FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ANATOMY
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
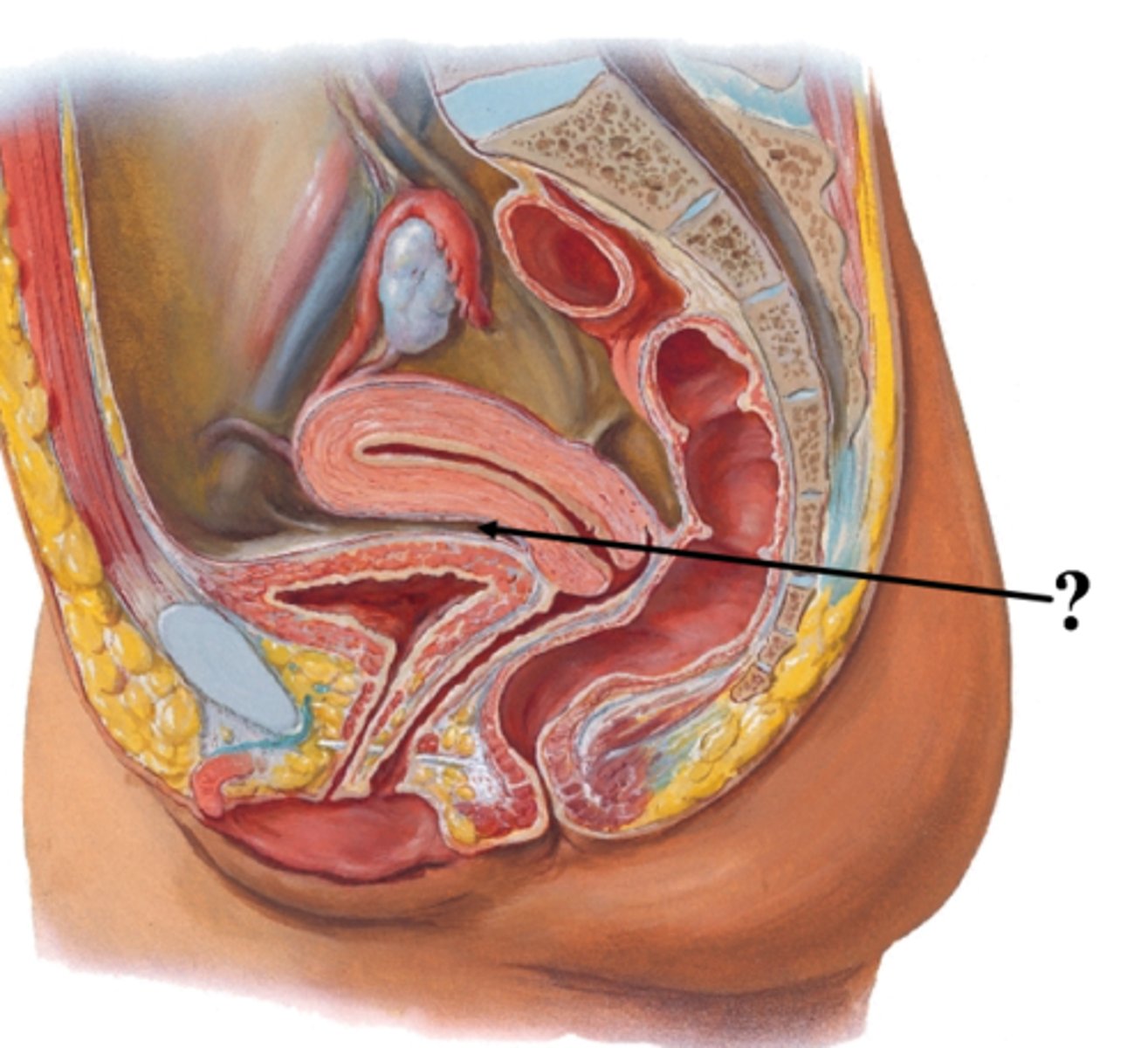
What is the vesicouterine pouch form?
lower party of pelvic cavity, in front of uterus
Urinary bladder picture
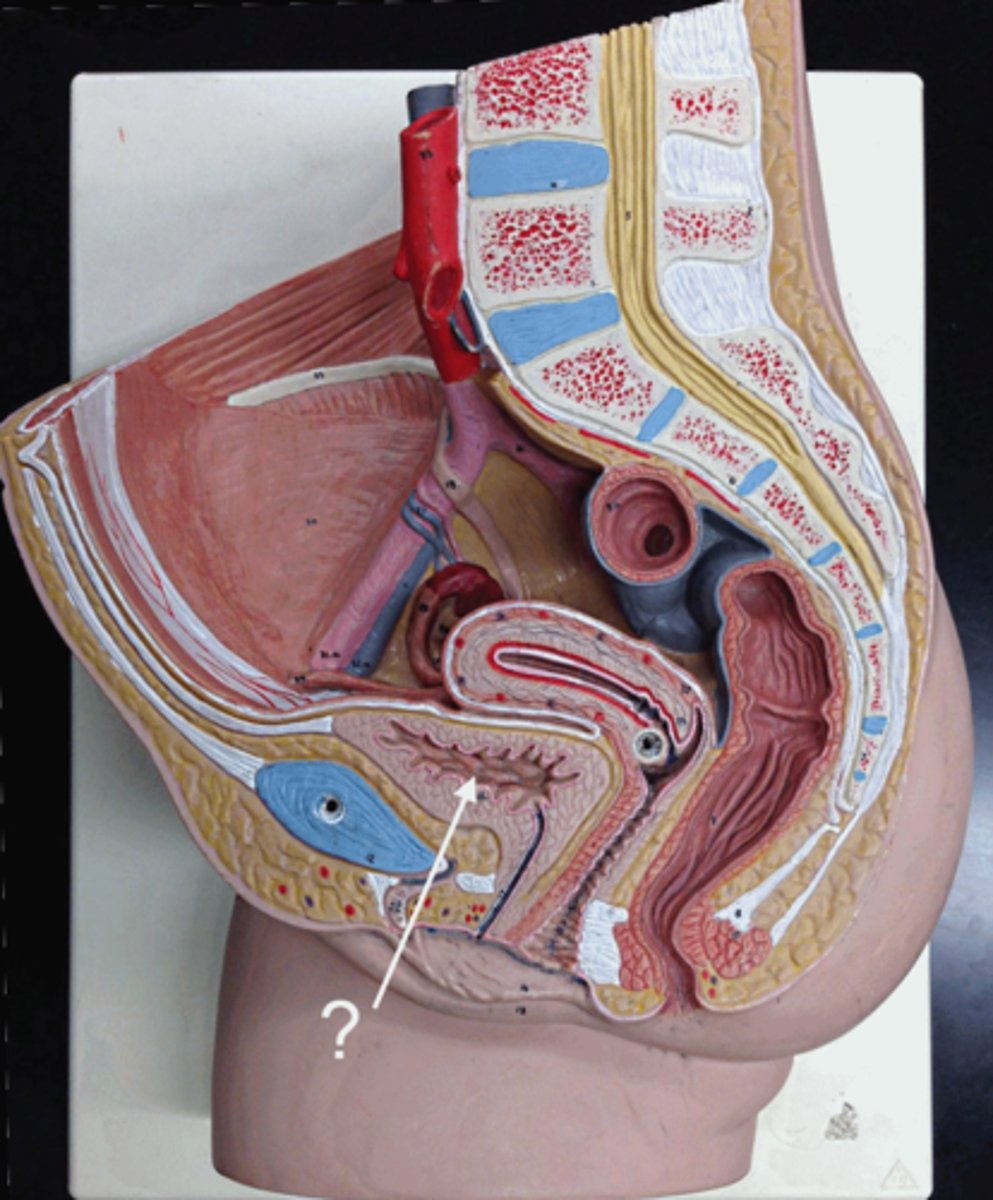
What is the pubic symphysis?
cartilage that bones are attached to in the front
What is the clitoris?
erectile tissue, with blood vessels that help it become erect
-made out of areolar CT
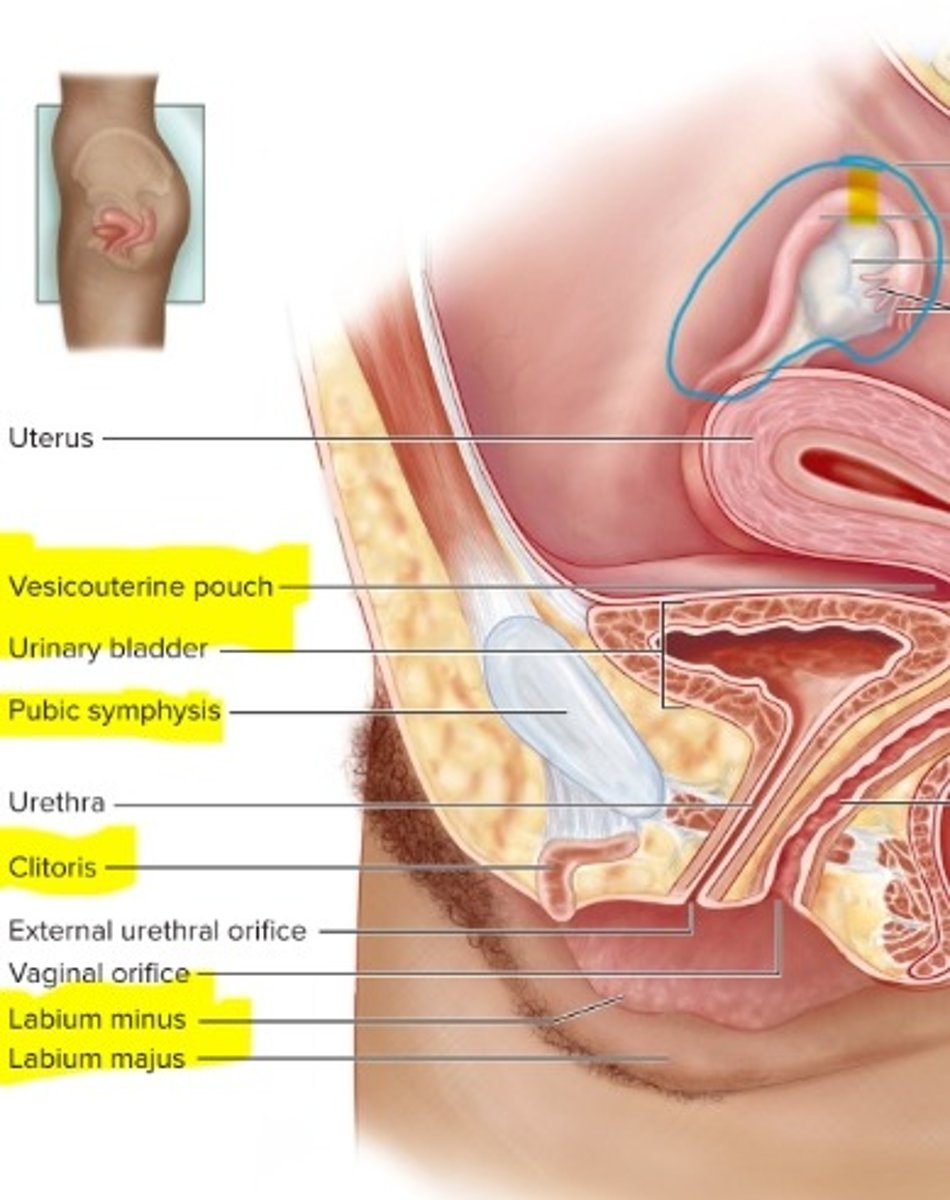
What is the labium minus?
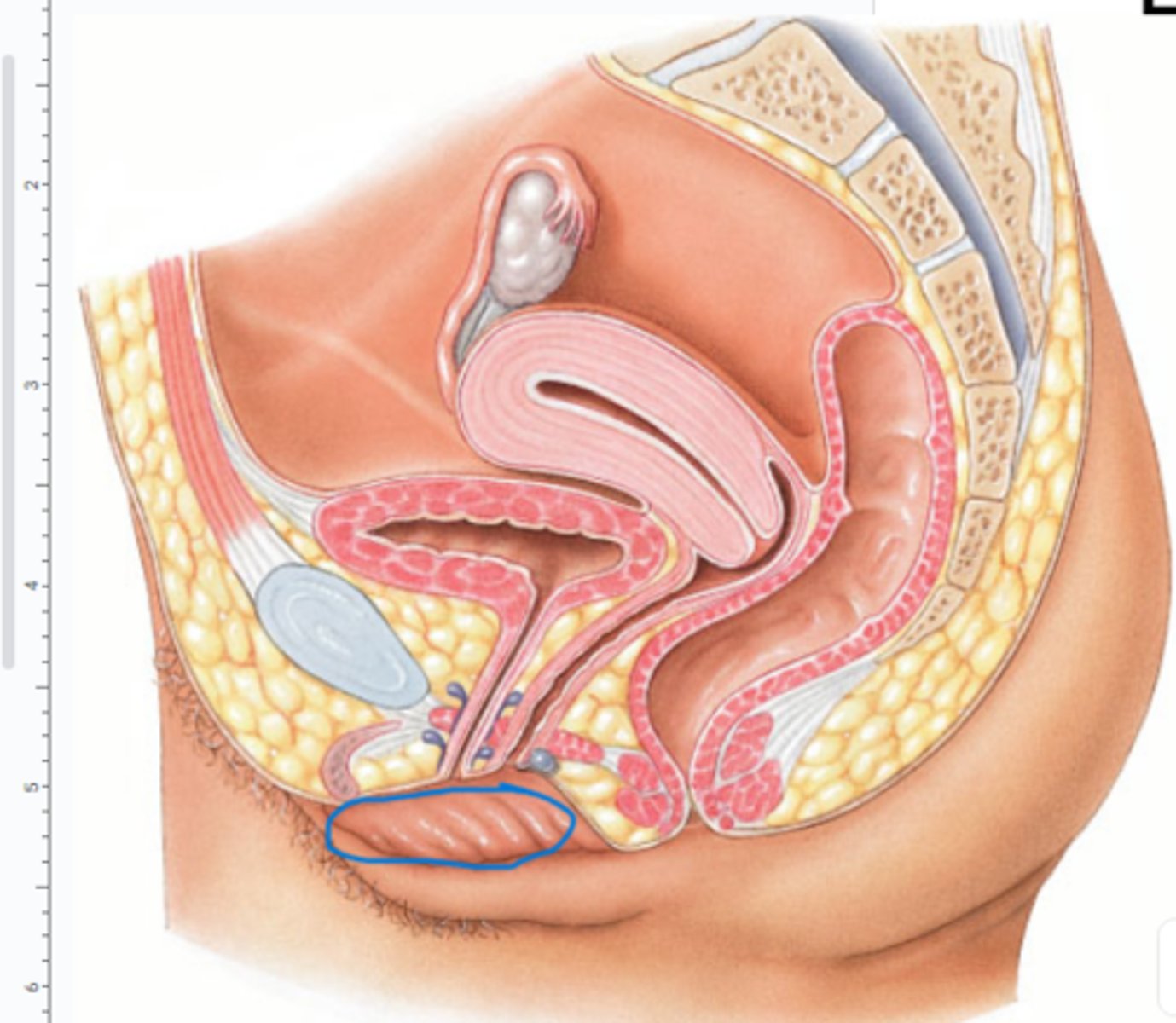
What is the labium majus?
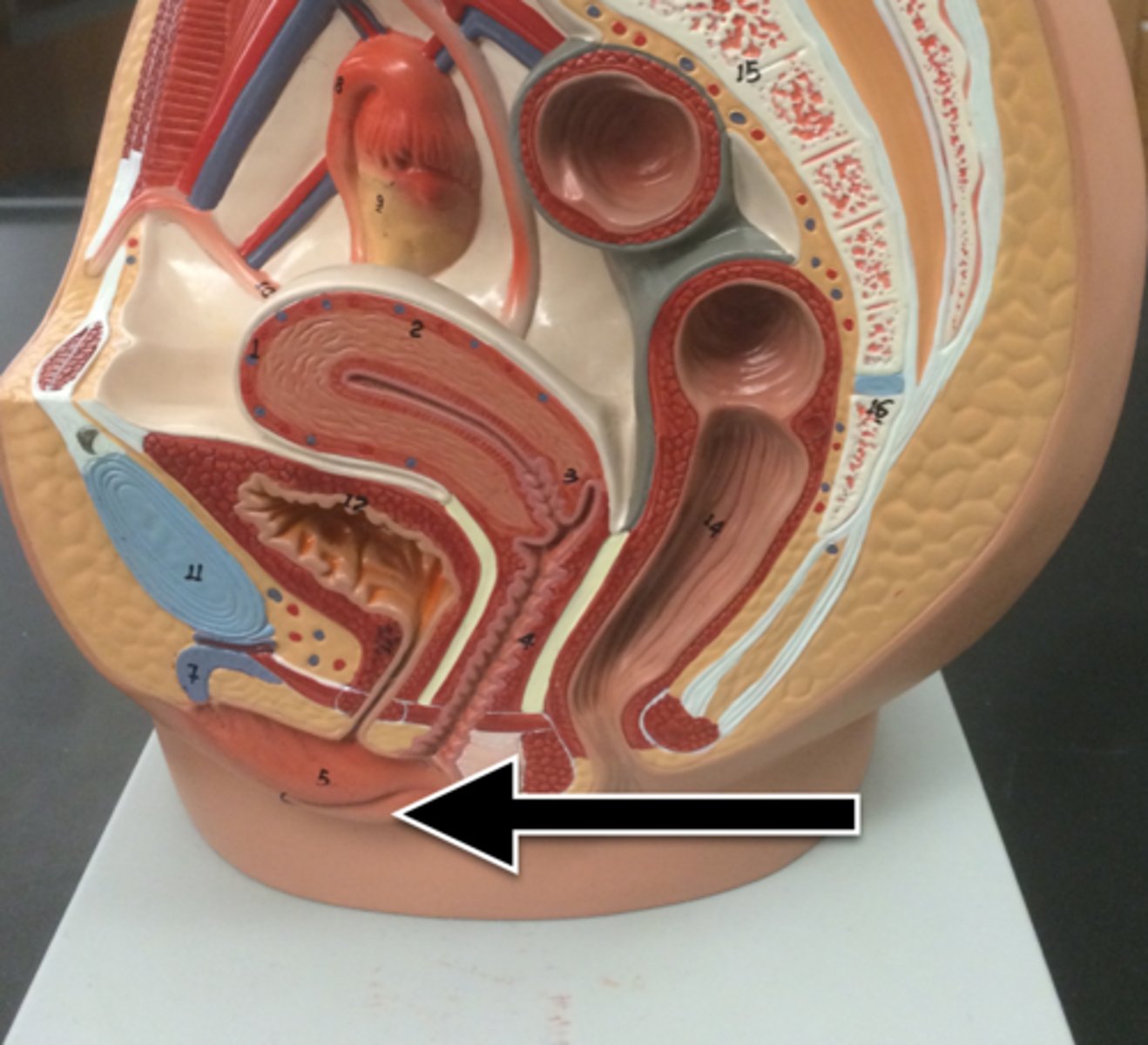
Rectouterine pouch
pouch between rectum and uterus
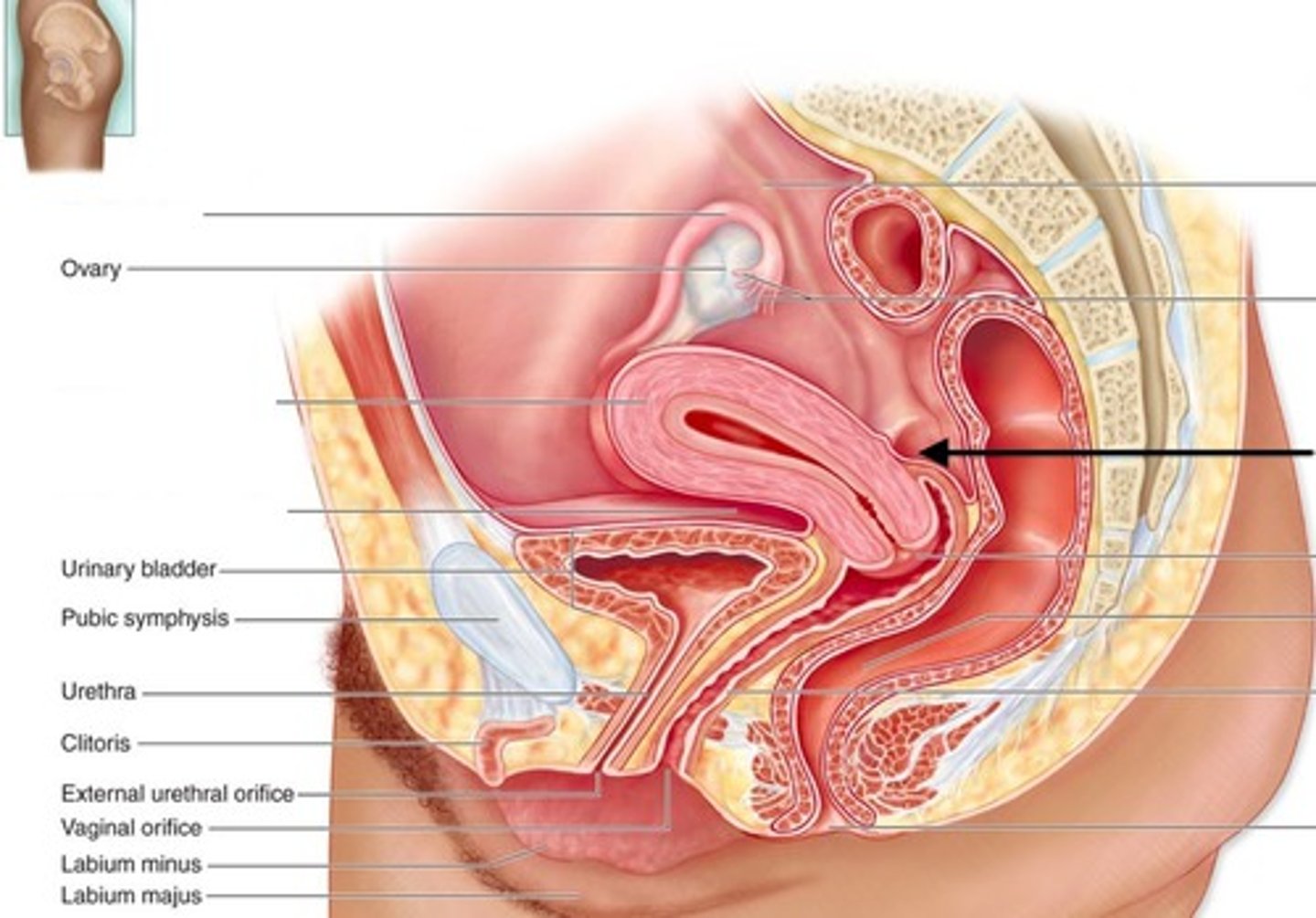
Fimbriae of uterine tube
finger like projections of the uterine tube that cover ovary during ovulation

Ovarian ligament anchors what?
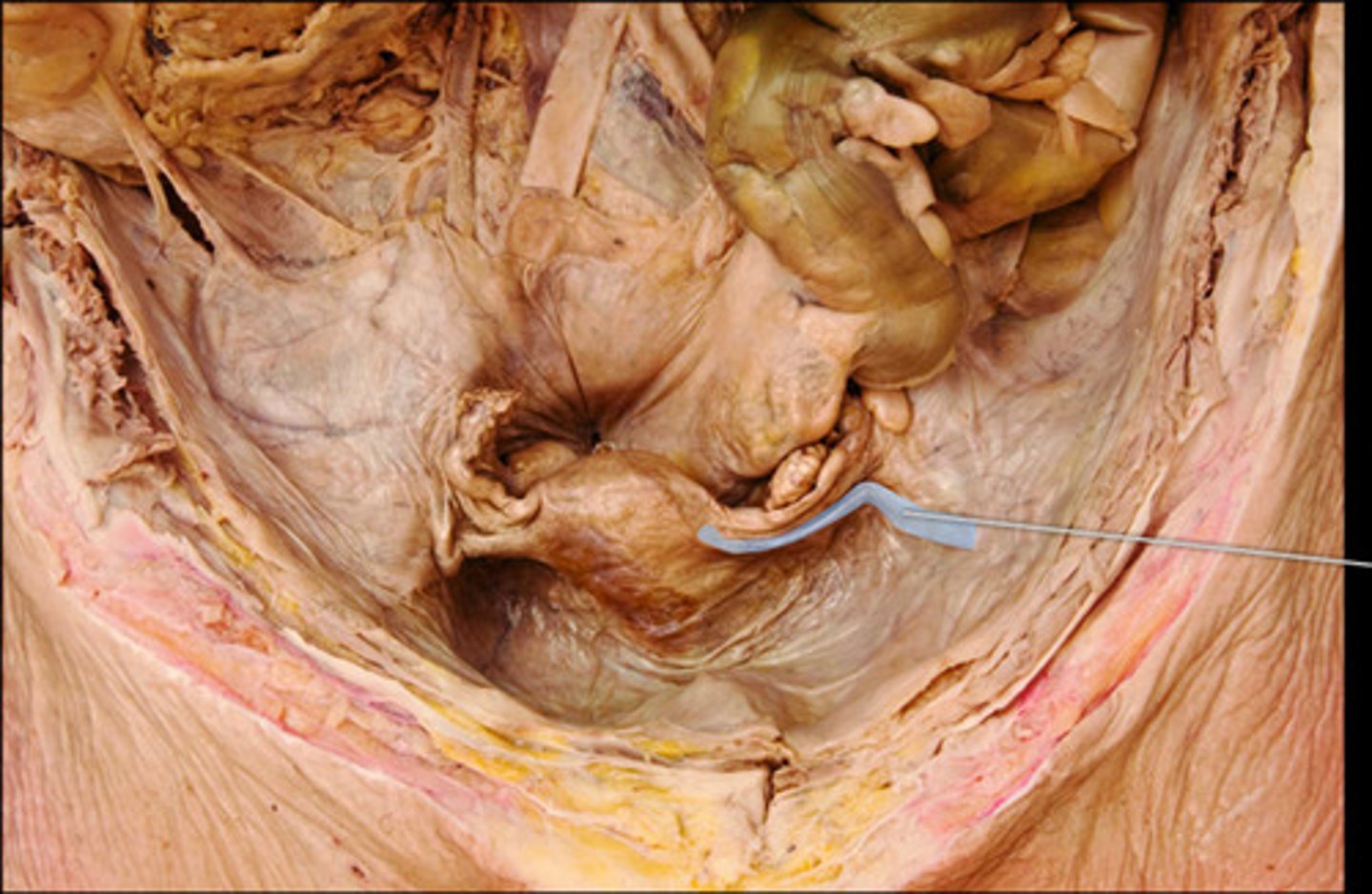
Suspensory liagment
anchors fallopian tubes laterally
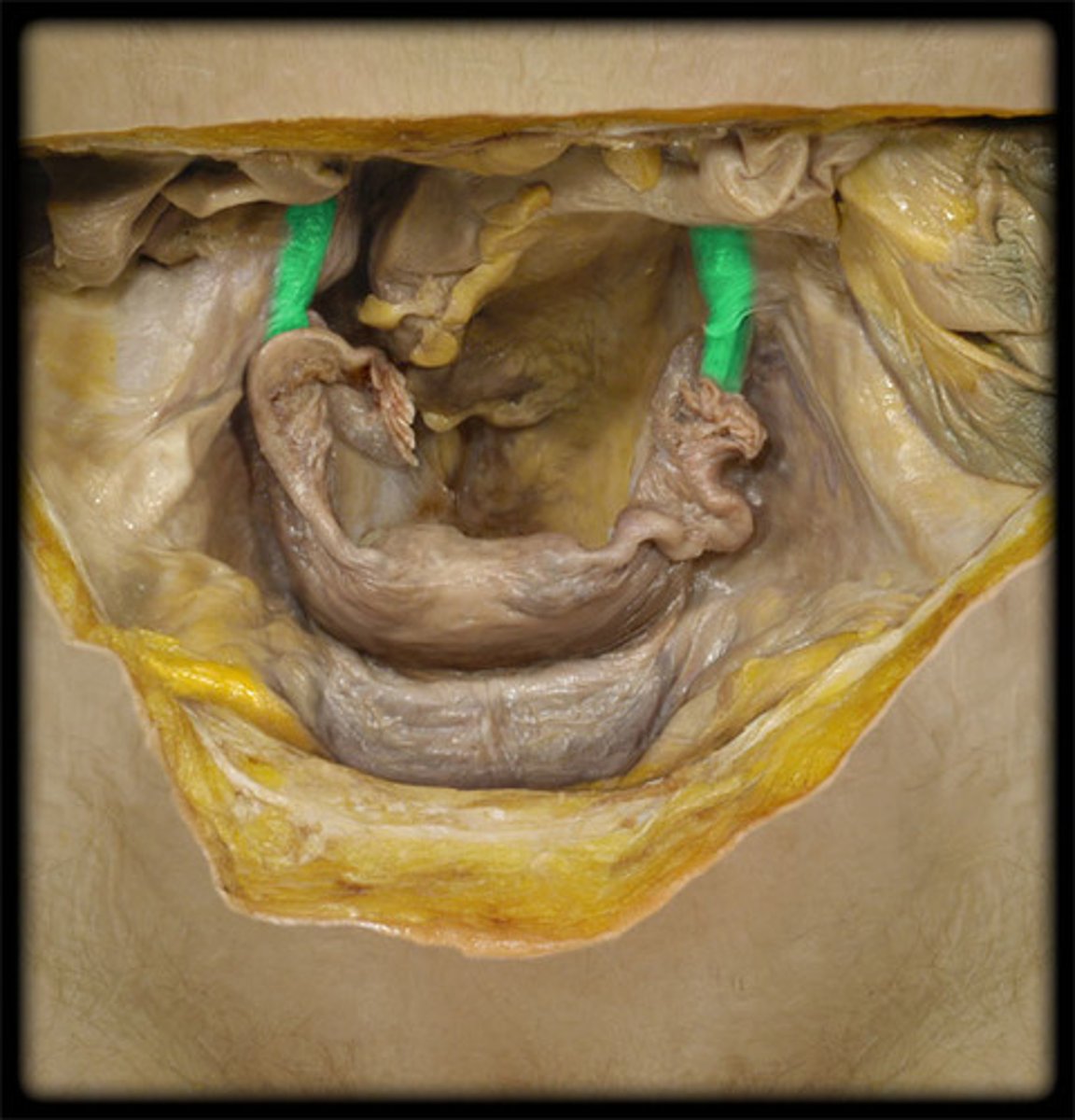
What does a round ligament look like ?
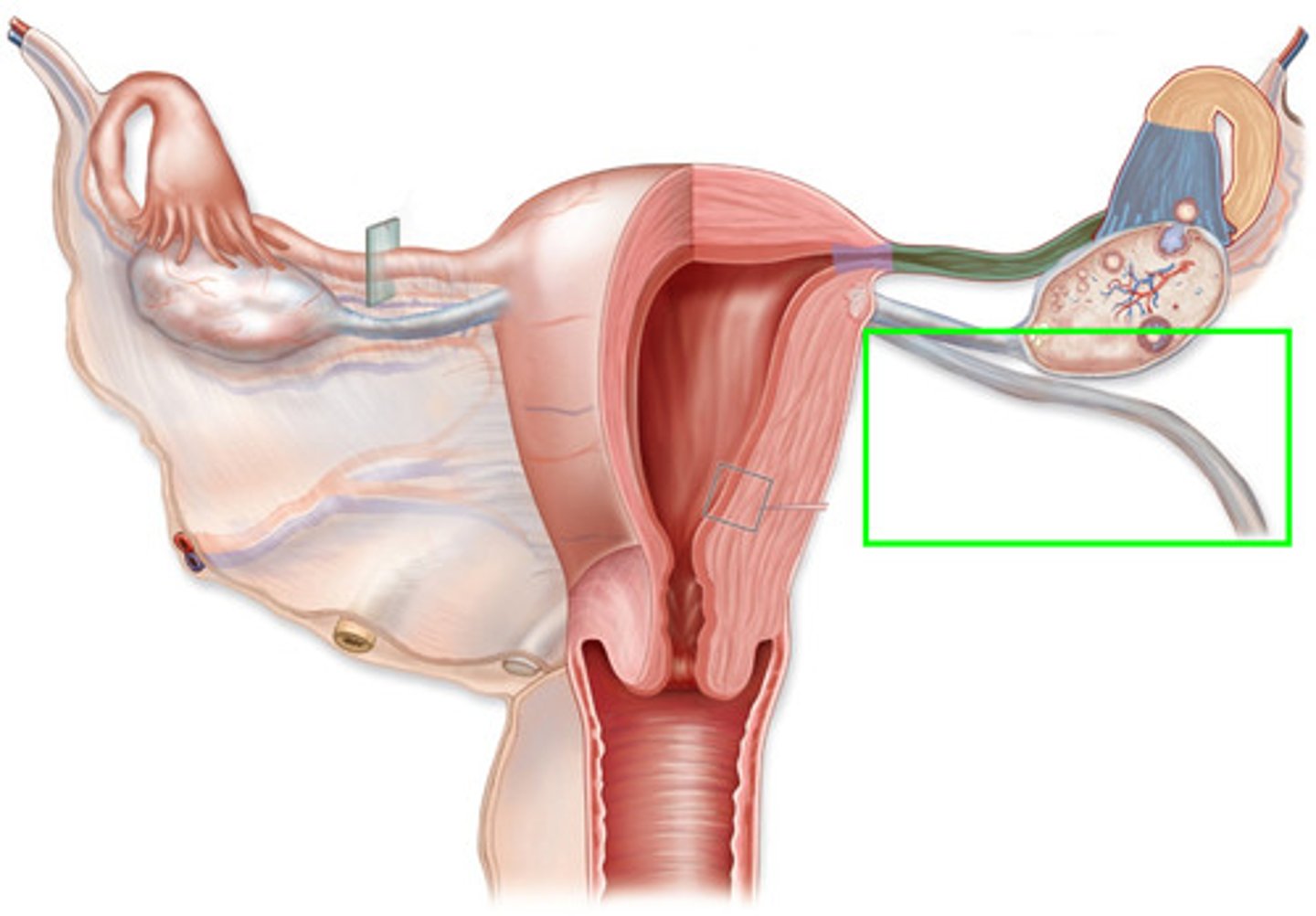
What does a broad ligament look like?
wings or sheets of tissue
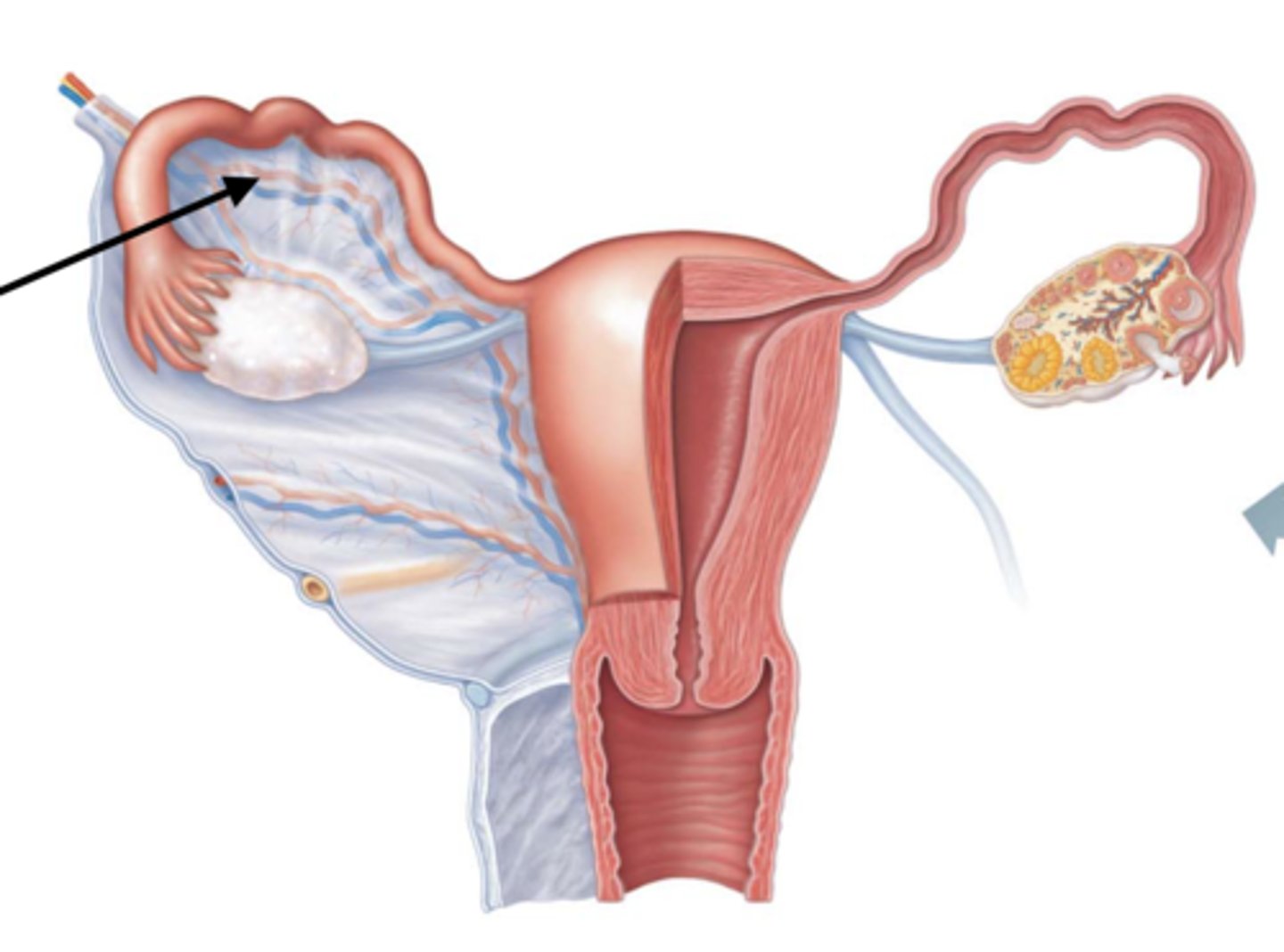
What is a uterosacral ligament?
inferior anchorage between bottom part of uterus and sacral bone
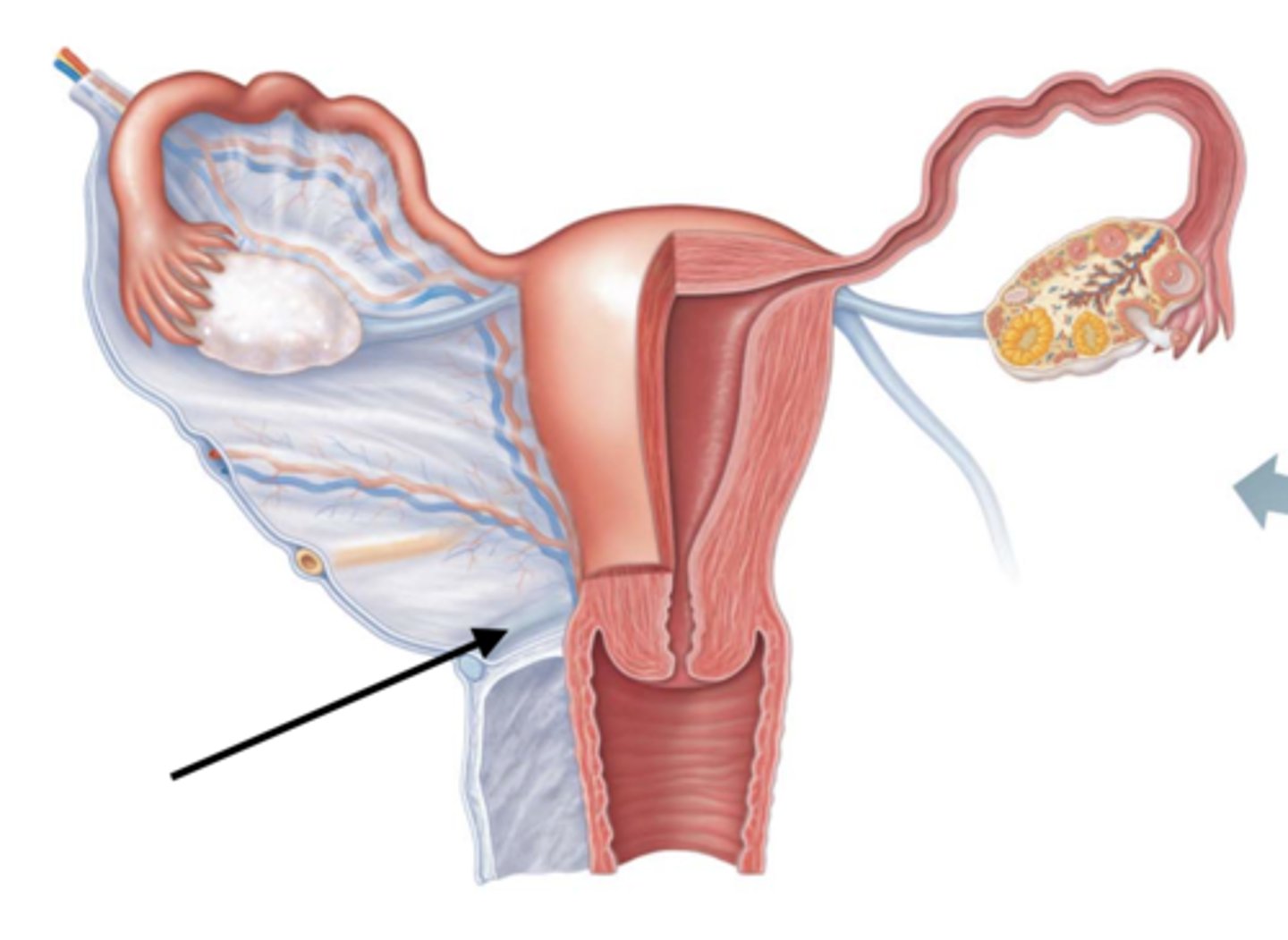
What are fimbriae?
distal end of fallopian tube
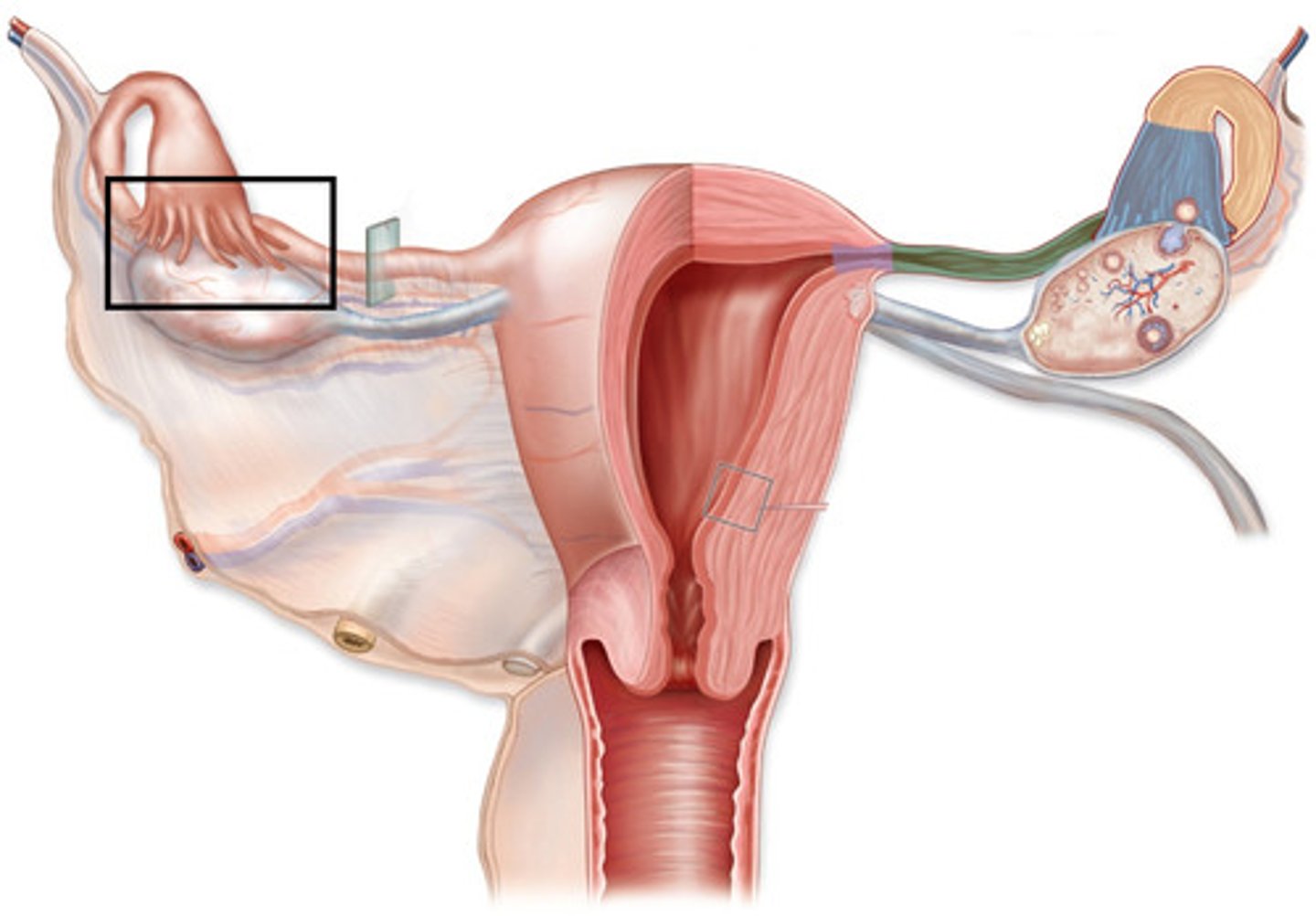
What are ovaries?
small shrivels of scar tissues from reproductive years
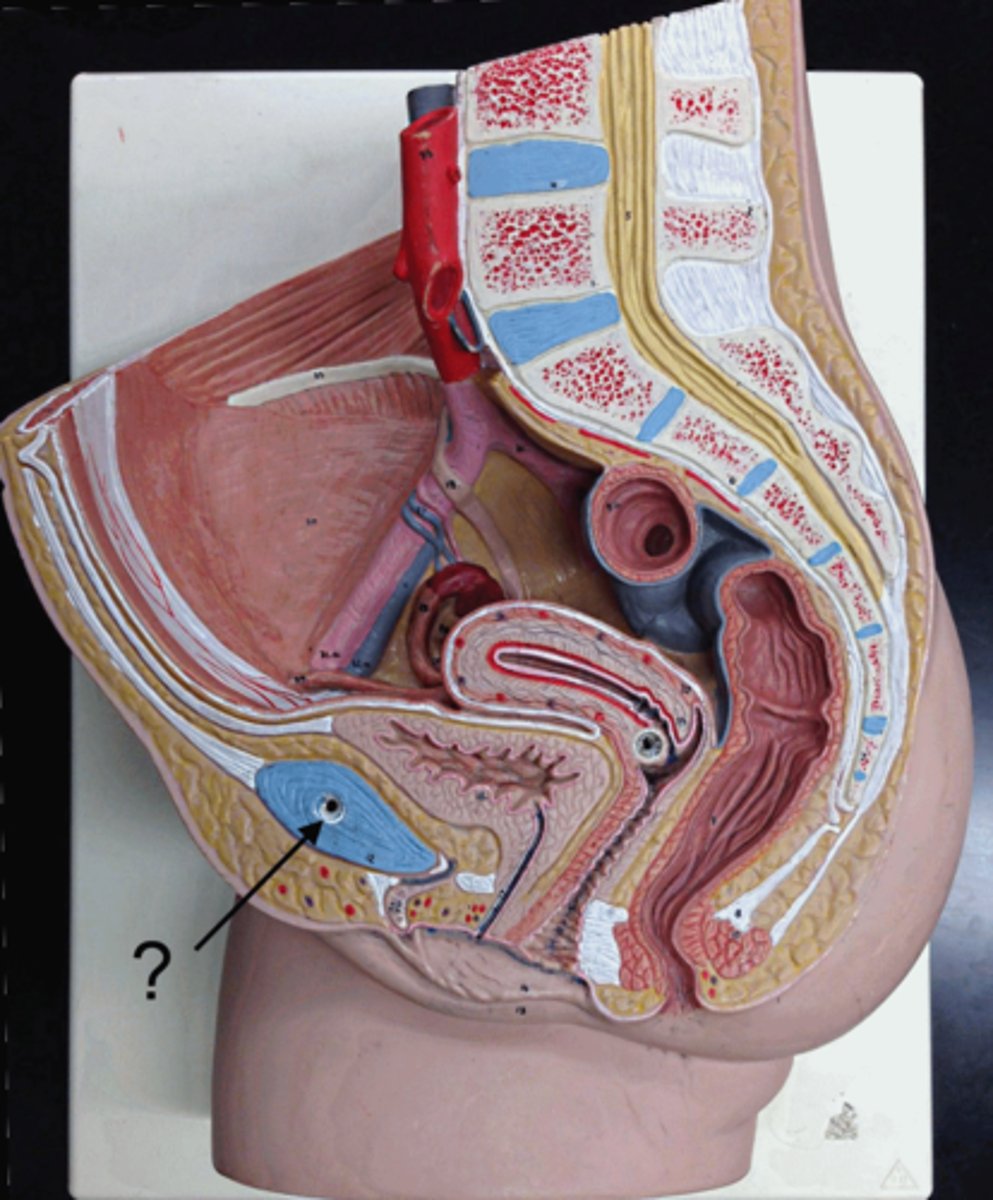
Picture of the urinary bladder
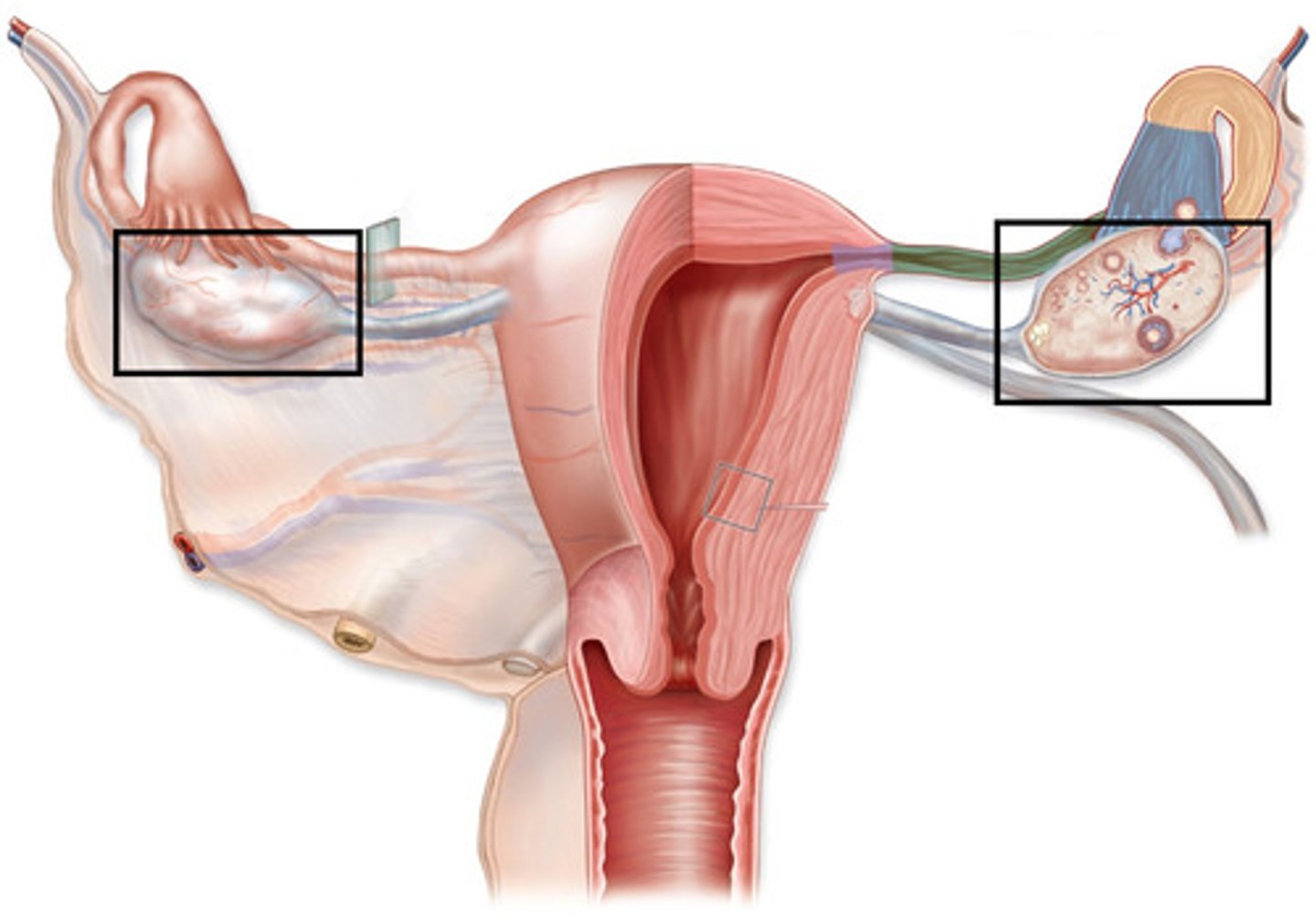
What is a postmenopausal ovary?
scar tissue that forms from ovulation
How many layers does the broad ligament contain?
4 tissues layers, 2 in back and 2 in the front
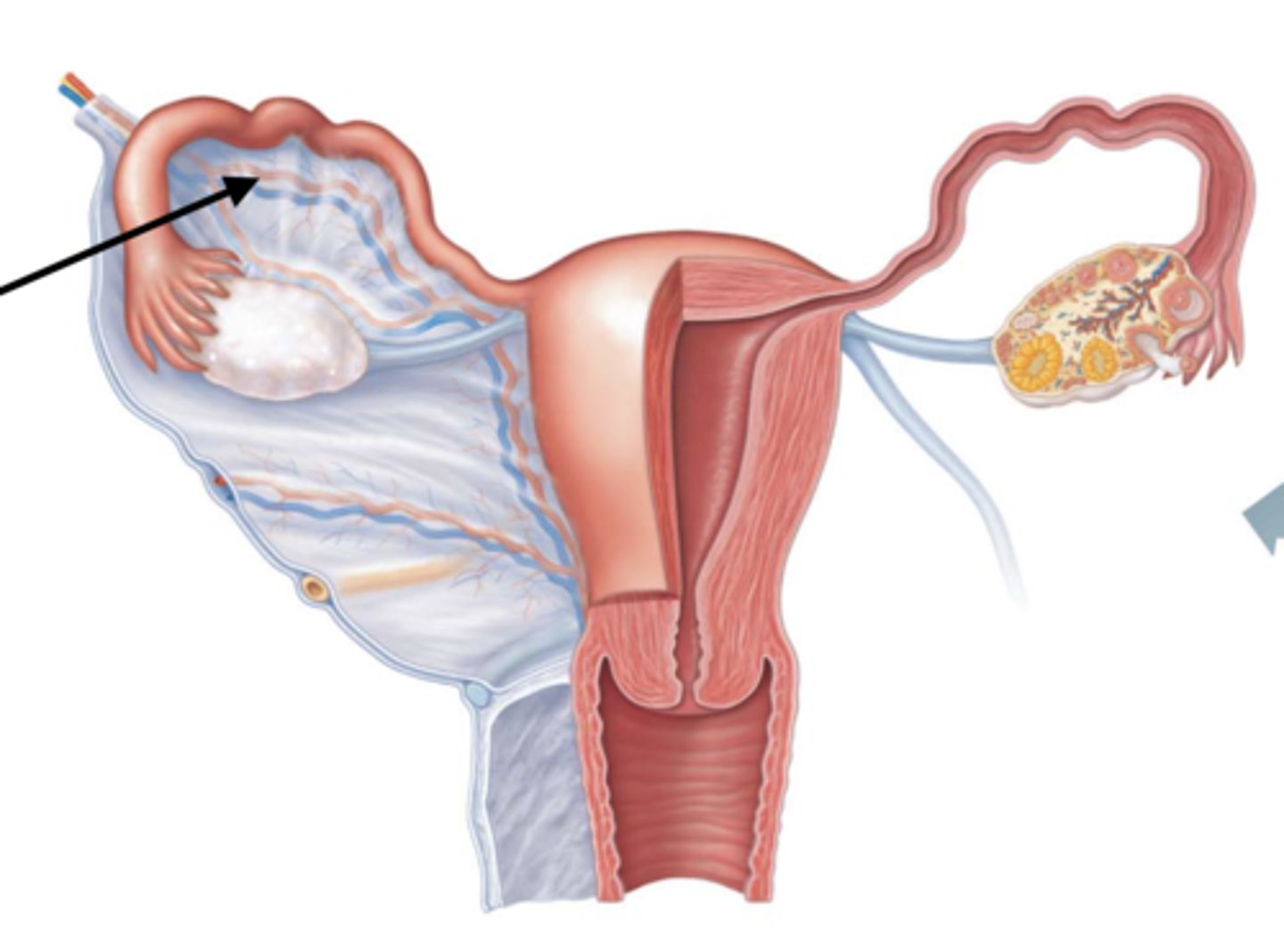
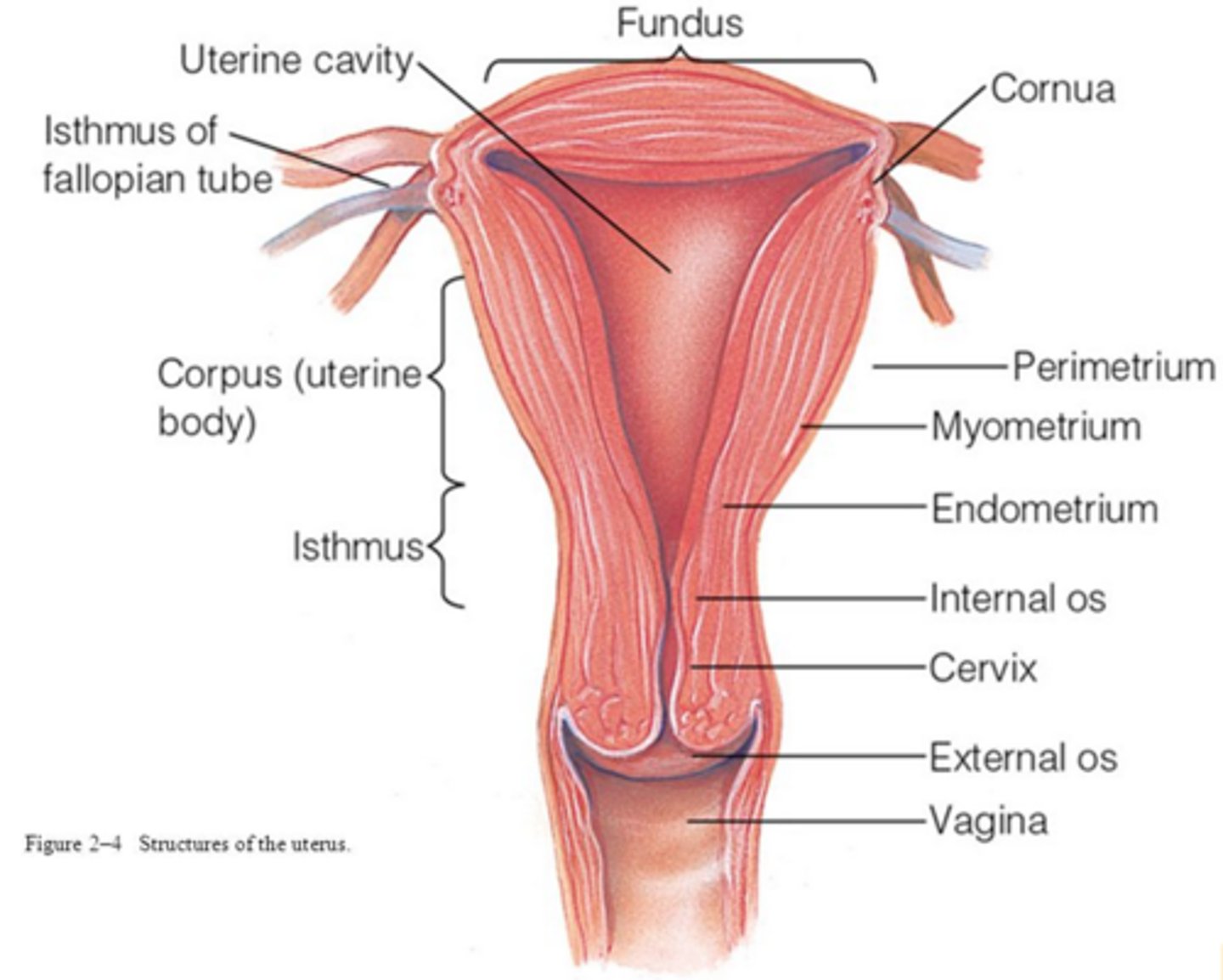
What makes up the cervix?
internal os, cervical canal, external os
What are the walls of the uterus?
endometrium, myometrium, perimetrium
The ureter has what?
a big lumen
Internal os is what?
beginning of the cervix
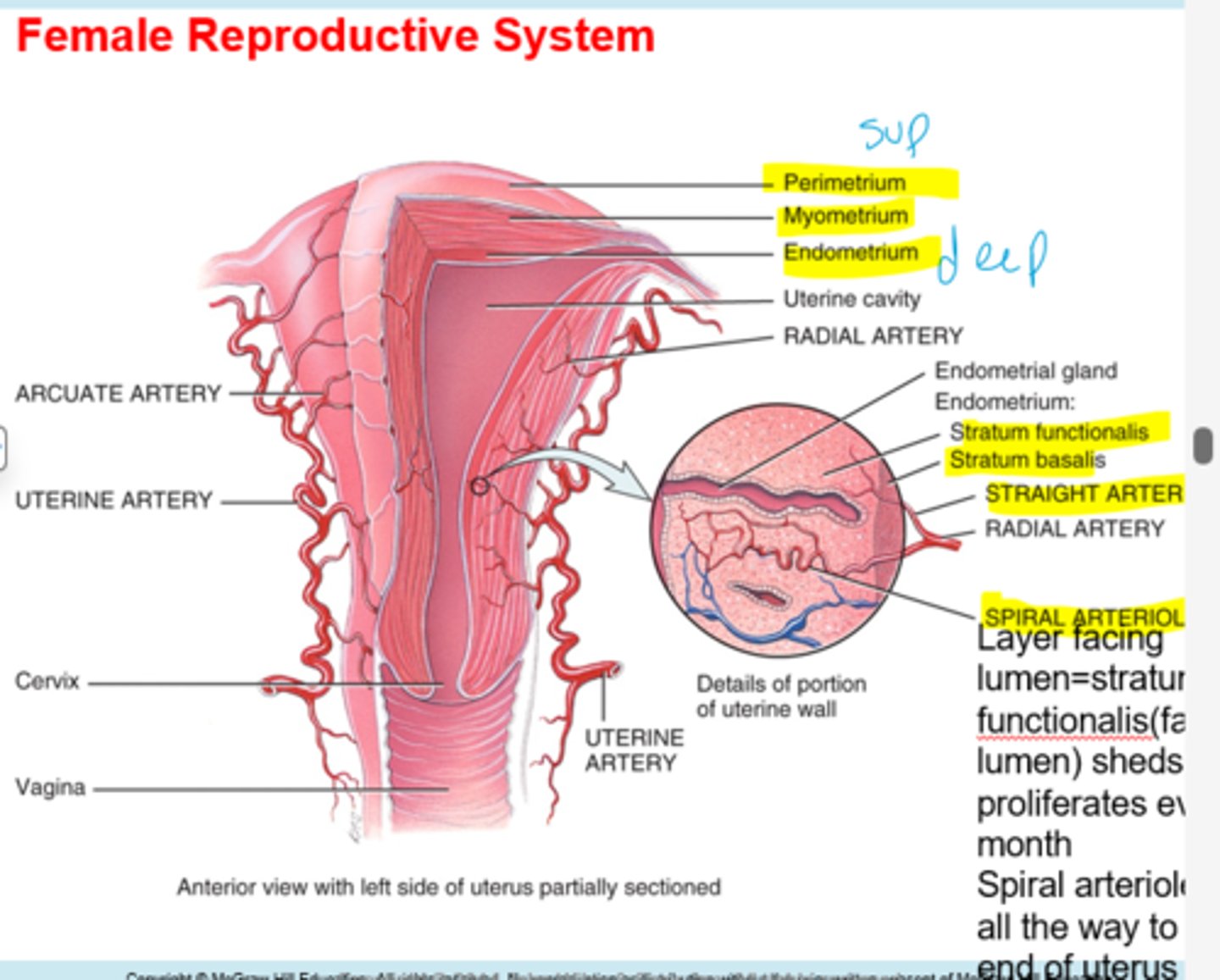
External os is what?
end of the cervix
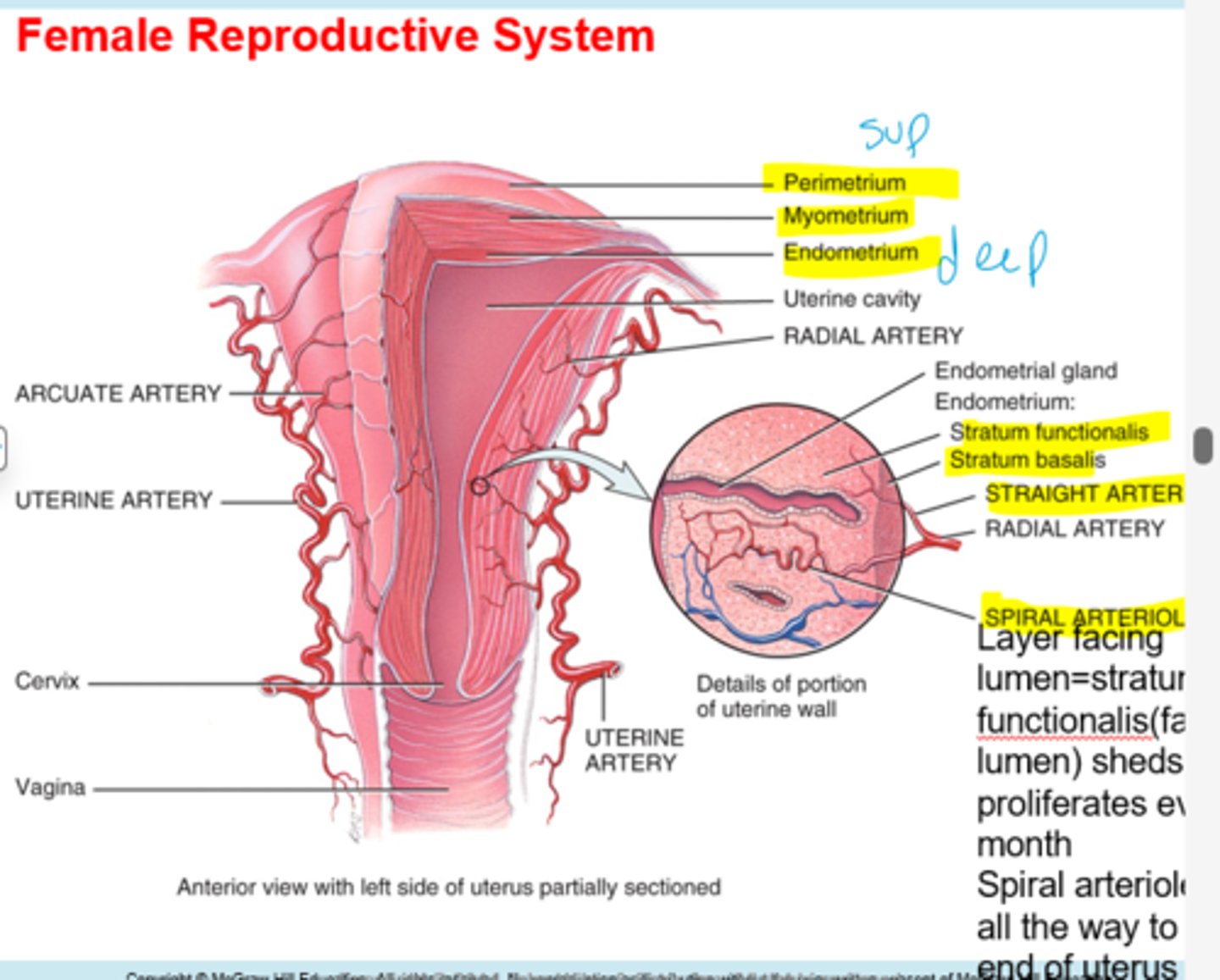
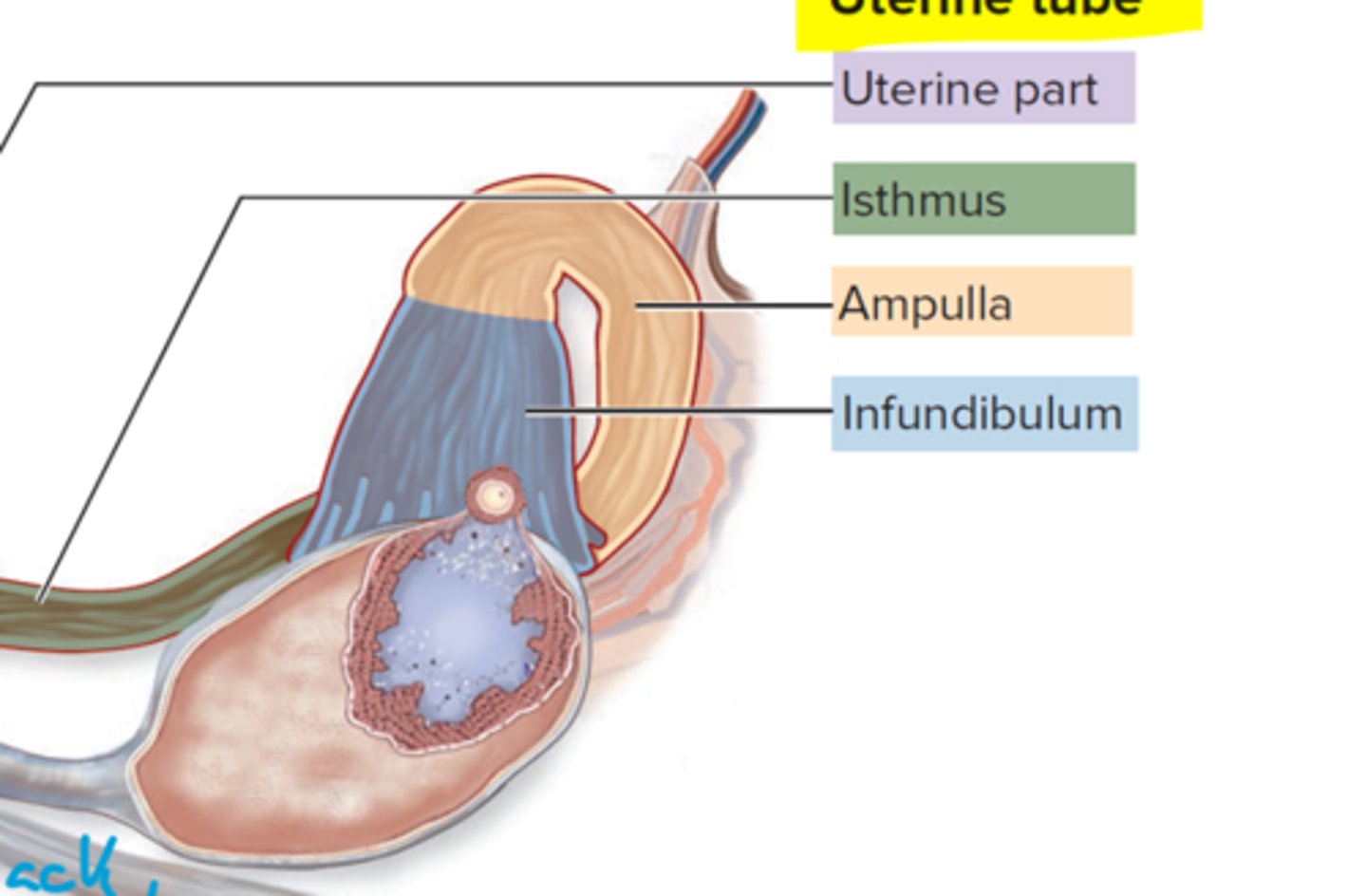
What is the uterine part?
junction between uterus and isthmus
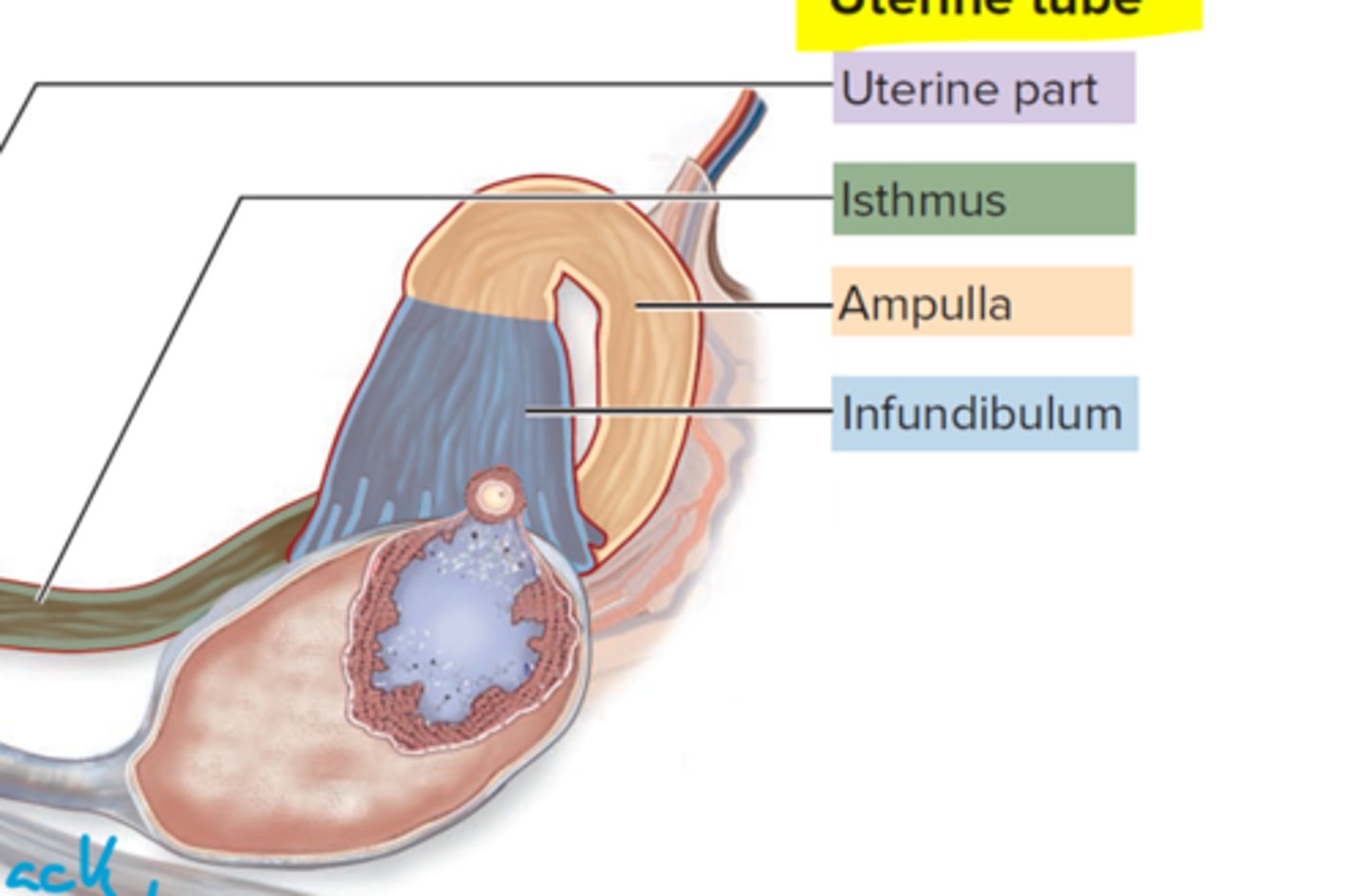
What does the isthmus do?
connects uterine part to distal
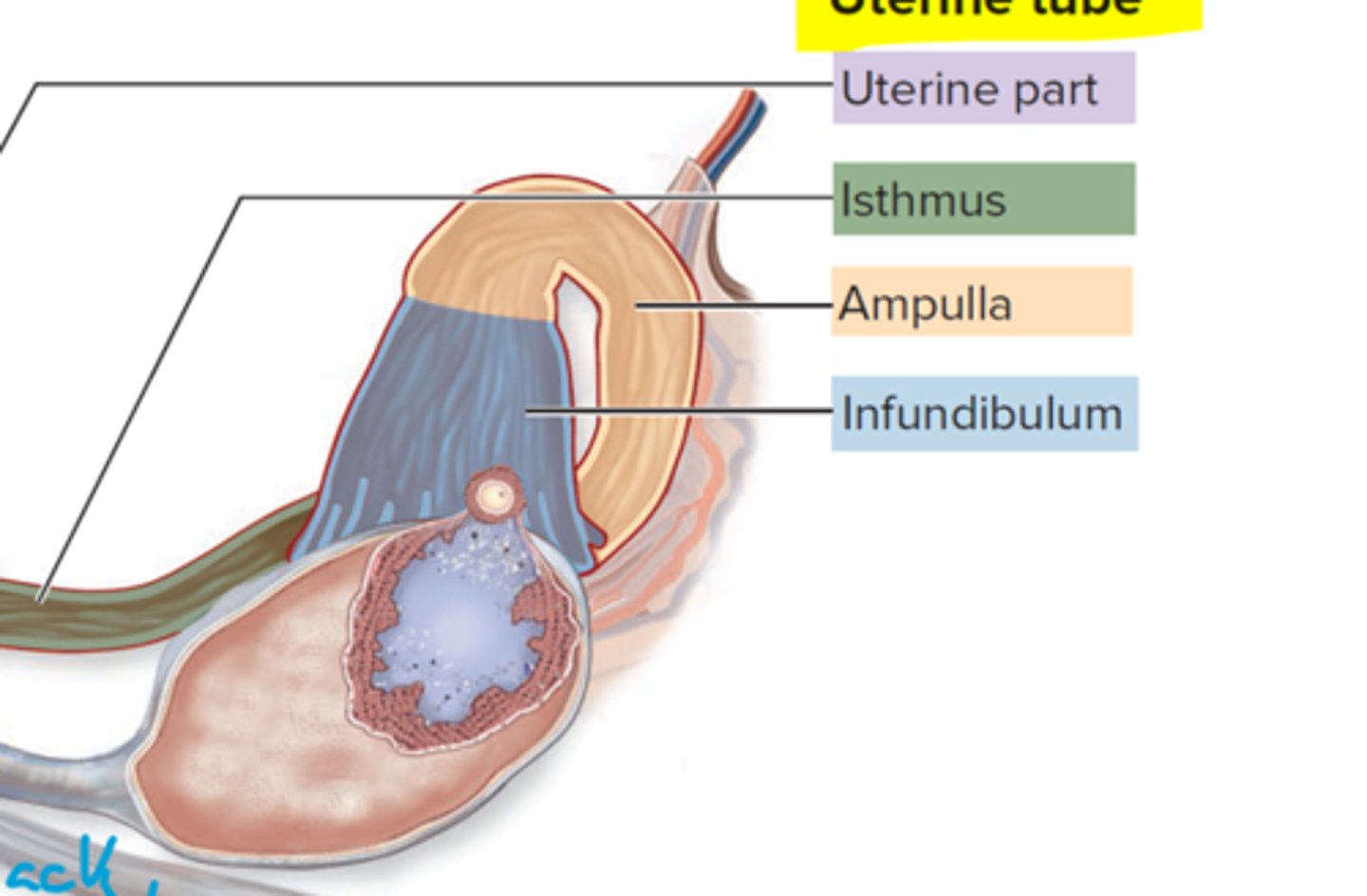
Ampulla does what?
Curves around wider than isthmus
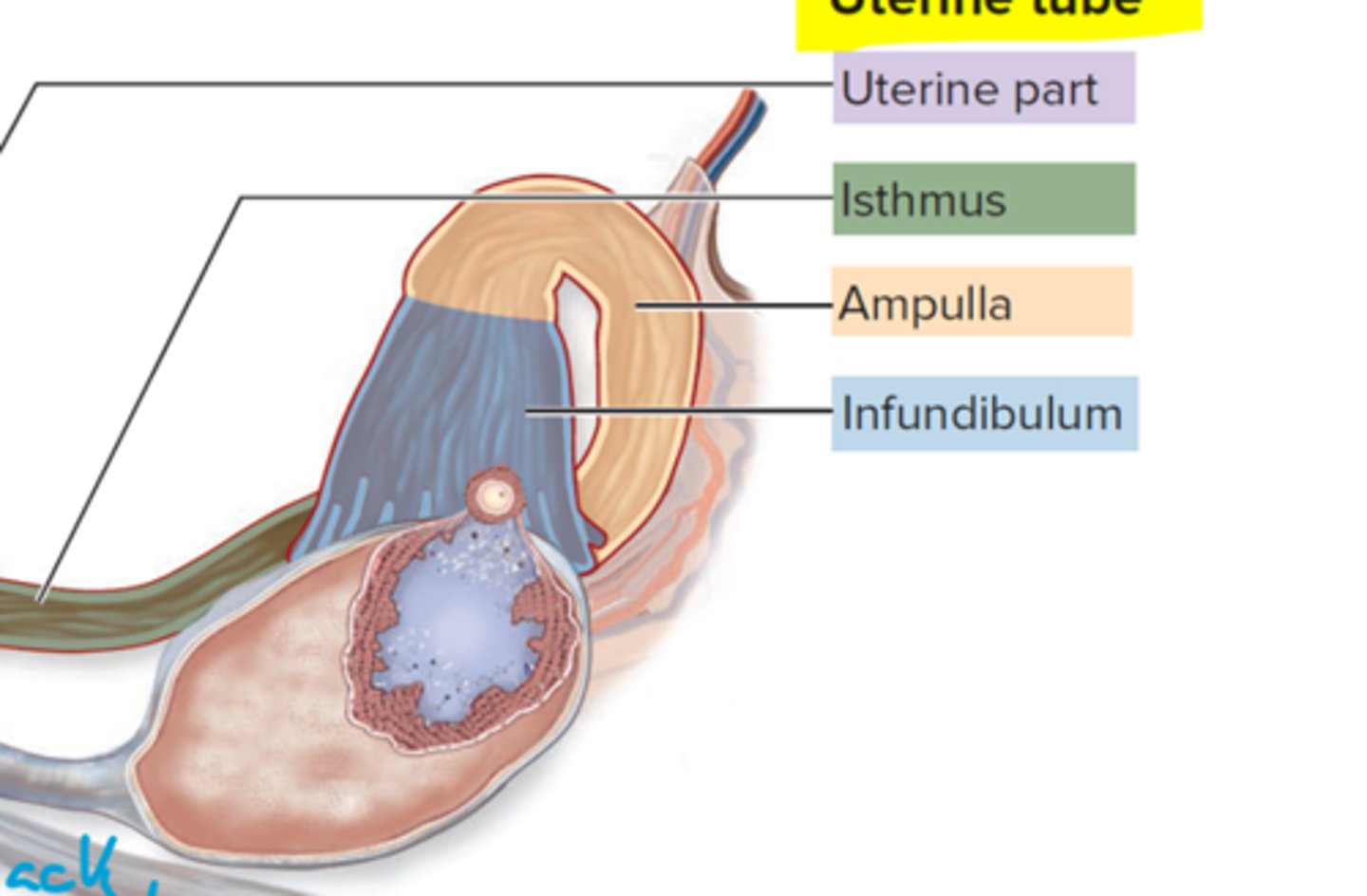
What is the infundibulum?
contains fimbriae
What is the perimetrium?
connective covering
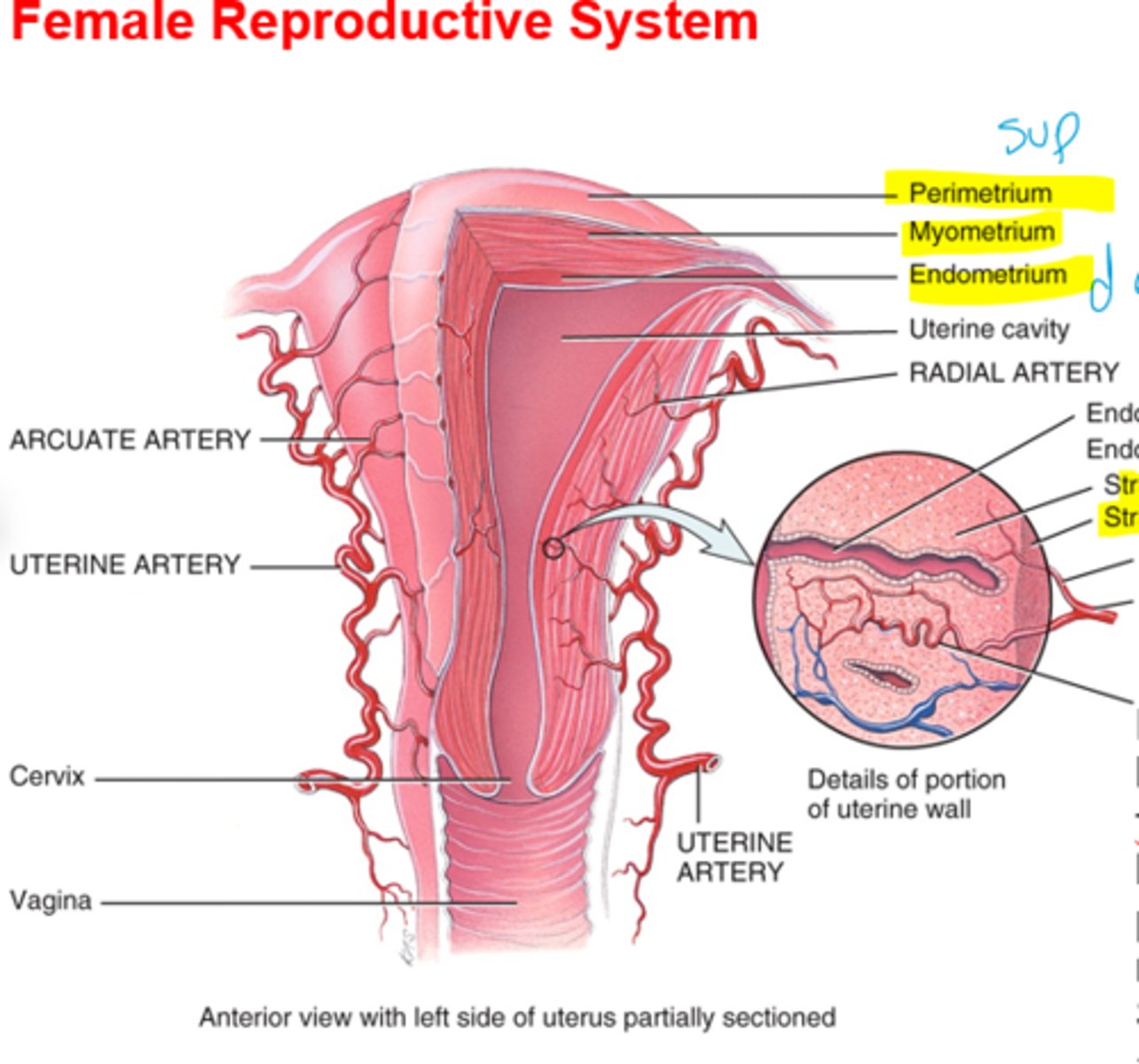
What is the myometrium?
muscle of smooth muscle cells
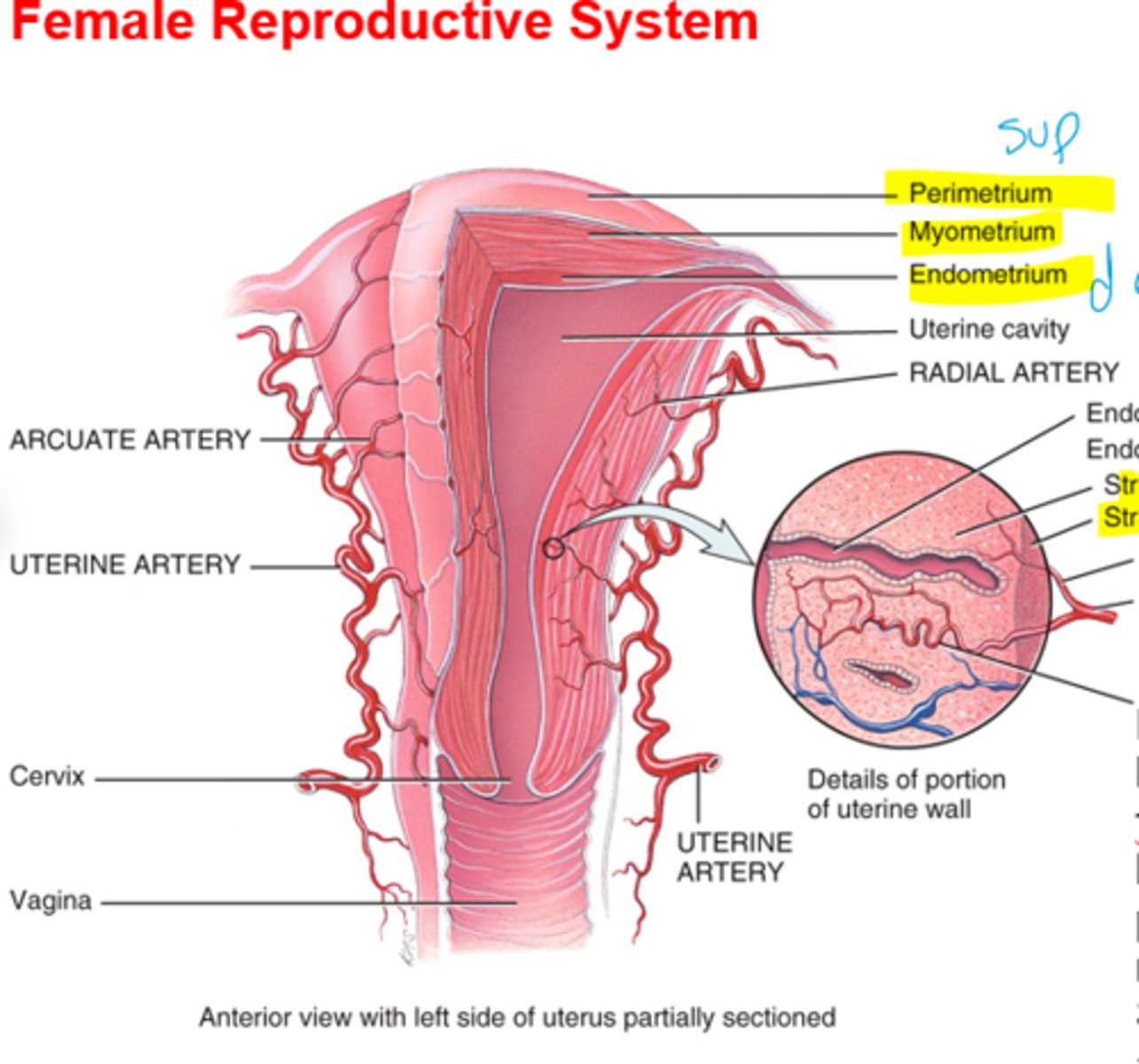
What is the endometrium?
inner most layer(proliferates each month and sheds)
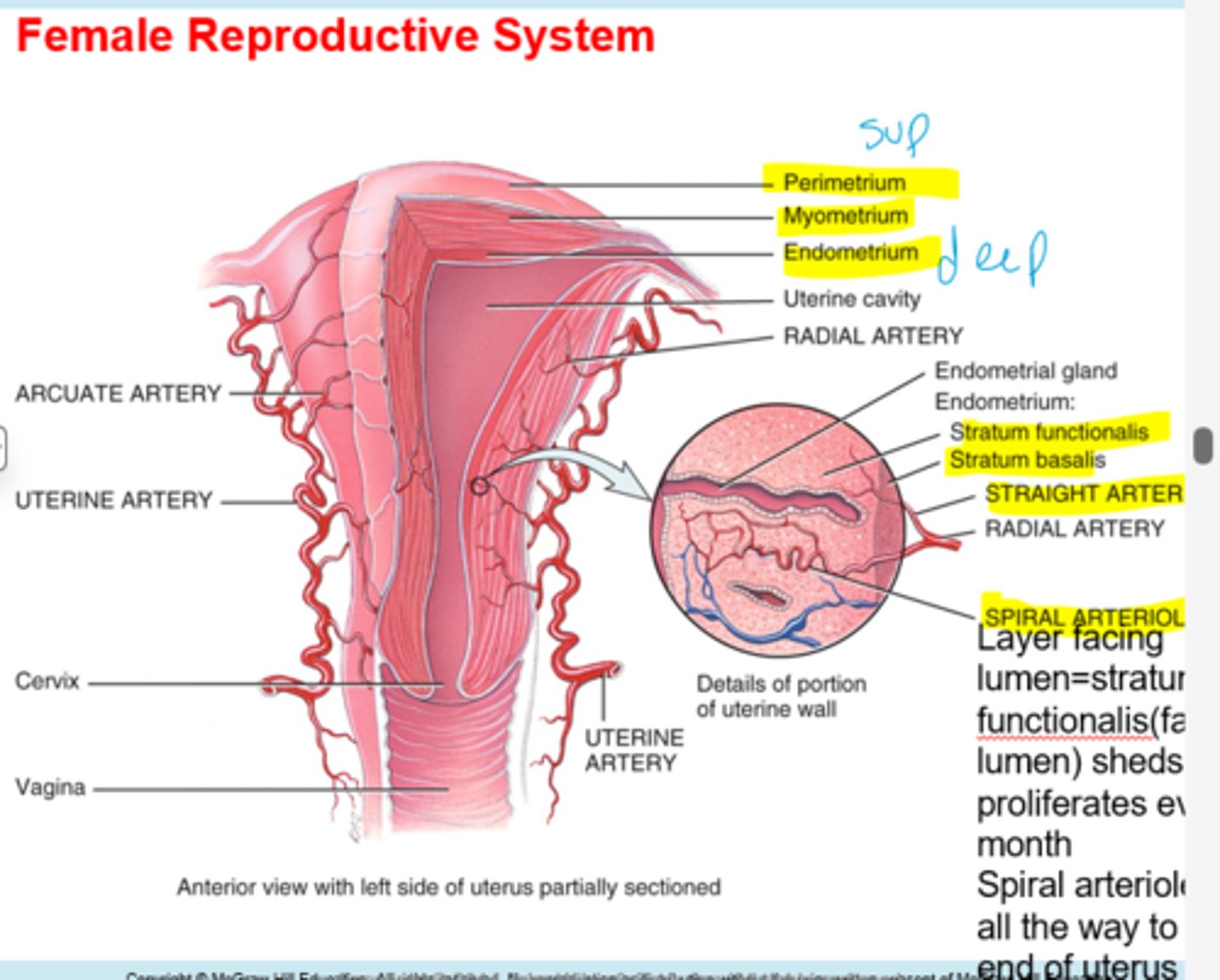
What is the stratum functionalis job?
sheds and proliferates every month
Whats the job of the stratum basalis?
anchors the functionalis, stays all the time
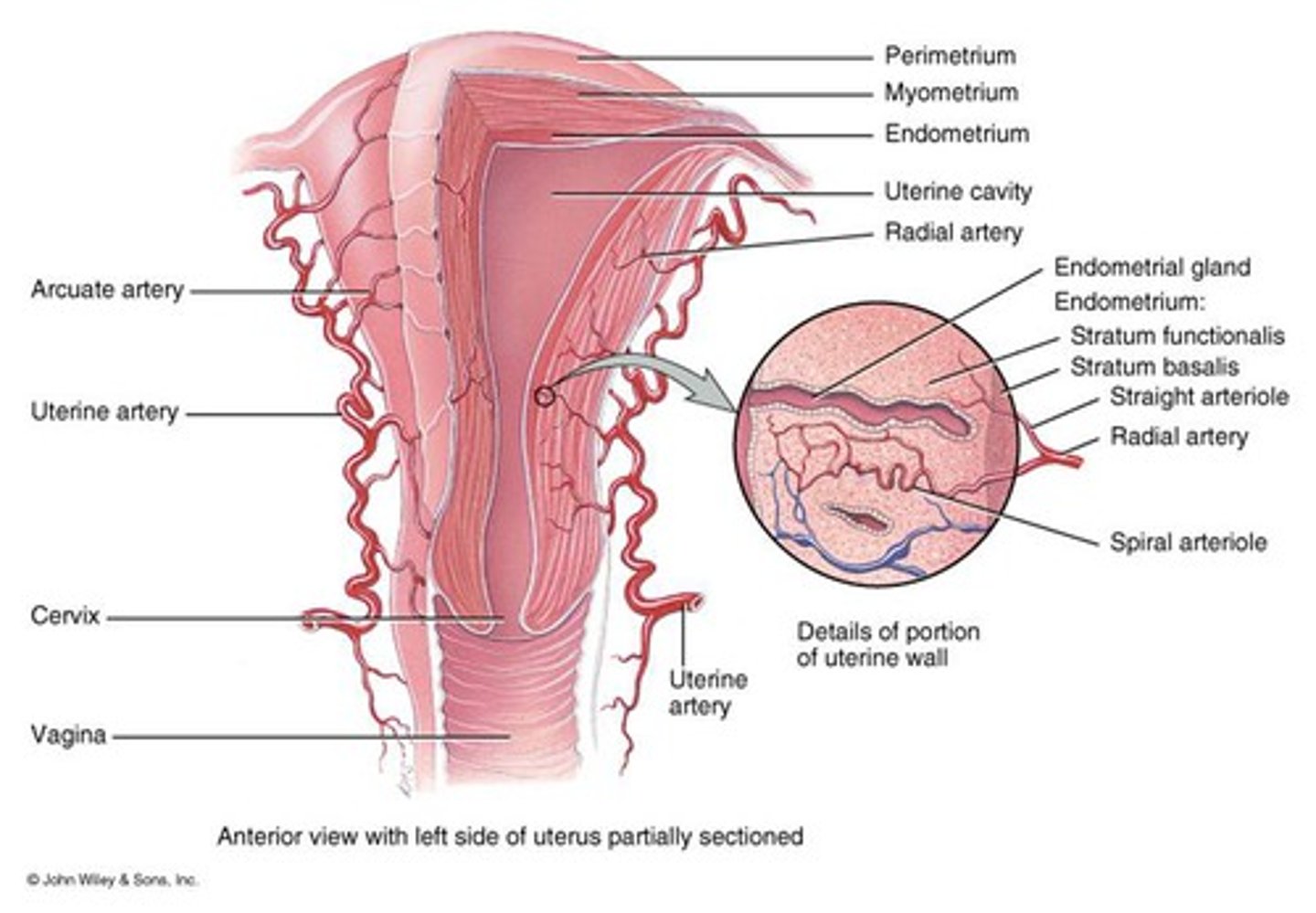
The spiral arteriole leads to?
distal end of uterus
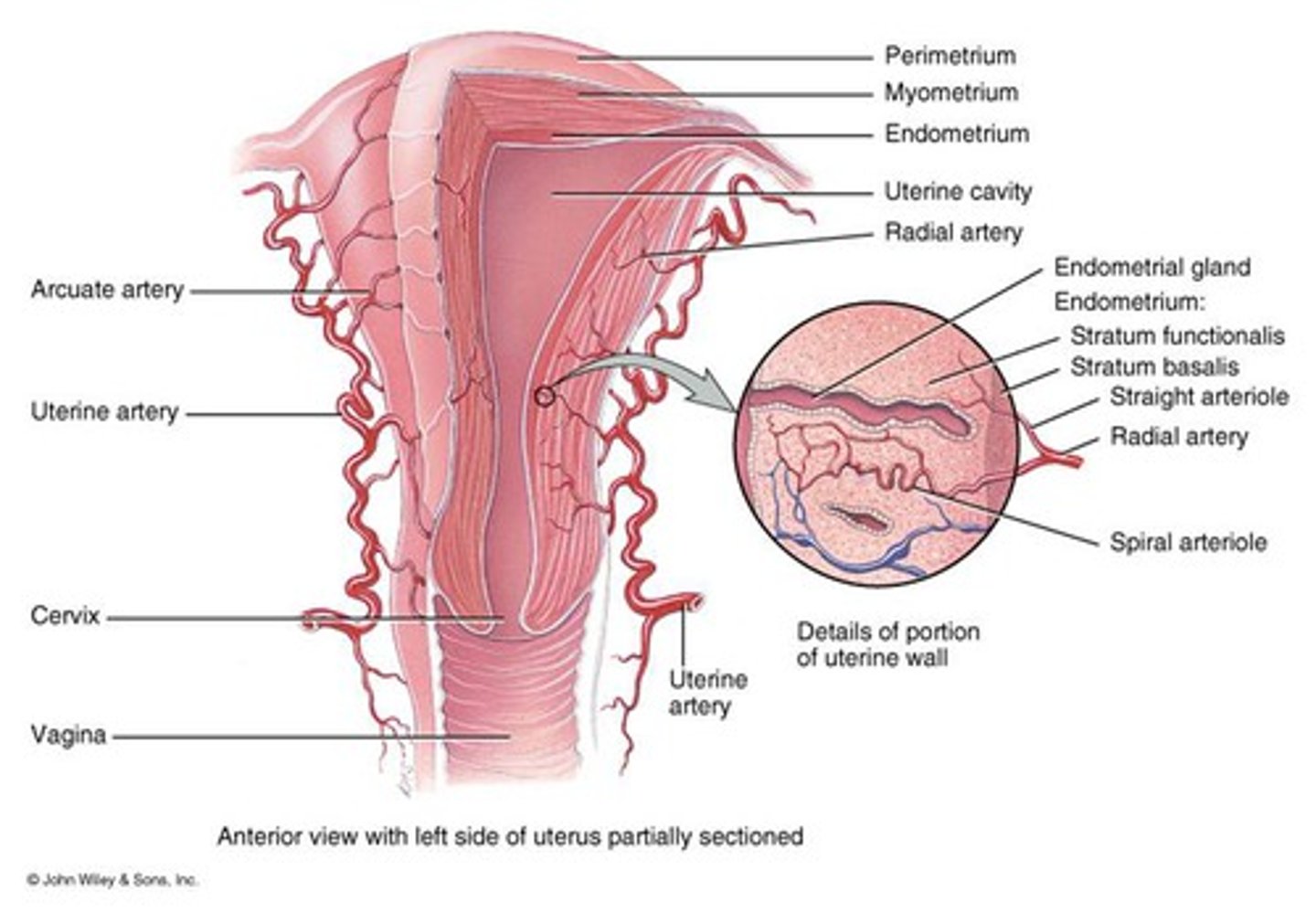
What do the endometrial glands do?
secrete fructose sugar for embryo
corpus luteum
rest of follicular cells that stay behind after ovulation
Graaffian follicle
mature follicle ready for ovulation
Antrium
big lake of fluid
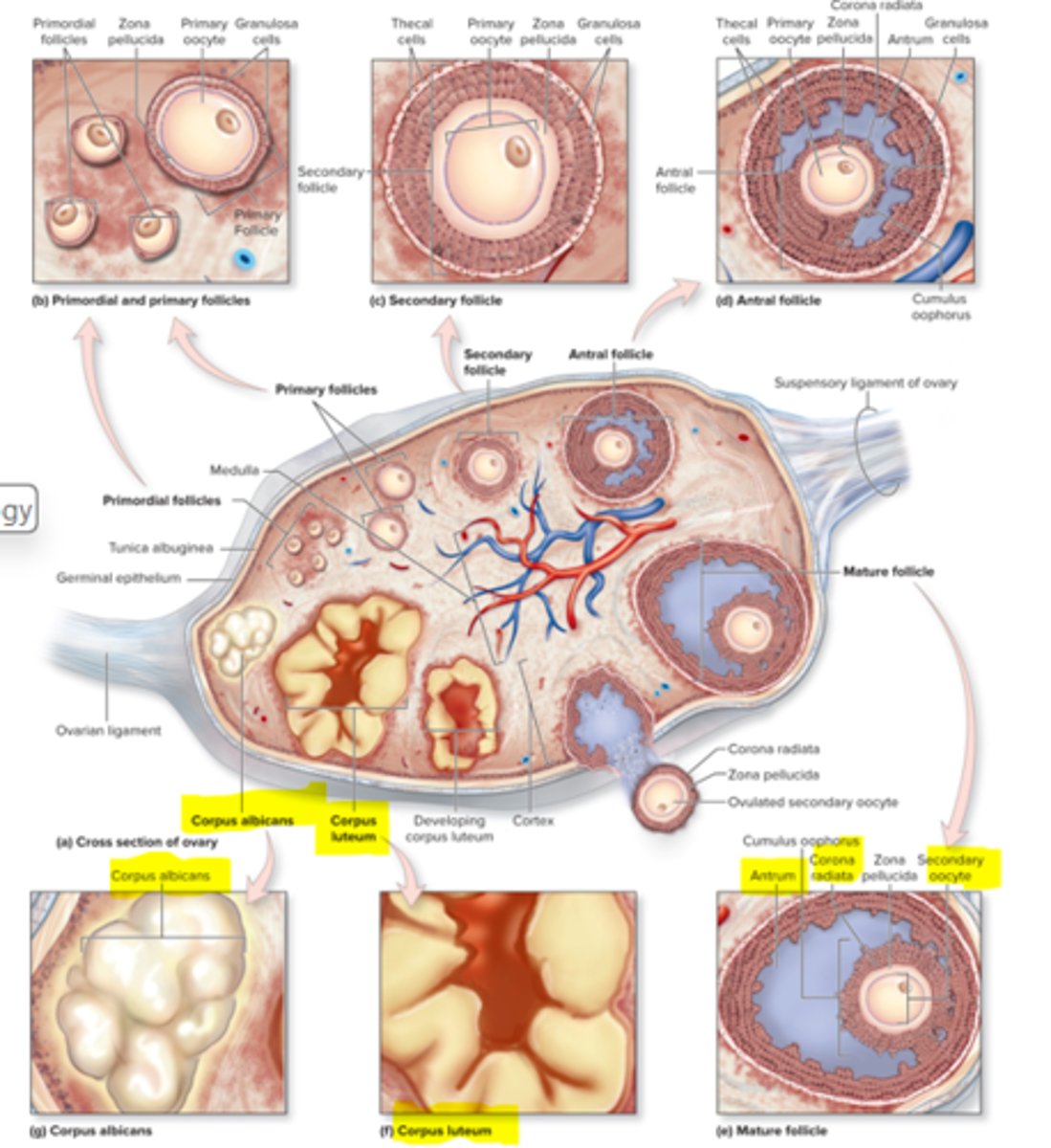
Corpus albicans
small deposit of scar tissue
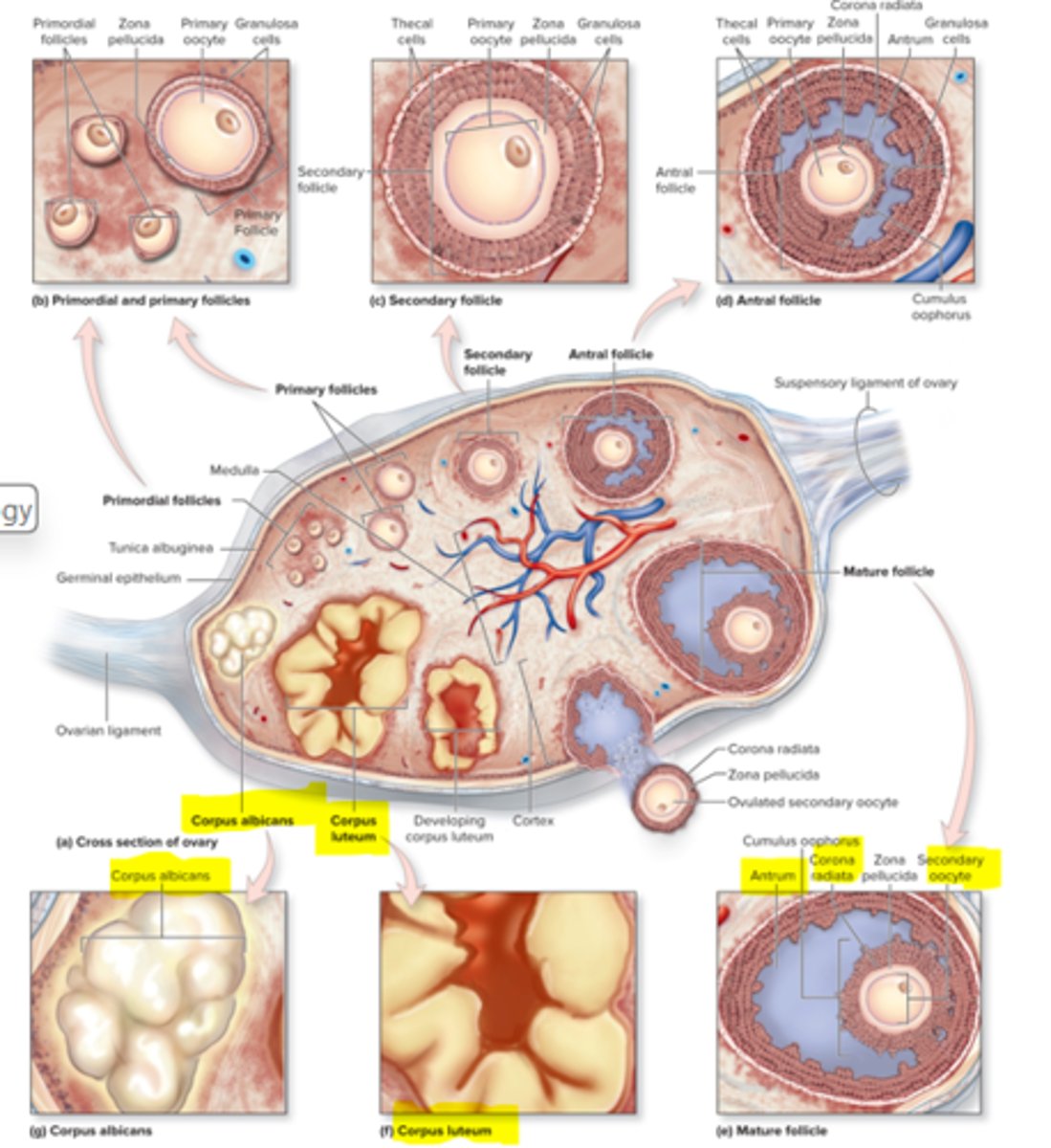
What are primordial follicles?
wait for hormones to come to become large
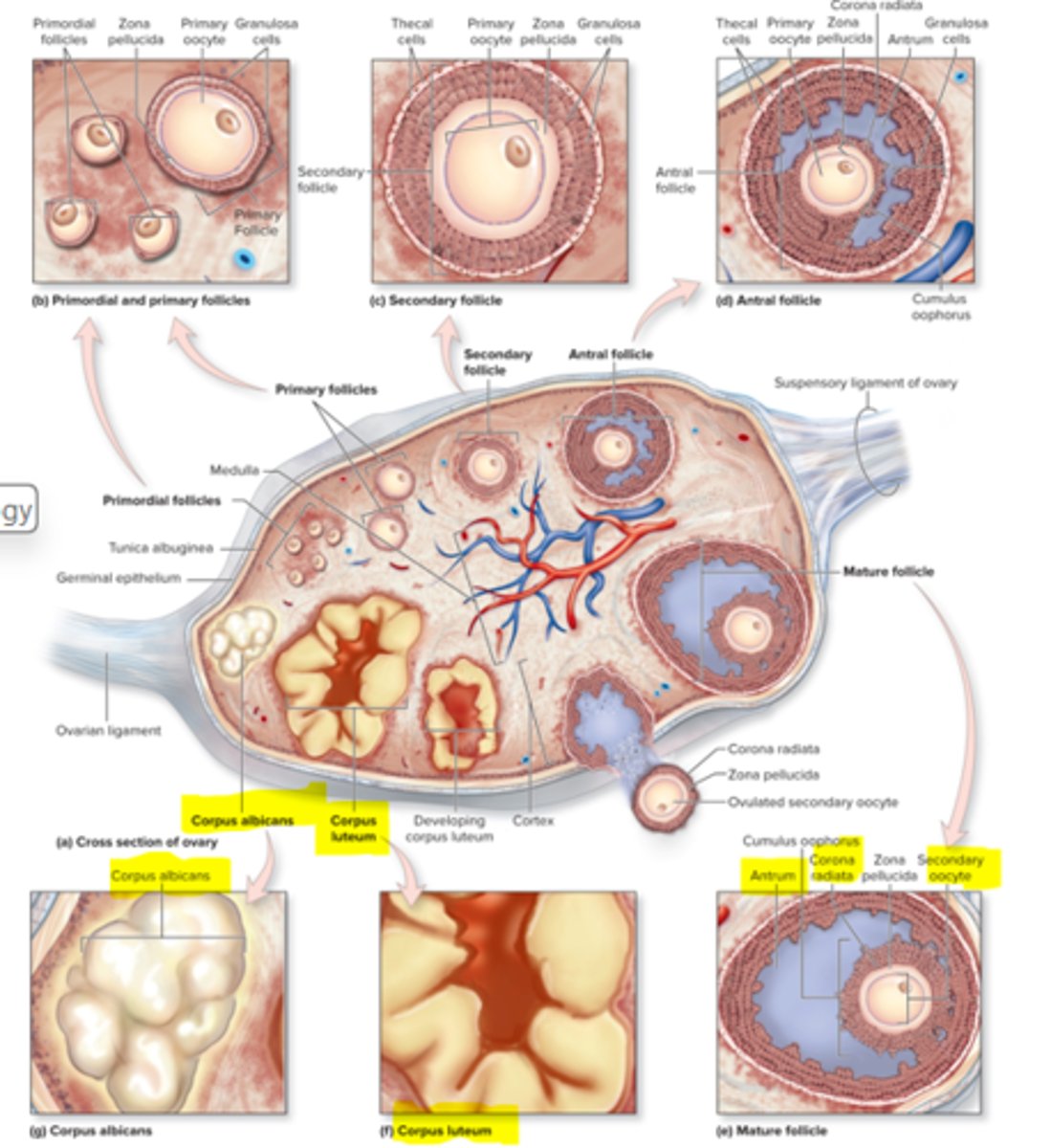
What happens when one of the large follicles rupture and mature?
oocyte comes out, goes to empty space to fertilized to fallopian tubes and uterus
Corona radiata job
provide nutrients to the egg and protects it
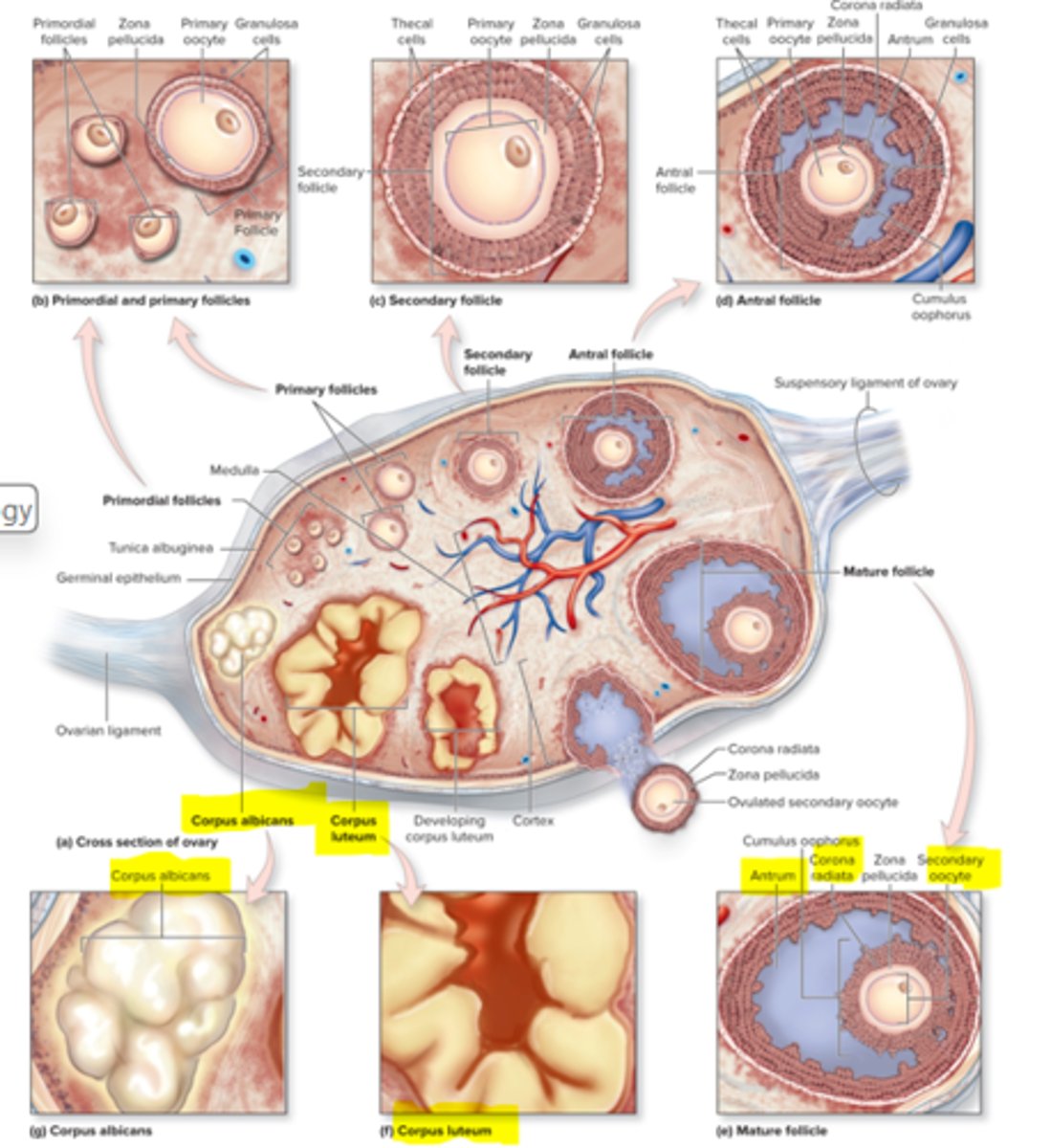
Cortex around the medulla is where
meiosis happens every month to create oocytes
Vestibule is?
opening to vagina
Lactiferous sinus
stores milk
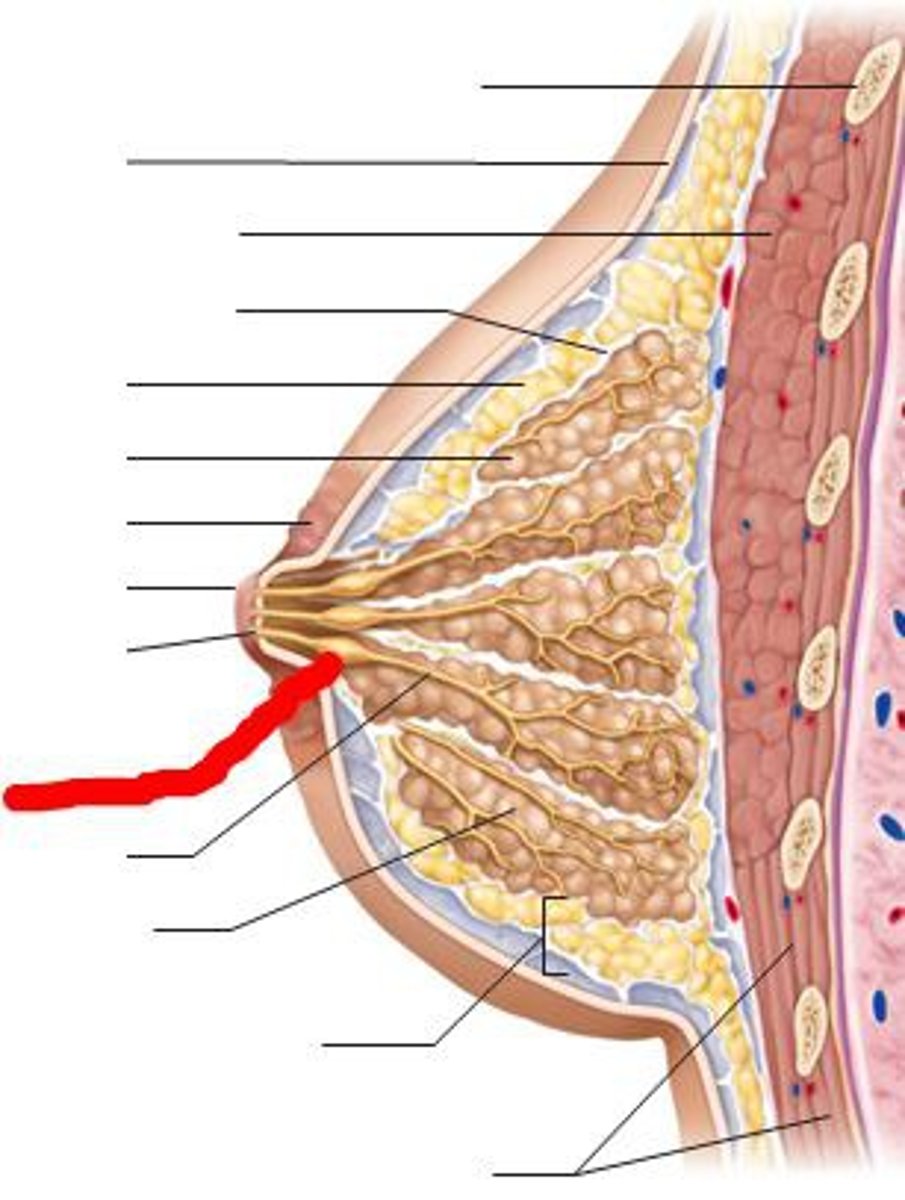
lactiferous ducts
tubes that carry milk within the breast
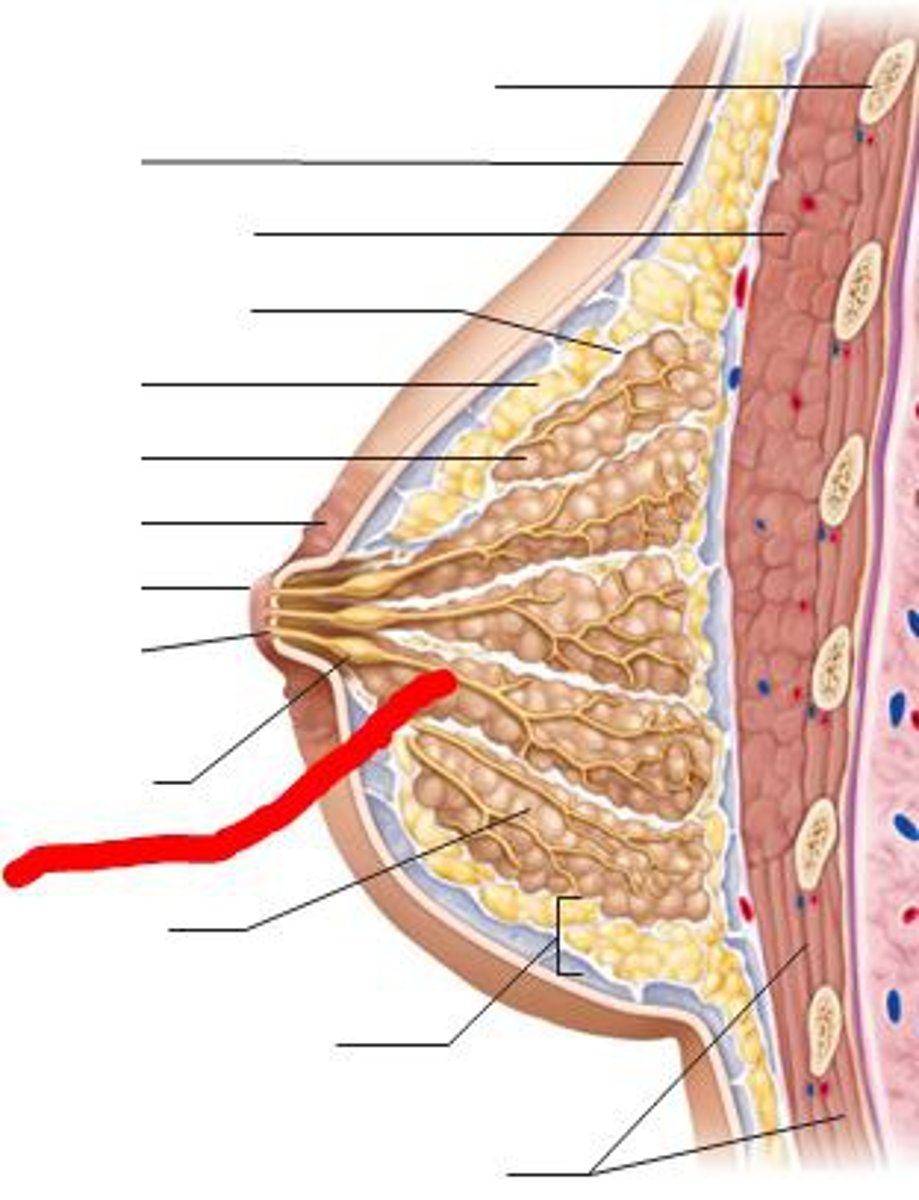
What's a lobule of the breast?
produces milk
What's menarche?
first menstrual cycle, depends on when mom got hers
1. Hypothalmus releases GnRH stimulates anterior pituitary gland
AP releases FSH and LH targets the ovary
What do FSH and LH help do?
support in case embryo shows up
Day 1 of menstrual flow means
day 1 next month's cycle
When does GnRH shut down?
when moderate amounts of estrogen and progesterone are present which shuts down hypothalamus
Very low levels of estrogen and progesterone means?
GnRH turns back on, next month's cycle continues
What happens after day 14?
estrogen and progesterone functionalis gets thicker and sugar secretes
2nd cycle what happens?
functionalis enters secretory phase to prepare for oocyte
If fertilization doesn't happen?
corpus luteum degenerates and becomes corpus albicans
corpus albicans will then produce
fewer hormones(takes a week)
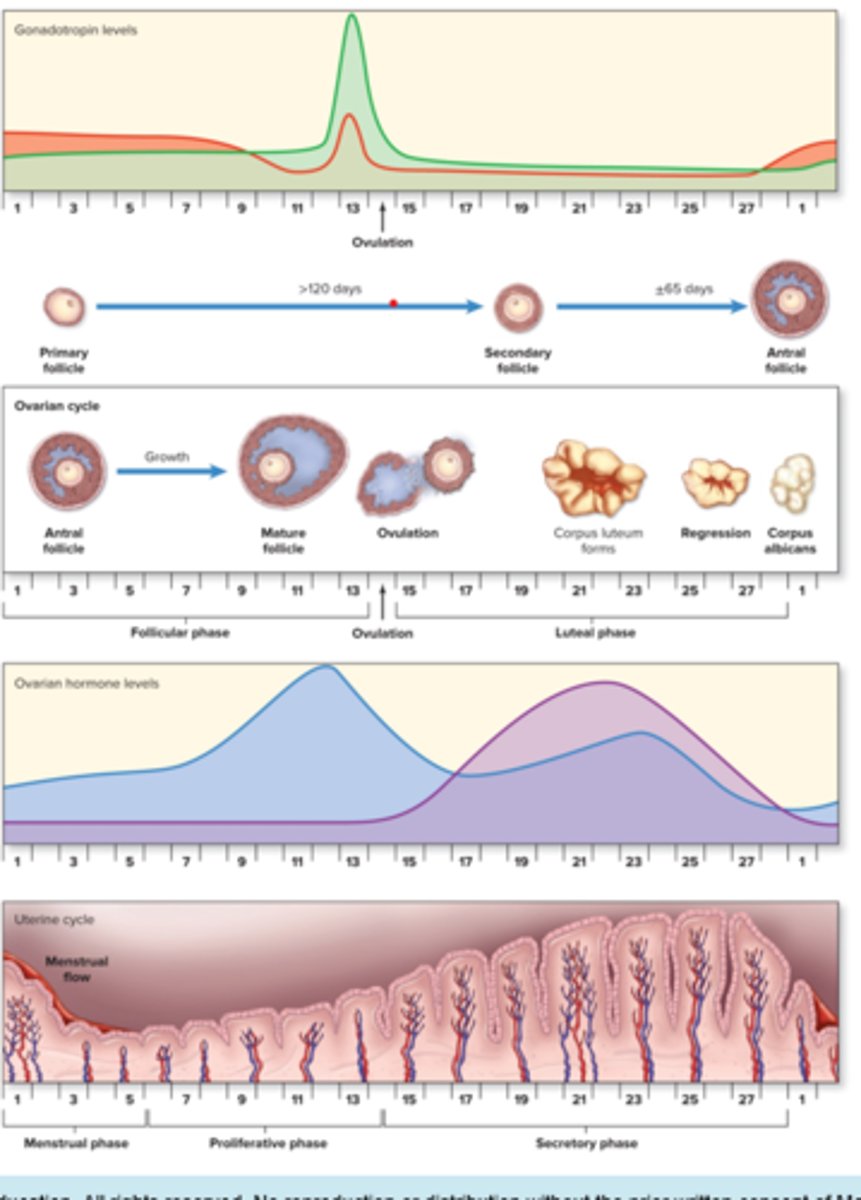
Low levels or progesterone and estrogen mean?
no baby coming, spasms of spiral arteries
-smooth muscle constricts and chokes off blood supply
-functionalis tissues dies off=menstrual flow
Menstrual phase is for
1-5 days
proliferative phase is
days 6-14 of cycle, develops functional layer of endometrium
Secretory phase is?
days 15-28 of cycle, increased progesterone secretion from corpus luteum
What happens when an egg gets fertilized?
secondary oocyte gets released to ampulla of fallopian tube
What are the steps of fertilization happening?
1. Corpus luteum has to stay for 6 months for embryo to have sugar from functionalis (CELL MUST NOT DIE)
2.You have to send hCG to maintain corpus luteum becomes placenta
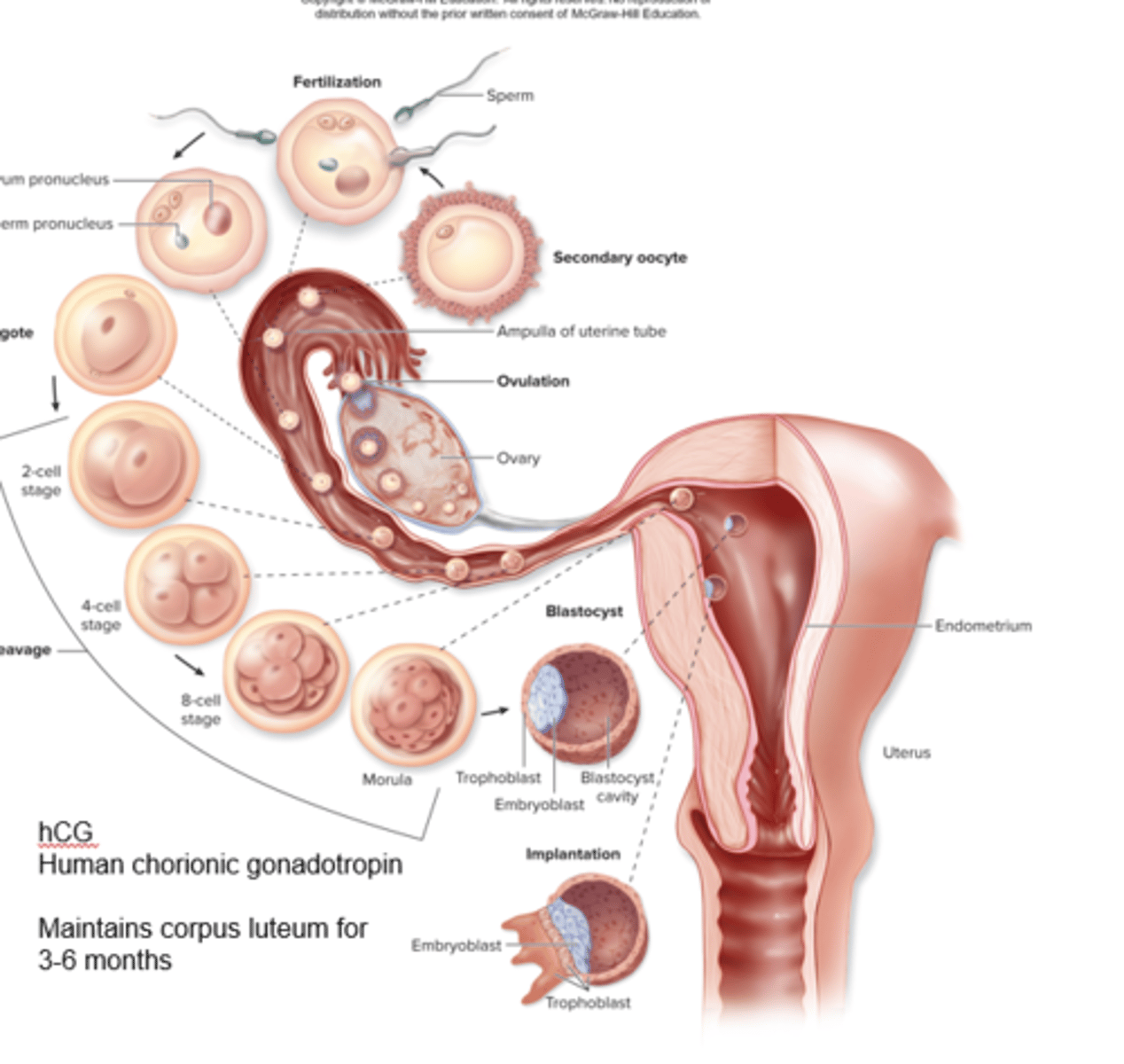
secondary Oocyte isn't around sperm so what happens?
secondary oocyte dies because meiosis isn't finished
Ovarian cycle
1. follicular phase: days 1-5
2. ovulation: days 6-12
3. luteal phase: days 15-28
oral contraceptives
package of 28 pills active and 7 sugar pills
What do active oral contraceptives contain?
estrogen and progesterone, acts like a moderate level of estrogen and progesterone to keep GnRH off