DTCC Anatomy Unit 4 Test
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
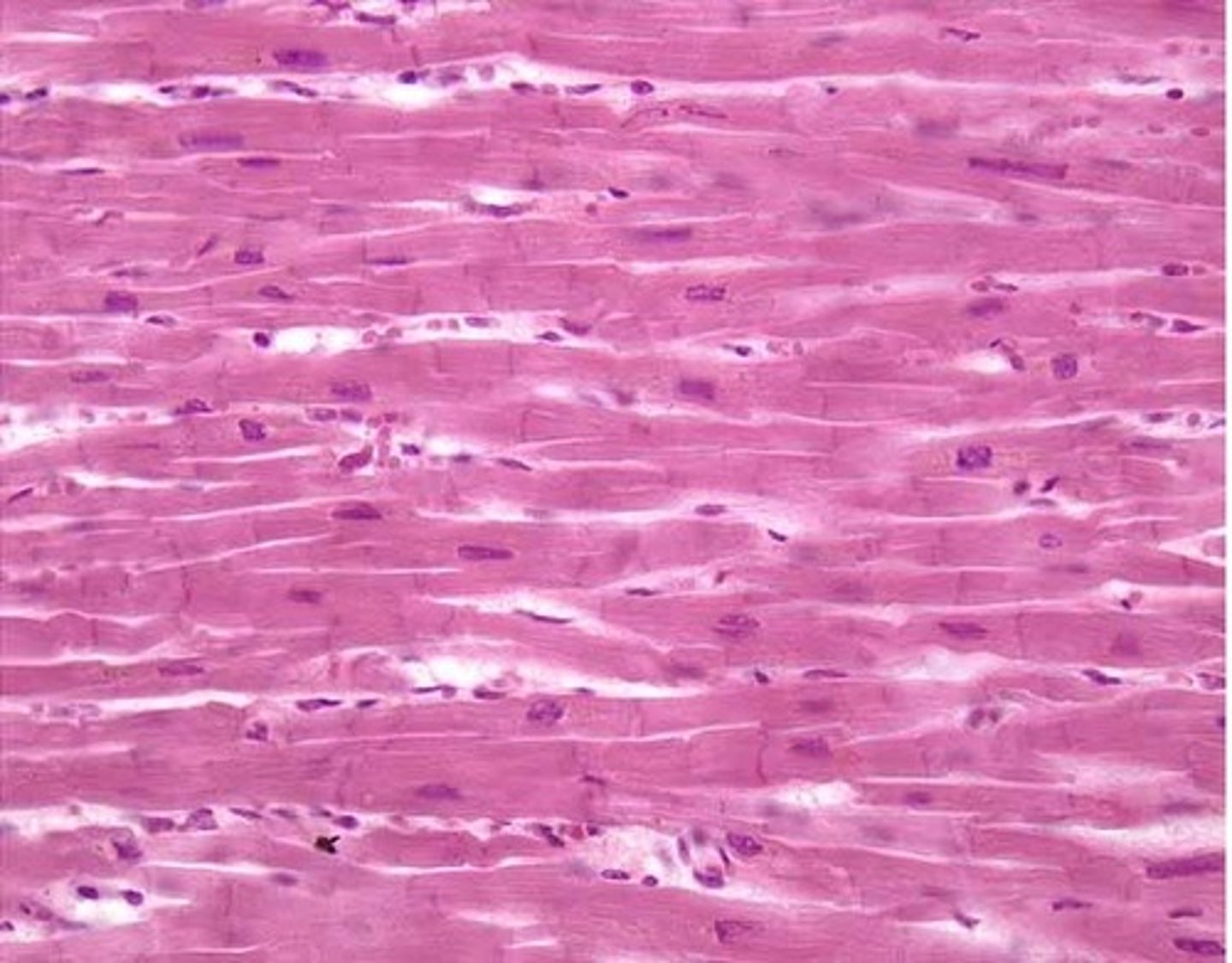
cardiac muscle
-branched and uni-nucleated cells
-striated
-makes up walls of the heart
-involuntary
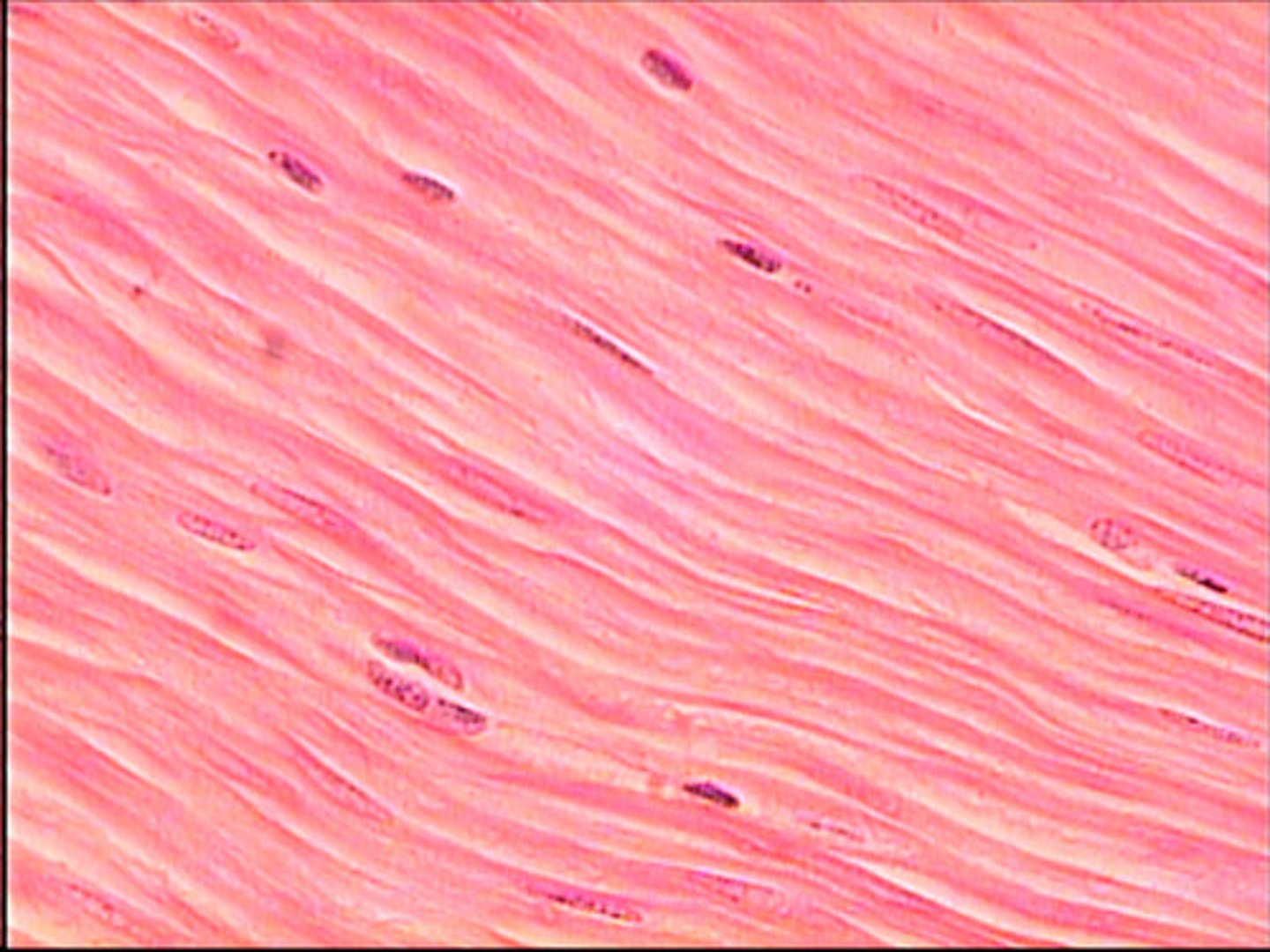
smooth muscle
-spindle-shaped, uni-nucleated cells
-non-striated
-makes up walls of hollow organs (NOT heart)
-involuntary
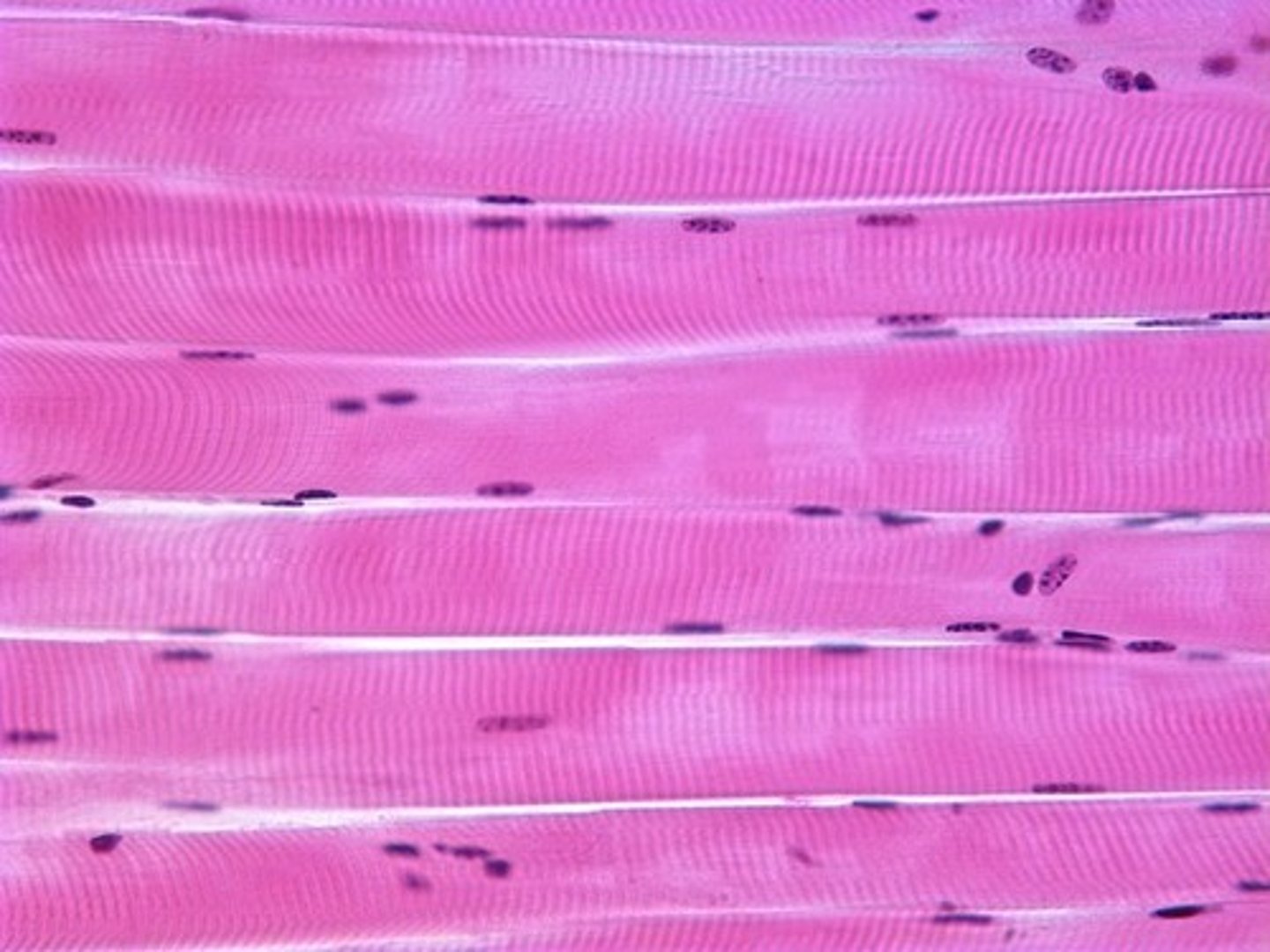
skeletal muscle
-long, cylindrical, multi-nucleated cells
-striated
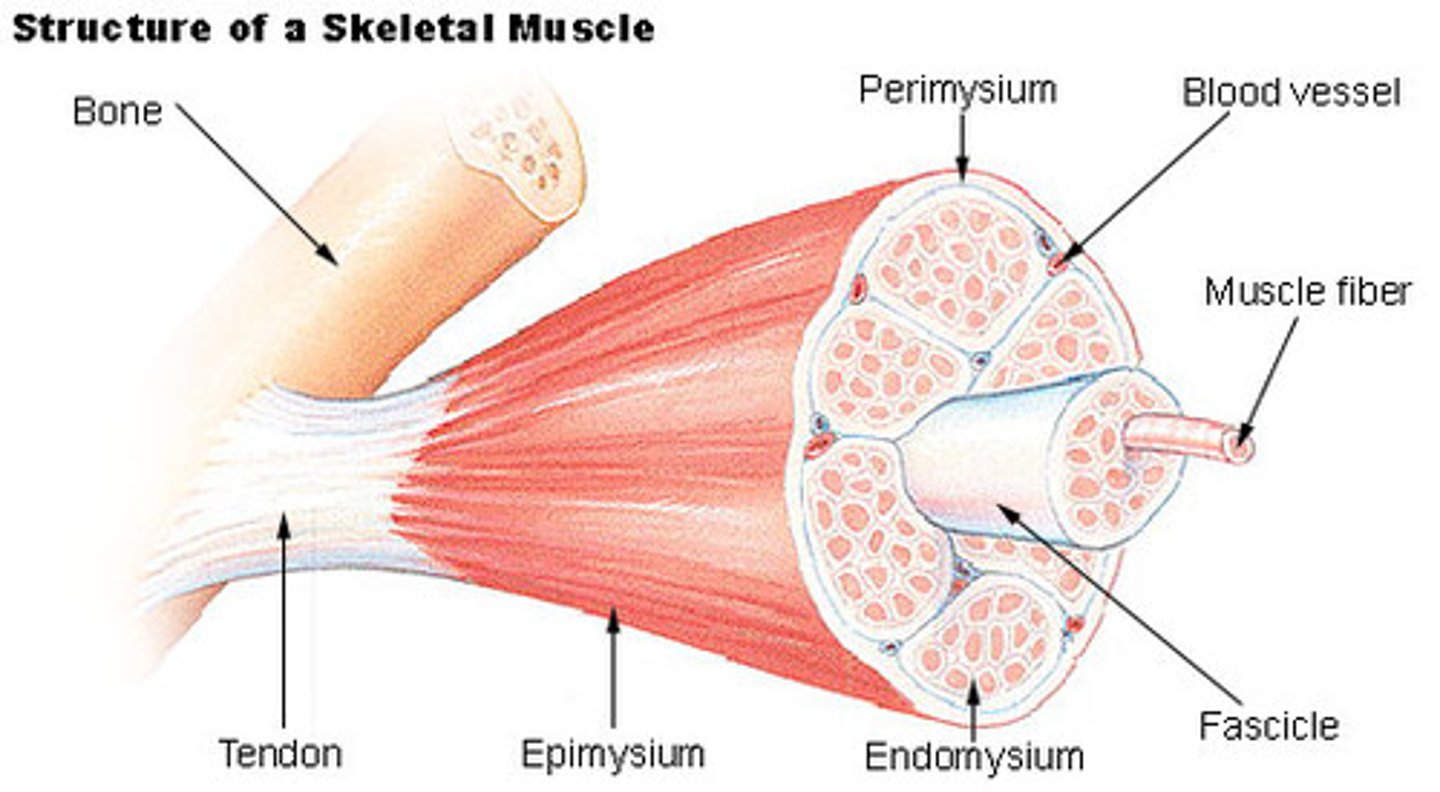
-attached to bones by tendons
-voluntary
4 functions of muscles
produce movement, maintain posture, stabilize joints, generate heat
4 functional characteristics of muscle
contractility, excitability, extensibility, elasticity
epimysium
layer of connective tissue around entire muscle
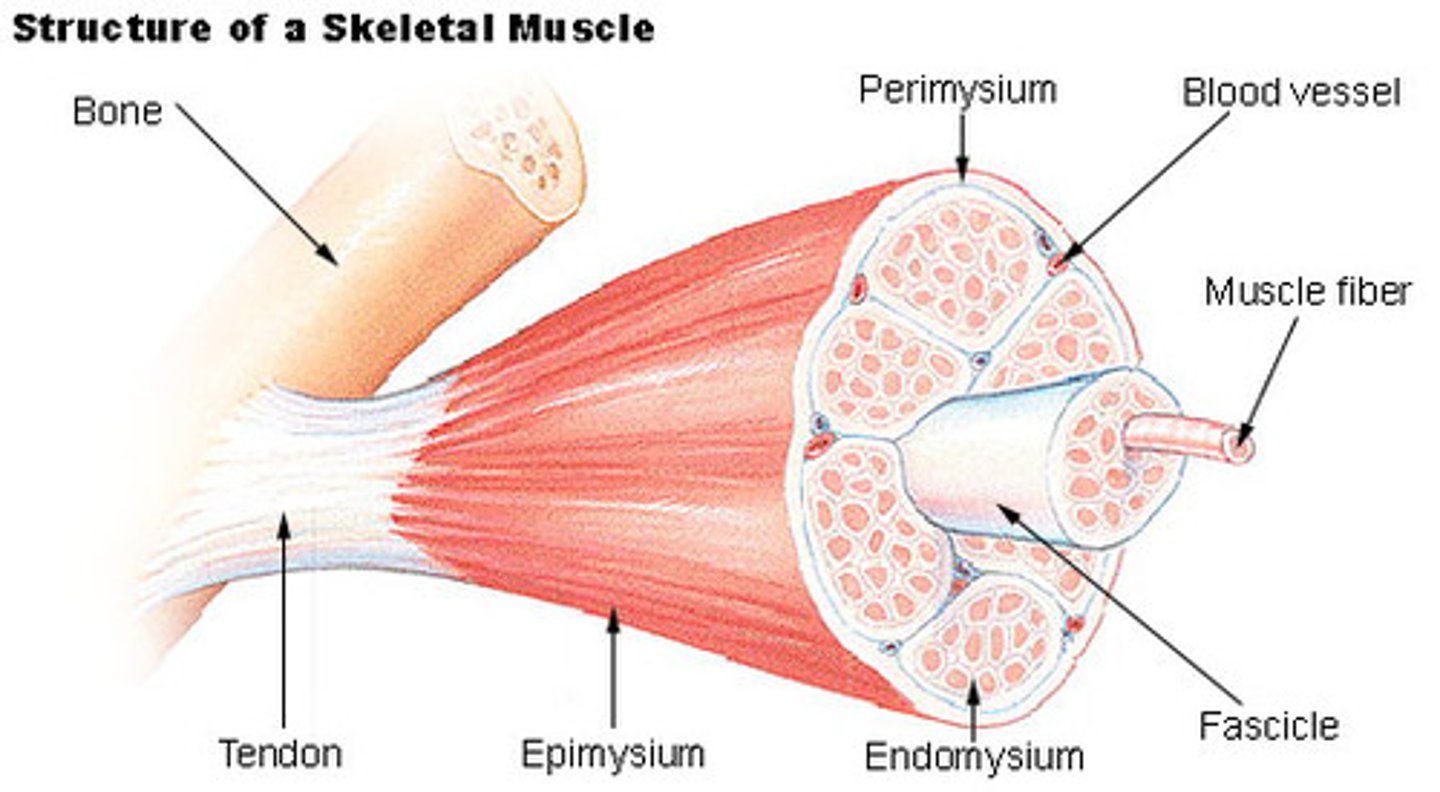
perimysium
holds fascicles together
endomysium
surround individual muscle cells/fibers
fascicles
bundles of muscle fibers
muscle fibers
individual muscle cells
insertion attachment
the movable bone attached to a muscle
orgin attachment
the immovable or less moveable bone attached to a muscle
myoglobin function
a red pigment that stores oxygen in muscle cells
glycosomes function
stores glycogen and then release glucose during muscle cell activity for ATP production
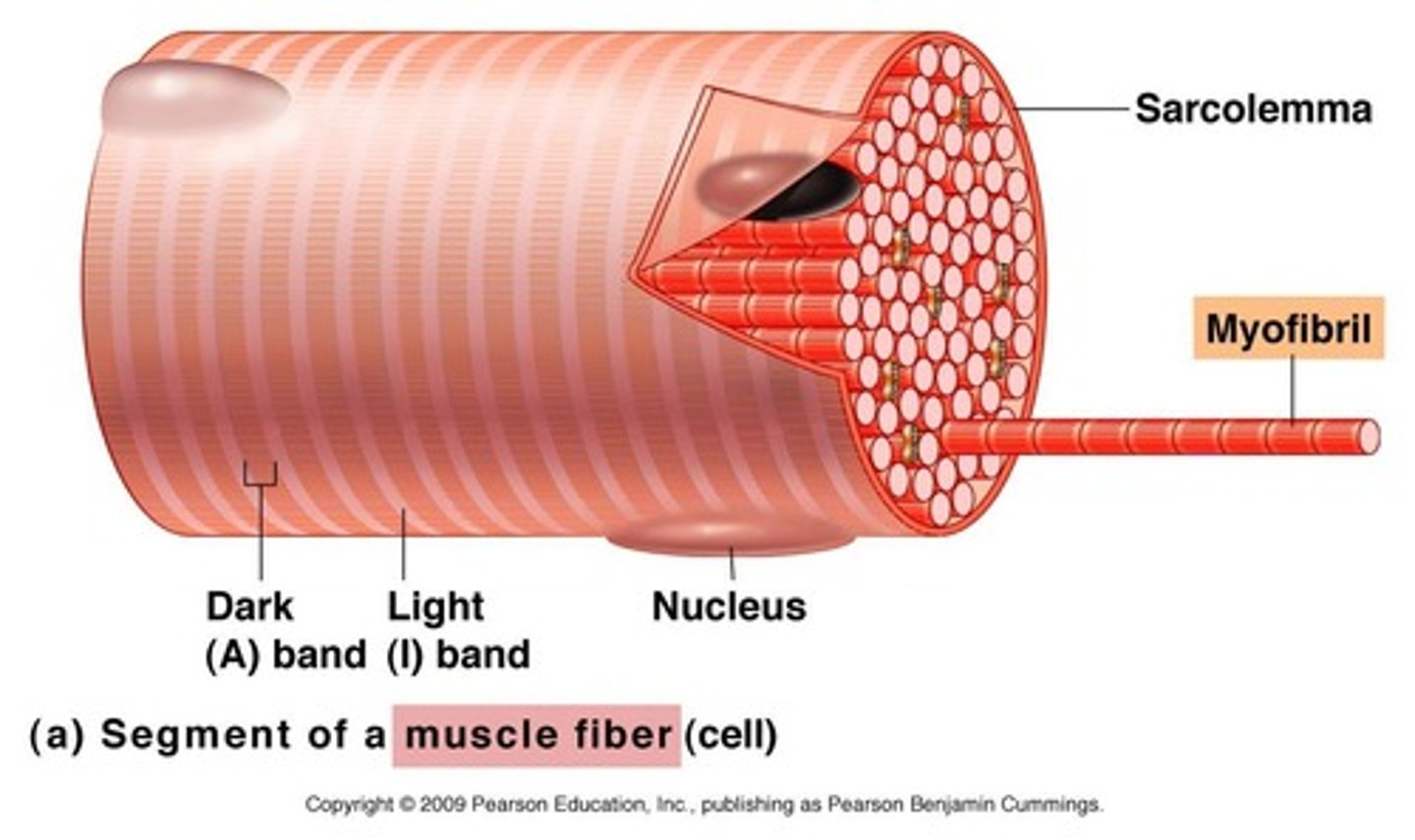
sarcolemma
muscle cell membrane
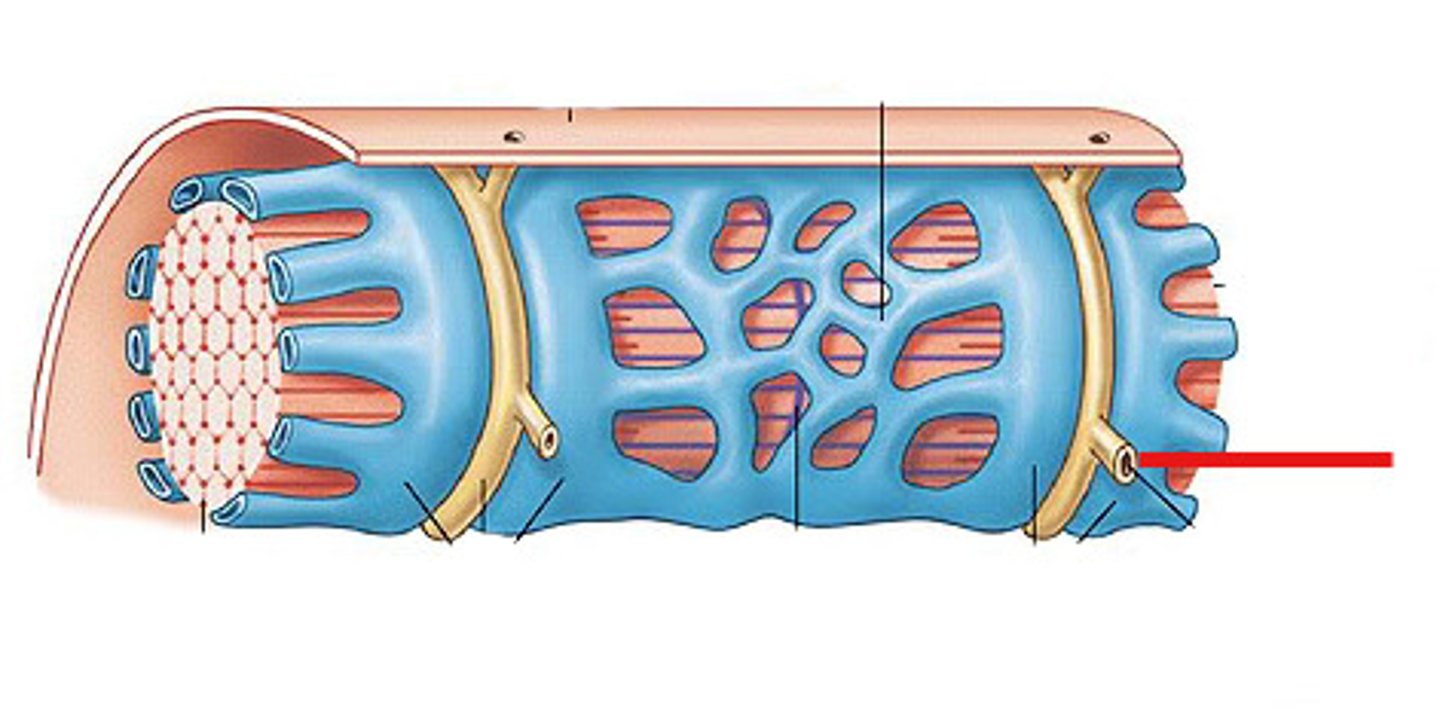
T-tubules
-channels of the sarcolemma that surround the myofibrils
-let glucose, oxygen, and calcium into the cell
-conduct action potentials to allow all myofibrils within a muscle fiber so they contract at the same time
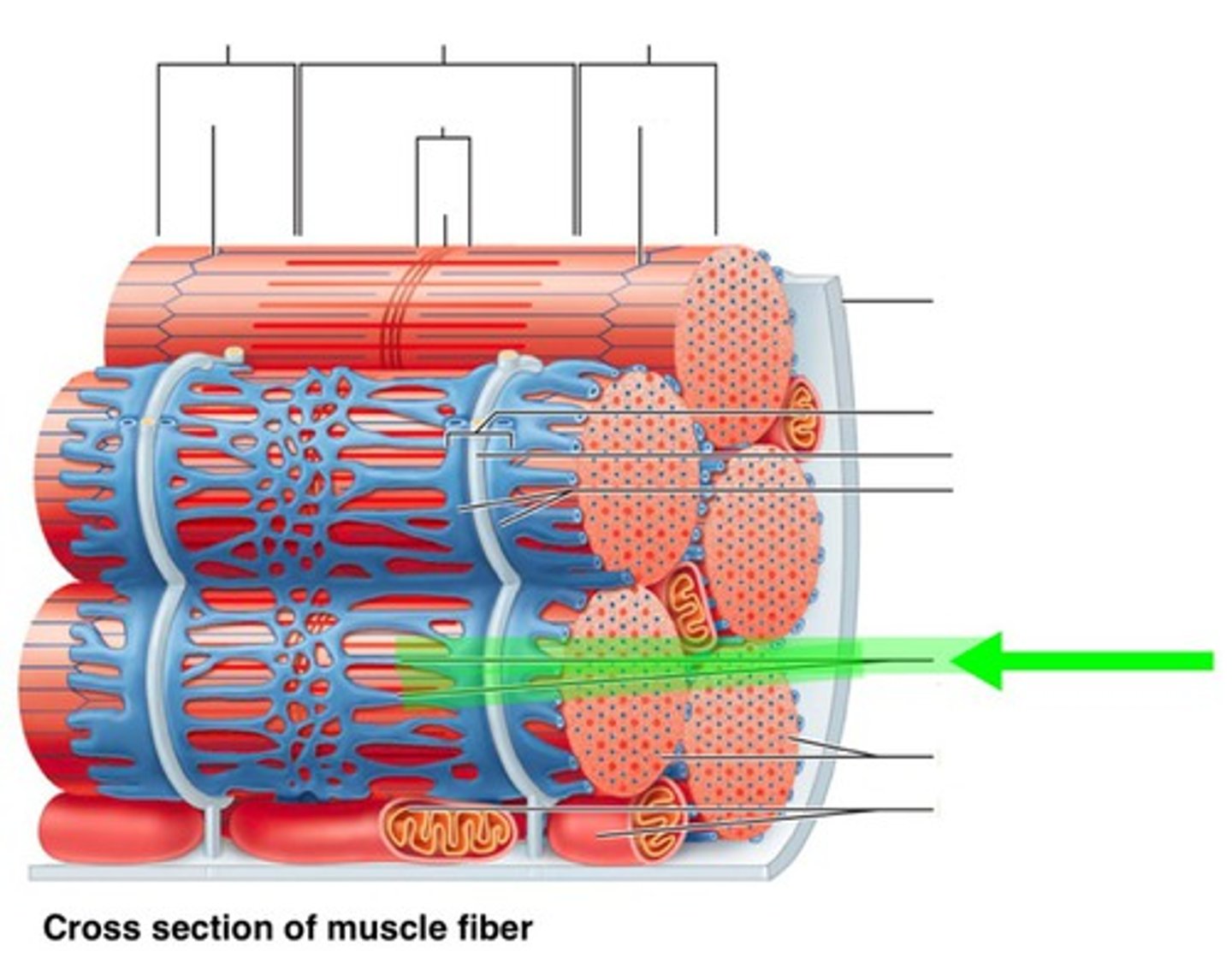
sarcoplasmic reticulum
-a system of tubes surrounding each myofibril
-stores calcium and releases it when an action potential runs down the T-tubule
myofibrils
-thin threads that extend the length of a muscle fiber and makeup muscle fibers
-contain myofilaments (thin and thick filaments)
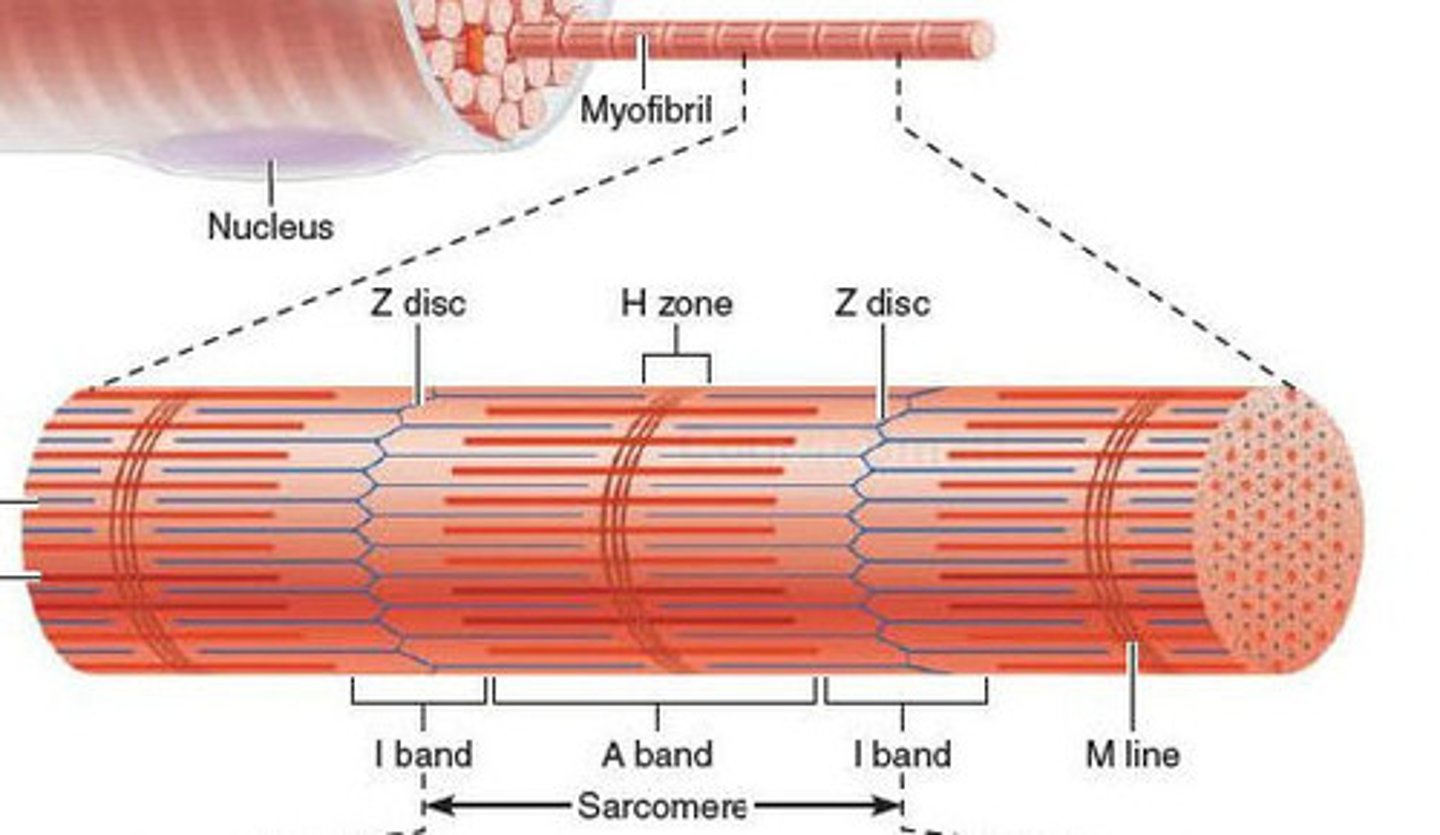
sarcomere
-segments of a myofibril, contractile element
-each contract individually
-align end to end
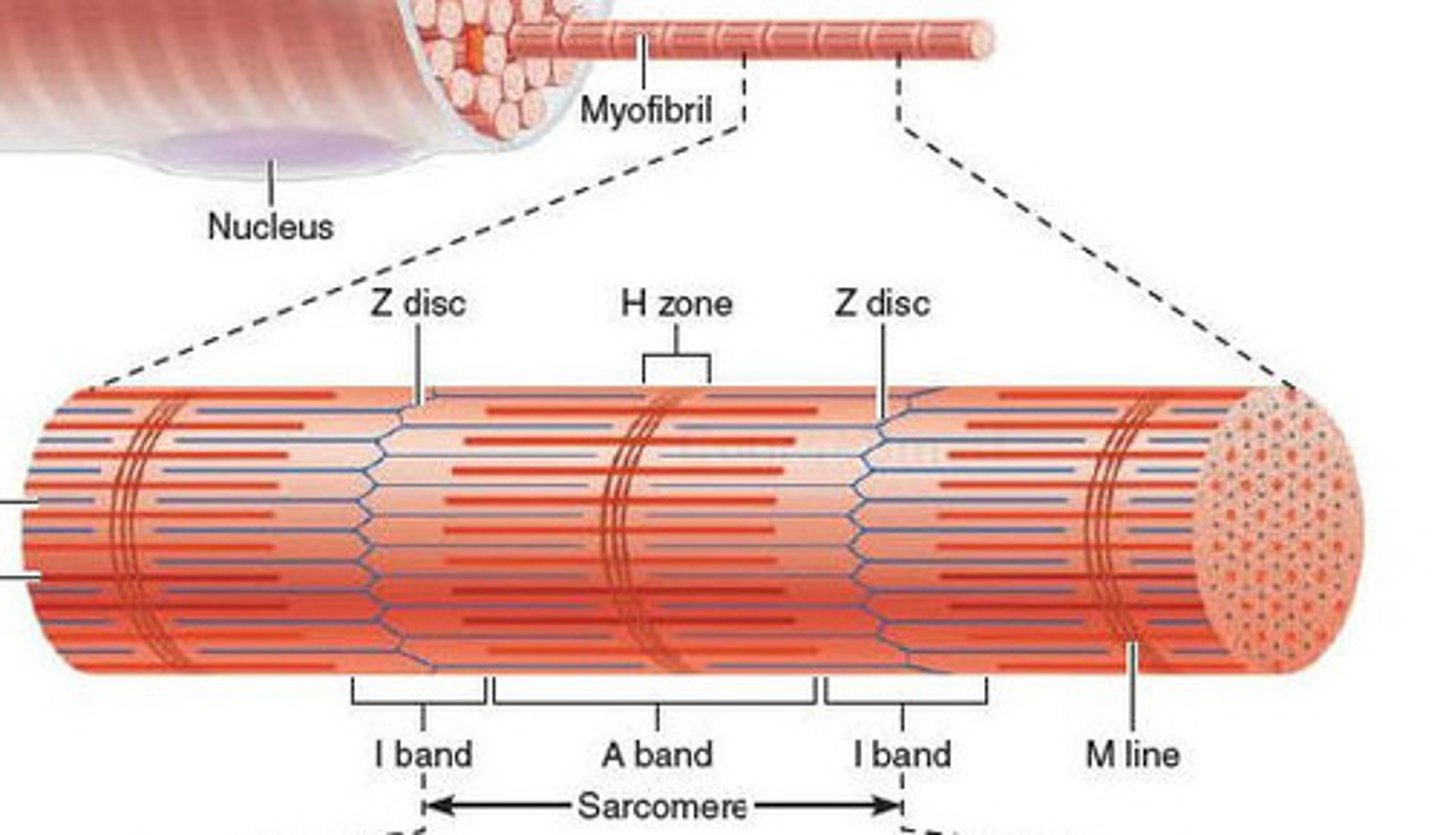
I band
space between thick filaments of 2 adjacent sarcomeres; where thin filaments are
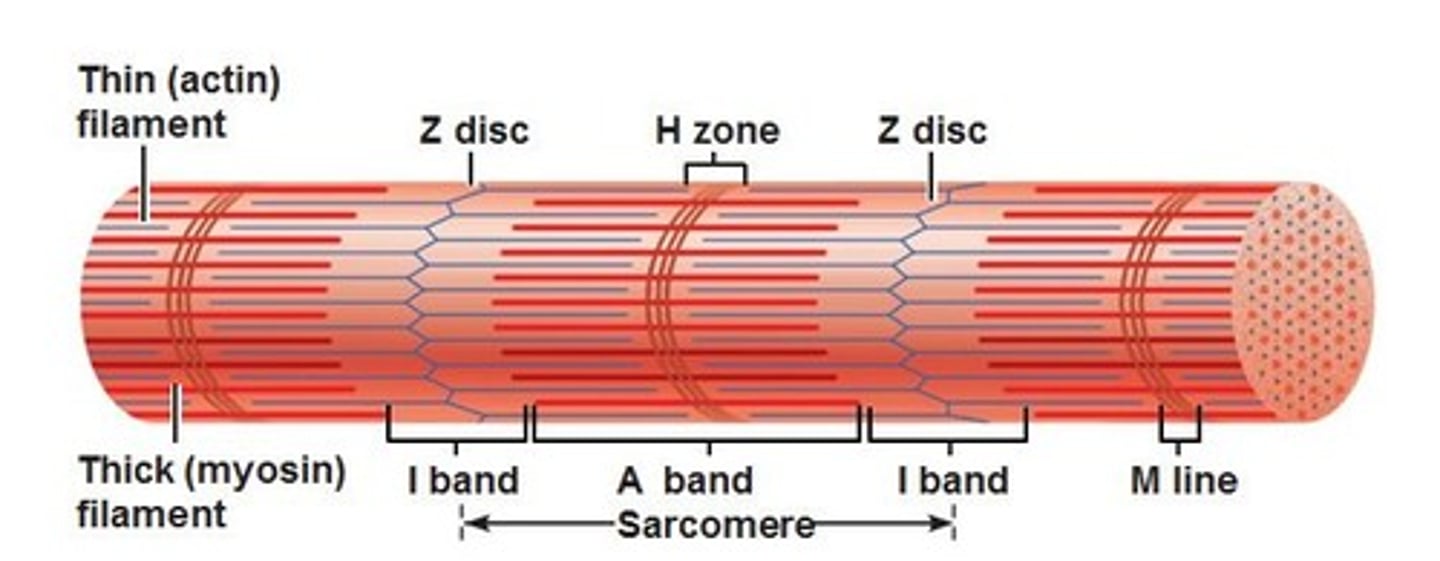
A band
dark band within striation pattern; length of thick filament and overlapping thin filament
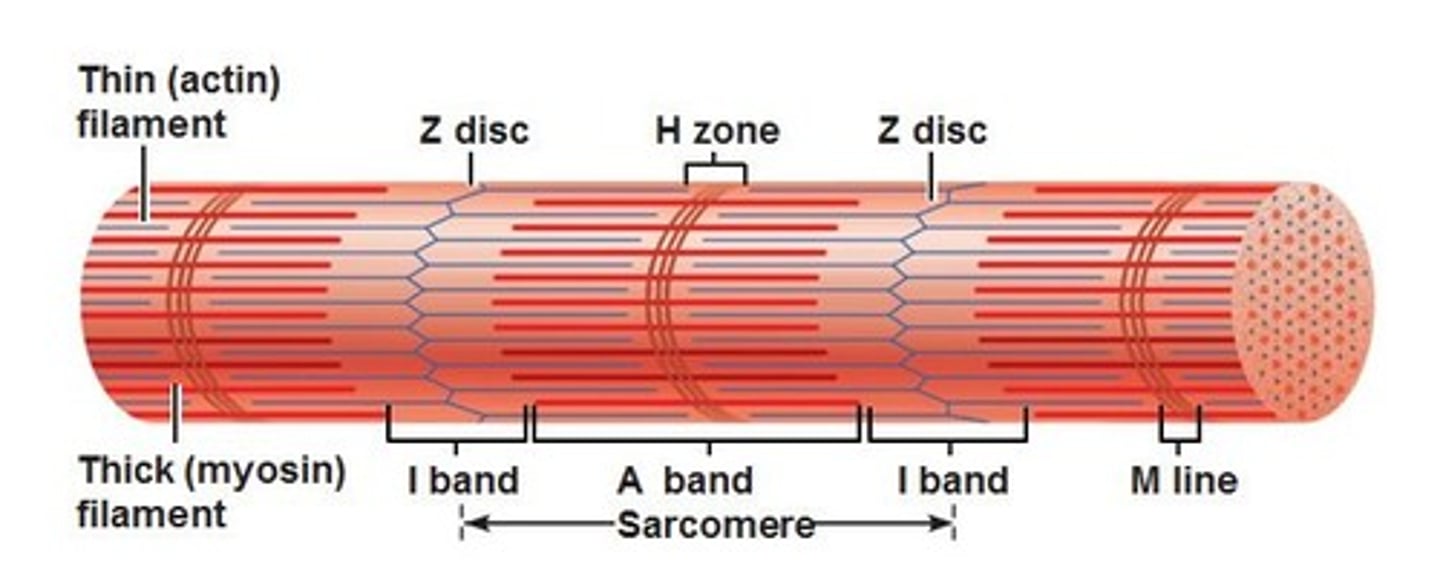
H zone
space in between thin filaments within A Band (contain M line)
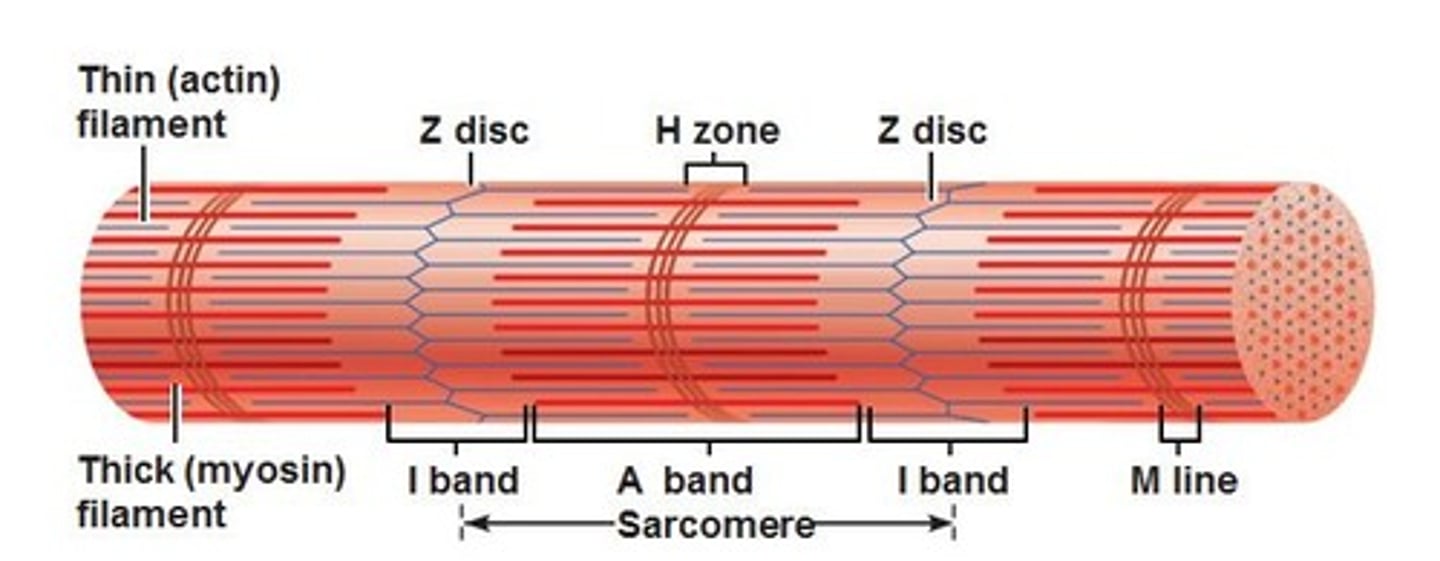
Z discs
boundaries of the sarcomere (have a zig-zag shape)
thick filaments
contain MYOSIN that attaches to the thin filament and performs the power stroke
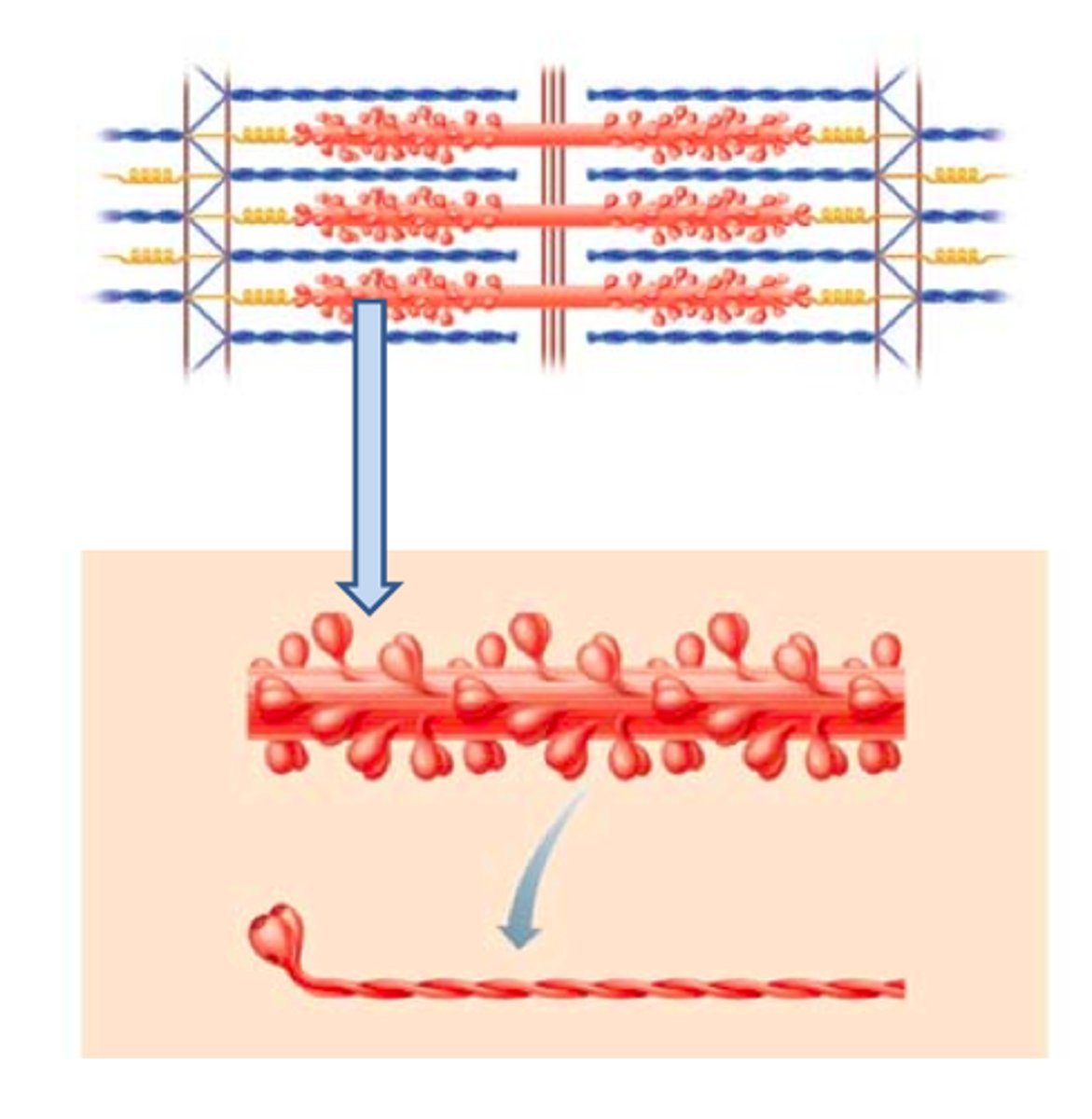
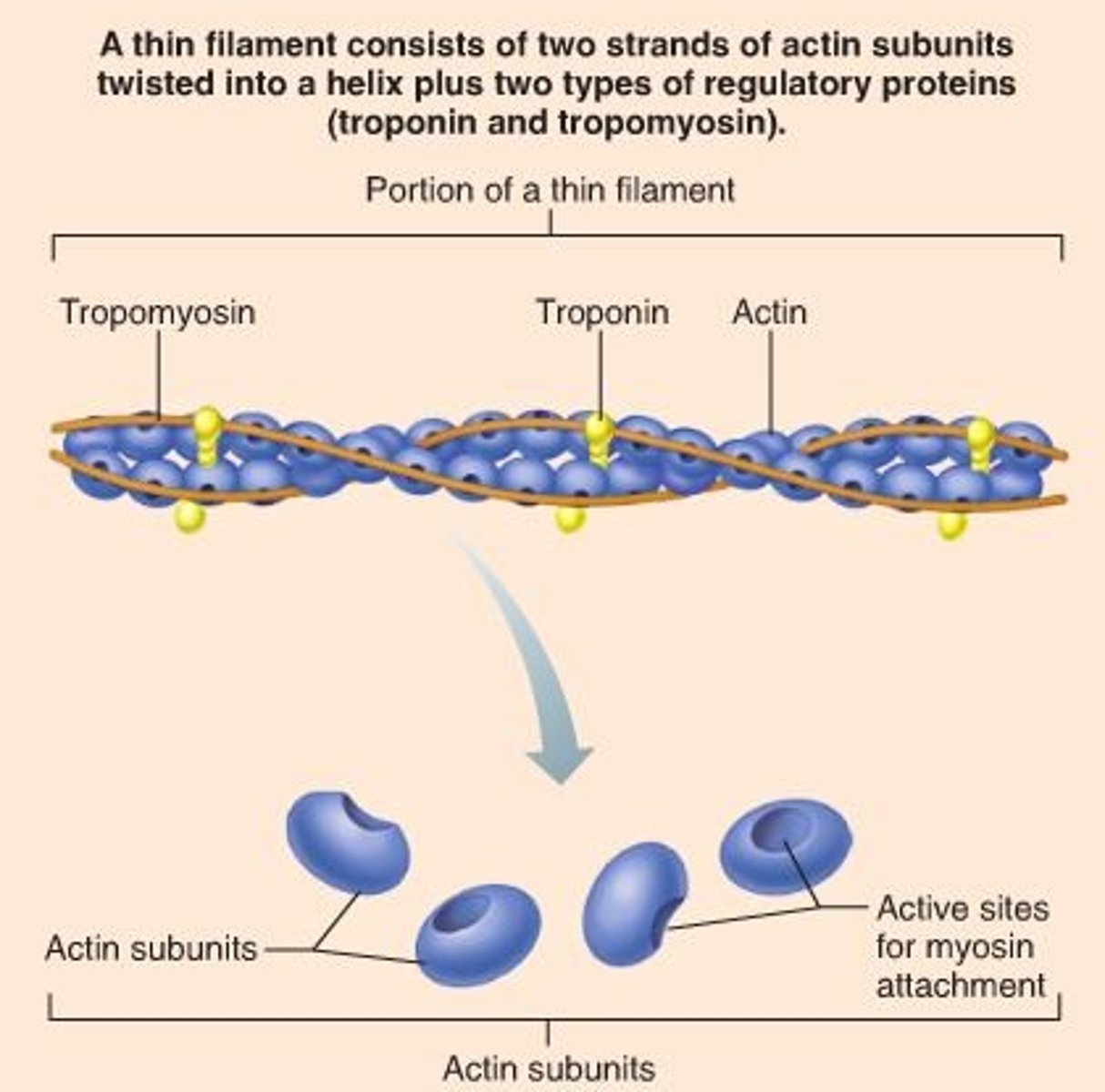
thin filaments
contain ACTIN; contain myosin-binding sites
Ca++ in Muscle Contraction
Ca2+ binds to troponin, which activates troponin to expose myosin-binding sites on the actin located on tropomyosin
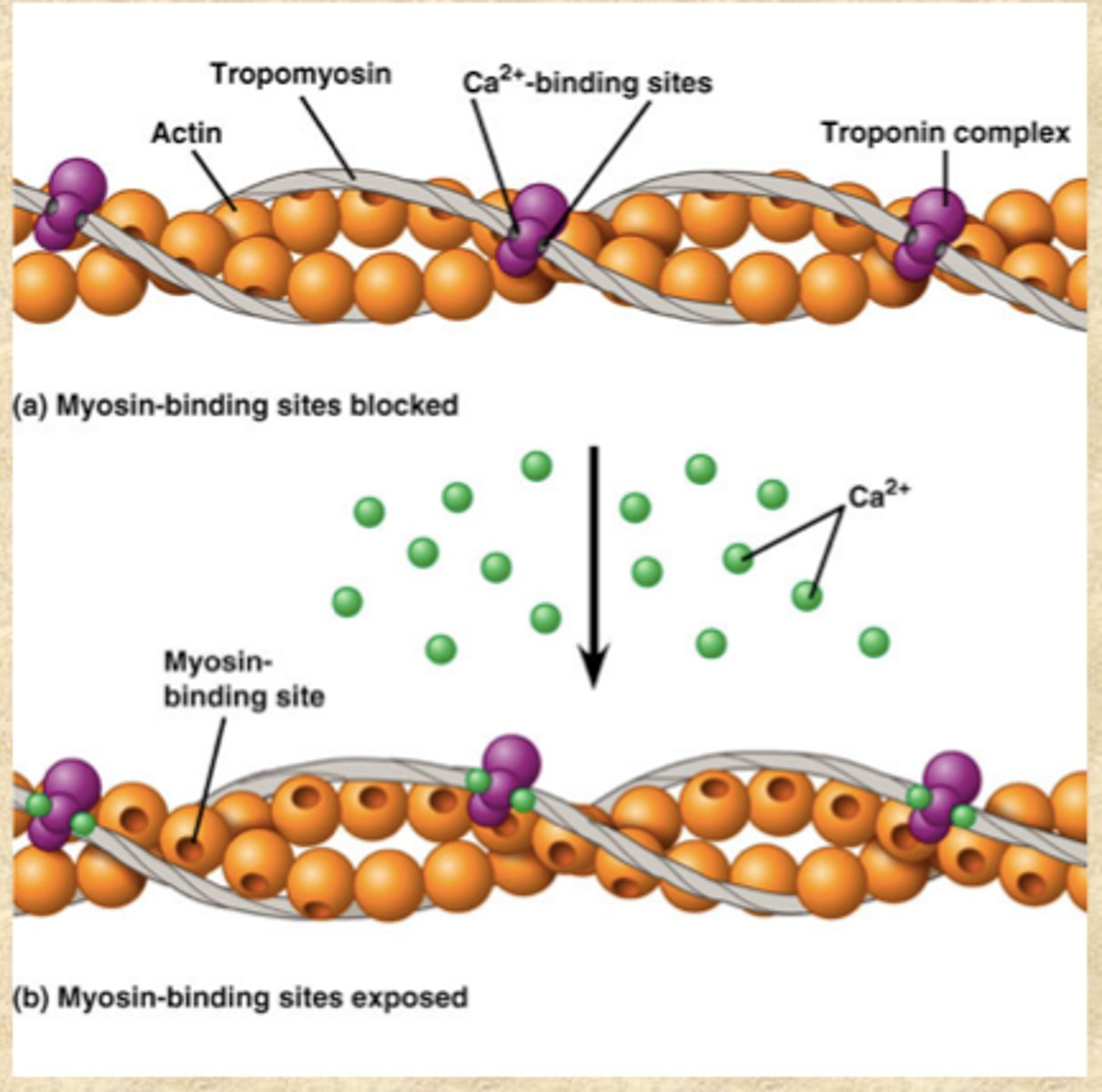
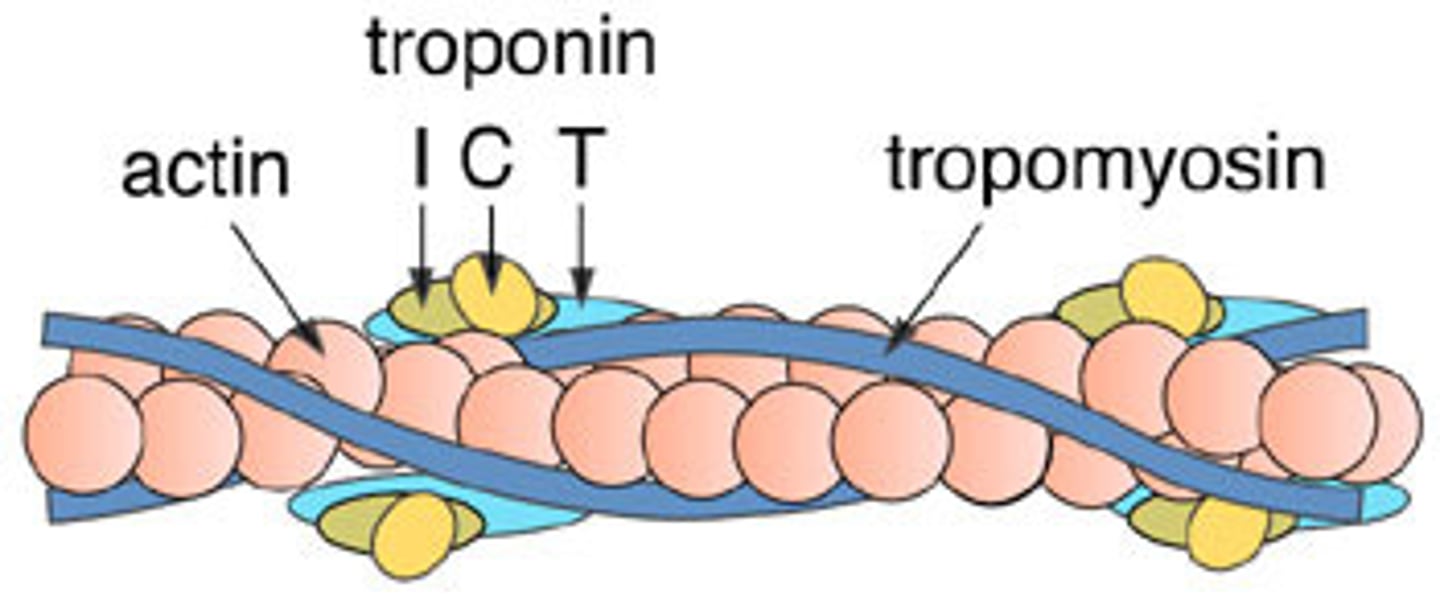
troponin
on thin filaments; regulatory protein that holds tropomyosin in place and assists with turning contractions on and off by exposing myosin-binding site on actin; Calcium activates troponin to expose binding sites
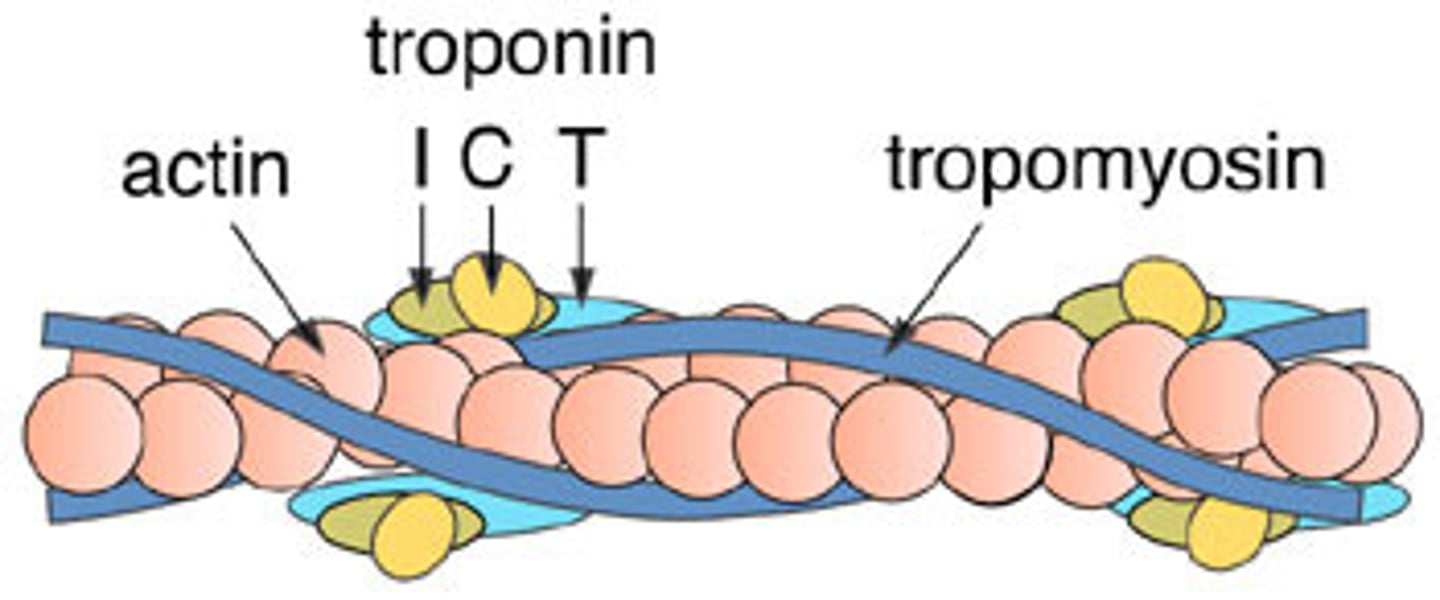
tropomyosin
on thin filaments; covers myosin binding sites on the actin; troponin moves tropmyosin to expose sites
crossbridge
forms when the myosin head attached to the actin of the thin filament
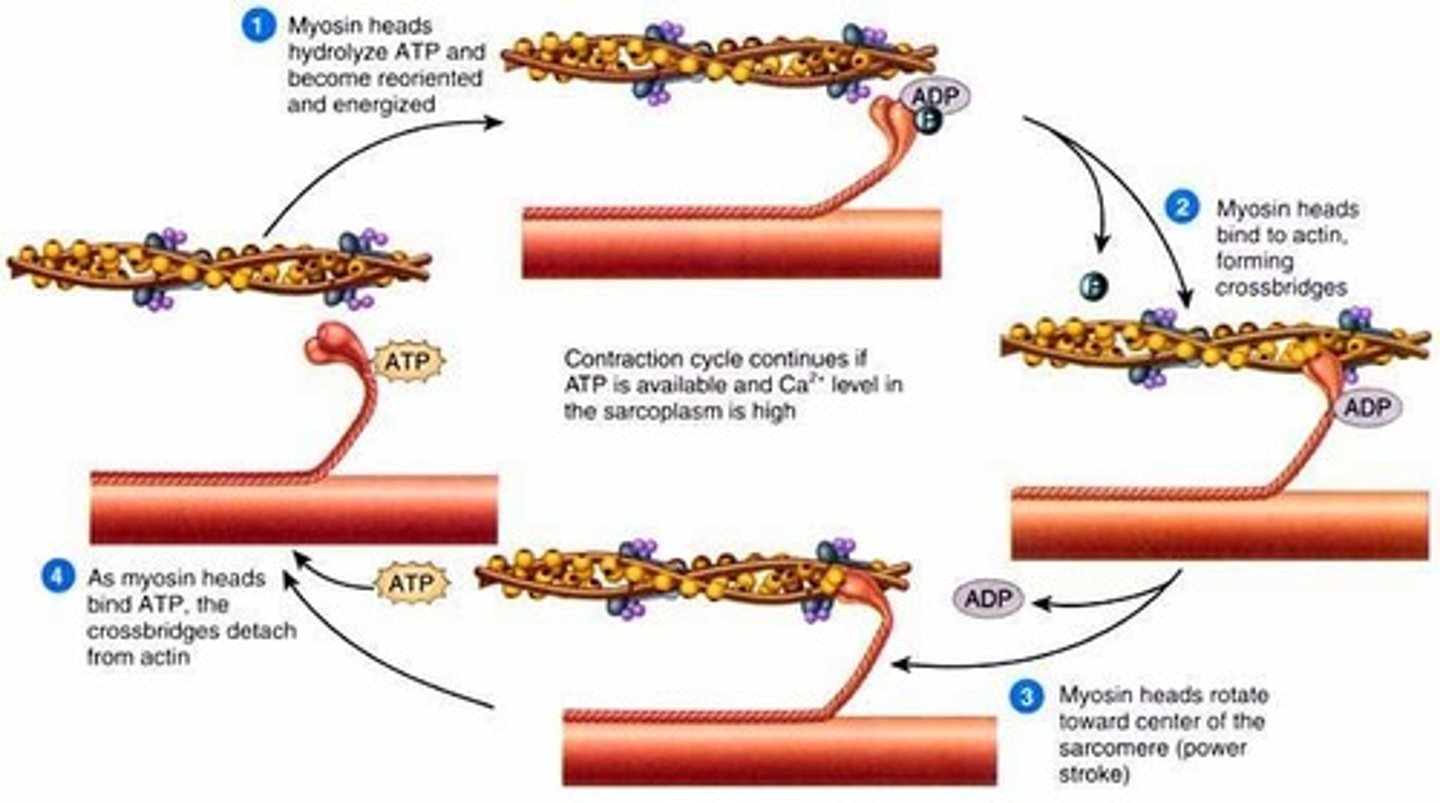
power stroke
forms when myosin head pulls thin filament/actin towards the M-line; going from high energy position to low energy position
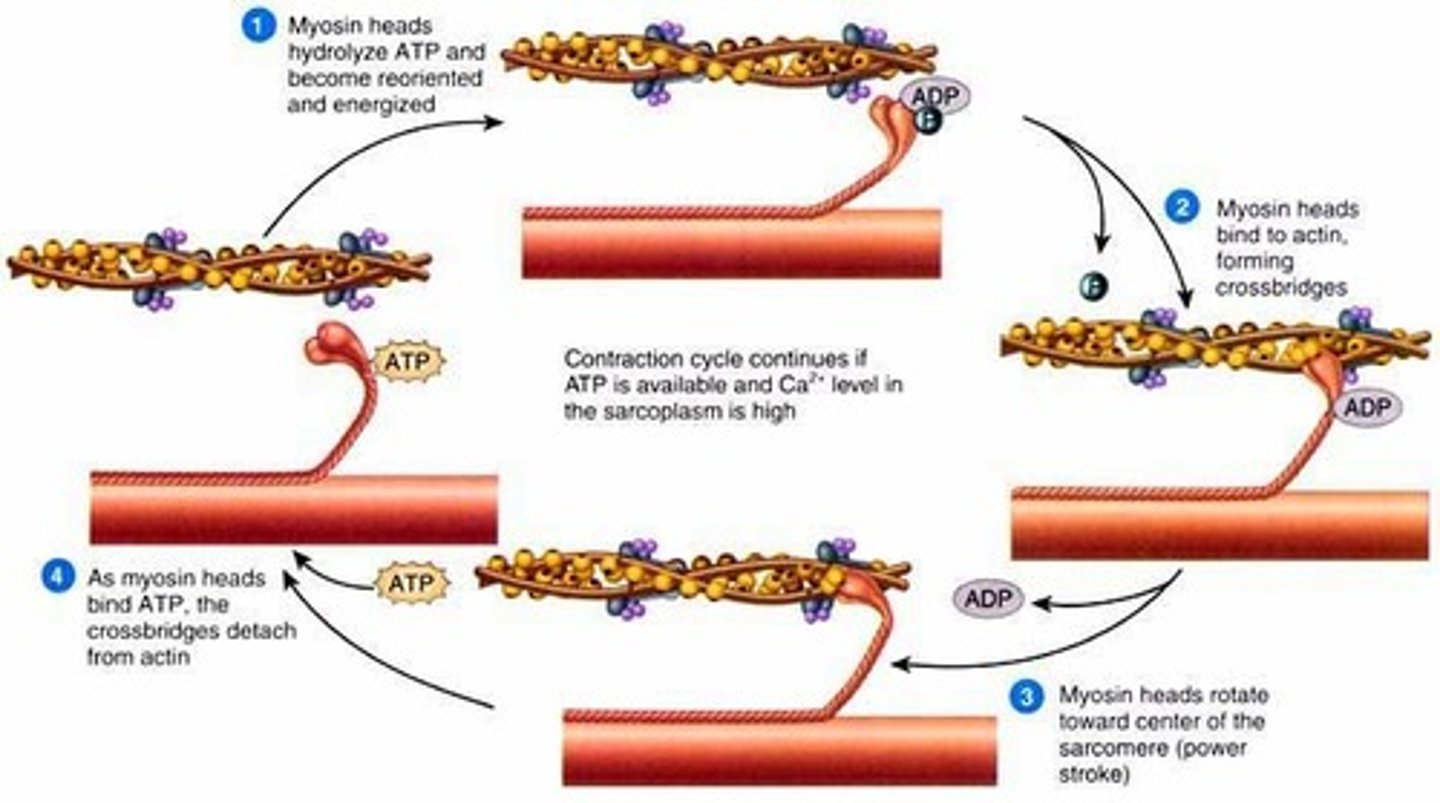
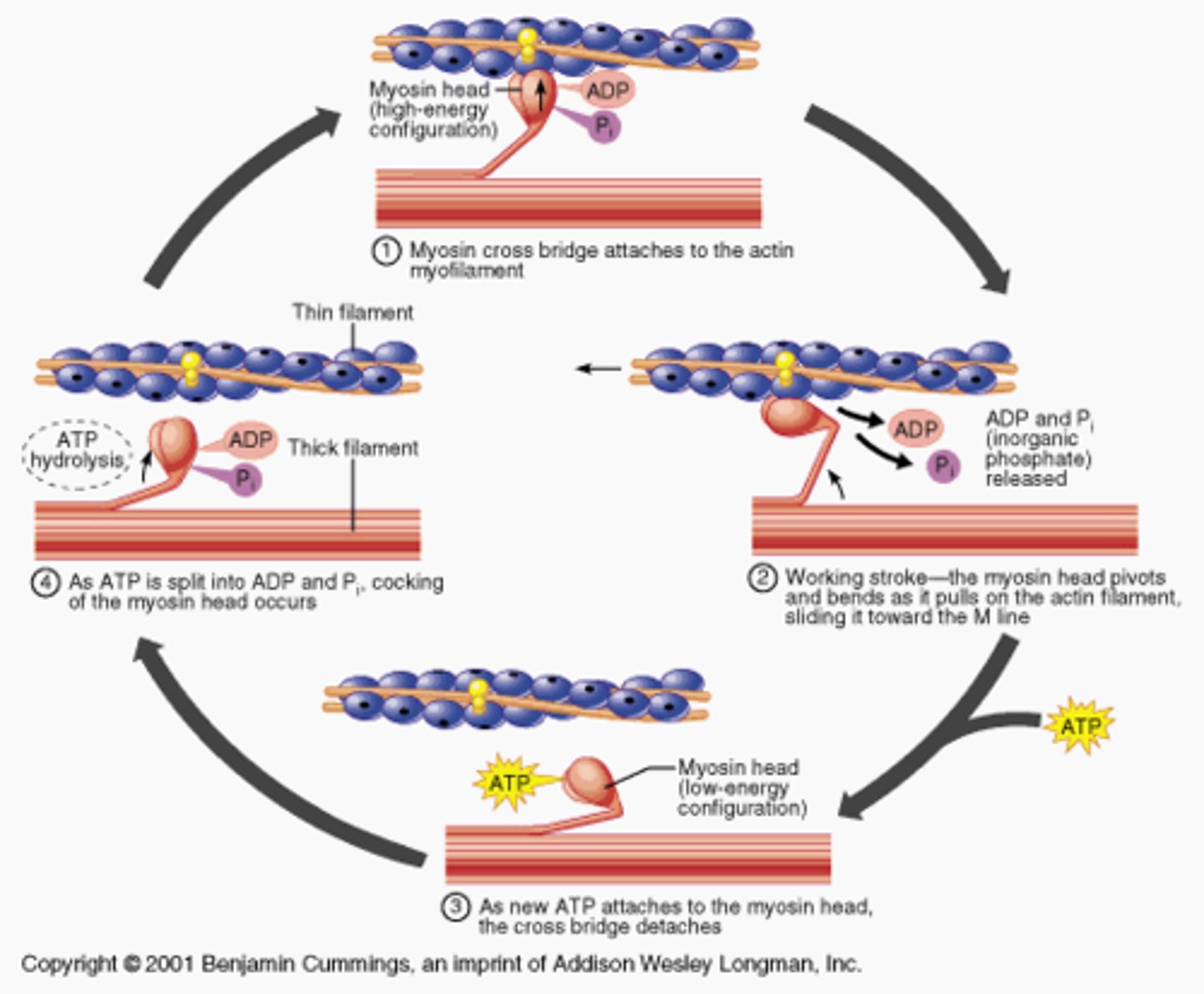
What is the role of ATP in muscle contraction?
-ATP causes myosin head to detach from actin (breaks cross bridge)
-ATP is used to move the myosin head to its high energy position, and ATP is broken into ADP and P
-prepares the myosin head for next power stroke, which causes the muscle to contract
Acetylcholine
causes muscle to contract by triggering an action potential which stimulates the opening of Ca++ channels
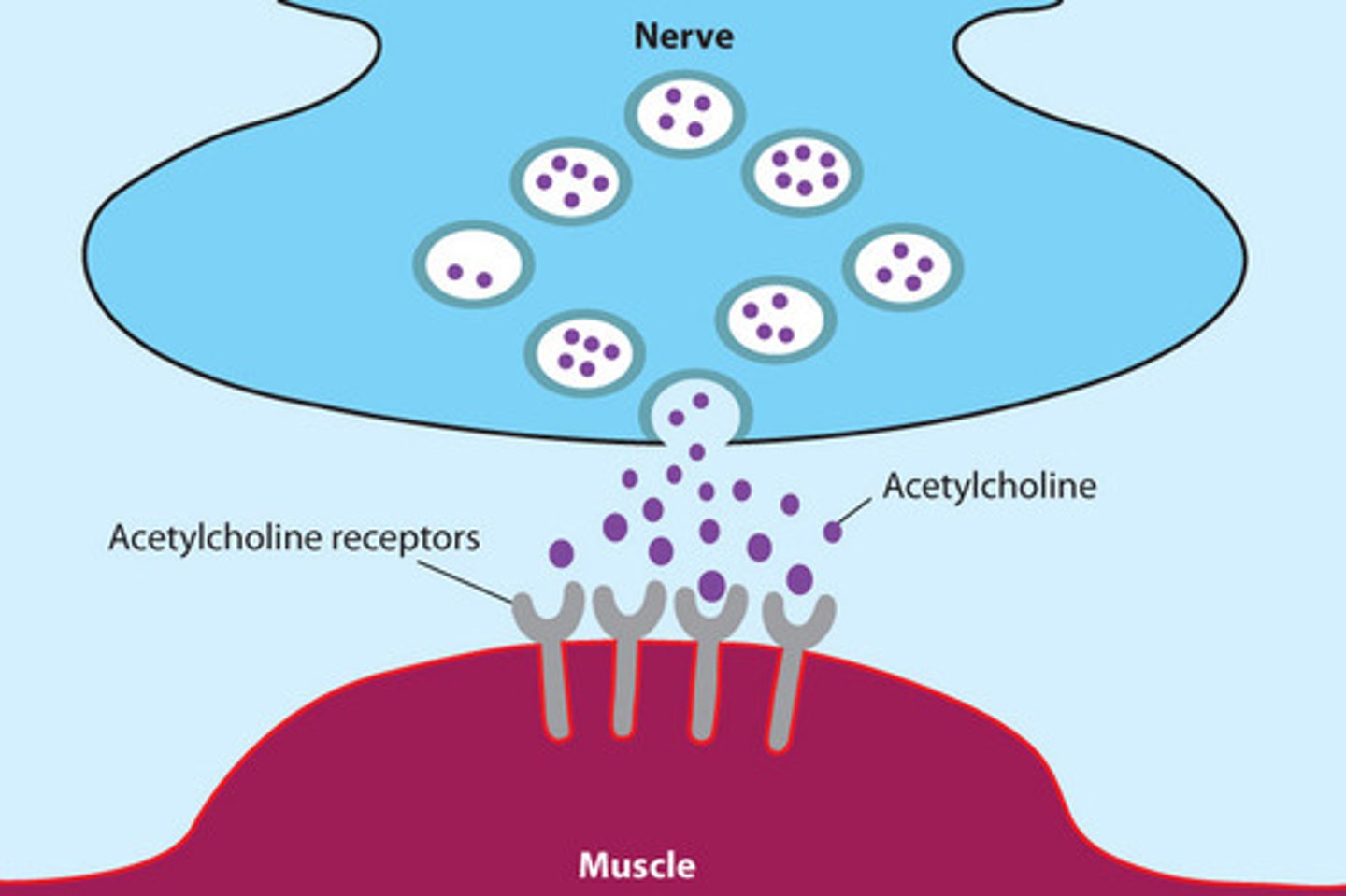
Acetylcholinesterase
breaks down acetylcholine, stopping the action potential which closes the Ca++ channels
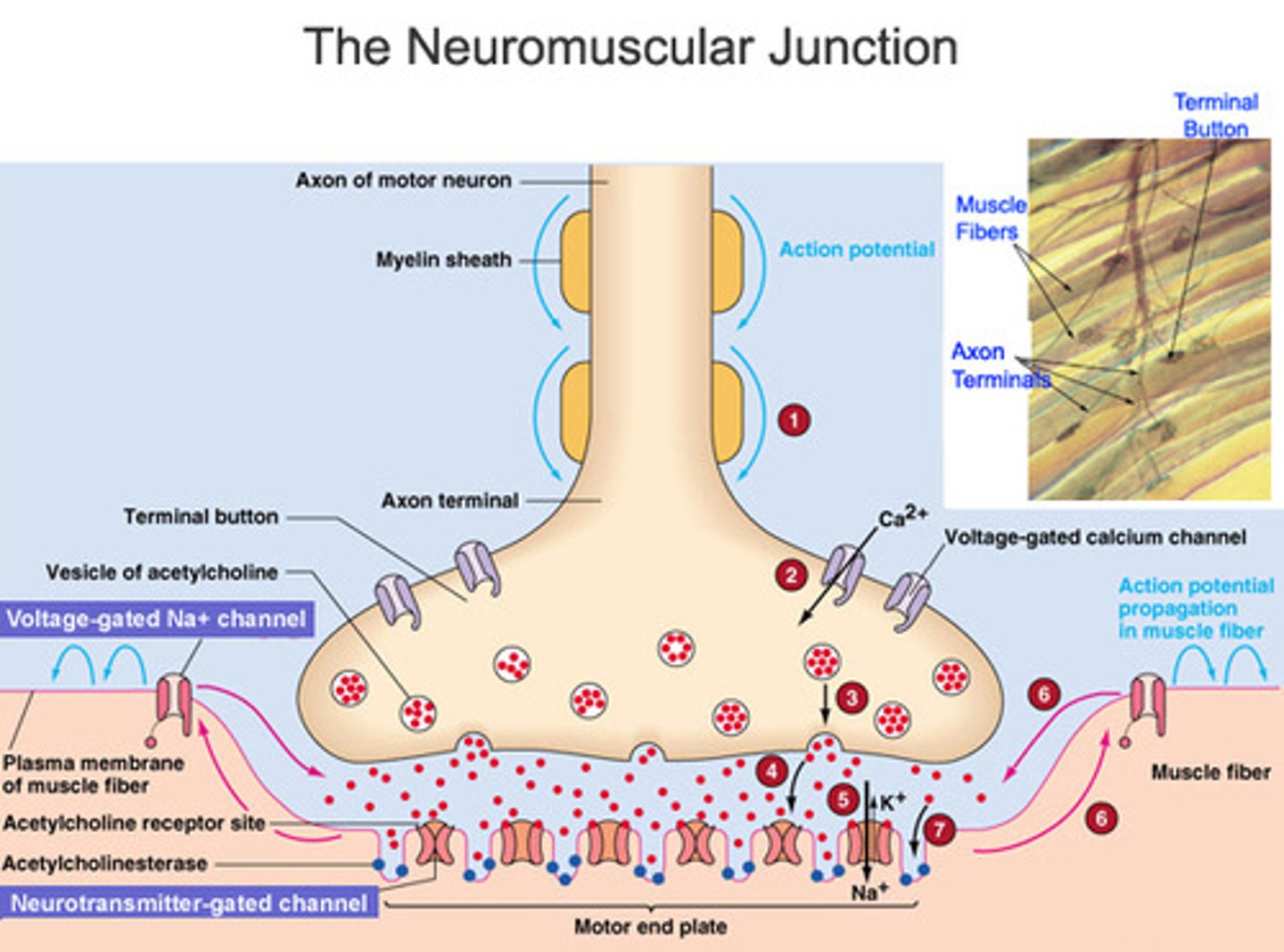
What happens to Ca++ when action potentials stop in the muscle cell?
the Ca++ gets pumped out by Ca++ active transport pumps, back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscle fatigue
physiological inability to contract

muscle fatigue causes
1. ionic imbalances
-too much K lost from cells during APs
-Na/K pump can't keep up
-K Accumulates in T-tubules and interferes with Ca++
2. When there is no ATP available contractures occur, a state of continuous contraction
-no ATP to detach the myosin head from actin, so myosin head cannot return to high energy position; myosin head remains up, forming cross bridge
motor unit
consists of one motor neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates or supplies; the smaller the motor unit the more precise the control
wave summation
this occurs when a second stimulus is received before the muscle fiber has relaxed, creating a second contraction that is stronger than the first; Leads to a build-up of tension
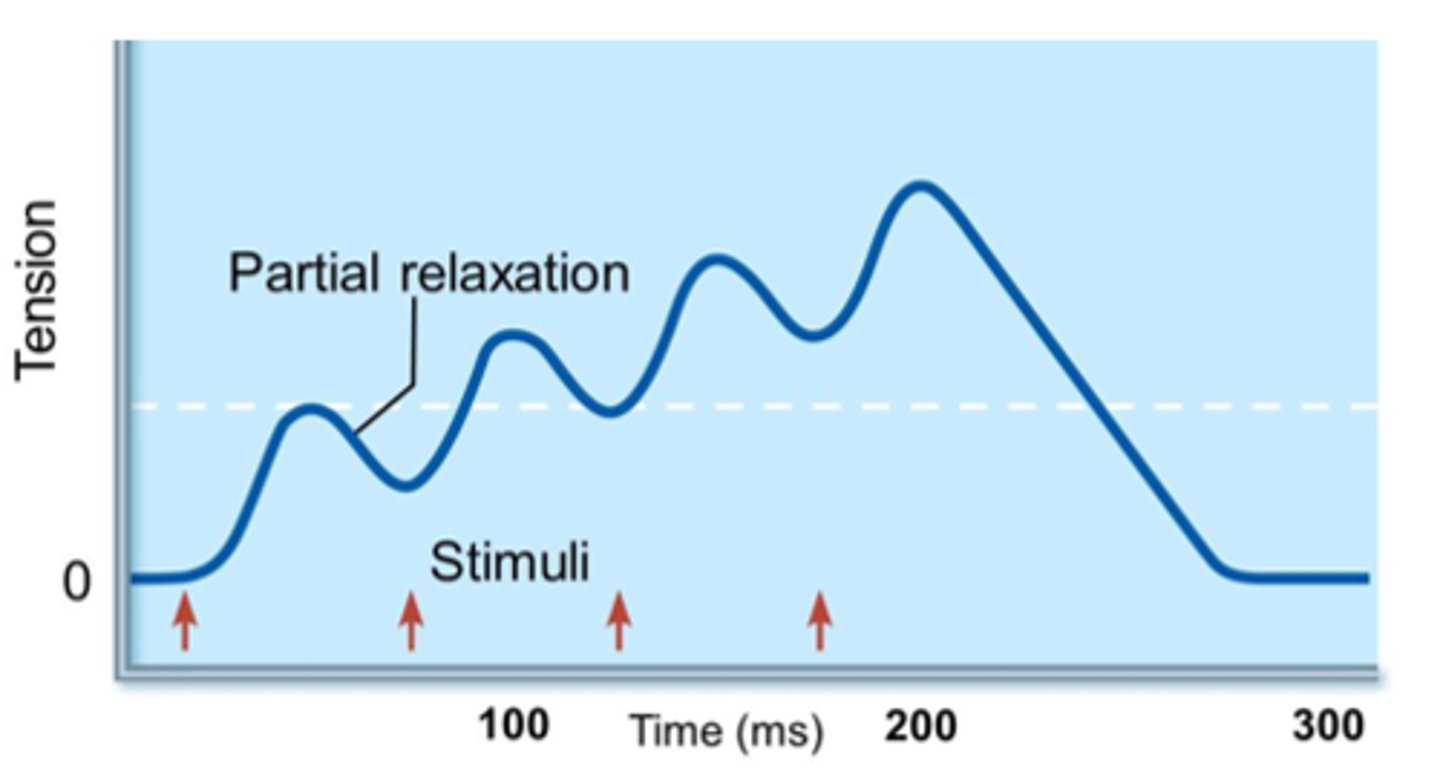
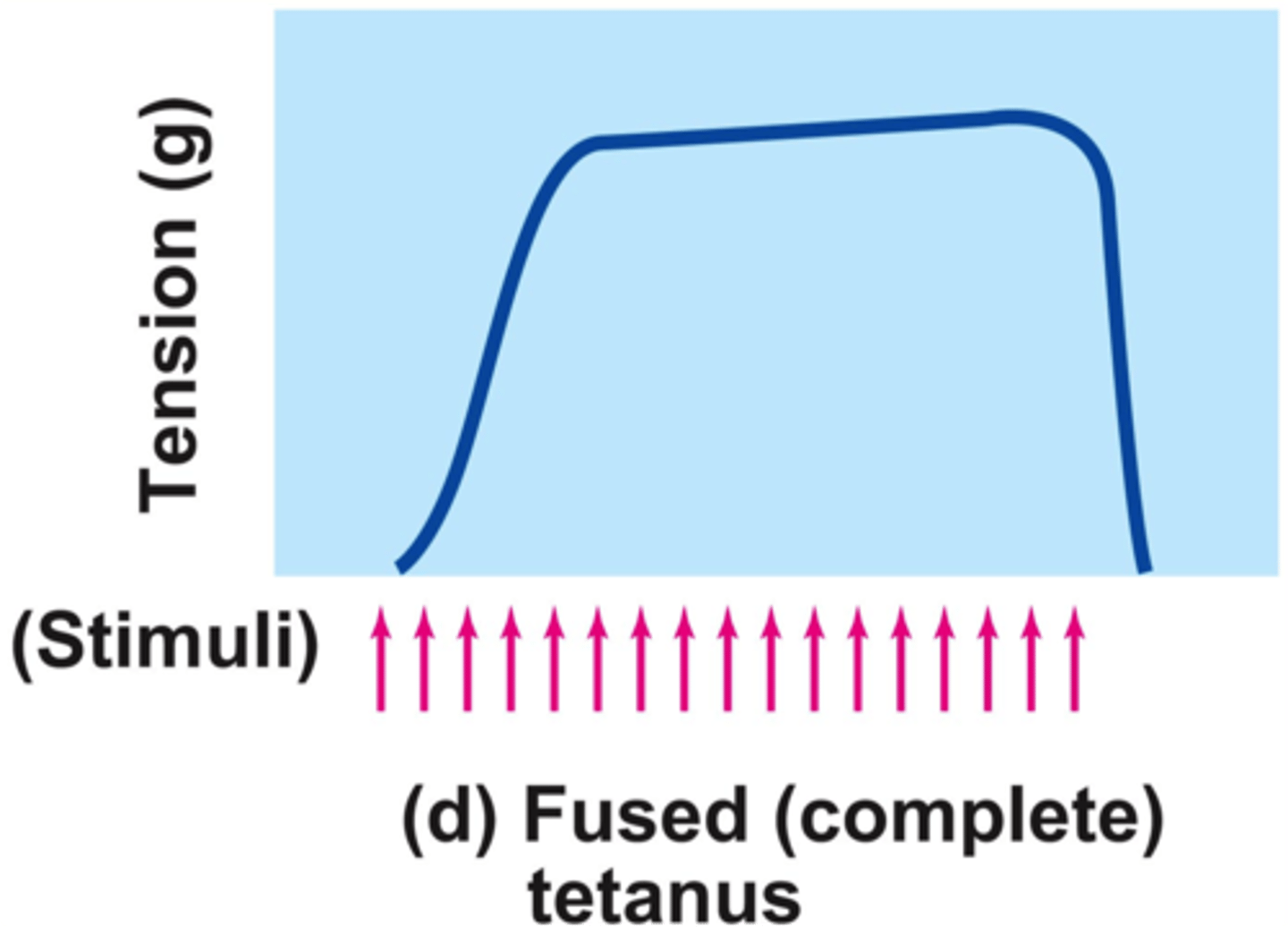
fused tetanus
when stimulus frequency is so high that no muscle relaxation takes place between stimuli
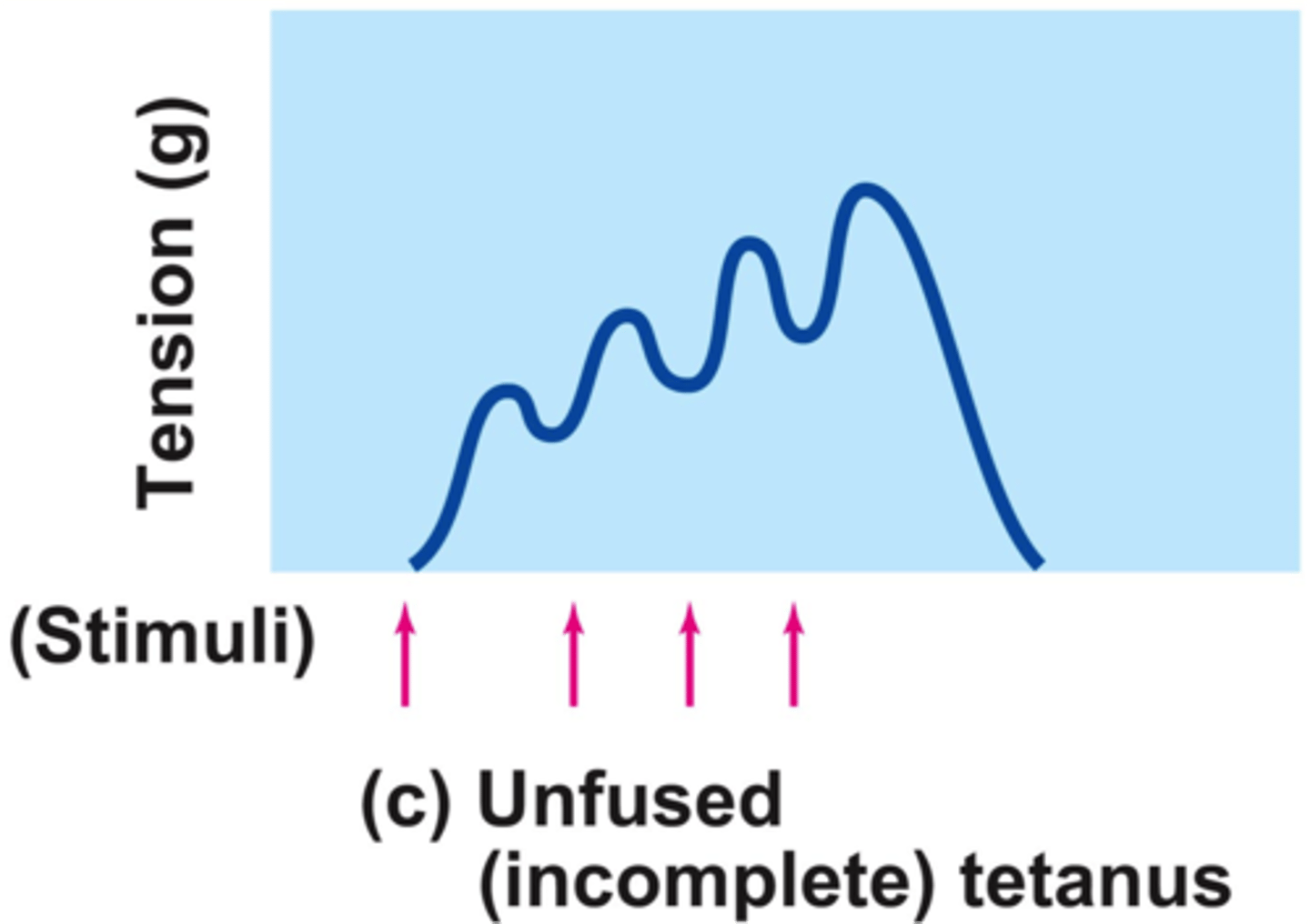
unfused tetanus
type of wave summation with partial relaxation observed between twitches
isotonic contraction
when muscle length changes during a contraction
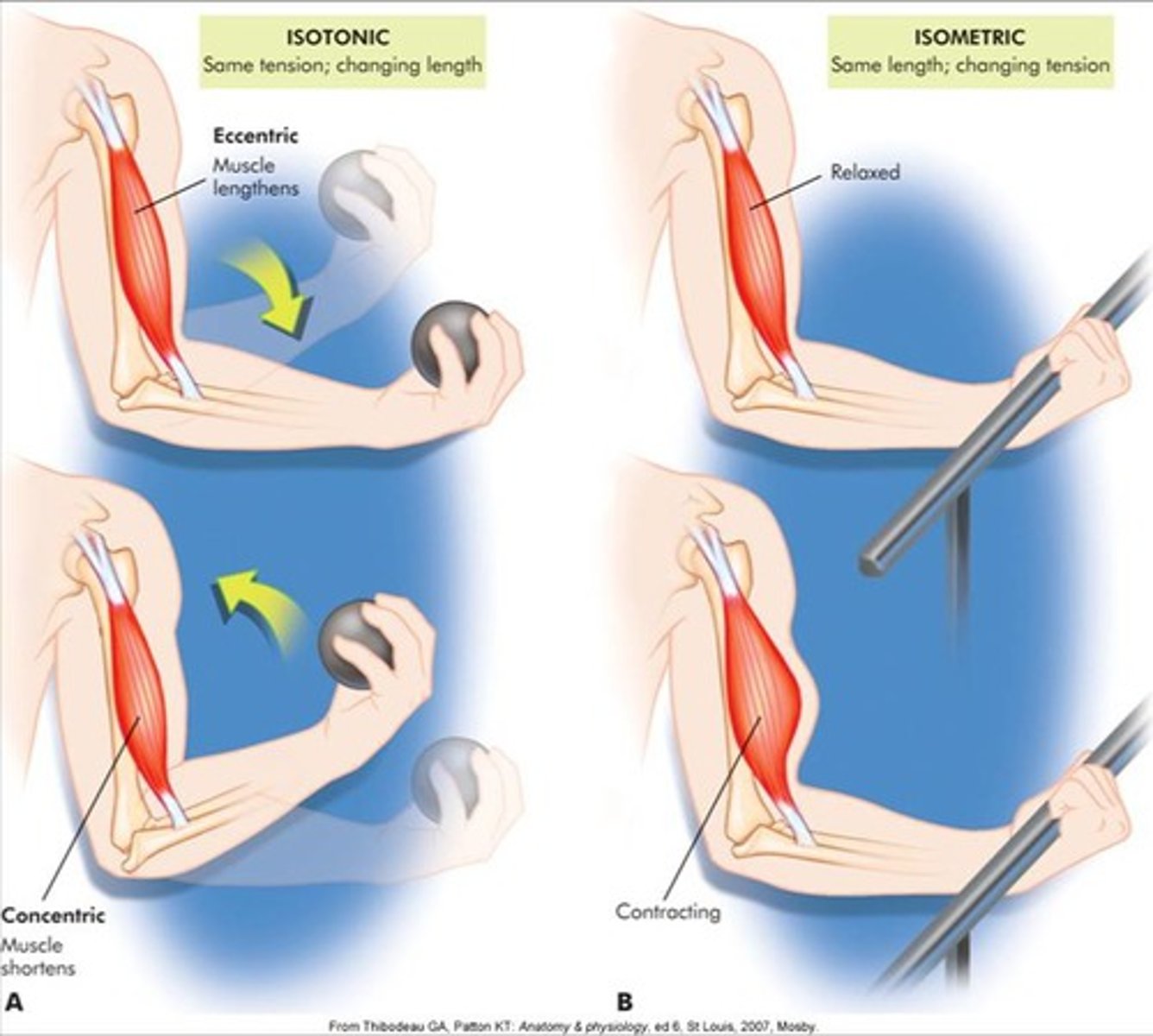
concentric contraction (isotonic)
muscle shortens during the contraction
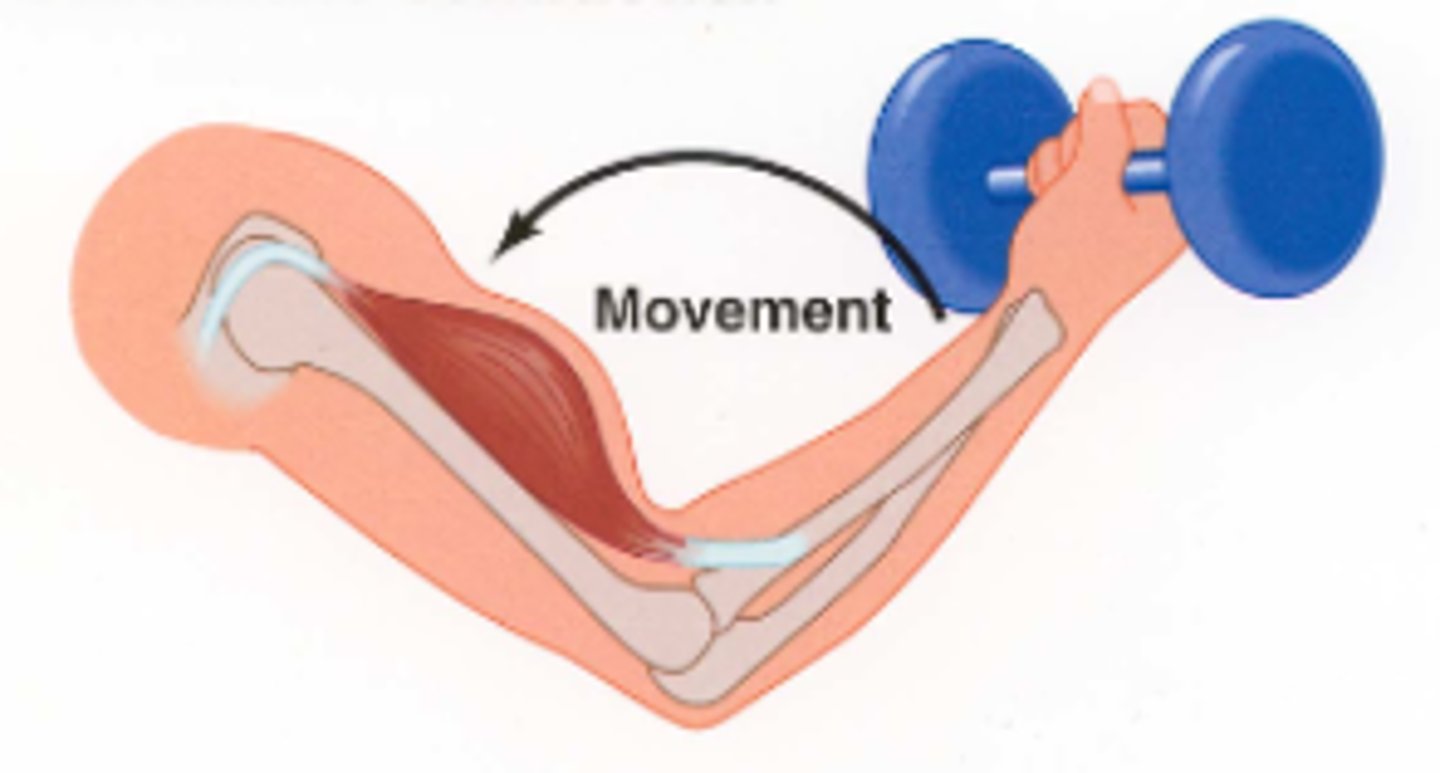
eccentric contraction (isotonic)
muscle lengthens during contraction
isometric contraction
used for posture; muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length; ex. when you are pushing against a wall

order energy pathways kick in during muscle contraction
creatine phosphate, anaerobic glycolysis, aerobic respiration
creatine phosphate
lasts 10-12 seconds, no oxygen is needed, 1 ATP produced
anaerobic glycolysis
lasts 45-60 seconds, no oxygen is needed, 2 ATP produced
aerobic respiration
lasts hours (as long as it is low intensity), oxygen is needed, 32 ATP produced
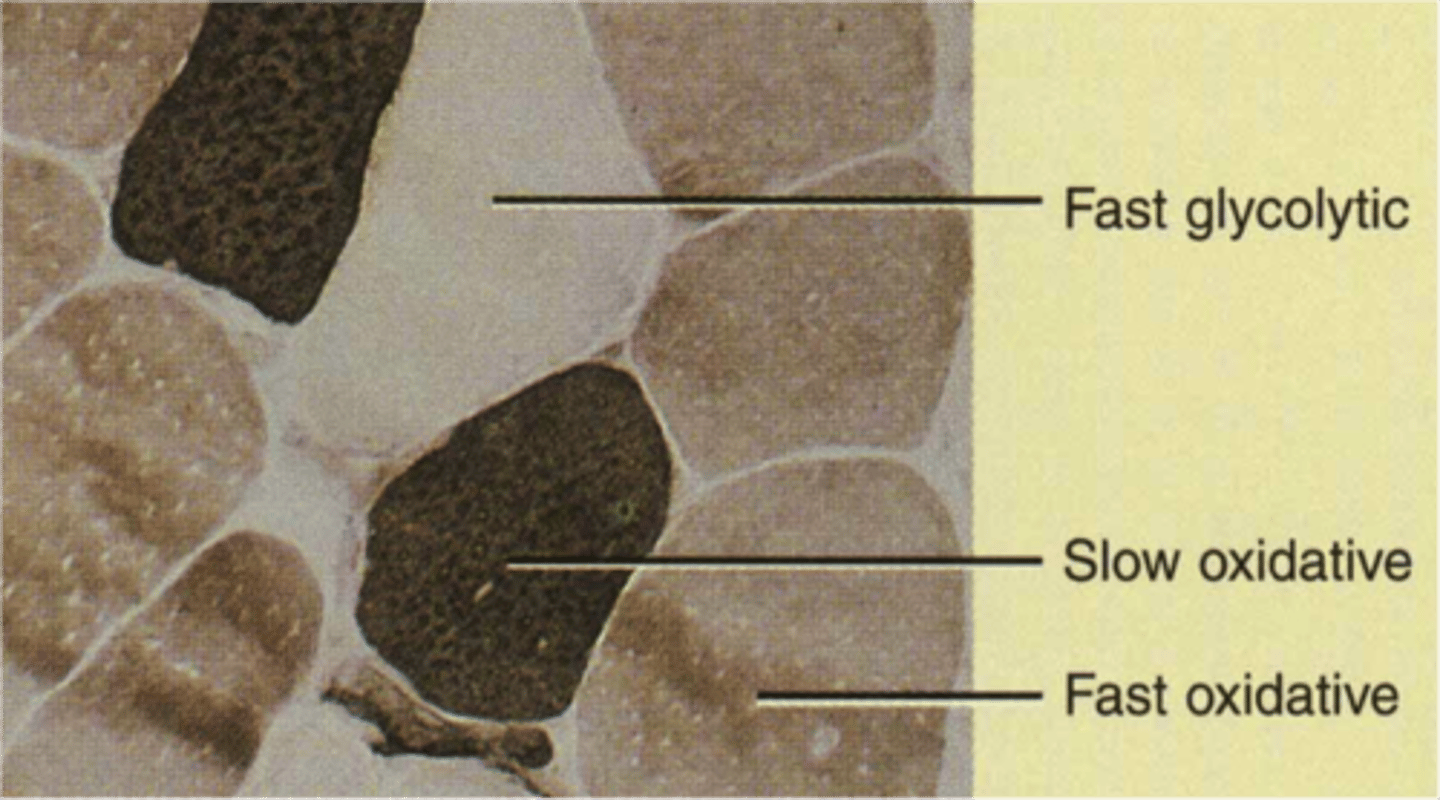
slow oxidative muscle fibers
-uses aerobic respiration
-high amounts of myoglobin
-slow to fatigue
-many capillaries
-small diameter
-red
-for endurance type activities; running a marathon; maintaining posture
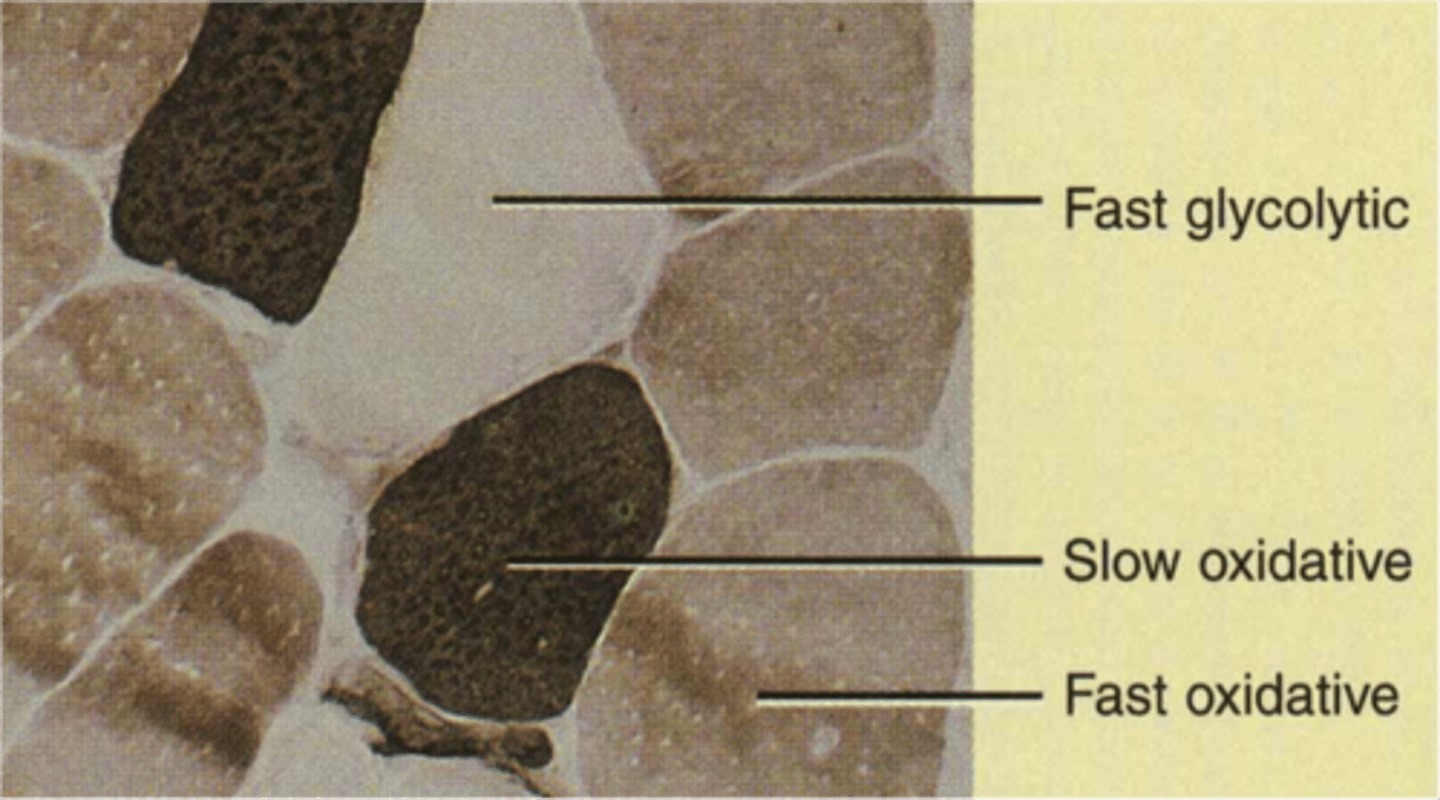
fast oxidative muscle fibers
-uses aerobic respiration (sometimes anaerobic glycolysis)
-high amounts of myoglobin
-intermediate to fatigue
-many capillaries
-intermediate diameter
-red/pink
-for sprinting or walking
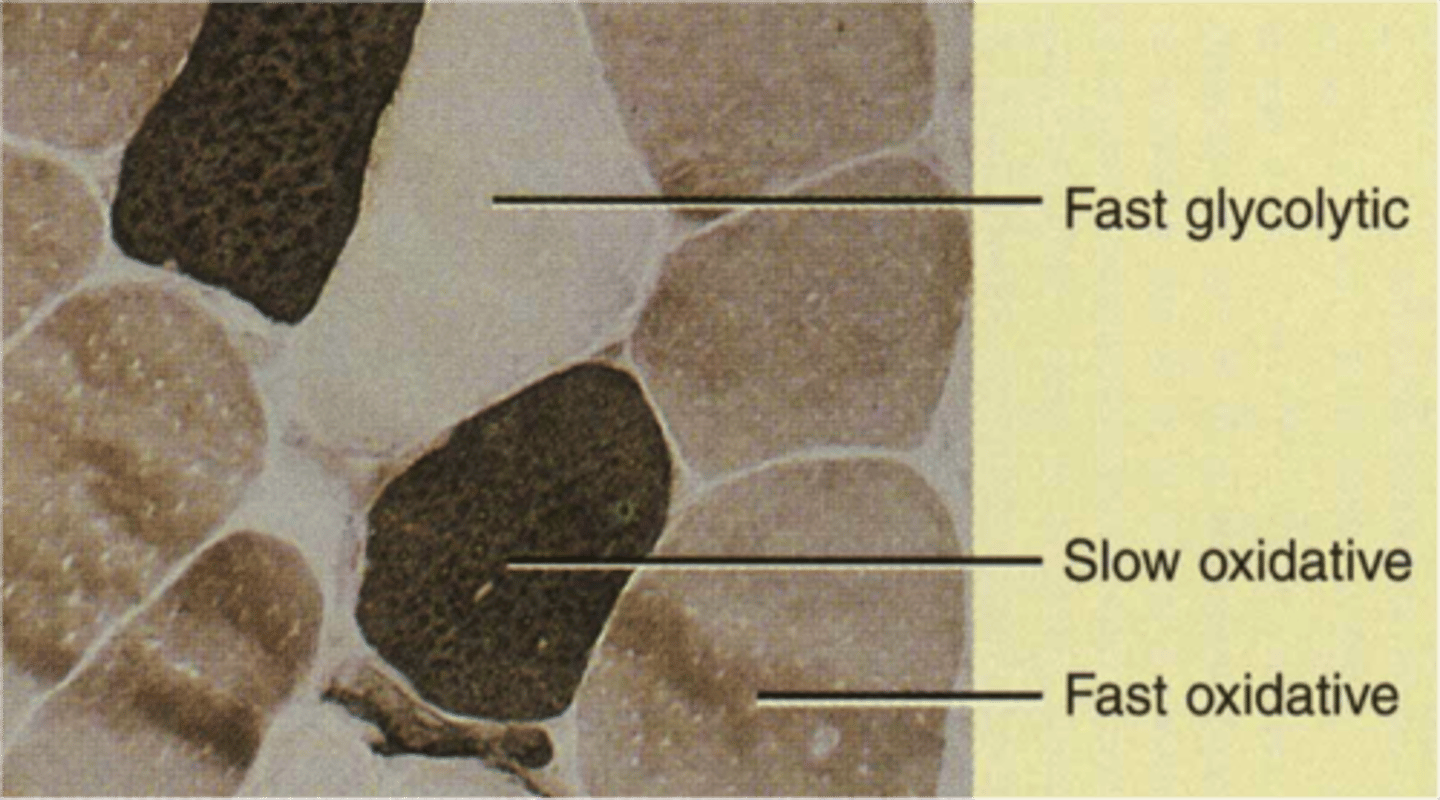
fast glycolytic muscle fibers
-uses anaerobic glycolysis
-low amounts of myoglobin
-fast to fatigue
-few capillaries
-large diameter
-white (pale)
-for short term intense or powerful movements; hitting a baseball
changes in muscle cells caused by aerobic exercise (swimming, jogging, walking, biking)
-changes result in an increase in strength and resistance to fatigue
-the number of mitochondria and capillaries increase
-increase amount of myoglobin
-increase fat stored in cells and ability to break it down for energy
-changes most dramatic in slow oxidative
-may also convert fast glycolytic to fast oxidative fibers with in the muscle
rigor mortis
-when no ATP available contractures occur a state of continuous contraction
-when someone has died, they are no longer getting oxygen, they can't make ATP, constant contraction, all their muscles stiffen and harden
agonist muscle
the muscle primarily responsible for the movement of a bone
antagonist muscle
the muscle opposing the movement
synergist muscle
Muscle that assists a prime mover; helping to accomplish the movement
fixator muscle
muscle stabilizing the orgin
parallel fascicle arrangement
run parallel to the long axis of the muscle; slender

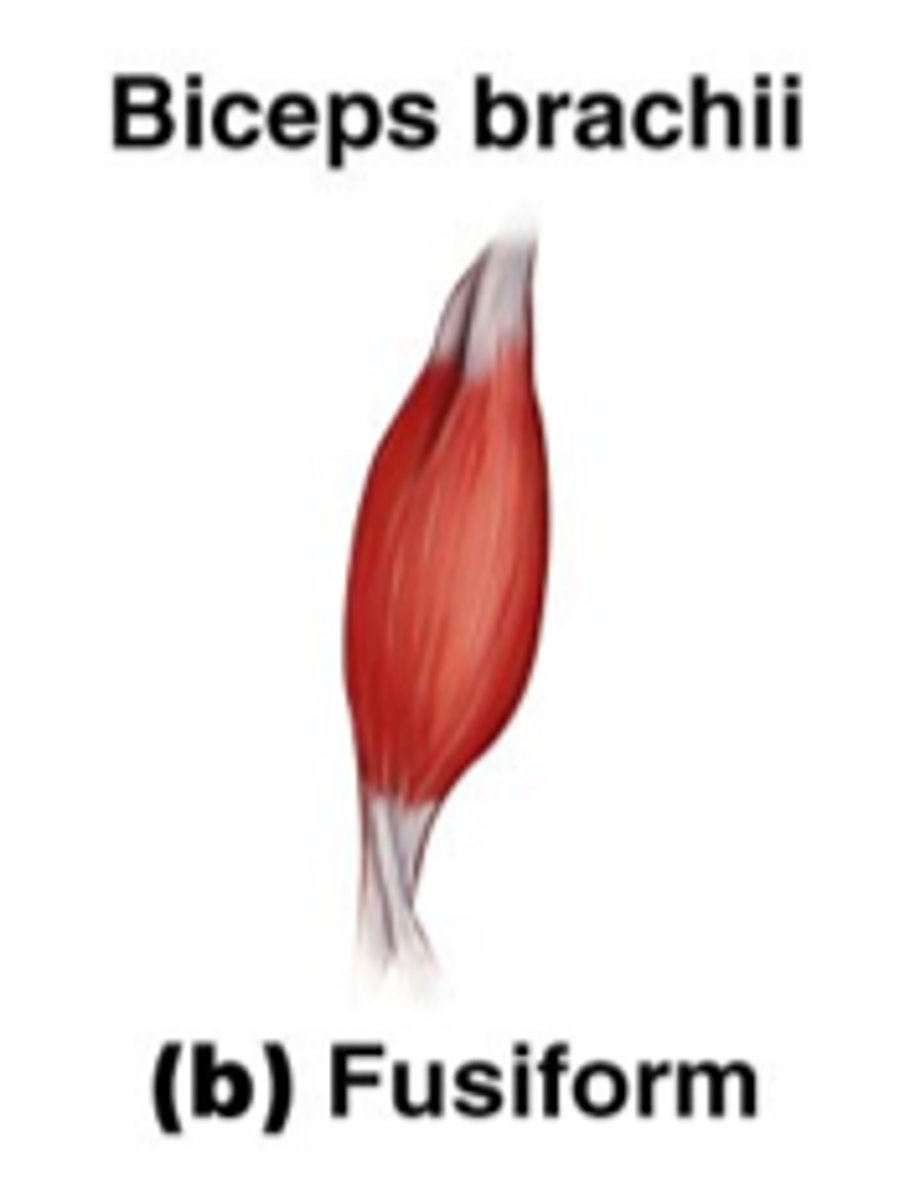
fusiform fascicle arrangement
spindle-shaped muscles with parallel fibers
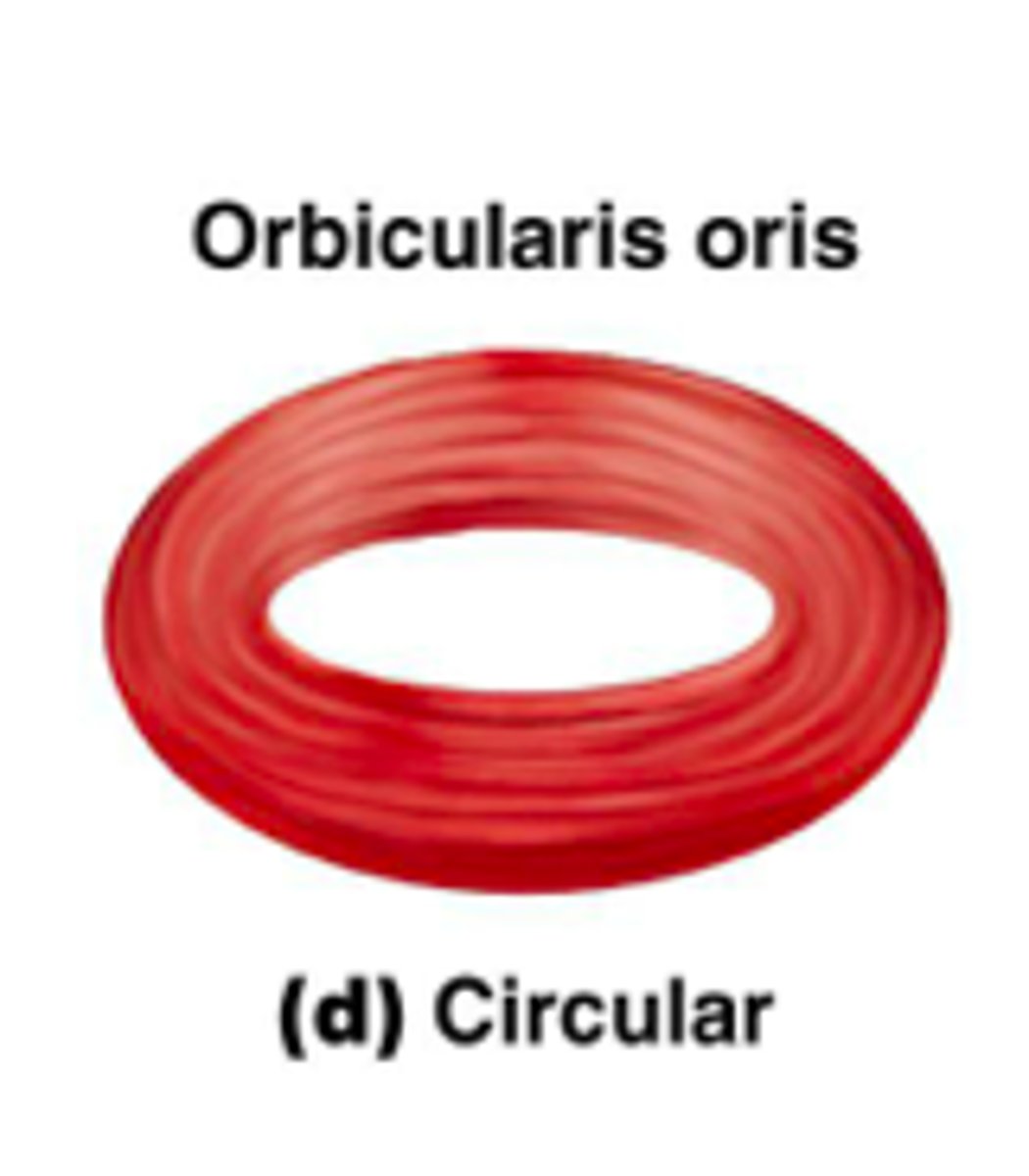
circular fascicle arrangement
fascicles arranged in concentric rings (sphincter)
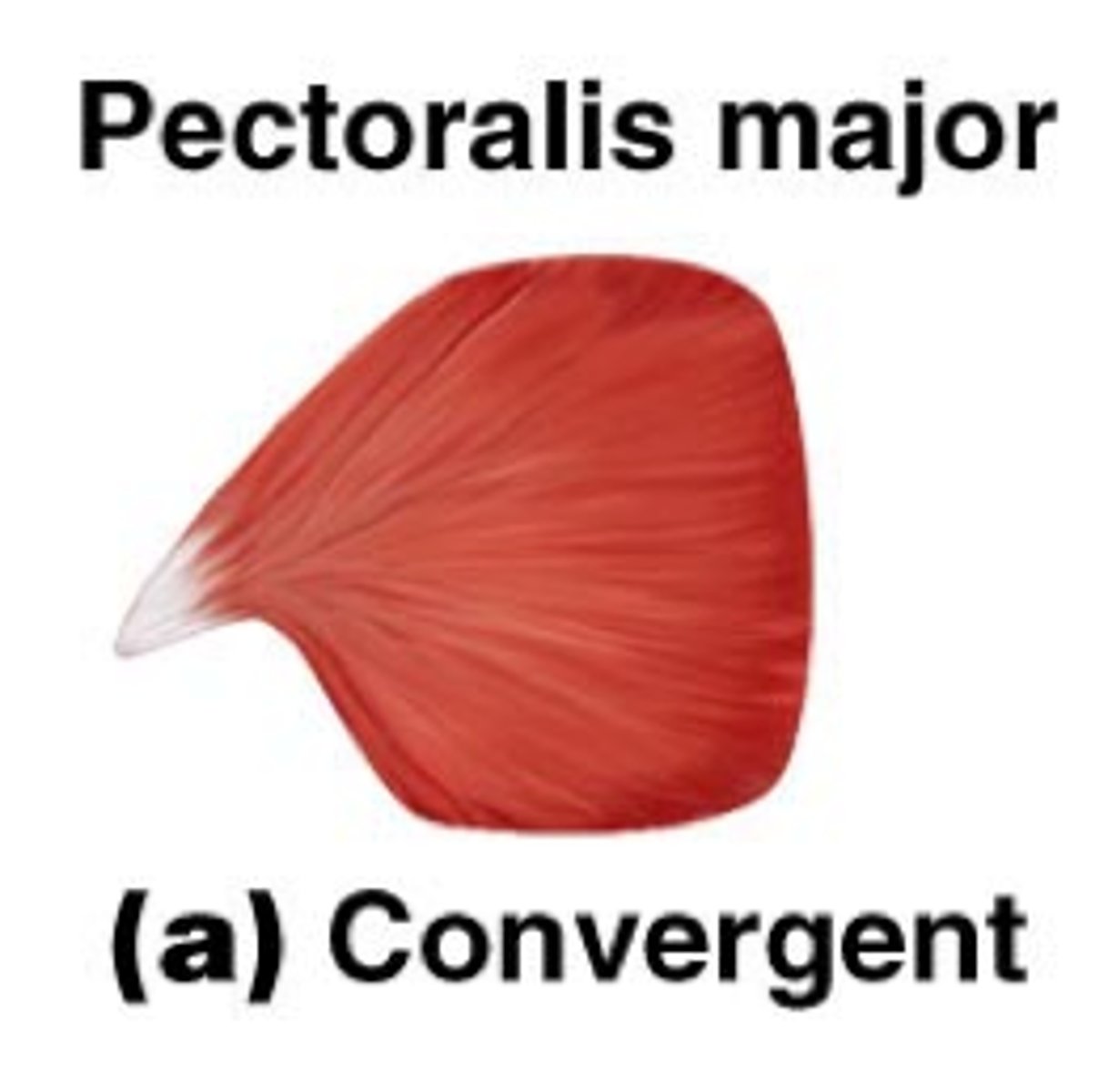
convergent fascicle arrangement
muscle origin is broad and fascicles converge toward a tendon of insertion
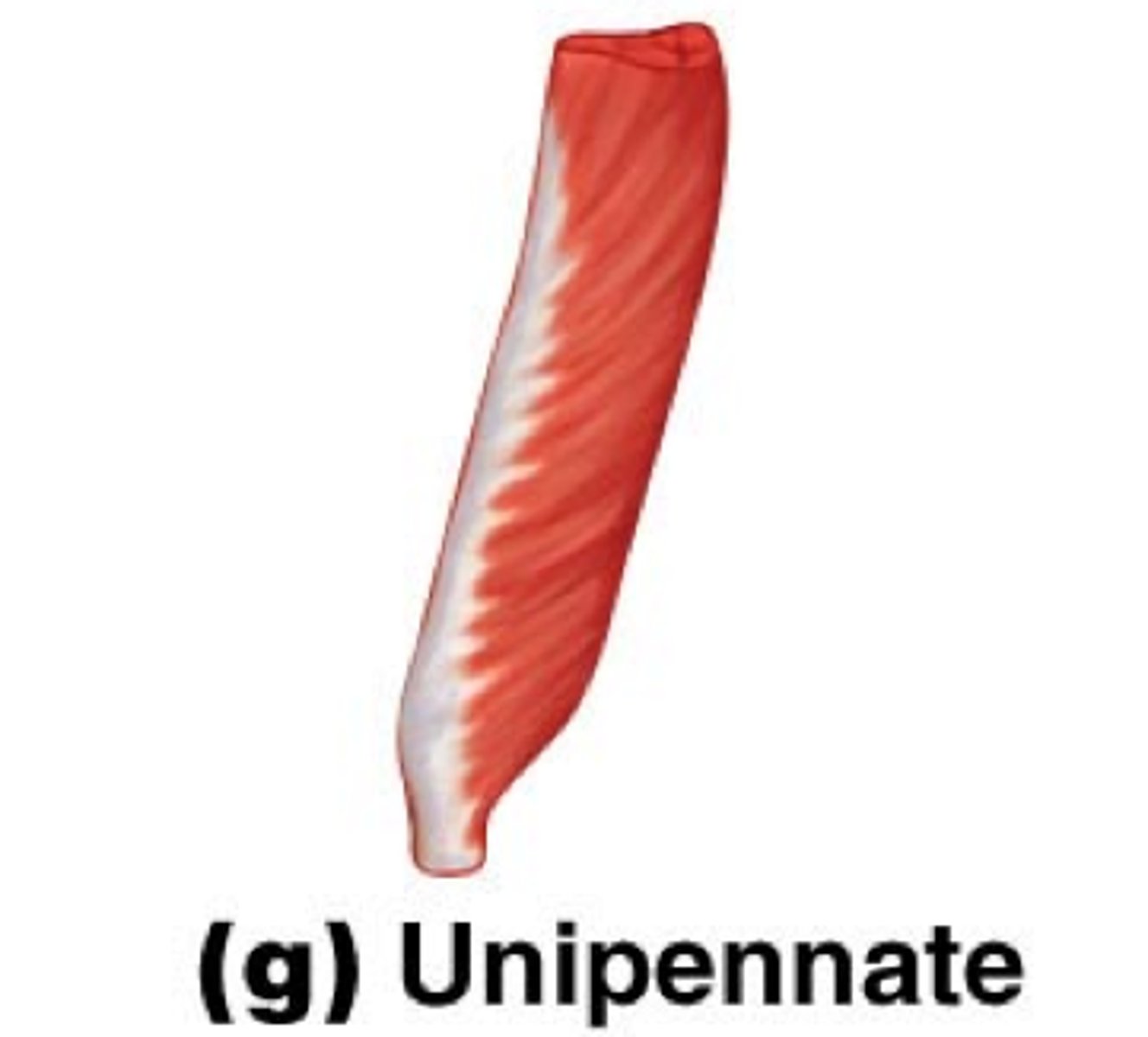
unipennate fascicle arrangement
fascicles insert into only one side of the tendon

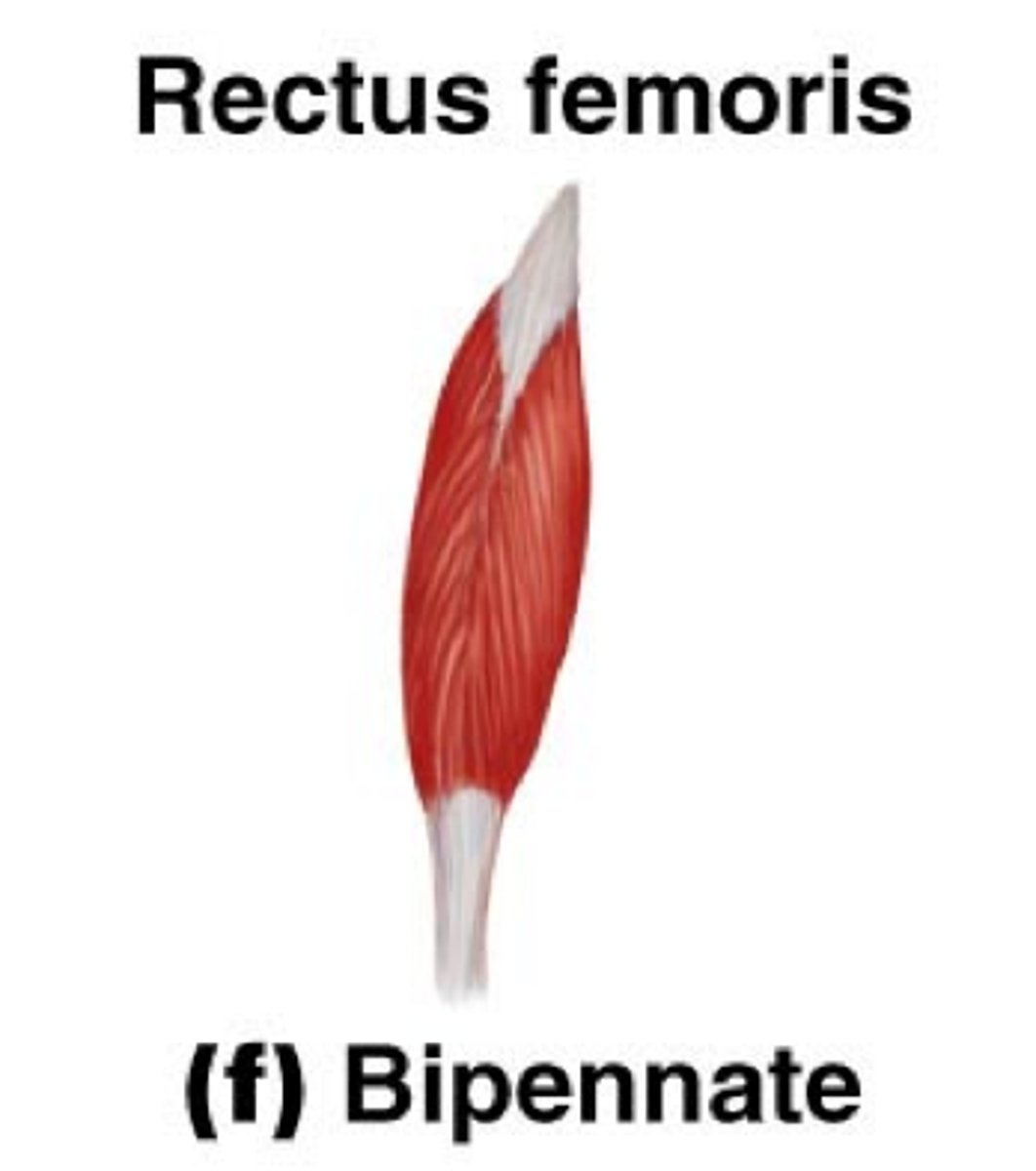
bipennate fascicle arrangement
fascicles insert into the tendon from both sides; muscle looks like a feather
multipennate fascicle arrangement
Fascicles attach obliquely from many directions to several tendons; looks like many feathers side by side, with all their quills (tendons) inserted into one large tendon
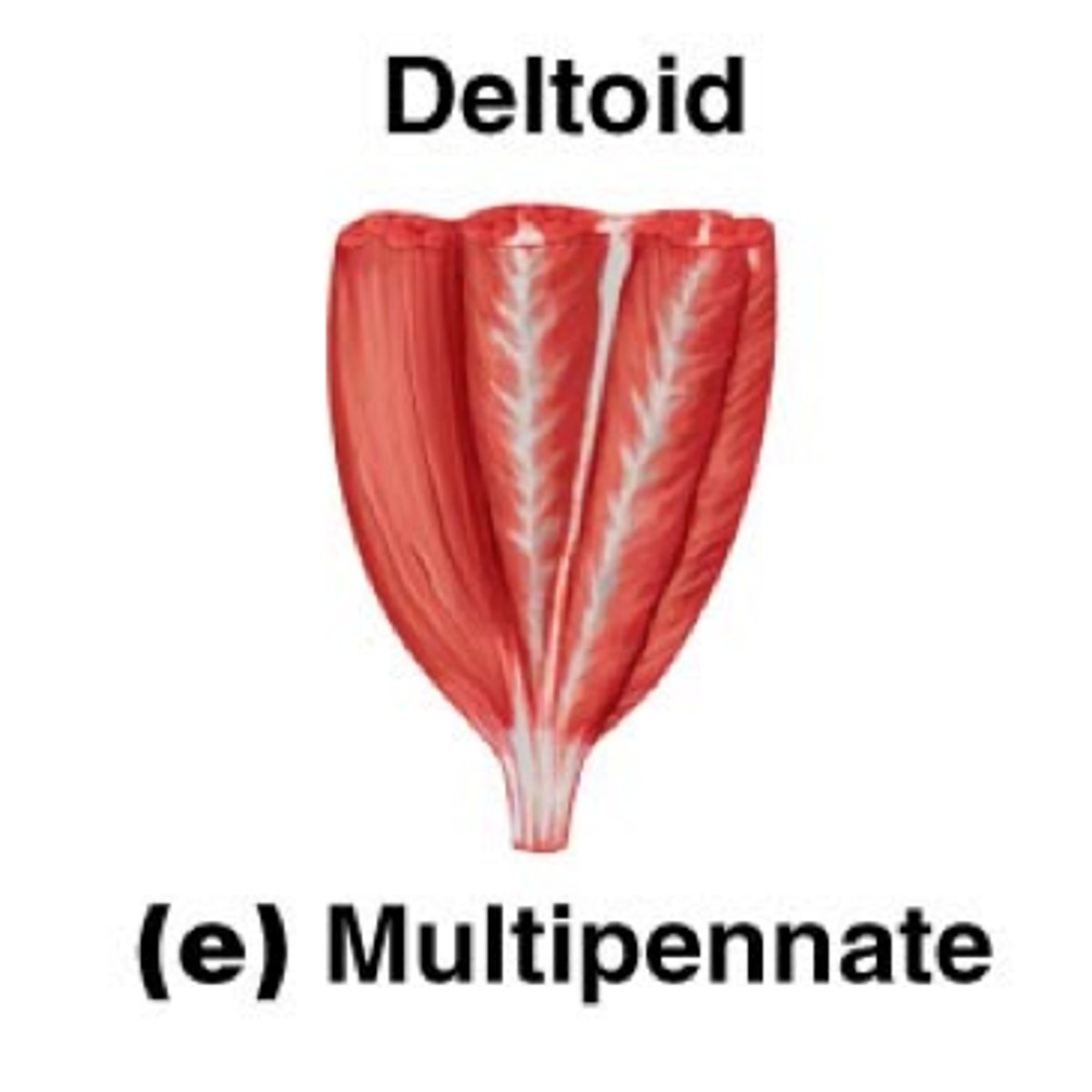
deltoid (shape of muscle)
triangular
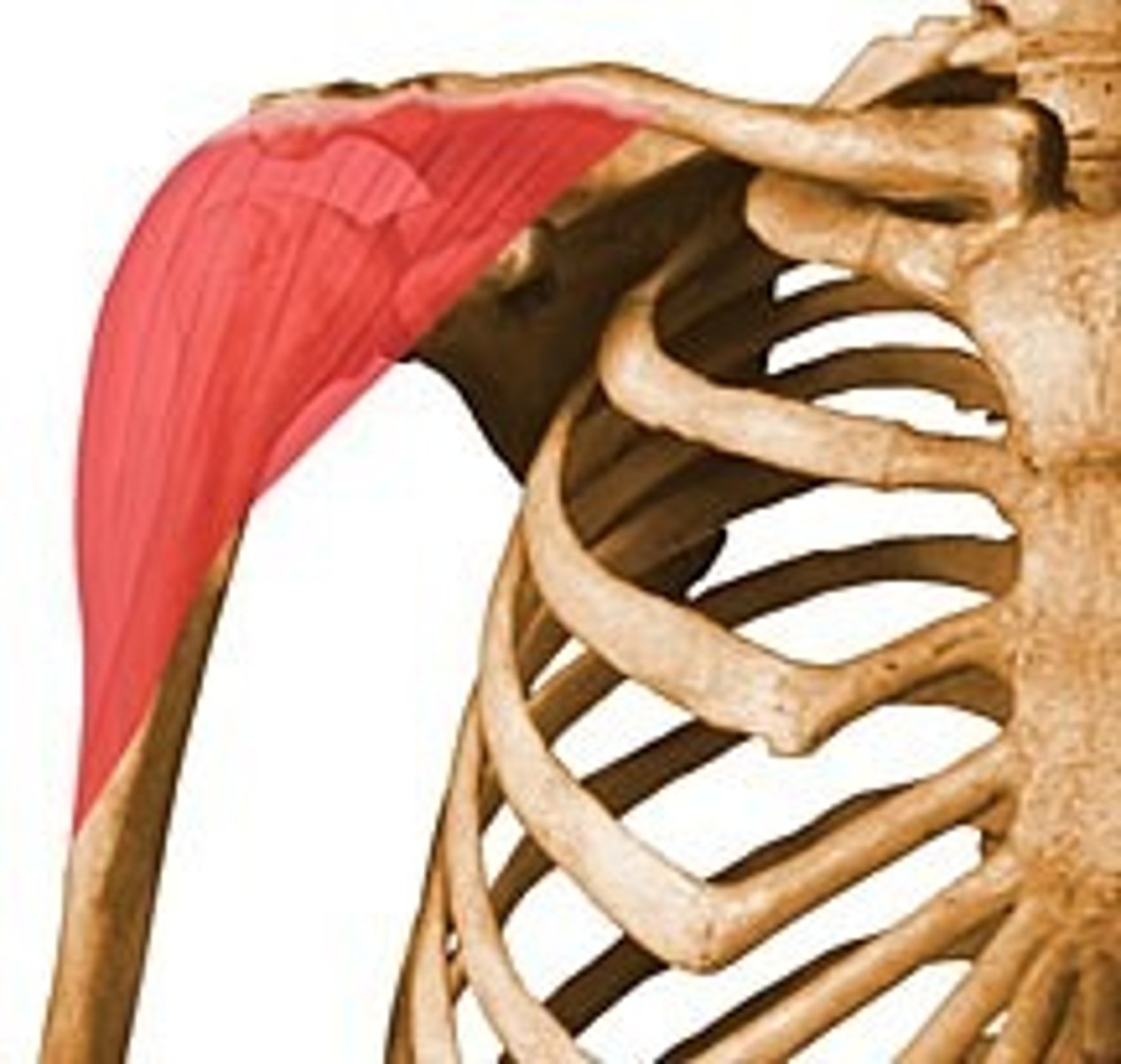
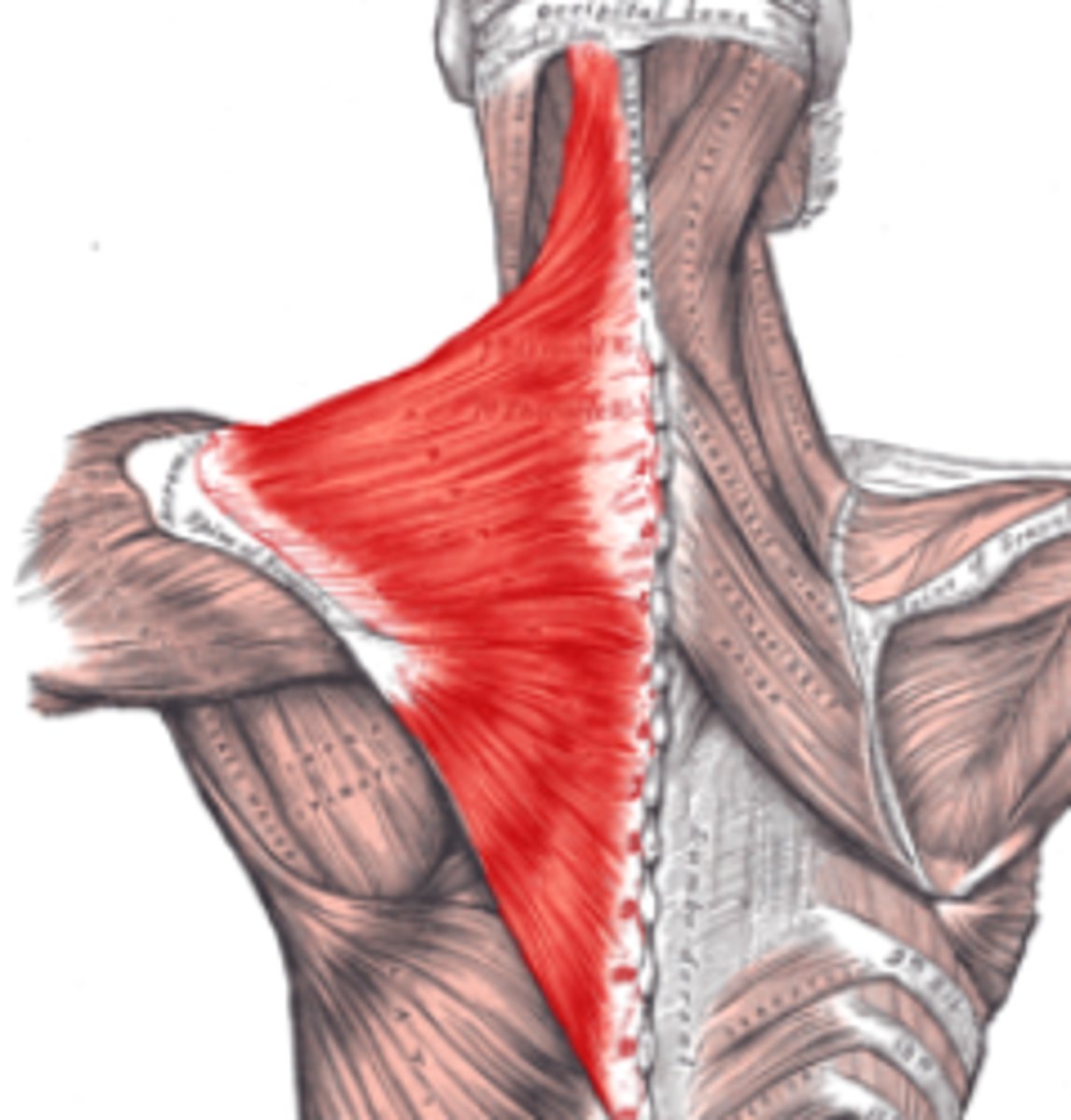
trapezius (shape of muscle)
trapezoidal
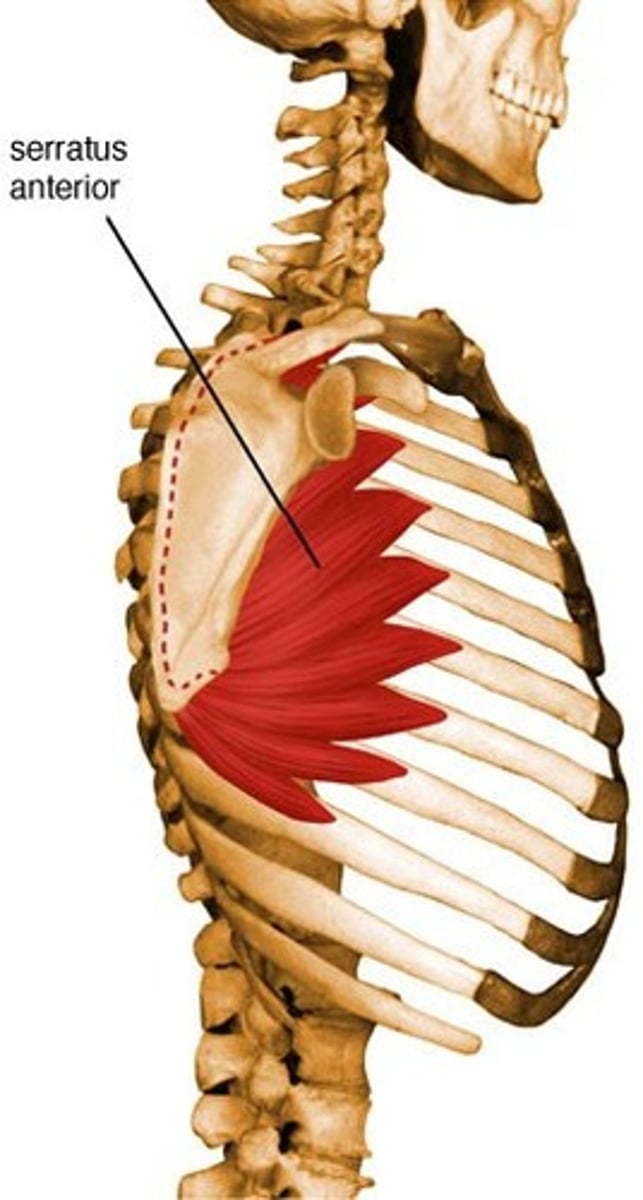
serratus (shape of muscle)
saw-toothed
orbicularis (shape of muscle)
round
gracilis (shape of muscle)
slender
maximus (size of muscle)
largest
minimus (size of muscle)
smallest
longus (size of muscle)
long
brevis (size of muscle)
short
rectus (direction of fibers)
parallel to midline; straight
transverse (direction of fibers)
perpendicular to midline
oblique (direction of fibers)
diagonal
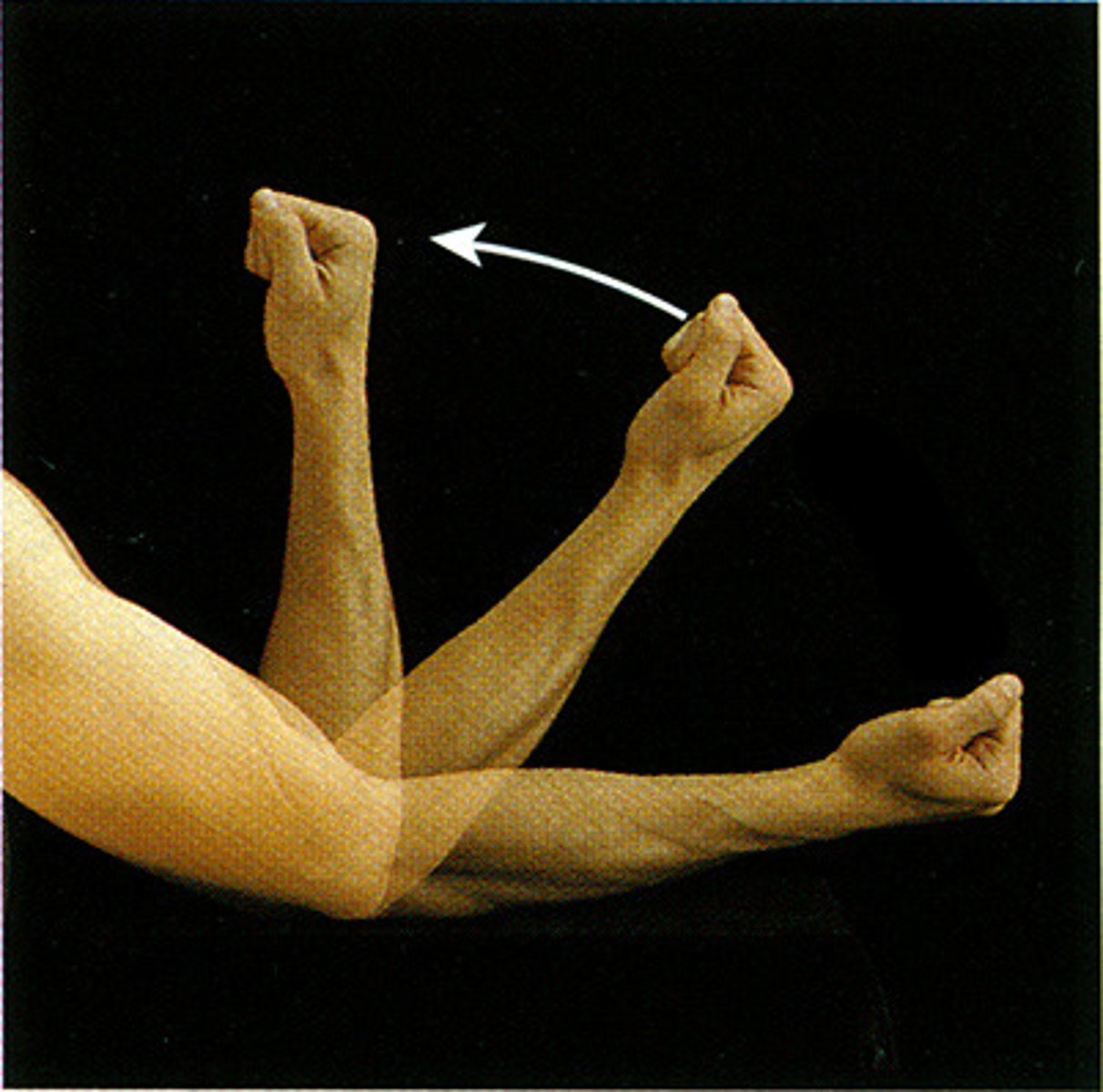
flexor (type of movement)
reduces joint angle
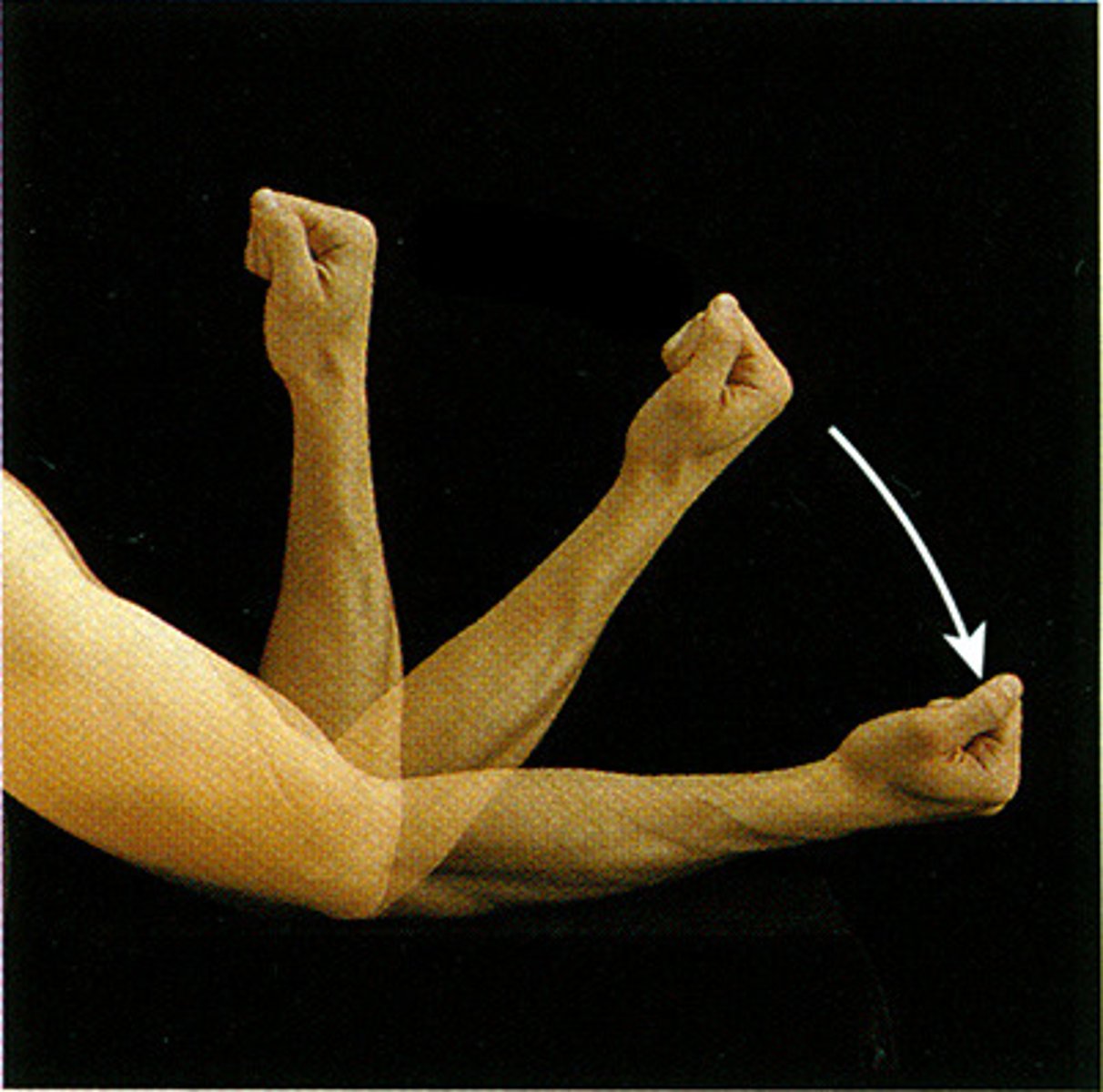
extensor (type of movement)
increases joint angle
adductor (type of movement)
moves bone closer to midline
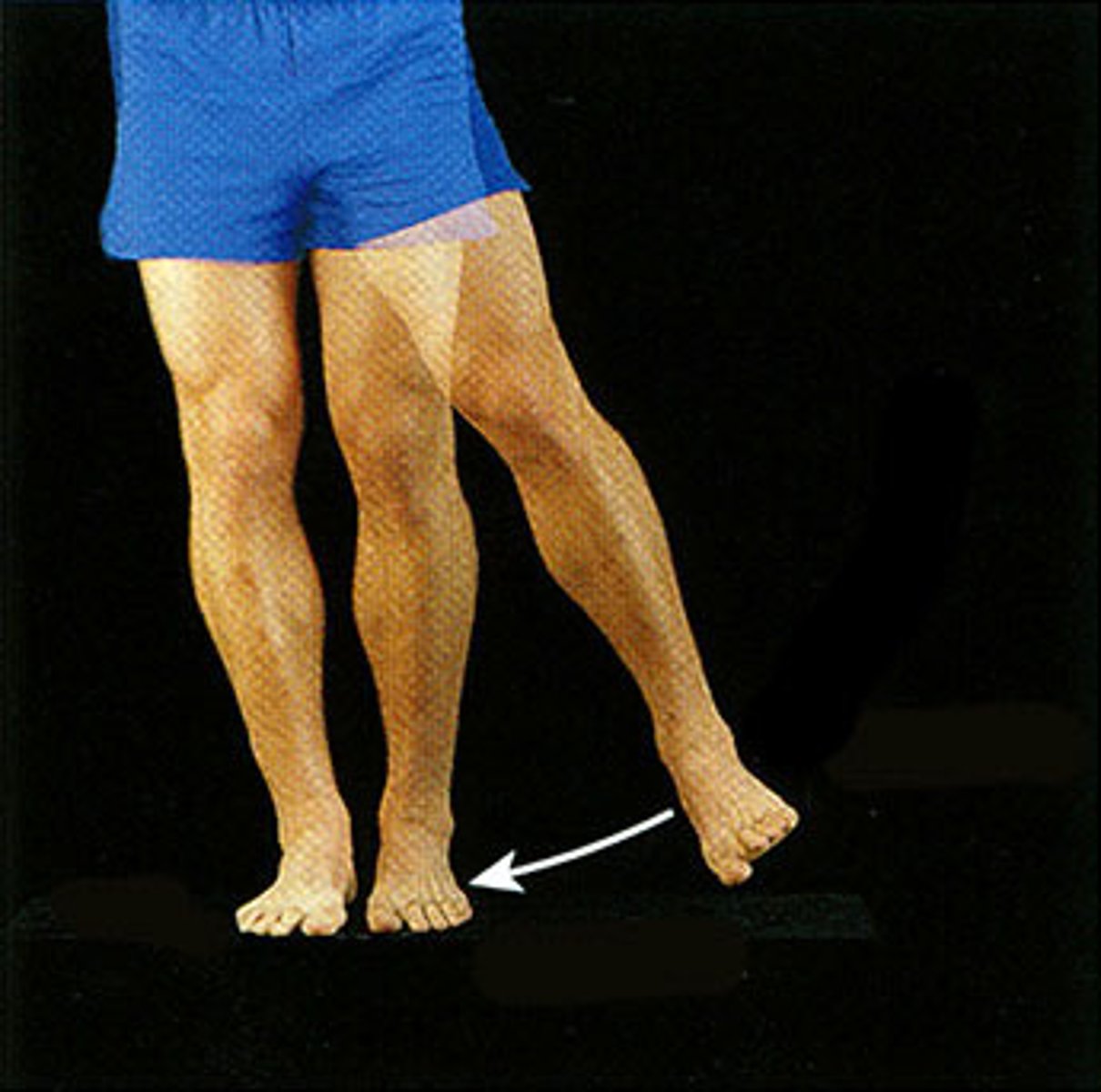
abductor (type of movement)
moves bone away from midline
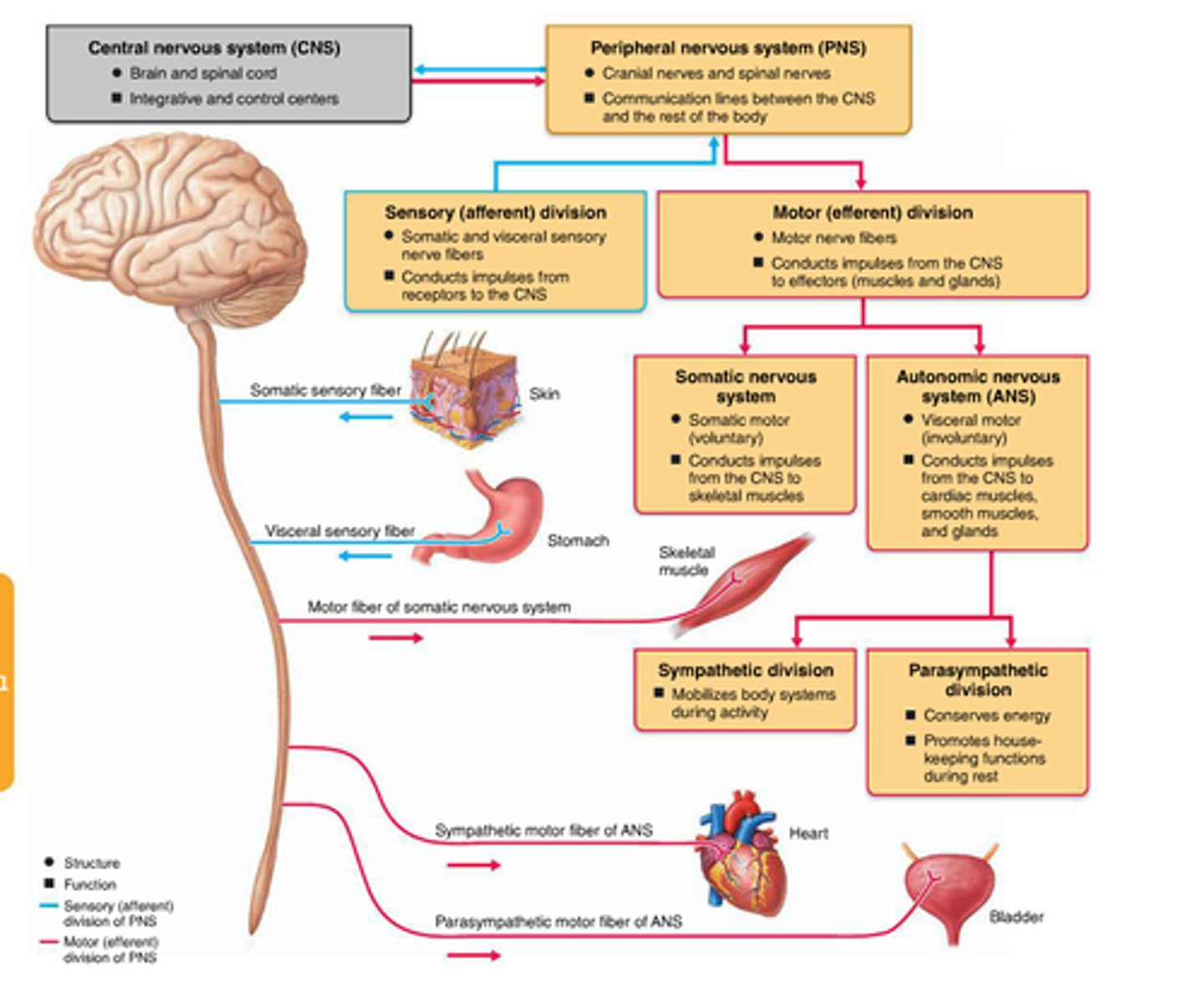
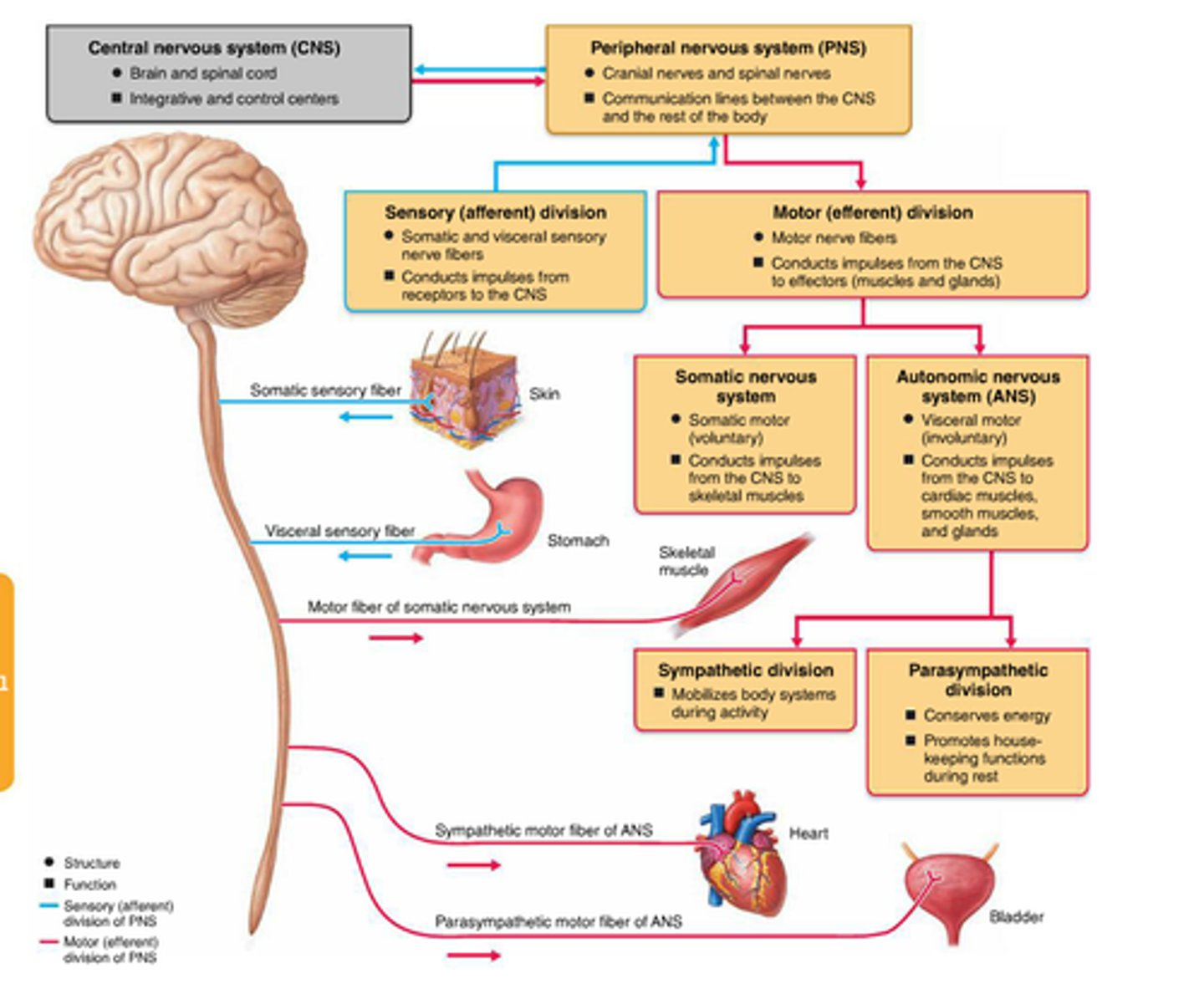
2 components of the CNS
brain and spinal cord
sensory division of PNS
carries information from receptor organs to the CNS
subdivisions: somatic sensory and visceral sensory
somatic sensory division
Carries information from skin, muscles, and joints to CNS
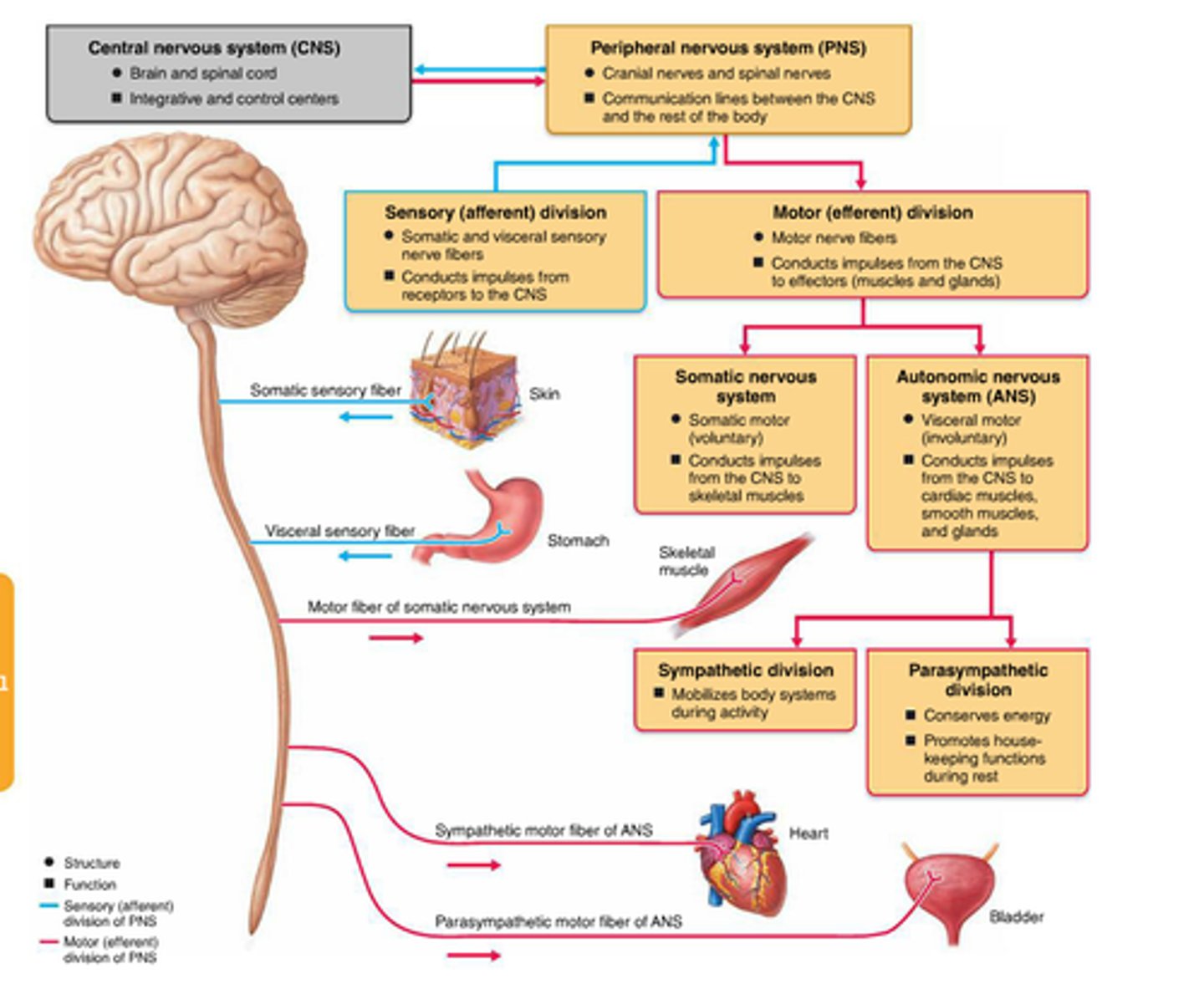
visceral sensory division
Carries information from internal organs to CNS
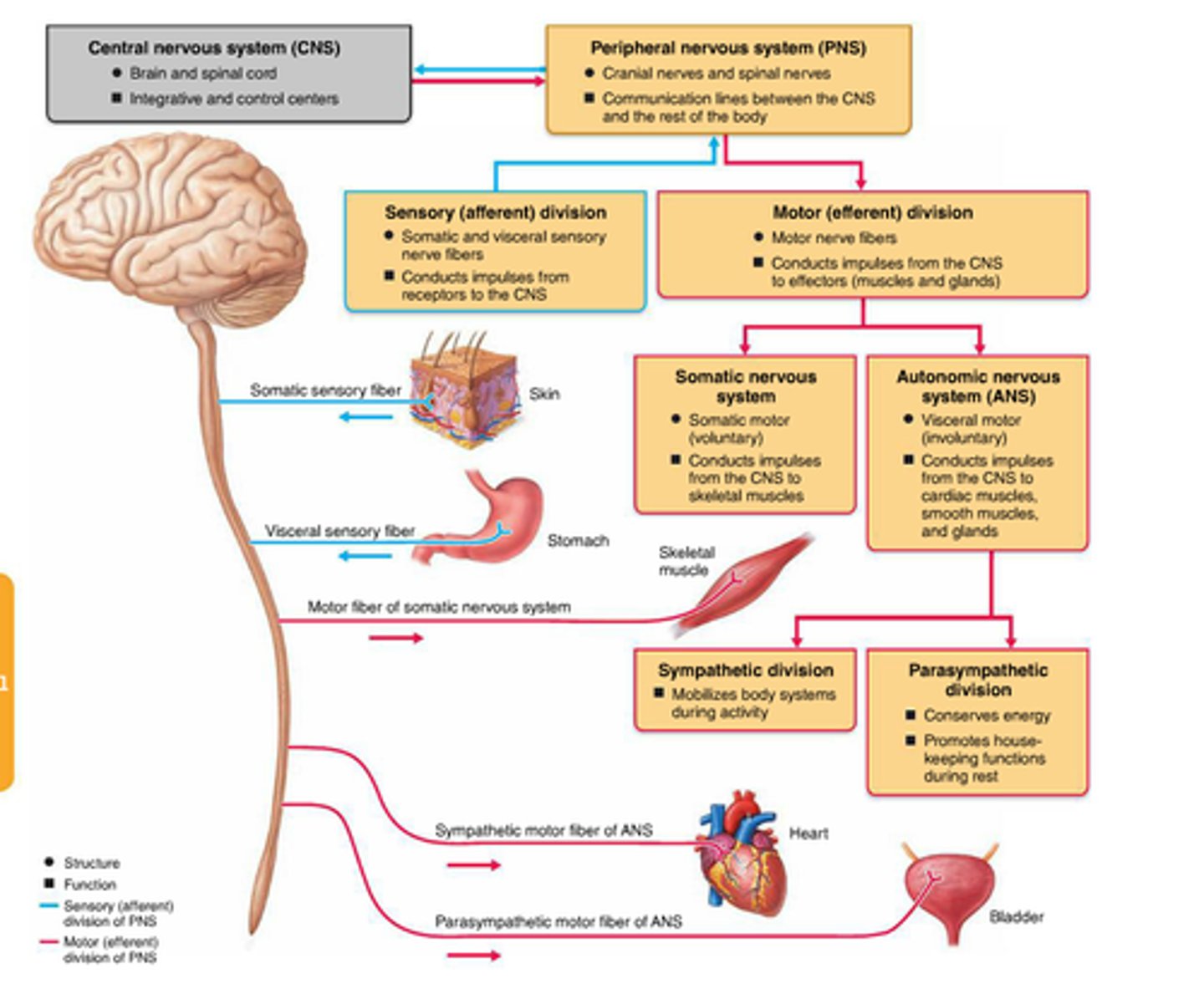
Motor Division of PNS
carries information from CNS to effector organs (muscles and glands)
subdivisions: autonomic motor division and somatic motor division
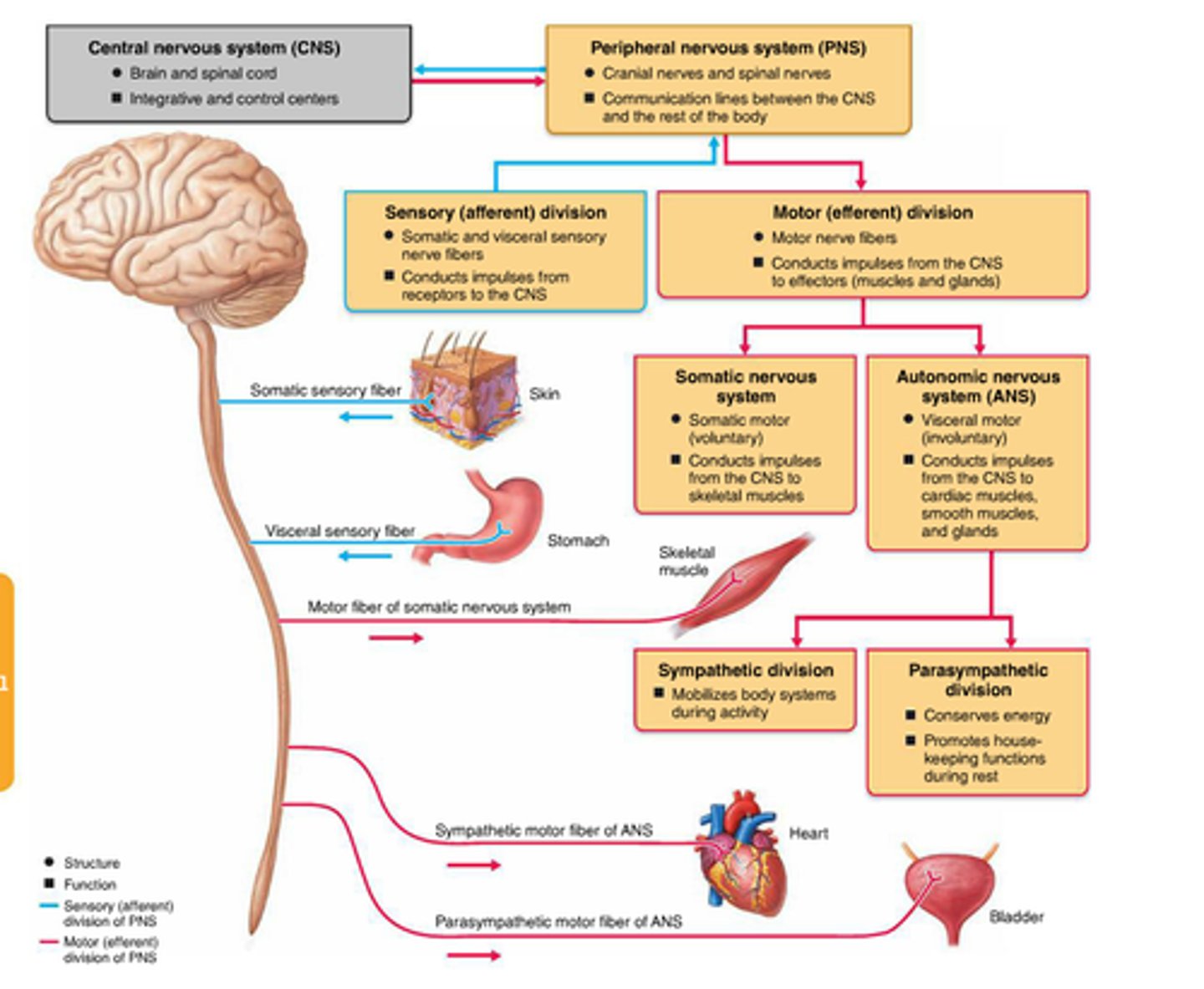
autonomic motor division
carries information to smooth muscle, cardiac muscle and glands; involuntary
subdivisions: sympathetic division and parasympathetic division
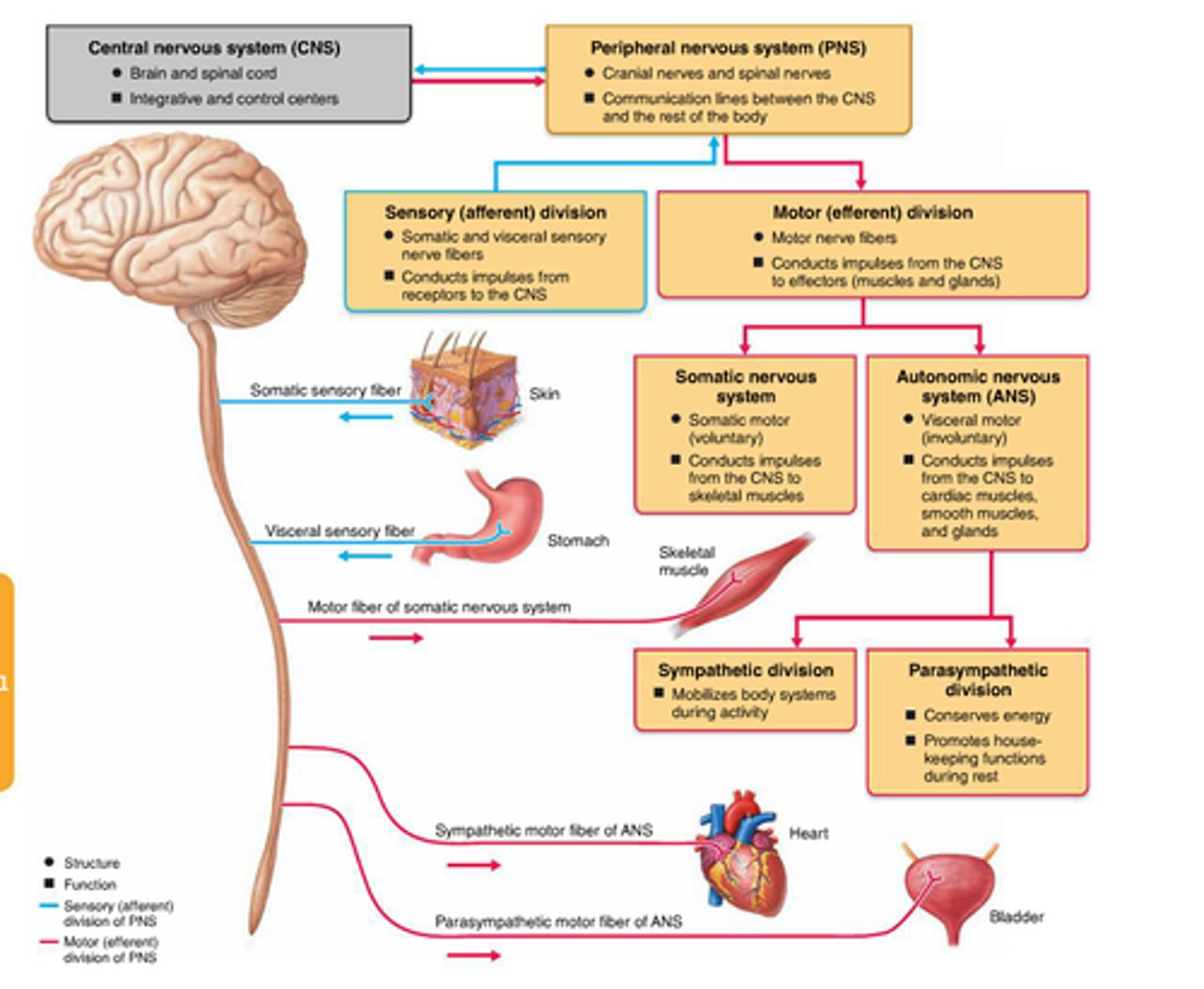
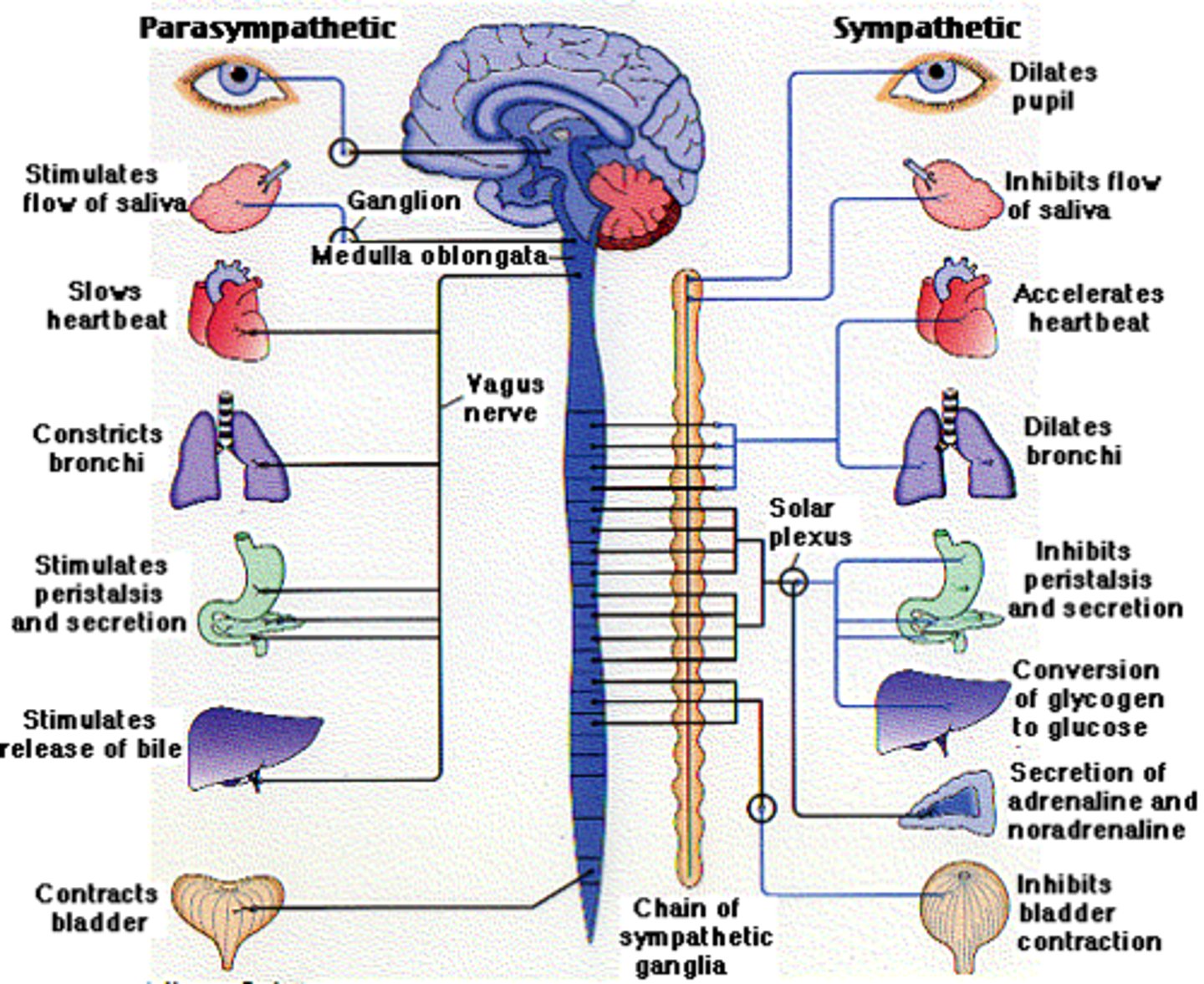
parasympathetic division
rest and rejuvenate/digest; digestive activities increased after eating
examples: constrict pupils, slows heart rate, constricts bronchi, salivary glands stimulated, stimulates pancreas and gallbladder
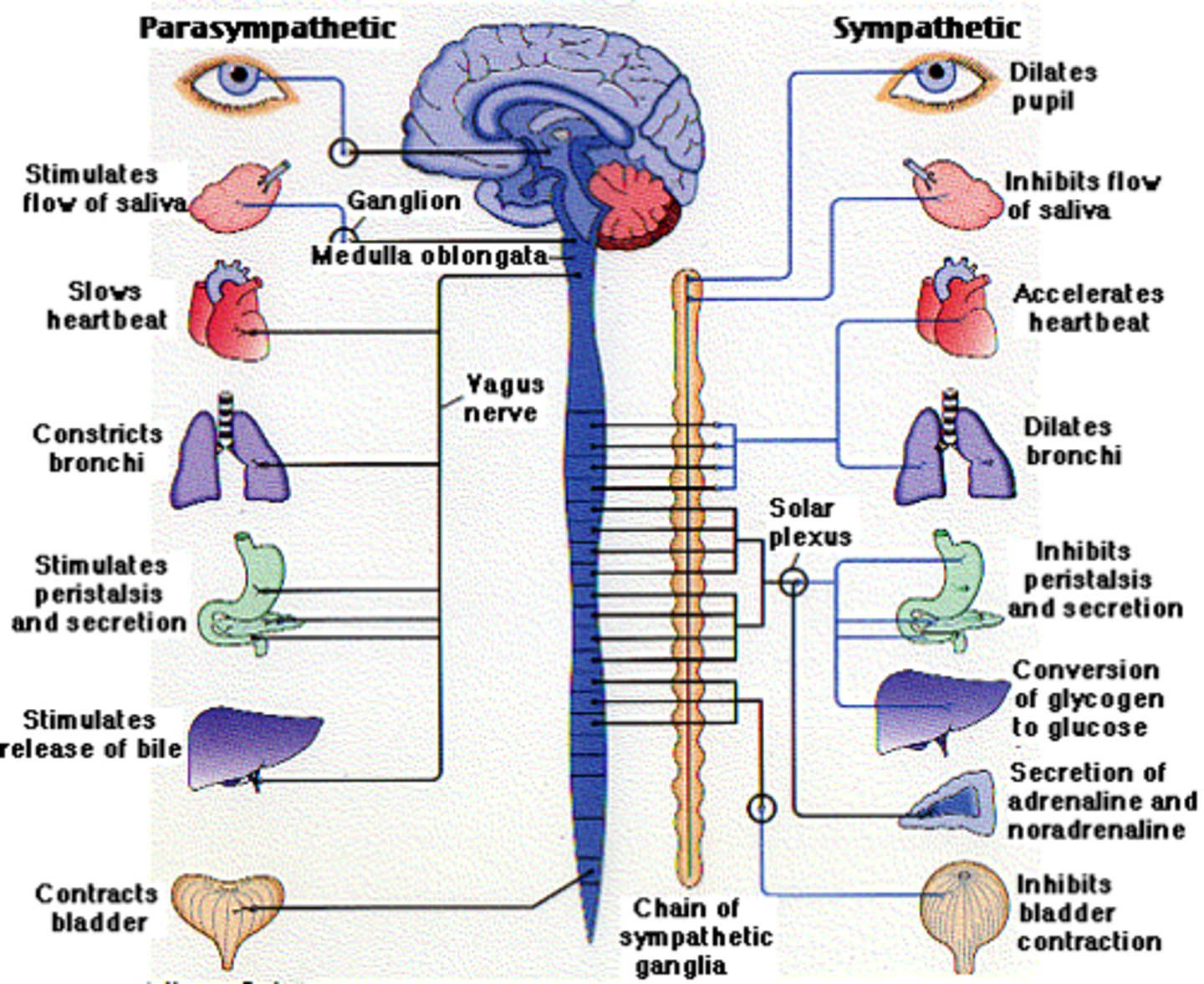
sympathetic division
fight or flight; digestive activities inhibited
examples: pupils dilate, heart rate increases, relaxes bronchi in lungs (more O2), more glucose released from liver, activates adrenal medulla
somatic motor division
carries information to skeletal mucles; voluntary
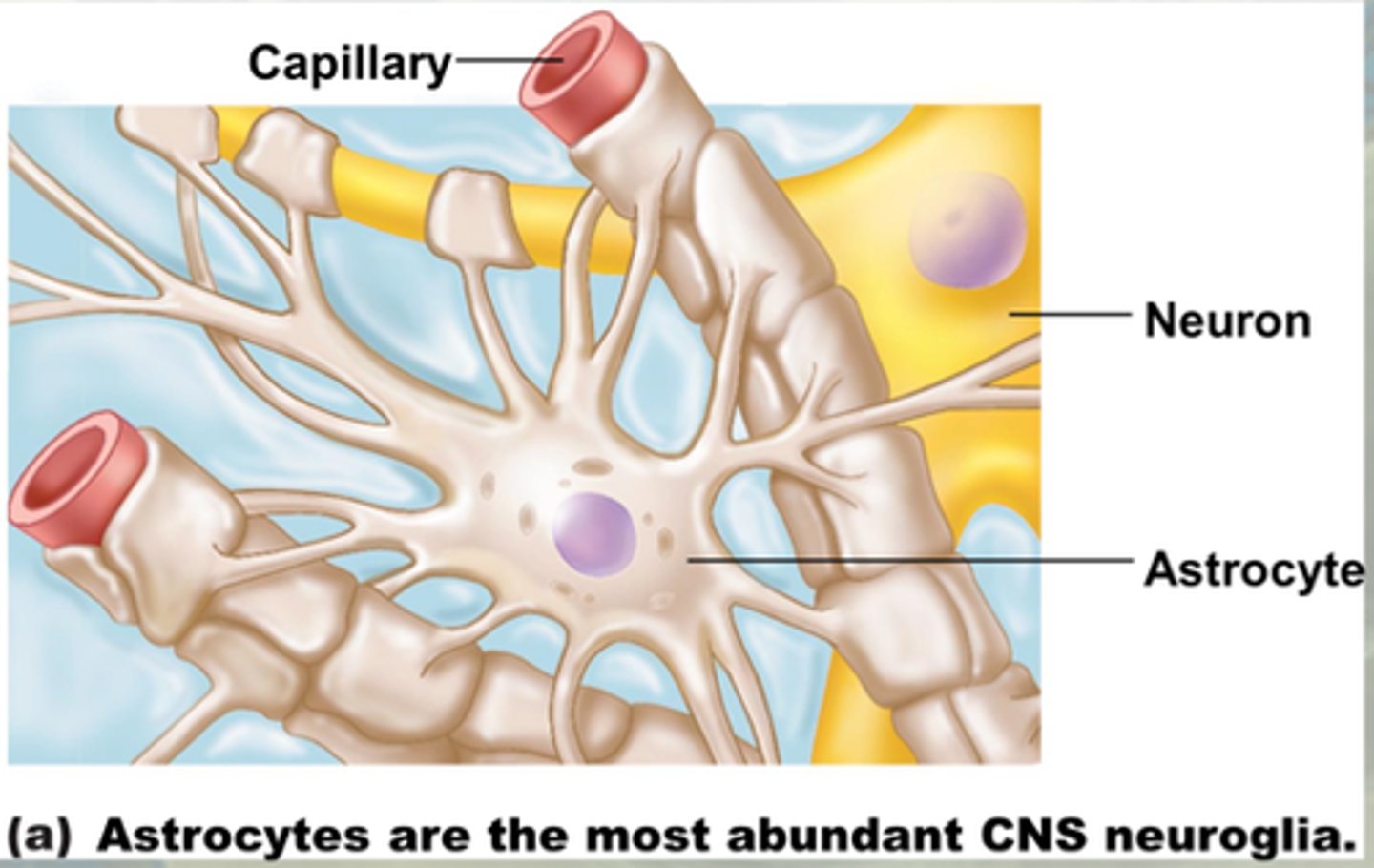
neuroglia in CNS
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells
astrocytes
-support and brace neurons; anchor them to a blood supply
-help form synapses between neurons
-mop up extracellular space
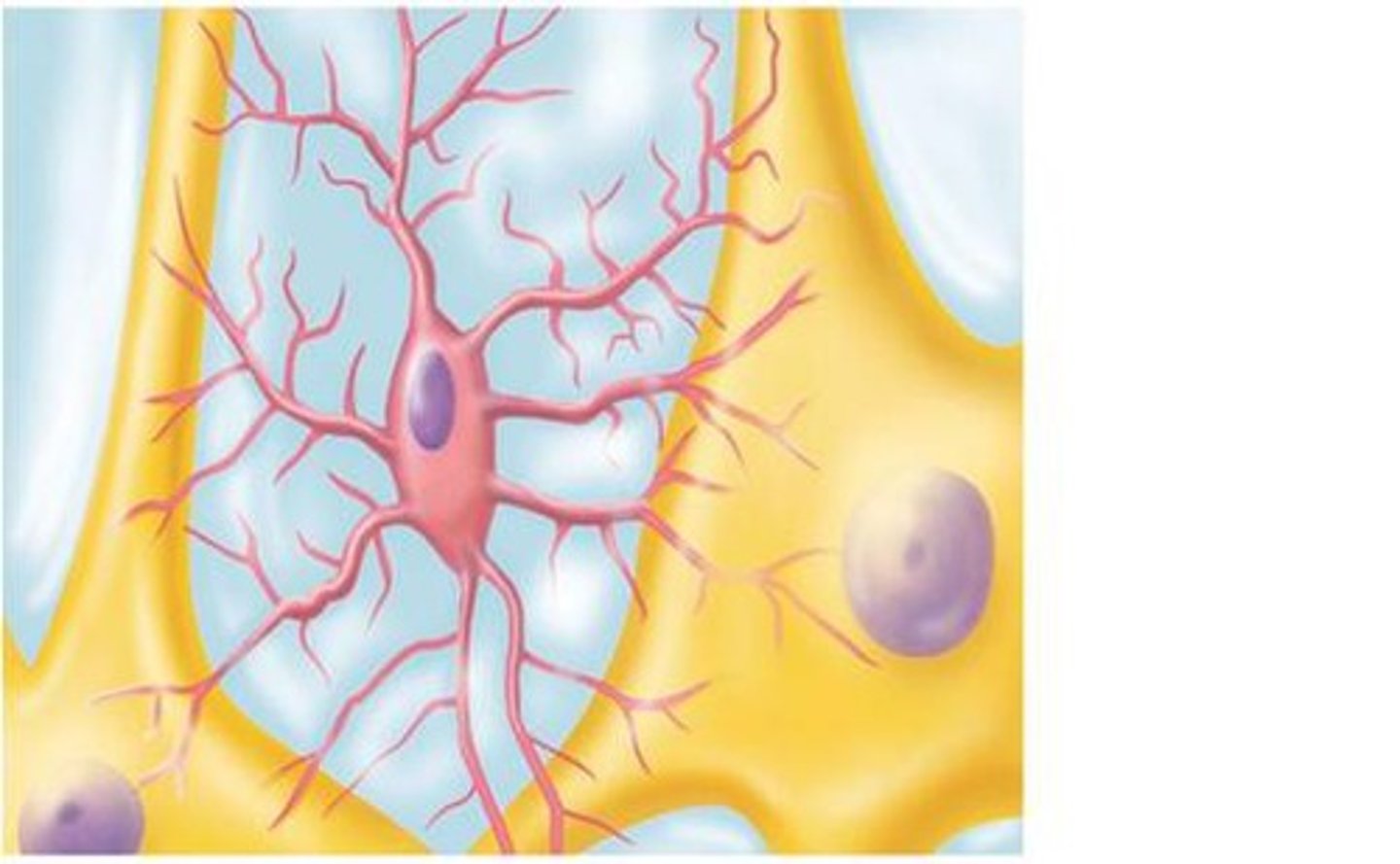
microglia
-monitor the health of neurons
-phagocytose microbes and dead neurons
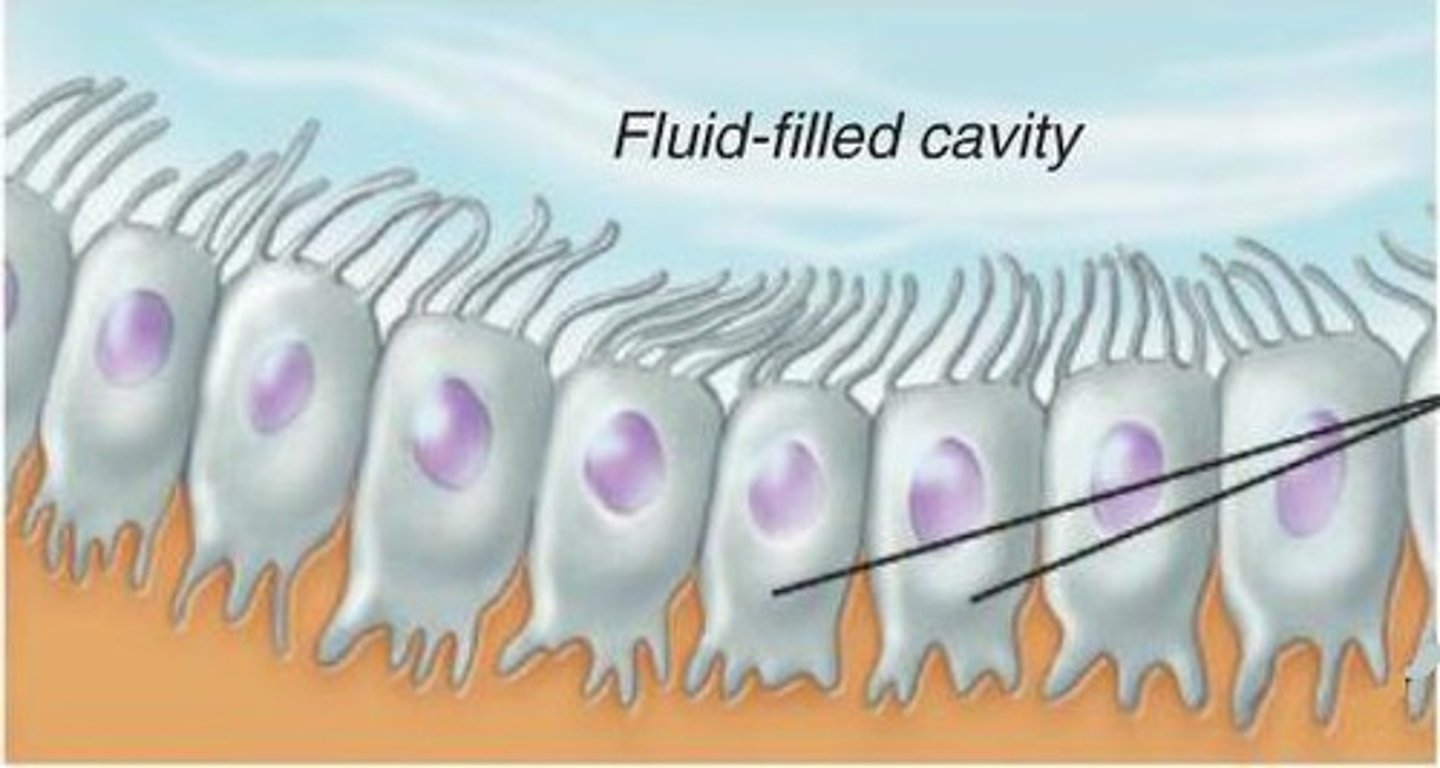
ependymal cells
-Epithelial layer lining cavities in brain and spinal cord
-ciliated
-circulate cerebrospinal fluid through cavities
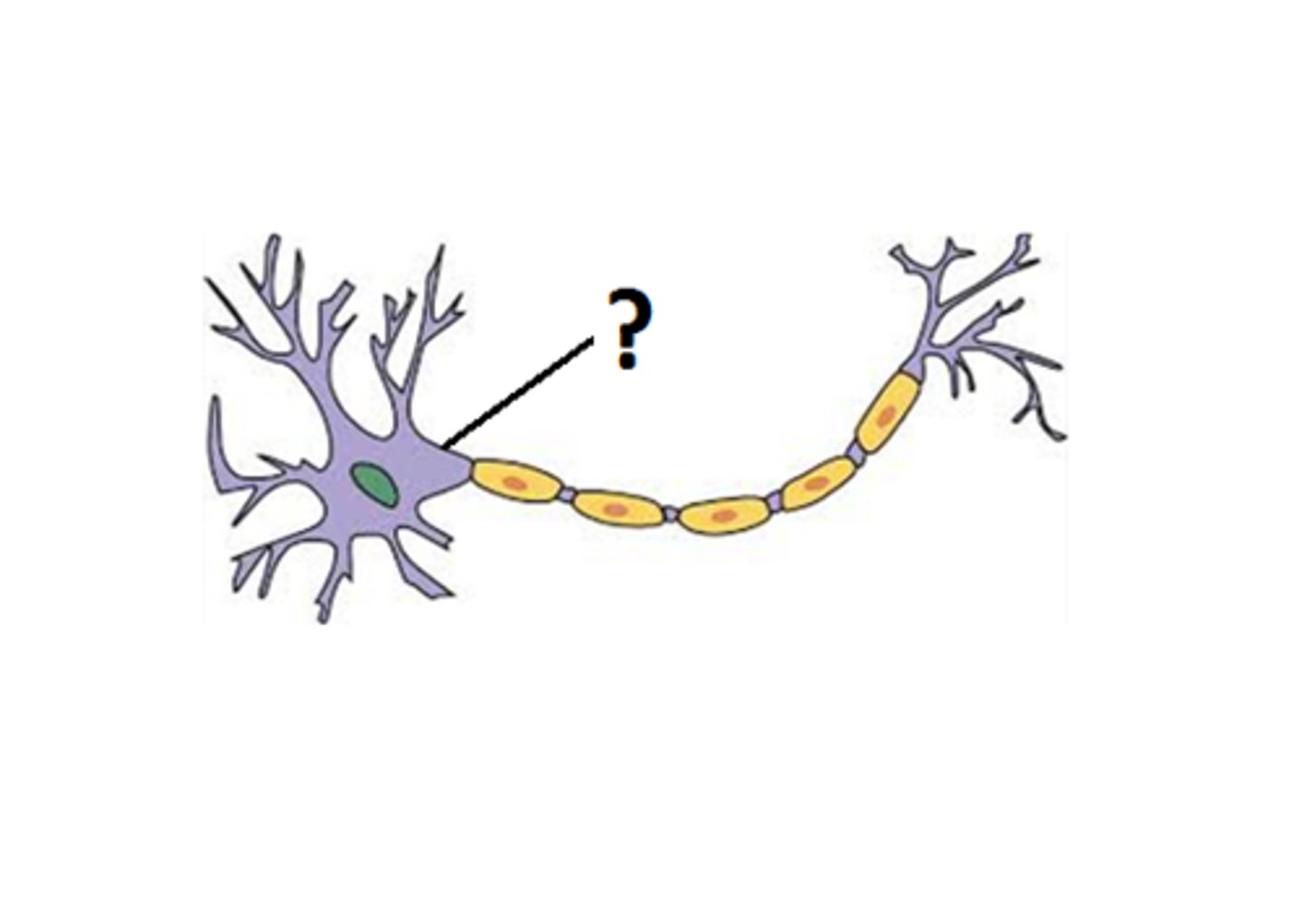
Oligodendrocytes
insulates axons within CNS with myelin sheath
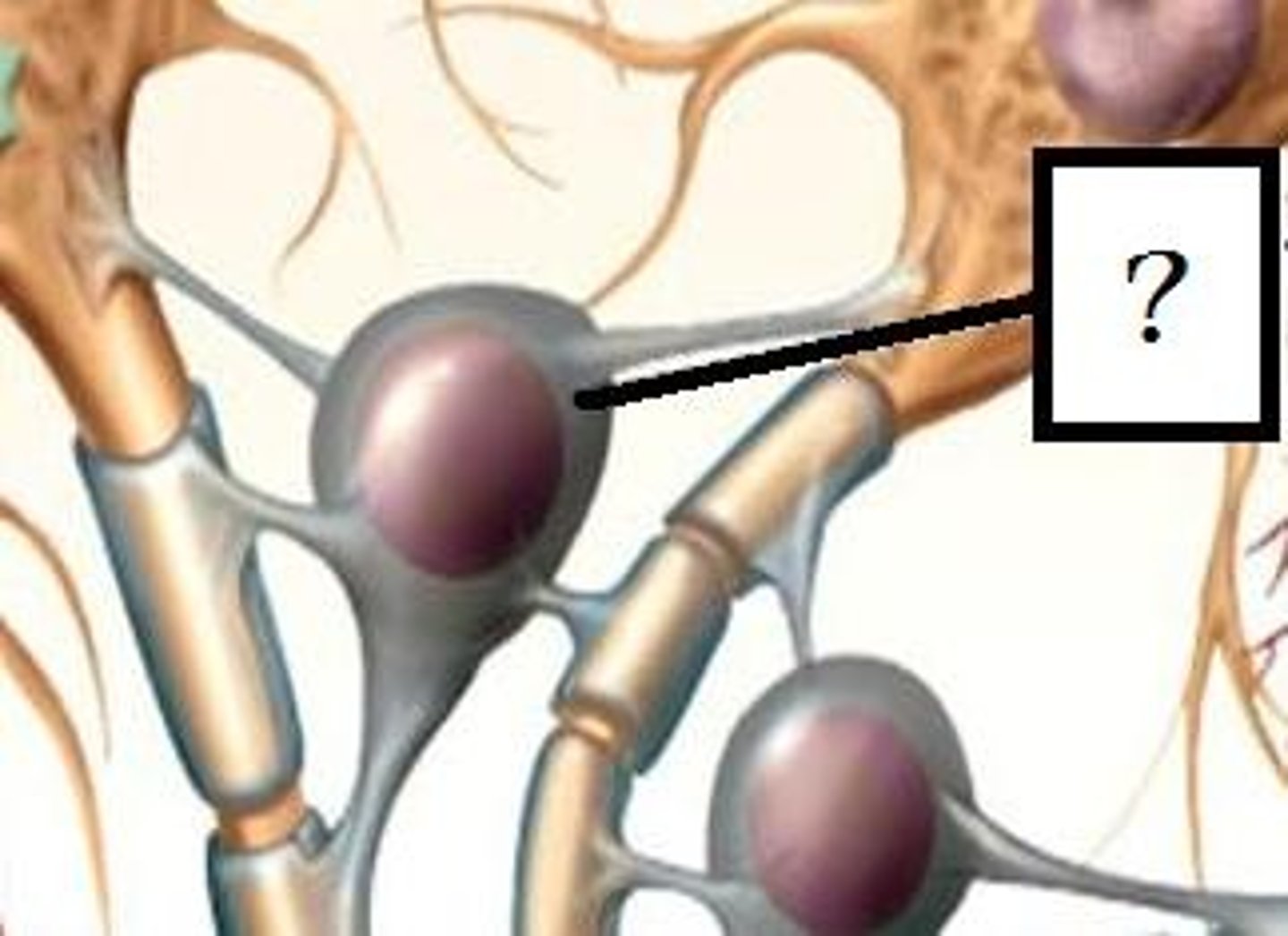
neuroglia of PNS
satellite cells and schwann cells
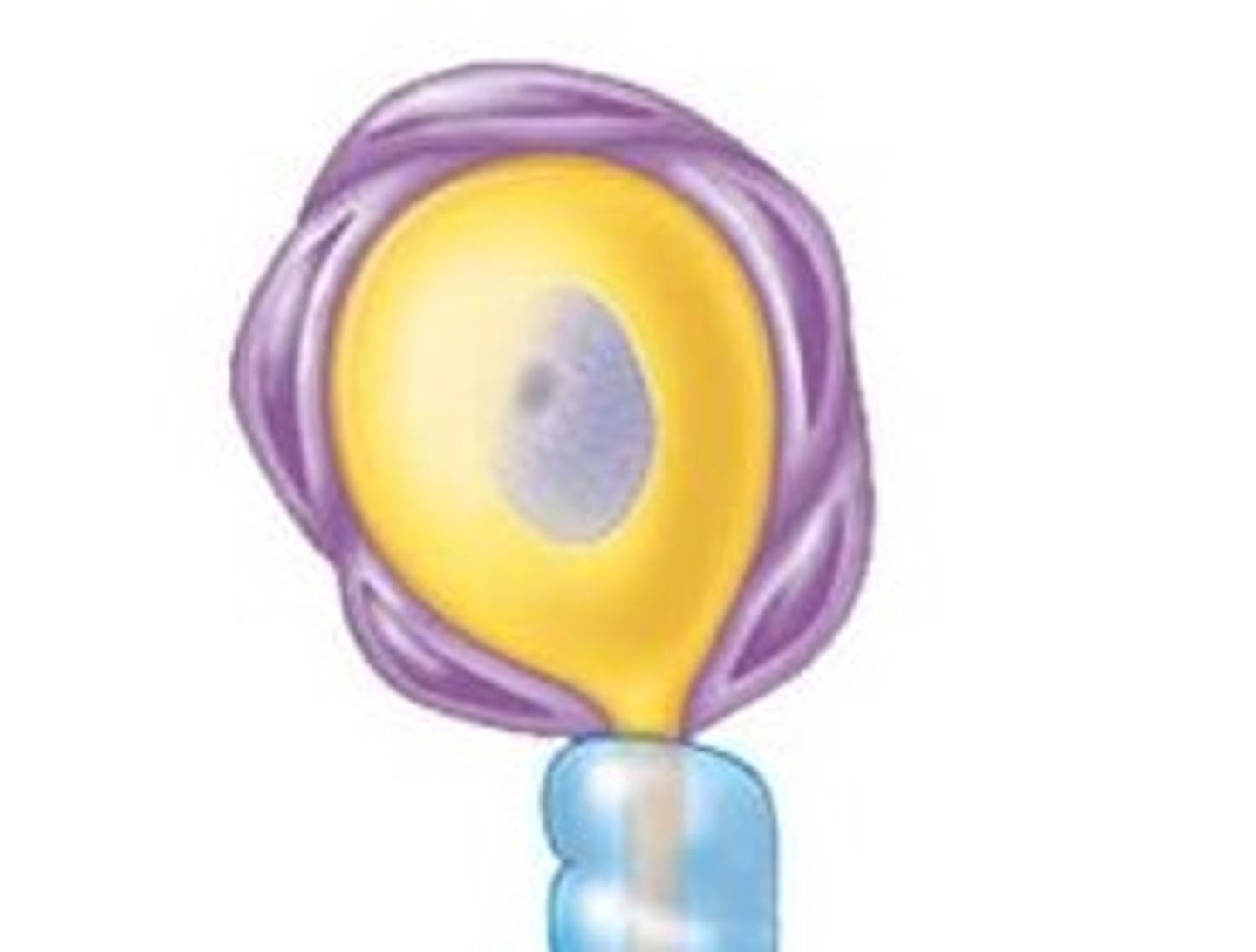
satellite cells
-surround cell body
-nutrient exchange
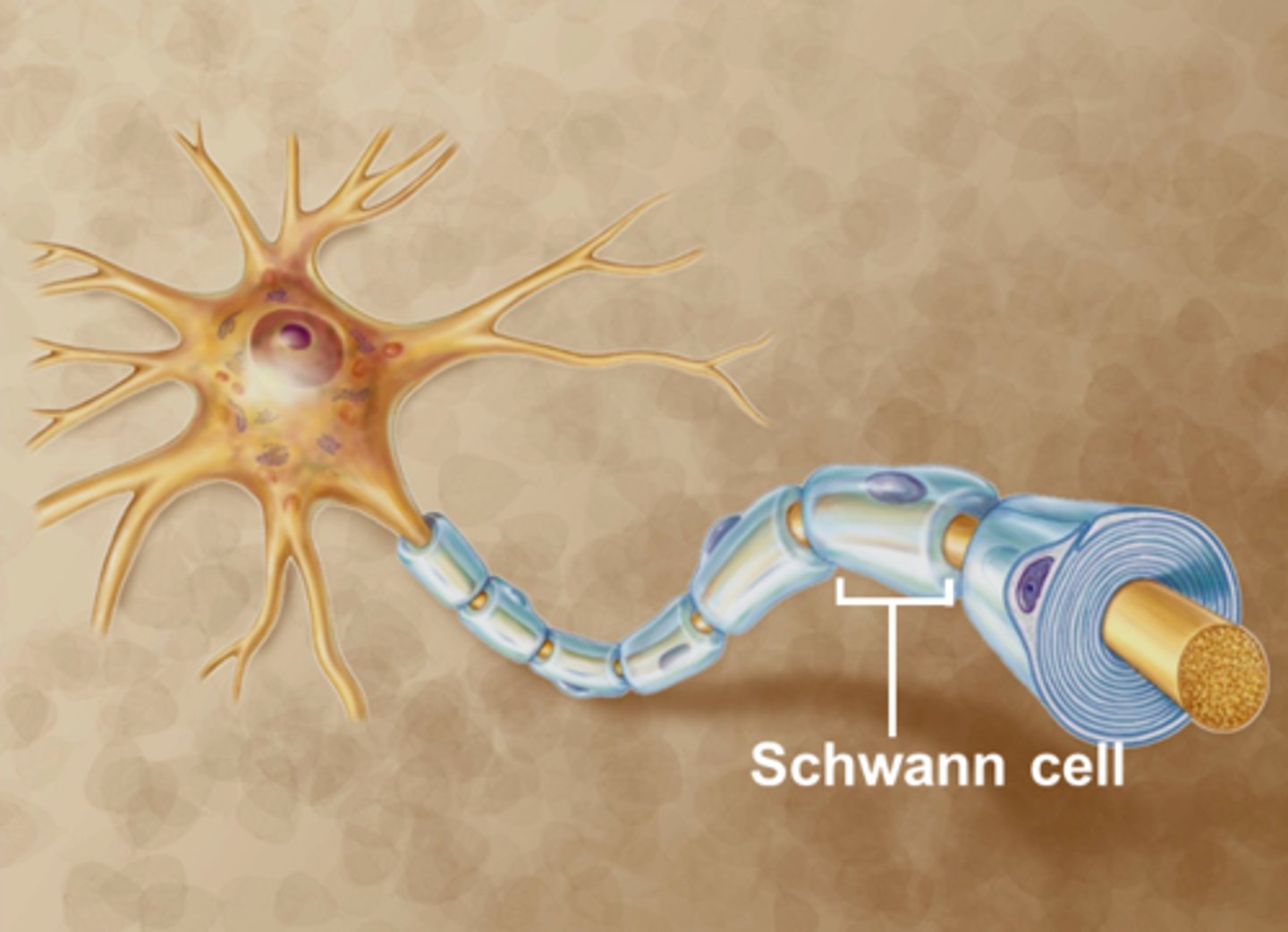
schwann cells
insulate axons with myelin sheath
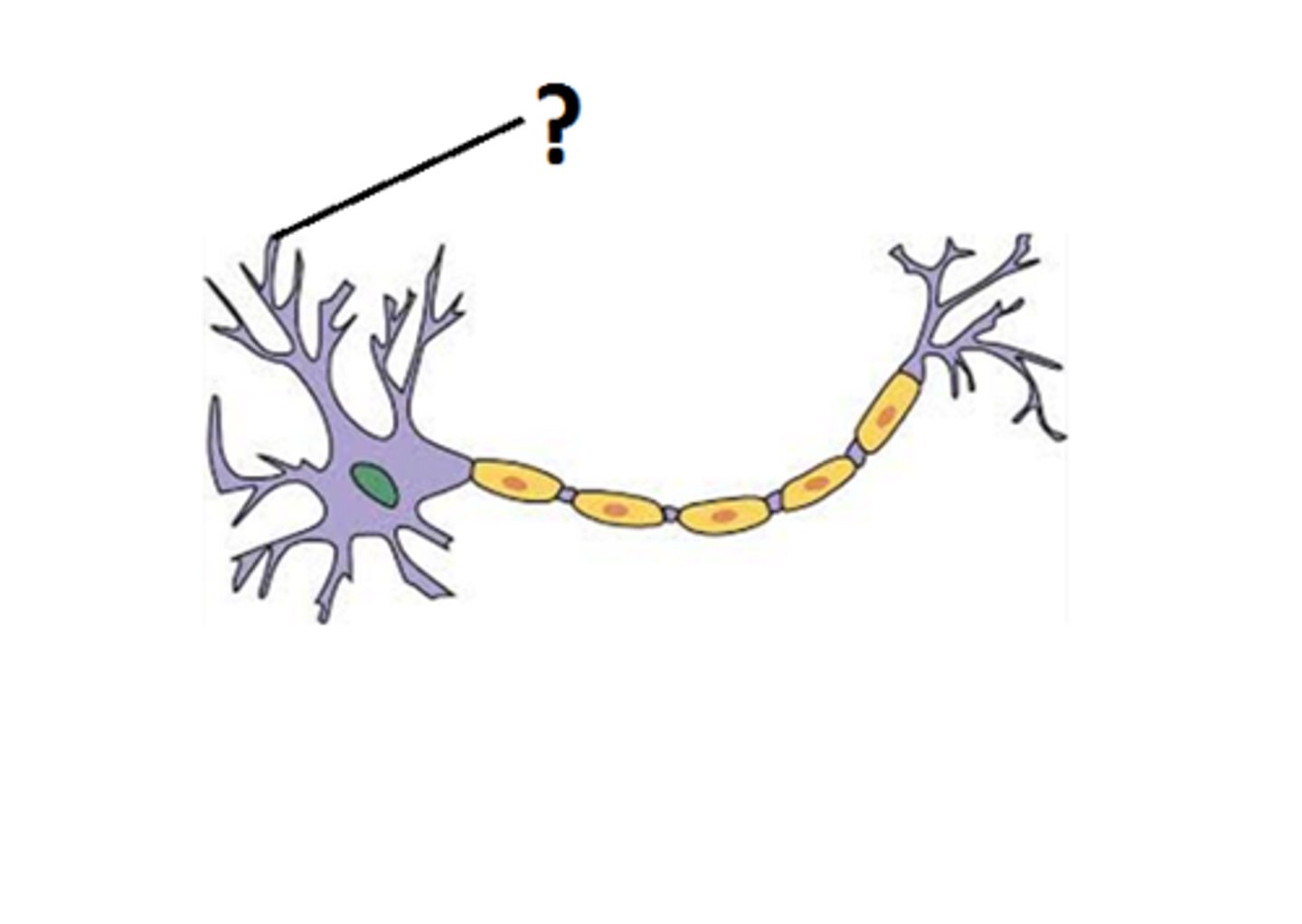
dendrites location and function
-100s of short branched projections (increase SA)
-receive info from sensory receptors or other neurons
-convey info to cell body as signals called graded potentials or postsynaptic potentials
soma location and function
where most of metabolism occurs in cell, location of nucleus, DNA and most organelles
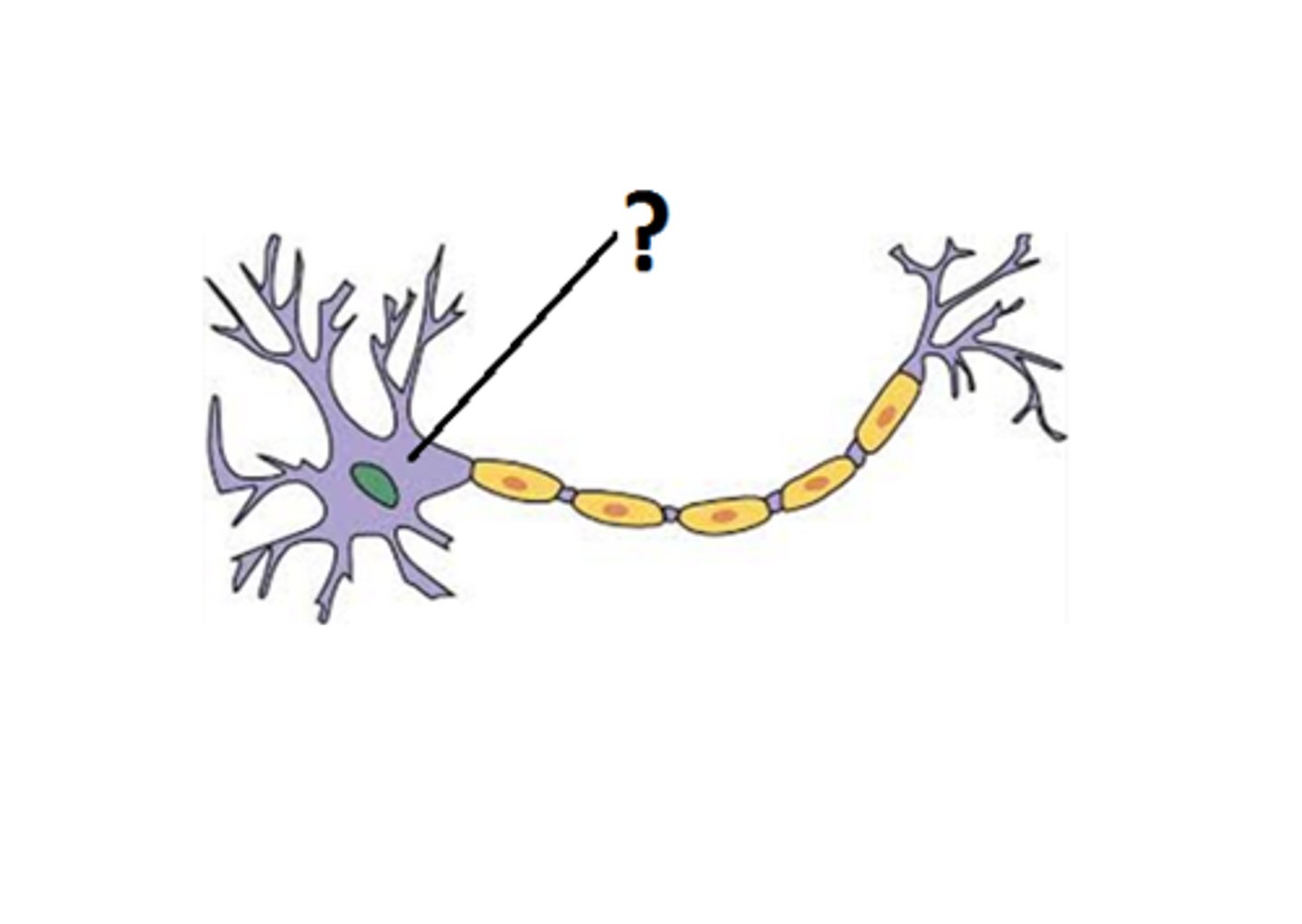
trigger zone location and function
within axon hillock, location where the electrical impulses are produced