Signal Transduction Pathway
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Signal Transduction Pathway
process by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted into a specific cellular response in a series of steps
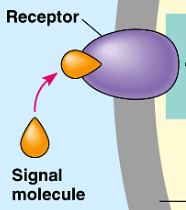
Reception
first step of cell signaling
detection of signal molecule coming from outside cell
Transduction
second step of cell signaling
convert signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response

Response
third step of cell signaling
specific cellular response to signal molecule

ligand
signal molecule
amplify
signal transduction pathways have the power to ? the binding of a single ligand into MANY responses
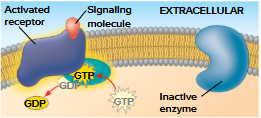
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
Cell-surface transmembrane receptors that work with G proteins
G proteins bind energy-rich GTP (similar to ATP)
all G proteins are similar in structure
GPCR systems are extremely widespread and diverse in function
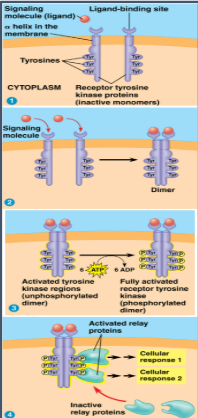
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase
Membrane receptors that transfer phosphate groups from ATP to another protein
can trigger multiple signal transduction pathways at once
abnormal RTK function is associated with cancer
Ligand-Gated Ion Channel
gate that opens and closes when the receptor changes shape
when a signal molecule binds as a ligand, gate allows specific ions (e.g. Na+ or Ca2+) through channel in receptor
cyclic adenosine monophosphate
secondary messenger that comes from ATP