Coordination Chem + complex ions
1/41
Earn XP
Description and Tags
unit 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are similar properties among transition metals
Mostly paramagnetic
High thermal and electrical conductivity
Most absorb visible light
More than 1 oxidation state
Form complex ions
What are disimilar properties among transition metals
their “hardness”
their ability to form oxides (Iron does, Au and Pt don’t)
melting points (may be solid or liquid at room temp)
Why do gemstones have colours?
they contain impurities (transition metals)
What metals have exceptions to their electron configurations?
chromium (Cr), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), palladium (Pd), silver (Ag), gold (Au),
In ATOMS, which subshell is lower in energy (3d or 4s)
The 4s subshell (better penetration)
in transition metals ions, does the 4s or the 3d subshell higher energy?
the 4s is higher energy
What are common oxidation states for period 4 elements (split into 2 halves)?
the elements in the first half of the period can lose all their 4s and 3d electrons
the second half tend to have oxidation states of +3 and +2
what are the 2 parts of a coordination compound?
the counter ions and the complex ion
what are the components of a complex ion? which is also a Lewis base?
the transition metal and the ligands
the ligands are the Lewis base since they donate electrons
What is the function of counter ions?
to maintain the charge neutrality of the compound
given a coordination number of 2, 4, and 6, what are the possible shapes of the complex ion?
2 - linear
4- tetrahedral or square planar
6- octahedral
what does ambidentate mean? polydentate?
ambidentate means the molecule could bind to the TM via one atom or another (not both)
Polydentate means several bonds are made between the ligand and the TM
what is the ligand name for:
CO
NO
H2O
NH3
carbonyl
nitrosyl
aqua
ammine
what are the 3 ambidentate ligands?
SCN, OCN, and NO2
Name of SCN vs SCN?
thiocyanato and isothiocyanato
name of OCN vs OCN
cyanato and isocyanato
when naming complex ions, when does the metal name end in “ate”
when the complex has a negative charge
if a metal ion has an electron configuration of nd8, what is the shape of the complex if CN = 4?
square planar
What is the charge of the bidentate ligand oxalate?
2-
what is the charge of the ligand EDTA? how many bonds does it form?
-4 and 6 bonds
how many bonds can diethylenetriamine make to the metal ion?
3 (triamine)
what is a chelate?
a complex when a metal ion is bound to a ligand by two or more coordinate covalent bonds. (polydentate ligand)
when must the prefixes bis, tris, tetrakis be used?
why cant H2O be polydentate even though it has >1 lone pair
the 2 lone pairs are on the same atom and are not positioned far enough apart/at the right angle to coordinate with the same metal ion simultaneously.
what are the two types of structural isomers possible for coordination compounds? what about 2 types of stereosimomers?
Structural = coordination, and linkage isomers
what is a coordination isomer?
what is necessary for a linkage isomer to be possible?
an ambidentate ligand
describe what a facial vs meridonial isomer is
in what 3 scenarios are optical isomers guaranteed?
what are enantiomers? what do chiral molecules do?
in crystal field theory, how are ligand to metal bonds characterised?
which d orbitals make up the eg set? the t2g set?
he eg set consists of the d(x²-y²) and d(z²) orbitals, which point directly at ligands and increase in energy, while the t2g set comprises the d(xy), d(xz), and d(yz) orbitals
why is the eg set higher energy for octahedral compounds?
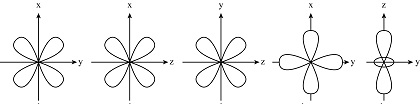
label

what is delta in crystal field theory?
what is a strong field ligand? do they make high or low spin complexes?
how are orbitals filled when delta is small? why?
promoting before pairing
because the pairing energy is greater than delta, making it more energetically favourable to promote electrons first
how is delta (splitting energy) related to wavelength of absorbed visible light?
they are inversely related (higher delta smaller wavelength)
delta = hc/λ
what is the light we observe (absorbed or transmitted)?
transmitted
why do tetrahedral complexes generally have a small delta value and high spin?
how are their eg and t2g sets organized differently than for octahedral complexes?
are square planar complexes usually high or low delta value and high or low spin?
order the general splitting energies (delta) of octahedral, square planar, and tetrahedral complexes from biggest to smallest
square planar > octahedral > tetrahedral