Quantum Numbers
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Louis de Broglie
French scientist who suggested that electrons be considered waves confined to the space around an atomic nucleus.
Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle
Physical observation that states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and the velocity of an electron or any other particle.
Schrodinger Wave Equation
A mathematical model that calculates the probability of finding an electron at a given place around a nucleus. Solutions to this equation indicate the four quantum numbers.
Quantum Number
A solution to the Schrodinger equation that specifies the properties of an atomic orbital and the electrons found in that orbital.
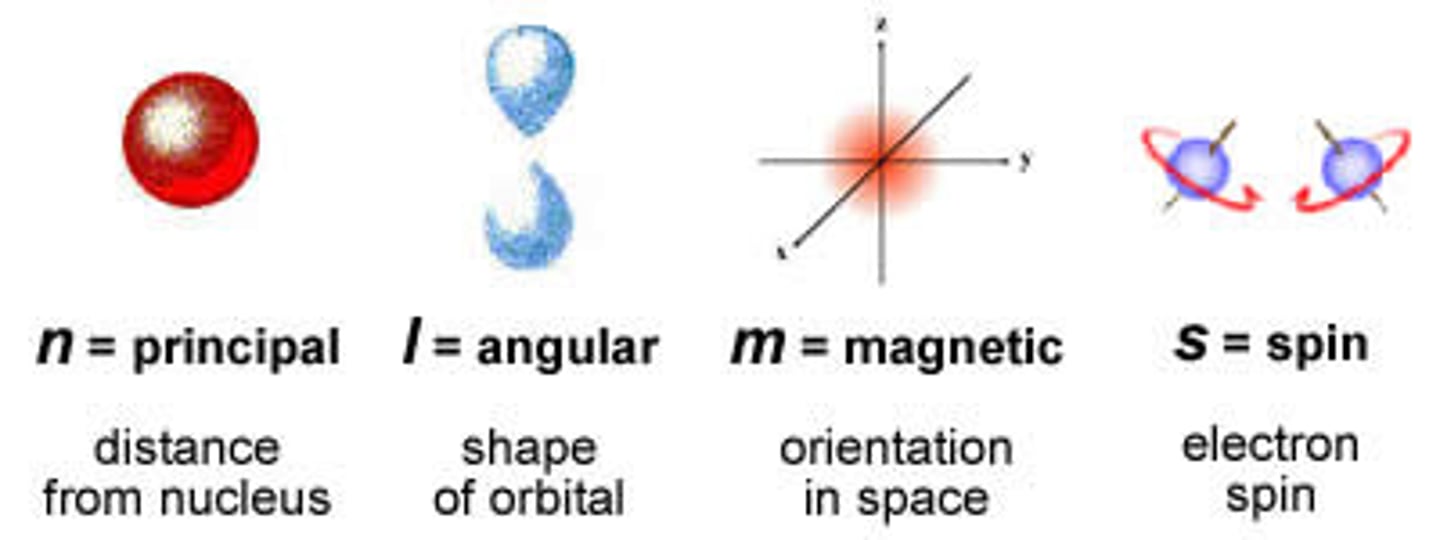
Principle Quantum # (symbol)
n
Angular Momentum Quantum # (symbol)
l
Magnetic Quantum # (symbol)
m
Spin Quantum # (symbol)
s
Principle Quantum # (definition)
Indicates the main energy level occupied by the electron.
Angular Momentum Quantum # (definition)
Indicates the shape of the orbital.
Magnetic Quantum # (definition)
Indicates the orientation of an orbital around the nucleus.
Spin Quantum # (definition)
Indicates the direction an electron rotates in its orbital.
What are the allowable values for n?
Any positive integer, from 1 to n.
What are the allowable values for l?
Any positive integer in the range [0, ..., n-1].
What are the allowable values for m?
Any integer in the range [-l, ..., +l].
What are the allowable values for s?
-1/2 and +1/2 only.
Orbital
A three-dimensional region around a nucleus that indicates the probable location of an electron, defined by specific values of n, l, and m.
Sublevel/Subshell
All similarly shaped orbitals that share the same values for n and l.
Energy Level/Shell
All orbitals that share the same value for n only.
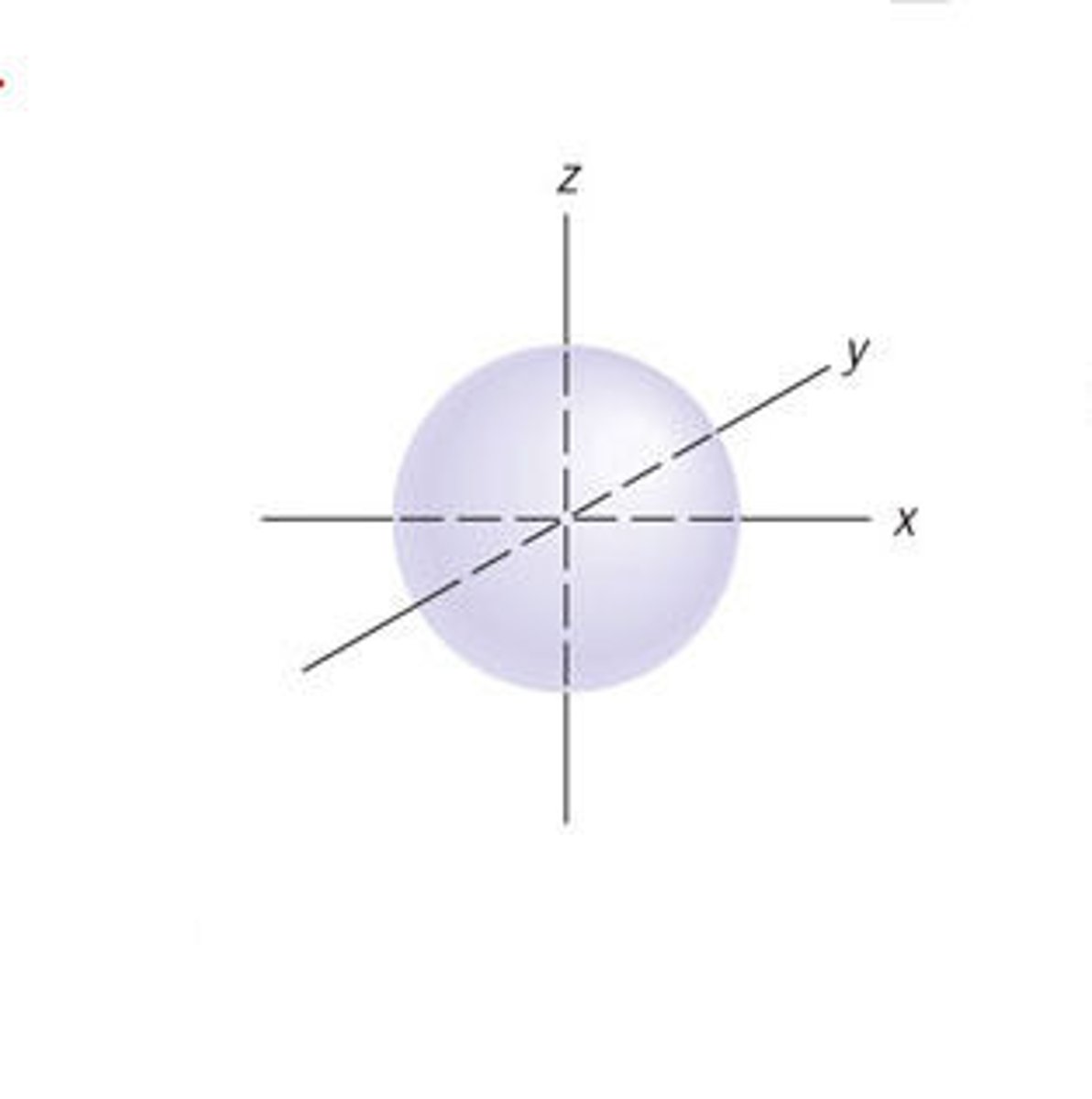
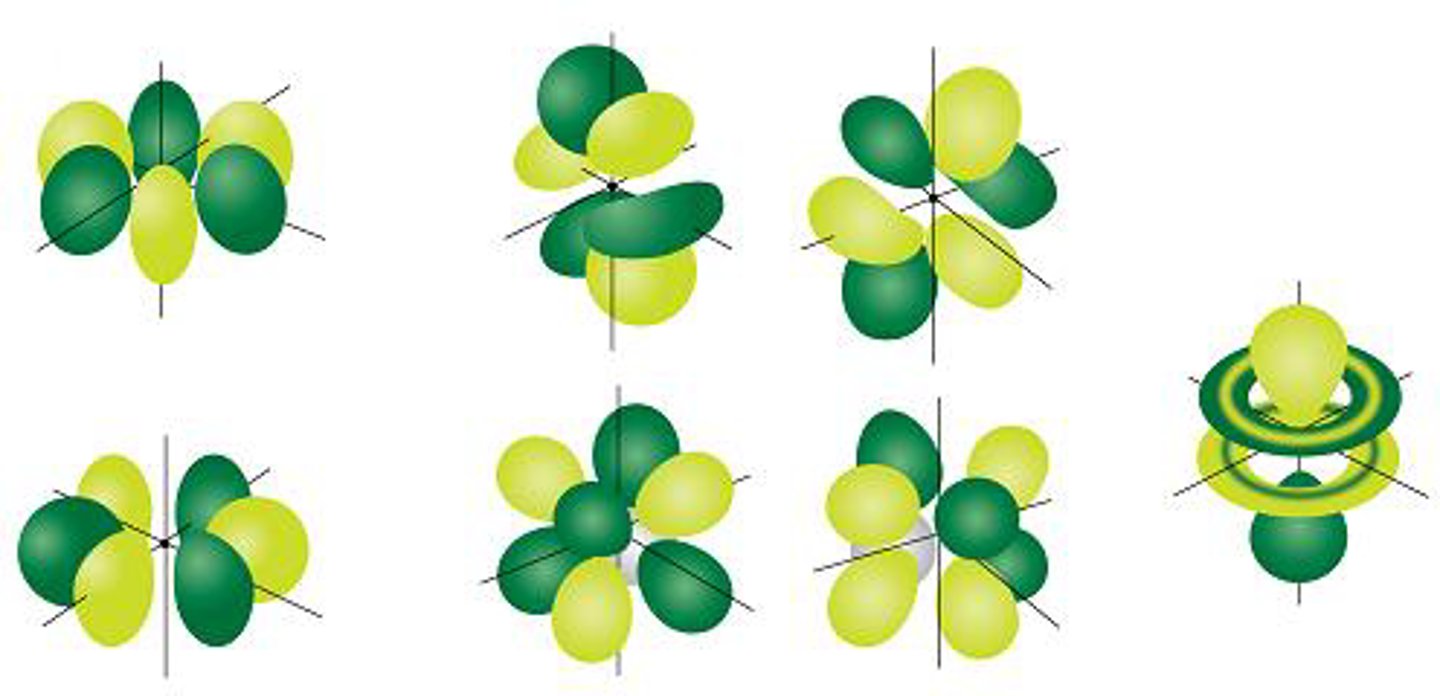
s-orbital
A spherical orbital defined by l=0
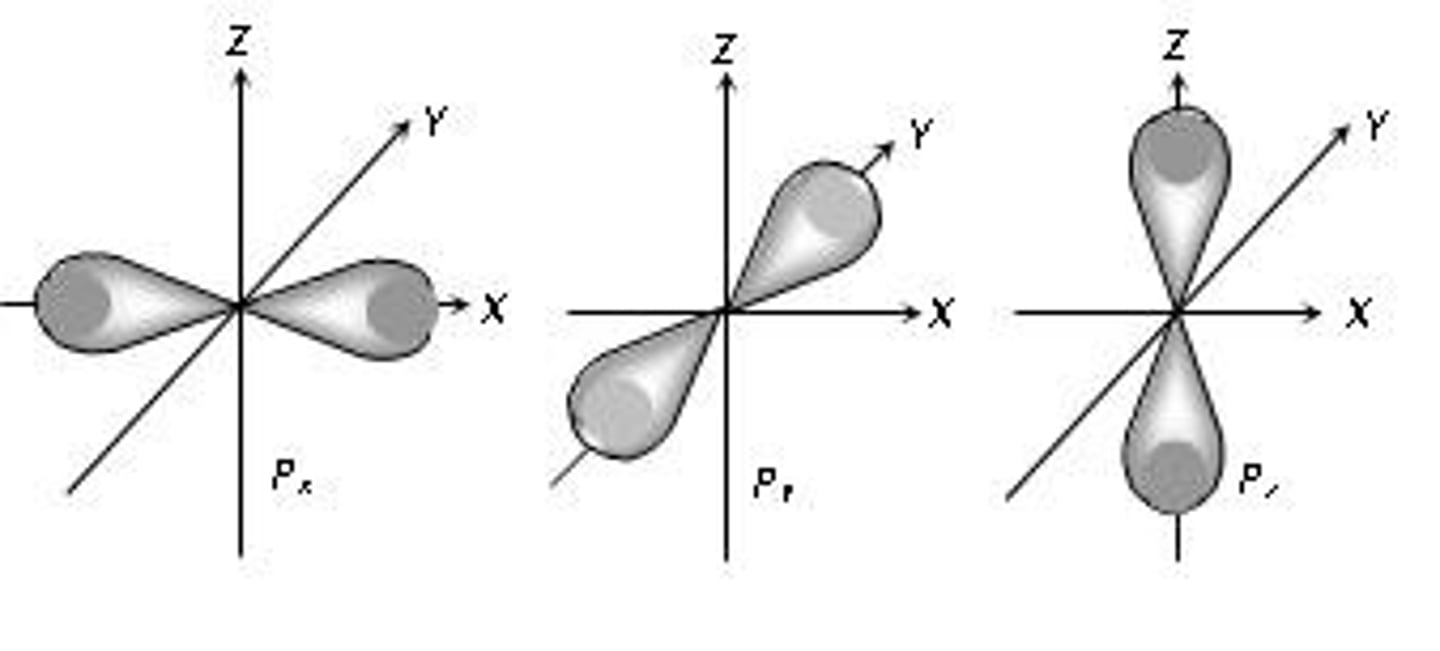
p-orbital
A dumbbell-shaped orbital defined by l=1
d-orbital
A cloverleaf-shaped orbital defined by l=2
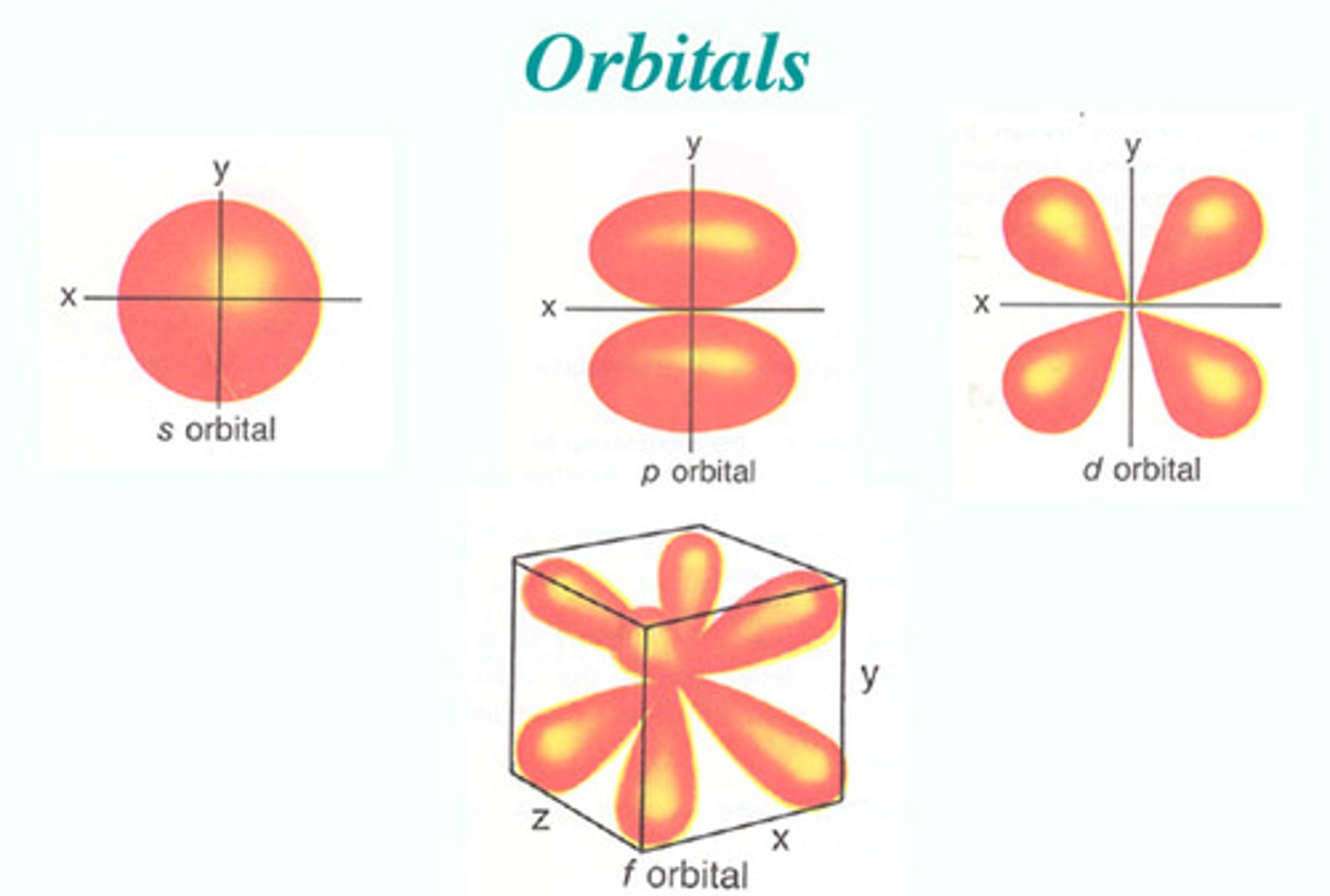
f-orbital
A complex orbital defined by l=3
How does n relate to the number or orbitals per main energy level (shell)?
The number of orbitals in shell (n) is equal to n^2.
How does n relate to the number of electrons allowed per main energy level (shell)?
The number of allowed electrons in shell (n) is equal to 2n^2.
What determines the number of possible orbital orientations in a sublevel?
The number of possible values of l.