3.1 Elements, bonding, and physical properties
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
What are chemical reactions?
Involve rearrangements of valence electrons (sharing, donating, or accepting)
The element does not change
What are nuclear reactions?
Involve changes in the nucleus (not electrons)
Often result in a change in element (since elements are define by the number of protons)
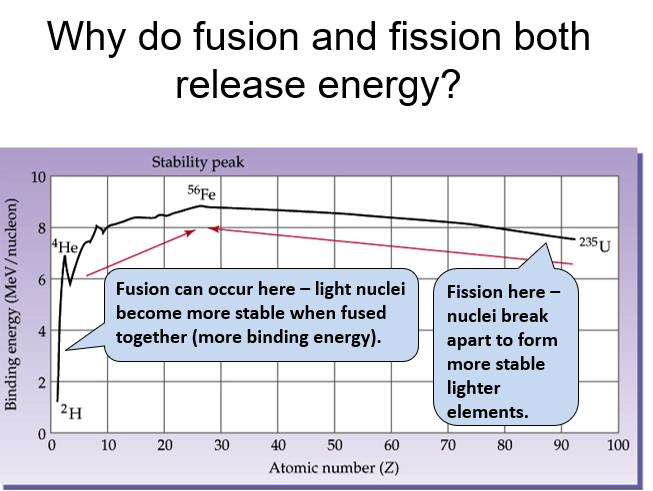
Fusion in nuclear reactions
Fusion is the process of adding two nuclei together to form a larger nucleus, releasing energy.
Example: Occurs in stars, like the Sun, where hydrogen nuclei fuse to form helium.
Fission in nuclear reactions
Fission is the process of breaking apart a nucleus into two smaller nuclei, releasing energy.
Example: Used in nuclear power plants, where uranium nuclei split to produce energy.
Radioactive decay in nuclear reactions
Radioactive decay is the process of emitting particles (such as α, β, γ) from the nucleus of an unstable atom, leading to a change in the atom
Example: Uranium-238 decays into thorium-234 by emitting an alpha particle (α).
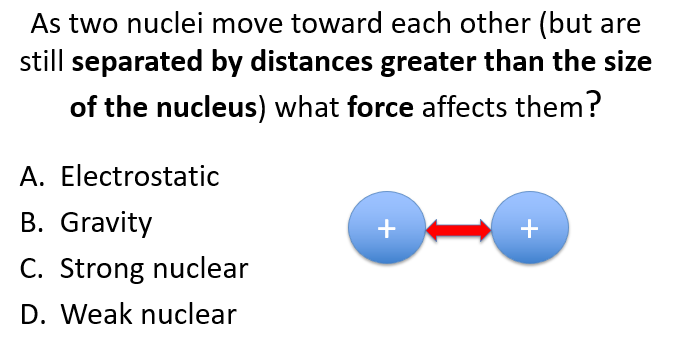
A
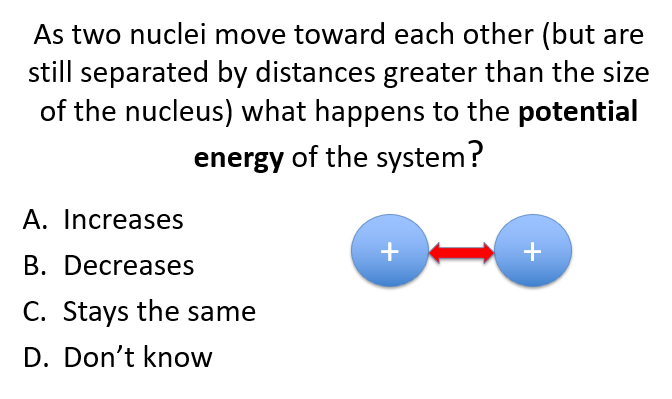
A

B
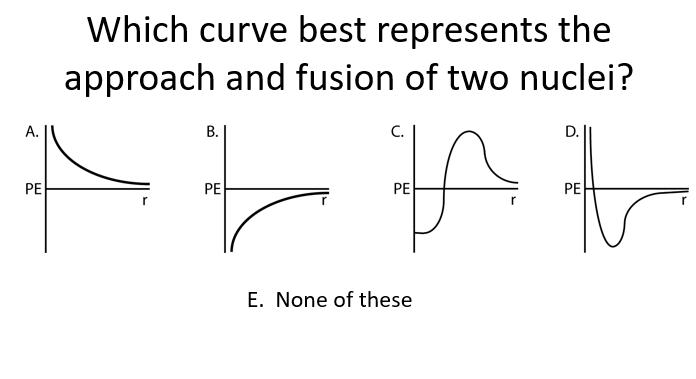
C
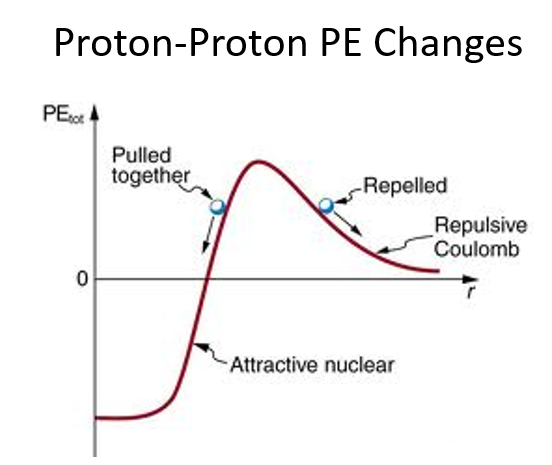
Before fusion: Potential energy increases due to electrostatic repulsion as the nuclei approach.
After fusion: Potential energy decreases sharply as the strong nuclear force takes over and the nuclei fuse.

A
B
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fission is the fragmentation of heavy nuclei into lighter, more stable ones, releasing energy in the process
Chain reaction in nuclear fission
Process: Neutrons released in the fission of 235U can induce three more fissions, which then induce nine more, and so on, creating a chain reaction.
Critical mass in nuclear fission
Critical mass is the minimum mass of material required for the chain reaction to become self-sustaining.
Radioactivity
Radioactivity occurs when a nucleus emits or captures particles or energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation.
Alpha Particle Emission
Type: Alpha particle emission
Description: The nucleus emits an alpha particle (2 protons and 2 neutrons)
Beta Particle Emission
Type: Beta particle (electron) emission
Description: A neutron decays into a proton, emitting a beta particle (electron).
Positron Emission
Type: Positron emission
Description: A proton decays into a neutron, emitting a positron (the electron’s antimatter counterpart)
Electron Capture
Type: Electron capture
Description: An inner orbital electron is captured by the nucleus, where it combines with a proton to form a neutron
Gamma Radiation
Type: Gamma radiation
Description: Electromagnetic radiation is emitted from the nucleus, typically following other types of decay.