Orgo Exam 2
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
a __ PKa is associated with a _ acid
a lower PKa is associated with a stronger acid
Stronger acid = ___ CB
Stronger acid = weaker CB
More stable base = __ base
More stable base = weaker base
Why does stabilizing a molecule = weaker base?
Stabilizing a molecule lowers the energy of the electrons and they’re less available to donate.
Resonance does what to bases?
Resonance stabilizes bases
More stable base; weaker base
Induction does what to bases?
EN atoms pull e- density away from a base which becomes less negative
Less negative = worse base
ex: F is EWG and stabilizes the negative charge
Explain why less negative = worse base
because (+) charge lowers the energy of the e-s and they are less available to donate
What does induction have to do with bases?
sp = most stable
More stable = weaker base
What side of the equation does equilibrium favor in an acid-base reaction?
Eq. favors the higher PKa
Reaction always proceeds from strong to weak acid
What’s the key to memorizing how to compare bases:
Atom
Resonance
Induction
Orbitals
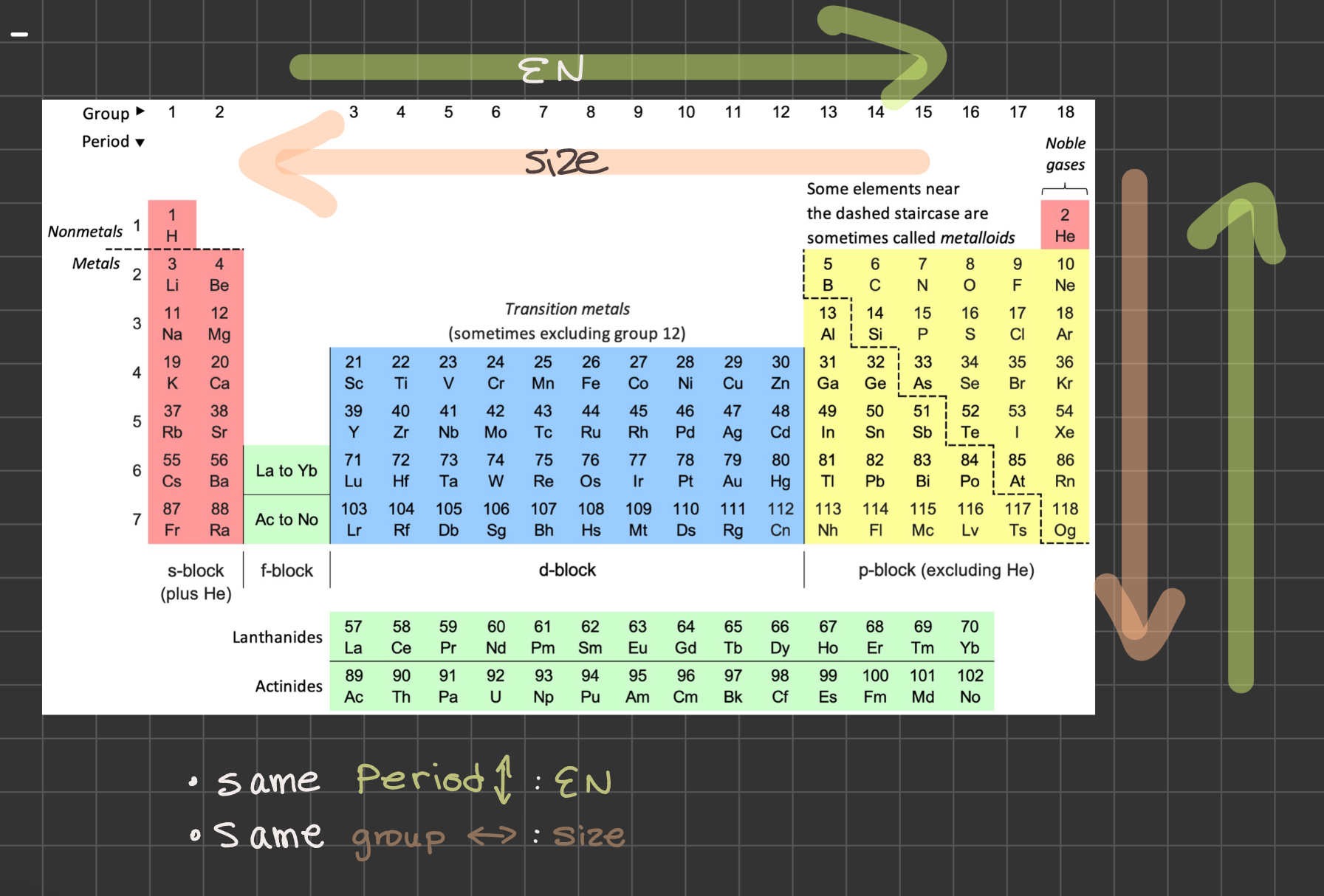
What’s the atom rule for comparing base strength?
Same period = EN trends
Same group = Size trends
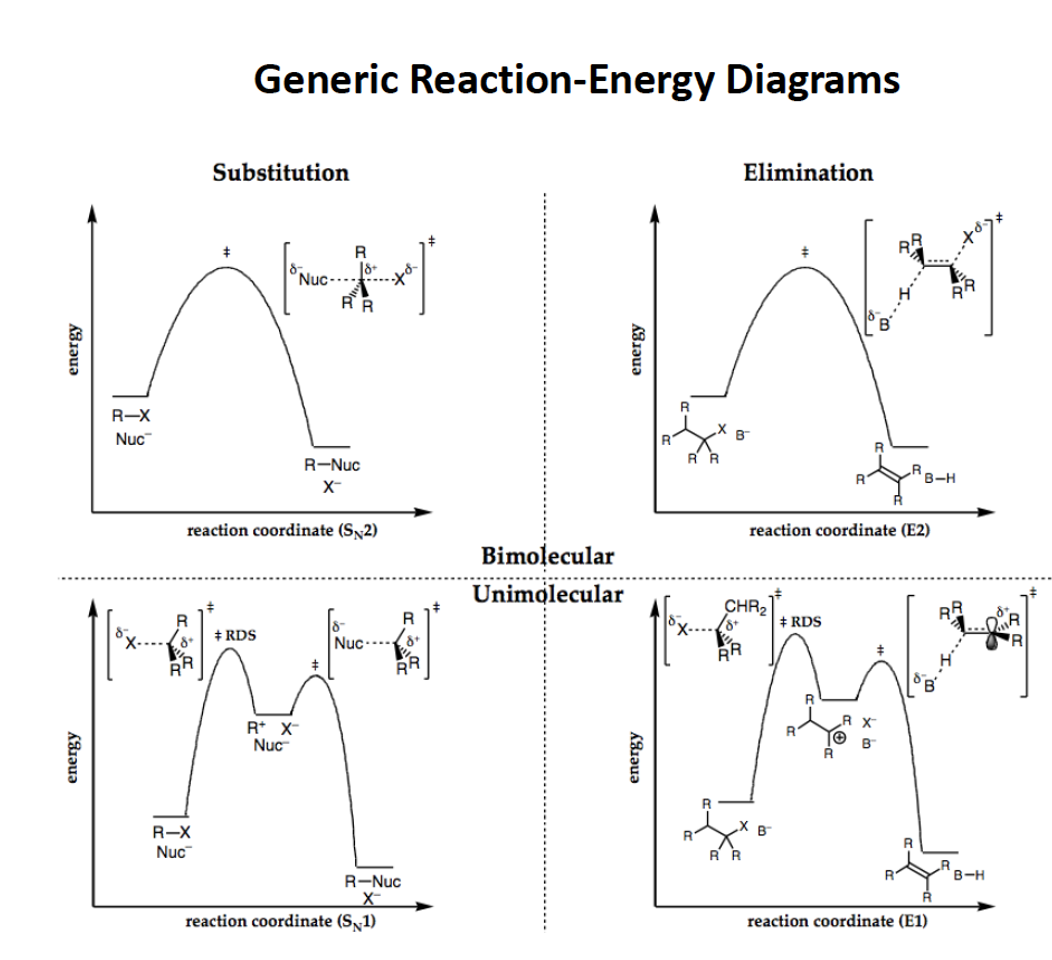
Rate laws for all mechanisms?
SN2: rate = K[Nu][E]
E2: rate = K[B][E]
units are M*s-1
SN1: rate = K[E]
E1: k[E]
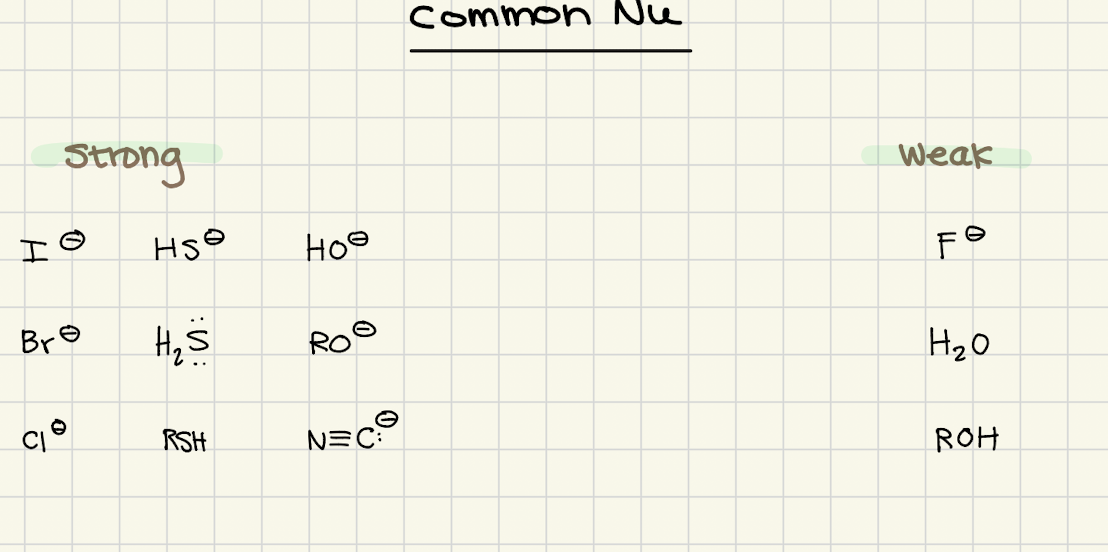
What are the common weak Nu?
3
Given H2SO4 or H3PO4 as the solvent what mechanism will occur?
E1
Heat promotes what
E1 over SN1
1* alcohols with HCl, HBr, or HI lead to what mech
SN2
Draw the RCD for E1, SN1, E2, SN2
Zaitsev Rule
more stable = more substituted
When is Hoffman’s Rule favored?
(never for E1) when a bulky base is used
Thee pKa of H3O+ is -1.7 and given that HN3 : H3O+ is 105 : 1, what is the pKa of HN3?
3.3 because every multiple of 10 is equal to 1.0 pKa.
-1.7 + 5 =3.3
A better leaving group is what?
Bigger, more polarizable
Cyclopropane is more acidic than cyclohexane, why? Consider s character and bond angles
The C-C-C bond angles of cyclopropane is 120 and the cyclohexane is 109. 120 has more S character and better able to stabilize electrons
Given this NU/Base what does the M stand for?
MCN
M = counter cation
Why is a five carbon ring better than a four
because there is less ring strain
When is Hoffman favored
during E2 when we use a statically hindering base
Write the four things for bases/nu
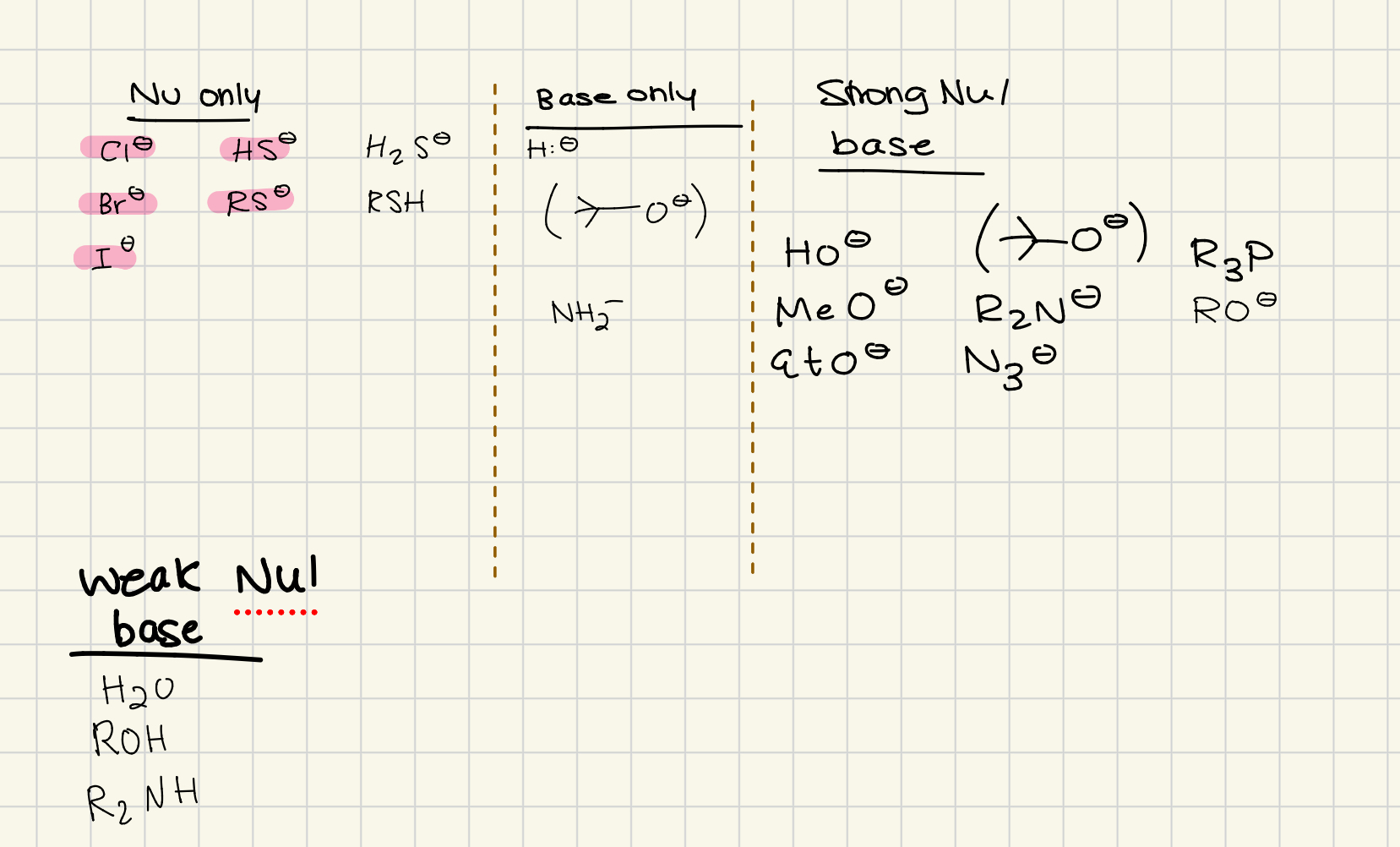
Nucleophile def
gives up/donates e-
electrophile
poor in e- density, has fewer electrons, wants electrons
What makes a good leaving group
weak base
More negative pKa better
stable
Big bulky, sterically hindered, bases
LDA, t-BuOK
Substitution vs. Elimination
Substitution:
Nu replaces LG
Elimination:
Double bond is formed
Beta hydrogens
Better LG is what
bigger atom, more polarizable