Physics 106 Final Exam Flashcards (Extremely Thorough Version😭)
1/524
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BYU Independent Study Physics 106
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
525 Terms
Is electric charge conserved?
Yes! Electrical charge is ALWAYS conserved (The law of conservation of electrical charge).
What is a conductor and what are some examples?
Materials in which electrical charges move freely. Net charge resides on its surface.
Ex: Copper, Aluminum, and Silver.
What is a insulator and what are some examples?
Materials in which electrical charges do not move freely.
Ex: Glass & Rubber.
What is a semiconductor and what are some examples?
Have properties of both an insulator and a conductor..
Ex: Silicon and Germanium.
What is Coulomb’s Law and what is its associated equation? What is the purpose of this equation?
Coulomb’s Law = Law of electrical force between two STATIONARY charged particles.
Purpose = Calculates the force exerted on one charge by the other with NO physical contact.
Equation = See photo.

What is the centripetal force equation?
See photo.

If electrostatic force is equal to the gravitational force, then what is the associated equation?
See photo.
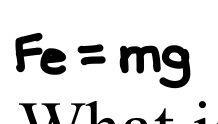
What is the value of Coulomb’s constant?
8.99 ×10^9 Nm²/C²
What is the elementary unit of charge? What is its numerical value? Is it quantinized?
e = 1.6 × 10^-19 C (Coulombs)
Yes: ±e, ±2e NOT 1.5e (No fractions)
When a conductor is connected to the Earth by a conducting wire, this is an example of what?
Grounding.
What does Earth have an infinite reservoir of?
Electrons (The Earth accepts or supplies them).
What does charging by induction require?
No contact with the object inducing the charge.
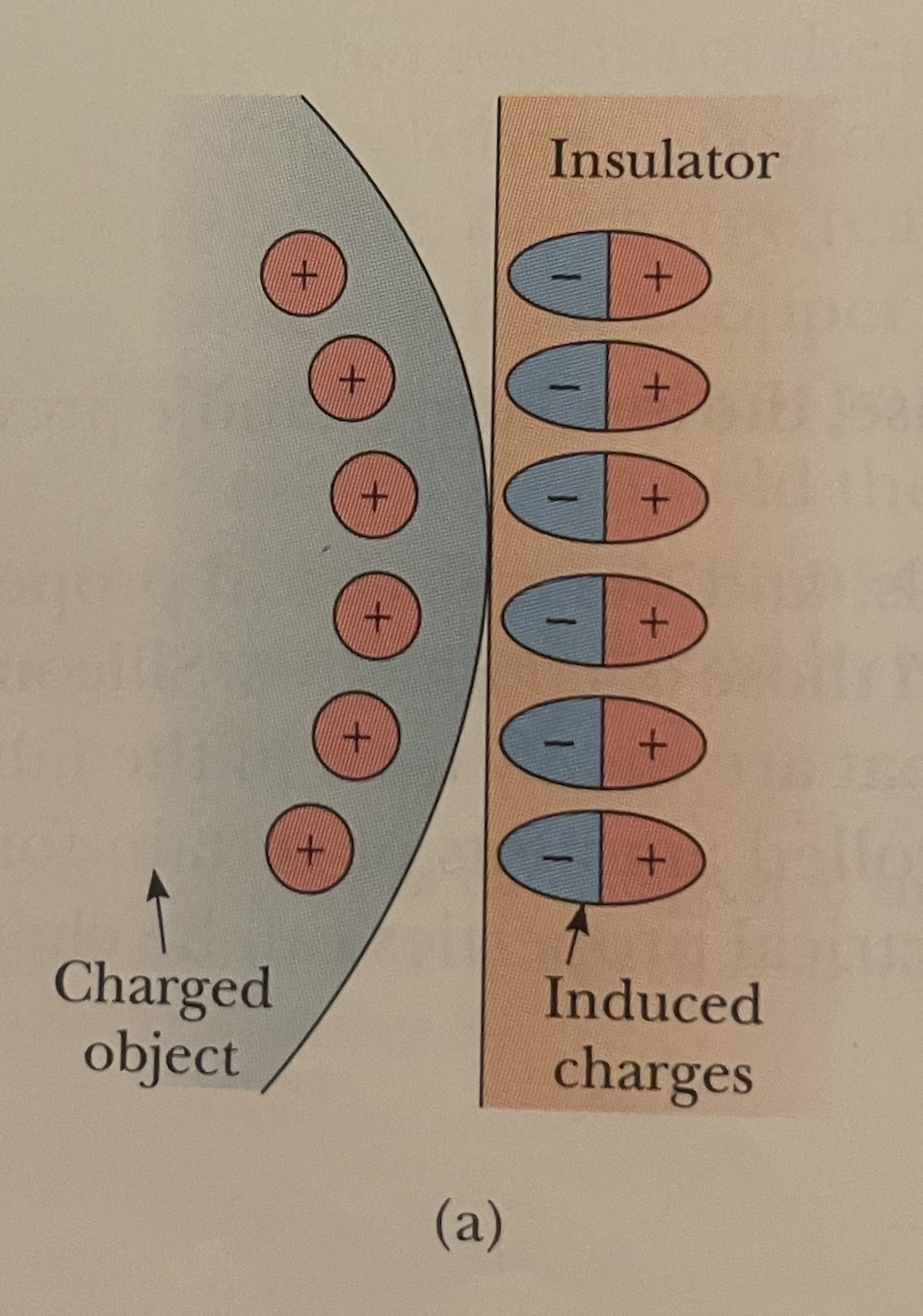
Draw what happens when you hold a charged object close to an insulator.
See photo.
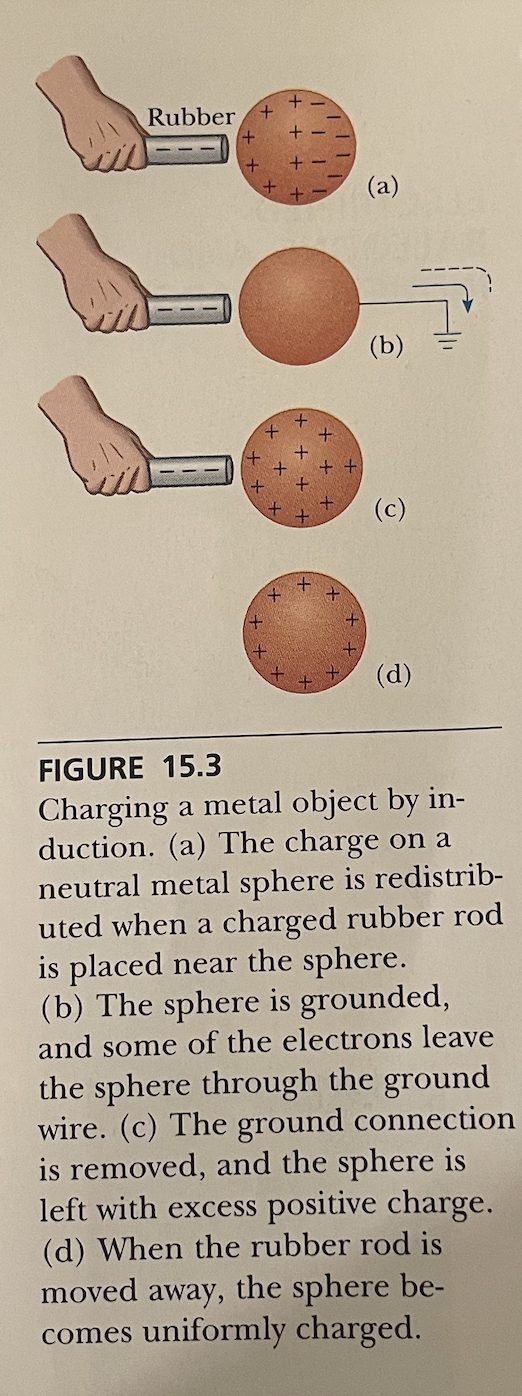
Explain what it would look like to charge a metal object by induction.
See photo.
What is the equation that define the electric field E?
See photo.

What is an electric field produced by?
Produced by Q not q0.
How is the direction of the electric field E defined?
The direction of E at a point = the direction of the electrical force that would be exerted on a small positive charge placed at that point. See photo.
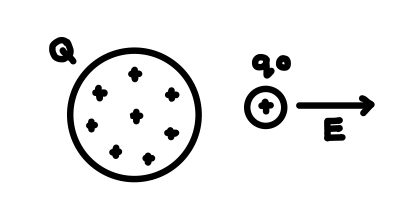
For an electrical field, what is the condition for the test charge? What would a test charge look like?
The test charge must be small enough to have a negligible effect on the charges on the sphere.
See photo.
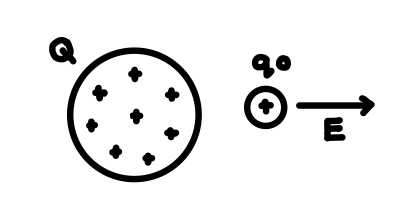
What does electrostatic equilibrium mean?
There is no net motion of charge.
What occurs in an isolated conductor?
There is zero electric field. Charge accumulates in sharp points (areas that have a small radius of curvature).
What is the expression for the electric field strength at a distance r from a point Q?
See photo.
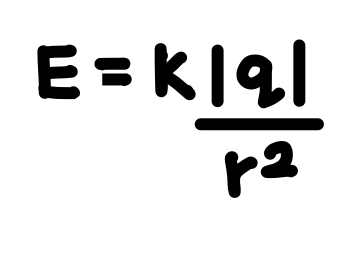
What is meant by the principle of superposition as it applies to electric fields?
If there are more than two charges present, the you must find the net electric force. The resultant force on any one charge = the vector sum of the forces exerted by the individual forces that are present.
See photo for an example.
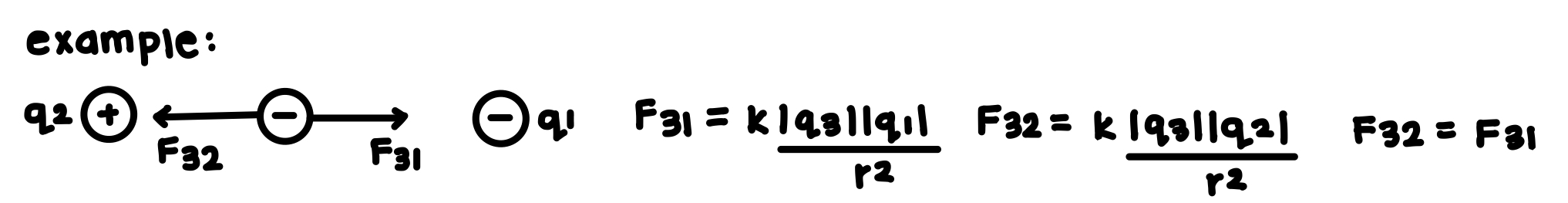
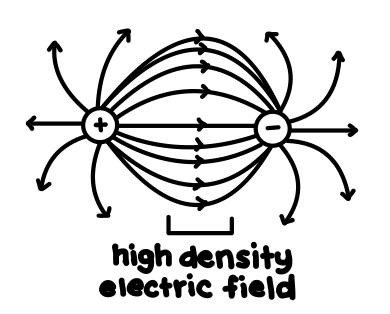
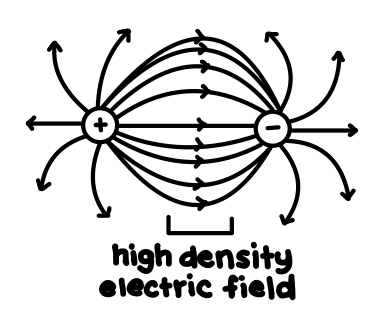
Draw the electric field lines between a positive and negative charge.
See photo.
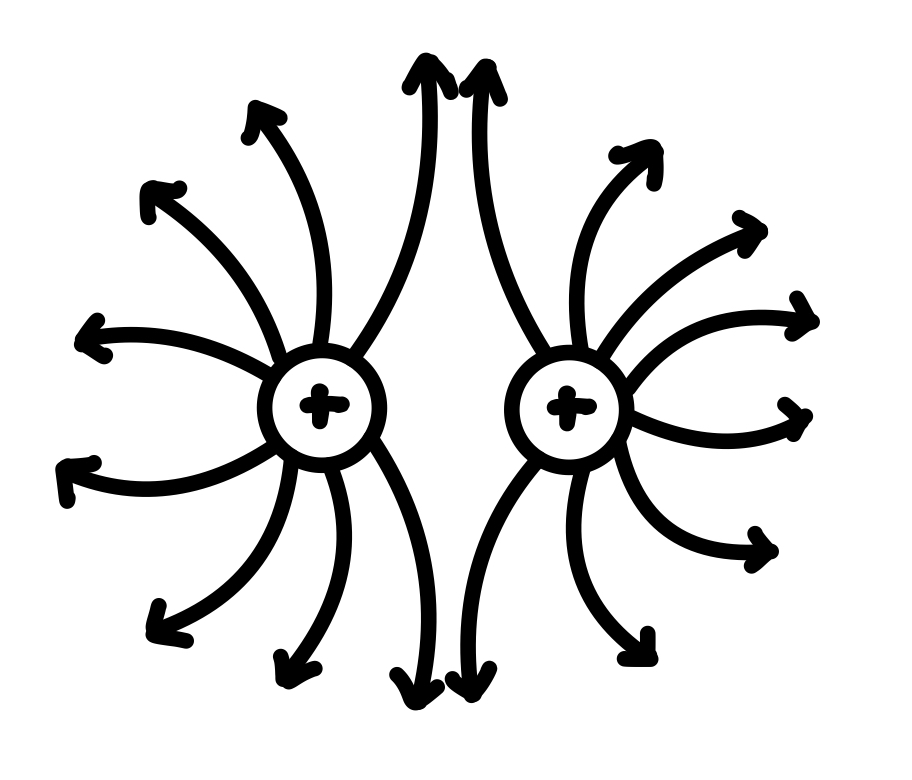
Draw the electric field lines between two positive charges.
See photo.
If you are drawing the electric field lines between a +2q and a -q and the +2q has 14 lines coming from it, how many lines are “connecting” to the -q? Why?
7 lines because the geometry of electric fields requires that the number of lines must be proportional to the magnitude of charge.
When drawing electric fields, a large E means that you draw the lines closer together or further apart?
Closer together. See photo.
When drawing electric fields, a small E means that you draw the lines closer together or further apart?
Further apart.
Can field lines cross?
NO! See photo for an example.
What happens when a glass rod is rubbed with silk?
Electrons are transferred from the glass to the silk. Because of the conservation of charge, each electron adds negative charge ti the silk, and an equal positive charge is left behind on the rod.
What happens when you rub two balloons with a cloth then place them next to each other?
The two balloons separate (repel each other) because they have like charges.
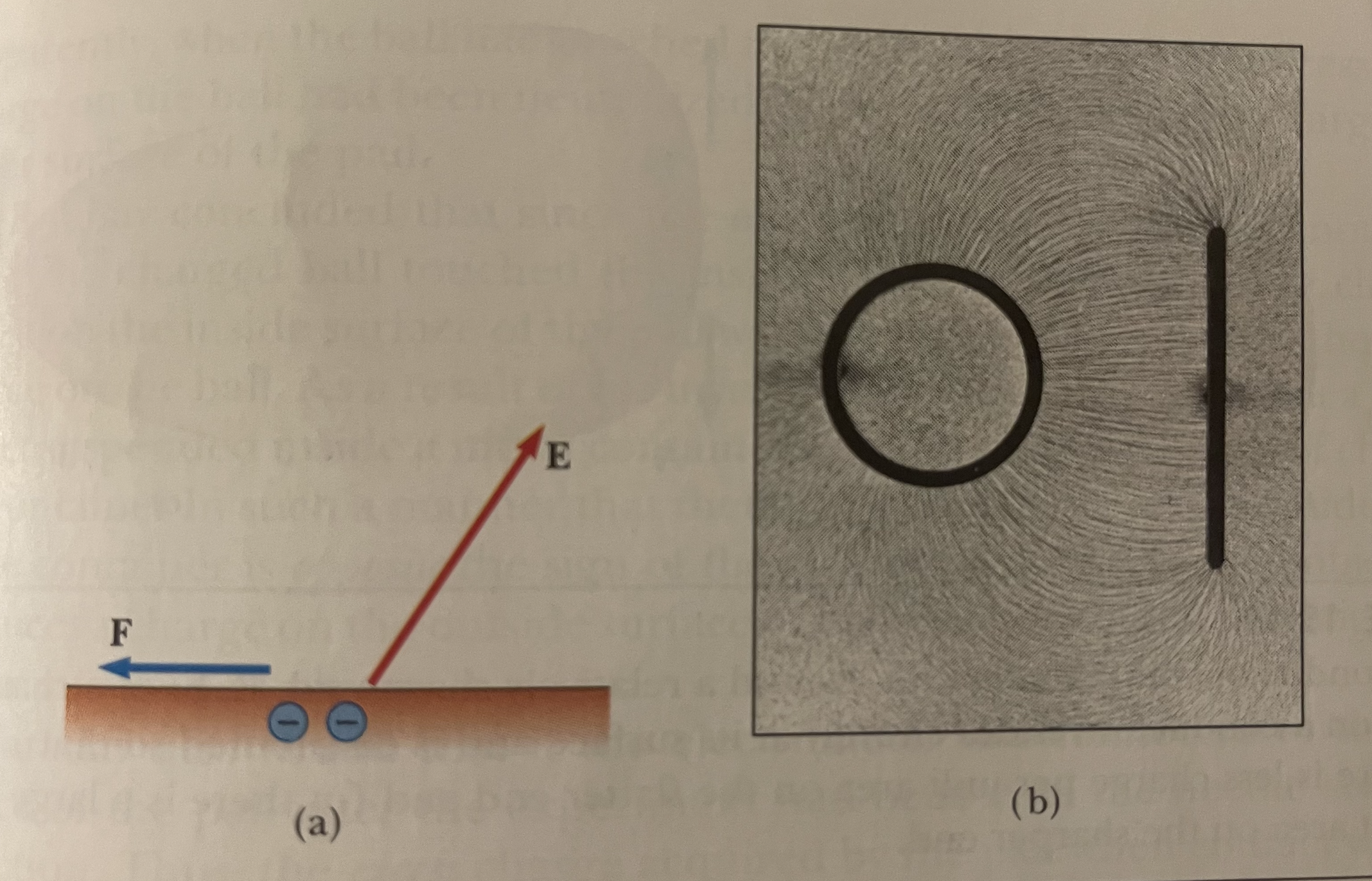
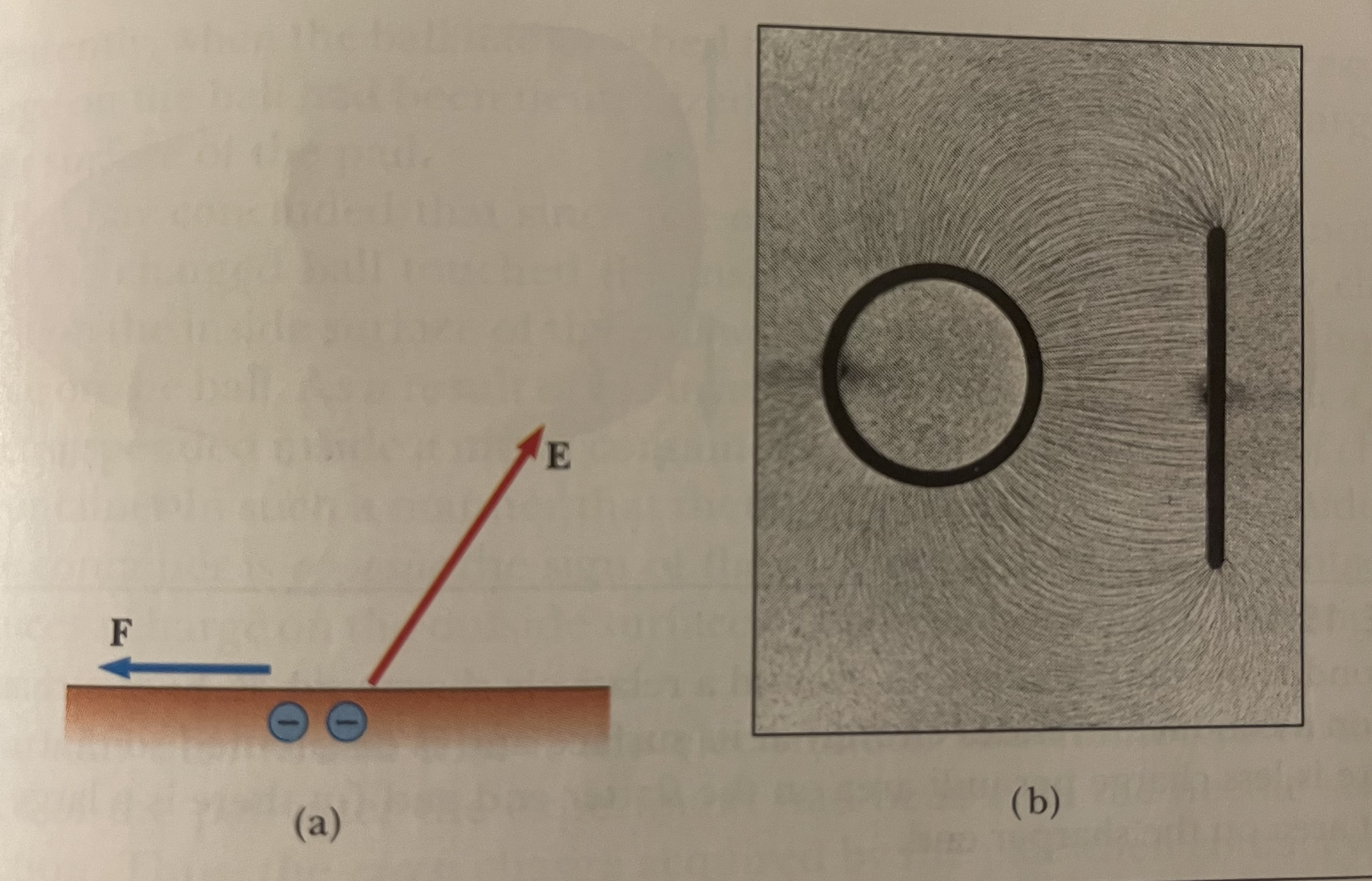
How can you make a balloon stick to a wall?
By making the balloon charged (by rubbing it with a cloth) then placing it next to the wall. The balloon induces a charge of the opposite sign on the surface of the insulating wall next to it. The opposite charges attract. See photo.
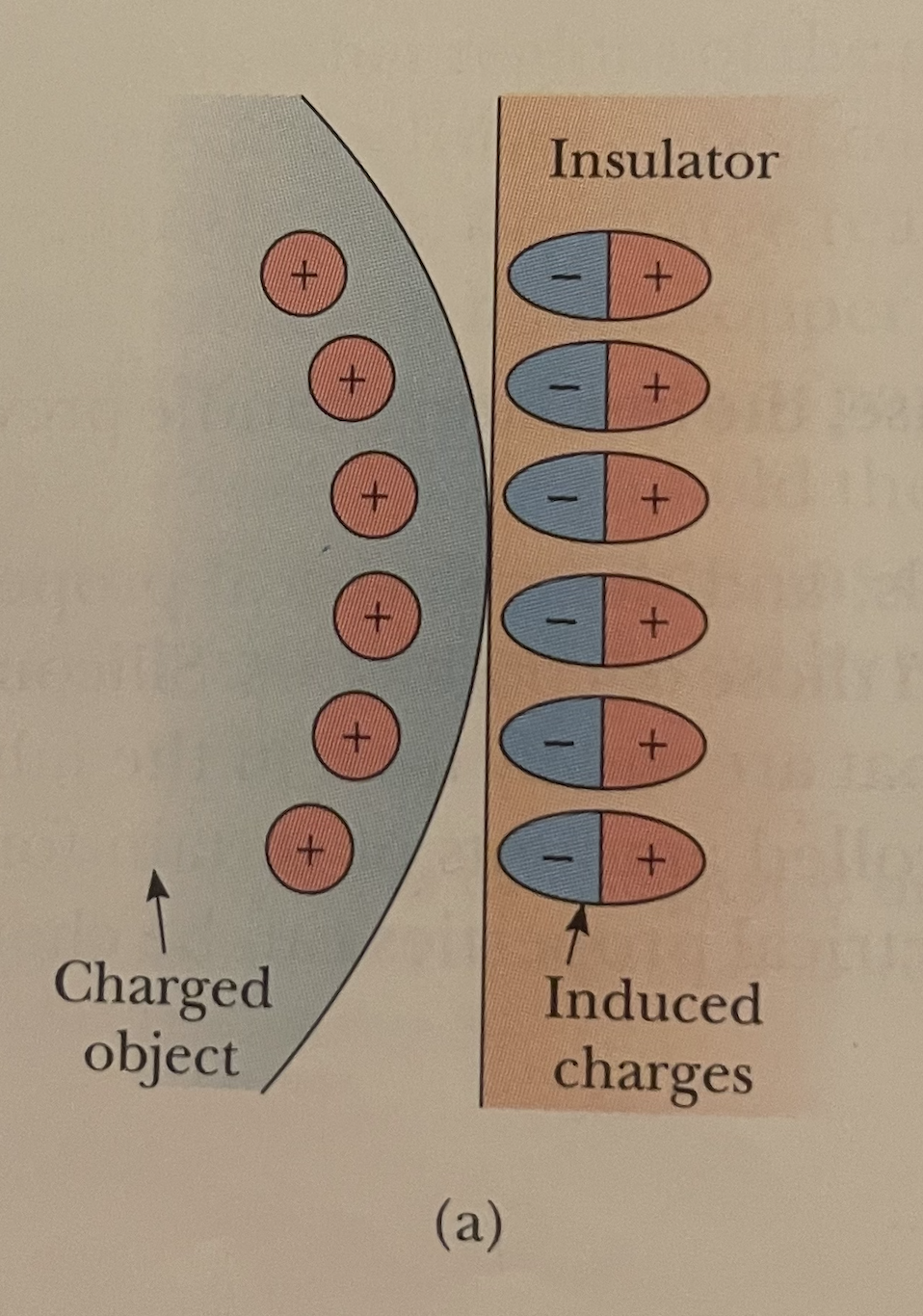
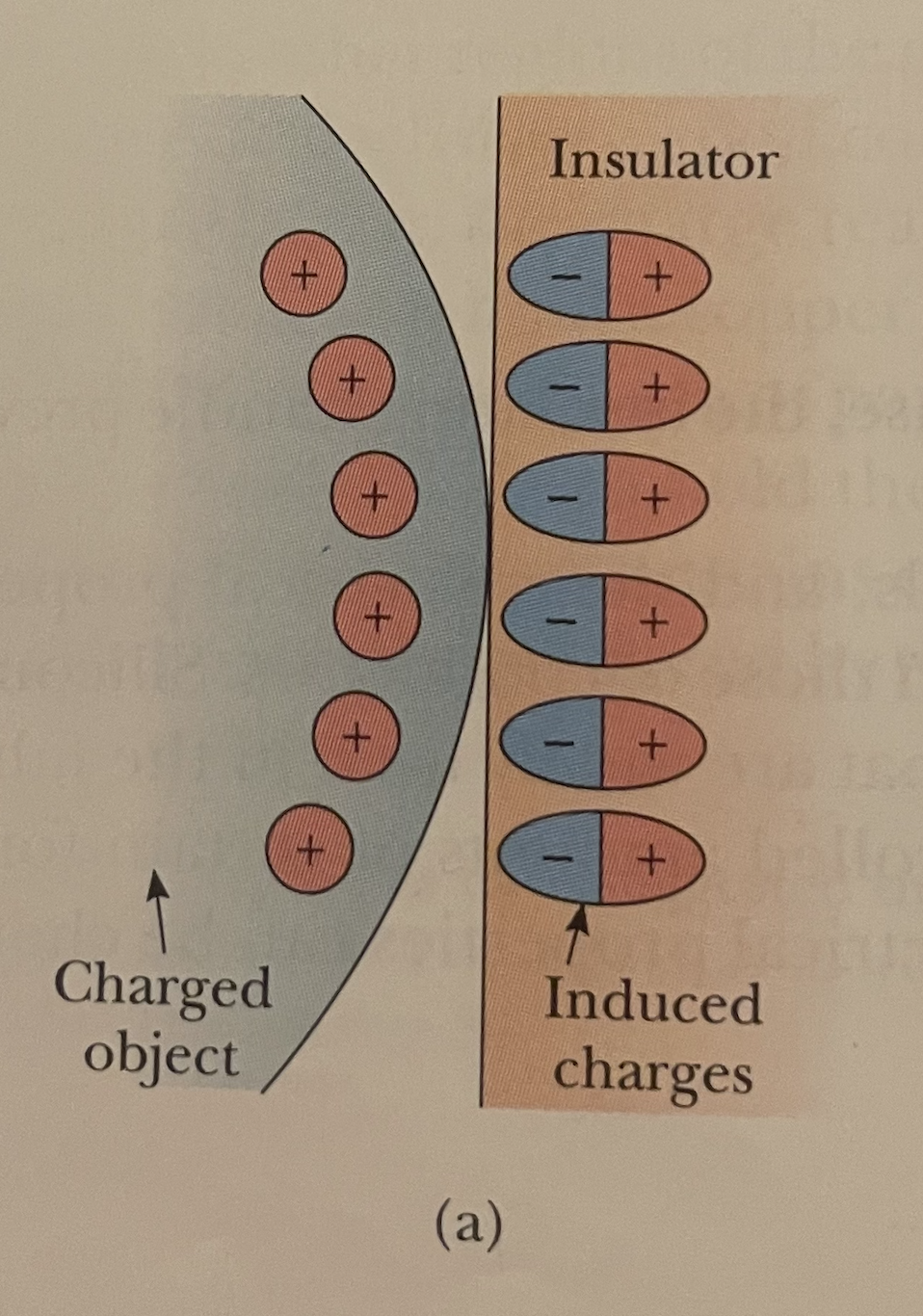
What is this an example of? Specifically refer to the insulator side.
Polarization.
In Coulomb’s force law, is force a vector quantity?
Yes.
Electric forces can be either attractive or repulsive, but gravitational forces are always ____.
Attractive.
What did Coulomb use to measure electric forces between charged objects? What does this device measure?
A torsion balance.
The angle of rotation increases = charge on the object increases.
Where does an electric field exist?
In the region of space around a charged object.
SKIP
SKIP
When drawing electric field lines, where must these lines begin and end?
They must begin on positive charges (or infinity) and must terminate on negative charges (or infinity in the case of excess charge
Where is an electric field zero?
Inside an isolated conductor that is in electrostatic equilibrium. See Photo.
In an isolated conductor that is in electrostatic equilibrium, in what direction does E point?
Perpendicular to the surface of the isolated conductor because if it pointed along the surface of the isolated conductor, the charges would move = not in electrostatic equilibrium. See photo.
Describe what a lightning rod and why they are put on the tops of tall buildings.
Spikes placed on tops of buildings that are connected to a copper rod that goes all the way down the building and connects to a copper plate deep into the ground.
When a negatively charges cloud passes over the building, the negative charges go down the copper rod, leaving the spikes the have a high density of positive charges.
The positively charges spikes ionize the nearby air, leaving the air positively charged.
The positively charges air surrounding the building, neutralizes the negatively charge cloud lowering its electrical potential.
This protects the building from being struck by lighting and causing a fire.
See photo.
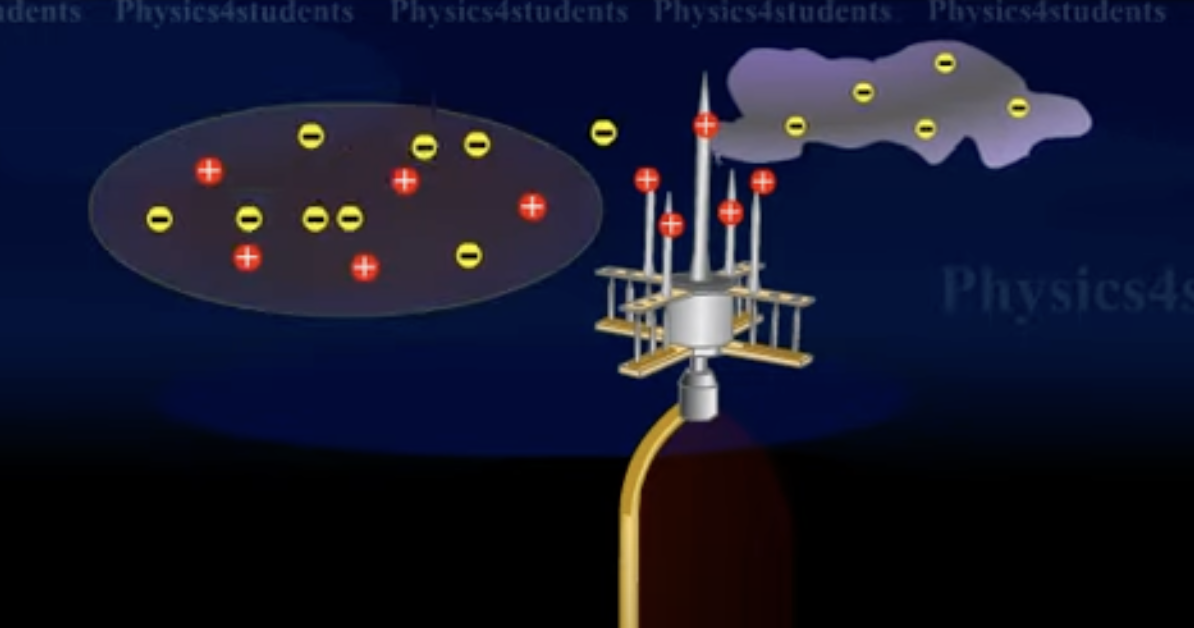
How do you create an isolated conductor?
You put an insulator under it so it is isolated from the ground.
Describe Faraday’s Ice Pail Experiment (Use metal sphere example in the book).
Setup: You have a isolated conductor (conductor with an insulator below it so it is not grounded) which is a metal ice bucket. You have a device that measures if there is an electric field present with the deflection of gold leaf. You also have a positively charged metal sphere.
Stick an uncharged metal sphere into the bucket = no electric field detected.
Place positively charges metal sphere into bucket.
The bucket now is negatively charged on the inside and positively charged on the outside = electric field detected.
Touch the positively charged metal sphere to the bottom of the bucket.
Negative charges neutralize metal sphere, leaving only the positive charges on the outside of bucket.
Remove the neutralized metal sphere.
Positive charges still remain on the outside of the bucket = electric field detected.
See photo.
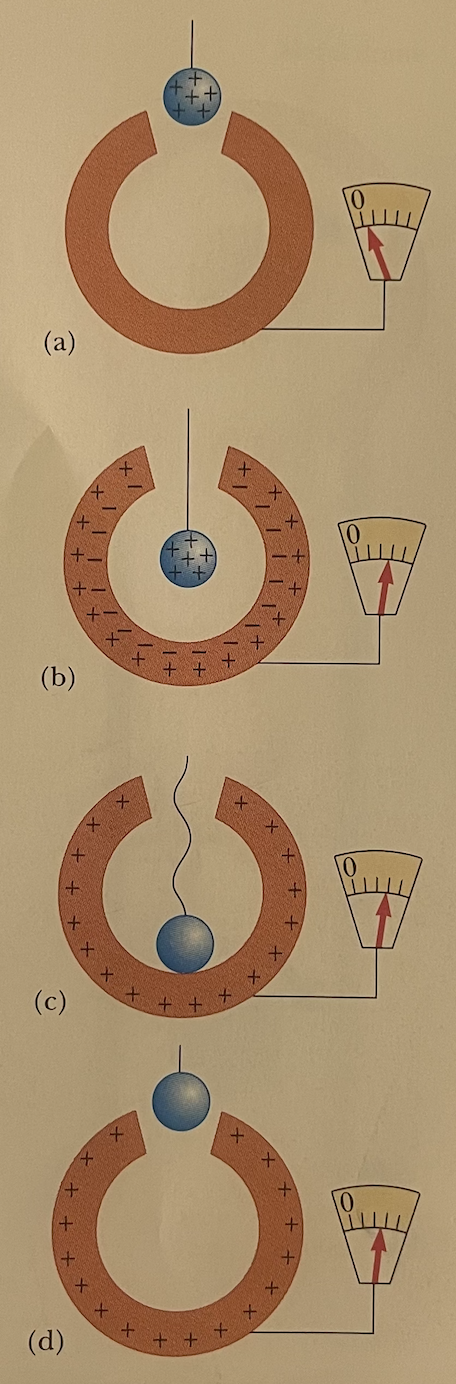
Briefly describe Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment.
Oil mist sprayed.
Air surrounded oil droplets ionized by an x-ray.
Oil droplets captured an electron and became charged.
When measuring the charge, Millikan discovered that the charged of an electron was quantized and that q = ne where n = 1, 2, 3, …
Describe what happens in a Van Graaf Generator.
The belt starts rolling.
Electrons jump from cotton belt to the roller, causing it to become negatively charged.
The metal comb under the roller becomes positively charged at the tips due to the electrons being repelled by the negatively charged roller.
The electric field between the roller and the comb, causes the air to ionize, and the electrons from the air neutralize the comb.
The positive electrons left in the air are attracted to the roller but are scooped up by the belt and taken to the top roller.
The electrons in the top roller neutralize the belt, causing the roller to become positive.
The negative charges in the air are attracted to the roller and neutralize it.
The positive charges left in the air cause the tip of the comb above the roller to become negative.
The positive charges that leave the comb spread out on the surface of the metal dome.
A grounded wand comes close enough to discharge it.
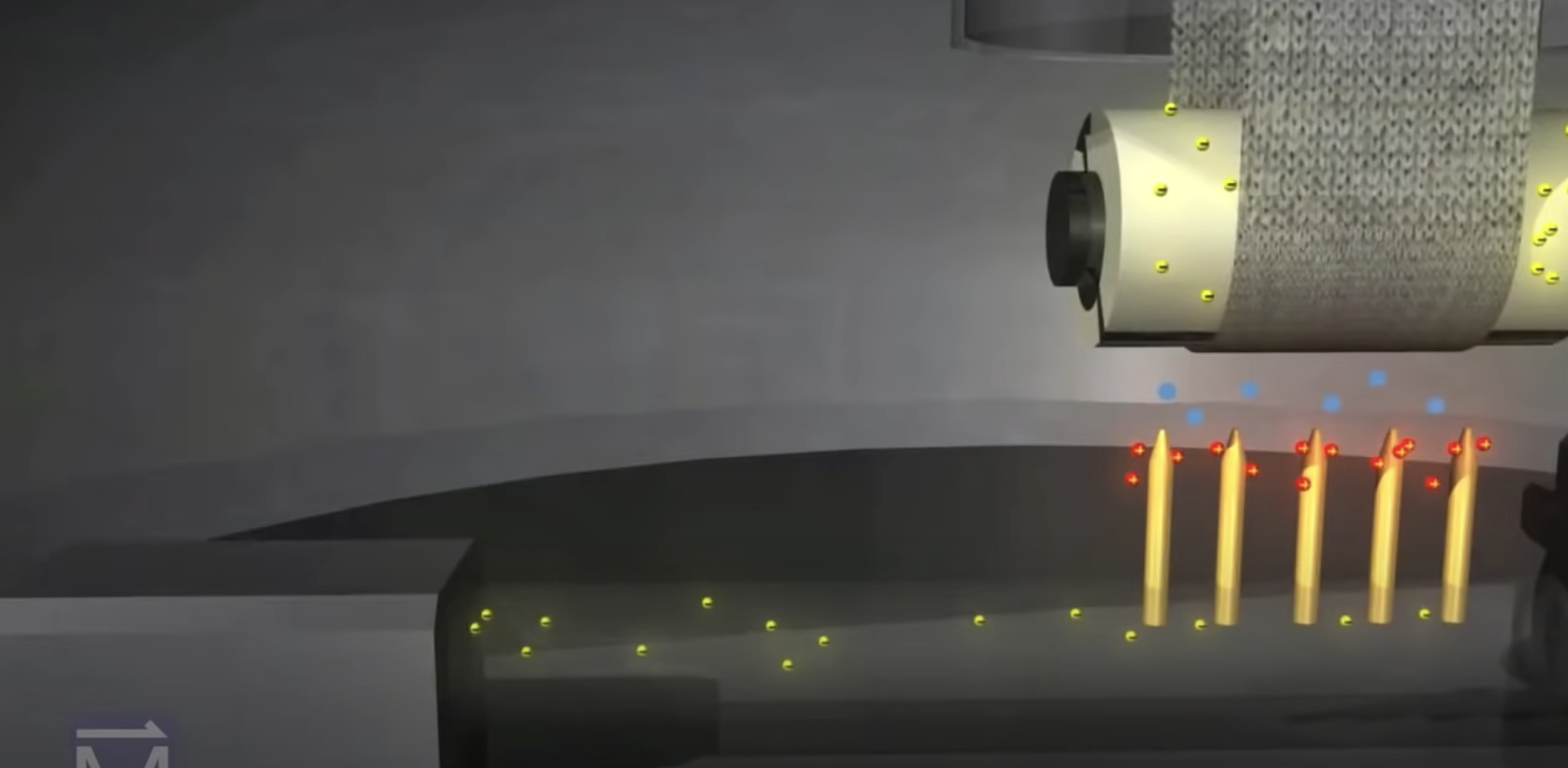
What does an oscilloscope do? What is it made up of? What is displayed on the oscilloscope?
Creates a visual display of electronic information.
Uses a cathode tube, electron gun, anodes, deflection plate, and florescent screen to do so.
Sinosoidal waves created.
Can both conductors and insulators experience polarization.
Yes.
If a suspended object, A, is attracted to. object B, which is charged, can we conclude that object A is charged?
Not necessarily. Although the attraction could be due to unlike charges, it also could be due to polarization of a neutral object.
An uncharged, metallic coated ping pong ball is placed in the region between two vertical parallel metal plates. If the two plates are charged, one positive and one negative, describe the motion that the ball undergoes.
What would happen if the ball were to touch the negative plate?
The two charged plates create a uniform electric field between the two = ball would experience no net force.
If the ball touched the negative plate, it would acquire some negative charge, causing it to accelerate towards the positive plate. If it touches the positive plate, it would acquire a positive charge and accelerate back towards the negative plate.
How many significant figures in 0.000395?
3
How many significant figure in 564,000?
3
If you are confused about significant figures, what should you do?
Put it into scientific notation.
How many significant figures in 0.23900?
5 because trailing zeros in decimals are ALWAYS significant.
How many significant figures for the answer of this problem:
1245 - (14 × 2.3 )
14 × 2.3 = 32 (two sig figs)
- 32. = 1213. (because the decimal point is in the same place = rule for subtraction and addition).
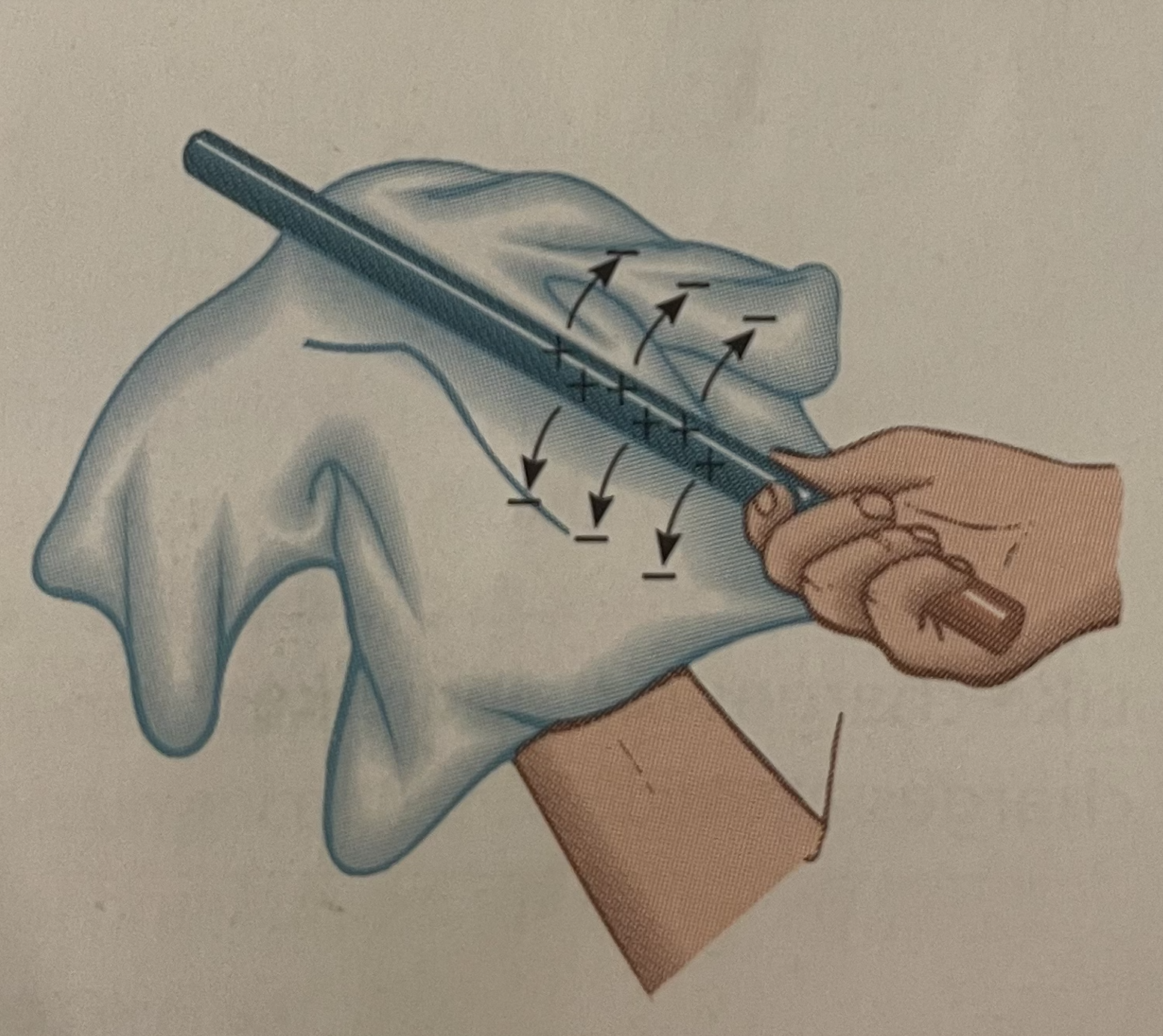
What happens when you rub a copper rod with wool then hold it next to a paper?
What happens if you hold the copper rod with an insulated handle instead?
The excess charge formed from rubbing is sent through your body to the Earth = grounded.
But when you have an insulated handle, the excess charge remains in the rod and attracts the piece of paper.
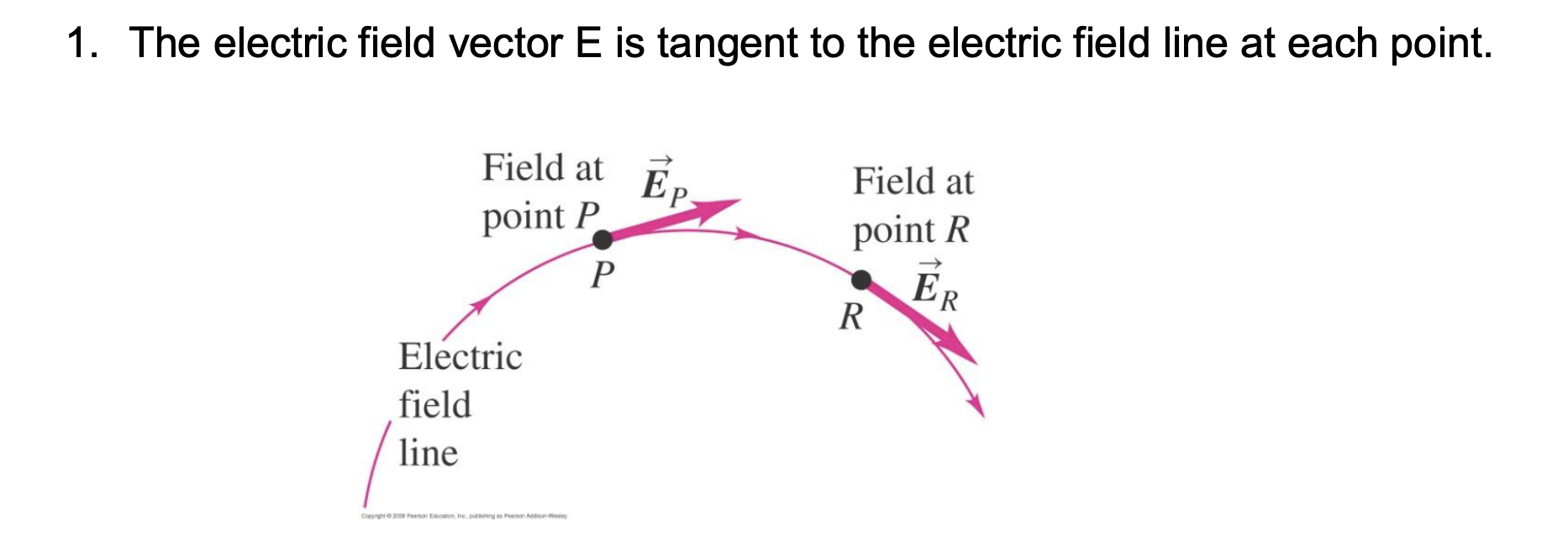
The electric field vector is ____ to the electric field lines.
Tangent. See photo.
What is the change in electric potential energy equation?
See photo. Only valid for a uniform electric field!
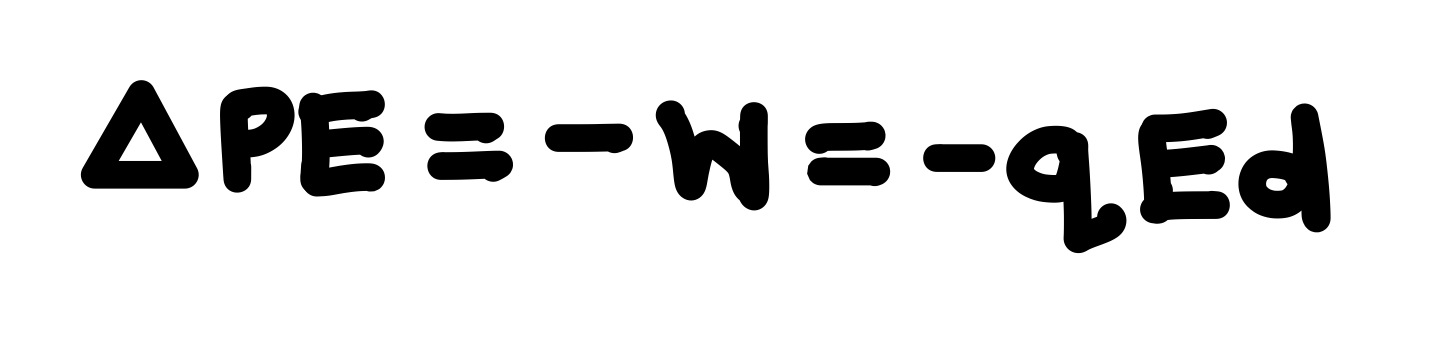
What is the equation for the work done on the charge by the electric force?
W = Fd = qEd
What are the units of electric potential?
1 Joule/Coulomb = 1 Volt (V)
How do we compute the work done in moving a charge from one point at a potential V1 to another point at a potential V2?
See photo.
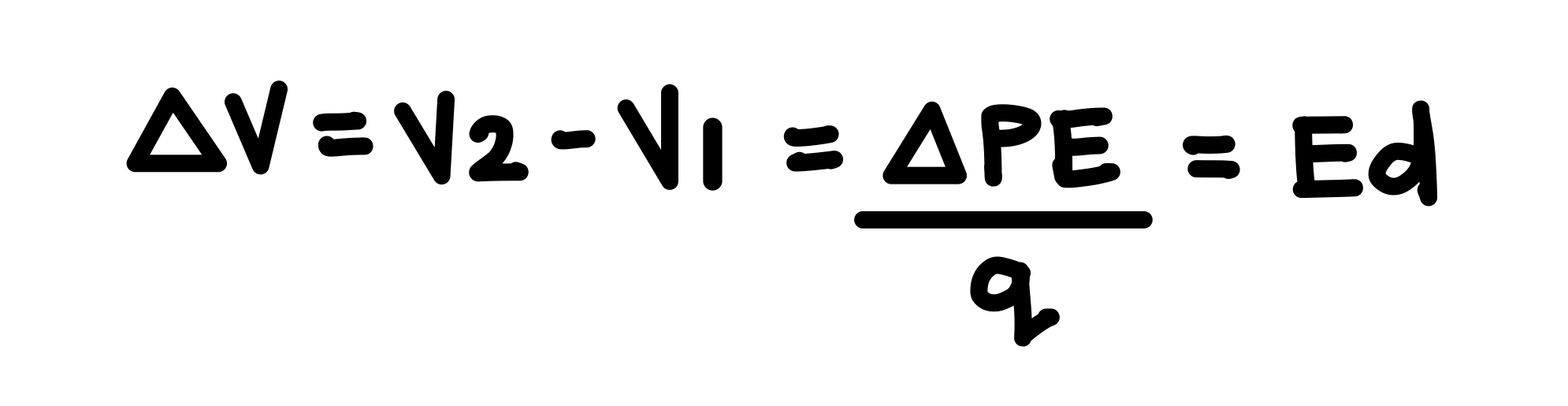
If you gain PE, you lose …
KE. See photo.
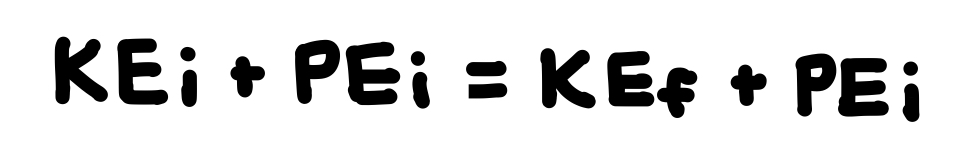
How do kinetic energy and potential difference relate?
See photo.
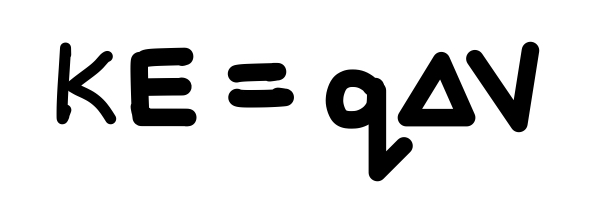
Write the equation for the potential at a point P at a distance r from a point charge Q.
See photo.
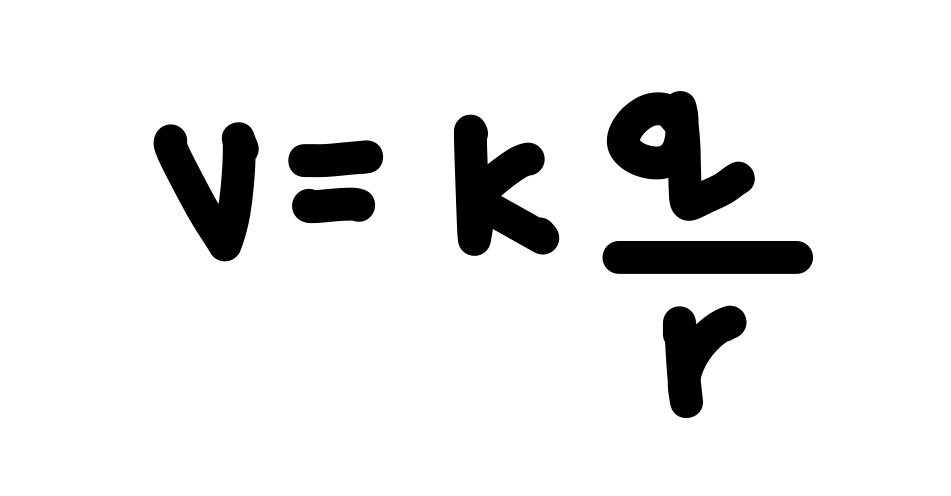
What does it mean if you get a negative potential energy as your answer for when two point charges are brought near one another.
That positive work must be done on the charges to separate them. Remember PE = - W.
How is the electric field E between two parallel conducting plates related to the distance d separating the plates and the voltage (i.e., potential) difference V between them?
V = Ed
What is the equation for capacitance?
See photo.
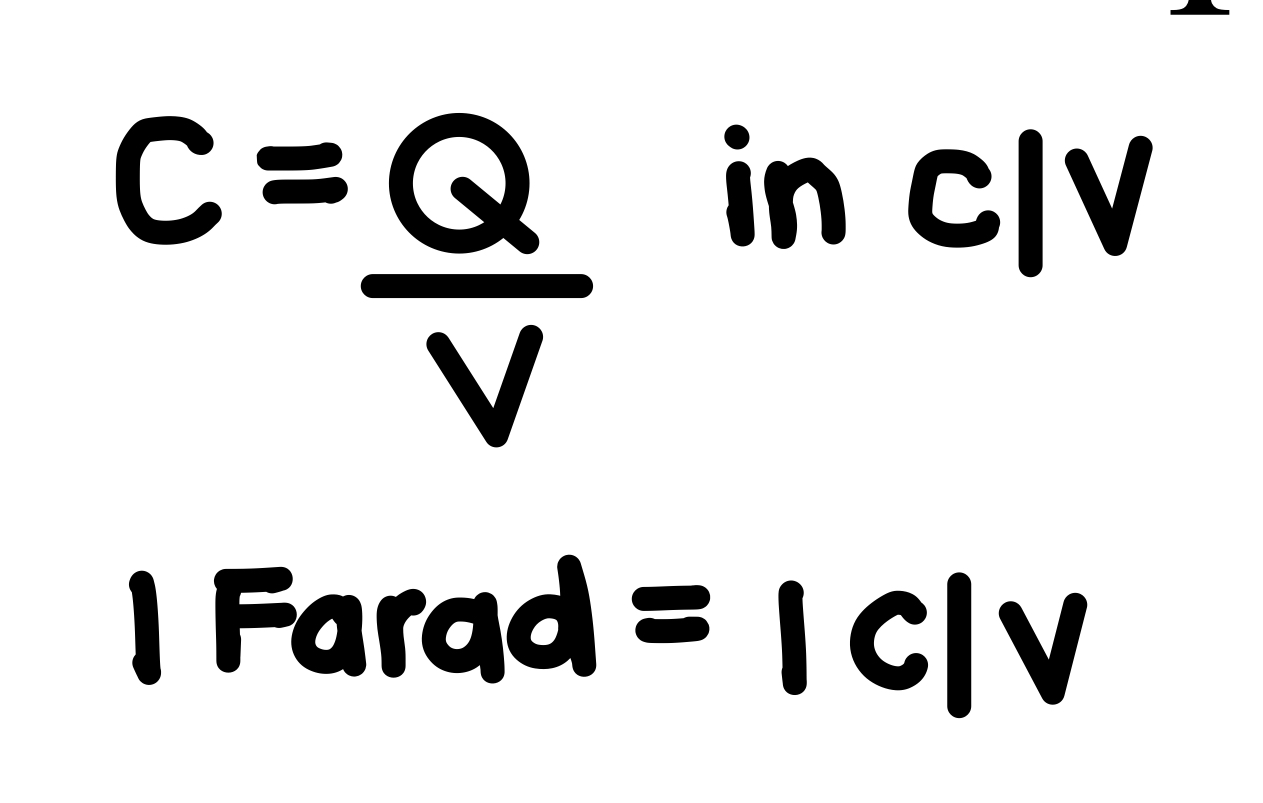
1 C/V = ?
1 Farad.
A positive charge gains electrical potential energy when it is moved in the same or opposite direction of the electric field? What happens when the charge is released from rest?
Opposite. This is analogous to a mass gaining gravitational potential energy when it rises to higher elevations in the presence of gravity.
It accelerated downwards (in the direction of the electric field) = gains KE = loses PE.
A negative charge loses electrical potential energy when it is moved in the same or opposite direction of the electric field? What happens when the charge is released from rest?
Opposite.
Accelerates in the direction opposite of the field = Gains KE = loses PE.
Does the superposition principle apply to electric potentials?
Yes!
What is the equation for calculating the PE for a pair of charges?
See photo.
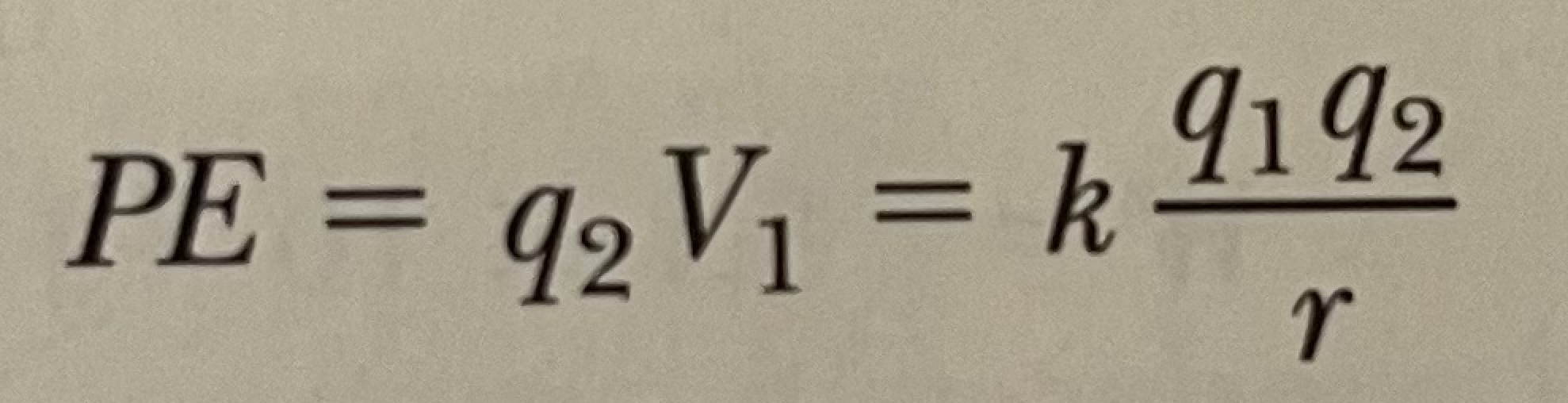
When like charges repel, what type of work must be done to bring the two charges near each other?
Positive work.
With charges of opposite sign, what type of work must be done to bring the charges close together?
Negative work, because the force is attractive.
How does work relate to potential difference? So how much work is required to move a charge between two points that are at the same potential?
See photo. Zero work required.
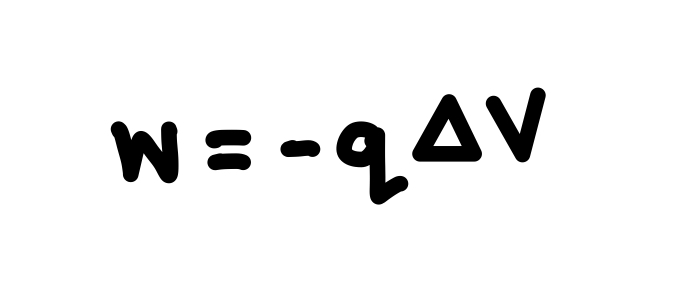
What happens to the electric potential of a charged conductor in equilibrium?
The electric potential is constant for all points.
Is work required to move a charge between two points inside an isolated charged conductor in electrostatic equilibrium?
No, because there is no electric field, so no work is required! If work = 0 → Electric potential difference = 0. This the electric potential inside is constant.
What is the electron volt defined as?
The energy that an electron or proton gains when accelerated through a potential difference of 1 V.
What does 1 eV equal?
1 eV = 1.6 × 10^-19 CV = 1.6 × 10^-19 J.
What is an equipotential surface?
A surface in which all points are at the same potential.
Is work required to move a charge at a constant speed on an equipotential surface?
No.
Draw the electric field lines and equipotential lines for a positive charge.
See photo.
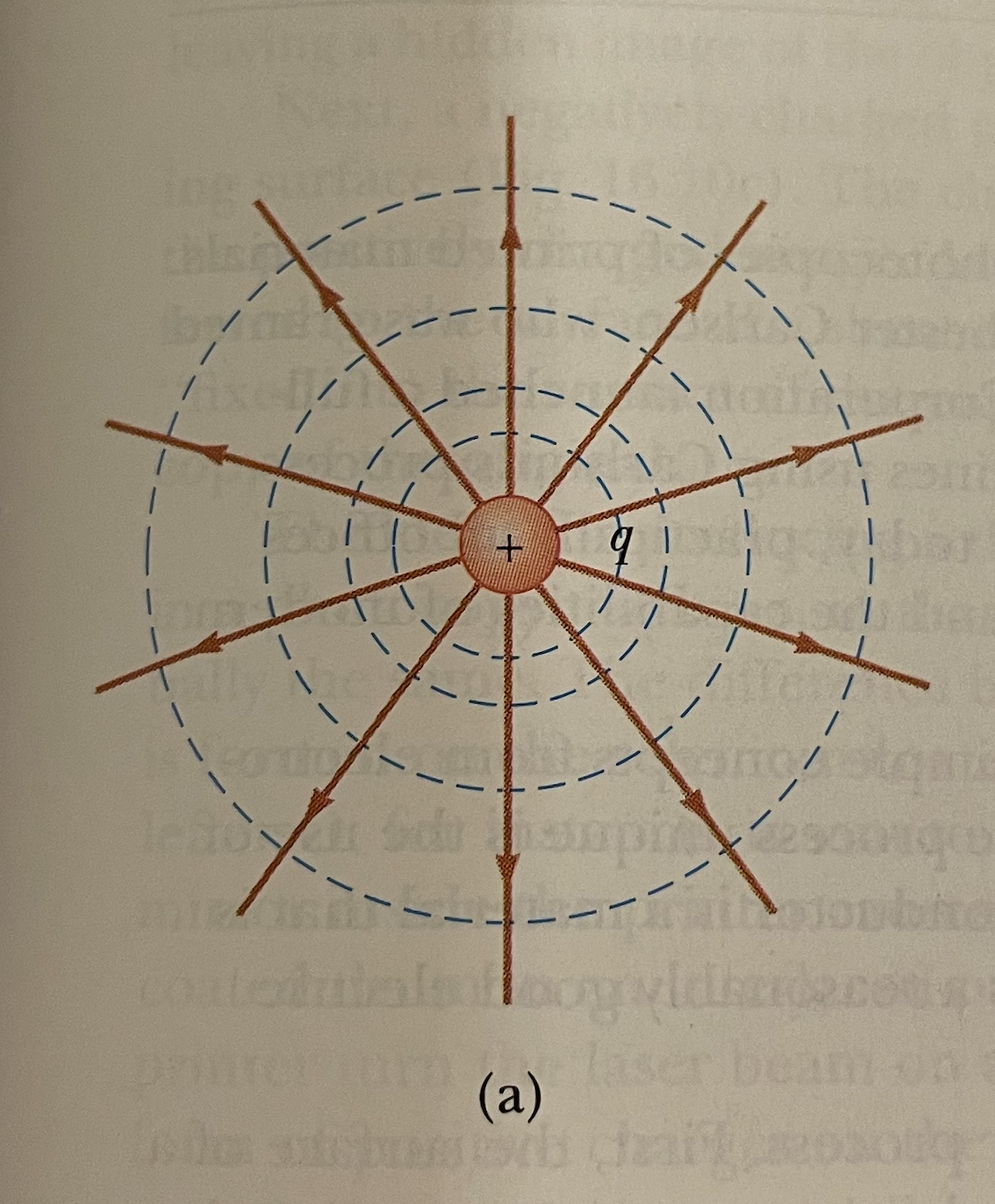
What does a charged capacitor act as?
A storehouse of charge and energy that can be reclaimed when needed.
Write an expression for the capacitance of a parallel plate conductor having an air gap d between the plates.
See photo.

How is the permittivity of free space related to Coulomb’s constant.
See photo.

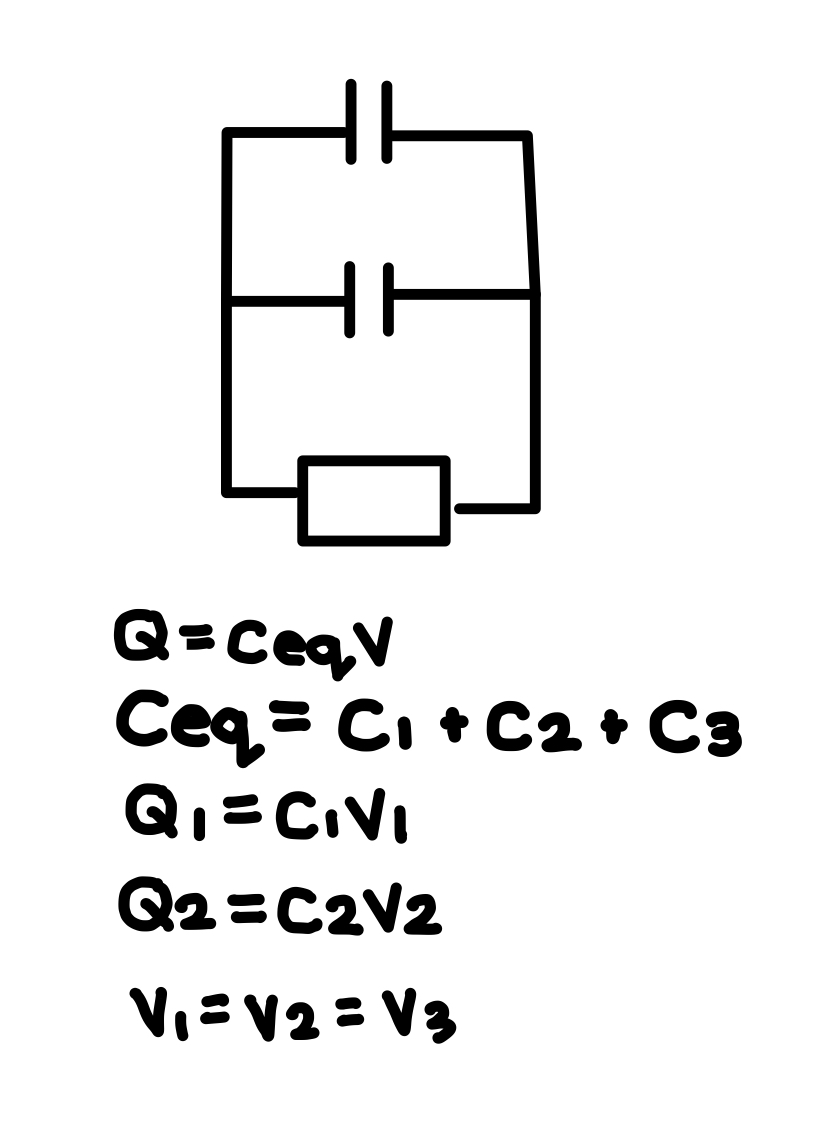
What must be the same in parallel capacitor combination? What is different. What are the associated equations?
The voltage (potential differences) across the capacitors are the same. The charge is different. See photo.
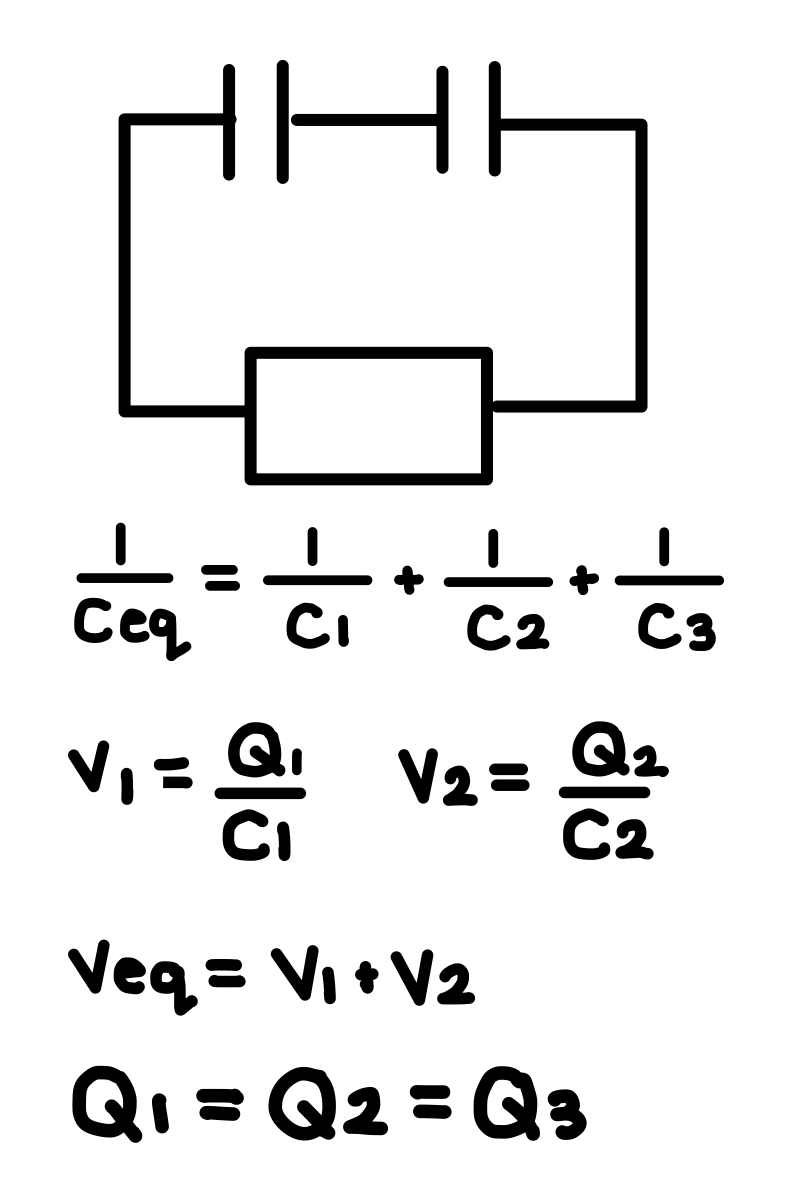
What must be the same in series capacitor combination? What is different. What are the associated equations?
The charge is the same. The voltages (potential differences) are different. See photo.
What is the formula for calculating the energy stored in a capacitor?
See photo.
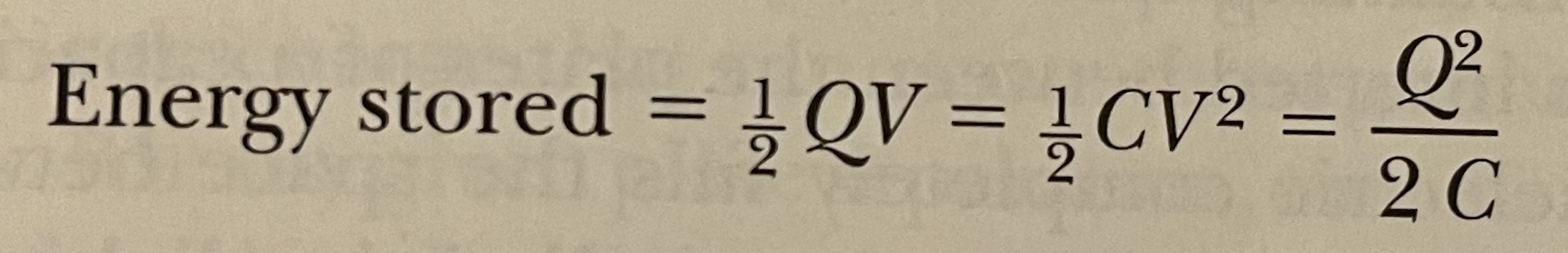
What are defibrillators?
Charged capacitors.
What is a dielectric and what happens when it is inserted between the plates of a capacitor?
An insulating material such as rubber, glass, or wax paper. When inserted, capacitance increases.
What is the formula that shows what happens to capacitance when a dielectric fills the space between the two capacitors?
See photo.
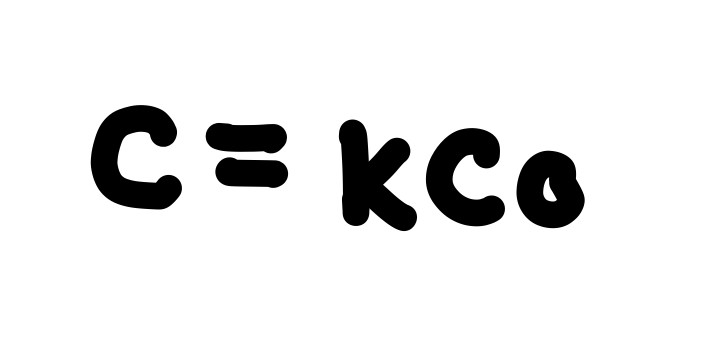
What happens to a dielectric when it reaches its maximum electric field (dielectric strength)?
It breaks down and begins to conduct.
How does a stud finder work?
In a stud finder, its capacitor plates are arranged side by side instead of facing each other. So, when a stud finder comes across a stud, the dielectric constant of the material between the plates changes. This change in capacitance causes a light to turn on in the stud finder.
Explain the difference between electric potential energy & electric potential difference. State the equations associated with both.
Electric potential energy is a property of a charged object, by virtue of its location in an electric field. Electric potential energy exists if there is a charged object at the location.
Electric potential difference, also known as voltage, is the external work needed to bring a charge from one location to another location in an electric field. Electric potential difference is the change of potential energy experienced by a test charge that has a value of \[+1\].
See photo.
![<p><strong>Electric potential energy</strong> is a property of a charged object, by virtue of its location in an electric field. Electric potential energy exists if there is a charged object at the location.</p><p><strong>Electric potential difference</strong>, also known as <strong>voltage</strong>, is the external work needed to bring a charge from one location to another location in an electric field. Electric potential difference is the change of potential energy experienced by a test charge that has a value of <span style="font-size: inherit; font-family: inherit">\[+1\]</span>.</p><p>See photo. </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/41caf95f-eabc-4e08-9cea-f451632048ec.png)
What does xerography use?
Uses photoconductive material to form an image.
Usually Selenium.
A photoconductor = poor conductor in dark but good conductor in light.
Describe the xerography process.
The surface of the plate or drum is coated with a thin film of photoconductive material. The photoconductive material has a positive charge in the dark.
The page to be copied is then projected onto the charged surface.
The photo-conducting surface becomes conducting only in areas where the light strikes.
There the light produces charge carriers in the photoconductor, which neutralize the positively charged surface.
The charges remain on those areas of the photoconductor not exposed to light, however, leaving a hidden image of the object in the form of a positive charge distribution.
A negatively charged powder (toner) is dusted onto the photo-conducting surface.
The charged powder only adheres to the areas that contain the positively charged image.
The image becomes visible.
Transferred to a piece of paper and “fixed” to the paper using heat.
Results in a permanent copy of the original.
Describe how a laser printer works.
Similar process to xerography but the difference is how the image is formed on the selenium-coated drum:
Command is sent from a computer to the laser.
A rotating mirror inside the printer causes the beam of the laser to sweep across the drum in a interlaced pattern (electrical charges cause the laser to turn off and on).
Image traced.
Toner applied to drum.
The transfer to paper is accomplished as in a photocopy machine.
When does a current exist?
When charges of like sign move.
What is the equation for current?
See photo.
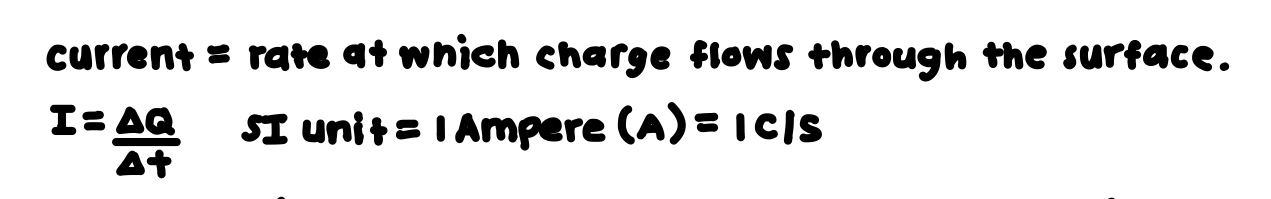
It is conventional to give the current the same direction as the flow of ____ charge.
Positive. For example, if negative charges are flowing, the current is in the opposite direction.
What is meant by drift speed?
The speed of charge carriers.