Lecture Exam #4 Review
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BIO 047
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
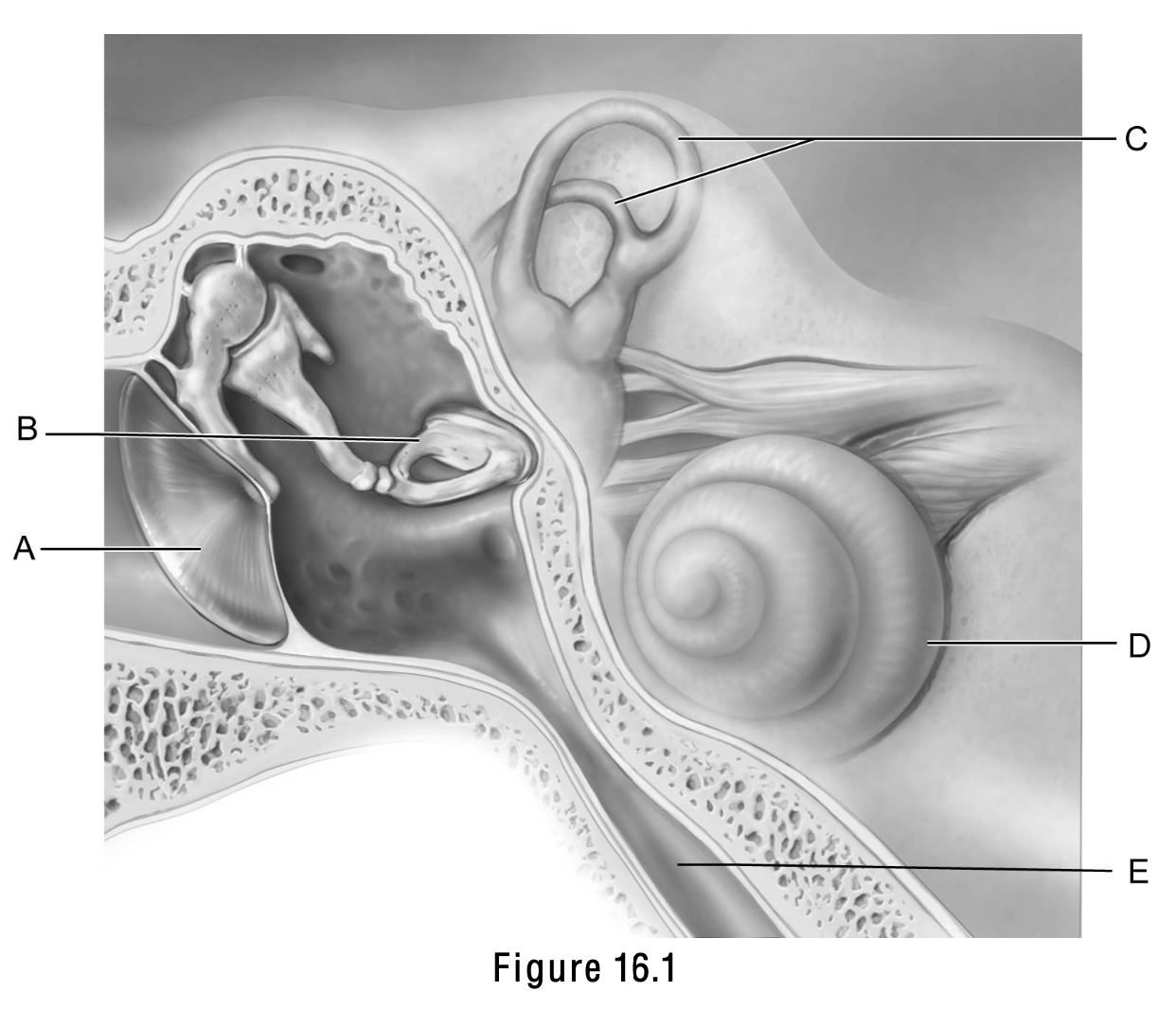
This structure is important in equalizing air pressure on both sides of the eardrum
E
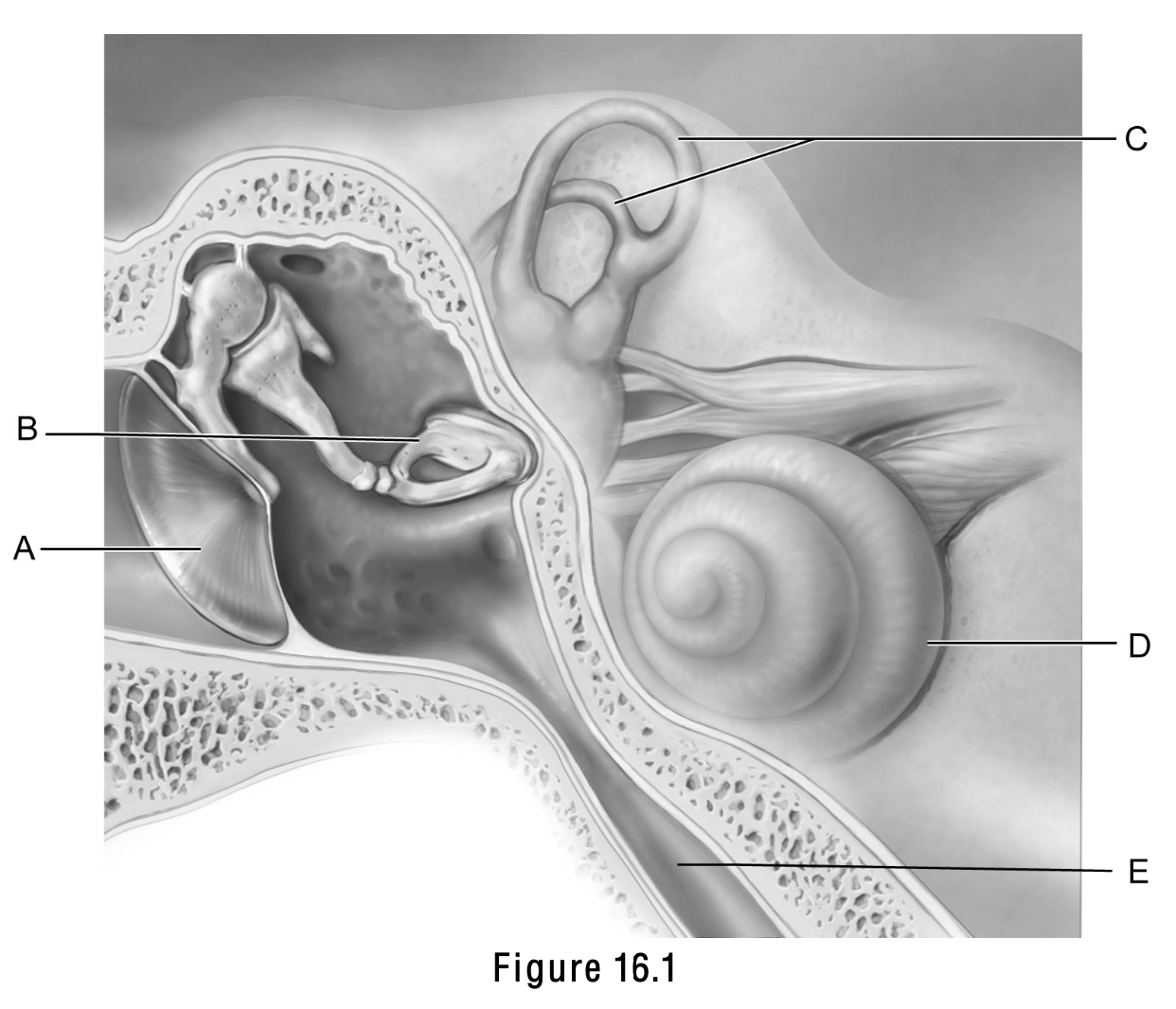
This structure is the boundary between the external and middle ear.
A
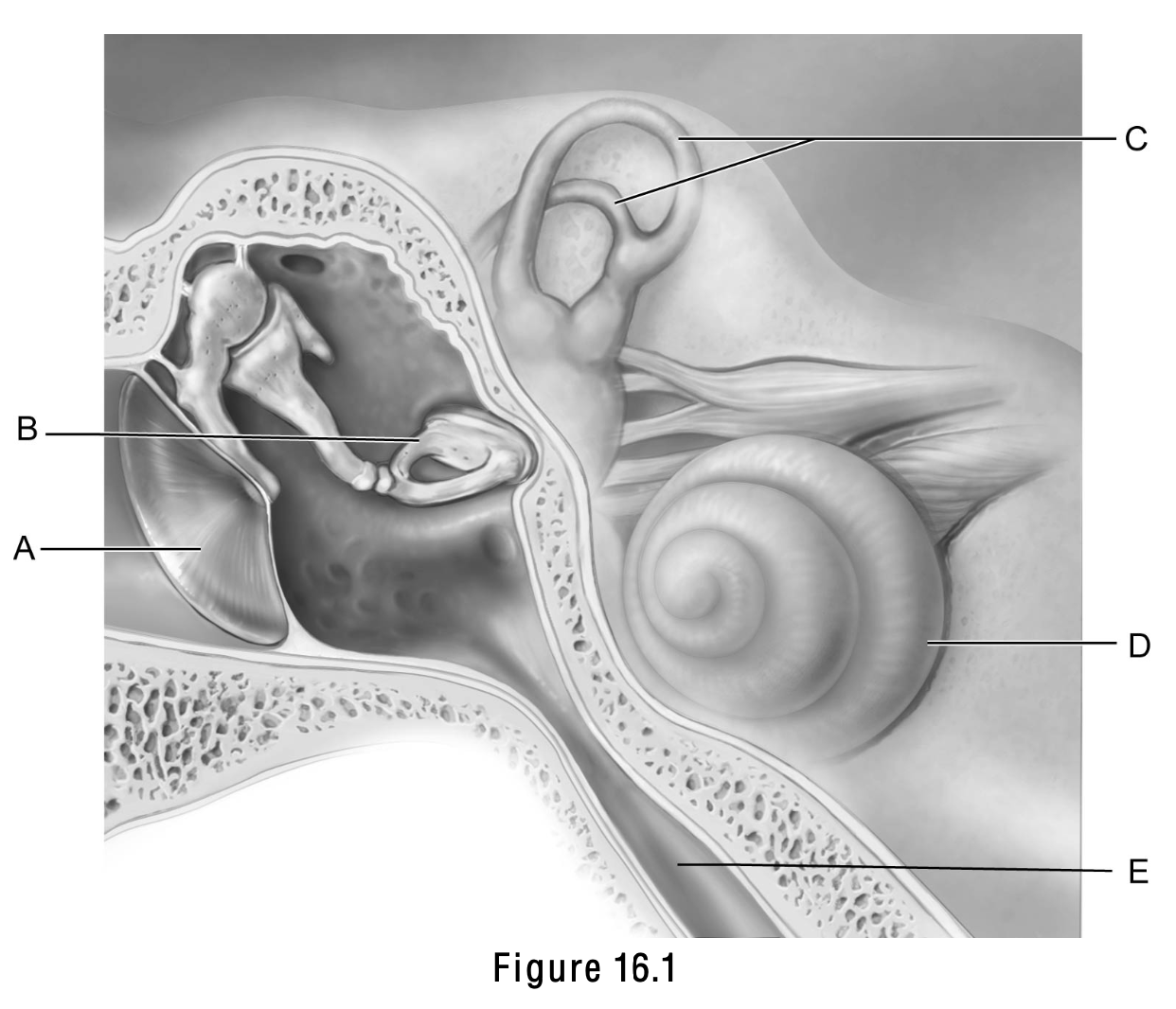
This structure is called the cochlea.
D
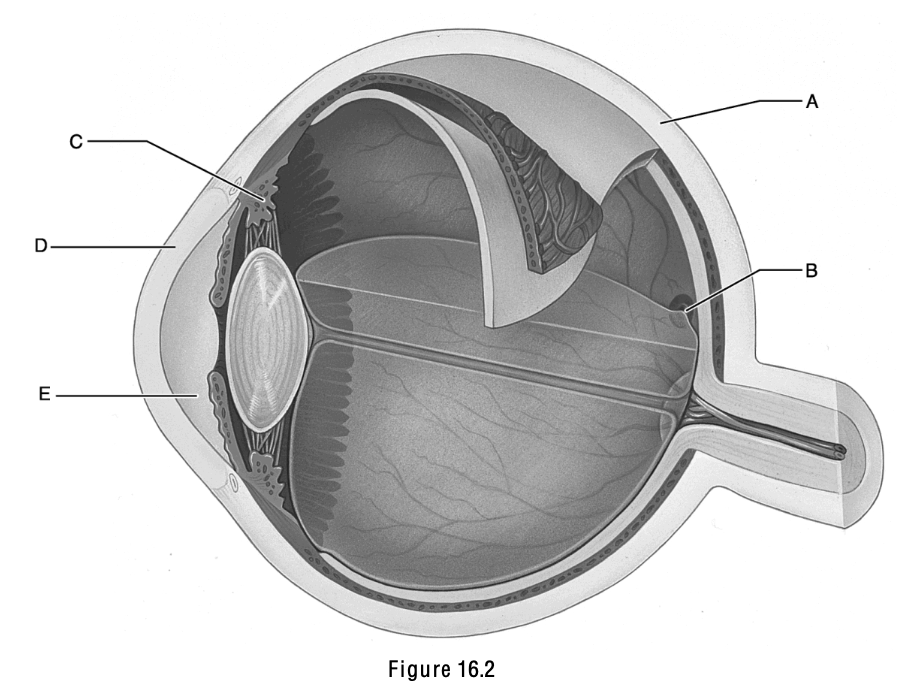
Transparent portion of the fibrous layer.
Cornea
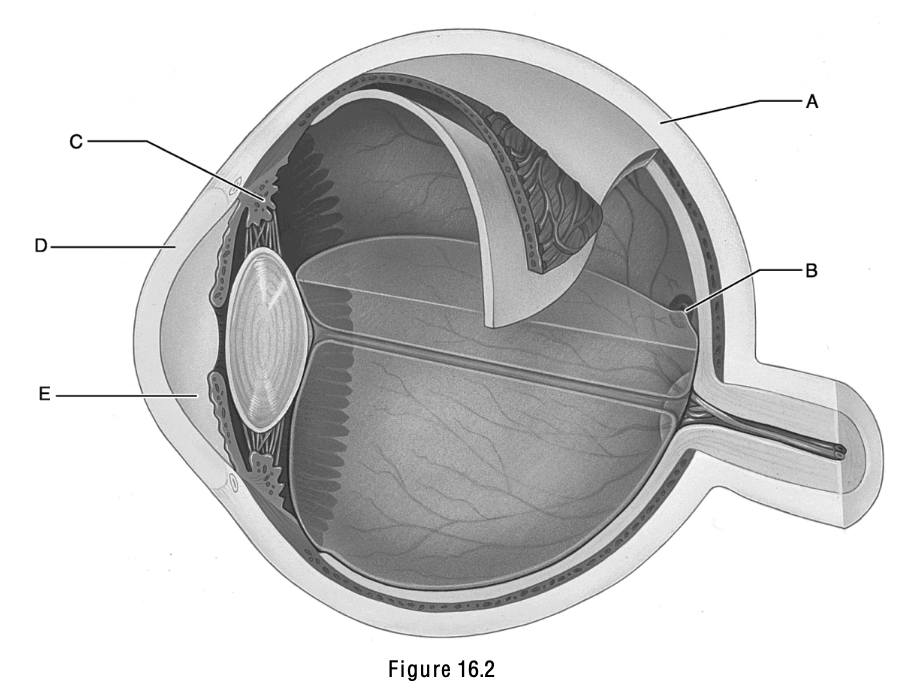
This structure is the ciliary body.
C
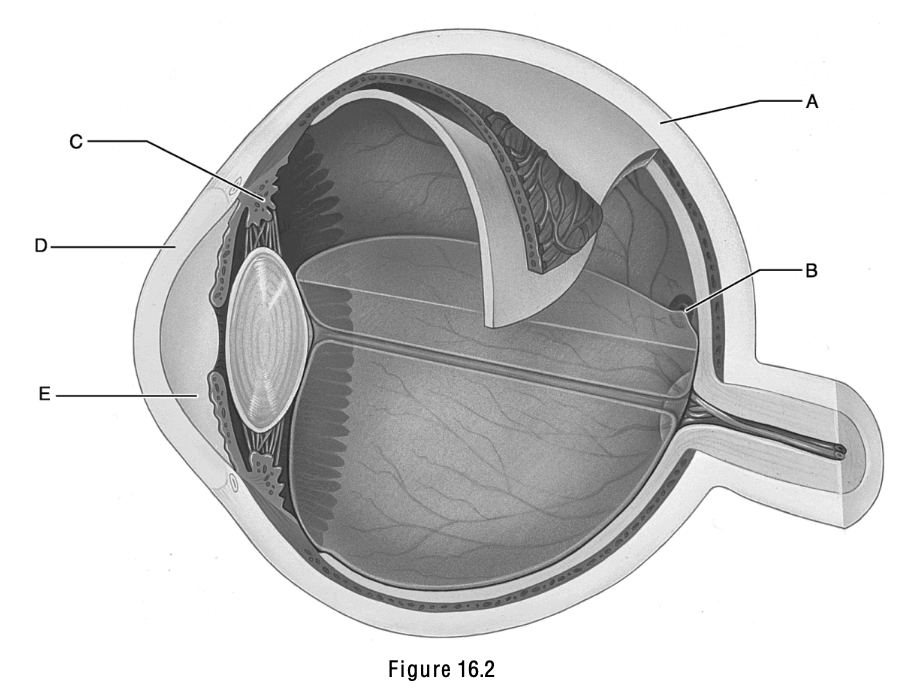
This is the anterior segment, which is filled with aqueous humor.
E
T or F? The superior oblique muscle of the eye enables the eye to look upward and laterally.
False
T or F? The vestibule of the ear lies between the semicircular canals and the cochlea
True
T or F? Lacrimal fluid is produced by the lacrimal sac in the medial canthus of the eye.
False
Which of the following structures in the eye are pigmented?
a. lens
b. the cornea
c. the retina
d. sclera
c. the retina
Which of the following areas has the highest concentration of cones?
a. the fovea centralis
b. the optic disc
c. the ora serrata retinae
d. the macula lutea
a. the fovea centralis
Which of the following statements does NOT correctly describe the spiral organ of Corti?
a. The “hairs” of the receptor cells are embedded in the tectorial membrane.
b. The tectorial membrane bends with vibrations, whereas the basilar membrane is rigid and fixed.
c. The spiral organ is part of the cochlear duct, whereas the basilar membrane is rigid and fixed.
d. High-frequency sounds stimulate hair cells at the basal end of the basilar membrane.
b. The tectorial membrane bends with vibrations, whereas the basilar membrane is rigid and fixed.
Hair cells are receptor cells for
a. fine touch
b. both hearing and equilibrium
c. smell
d. taste
b. both hearing and equilibrium
The middle ear cavity is normally filled with
a. endolymph
b. mucus
c. perilymph
d. air
d. air
The cristae in the inner ear contain the receptors for
a. rotational equilibrium
b. static equilibrium
c. all aspects of equilibrium
d. all aspects of hearing
a. rotational equilibrium
The oil component found in tears is produced by the
a. lacrimal glands
b. endocrine glands
c. conjunctiva
d. tarsal glands
d. tarsal glands
Which of the following controls the amount of light entering the eye?
a. levator palpebrae
b. ciliary muscle
c. dilator pupillae
d. medial rectus
c. dilator pupillae
The ossicle that is shaped like the stirrup of a saddle is the
a. incus
b. tympanic membrane
c. malleus
d. stapes
d. stapes
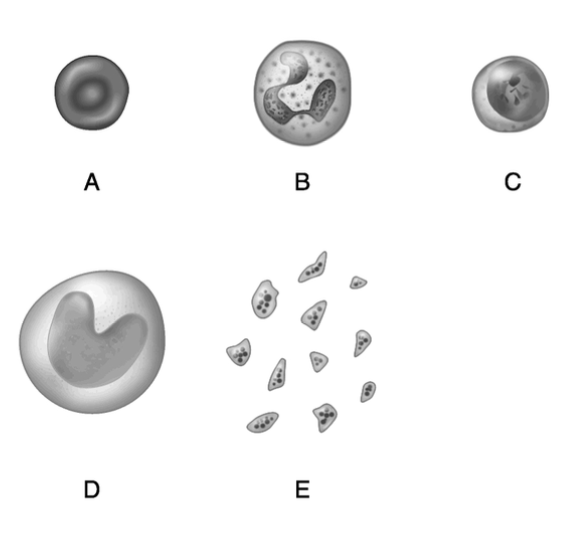
Packed with molecules of hemoglobin.
A
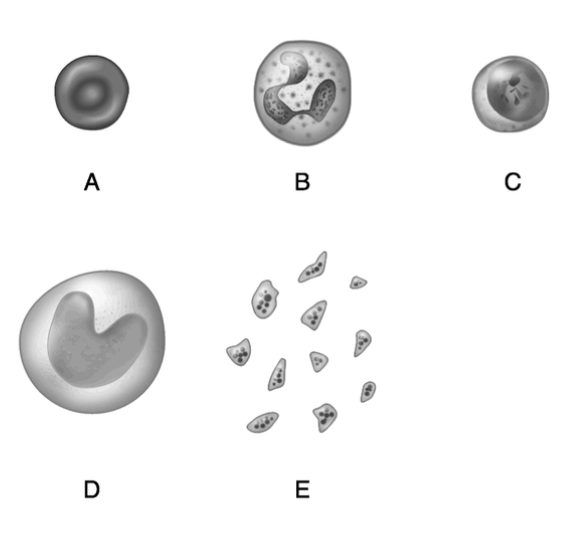
Important in blood clotting.
E
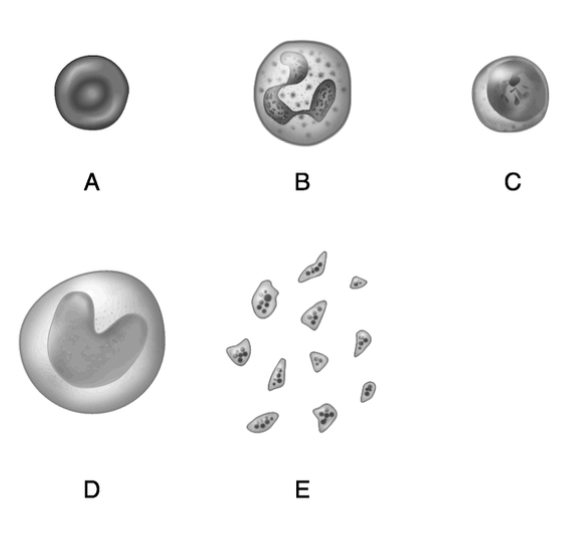
Produces antibodies.
C
T or F? Hematocrit is the percentage of blood consisting of erythrocytes.
True
T or F? The least abundant type of leukocyte is the monocyte.
False
T or F? Erythrocytes and neutrophils both arise from myeloid stem cells.
True
T or F? The reticulocytes secrete the reticular fiber network of bone marrow.
False
The most common formed elements in the blood are
a. platelets
b. erythrocytes
c. macrophages
d. leukocytes
b. erythrocytes
What type of white blood cell increases dramatically during parasitic infections or allergic reactions?
a. basophil
b. monocyte
c. eosinophil
d. neutrophil
c. eosinophil
Which white blood cells contain granules of histamine?
a. neutrophils
b. eosinophils
c. basophils
d. lymphocytes
c. basophils
Which of the following cells develop into macrophages?
a. lymphocytes
b. neutrophils
c. basophils
d. monocytes
d. monocytes
Which of the following is NOT a committed cell in a blood cell line?
a. blood stem cell
b. megakaryoblast
c. myeloblast
d. proerythroblast
a. blood stem cell
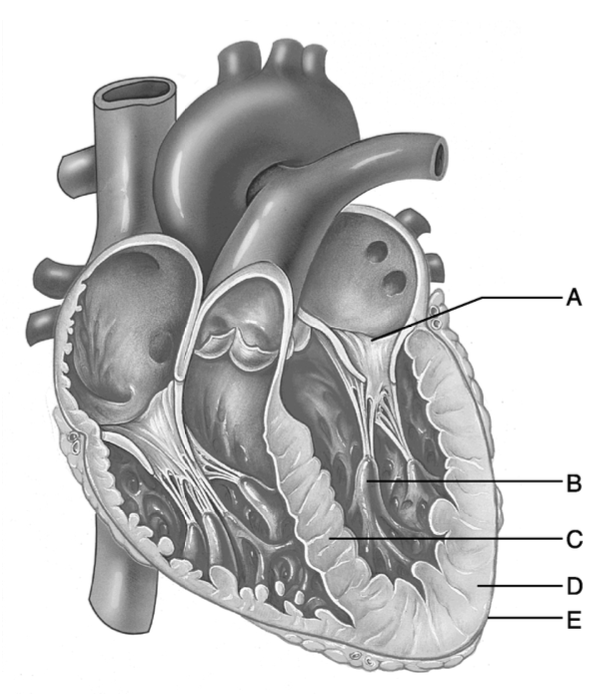
Anchor points on the myocardium for chordae tendinae.
B
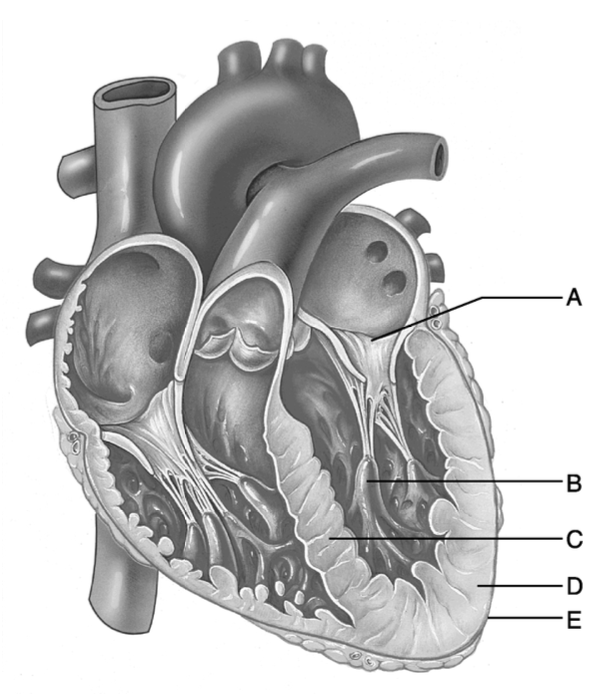
This structure contains the bundle branches.
C
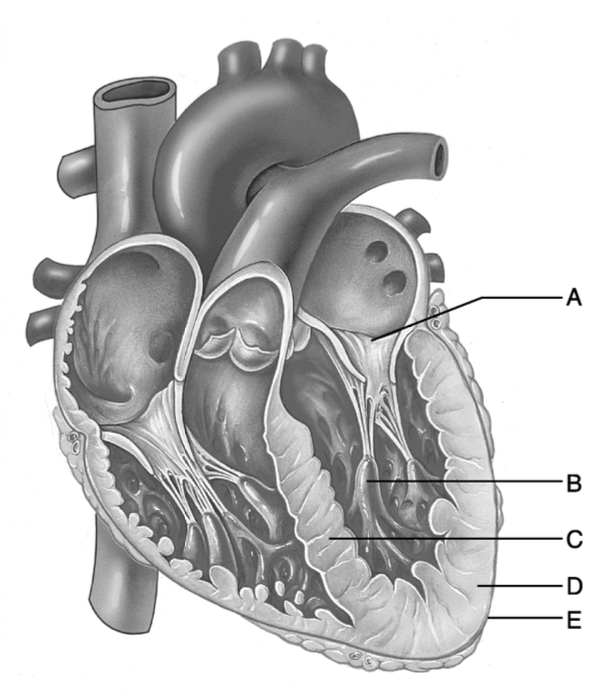
This structure prevents backflow of blood from the ventricle to the atrium.
A
T or F? Papillary muscles are horizontal ridges in the walls of the atrium.
False
T or F? Contraction of the ventricles begins at the apex and proceeds superiorly.
True
T or F? The right and left coronary arteries arise from the descending aorta.
False
The pericardial cavity lies between
a. the fibrous pericardium and the diaphragm
b. the serous pericardium and the epicardium
c. the parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium
d. the fibrous pericardium and the parietal pericardium
c. the parietal pericardium and the visceral pericardium
The inner endothelial layer that lines the heart is the
a. endocardium
b. epicardium
c. myocardium
d. pericardium
a. endocardium
Which of the following vessels does NOT carry oxygen-poor blood to the right ventricle?
a. the pulmonary vein
b. the superior vena cava
c. the inferior vena cava
d. the coronary sinus
a. the pulmonary vein
The right ventricle pumps blood into which vessel?
a. the pulmonary trunk
b. the superior vena cava
c. the aorta
d. the pulmonary vein
a. the pulmonary trunk
A drop of blood returning to the heart from the head region would enter the heart through which vessel?
a. a pulmonary vein
b. the superior vena cava
c. the coronary sinus
d. the inferior vena cava
c. the coronary sinus
The cusps of the valves of the heart are made of
a. modified epicardium
b. endocardium
c. myocardium
d. epicardium
b. endocardium
Semilunar valves are located
a. between the ventricles and the great arteries
b. between the great veins and the atria
c. between the atria and the ventricles
d. only between the left ventricle and the aorta
a. between the ventricles and the great arteries
Which vessel returns most of the venous blood from the heart to the right atrium?
a. the coronary sinus
b. the posterior interventricular vein
c. the anterior cardiac vein
d. the great cardiac vein
a. the coronary sinus
During ventricular systole, blood is
a. forced from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary trunk
b. flowing from the systemic and pulmonary circuits into both the atria and ventricles
c. not flowing into or out of the heart
d. forced from the atria into the ventricles
a. forced from the ventricles into the aorta and pulmonary trunk
The epicardium is the same as the
a. visceral layer of serous pericardium
b. fibrous pericardium
c. endocardium
d. pericardium
a. visceral layer of serous pericardium
The heart chamber that pumps oxygenated blood around the systemic circuit is the
a. right ventricle
b. left atrium
c. left ventricle
d. right atrium
c. left ventricle
If the beating heart makes a “lub-dup” sound, the “dup” sound is caused by
a. vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut
b. a stetonic atrioventircular valve
c. the apex of the heart hitting the anterior chest wall
d. the large force of the contracting ventricles
a. vibrations that result from the semilunar valves slamming shut
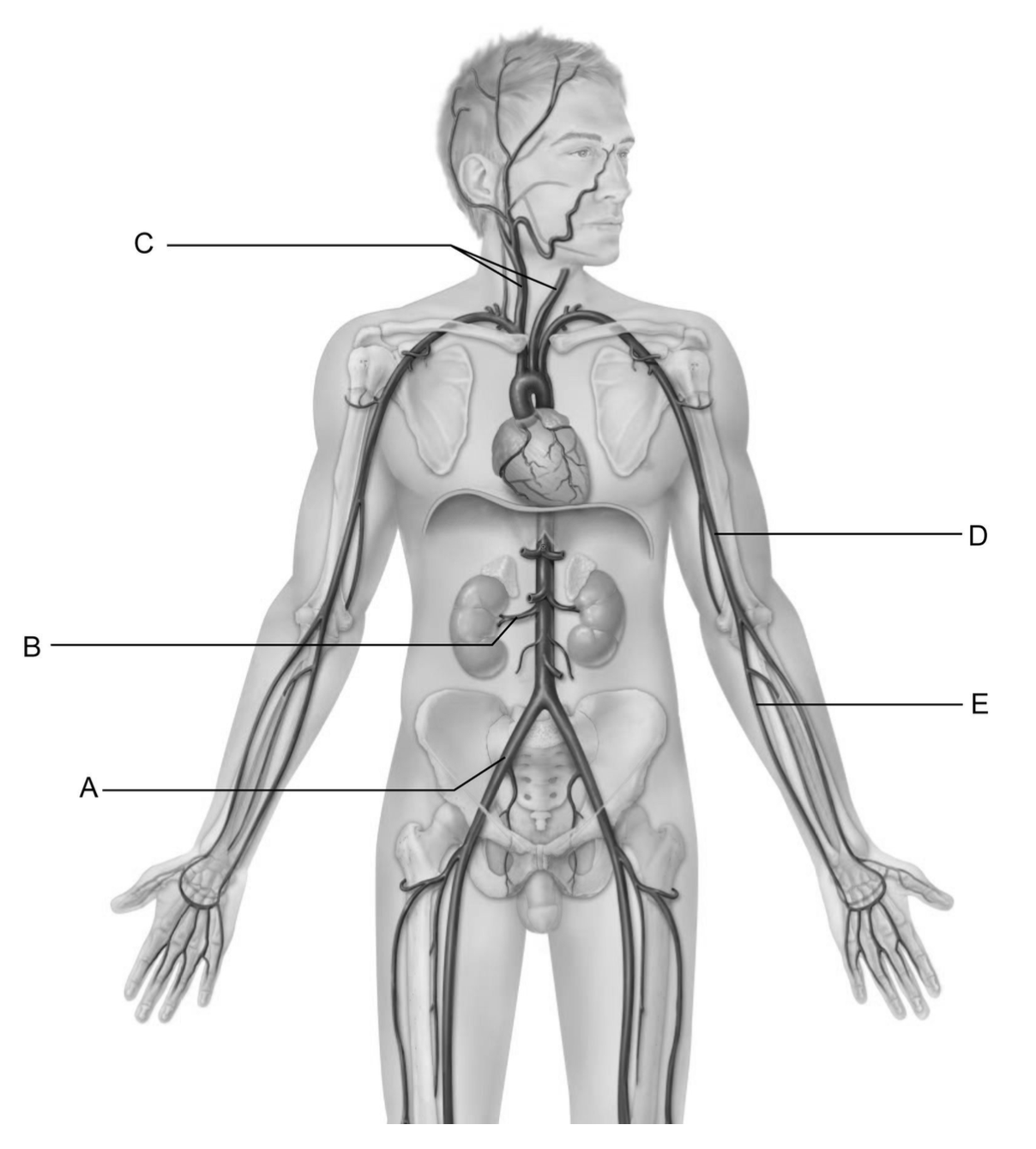
These vessels are the common carotid arteries.
C
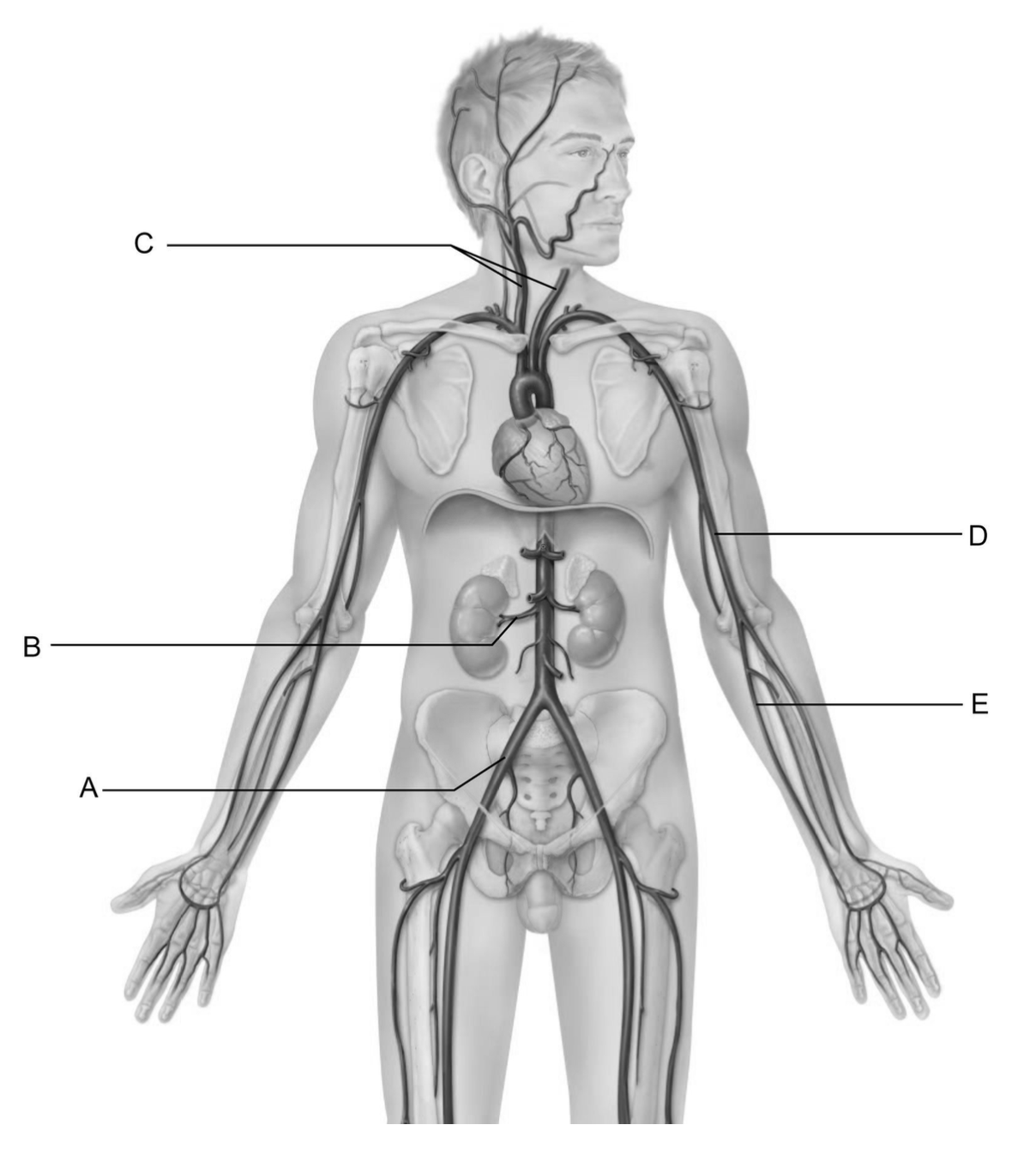
This vessel is the common iliac artery.
A
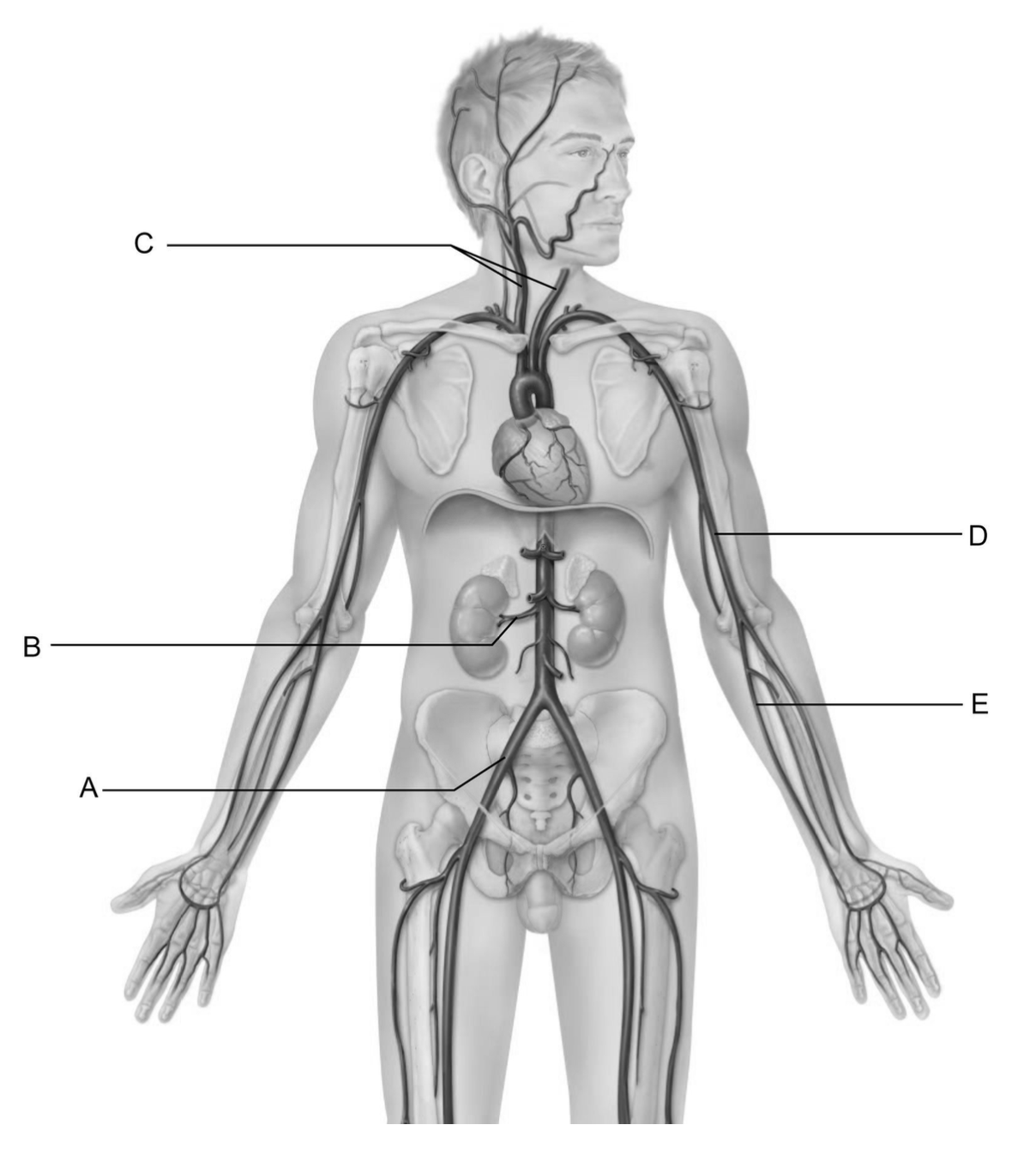
This vessel is the renal artery.
B
T or F? All arteries carry oxygen-rich blood, whereas veins carry oxygen-poor blood.
False
T or F? Arterioles and venules have a vasa vasorum to provide nutrients to their outer walls, whereas the inner walls receive nutrients from blood in the lumen.
False
T or F? The middle and posterior cerebral arteries are connected by the posterior communicating arteries.
True
Which layer of blood vessels contains smooth muscle tissue?
a. tunica externa
b. tunica media
c. tunica intima
d. tunica adventitia
b. tunica media
Blood pressure is highest in the
a. elastic arteries
b. arterioles
c. capillaries
d. veins
a. elastic arteries
The hepatic portal system has two distinct capillary beds separated by a portal vein. What are the functions of these two capillary beds?
a. the first provides oxygen to the liver, and the second picks up nutrients from the liver.
b. the first nourishes the digestive tube, and the second picks up nutrients from the digestive tube
c. the first picks up digested nutrients, and the second delivers these nutrients to liver cells.
d. the first picks up toxins from the liver, and the second delivers them to the digestive tube for detoxification
c. the first picks up digested nutrients, and the second delivers these nutrients to liver cells.
Which vessel is most commonly used to bypass a damaged coronary artery in coronary surgery?
a. internal thoracic artery
b. femoral artery
c. azygos vein
d. great saphenous vein
d. great saphenous vein
Which branch (or branches) of the abdominal aorta supplies the stomach?
a. inferior phrenic arteries
b. suprarenal arteries
c. superior mesenteric artery
d. celiac trunk
d. celiac trunk
The abdominal aorta divides at its distal end into which arteries?
a. the femoral arteries
b. the common iliac arteries
c. the external iliac arteries
d. the internal iliac arteries
b. the common iliac arteries
The correct sequence of the three vessels branching from the aortic arch is
a. brachiocephalic, left subclavian, left common carotid
b. brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
c. left common carotid, left subclavian, brachiocephalic
d. left subclavian, left common carotid, brachiocephalic
b. brachiocephalic, left common carotid, left subclavian
Fenestrated capillaries
a. permit the movement of very few molecules
b. occur in most of the organs of the body
c. have pores in their walls
d. are located in the CNS
c. have pores in their walls
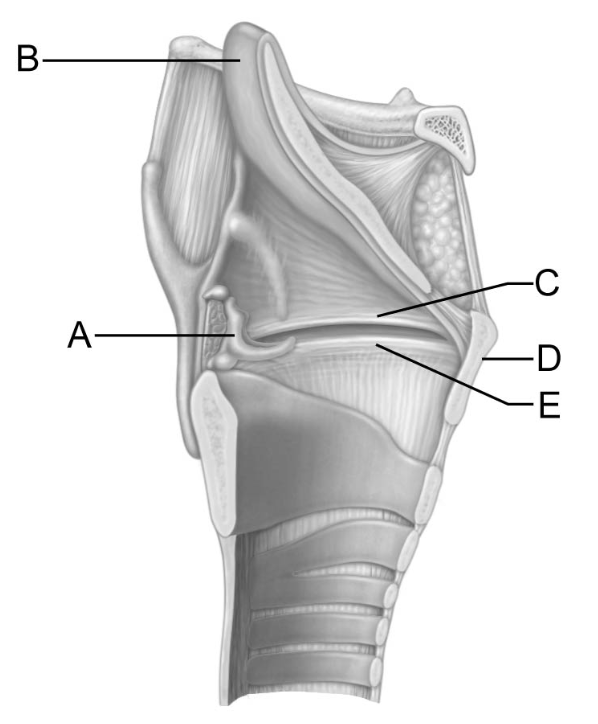
This structure has a laryngeal prominence that is also known as the “Adam’s apple"
D
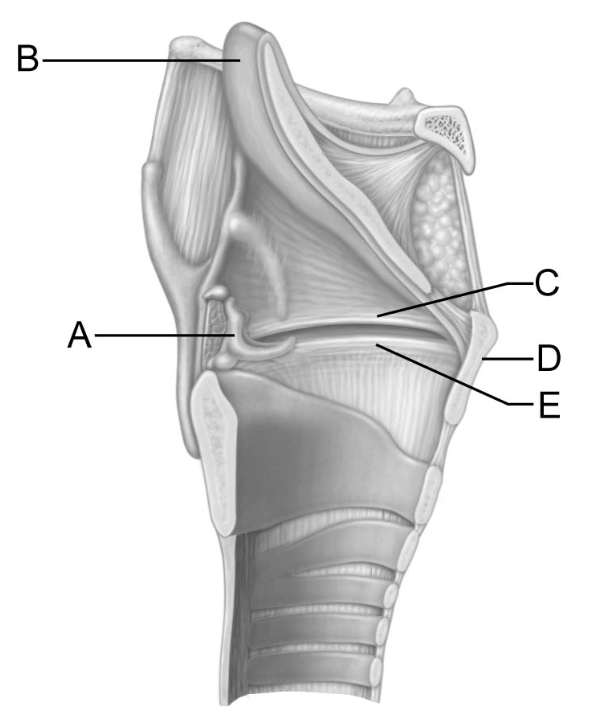
This structure is the vocal fold, or true vocal cord.
E
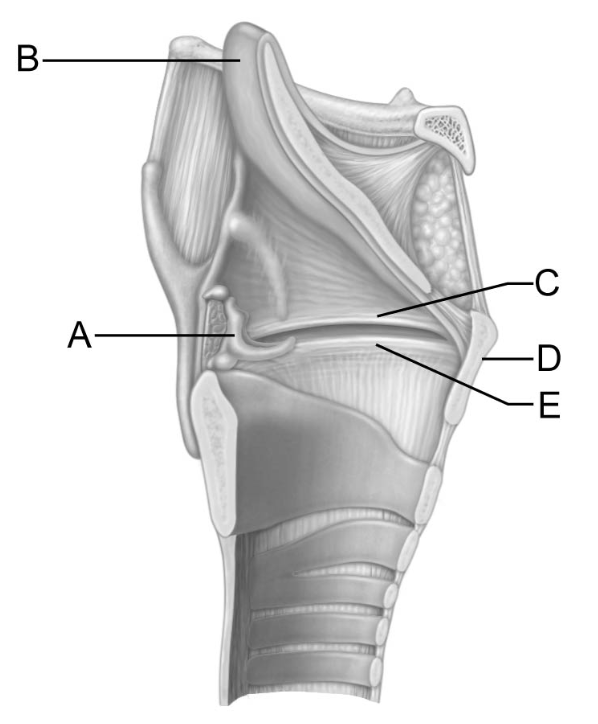
The action of this structure keeps food out of the lower respiratory tubes.
B
T or F? The trachea, bronchi and bronchioles are all located within the lungs.
False
T or F? Changes in the size of the thoracic cavity bring about inspiration and expiration.
True
T or F? Type II alveolar cells produce pleural fluid to keep the walls of the alveoli from sticking together.
False
T or F? The number of secondary, or lobar, bronchi is a distinguishing characteristic of the right and left lungs.
True
What type os epithelium occurs in the respiratory mucosa?
a. simple squamous epithelium
b. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
c. stratified squamous epithelium
d. simple columnar epithelium
b. pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Most foreign substances in inspired air fail to reach the lungs because of the
a. action of the epiglottis
b. abundant blood supply to the nasal mucosa
c. ciliated epithelium and mucus that line the respiratory passages.
d. porous structure of the nasal conchae
c. ciliated epithelium and mucus that line the respiratory passages.
The trachealis muscle
a. initiates the cough reflex
b. controls the length and tension of the vocal cords
c. raises the larynx when swallowing
d. constricts the trachea
d. constricts the trachea
Supportive cartilage disappears from the bronchial tree at the level of the
a. alveolar duct
b. respiratory bronchiole
c. lobar bronchi
d. bronchioles
d. bronchioles
Alveolar pores
a. allow gases to transfer from the alveoli to the blood
b. allow pleural fluid to enter the alveoli and keep their walls from sticking together
c. equalize air pressure throughout the lung
d. are the openings between the alveolar duct and the alveolus
d. are the openings between the alveolar duct and the alveolus
When the diaphragm contracts, the size of the thoracic cavity _____, the pressure inside the thoracic cavity ____, and air flows ____ the lungs.
a. increases, drops, out of
b. decreases, rises, into
c. decreases, drops, out of
d. increases, drops, into
d. increases, drops, into