Ovaries: Simple Cysts, Complex Masses, Solid Tumors, Doppler the Ovaries
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
What is the function of an ovary?
Matures oocytes until ovulation under the influence of LH and FSH hormone from the pituitary gland
The ovaries synthesizes ________ and converts them into ________.
Androgens; estrogens
The ovaries produce __________ AFTER ovulation to sustain ______ pregnancy until the placenta can take over 10-12 weeks of gestation.
Progesterone; early
Majority of SIMPLE cysts, MOST of which are benign or malignant?
Benign
What is the sonographic appeareance for SIMPLE cyst?
Thin
Smooth wall
Anechoic contents
Acoustic enhancement
The resulting corpus luteum ot an abnormal unruptured follicle can persist as a SIMPLE or COMPLEX cystic structure from ___ to _____cm.
1-10 cm
If a cyst is GREATER than ____ cm and persists more than ___ weeks, what may be considered?
6 cm; 8 weeks; surgical intervention
What has become another option for reducing recurrent SIMPLE ovarian cysts?
Ultrasound-guided needle aspiration
In PREmenopausal women, SIMPLE cysts are usually what?
Functional
Small, anechoic cysts may be seen in ______menopausal women.
Post
Surgery is generally recommended for POSTmenopausal cysts GREATER than ______ cm and for those containing what?
5 cm; internal septations or solid nodules
In patients of REPRODUCTIVE age, classic differential considerations of COMPLEX adnexal mass are what?
Ectopic pregnancy
Endometriosis
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
What do you see?
What else could it be?
Sonographically describe it?
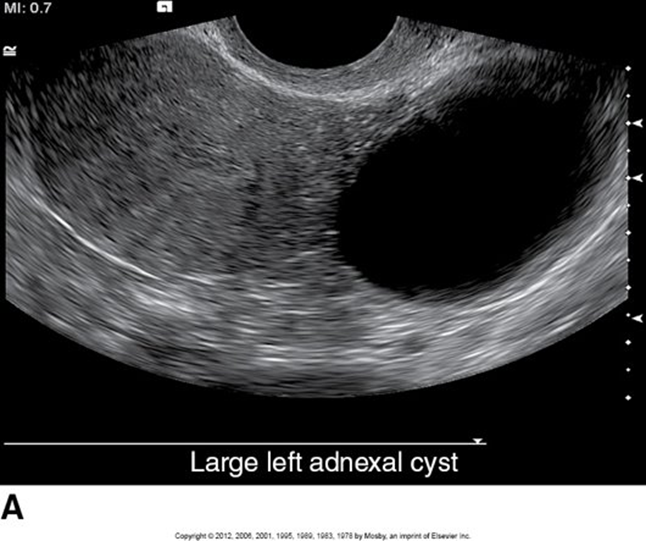
Simple cysts
Dominant Follice; its important to know where they are in their cycle to confirm if it could be cystic
Anechoic round stucture inferior to the uterus with smooth walls and well-circumscribed borders
What do you see?
What else could this be?
What might you see?
What should you notice with these type of pathology?
Sonographically describe it?
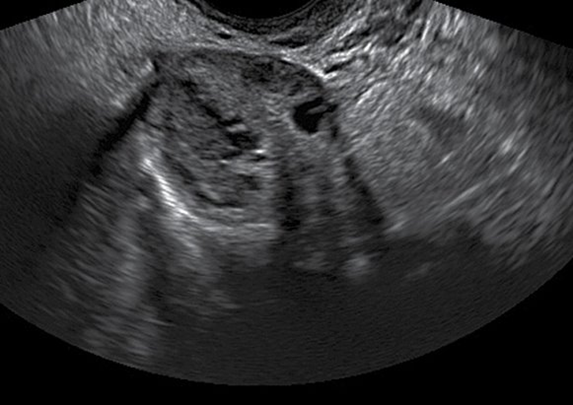
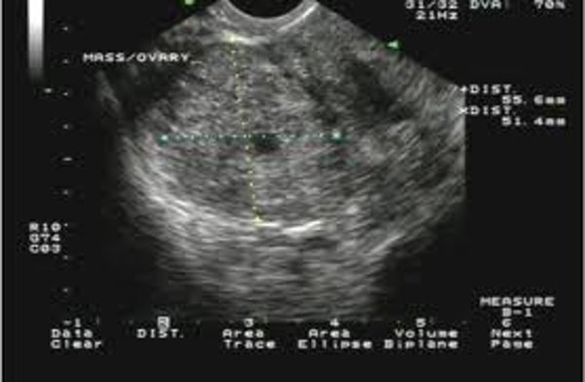
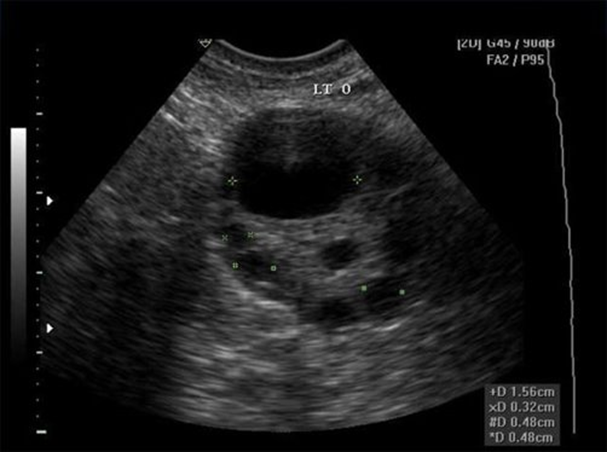
Complex masses
Hemorrhagic cyst
Might see some enhancement if there are some cystic compents
Does the mass completely take over the ovary or do you still see some ovarian tissue
Heterogenous, rounded complex stucture with some posterior enhancement
Any SIMPLE cysts that hemorrhages as it involutes may appear as what?
Complex mass
Mixed SOLID to CYSTIC ovarian masses are typical of all _______ tumors.
Epithelial
What are the MOST common types of epithelial tumors?
Serous types: cystadenoma (benign) and cystoadenocarcinoma (malignant)
During the peak FERTILE years, only ___ in ____ is MALIGNANT; this ration becomes _____ in ____ after the age of ____.
1 in 15
1 in 3
40
More sonographically COMPLEX the tumor, MORE likely to be ________, espeically if it is assocaited with what?
Malignant; ascities
Epithelium of serous tumors TUBAL in type; may be what (appearence wise)?
One or multiple cysts
Are epithelium tumors unilateral or bilateral? How may of them?
¼ are bilateral
MOST epithelial tumors occur in what AGE of women?
Greater than 40
Are epithelial tumors large or small? They often fill the what?
Large; pelvic cavity
Why are adnexal masses often DIFFICULT to diagnose?
The NORMAL ovarian size varies WIDELY.
When a SOLID mass is found, what should the tech do?
Take care to identify a connection with the uterus to differentiate an ovarian lesion from a pedunculated fibroid
ABSENSE of flow usually indicates a _______ lesion.
Benign
Malignancies require what type of Color Doppler flow?
It requires blood flow that has a HIGH diastolic flow (decreases/low resistance→needs that blood flow to supply the cancer)
Patients with NORMAL menstrual cycels are BEST scanned in the first ___ days of cycle. What does this avoid?
10 days; avoids confusion with normal changes in intraovarian blood flow because HIGH diastolic flow occurs in the LUTEAL phase
During the LUTEAL phase, the ovary is reacting in case of a __________, so it will have a very ____ diastolic flow, ____ resistance.
Prengancy; HIGH, LOW
This image shows that the patient was receiving infertility treatment. How does this affect the ovary and how would Color Doppler look?
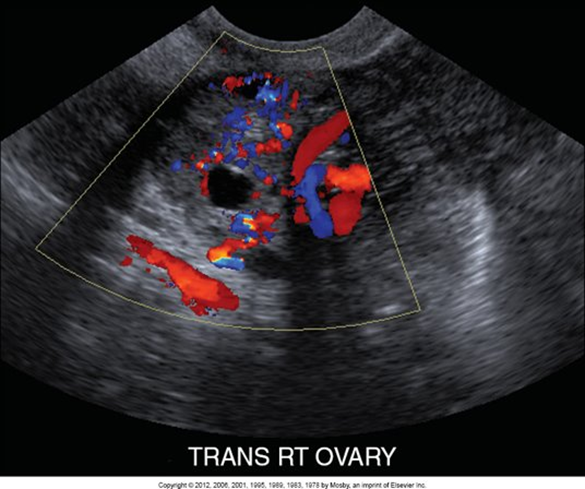
There will be ALOT more blood flow to the ovary because of the infertility treatment causing hyperstimulation.
What does does LOW resistance, LOW velocity of the ovary mean?
This means it NEEDS blood flow, but SPEED of blood flow is SLOW!
_________ waveforms can be seen in:
Inflammatory masses
Metabolically active masses (including ectopic pregnancy)
Corpus luteum cysts
Abnormal
What is the MOST significant problem in using an RI?
RI is NOT a senstitive indicator of malignancy
Benign or Malignant:
Mass showling COMPLETE absense ot MINIMAL diastolic flow.
Do they have very HIGH or LOW RI and PI?
Bengin; High (elevated)
When it comes to Dopplering the ovaries, what are the signs that may be worrisome fot malignancy?
Intramural nodules
Low-resistance flow
Absense of normal diastolic notch in Doppler waveform
Inflammatory masses, active endocrine tumors, and trophoblastic disease (ectopic pregnancies) may give LOW incidences, mimicking what?
Cancer
Trophoblastic disease will have a postitive or negative pregnancy test?
Positive
If Doppler is SUSPICIOUS, what should happen?
A repeated study should be performed to confirm the ABNORMAL indices in the first week of another cycle.
HIGH resistance is going to have a lower or higher diastolic flow?
Lower