The reproductive system
1/79
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Anat & physiology 12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Testis (singular testis)
Paired organs that are developed from the gonads within the abdomen of fetus
Scrotal sacs
During last 2 months of fetal development, where testis descend through a canal into here. It is a patch of skin located below the pelvic region
Scrotum
Maintains testes at cooler temperature than the abdominal cavity. Necessary for producing viable sperm.
Seminiferous tubules
Coiled tubules packed into lobes of the testes that produces sperm
Sertoli cells
Inside seminiferous tubules that nourish the developing sperm cells
Interstitial cells
AKA Leydig cells. surround the seminiferous tubes and produces testoterone
Spermatogenesis
Takes about 9 to 10 weeks, process by which germ cells develop into sperm cells in the seminiferous tubules.
Lubules
Sections in testes that has one to three seminiferous tubules with total length of 250 meters.
Epydidymides
Where mature sperm are stored in this 8m long coiled tube behind each testes.
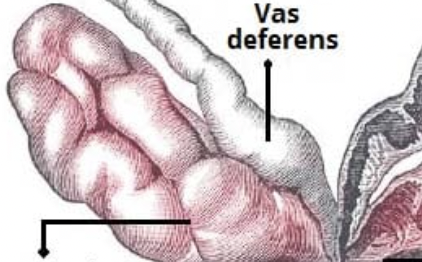
Vas deferens
Where sperm is propelled into by muscle contraction and into the ejaculatory duct. These paired tubes function to move sperm away from its storage place in the testicle to the urethra where it leaves the body during ejaculation.
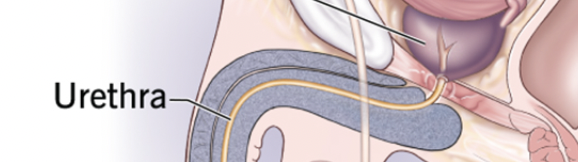
Urethra
The duct by which urine is conveyed out of the body from the bladder, and which in male vertebrates also conveys semen.
Acrosome cap
On the tip of the head of the sperm. Contains enzymes needed to penetrate the outside barriers of the egg.
Middle piece
The middle of the sperm. Has numerous mitochondria to aid with sperm movement. Have microtubules of cilia and flagella.
Tail
The end of the sperm. Have microtubules of cilia and flagella.
Penis
A cylindrical organ that hangs in front of the scrotum.
Spongy tissue
Inside the shaft of the penis that is flaccid with normal blood flow and erection with increased blood flow
Impotency
Failure to become erect
Semen
A thick, whitish fluid containing sperm and secretions from three organs, seminal vesicals, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands
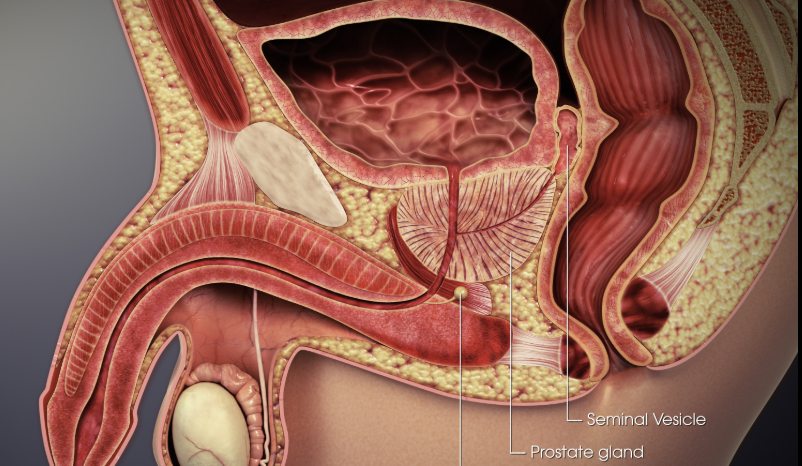
Seminal vesicals
Secretes vesicles that contains fructose for the sperm, as well as prostaglandis that causes reverse pristalsis of the uterus and the fallopian tubes, fluid then joins with sperm fromthe ejaculatory duct
Prostate gland
Surrounds urethra below bladder; secretes milky alkaline fluid that aid sperm mobility and survival (helps with the acidic nature of the vagina)
Bulbourethral glands
Often called Cowper’s Glands, have mucous secretions with lubricating effect.
Hormones
Control the negative feedback loop of the male reproductive system. Four hormones involved, GnRH, FSH, LH (aka ICSH), and Inhibin
Gonadotropic-releasing hormone (gnRH)
When hypothalamus control the testes it releases this hormone, which triggers anterior pituitary to produce FSH and ICSH
Follical-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Released by the anterior pituitary. Promotes spermatogenesis in seminiferous tubules. Enters Sertoli cells to take up more testoterone and make more sperm.
Sertoli cells
Specialized cells found in the seminiferous tubules of the testes, crucial for male reproductive function
Inhibin
A hormone produced in the gonads (testes in males, ovaries in females) that plays a crucial role in regulating follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) secretion from the pituitary gland. More is created gradually. Hypothalamus and anterior pituitary will reduce release of GnRH and FSH, causing a negative feedback cycle.
Interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH, luteinizing hormone in females)
Controls production of testoterone by interstitial cells. Causes increase in testoterone level in blood, which stop production of GnRH, negative feedback cycle.
Testoterone
Hormone that promotes normal development and function of primary sexual organs of male. Causes secondary sexual characteristics. Increases oil and sweat glands, side effect for baldness.
Anabolic steroids
Used by athletes to promote testorone levels. Make breast bigger for male, acne, balding, high blood cholesterol, liver disease, stunts growth.
Ovum
Female gamete
Ovaries
Two olive shaped organs on each side of the uterus in the pelvic abdominal cavity. Produce eggs (ova) and sex hormones estrogen & progesterone. Held in place by ligaments.
Ovulation
When ovury produces an egg (oocyte) and it bursts out
Follicles
tiny sacs inside ovaries that contain the oocyte and follicle cells to help it mature
1^o follicle
The first stage of follicle containing 1^o oocyte. Produce estrogen.
2^o follicle
Where theres fluid-filled space and there is now a 2^o oocyte. Produce estrogen and progesterone.
Graafian follicle
Mature follicle. Bursts and release ovum that was inside.
Corpus Luteum
Remains of graafian follicle after oocyte is released. Produces female sex hormones.
Fallopian tubes (Oviducts)
Tubes to the uterus, extends near ovaries into uterus. Sweeps up egg from ovary using cilia lining and wafting fimbria at end of the fallopian tubes. Fertilization occurs in the upper part of this.

Cilia
Beating ____ and muscular peristalsis propels egg to uterus
Fimbrae
Finger like projections at end of oviducts that pick up egg
Uterus
A thick-walled muscular, hollow, pear-shaped organ for nurturing embryo. Opening in cervix lead to vagina.
Endometrium
The lining of the uterus. It’s composed of connective tissue, glands, and blood vessels. Forms the placenta if pregnancy occurs.
Myometrium
The muscular middle layer of the uterus, composed primarily of smooth muscle cells beneath the endometrium that contracts during labor.
Hysterectomy
The surgical removal of the uterus
Cervix
Located at the end of the vaginal canal, contains opening to uterus
Vagina
A muscular tube with mucosa lining, makes 45 degrees with small of back. Serves in intercourse and birth canal during childbirth.
Vulva
The external genitals, Mons pubis is fatty prominence under pubic hair.
Labia
There are two sets of skin folds. Outermost is called labia majora, and it enclose labia minora. Extends from vaginal opening to encircle clitoris at front.
Clitoris
An erectile organ, partly enclosed by the labia minora, sensitive to stimulation
Hymen
A ring of tissue that may partially close the vaginal opening.
Follicular phase
Before ovulation, when a follicle is developing in an ovary. Menstration occurs and there’s a rebuilding of the uterine lining. Increase level of hormones, estrogen predominates. LH surge for ovulation on day 14.
Luteal phase
After ovulation, when a follicle release an egg and is called a corpus luteum
The ovarian cycle
Divided into follicular phase and luteal phase
Menstruation
Day 1 to 5 of the follicular phase, when low levels of female hormones (estrogen, progesterone, FSH, LH, GnRH) promotes this. Part of lining of uterus and blood is lost, endometrium is thin.
GnRH
Released and sent to the anterior pituitary gland when low levels of female hormone sis detected by the hypothalamus. Causes release of FSH and LH.
FSH
Stimulates follicle development in the ovary and let it mature, which releases estrogen, which causes more GnRH. Positive feedback loop. Days 7 to 13. Large amount causes negative feedback loop and less GnRH.
LH
Large amount is released when a large amount of estrogen triggers the GnRH from the pituitary on day 13, causing ovulation on day 14. This releases the egg.
Proliferative phase
A stage in the menstrual cycle where the uterine lining (endometrium) thickens and prepares for a potential pregnancy during days 6 - 13 from rising levels of estrogen. Proliferation in the amount of blood vessels and mucus glands.
Progesterone
Dominates the luteal phase, released by the corpus luteum. Makes endometrium double in thickness and secretes mucus. At a high level, negative feedback as anterior pituitary glands release less LH at day 24 or 25.
Secretory phase
During luteal phase, where there’s mucus on the uterus lining.
Less LH effect
The corpus luteum will degenerate due to this. Less and less progesterone and estrogen are made.
Low level of progesterone
When corpus luteum degenerate, causes the endometrium to disintegrate by day 28.
Zygote
When acrosome release enzymes to break through outer layer of the egg, sperm and egg nucleus fuse and conception is made.
Implantation
When embryo embeds in Endometrial lining several days after fertilization
Placenta
Forms from maternal and fetal tissue to exchange molecules between fetal and maternal blood. Produces Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (HCG), which temporarily maintains the corpus luteum. Eventually makes own progesterone and estrogen,
Progesterone and estragen from placenta
Shut down the release of FSH and LH so no new follicles mature and maintain tining of uterus so corpus luteum isn’t needed
Labor
Contractions lasting over 40 seconds every 15 - 20 minutes
Cesarean section
When babie’s head is not pointed towards the cervix
Oxytocin
Made in the hypothalamus, stored in the posterior pituitary, cause uterus to contract. Detected when baby’s head hit the cervix. Stimulates the release of milk. Positive feedback as baby hit cervix more.
Childbirth
Called parturition. Include labour and expulsion of fetus. Occurs in three stages.
Stage 1 of childbirth
Cervix dilates; mucus plug from cervical canal is expelled; amniotic membrane ruptures to release amniotic fluid (i.e. "water" breaks); stage ends when cervix is fully dilated.
Stage 2 of childbirth
Baby emerges from uterine contractions that occur every 1 - 2 minutes, lasting one minute each; if vagina cannot expand enough, an episiotomy is performed and baby is born. Umbilical cord is cut, shriveling and leaving scar that becomes navel.
Stage 3 of childbirth
Placenta (afterbirth) is expelled from uterus about 15 minutes after delivery of baby.
Estrogen at puberty
Stimulate growth of uterus and vagina. Growth of body, underarm, and pubic hair. Stimulate fat deposit. Wider pelvic development, and breast development.
Breasts
Produces milk. Contain one to two dozen lubules. Each with mammatory ducts that end in sacs of alveoli.
Areola
Pigmented area of nipple. lacks hair and sweat glands but has saliva-resistant lubricant.
Prolactin
Hormone stimulates alveoli to produce milk; feedback inhibition suppresses milk production during pregnancy.
Colostrum
During couple of days after childbirth and before milk production is underway, a watery, yellowish- white fluid is secreted; contains more protein, less fat.
Menopause
The ovaries don’t respond. No longer respond to FSH and LH, stop producing estragen and progesterone. Menstration irregular. "hot flashes" from irregular circulation, dizziness, headaches, depression, either insomnia or sleepiness...or no symptoms at all.
Androgens
Produced by the adrenal cortex that may increase sex drive after menopause