Chemistry - Y8 EOY
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
state the reactivity series from most reactive to least reactive
potassium, sodium, lithium, calcium, magnesium, aluminium, carbon, zinc, iron, tin, lead, hydrogen, copper, silver, gold
Please Stop Calling Me A Careless Zebra Instead Try Learning How Copper Saves Gold + lithium after sodium
state the properties of potassium, sodium, lithium, and calcium
can react with cold water to make a metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas, incredibly alkali
state the properties of magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron, tin, and lead
can react with acids to make a salt + hydrogen gas
state the properties of copper, silver, and gold
not reactive enough to react with acids
why is potassium stored in oil?
so it does not react with oxygen and water in the environment
define an element
A substance made of only one type of atom
define a compound
A substance made of two or more different atoms chemically bonded together
define a mixture
A substance made of two or more different atoms not chemically bonded together
state the properties of a metal oxide
A solid which either - dissolves in water, forming an alkali
or - is insoluble
state the properties of a non metal oxide
Usually gases and dissolve in water forming acids
state the properties of metals
dense, conduct heat + electricity, high melting point, malleable, sonorous, ductile, thermal insulator
state the properties of non metals
light/low density, do not conduct heat + electricity, low melting point, brittle, dull, soft
state the 3 main acids
hydrochloric, sulfuric, nitric
state the acids' salt names
chloride, sulfate, nitrate
state the formula for hydrocloric acid
HCl
state the formula for sulfuric acid
H2SO4
state the formula for nitric acid
HNO3
why does hydrochloric acid's salt name end in 'ide', when sulfuric and nitric acids' salt names end in 'ate'?
because hydrochloric acid doesn't contain oxygen, whilst sulfuric and nitric acid do
what is the word equation for neutralisation?
base + acid --> salt + water
alkali + acid -->
water + salt
base + acid -->
water + salt
carbonate + acid -->
water + salt + carbon dioxide
where does the first part of the salt's name come from?
the metal reacting into the salt
where does the second part of the salt's name come from?
the salt name of the acid the metal reacts with
very reactive metal + water -->
metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
reactive metal + water -->
metal oxide + hydrogen gas
sulfur + oxygen -->
sulfur dioxide
carbon + oxygen -->
carbon dioxide
state the definition of reactivity
how easily a metal will react with another substance, e.g. water, acid
state the definition of displacement
a reaction where a more reactive metal takes the place of a less reactive metal from its compound
e.g. potassium + magnesium oxide --> potassium oxide + magnesium
what can be seen when displacement is occuring?
bubbles, colour change, temperature change
what would happen in a less reactive metal or the same metal tried to displace itself?
nothing. less reactive metals cannot take the place of more reactive metals, and the same metal cannot displace itself
define diffusion
The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
describe the particle structure in solids
The particles of a solid is densely packed, in constant contact with others, and vibrating in place.
describe the particle structure in liquids
The particles of a liquid are relatively close together, in constant contact with others, and move about relative to each other. Particles in a liquid are not easily compressible.
describe the particle structure in gases
The particles in a gas are far from each other, not in contact with other particles, able to move freely. gases are compressible
Define Brownian motion
the random movement of tiny particles suspended in a fluid due to collisions between the particles and surrounding molecules
When did Brownian first study these fluctuations?
1827
does the concentration of an acid affect reaction rate?
yes
why does the concentration of an acid affect reaction rate
when an acid is of higher concentration, there are more acid particles which means more collisions, more reactions, and so also a faster reaction rate.
gas to solid is called:
deposition
solid to gas is called:
sublimation
why can't diffusion occur in solids?
solids cannot move as strong intermolecular forces hold the particles in fixed positions
define a concentrated solution
a solution which has lots of reactive particles in a cm3
plan an experiment to see if water temperature affects the rate of diffusion
petri dish, different temperature waters, and potassium permanganate, which is purple, so its radius of diffusion is visible.
what happens when ammonia reacts with hcl?
when two cotton balls one soaked in ammonia the other in hcl are put either sides of a tube, a spiral forms where hcl and ammonia react, closer to the ammonia side, because ammonia is lighter than hcl
what is the salt name for the spiral formed when ammonia reacts with hcl in this experiment?
ammonium chloride
state the formula for sodium chloride
NaCl
what is distilled water on the PH scale?
7
what are acids on the PH scale?
0-6
what are alkalis on the PH scale?
8-14
on the universal PH scale, what colour is 7?
green
what's the difference between a base and an alkali?
alkalis are soluble bases, alkalis are hydroxides, bases are oxides
what colour does sodium turn in a flame test?
yellow
what colour does potassium turn in a flame test?
lilac
what colour does calcium turn in a flame test?
red
what colour does copper turn in a flame test?
green
how do you test for chloride in a salt?
add dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate. a white precipitate forms if the salt was a chloride
how do you test for sulphate in a salt?
add dilute nitric acid and barium chloride solution. a white precipitate forms is the salt was a sulphate
what is equipment is used in titration?
burette
draw a diagram for titration
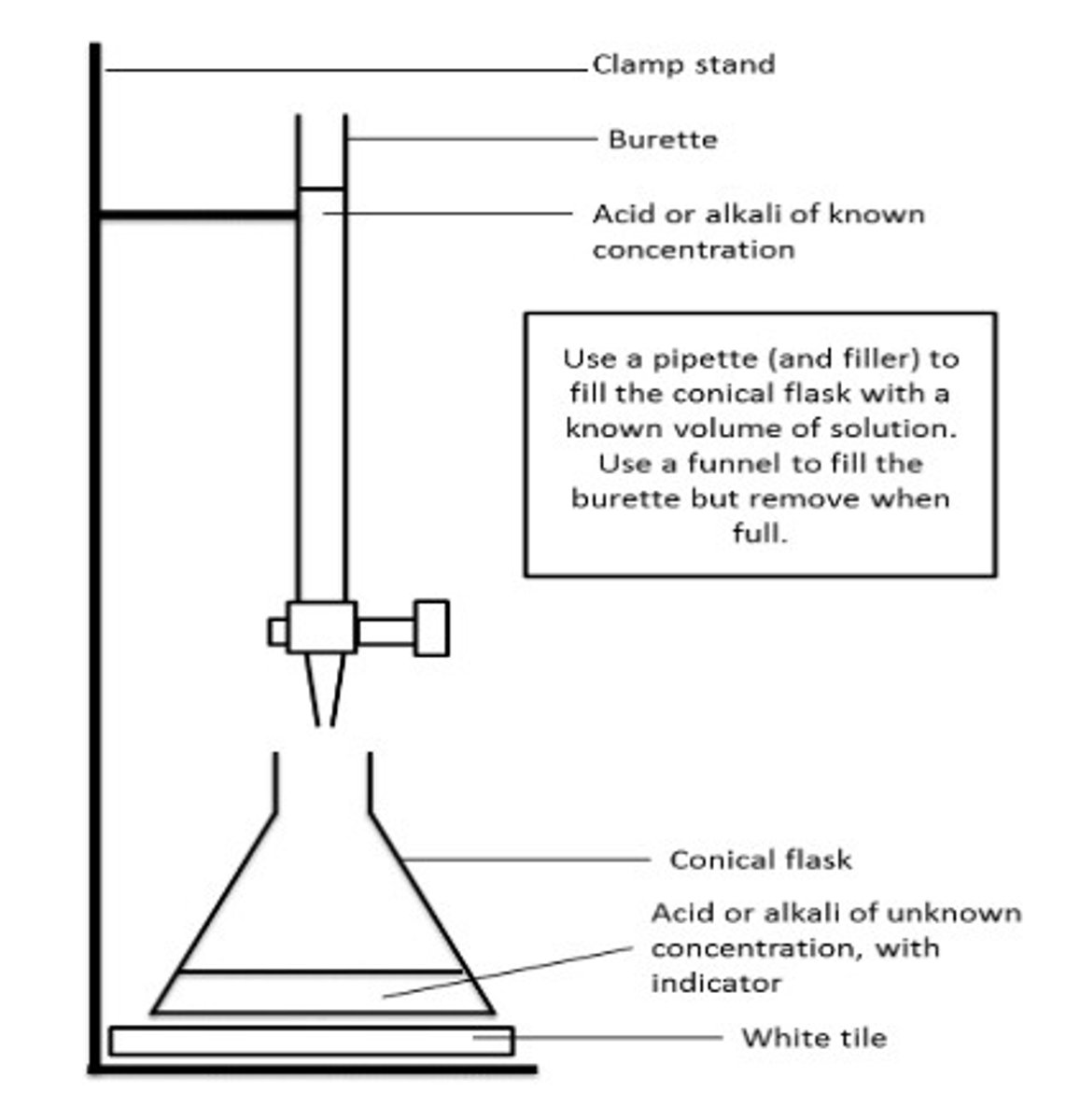
how to test for oxygen?
hold a glowing splint under a boiling tube of the gas. if the gas relights the glowing splint, the gas is oxygen
how to test for carbon dioxide?
Bubble the gas through limewater. if the gas is carbon dioxide, the limewater will turn cloudy
how to test for hydrogen?
hold a lit splint under a tube of the gas. if the splint makes a squeaky pop, the gas is hydrogen
what colour does red litmus paper go when in contact with an alkali?
blue
what colour does blue litmus paper go when in contact with an acid?
red