periodicity period 3
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of sodium with oxygen. State symbols required.
Na(s) + ½ O₂ (g) →Na₂O (s)
What would you observe during the reaction of sodium with oxygen.
Yellow flame. White solid produced.
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium with oxygen. State symbols required.
Mg(s) + O₂ (g) → MgO (s)
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of aluminium with oxygen. State symbols required
2Al(s) + 1.5 O₂ (g) → Al₂O₃ (s)
What would you observe during the reaction of aluminium with oxygen.
Bright white flame
White solid produced
What type of structure and bonding does aluminium oxide have?
Giant ionic
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of silicon with oxygen. State symbols required.
Si(s) + O₂ (g) → SiO₂ (s)
What type of structure and bonding does silicon dioxide have?
Giant covalent
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of phosphorous with oxygen to produce phosphorous(V) oxide. State symbols required.
4P(s) + 5O₂ (g) → P₄O₁₀ (s)
What would you observe during the reaction of phosphorous with oxygen.
Yellow or white flame
Clouds of white phosphorous oxide produced
What type of structure and bonding does phosphorous(V) oxide have?
Simple molecular
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur with oxygen. State symbols required.
S(s) + O₂ (g) → SO₂ (g)
What would you observe during the reaction of sulphur with oxygen.
Blue flame
bonding does sulphur dioxide have?
Simple molecular
What is the oxidation number of phosphorous in P₄O₁₀?
+5
What shape is SO₂? Give bond angles too.
Bent. 118-119⁰
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of sodium oxide with water. State symbols required.
Predict the pH of the solution formed
Na₂O(s) + H₂O(l) → 2 NaOH (aq)
pH 14
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium oxide with water. State symbols required.
Predict the pH of the solution formed
MgO(s) + H₂O(l) → Mg(OH)₂ (aq)
Sparingly soluble
pH 10
Why does aluminium oxide not dissolve in water?
There are strong electrostatic forces of attraction between Al³⁺ and O²⁻ ions. The lattice enthalpy is greater in magnitude than the hydration enthalpy.
Why does silicon dioxide not dissolve in water?
Giant covalent structure. Strong covalent bonds between atoms.
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of phosphorous(V) oxide with water. State symbols required.
Predict the pH of the solution formed
P₄O₁₀(s) + 6H₂O(l) → 4H₃PO₄(aq)
pH 1
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur dioxide with water. State symbols required.
Predict the pH of the solution formed
SO₂(s) + H₂O(l) → H₂SO₃(aq)
pH 2-3
Write the chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur trioxide with water. State symbols required.
Predict the pH of the solution formed
SO₃(s) + H₂O(l) → H₂SO₄(aq)
pH 1
Which period 3 oxides are acidic?
P₄O₁₀ , SO₂, SO₃
Which period 3 oxide is amphoteric?
Al₂O₃
What is meant by the term 'amphoteric'?
A chemical that can behave both as an acid and a base
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of magnesium oxide with hydrochloric acid
MgO + 2HCl → MgCl₂ + H₂O
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of aluminium oxide with sulphuric acid.
Al₂O₃ + 3H₂SO₄ → Al₂(SO₄)₃ + 3H₂O
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of aluminium oxide with sodium hydroxide
Al₂O₃ + 2NaOH + 3H₂O →2NaAl(OH)₄
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur dioxide with sodium hydroxide to form sodium sulphate(IV)
SO₂ + 2NaOH → Na₂SO₃ + H₂O
Write a chemical equation for the reaction of sulphur trioxide with sodium hydroxide to form sodium sulphate(VI)
SO₃ + 2NaOH → Na₂SO₄ + H₂O
What structure and bonding does NaCl have?
Giant ionic
What is the pH of the solution formed when NaCl is added to water?
pH 7
What is the pH of the solution formed when MgCl₂ is added to water?
pH = 6.5
MgCl₂ forms a slightly acidic solution of pH=6.5 when it dissolves in water because it undergoes partial hydrolysis. Write an equation for the hydrolysis of MgCl₂ and identify the species that causes the decrease in pH.
MgCl₂ + H₂O → Mg(OH)Cl + HCl
Aluminium chloride hydrolyses rapidly in water forming an acidic solution of pH=3. Write a balanced equation for this reaction.
AlCl₃ + 3H₂O → Al(OH)₃ + 3HCl
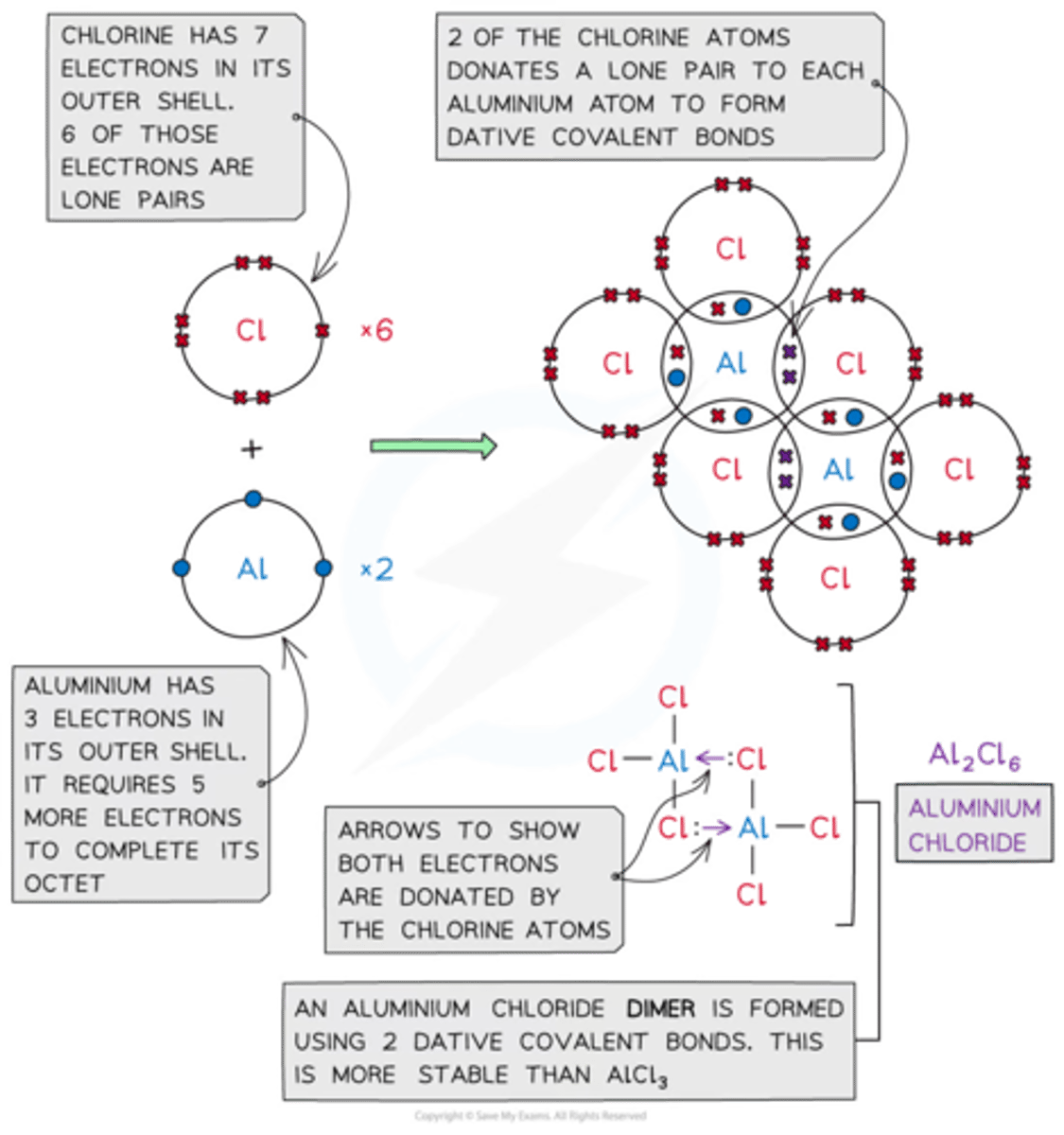
Aluminium chloride can exist as a dimer of Al₂Cl₆. Draw a diagram of this molecule.
See image.
Silicon chloride and Phosphorus chloride will react with water to produce steamy white fumes. Name the substance that causes these steamy fumes.
Hydrogen chloride
SiCl₄ is hydrolysed in water, releasing white fumes of hydrogen chloride gas as well as a white precipitate. Write a chemical equation for this reaction.
SiCl₄ + 2H₂O → SiO₂ + 4HCl
Explain why SiCl₄ is readily hydrolysed but CCl₄ is not.
Silicon has low lying, vacant 3d orbitals which can accept lone pairs from water molecules. Carbon does not have low-lying 3d orbitals as it is in Period 2.
Phosophorus (V) chloride hydrolyses in water to form two acidic products. Write the equation for the reaction including state symbols.
PCl₅ (s) + 4H₂O (l) → H₃PO₄ (aq) + 5HCl (g)
Which period 3 chlorides produce strongly acidic solutions when hydrolysed?
AlCl₃, SiCl₄ and PCl₅