ORAD800: Benign Fibro-osseous Lesions and Other Bone Pathology
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
Fibro-Osseous Lesions
lesions characterized by replacement of normal bone by fibrous connective and abnormal immature bone
What lesion is replaced by fibrous connective tissue?
Fibro-Osseous
What are the 4 categories that Fibro-Osseous Lesions can be??
Developmental
Reactive
Dysplastic
Neoplastic
Fibrous Dysplasia
localized change in normal bone metabolism, replacement of cancellous bone by fibrous tissue
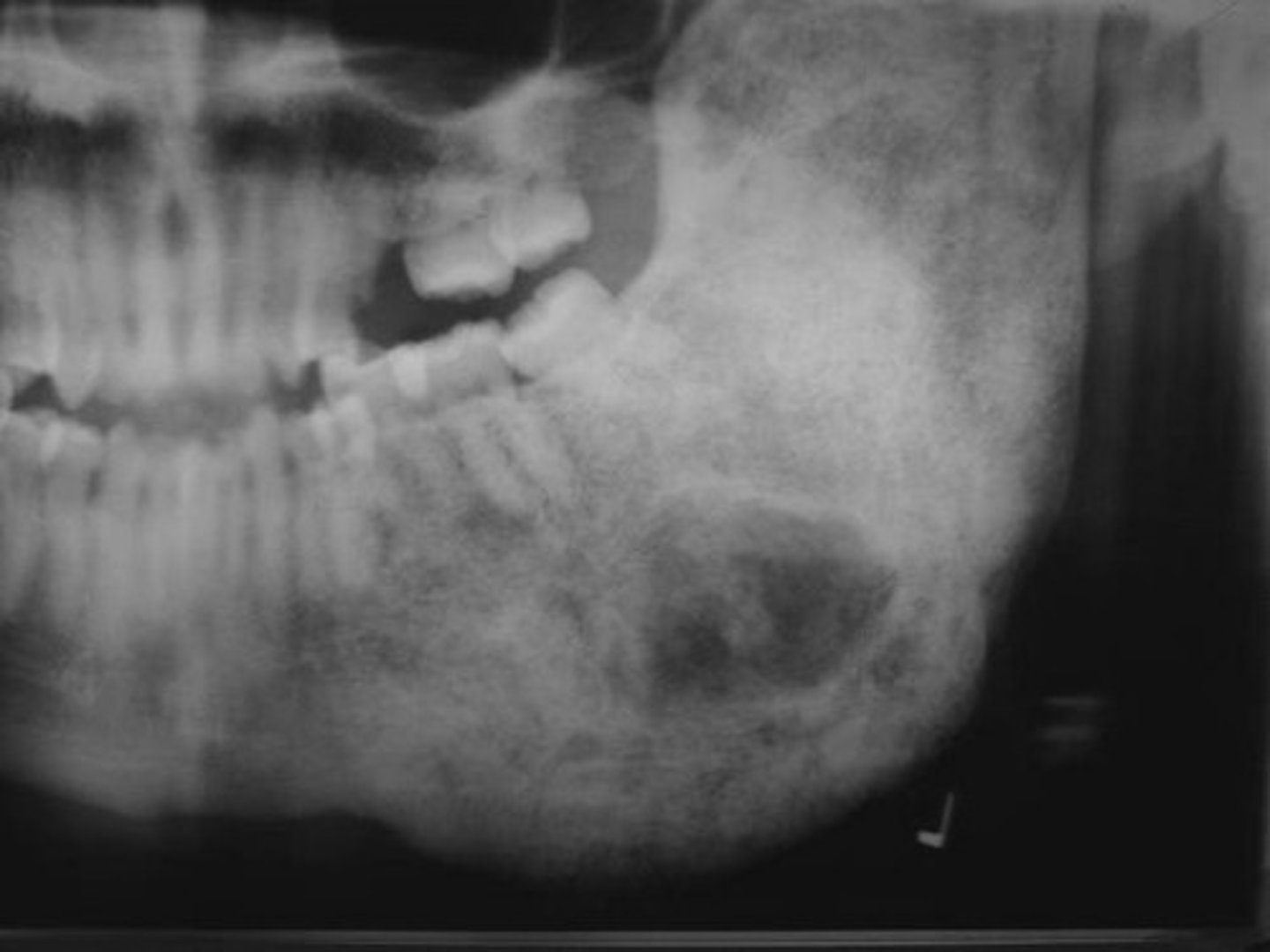
What fibrous lesion is a change in the normal bone metabolism?
Fibrous Dysplasia
Solitary Type Fibrous Dysplasia
one bone involved
One bone involved
Solitary Type Fibrous Dysplasia
Jaffe Type Fibrous Dysplasia
multiple bones involved
Multiple bones involved
Jaffee Type Fibrous Dysplasia
McCune Albright Syndrome
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia, cutaneous pigmentation, hyperfunction of one or more adrenal glands
Clinical Features of Fibrous Dysplasia
young adults
posterior maxilla
enlargement of alveolar process
unilateral facial swelling
growth ceases after adolescence
T/F: Fibrous Dysplasia is common in younger people?
TRUE
T/F: Fibrous Dysplasia ceases after adolescence?
TRUE
Location of Fibrous Dysplasia
maxilla, posterior region, unilateral
Periphery of Fibrous Dysplasia
ill-defined
blended
normal trabeculae
Internal Structure of Fibrous Dysplasia
RI, RO, mixed, ground glass, cotton wool, orange peen
T/F: Fibrous Dysplasia can cause superior displacement of the IAN?
TRUE
Periapical Cemental Dysplasia
localized change of normal cancellous bone with fibrous tissue and cementum-like material
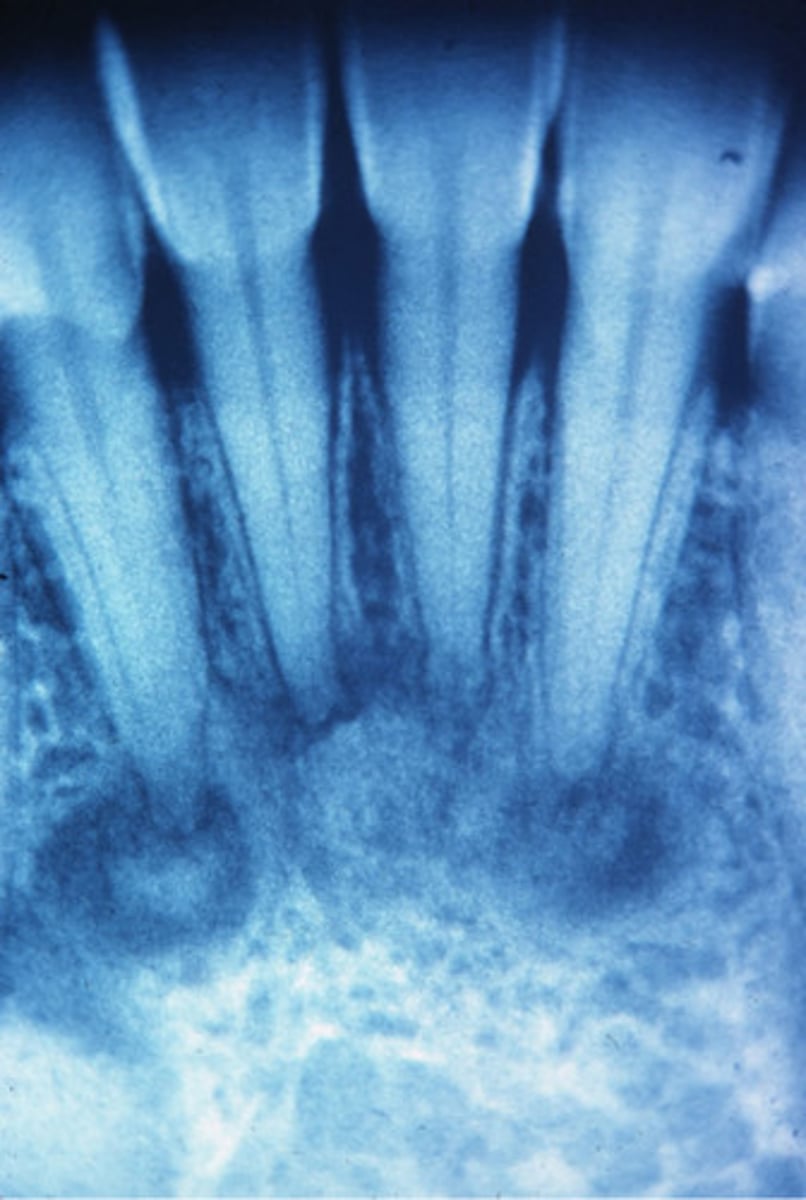
Clinical Features of Periapical Cemental Dysplasia?
middle aged woman
african american, asian
Vital Teeth
Large expansion of alveolar process
T/F: Periapical Cemental Dysplasia is common in white men
FALSE
T/F: Periapical Cemental Dysplasia is common in non-vital teeth
FALSE
Location of Periapical Cemental Dysplasia
Apex, mandibular anterior teeth
Periphery of Periapical Cemental Dysplasia
well defined,RL border
Internal structure of Periapical Cemental Dysplasia
early stage (apical RL), mixed stage, mature
Florid
widespread
Florid Osseous Dysplasia
widespread form of PCOD.
Normal bone replaced with dense, acellular cemento-ossoeus tissue in background of connective tissue.
poor vascular supply
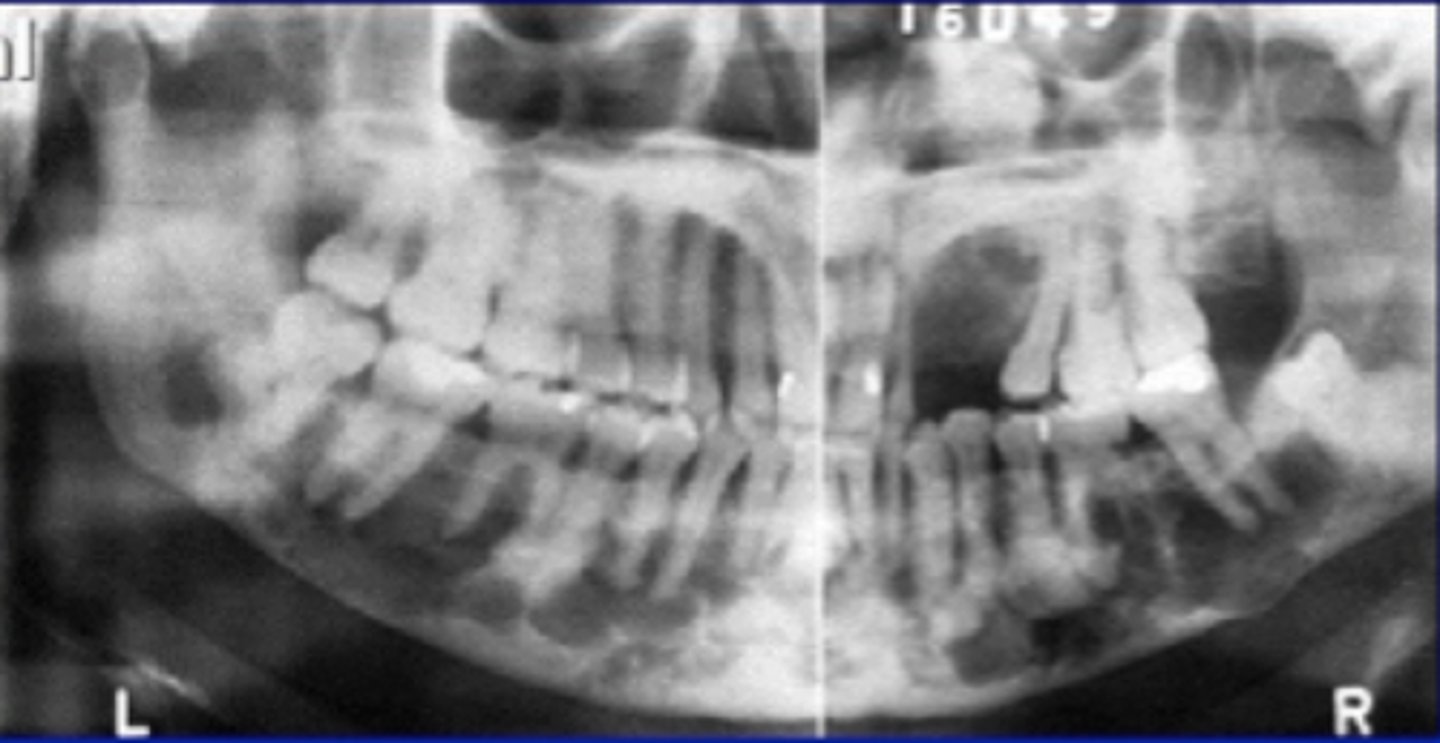
Clinical Features of Florid Osseous Dysplasia
females
poorly localized
extensive lesions
Cementoosifying Fibroma
benign bone neoplasm
3-4th decade
mandible > maxilla
asymptomatic
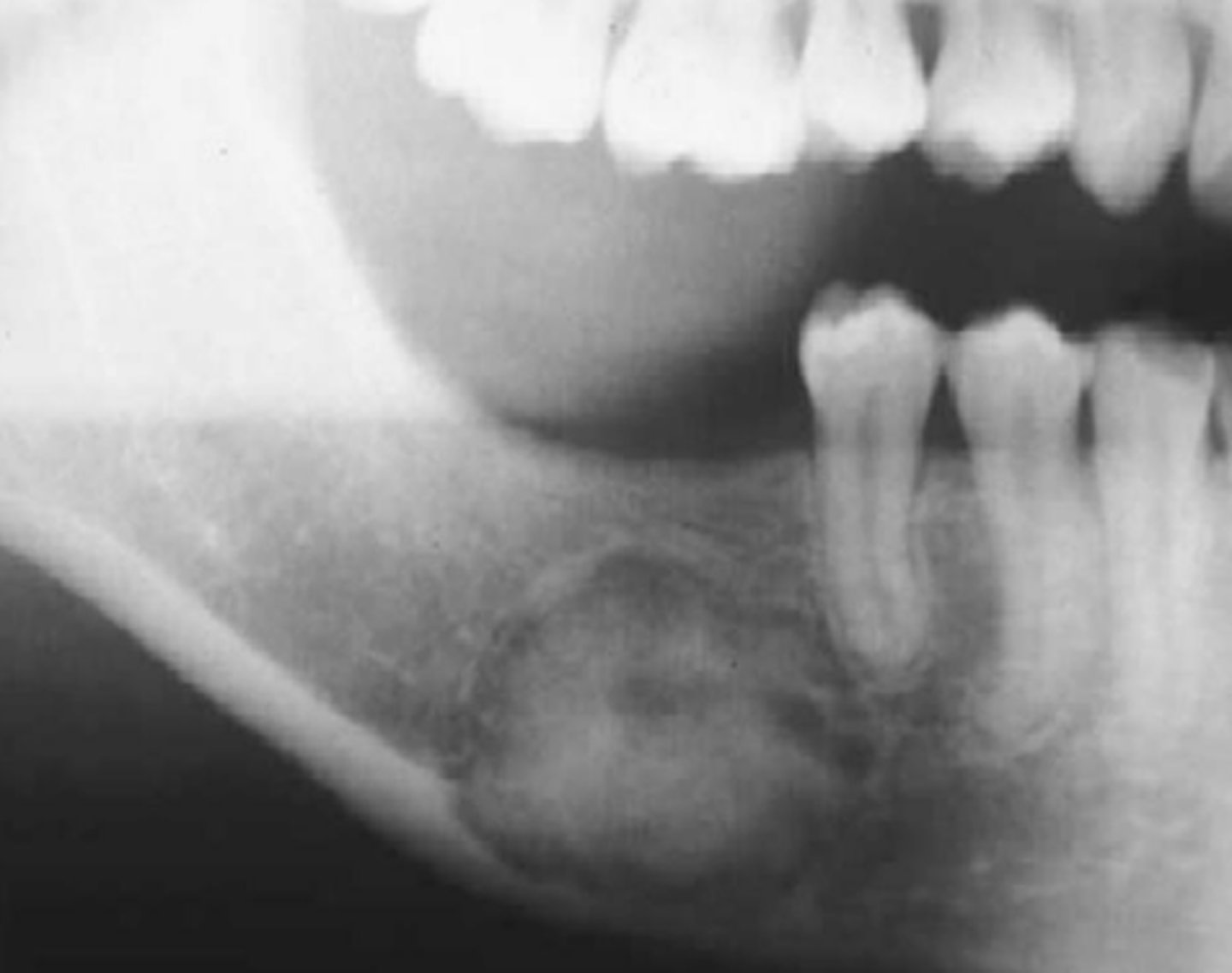
Location of Cementoosifying Fibroma
mandible
maxilla
Periphery of Cementoosifying Fibroma
well defined, sclerotic border, RL capsule
Internal Structure of Cementoosifying Fibroma
mixed
T/F: Cementoosifying Fibroma has an intact lamina dura
FALSE
Juvenile Cementoosifying Fibroma
rapid growth and jaw deformity
30-58% recurrence rate
involves orbital, frontal bone and paranasla sinuses
maxilla common
Osteoma
benign tumor
asymptomatic
slow growing
mandibular body/condyle
paranasal sinus osteoma
Osteoblastoma
benign neoplasm of osteoblasts
common in vertebrae of young person
TMJ
Benign Cementoblastoma
slow growing, mesenchymal neoplasms composed of cementum primarily
bulbous growth around/ attached to apex of tooth root
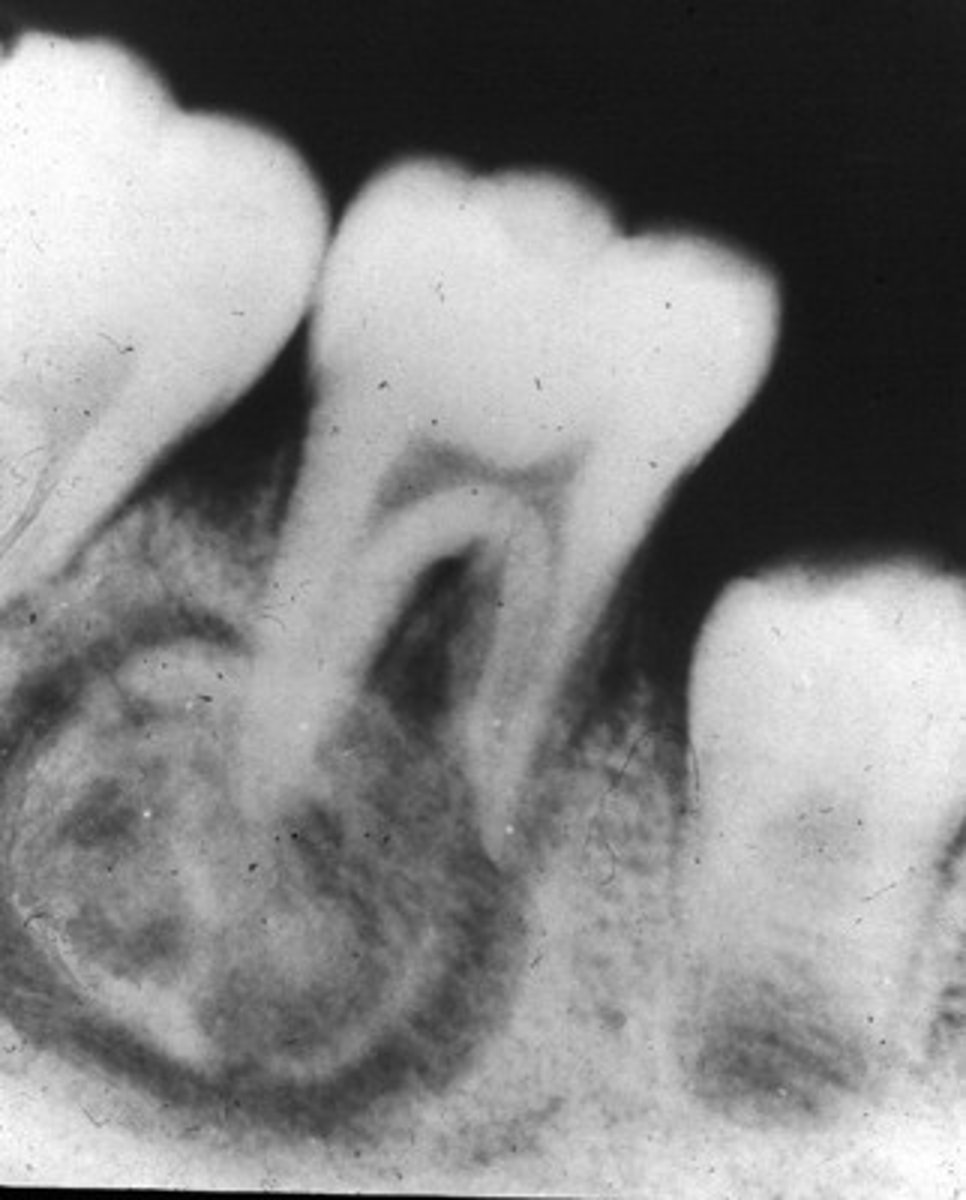
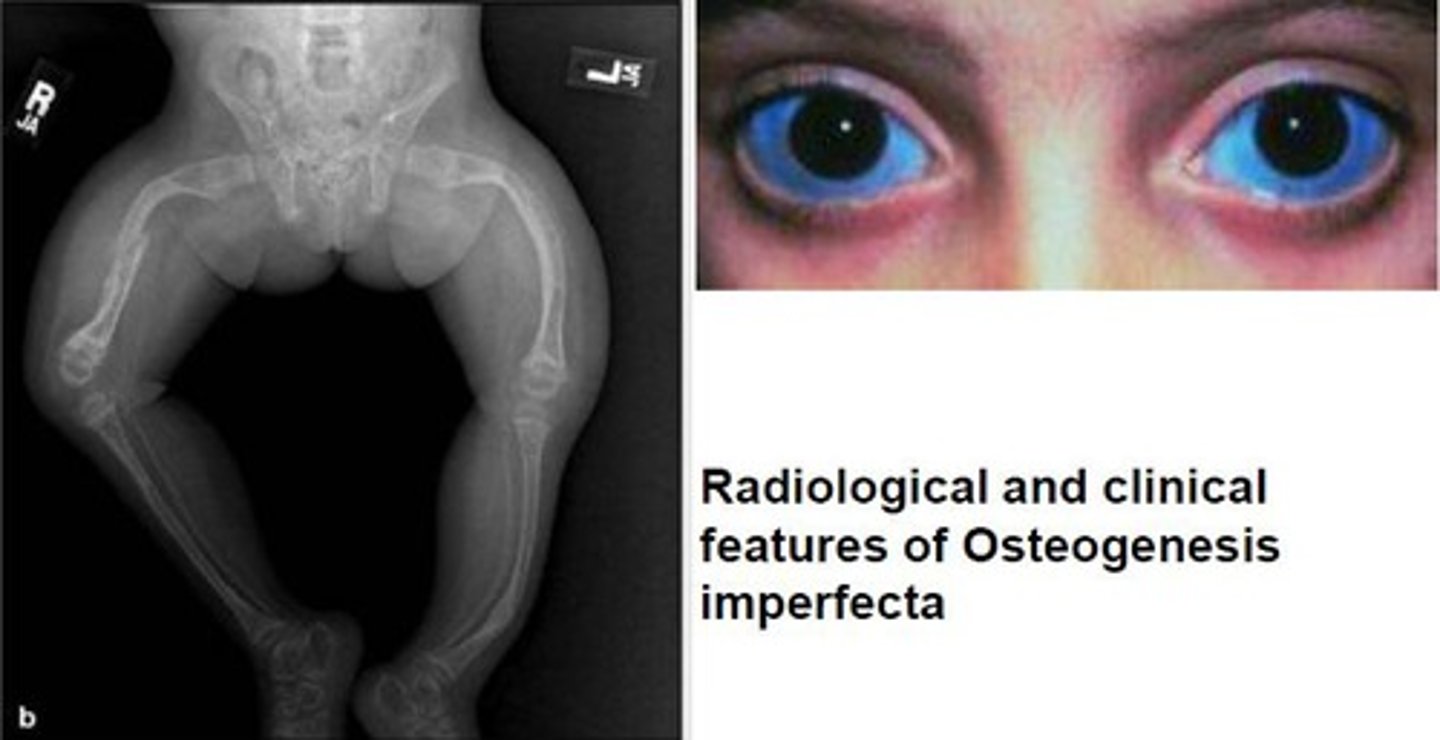
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
autosomal dominant/ recessive an inherited disorder characterized by extreme fragility of the bones.
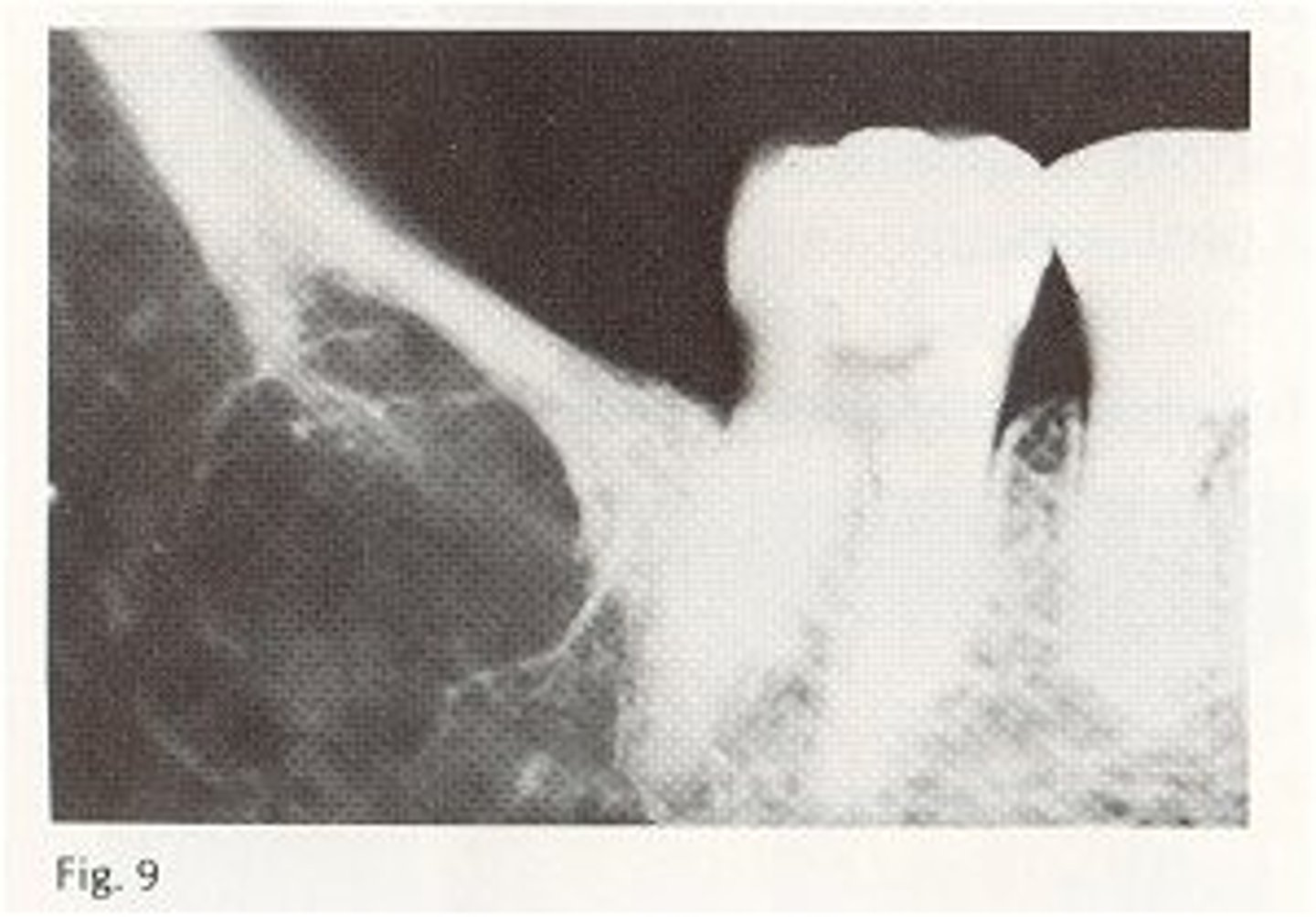
Focal Osteoporotic Marrow Defect
not a pathologic process but radiographic features can be confused with pathology
radiolucent area with fine central trabeculation within the lesion
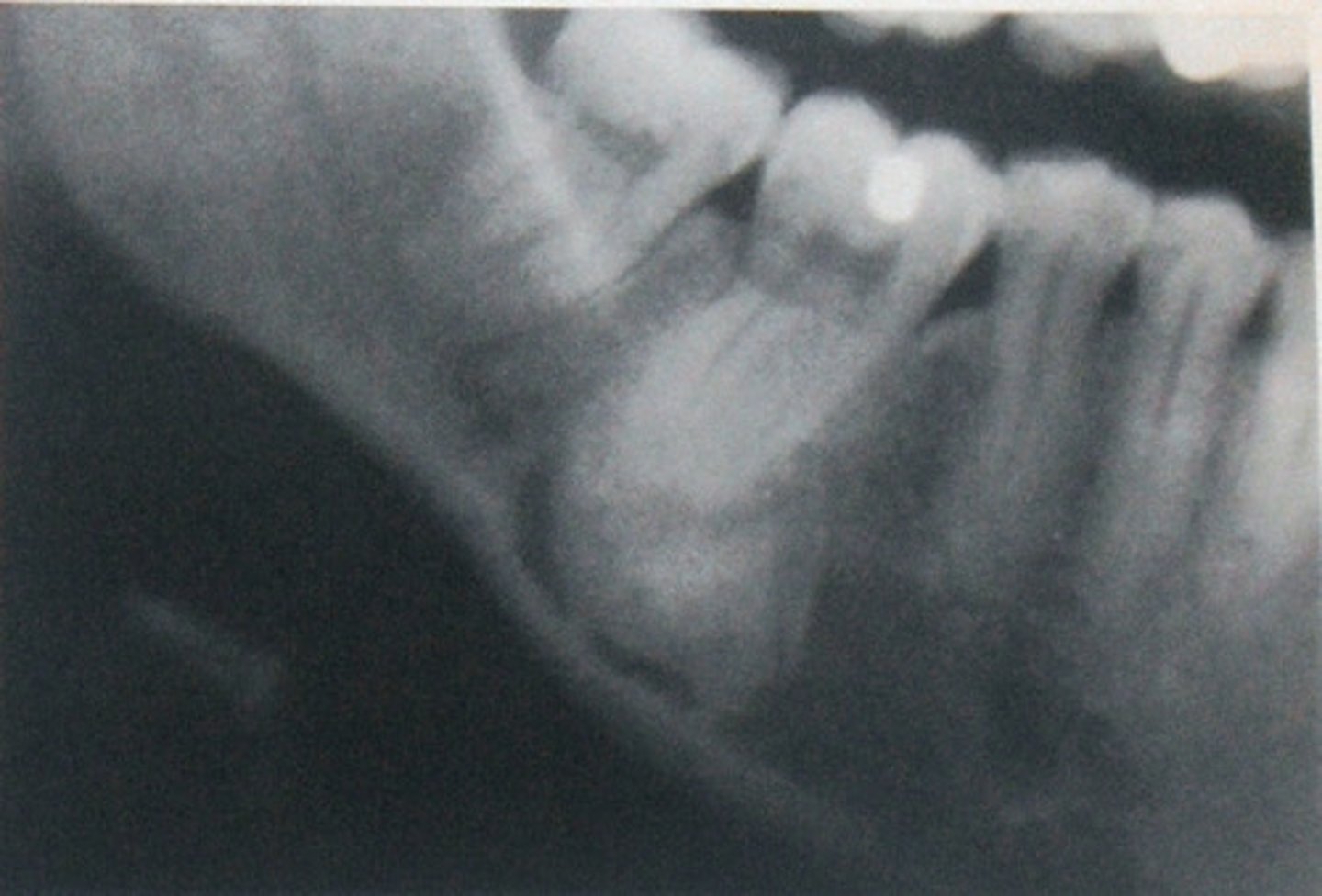
Focal Idiopathic Osteosclerosis
asymptomatic, radiopaque, unknown origin, no inflam./dysp./neop. etiologies
Paget's Disease
abnormal resorption and deposition of osseous tissue
Paget's Disease has what levels elevated?
alkaline phosphatase
hydroxproline in urine
Central Giant Cell Granuloma
reactive lesion
multinucleated giant cells
What is a clinical feature of Central Giant Cell Granuloma?
purple overlying mucosa
Location of Central Giant Cell Granuloma
mandible
Periphery of Central Giant Cell Granuloma
well defined RL margin
Internal Structure of Central Giant Cell Granuloma
RL, granular pattern, wispy septae
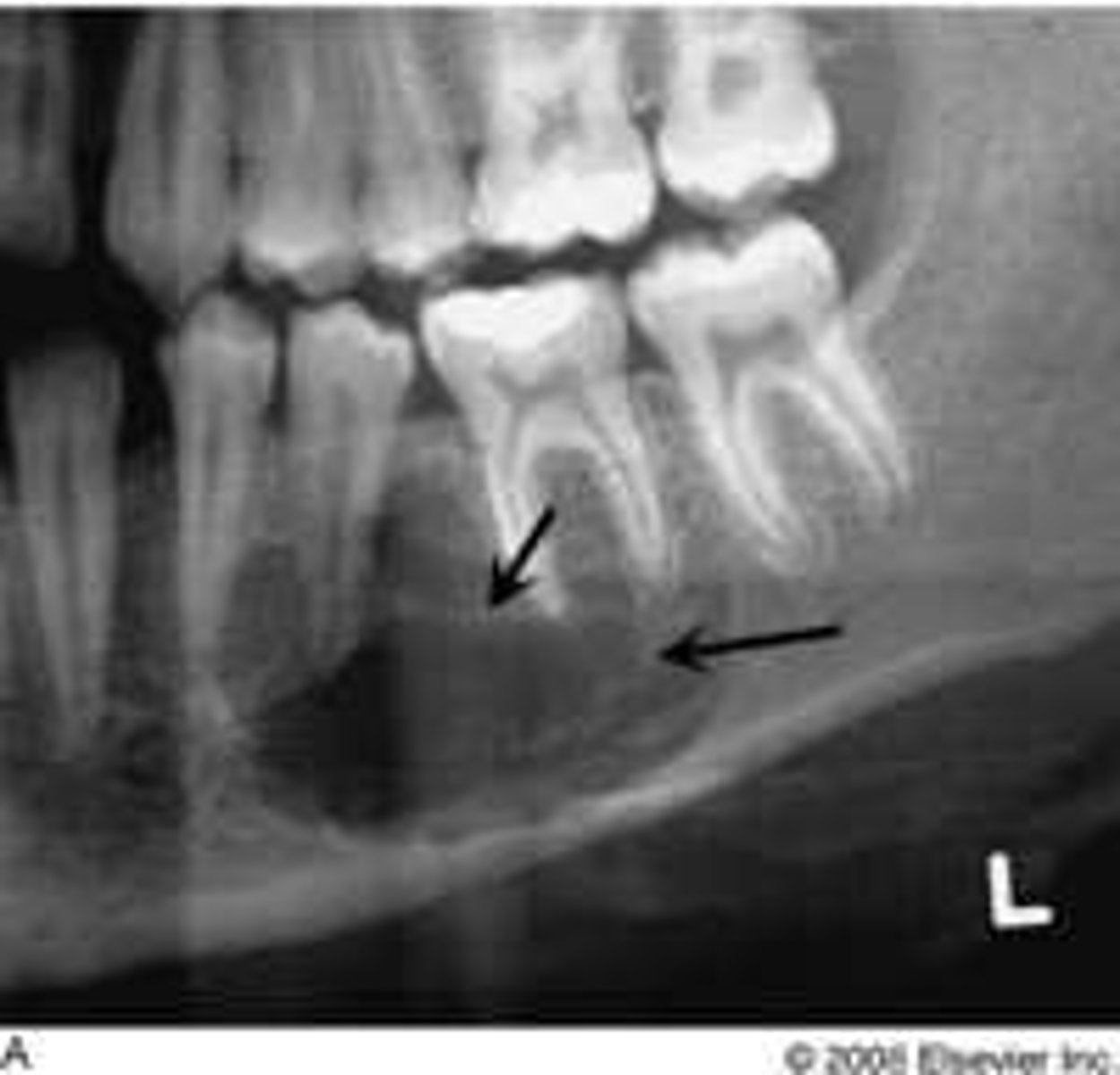
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
reactive lesion of bone
exaggerated, localized proliferative response of vascular tissue in bone
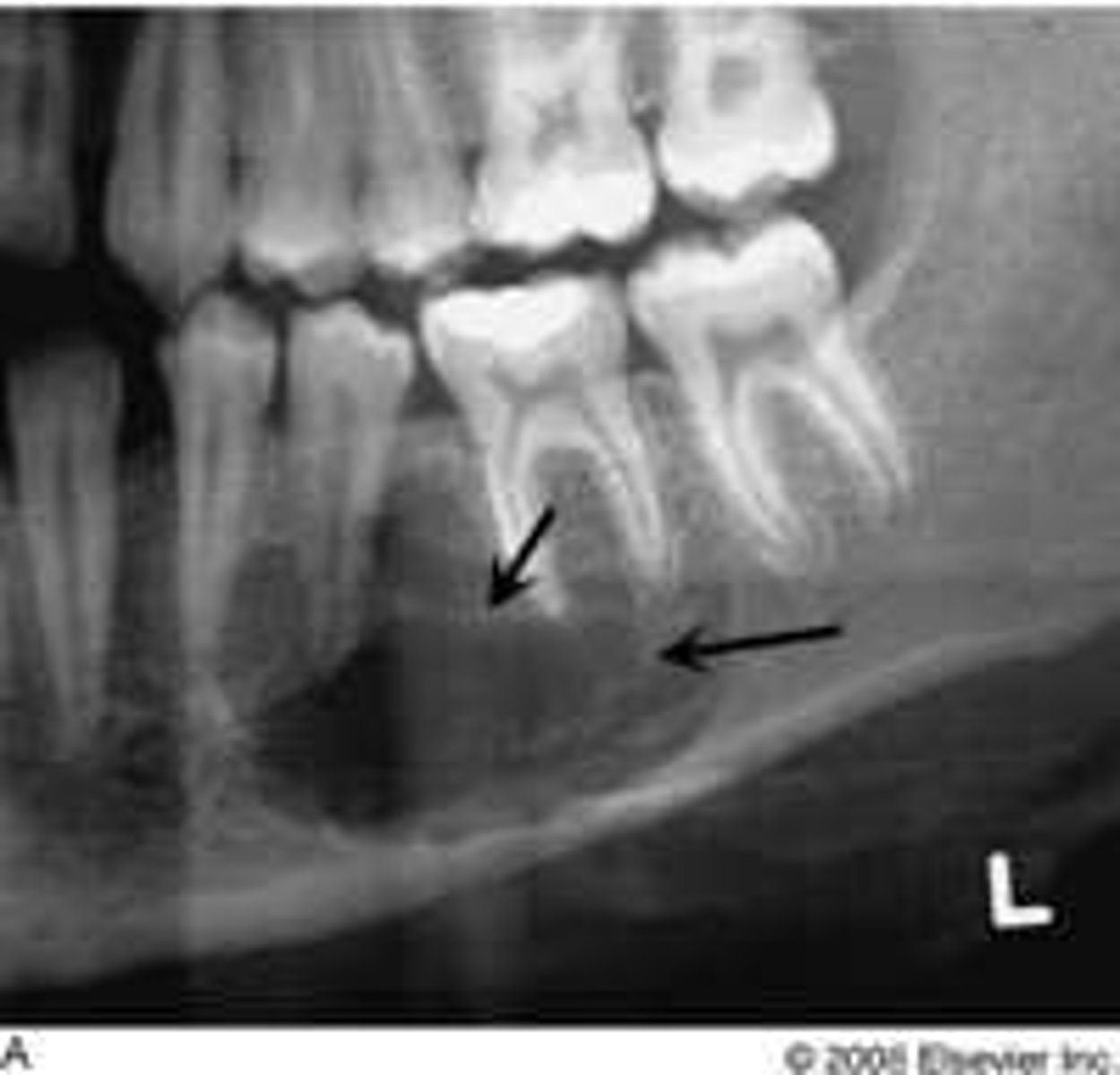
Clinical Features of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
under 30
predilection females
rapid bone swelling
pain
tender on palpation
Location of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
mandible
Periphery of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
well-defined
Internal structure of Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
multilocular
Cherubism
inherited developmental abnormality
bilateral enlargement of jaws
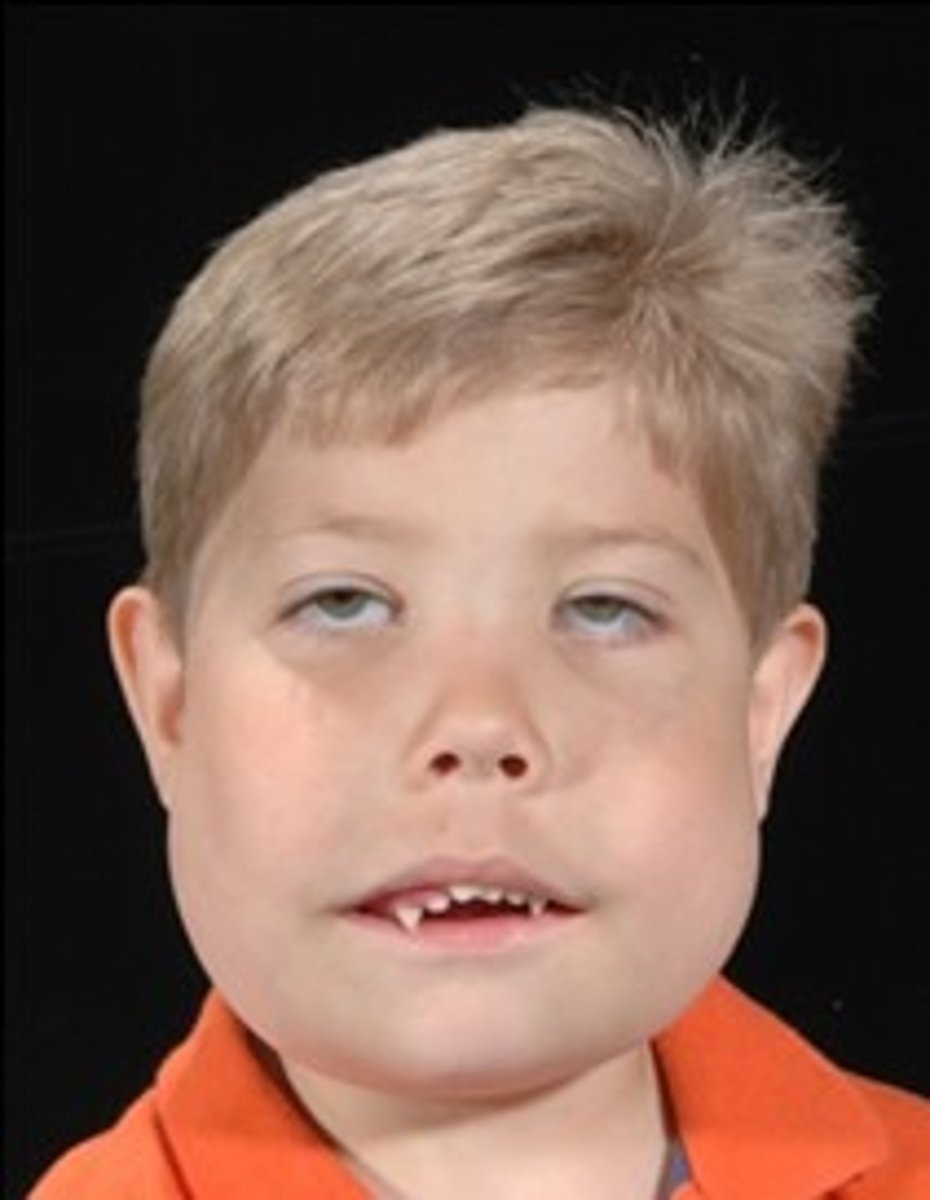
Simple Bone Cavity
well-delineated, unilocular radiolucency