Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms (Honors Chemistry)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
electromagnetic radiation
energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space
electromagnetic spectrum
all forms of electromagnetic radiation, which all move at a constant speed (the speed of light).
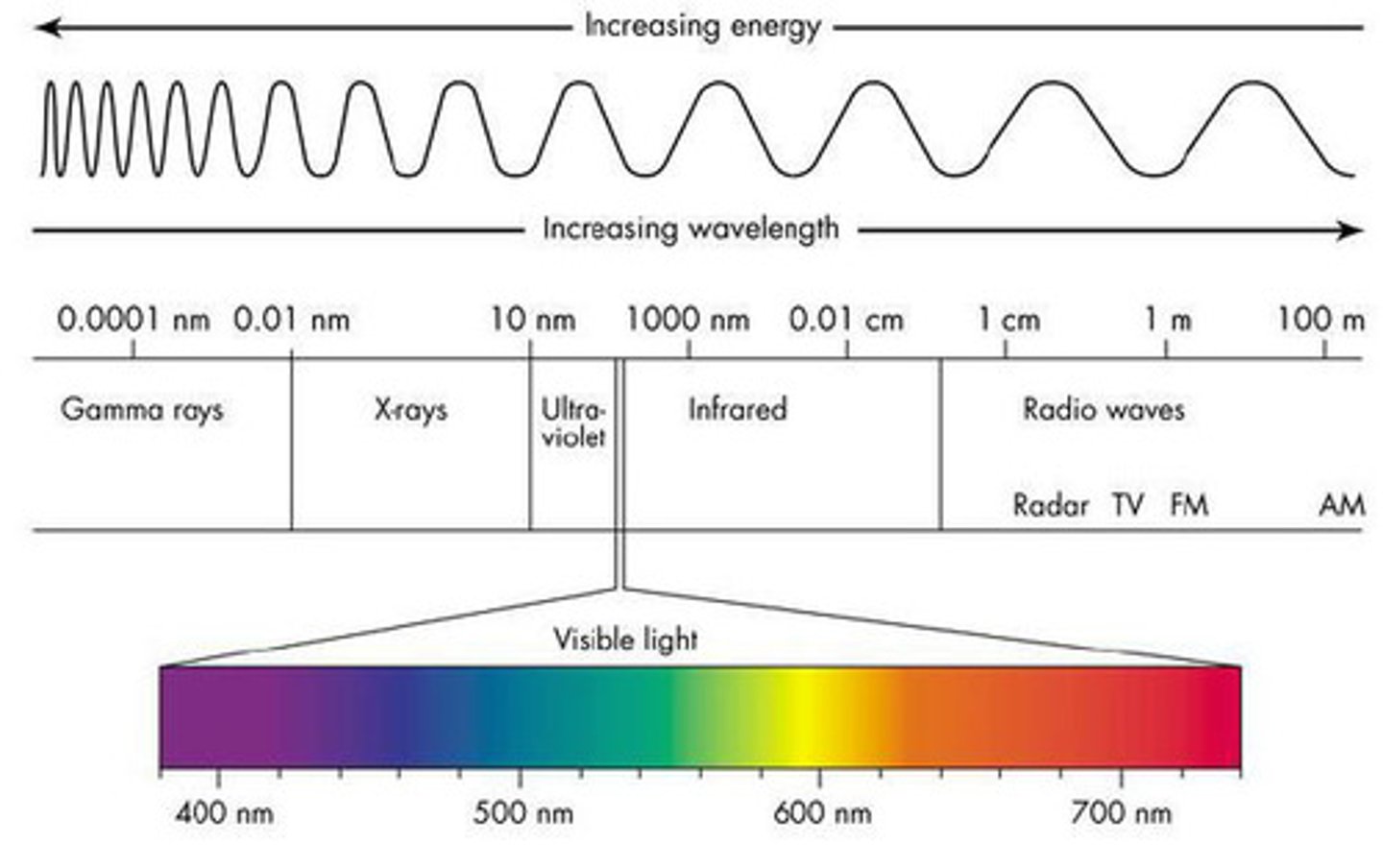
the speed of light (c)
3.00 x 10⁸ meters per second (m/s)
wavelength (λ)
the distance between corresponding points on adjacent waves
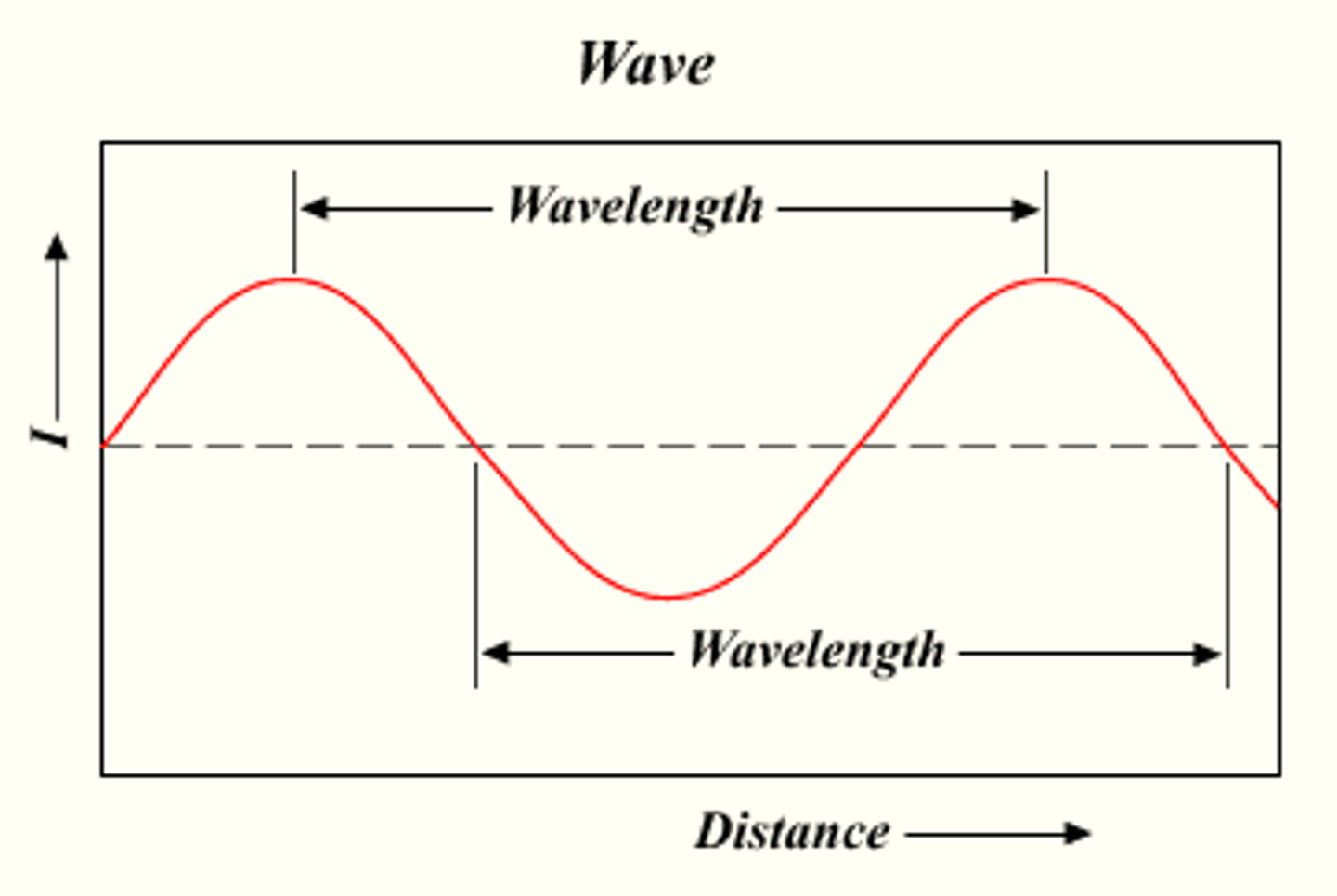
meters (m) / nanometers (nm)
how wavelength is measured
frequency (ν)
the number of waves that pass a given point in a specific time
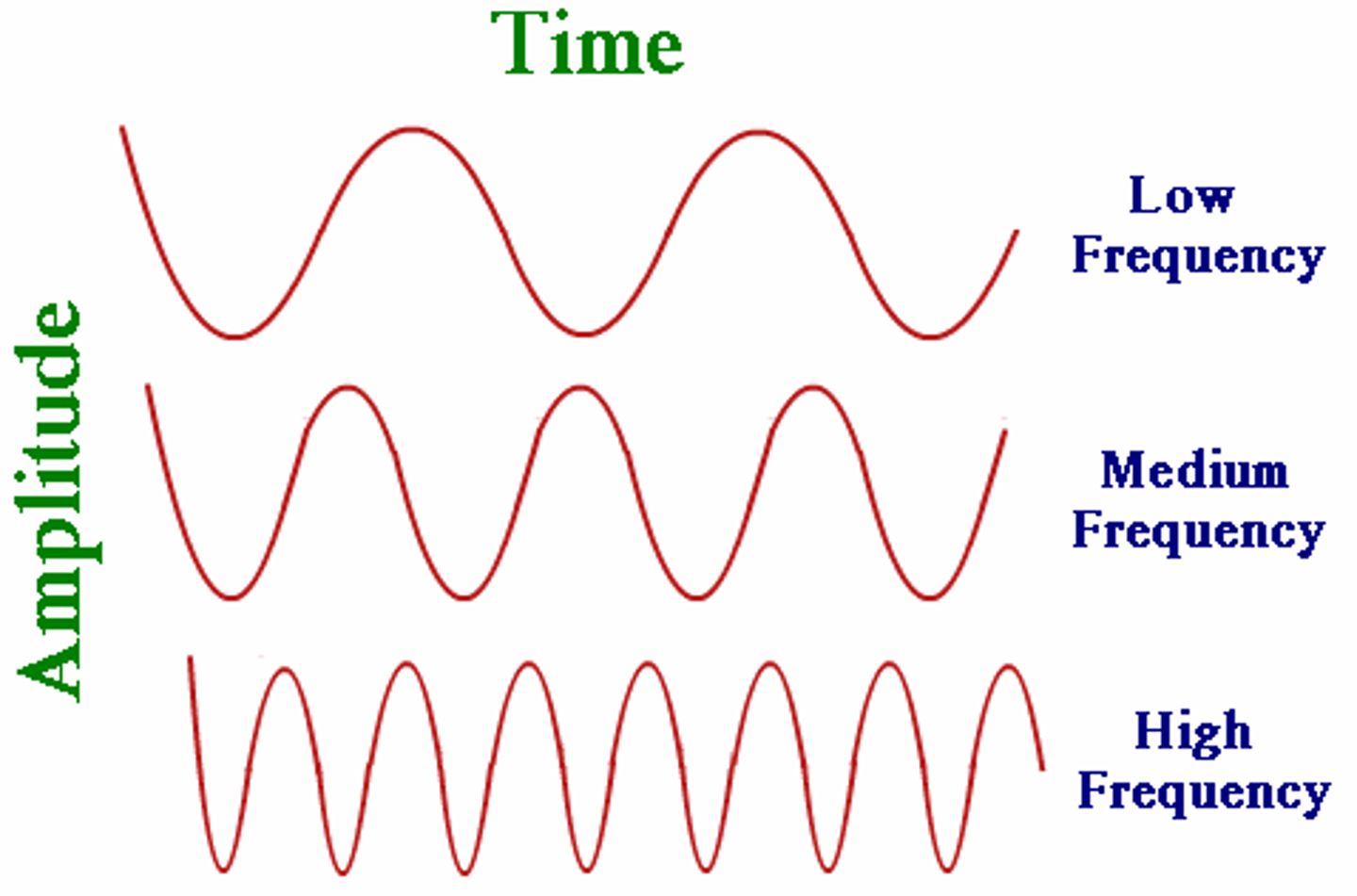
hertz (Hz) / 1 wave per second
how frequency is measured
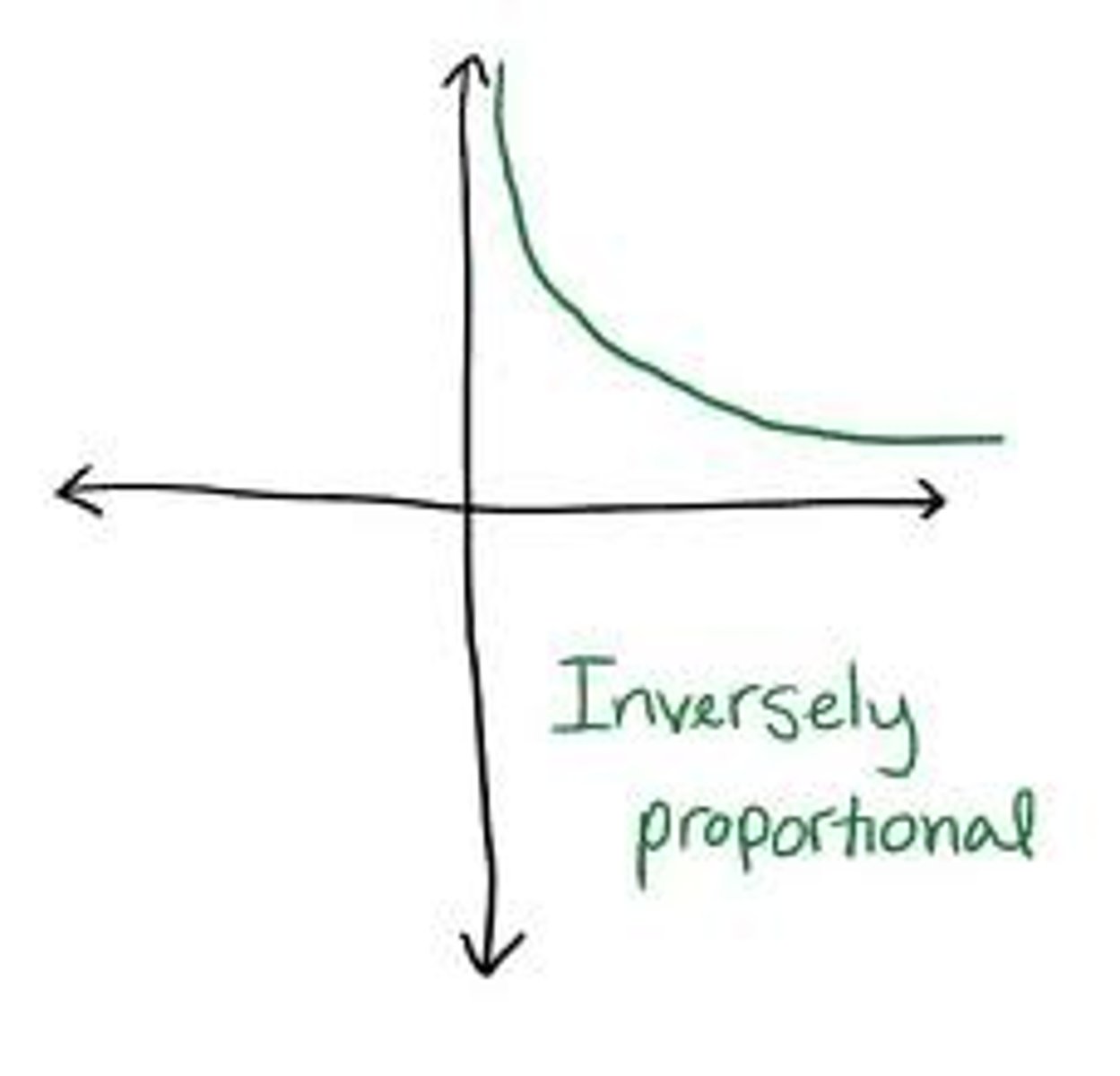
c = λν
the relationship between frequency (ν) and wavelength
inversely proportional
as one value goes up, the other goes down (ex. wavelength and frequency)
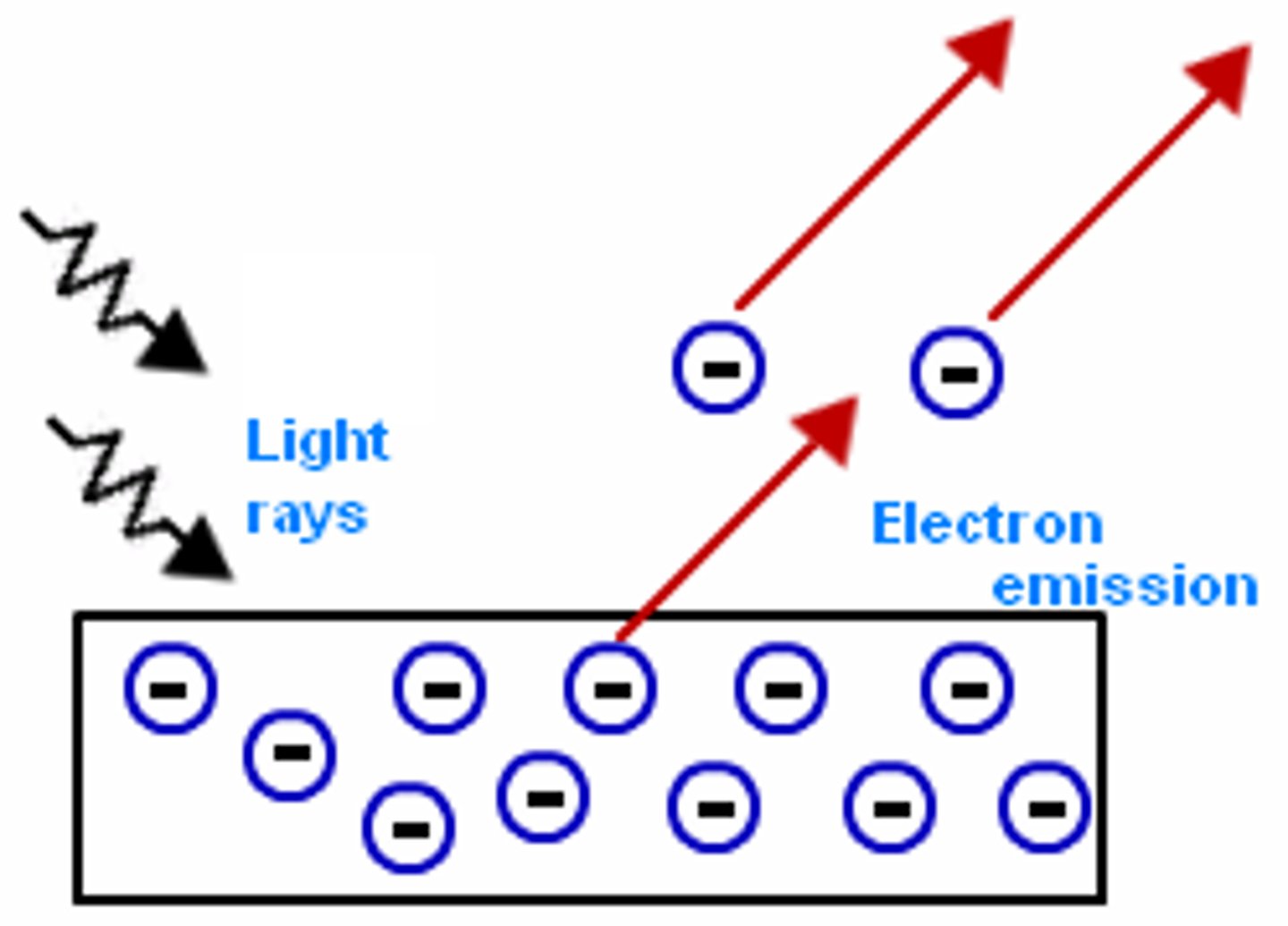
photoelectric effect
the emission of electrons from a metal when light shines on it
quantum
the minimum amount of energy that can be lost or gained by an atom
Planck's constant (h)
6.626 x 10⁻34 J*s (joule-seconds)
energy (E)
measured in J (joules)
E = hν
the relationship between a quantum of energy (E) and the frequency of radiation (ν)
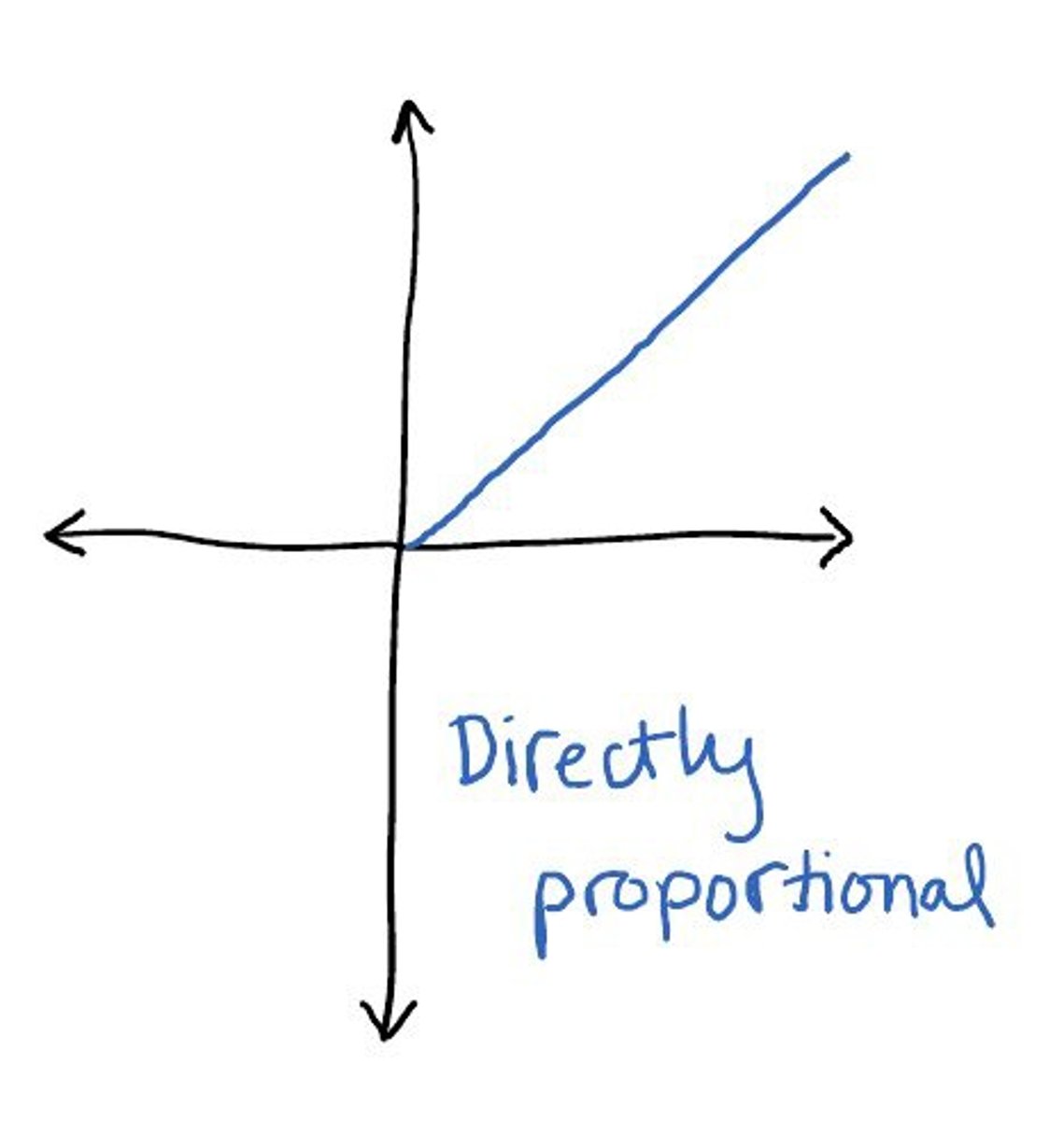
directly proportional
as one value goes up, the other does as well (ex. energy and frequency)
photon
a particle of electromagnetic radiation with zero mass carrying a quantum of en energy
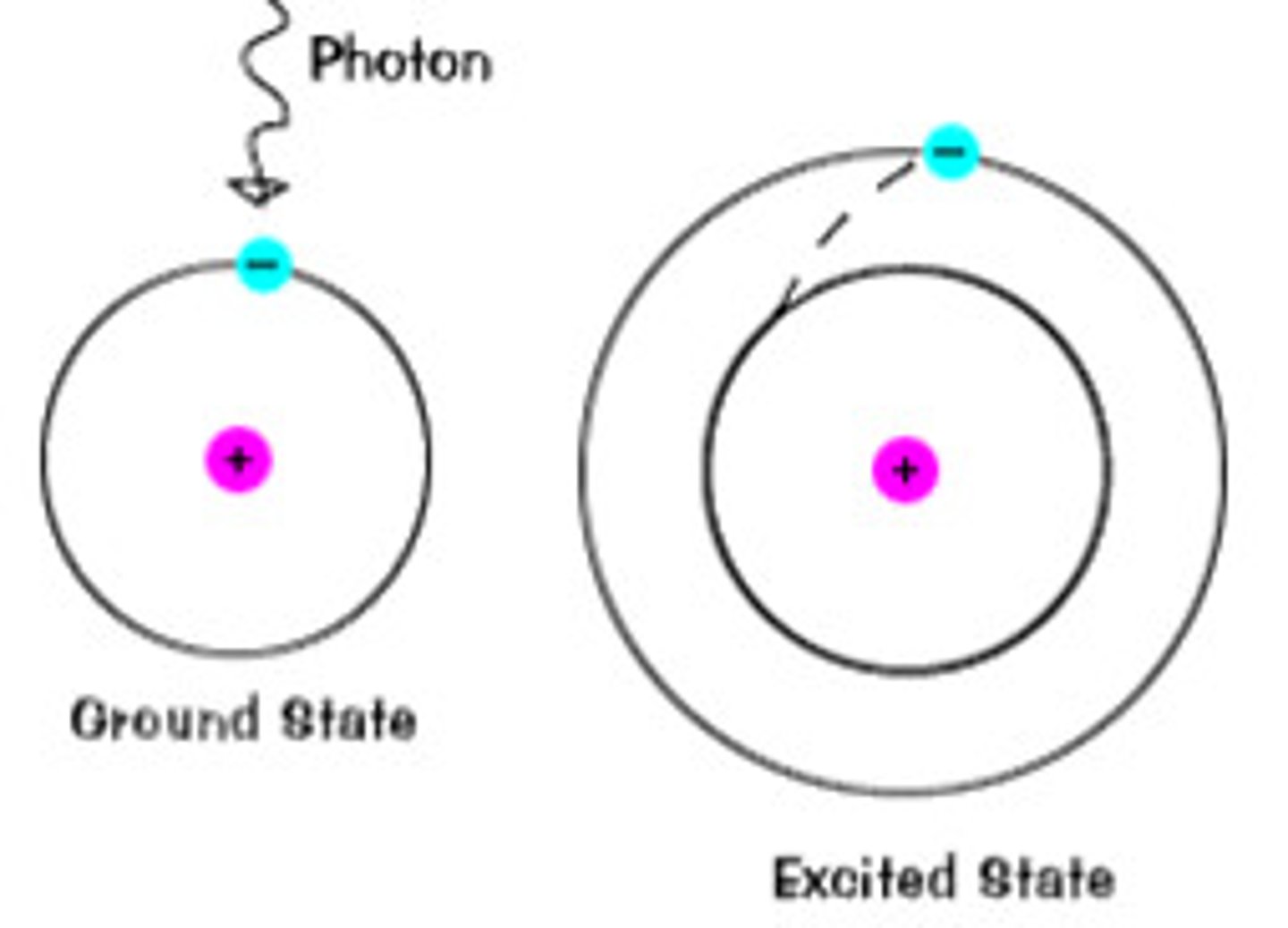
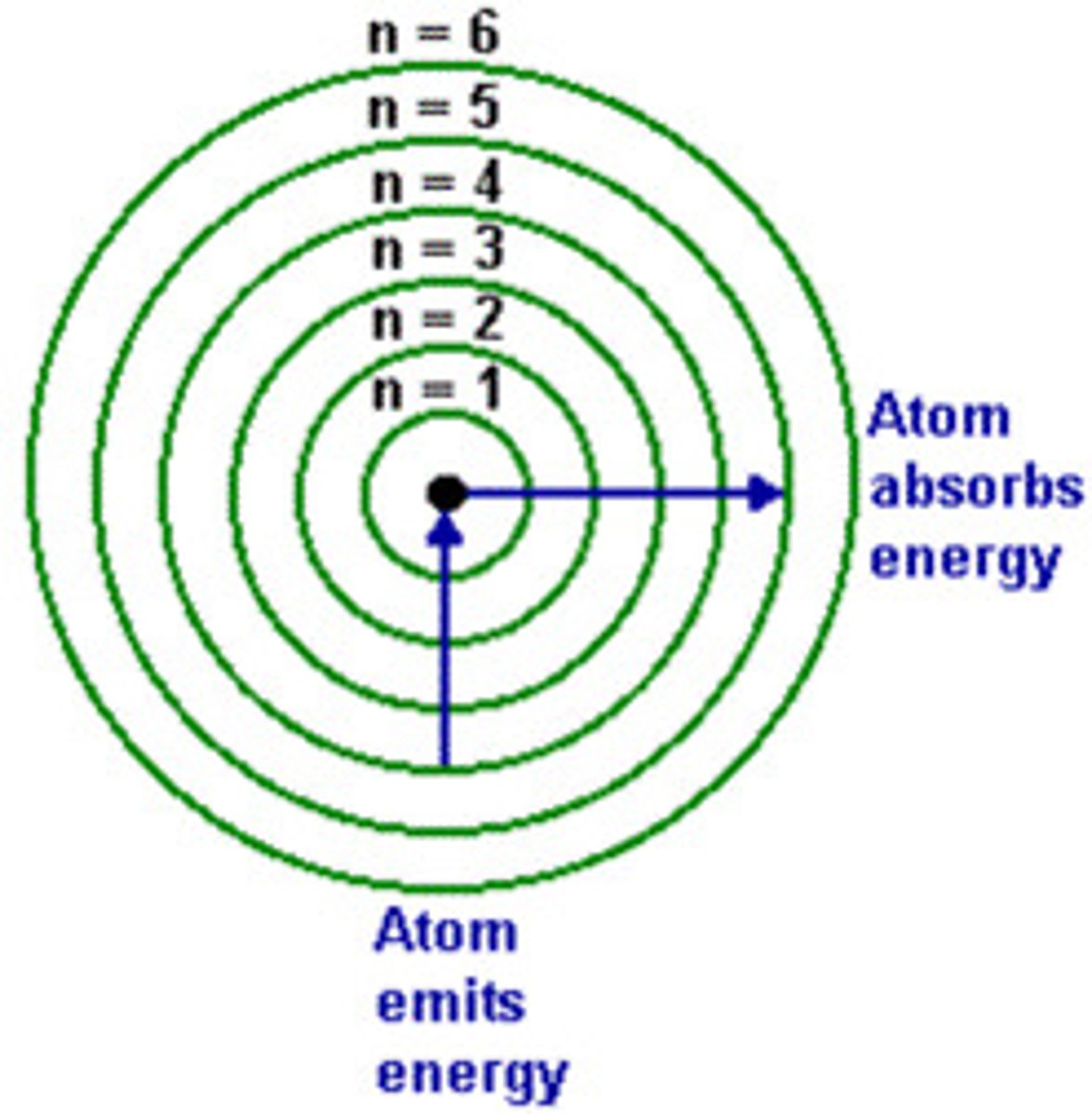
ground state
the lowest energy state of an atom
excited state
a state higher than the ground state of an atom
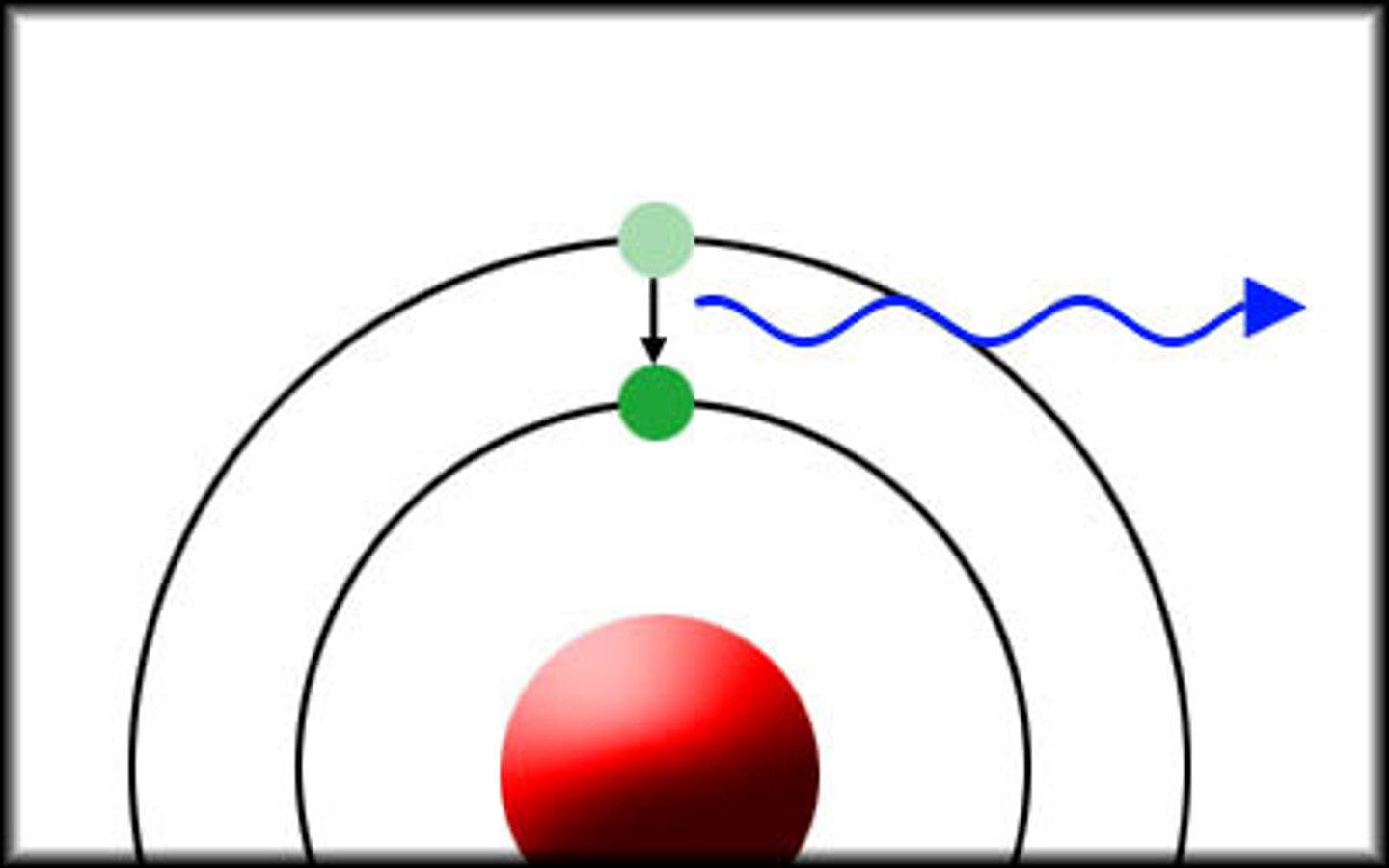
photon emission
occurs when an electron drops from a higher energy state to a lower one
photon absorption
occurs when an electron rises from a lower energy state to a more excited one
electron orbital
the three-dimensional space where an electron is found 90% of the time
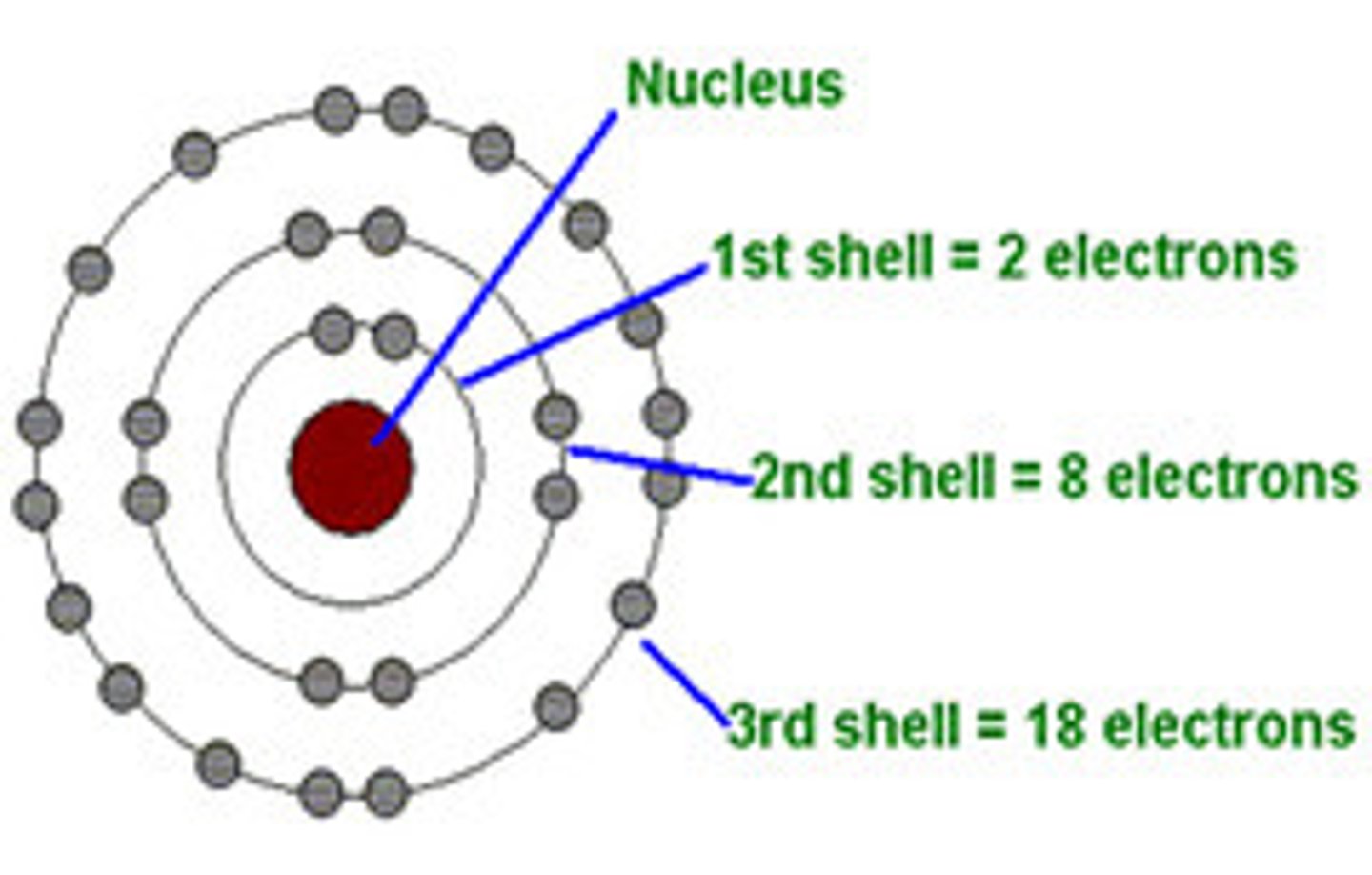
electron shell
an energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
electron sublevel
grouping of orbitals found within an energy level; s, p, d and/or f
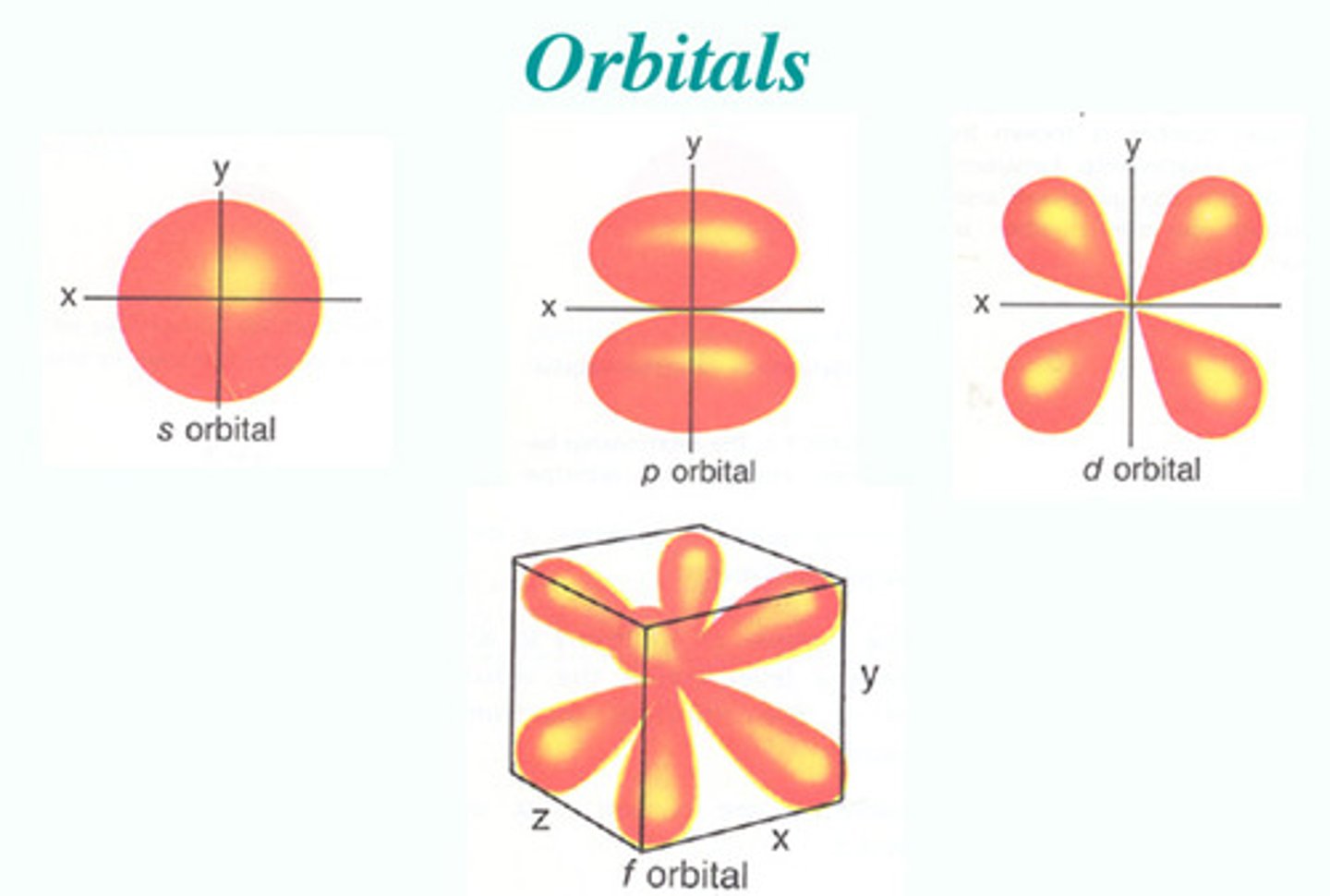
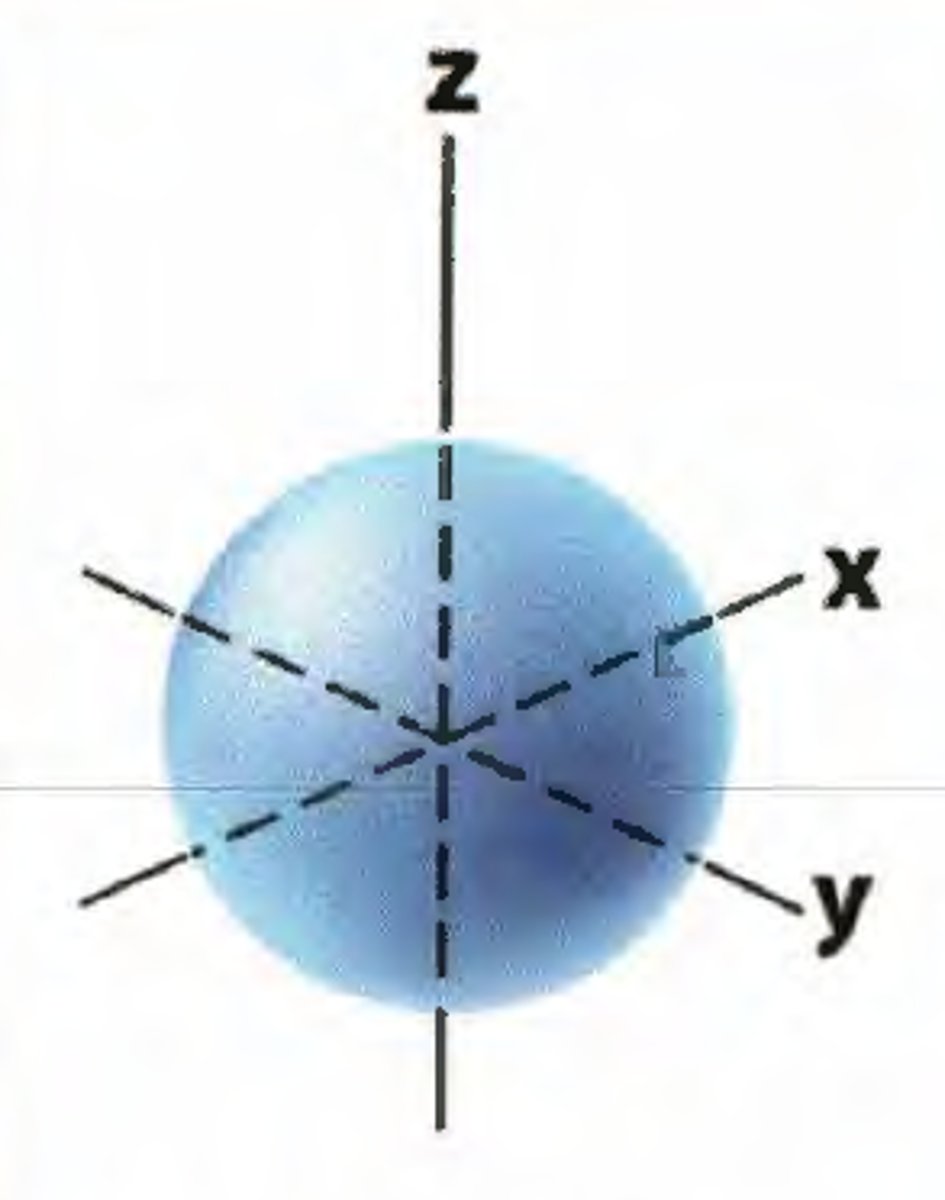
s sublevel
spherical, holds 2 electrons, only 1 type
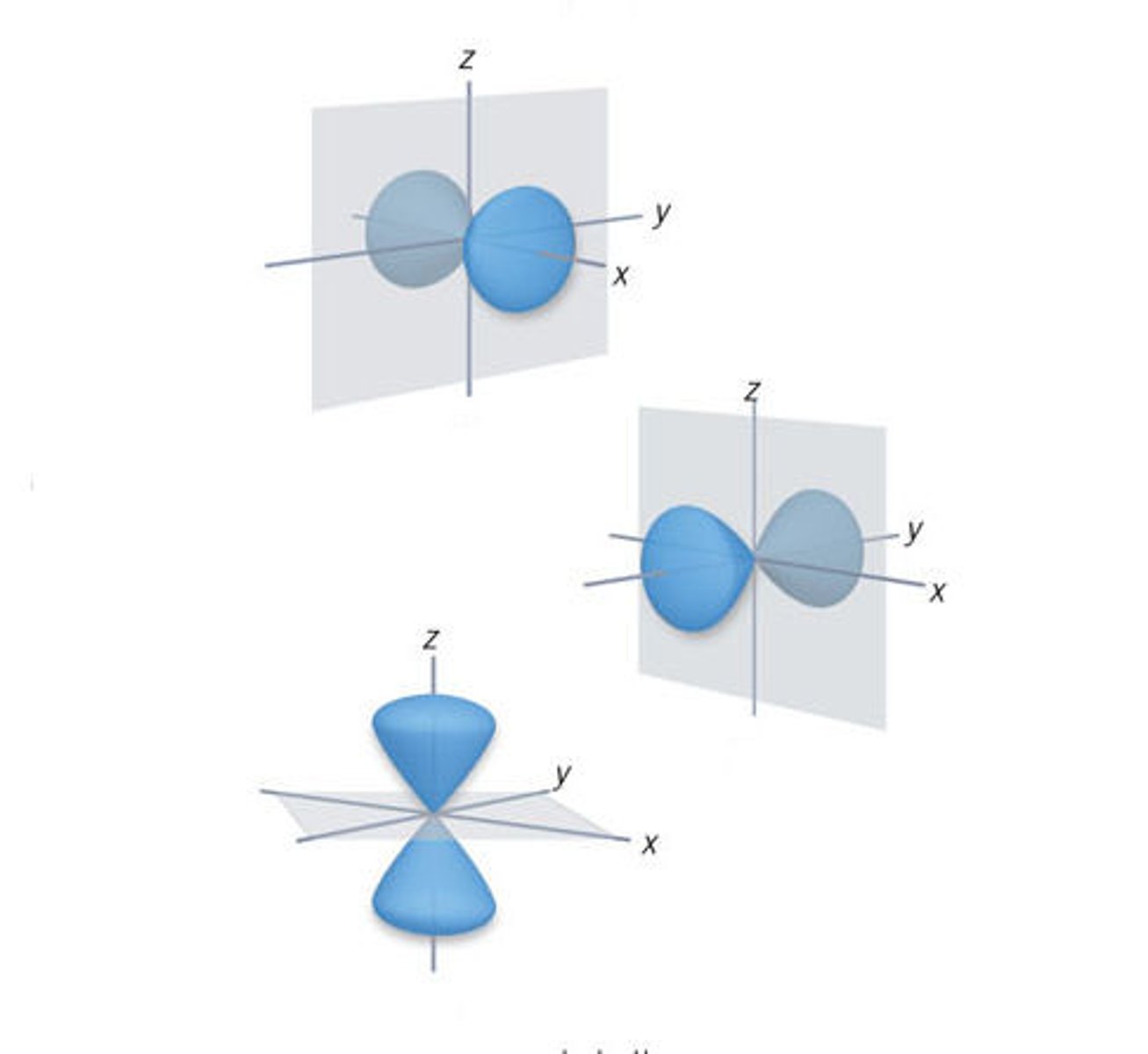
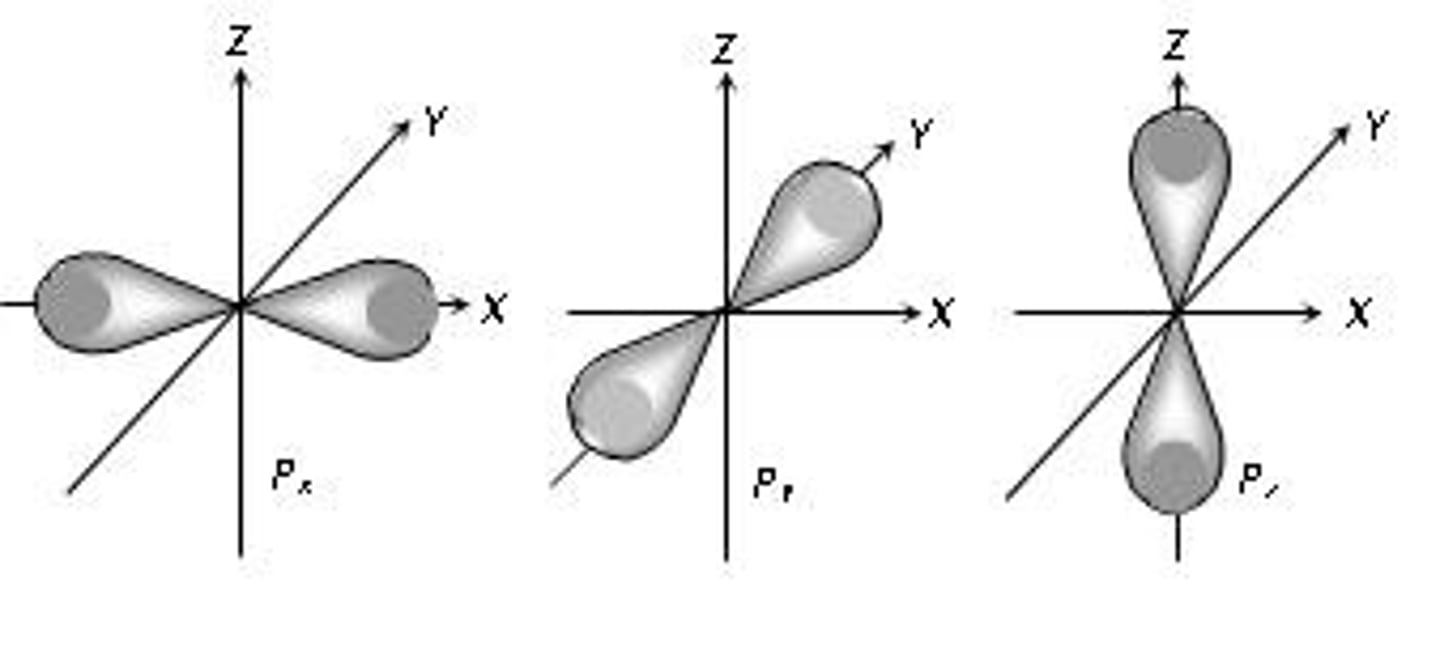
p sublevel
dumbbell shaped, holds 6 electrons, 3 types
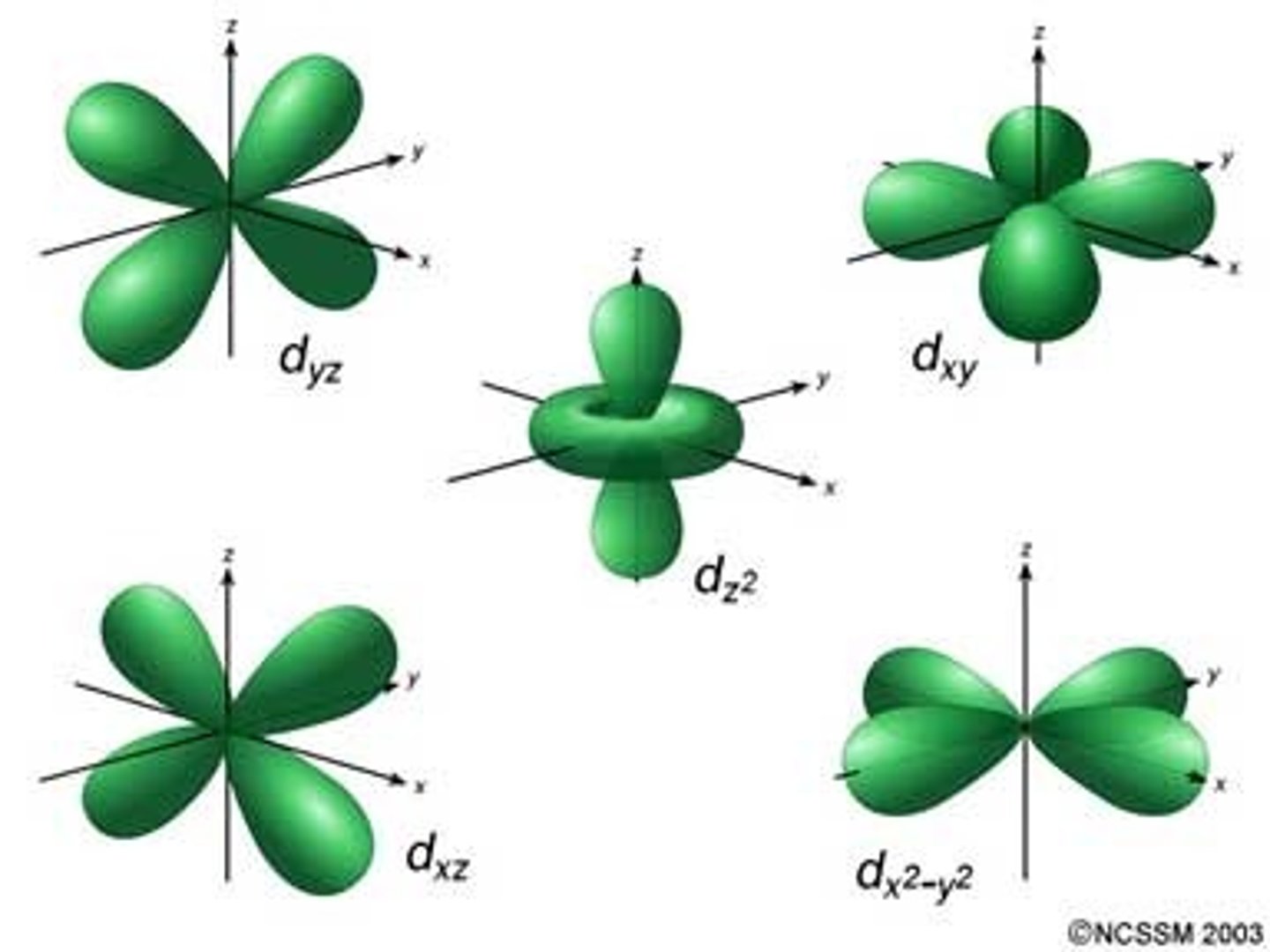
d sublevel
clover shaped, holds 10 electrons, 5 types
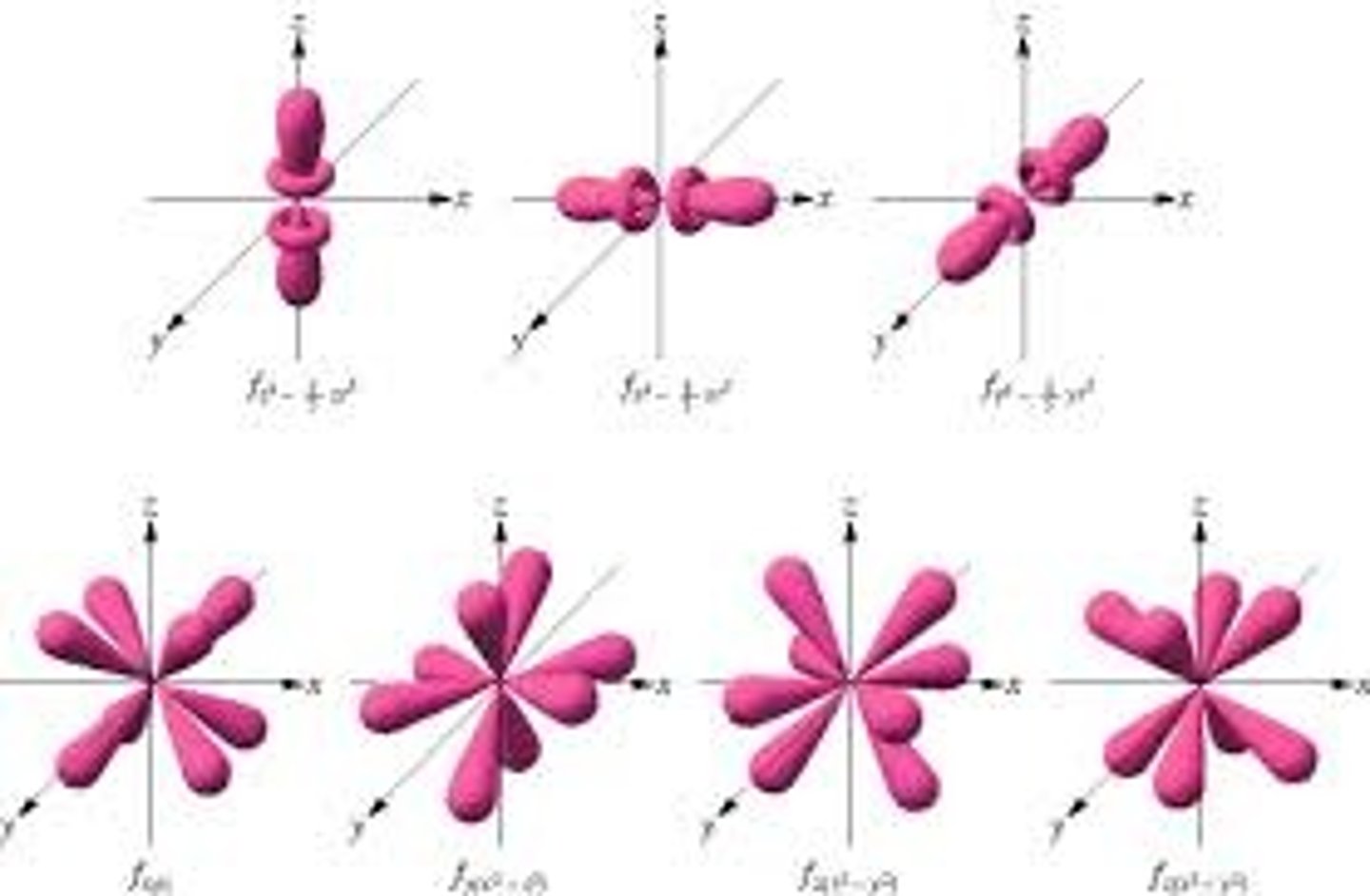
f sublevel
complex, holds 14 electrons, 7 types
electron configuration
describes the arrangement of electrons in atoms at ground state (# on the left is the sublevel, exponent is the # of electrons)
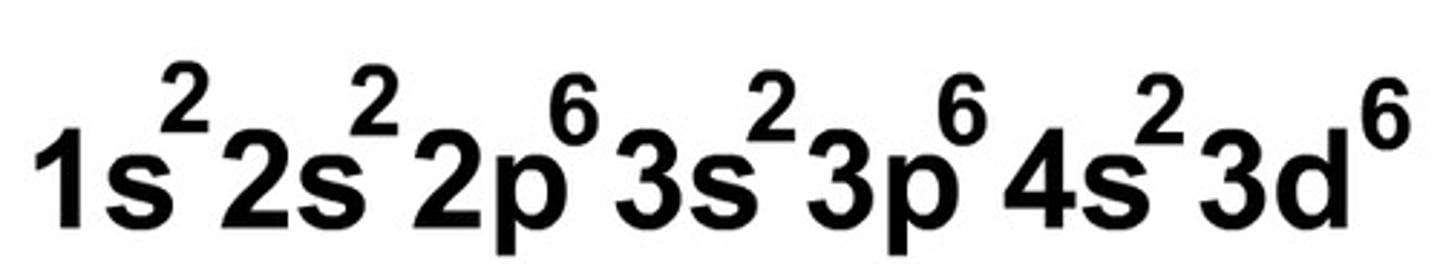
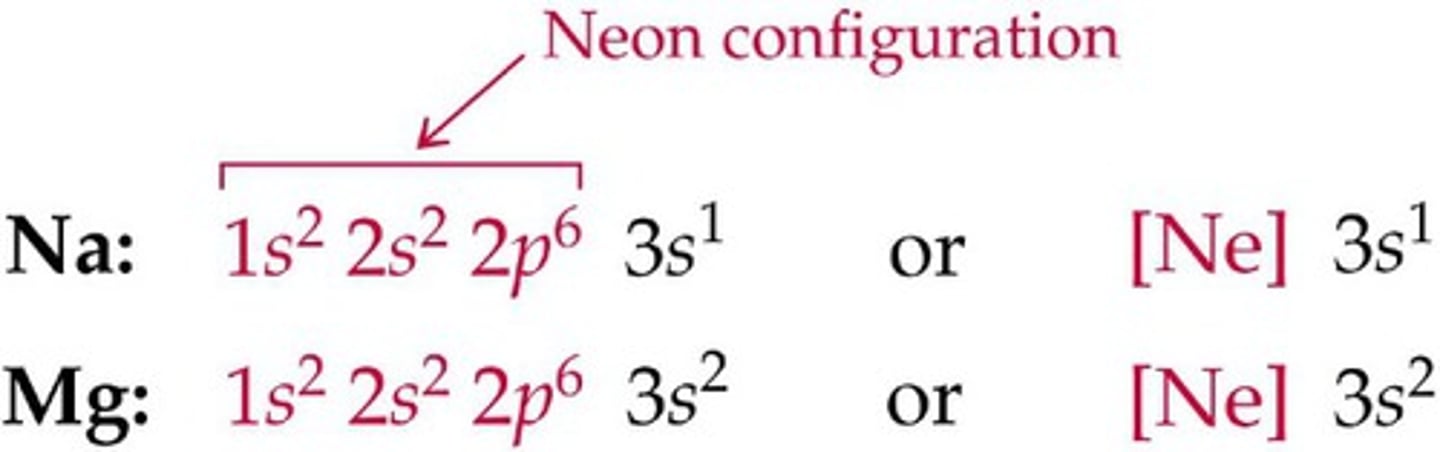
noble gas notation
an abbreviated electron configuration of an element in which filled inner shells are represented by the symbol of the noble gas before
orbital notation
a diagramic representation that uses dashes and arrows to show the principal energy levels and sublevels for all the electrons in an atom

Aufbau Principle
an electron occupies the lowest-energy orbital that can receive it

Hund's Rule
orbitals of equal energy are each occupied by one electron before any orbital is occupied by a second electron
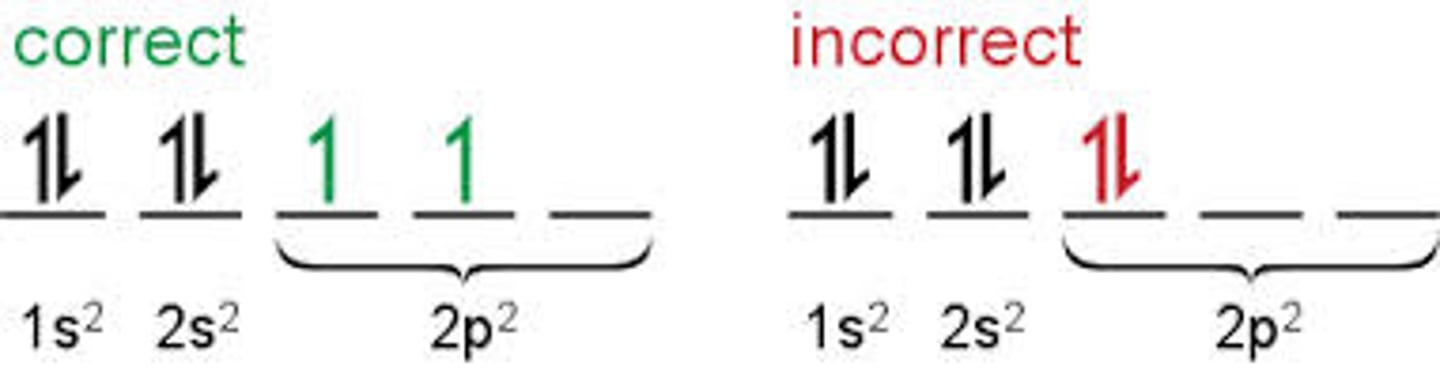
Heisenberg's Conclusion
determining the velocity and position of an electron simultaneously is impossible
Pauli's Exclusion Principlee
no two electrons have the same quantum number
quantum number
a number that describes the properties of atomic orbitals and the electrons in them
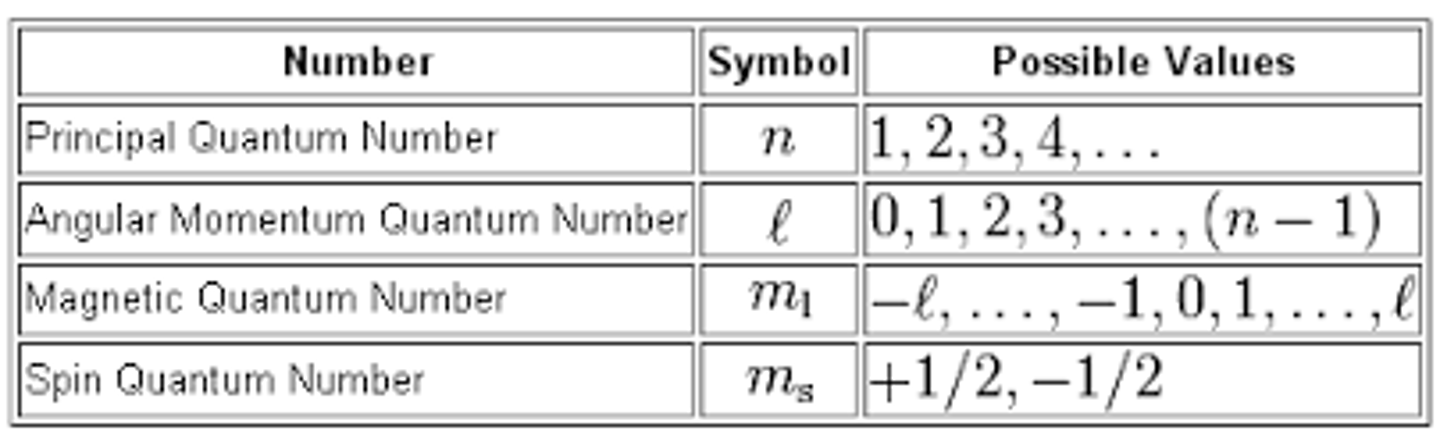
principal quantum number (n)
the energy level of the electron (only positive integers)
n²
the amount of orbitals in one shell
2n²
total electrons possible in one energy level
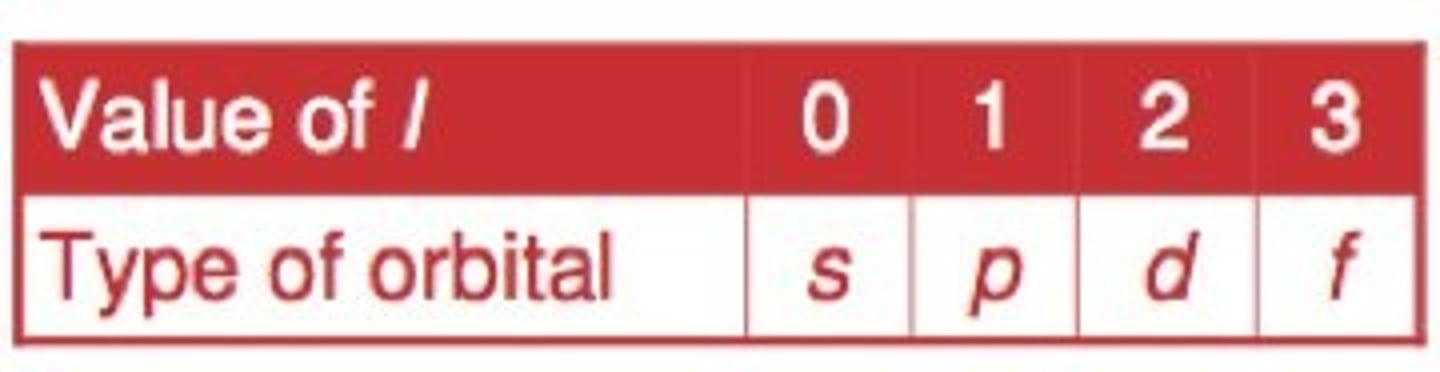
angular momentum quantum number (l)
indicates the shape of the orbital (0, 1, 2, or 3)
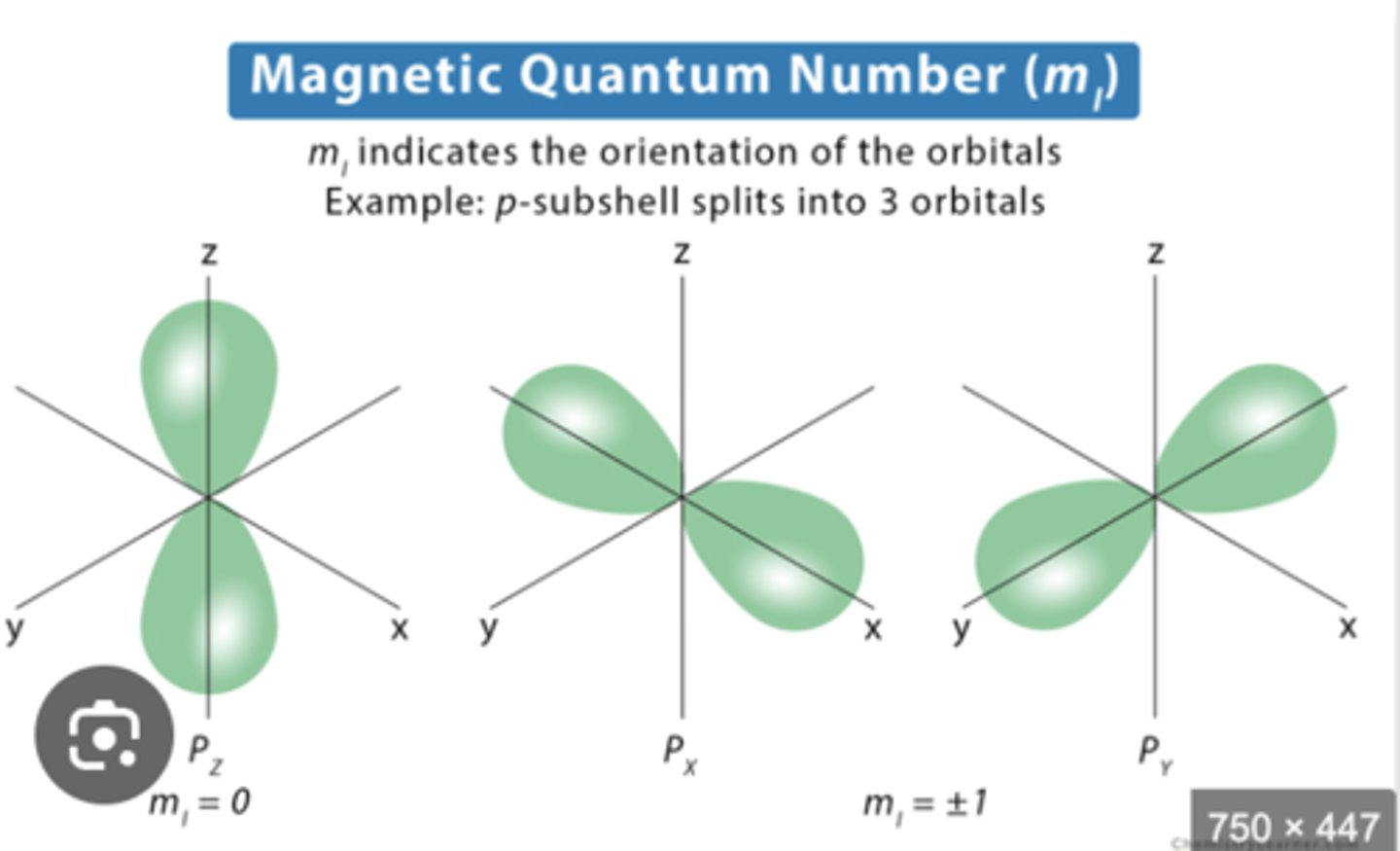
magnetic quantum number (mₗ)
indicates the orientation of the orbital (ranges from -l to l)
spin quantum number (mₛ)
indicates the spin of the electron (either 1/2 [↑] or -1/2 [↓])
![<p>indicates the spin of the electron (either 1/2 [↑] or -1/2 [↓])</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/fec6e95c-923d-40c7-b2fd-2253fec78f8c.jpg)