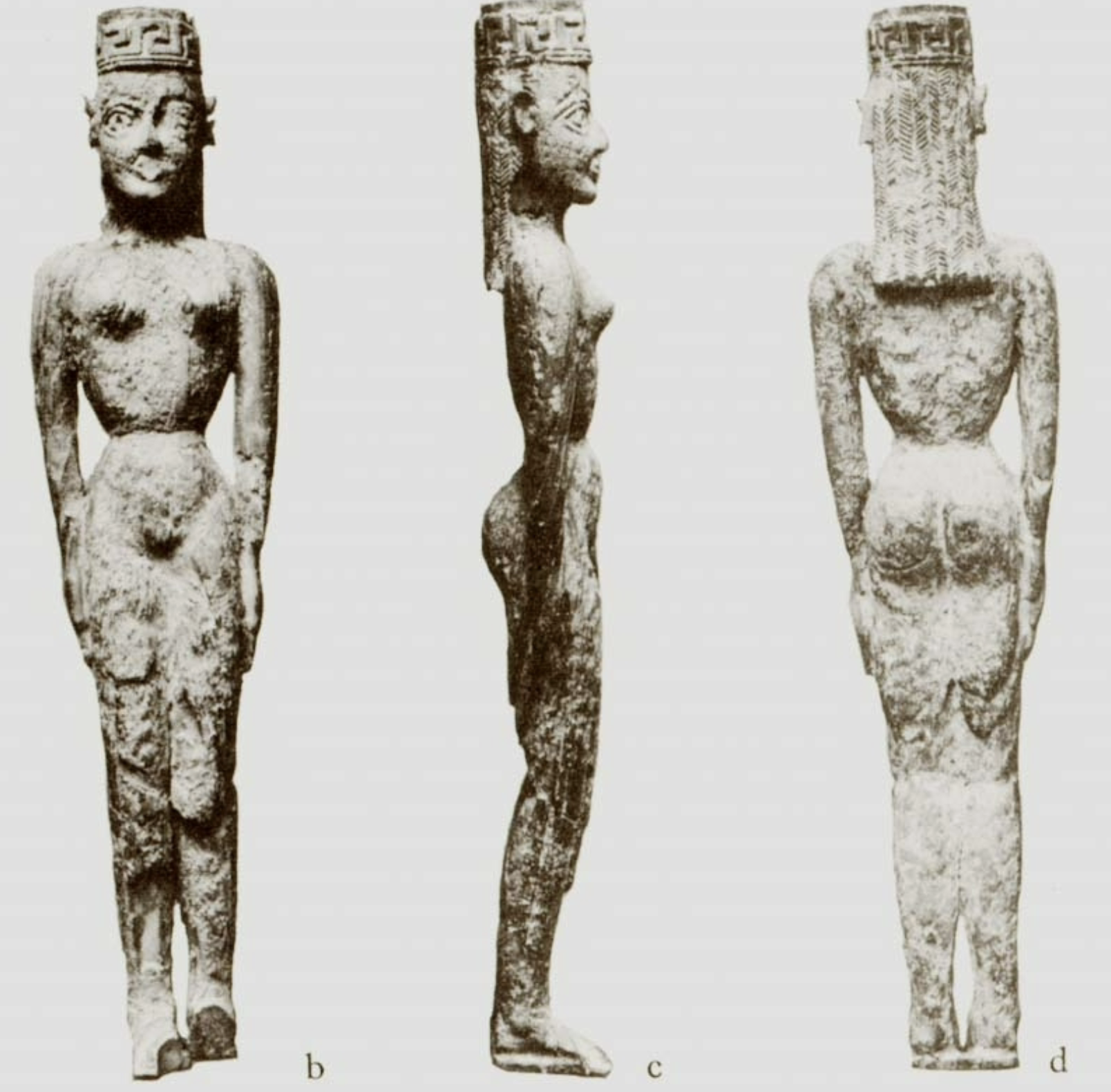

Ivory figurine
WHEN: 730-720 BC
WHERE: Athens
WHY: artistic expression, religion, worship, offerings, influenced by Near Eastern art styles using imported ivory material
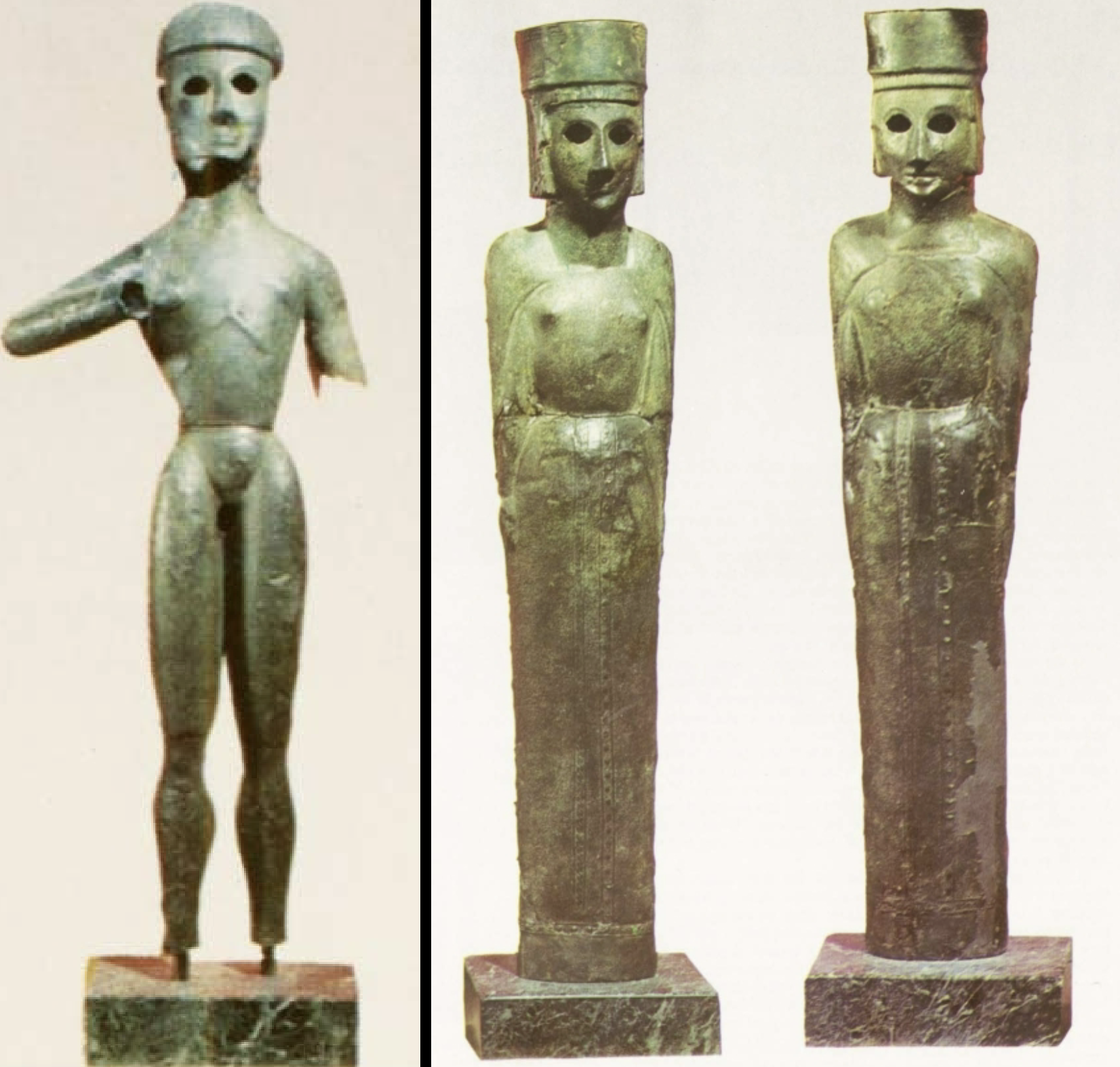

Bronze cult statues
WHEN: 700 BCE
WHERE: Dreros
WHY: technical skill (bronze sheets hammered over wood), artistic development (anatomically detailed), hints at religion, worship, how gods were perceived

Dreros inscription: kosmos and polis
WHEN: 625-600 BCE
WHERE: Dreros
WHY: first mention of a state (polis) anywhere in the greek world, a sort of constitution declaring that 1 man cannot be kosmos/chief more than once within 10 years → political structure, preventing monopoly, communal rule
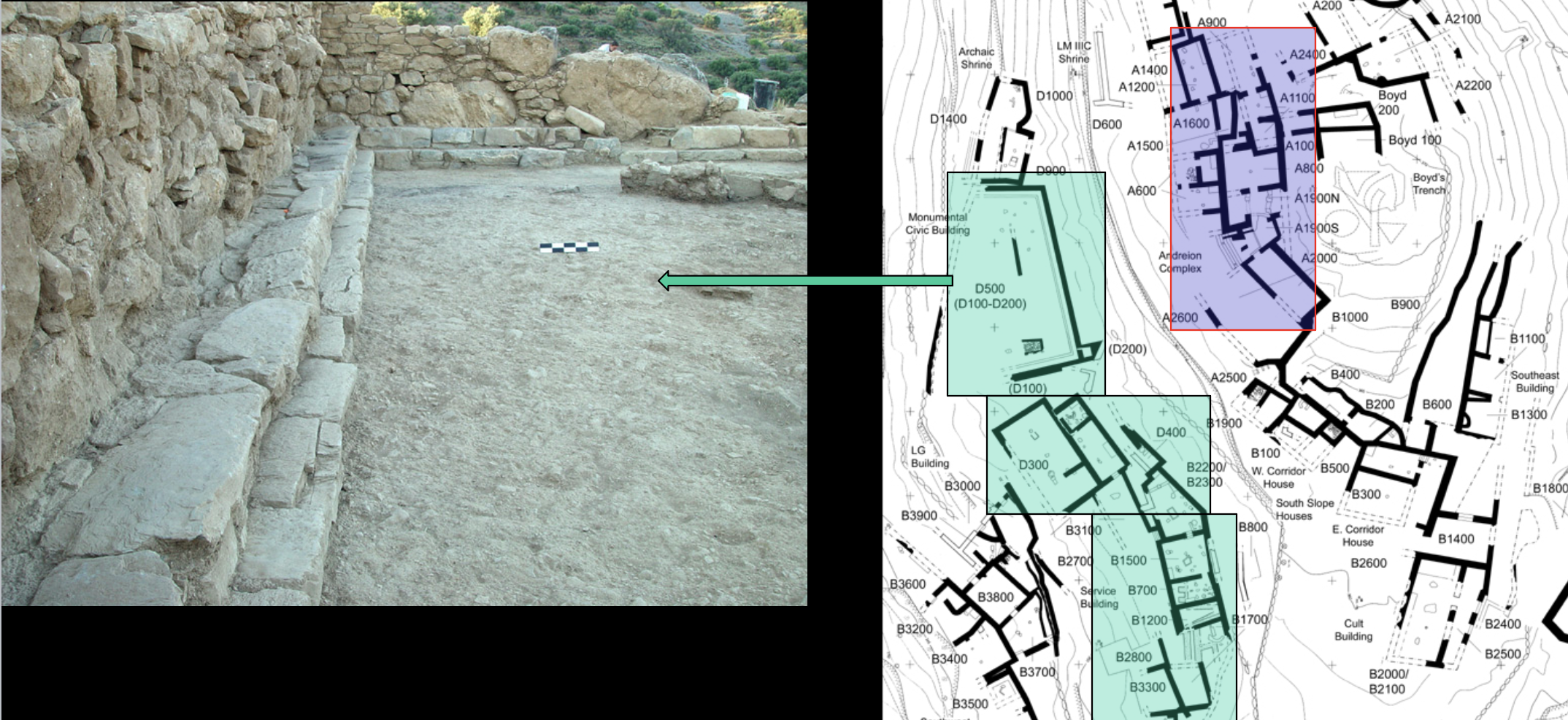
Azoria & andreion
WHEN: 600 BCE
WHERE: Crete
WHY: communal city → formation of early Greek cities w/ houses, dining halls, civic architecture → storage, religious ritual, communal feasting → social/political organization: standardized dishes & animal bones
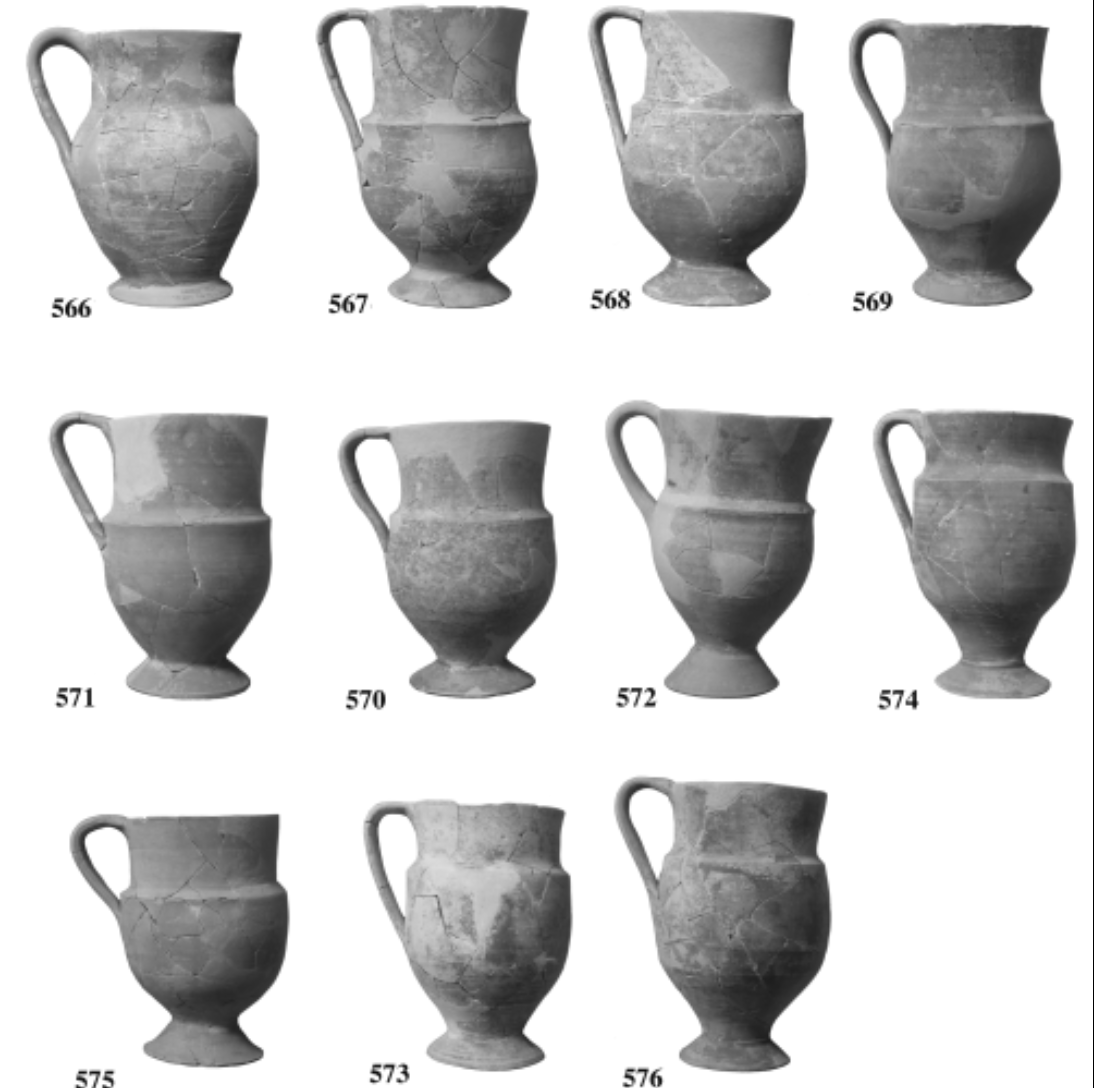

Cretan drinking cups
WHEN: 600 BCE
WHERE: Crete, Azoria
WHY: all standardized & uniform, plain → indicative of austerity & community equality within the dining halls → social structure
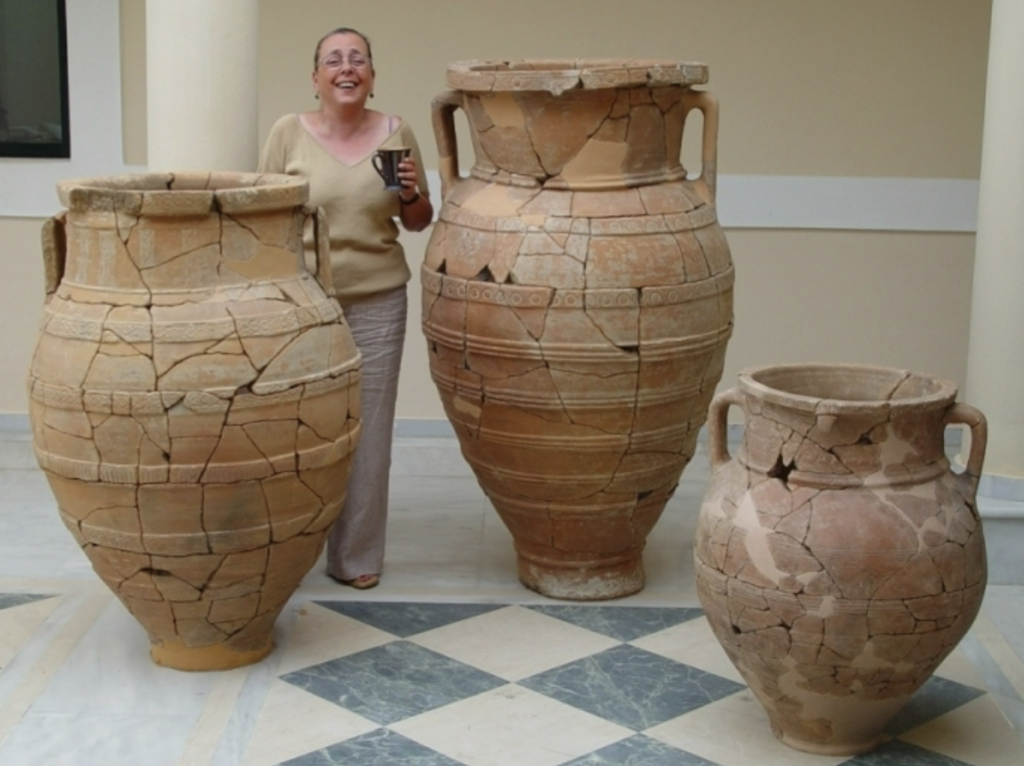

Pithos jars
WHEN: 600 BC
WHERE: Azoria/Crete
WHY: bulk storage of grains, oil, mostly wine → indicative of large population
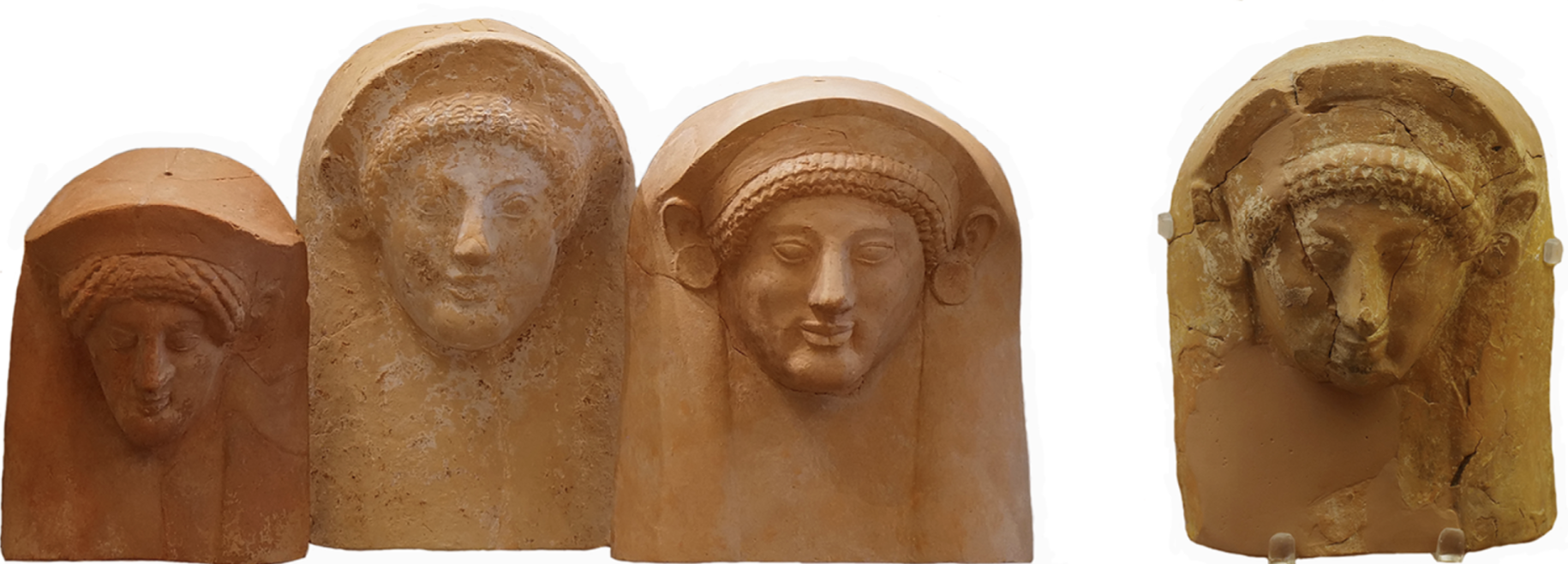

Goddess “masks”
WHEN: early 5th century BCE
WHERE: Olous, Crete & Rhodes
WHY: highlighting worship/religious ceremonies, used to honor & portray important female deities in festivals and cult gatherings = divine presence / goddesses embody protection & power expressed through ritual masks → trading across islands for local religion
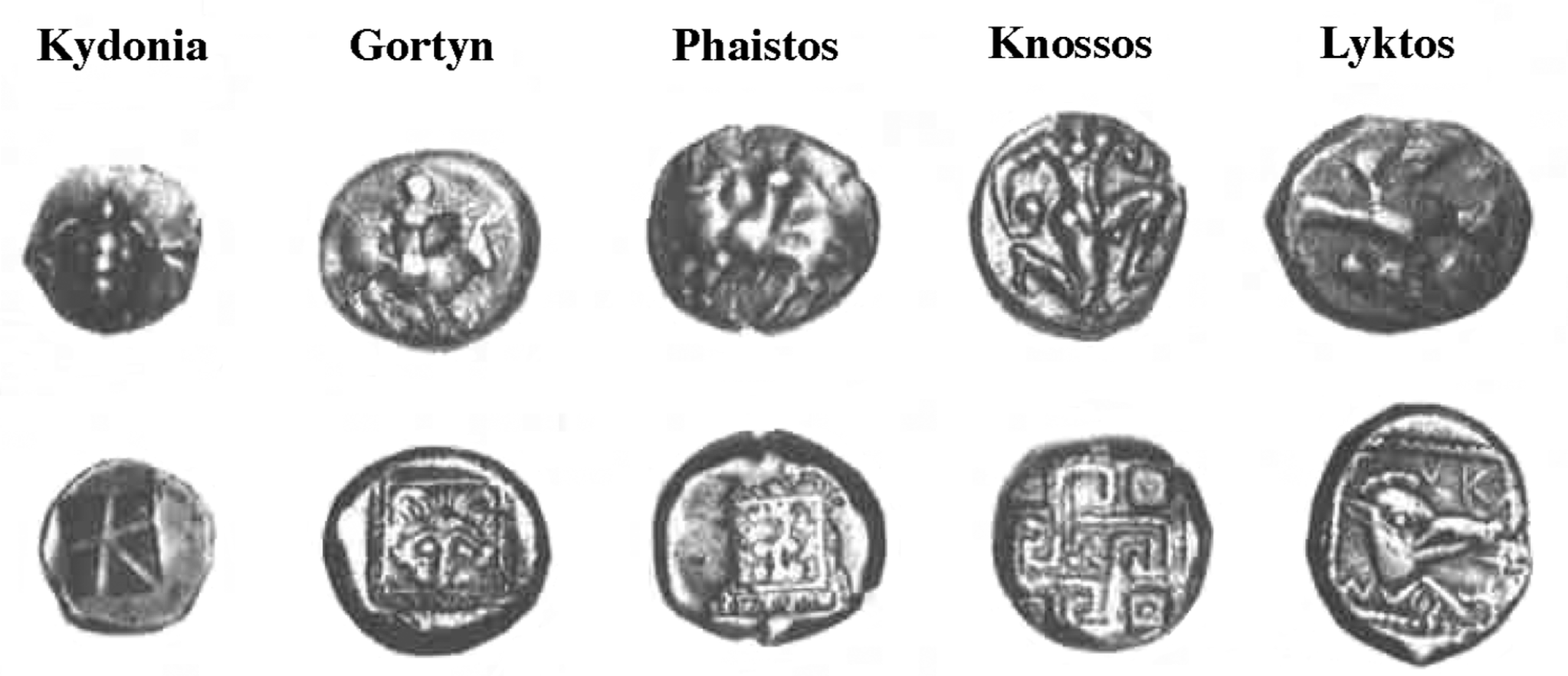

Earliest Cretan Coins
WHEN: 5th century BCE
WHERE: Crete
WHY: emergence of city state representation, trade, independent economies, symbols of mythology & politics
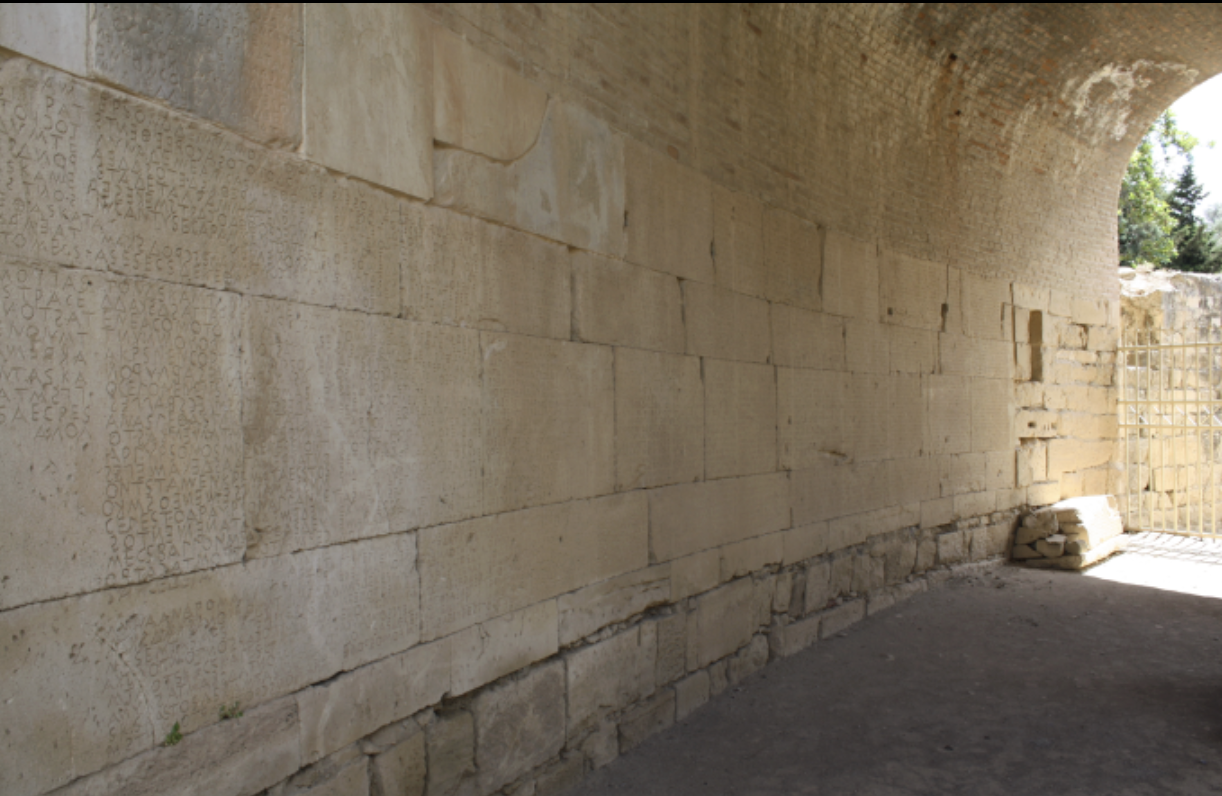

Gortyn law code
WHEN: 450 BCE
WHERE: Gortyn, Crete
WHY: most extensive evidence of civil & social laws and expectations in ancient Greece w/ rules regarding marriage, property, slavery, crime

Tylissos inscription
WHEN: 450 BCE
WHERE: Tylissos, Crete
WHY: political & social expectations, discussion about religion & ritual → Tylissos = administrative hub/religious site. inter-city relations & maintaining territories w Argos and Knossos
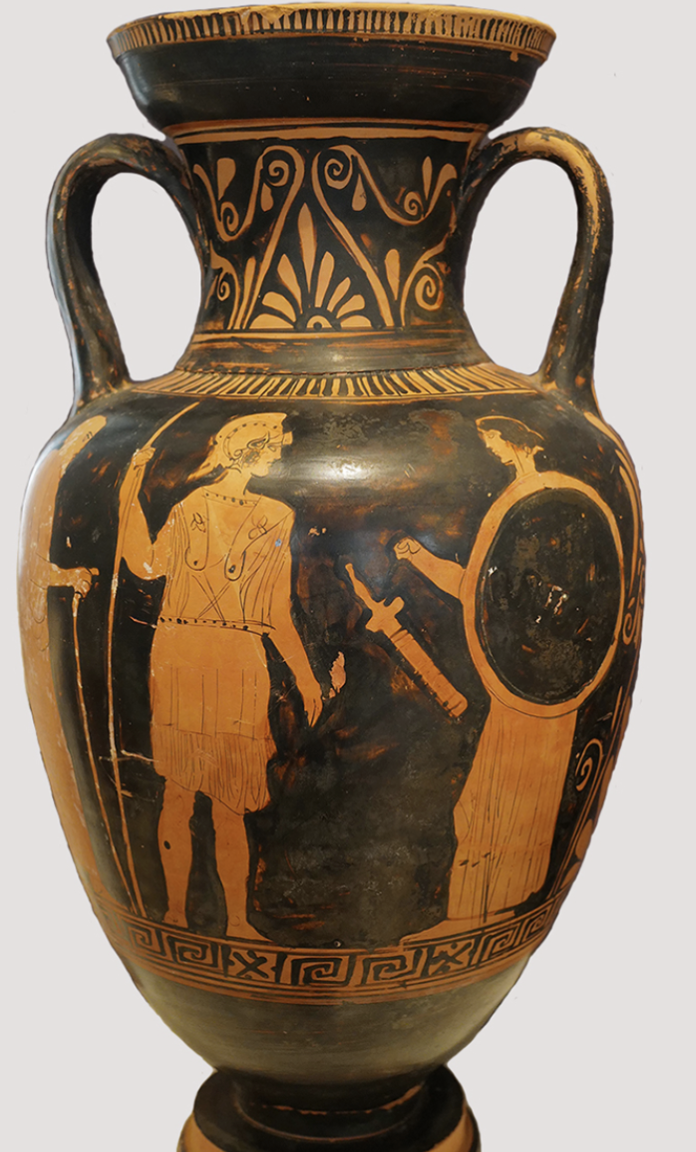

Athenian (Attic) red figure pot
WHEN: 450 BCE
WHERE: Athens
WHY: new artistic development allowing for naturalistic detail & exceptional drawings of figures w/ black background → led to great amount of exports/profit from art