5.2 Moving blood through the body
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Chambers
The heart consists of four muscular chambers.
Septum: separates the two chambers on the left hand side from the two on the right.
Atria: upper chambers, receive blood transporting it to the ventricles,
Ventricles: lower chambers, pump blood out to the body.
Valves
The four valves control the direction of the blood.
Chordae tendinae - strong tendons that hold the atrioventricular valves in position.
Veins - contain valves to prevent the back-flow of blood.
Valves snapping shut causes the heart’s thumping sounds.
Blood vessels
Arteries - muscular blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart.
Arterioles - small arteries; direct blood flow to various tissues.
Capillaries - microscopic blood vessels that connect arterioles and venules, enable the exchange of substances between blood and surrounding tissues.
Veins - carry blood towards the heart.
Venules - small veins.
Blood vessel layers
Arteries
Present tunica interna,
Well developed tunica media,
Relatively thin tunica externa.
Capillaries
Present tunica interna,
No tunica media,
No tunica externa.
Veins
Present tunica interna,
Relatively thin tunica media,
Well developed tunica externa.
Artery structure
Elastic walls - expansion and contraction with changes in blood pressure.
Muscular walls - allows vasoconstriction and vasodilation to control blood flow.
Narrow lumen size - helps maintain high pressure in arteries.
Vein structure
Walls are not elastic or muscular.
Thin walls.
Valves present - prevent backflow of blood.
Large lumen size.
Double circulation
All mammals including humans have double circulation:
Systematic circulation,
Pulmonary circulation.
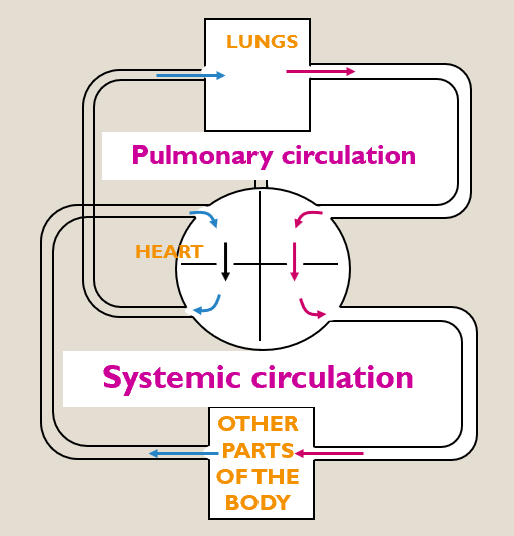
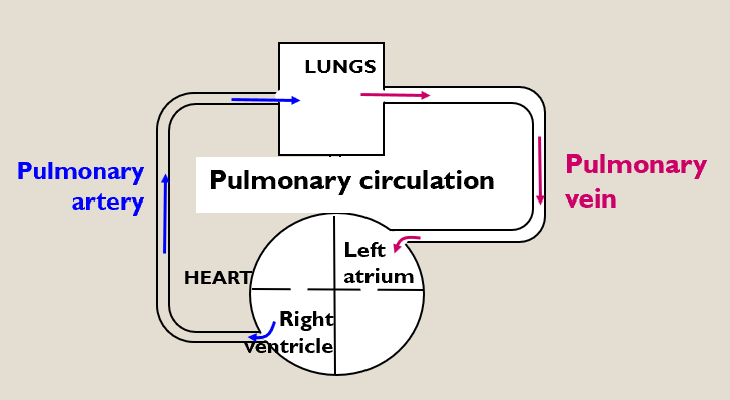
Pulmonary circulation
Takes deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the left atrium.
Right ventricle - the pump for the pulmonary circulation.
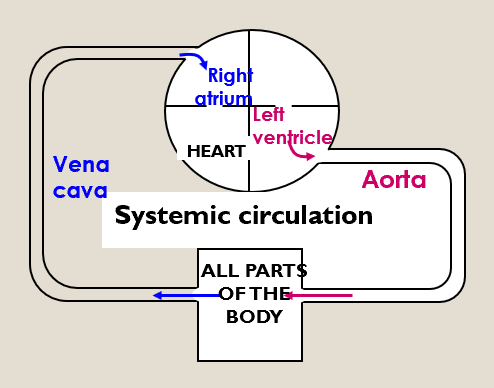
Systematic circulation
Takes oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to all the tissues of the body and returns deoxygenated blood to the right atrium.
Left ventricle - the pump for the systematic circulation.
Cardiac cycle
Also known as the heart beat - the sequence of events that occurs in one complete beat of the heart.
Diastole: the filling phase of the cycle when heart muscle relaxes,
Systole: pumping phase of cycle when heart muscle contracts.
Rate of blood flow
Depends on:
Vasoconstriction and vasodilation of blood vessels throughout the body,
How fast the heart is beating,
How much blood is pumped with each beat.
Heart rate: beats per minute.
Stroke volume: volume (mL) of blood forced from a ventricle with each contraction.
Cardiac output: the volume (mL) of blood leaving one of the ventricles every minute.