chemistry revision 2025, 2024, 2023 igcse papers
1/186
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
187 Terms
2025 43m/j
what is an alloy-
a mixture of a metal with other elements
Give two observations which show that the zinc carbonate is in excess in -
M1 solid stops dissolving / disappearing M2 no more bubbles / fizzing / effervescence on addition of solid
Step 1 is repeated using large pieces of zinc carbonate instead of powdered zinc carbonate. All other conditions are the same. The rate of reaction decreases. Explain why the rate of reaction decreases. Give your answer in terms of particles
smaller surface area
frequency of collisions between particles decreases
hydrated crystals form in step 4. State what is meant by the term hydrated.-
crystals that are chemically bonded with water
THE SULFUR DIOXIDE TO SULFUR TRIOXIDE REACTION IS A ___________________
REVERSE REACTION
rate and yield doesnt become low- they _________
decrease
NEVER EVER EVER SAY BUTANOL OR PROPANOL
ITS ALWAYS BUTAN-1-OL AND PROPAN-1-OL
LIthium added to water- (a solid at room temperature btw)
solid dissolves / disappears • fizzing/ bubbles / effervescence • solid floats • solid moves (on surface)
at room temperature and pressure- chlorine is
CHLORINE IS PALE YELLOW GREEN IN COLOUR and GAS
2025 42 m/j
covalent bond-
a pair of electrons shared by two atoms
Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why Cl 2O boils at a low temperature and does not thermally decompose into its constituent elements, Cl 2 and O2
there is weak attraction between molecules and strong covalent bonding between atoms
therefore, during boiling, at a low temperature (weak) forces of attraction between molecules is broken
during thermal decomposition, high energy or high temperatures are required to break covalent bonds between Cl2 and O2 atoms
Give two reasons why liquid Cl 2O is a poor conductor of electricity.-
no ions
no MOBILE electrons
copper(II) sulfate is what colour (in solution)
BLUE
Electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate is carried out using the apparatus shown in Fig. 3.1. The electrodes are made of platinum. Describe the change in appearance, if any, of the electrolyte when platinum electrodes are used.
becomes paler blue or becomes colourless
what is the formula of chromite
FeCr2O4
Suggest one disadvantage of extracting chromium by reacting chromite with carbon.
chromium will need to be separated from iron
identify the alkali metal which: (i) has the highest melting point
Lithium
WHY IS SO AND SO UNSATURATED-
it has a carbon-carbon bond which is not a single bond
State one reason why alloys are more useful than pure metals-
harder or stronger
brass contains-
copper + zinc
Bronze contains
copper + tin
Name a substance, other than copper(II) carbonate, that can be added to dilute sulfuric acid to produce aqueous copper(II) sulfate.-
since copper carbonate is insoluble- name an insoluble copper compound (AND IF YOU DONT KNOW ONE PLEASE STUDY THE DAMN NOTES)
remember to show in equations that haber’s process and contact process are reversible
also remember the symbol
iodine is _______ colour at room temperature
grey-black
2025 f/m
State what is meant by the term ionic bond.-
Strong electrostatic attraction between ions of opposite charge
in a closed system-
no reactants or products can enter or leave
State what the symbol ΔH represents.
enthalpy change- overall energy change
State which other property of manganese is shown by the formation of several oxides
variable oxidation state
reducing agent-
a substance that reduces another substance and is itself oxidised
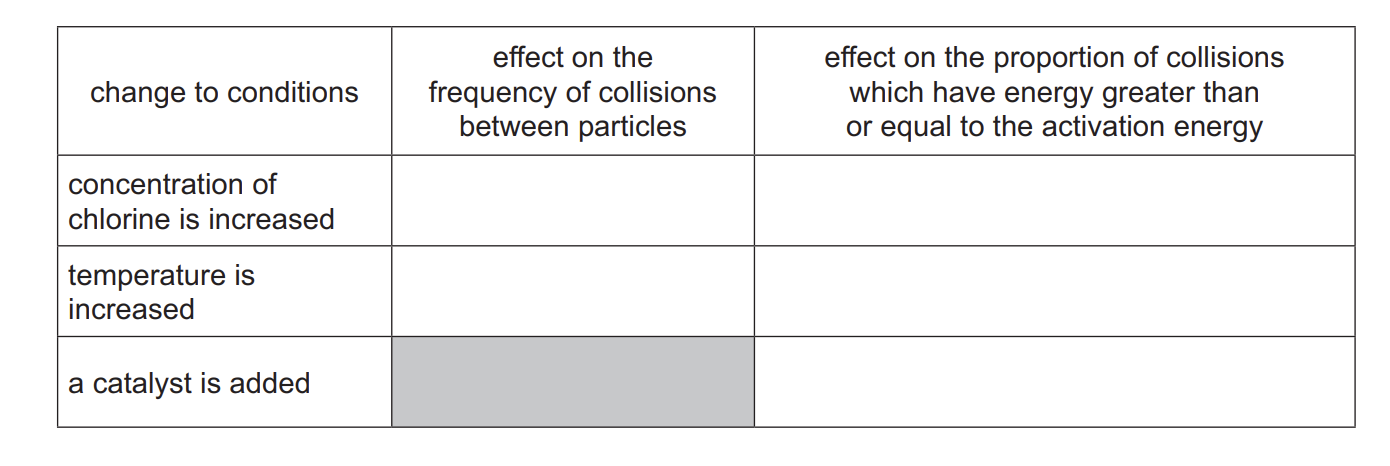
Explain, in terms of collision theory, why decreasing the temperature decreases the rate of this reaction.
kinetic energy of particles decreases
frequency of collisions between particles decreases
Fewer of the collisions / particles have energy greater than / equal to activation energy
2024 o/n 43
State the meaning of the term amphoteric.
reacts with acids and with bases to produce a salt and water
Tin is a metal that forms both covalent and ionic compounds. Suggest why this is unusual for a metal.
metals form ionic compounds or ionic bonds only OR covalent compounds contain non-metals only
Tin(II) oxide, SnO, is ionically bonded. The melting points of SnCl 4 and SnO are shown in Table 3.1. Table 3.1 melting point/°C SnCl 4 –33 SnO 1080 Explain, in terms of structure and bonding, why SnCl 4 has a much lower melting point than SnO.
attraction between molecules or intermolecular forces in tin(IV) chloride
tin(II) oxide has a giant ionic structure
M3 weaker attraction (between particles) in tin(IV) chloride ORA
When aluminium foil is added to aqueous tin(II) sulfate, a reaction does not occur even though aluminium is above tin in the reactivity series. Explain why a reaction does not occur.
unreactive coating of aluminium oxide (side question- have you memorised the reactivity table??)
State what is meant by the term hydrated.
substance that is chemically combined with water OR containing water of crystallisation
do you know the colour changes of all the indicators
IF NOT PLEASE GO STUDY IT
Suggest why universal indicator is not used for this titration
too many colour changes
A student is provided with an aqueous solution of sodium sulfate. Describe how to prepare a pure sample of sodium sulfate crystals from this solution
heat the solution / warm the solution /boil the solution / leave solution in hot place
to saturation (point)/ crystallisation point AND leave to cool
suitable method of drying
0.325g of Zn is added to dilute sulfuric acid which contains 0.0100 moles of H2SO4 . The equation for this reaction is shown. Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2 (i) Determine whether Zn or H2SO4 is the limiting reactant. Explain your answer
M1 moles of Zn = 0.005 / 5 10–3 (mol),, ,,Zn is limiting because moles of H2SO4 is greater than moles of Zn AND 1:1 ratio required for reaction
In another experiment, 48.0cm3 of hydrogen gas, H2 , is produced. The experiment is carried out at room temperature and pressure, r.t.p. Calculate the number of molecules in 48.0cm3 of H2 gas measured at r.t.p. The value of the Avogadro constant is 6.02 × 1023 .
M1 (48.0 ÷ 24 000 =) 0.00200 (mol) M2 1.20 1021 (molecules)
After a certain time the reaction stops. Explain why the reaction stops.
____________ is used up
Suggest why it is not possible to use the results in Table 5.1 to determine the exact time when the reaction stops.
time intervals are too large
Explain why the method shown in Fig. 5.3 will not allow the reaction to reach equilibrium
not a closed system
State the meaning of the term hydrocarbon
compound containing carbon and hydrogen only
2024 o/n 42
types of functional groups used in condensation polymerisation
dicarboxylic acid, diol and diamine…… polyesters contains- dicarboxylic acid and diol……. polyamides contains dicarboxylic acid and diamine
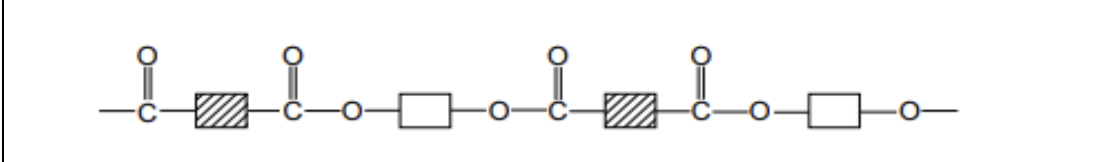
when condensation polymer, make sure that the inside the block of each monomer has a different design
State the source of the large alkane molecules used in cracking
petroleum (may close attention to the spelling)
Suggest the type of chemical reaction which happens during cracking.
Thermal decomposition
S2Cl 2 (g) + Cl 2 (g) (symbol of reverse reaction) 2SCl 2 (g) (forward reaction is exothermic)
M1 increases M2 no change M3 increases M4 increases M5 increases
what is activation energy?-
the minimum energy that colliding particle must have to react
State why aluminium is used in food containers
aluminium is resistant to corrosion
2024 o/n 41
Suggest why these two isotopes have identical chemical properties.
same number of electrons
same electronic configuration
Write the formula of hydrated copper(II) sulfate
CuSO4•5H2O
Describe what is seen at the cathode during the electrolysis of aqueous copper(II) sulfate.
pink AND solid
State two differences seen if the electrolysis is repeated using copper electrodes instead of graphite electrodes. (the electrolyte est copper sulfate)
• colour remains constant • no bubbles at the anode • anode dissolves
advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cell instead of gasoline in vehicle engines.
advantages- • water is the only product • no carbon dioxide produced • more efficient
disadvantages- • hydrogen needs to be stored at high pressure • hydrogen hard to store • heavy tanks needed to store hydrogen • fewer (hydrogen) filling stations • less efficient
Organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms. Calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in 44.0g of the ester methyl propanoate, CH3CH2COOCH3 . One mole of CH3CH2COOCH3 contains 6.02 × 1023 molecules. Give your answer in standard form.
M1 Mr of CH3CH2COOCH3 = 88 M2 mol of CH3CH2COOCH3 = 44 / 88 = 0.5 M3 mol of H = 0.5 8 = 4.0 M4 no of H atoms = 4.0 6.02 1023 = 2.408 1024
retention factor formula
M1 distance travelled by substance/ distance travelled by solvent
Explain why the baseline is drawn in pencil
pencil is insoluble (in solvent)
Explain why in Fig. 6.6 only two spots are seen from the mixture of three amino acids.
same Rf value
Suggest how the experiment can be changed to separate all three amino acids.
use a different solvent
2024 m/j 43
process used to produce ammonia from nitrogen
haber’s process
process used to produce ethanol from ethene
catalytic addition
titration
determine the volume of an acid required to neutralise a given volume of an alkali.
Name the reducing agent in the extraction of iron in the blast furnace
carbon monoxide
Explain, in terms of electrons, why magnesium is used for sacrificial protection
1 magnesium loses electrons more readily than / in preference to / instead of iron M2 magnesium is more reactive than iron
2024 o/n 42
why is nitrogen dioxide toxic?
responsible for both acid rain and photochemical smog
what is converted to what in a catalytic converter
nitrogen dioxide is converted to nitrogen
carbon monoxide is converted into carbon dioxide
a major component of stainless steel. (you should know all the components)
iron
what is the colour of iron sulfate, magnesium sulfate, copper sulfate (all are aqueous)
green, colourless, blue
Name the gas formed when strontium is added to cold water.
hydrogen
Name the alkaline solution formed when strontium is added to cold water
strontium hydroxide
One Group II metal reacts very slowly when placed in cold water. When heated, the metal reacts with steam to form a white solid. Identify this metal and name the white solid formed.
metal- magnesium, white solid- magnesium oxide
Under certain conditions, iron will react with steam to form an oxide of iron with the formula Fe3O4 . Fe3O4 reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form a mixture of iron(II) and iron(III) salts and water. Deduce the symbol equation for the reaction between Fe3O4 and dilute hydrochloric acid
Fe3O4 + 8HCl → 2FeCl3 + FeCl2 + 4H2O
Calculate the volume of ammonia, NH3 , measured at room temperature and pressure, which forms when 1.12g of CaO is heated with excess NH4Cl. [Mr : CaO, 56
M1 mol CaO = 1.12 / 56 = 0.02(00) M2 mol NH3 = M1 2 = 0.02(00) 2 = 0.04(00) M3 vol NH3 = M2 24000 = 0.04 24000 = 960
State why MgS has a high melting point
ionic bonds are strong
State two essential conditions needed for photosynthesis to happen
M1 energy from light M2 presence of chlorophyll
2025 m/j 41
obtain water from aqueous sodium chloride- __________ while, obtain sodium chloride from aqueous sodium chloride- ___________
distillation, crystallisation
Explain in terms of structure and bonding why sodium fluoride has a much higher melting point than fluorine
M1 ionic bonds in NaF(1) M2 attraction between molecules or intermolecular forces in F2(1) M3 weaker attraction (between particles) in F2 ORA (1)
Suggest why the colour of the mixture of gases turns darker purple
iodine particles or molecules (forced) closer together OR same number of iodine particles or molecules in a smaller volume
State the effect that a catalyst has on the activation energy, Ea, of a reaction.
the activation energy is lower
substance that is added at the top of the blast furnace.
calcium chloride (study blast furnace if u havent already)
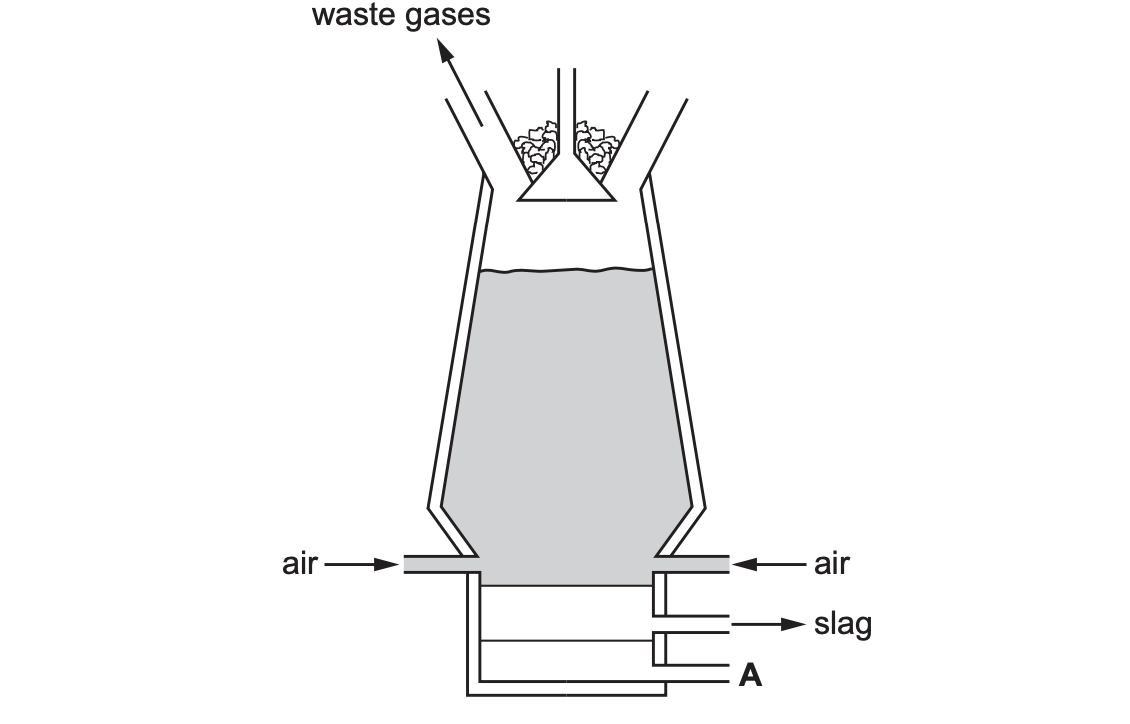
Name the substance that leaves the blast furnace at A
(molten) iron
Slag is produced from an impurity in iron ore. Name the impurity in iron ore that is converted into slag
silicon(IV) oxide OR silicon dioxide
Name two substances that react together to produce the high temperature in the blast furnace.
coke or carbon and oxygen
Name two waste gases that leave the blast furnace.
nitrogen carbon dioxide argon
Suggest why the zinc produced inside the furnace is a gas.
the temperature in the furnace is above or higher than the boiling point of zinc ORA OR the boiling point of zinc is below or less than the temperature of the furnace ORA
Name the process used to coat iron with zinc as a method of rust prevention.
galvanising
State the general name given to oxides that neutralise both acids and bases
amphoteric
24 f/m 42
State the purpose of the combustion of carbon in the blast furnace-
to provide heat