DMN 2: Lesson 99 Circulatory disorders and hepatic infiltrations
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What are some circulatory disorders?
Passive congestion
Congenital portosystemic shunt
Congenital portal vein hypoplasia
Portal hypertension with acquired vascular shunts
Telangiectasis
Passive congestion
Characterized by reduced hepatic outflow due to cardiac dysfunction
Caused by right-sided heart failure which produces elevated pressure in the caudal vena cava that extends to the hepatic vein and its tributaries
High pressure in the hepatic vein leads to centrilobular congestion of sinusoids
What are 2 common causes of right-sided heart failure resulting in hepatic congestion?
Valvular endocardiosis of the tricuspid valve in old dogs
Canine heart worm
Pathogenesis of passive congestion leading to liver disease
congestion —> hypoxia —> centrilobular degeneration —> atrophy and loss of hepatocytes
What does chronic hypoxic injury lead to?
Steatosis (fatty degeneration)
What does passive congestion lead to?
Enhanced lobular pattern (nutmeg liver)
What does the liver look like grossly from passive congestion?
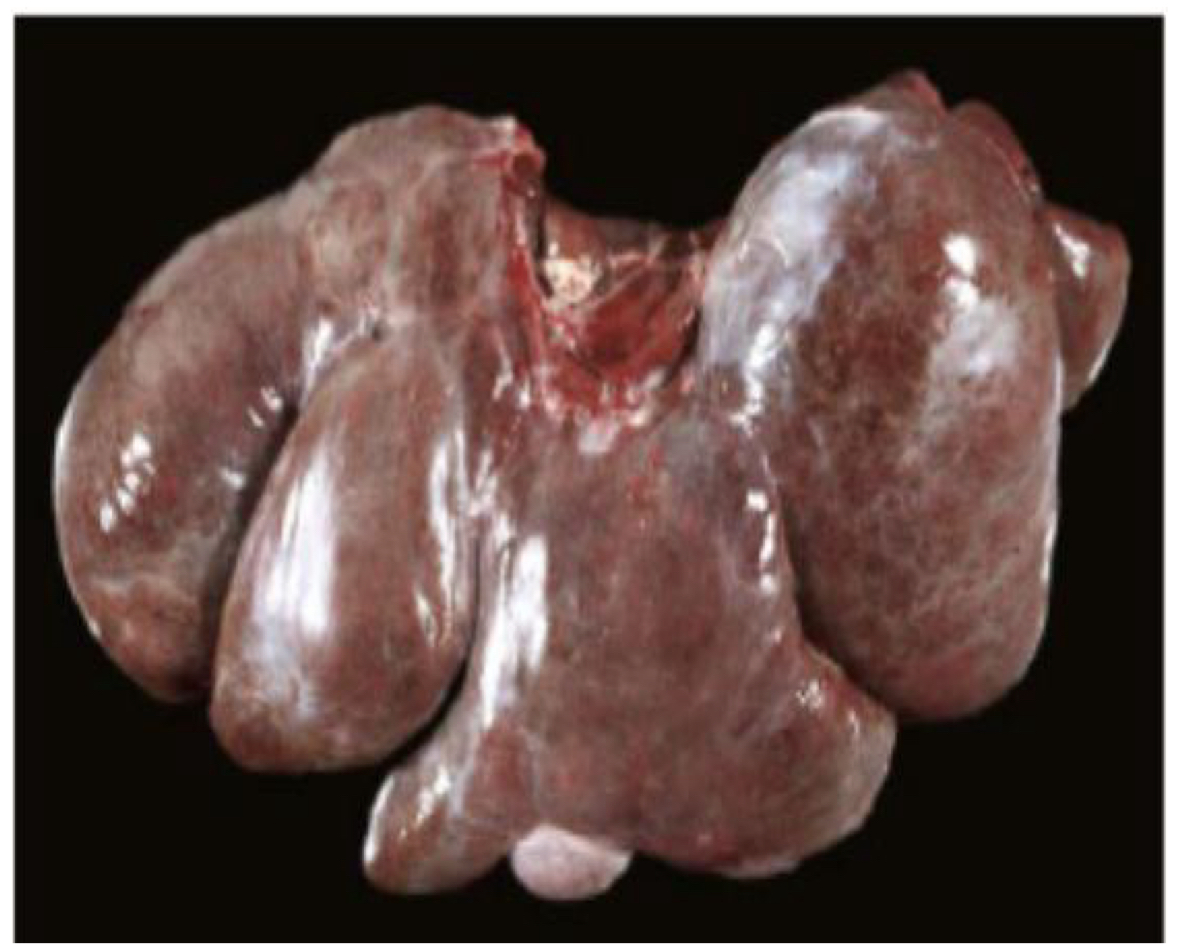
Lobes of the liver are enlarged with rounded edges
What does the cut liver surface look like from passive congestion?
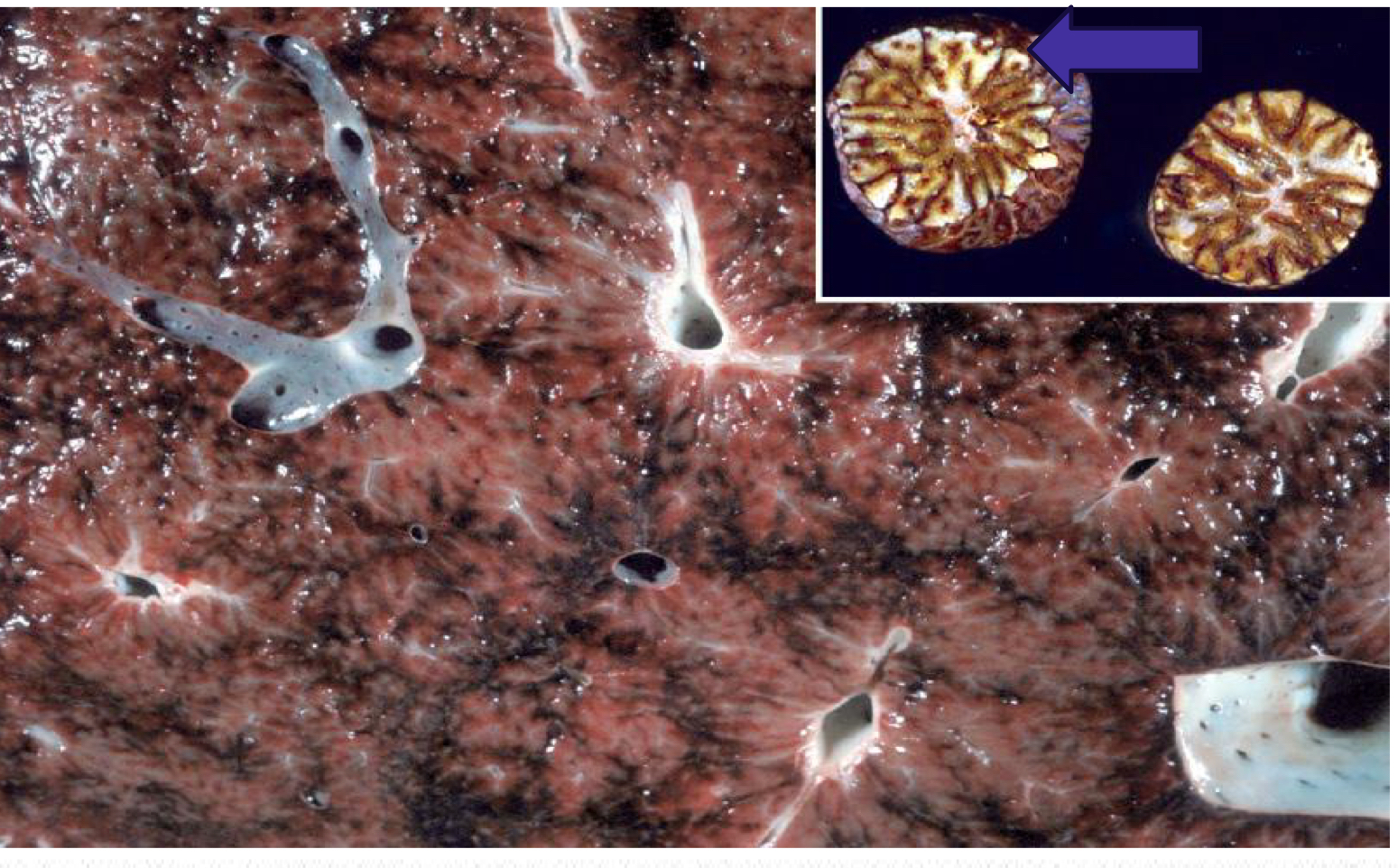
Enhanced lobular pattern - nutmeg liver
What is congenital portosystemic shunt (PSS)?
Abnormal vascular structure that allows portal blood to bypass the liver and drain directly into systemic circulation
How are animals affected by PSS?
Stunted
Frequently develop signs of hepatic encephalopathy due to hyperammonemia
Ataxia
Seizures
Blindness
Head pressing
Gross features and histology of congenital PSS
Grossly the liver is small (micro hepatica)
Single anomalous vessel connecting portal circulation with systemic circulation
Histologically there is lobular atrophy, portal miniaturization with small or absent portal veins, and reduplication of arterioles
What are the 2 types of congenital PSS?
Intrahepatic shunts
Extrahepatic shunts
Intrahepatic PSS
Commonly formed due to failure of closure of the ductus venosus (fetal vessel)
Most common in large breed dogs
Extrahepatic PSS
Portal vein to caudal vena cava anastomosis
Portal vein to azygous vein anastomosis
Most common in small breed dogs and cats
How may congenital PSS affect ammonia metabolism?
Dogs with PSS have abnormal ammonia metabolism —> can result in ammonium biurate crystalluria
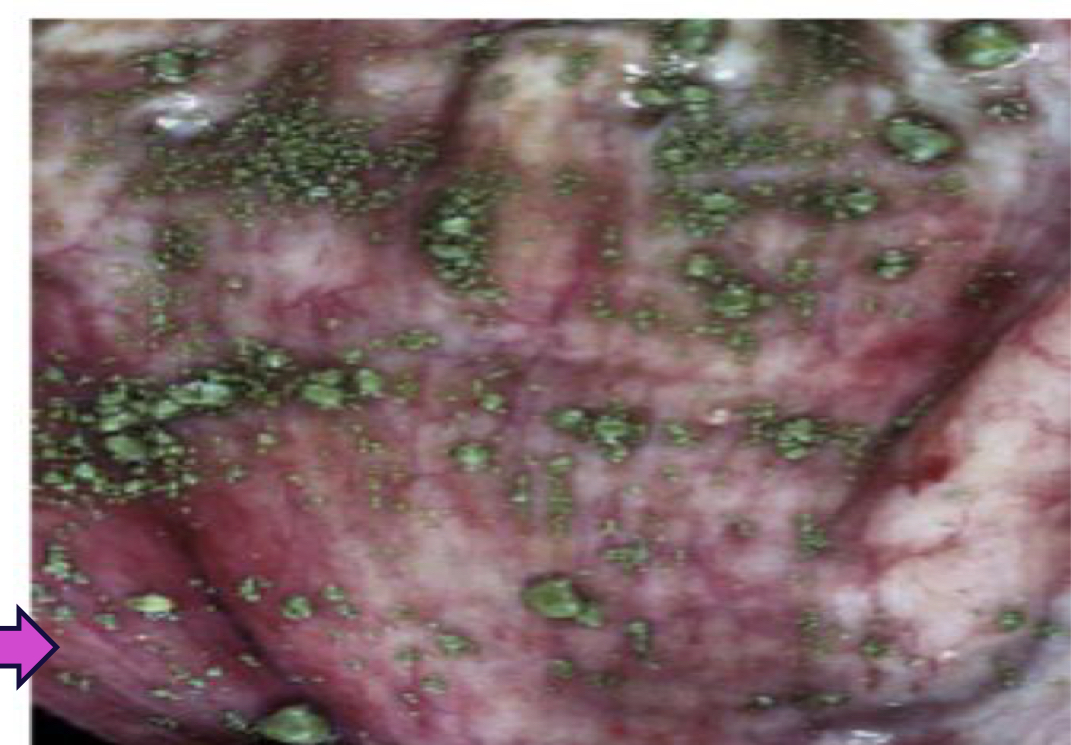
Congenital portal vein hypoplasia (hepatic microvascular dysplasia)
Congenital vascular anomaly of dogs and occasionally cats
Suspected inheritance in small breed dogs such as:
Yorkies
Maltese
Cairn terriers
Tibetan spaniels
Shih-tzus
Javanese
What is congenital portal vein hypoplasia and how does it effect the animal?
Characterized by abnormally small portal veins
Results in diminished hepatic perfusion and portal hypertension
Affected animals typically have micro hepatica and ascites
How to tell apart PSS and congenital portal vein hypoplasia
Indistinguishable
Radiology is recommended
What are some causes of portal hypertension?
Thrombosis or other types of occlusion within the portal vein or hepatic outflow
What are some causes of intrahepatic portal hypertension?
Fibrosis
Nodular regeneration
Lobular remodeling
Veno-occlusive disease
Microvascular dysplasia
Sinusoidal amyloidosis
What can persistent portal hypertension lead to?
Ascites and development of acquired portosystemic shunts
What are some hepatocellular infiltrations?
Amyloid
Copper
Iron
Bile pigments
Lysosomal storage diseases
Glycogen
Lipids
What are the main mechanisms of abnormal intracellular accumulations?
Inadequate removal and degradation
Excessive production of an endogenous substance
Deposition of an abnormal exogenous material
What are the 4 pathways in abnormal cellular infiltrations?
Defect in metabolism (ie lipidosis)
Defect in protein folding or transport (amyloidosis)
Lack of an enzyme resulting in failure to degrade a substrate due to inherited enzyme deficiencies (resulting in storage diseases)
Ingestion/inhalation of indigestible materials (ie accumulation of carbon after inhalation)
What is amyloidosis?
Extracellular deposition of abnormal proteinaceous substance in tissues —> protein misfolding disorder
Consists of 2 forms of proteins
What are the 2 types of proteins in amyloidosis?
Amyloid light chain protein
Amyloid associated protein
What is an amyloid light chain protein?
Derived from abnormal plasma cells secreting of light chain fragments into circulation
What is an amyloid associated protein?
Secreted by liver in response to cytokines
What is hepatic amyloidosis?
Occurs in many species
Commonly a result of secondary (reactive) amyloidosis due to prolonged systemic inflammation (amyloid AA)
What species and breeds has inherited or familial amyloidosis been reported in?
Shar-pei dogs, abyssinian and siamese cats
How does amyloidosis affect the liver?
Grossly, livers are enlarged with rounded edges, friable, and pale
severe cases can lead to hepatic failure
Severely affected livers are friable and susceptible to fracture and hemorrhage
Histological amyloidosis
Amyloid deposition within the space of dissent, portal tracts, and within and around blood vessels
Deposition starts in space of disse and extends into the sinusoids
When severe, this can result in pressure atrophy and necrosis of hepatocytes
What is the special stain used for amyloid?
Congo red
What does accumulation of copper lead to?
Production of reactive oxygen species
What does production of oxygen species cause?
Oxidative injury to mitochondria and cellular membranes and subsequent centrilobular necrosis
Where have disorders of copper metabolism been commonly described?
In dogs, specifically bedlington terriers and Labrador retrievers
Causes canine copper-associated hepatopathy
Canine copper-associated hepatopathy
Common cause of chronic hepatitis in dogs
Pathogenesis is poorly understood - diet? genetics- bedlington terriers (mutation in commd1 gene in this breed)
Pathogenesis of canine copper-associated hepatopathy
Copper accumulates in centrilobular regions and within kupffer cells —> leads to ongoing oxidative injury with hepatocellular necrosis, chronic inflammation, fibrosis, nodular remodeling, and eventual end-state liver
Hepatocellular copper accumulation in sheep
Copper storage is poorly regulated in sheep
Sheep are more susceptible to copper toxicosis
Low dietary molybdenum and sulfur in sheep exacerbates copper toxicosis
Rapid release of copper into blood can precede chronic copper accumulation in the liver resulting in hemolysis
Copper release may be triggered by stress or illness
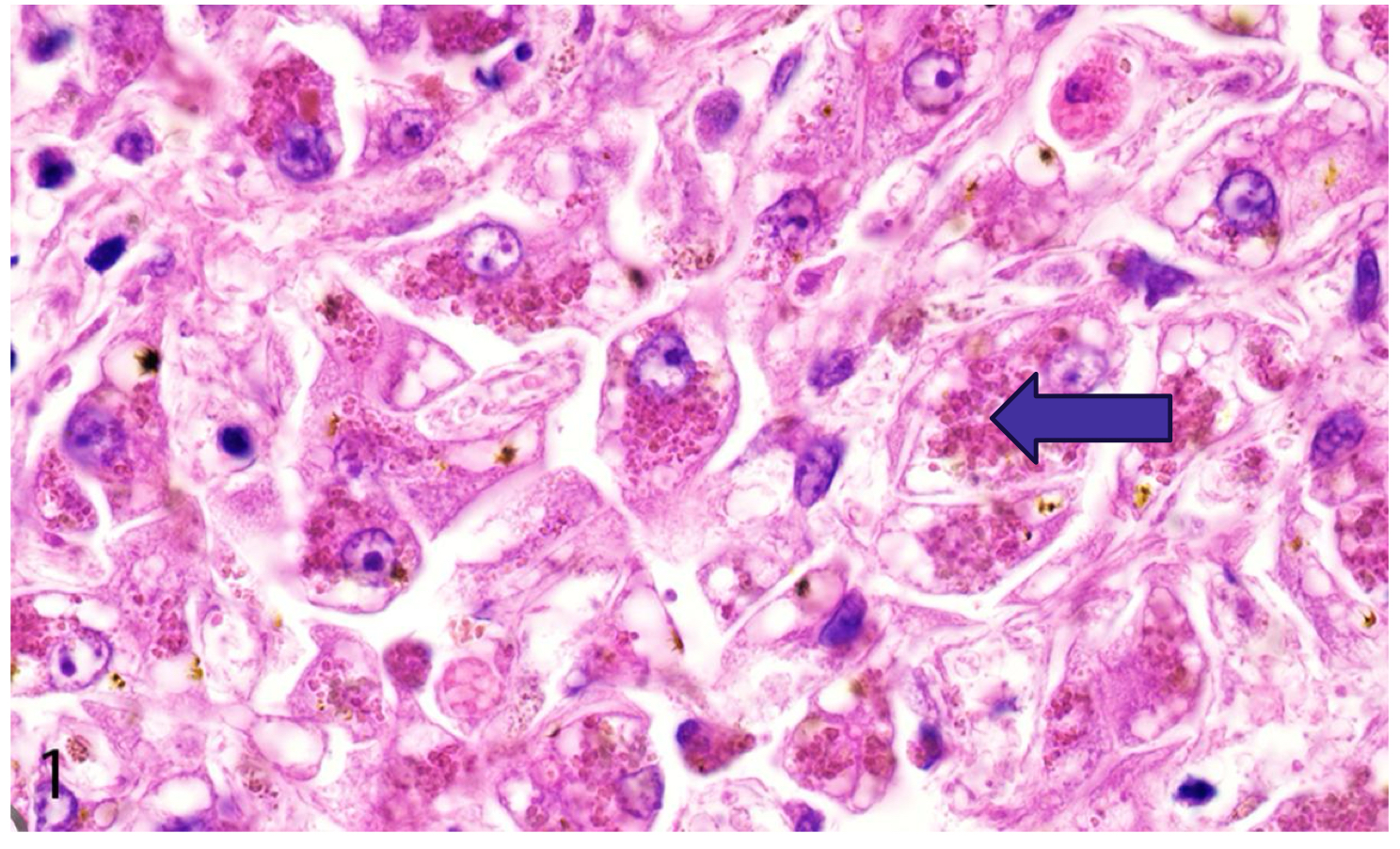
Copper accumulation, red intracytoplasmic granules
How to diagnose hepatocellular copper accumulation
Diagnosis requires biopsy
Rhodanine special stain is used to identify and quantify granules of copper
What is another name for iron storage disease?
Hemochromatosis
What is iron storage disease?
Abnormally increased amount of iron storage within the liver
Inherited condition reported in people, mynah birds, toucans, salers cattle, and horses
Excessive intake of dietary iron in pet birds may also lead to hemochromatosis
Bile pigment hepatocellular accumulation
Bile accumulates in the liver during cholestatic disease
Contributes to hepatocellular injury
Lysosomal storage disease
Large group of rare inherited metabolic disorders that result from defects in lysosomal function
Missing enzymes are inherited as autosomal recessive disorders
What does lysosomal storage disease lead to?
Leads to accumulation of substances within lysosomes which results in cytoplasmic swelling and vacuolization of hepatocytes, macrophages, neurons, and other cell types
Affected animals are usually young
Types of canine degenerative vacuolar hepatopathy
Glycogen-type VH
Lipid-type VH
Glycogen-type VH
Associated with stress, Cushing’s, genetic storage disease (inherited), glucocorticoid administration
Lipid-type VH
Associated with hypoxia, certain toxins, or with metabolic/endocrine disease such as hypothyroidism and diabetes mellitus
Severe cases of VH
Can result in progressive liver injury leading to end-stage liver (cirrhosis)
How to resolve VH?
Requires identification and treatment of the underlying disease
Liver biopsy is often pursued in these patients because of unexplained increase in serum ALP and mildly elevated ALT
Why would ALP be elevated in VH?
due to severe swelling of hepatocytes which can lead to blockage of bile canaliculi and intrahepatic cholestasis
Hepatocellular glycogen accumulation
Liver is enlarged, pale, with enhanced lobules
Diagnosis require liver biopsy
Treatment requires identification of underlying cause
How do steroids affect hepatocellular accumulation?
Glycogen accumulation
Feline hepatic lipidosis
Occurs in obese cats after a period of anorexia —> cats frequently develop hepatic failure, icterus, and hepatic encephalopathy
Bovine fatty liver disease
Common in dairy cows in late gestation or peak lactation, especially after any period of inappetence or anorexia
Hepatic lipidosis of ponies, mini horses, and donkeys
Occurs in overweight pregnant or lactating mares after a period of stress or anorexia