Scatter Radiation
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch 22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
What does Collimation improve and reduce?
Reduces patient dose
improves image contrast
What should collimation not exceed?
The beam should never exceed size of IR
What is scatter radiation from patient?
Emitted form patient in all directions
What is the source of exposure to the technologist and radiologist?
Scatter from patient
What are negative factors of scatter radiation?
reduces radiographic contrast
no useful information
What is used to reduce scatter radiation?
Collimation and grids are used to reduce scatter
3 factors that influence intensity of scatter → IR
kVp
field size
patients or part thickness
What is DIRECTLY proportional to Kilovoltage?
Compton Interaction
As energy increases, so does….?
Compton Scatter
Low kVp =
low scatter radiation
Low kVp = low scatter radiation; resulting in
high patient dose (because it is absorbing in the patient)
Field Size decrease =
Scatter decrease
Smaller field size =
Lower scatter
Lower scatter =
less optical density
Less optical density =
more technique needed
Optical Density -
overall blackening of an image
Part / Patient thickness
thicker body parts scatter more radiation than thinner parts
Four benefits of Compression Devices
improve spatial resolution by reducing patient thickness
brings object closer to image receptor
Reduces patient dose
improves contrast resolutions
Beam Restricting Devices
limits size of x-ray field only to anatomic structures of interest
3 types of beam-restricting devices
aperture diaphragm
Cones or Cylinders
Variable - aperture collimator
Aperture Diaphram
A lead or lead-lined metal plate attached to x-ray tube with an opening designed to cover just less than the size of image receptor used
Cones and Cylinders SHAPE
Usually circular shape
Cones and Cylinders CONs
difficult to align x-ray source, cone and image receptor
Where does OFF FOCUS RADIATION happen?
happens in the tube
What is OFF FOCUS RADIATION?
when x-rays hits any area other then target are on anode
What is the most common beam restricting device?
Light Localizing Variable Aperture Collimator
What does Light Localizing Variable Aperture Collimator help clean?
clean up OFF FOCUS Radiation
Collimation Filtration
Total filtration = inherent filtration + added filtration
What is the principal function of a GRID?
Principle function is to improve image contrast
How do GRIDs improve image contrast
Device that reduced the level of scatter radiation that will reach the image receptor
How much can a GRID absorb?
80 - 90 % of scatter
What is the GRID designed to do?
Designed to transmit only the x-rays whose direction is on a straight line from source to image receptor
What happens to the X-rays that exit the patient and strikes the grid strips?
they are absorbed and do not reach the IR
3 Important Dimensions (GRID)
grid ratio
grid frequency
grid material
Grid Ratio equation
(h) height of grid strip divided by (d) interspace width
which grid ratio is more effective?
High ratio grids are more effective in reducing scatter radiation than low ratio grids
What are grid ration ranges?
5:1 (85%) or 16:1 (97%) clean up
Grid ratio determines what?
amount of scatter radiation
What is the grid frequency?
Number of grid strips or grid lines per centimeter
What is the difference between HIGH fz and LOW fz grids?
High frequency grids show less distinct grids lines than low frequency grids
High frequency grids have thinner interspace strips and higher grid ratios = higher patient dose
Most grids frequency range
range of 25 to 45 lines per centimeter
What is the interspace in most grids made of?
either Aluminum or Plastic
Why aluminum?
absorbs low energy photons
What is the grid material made of?
lead strips
CIF
Contrast Improvement Factor
What is CIF?
Ratio of Contrast of an image made with the grid to the contrast of an image without a grid
CIF refers to?
Image Quality
Equation for CIF
K = Contrast with grid / Contrast without grid
CIF higher or lower for high ratio grids?
higher
Most grids improvement between?
1.5 and 2.5
Bucky Factor AKA
(B), Grid Factor
What is Bucky Factor?
Measured how much of an increase is technique is needed with and without a grid
What does Bucky Factor indicate?
indicates how large the patient dose will be with a particular grid
Higher grid ratio =
higher patient dose
higher grid ratio = higher patient dose =
higher bucky factor
Grid types
parallel grids
crossed grids
focused grids
moving grids
virtual grids
Grid Cutoff
Undesirable absorption of primary or useful x-rays by the grid
Example of Grid Cutoff
The grid is at an angle and the photons that should have gone through, don’t and get absorbed
Parallel Grid aka
Linear Grid
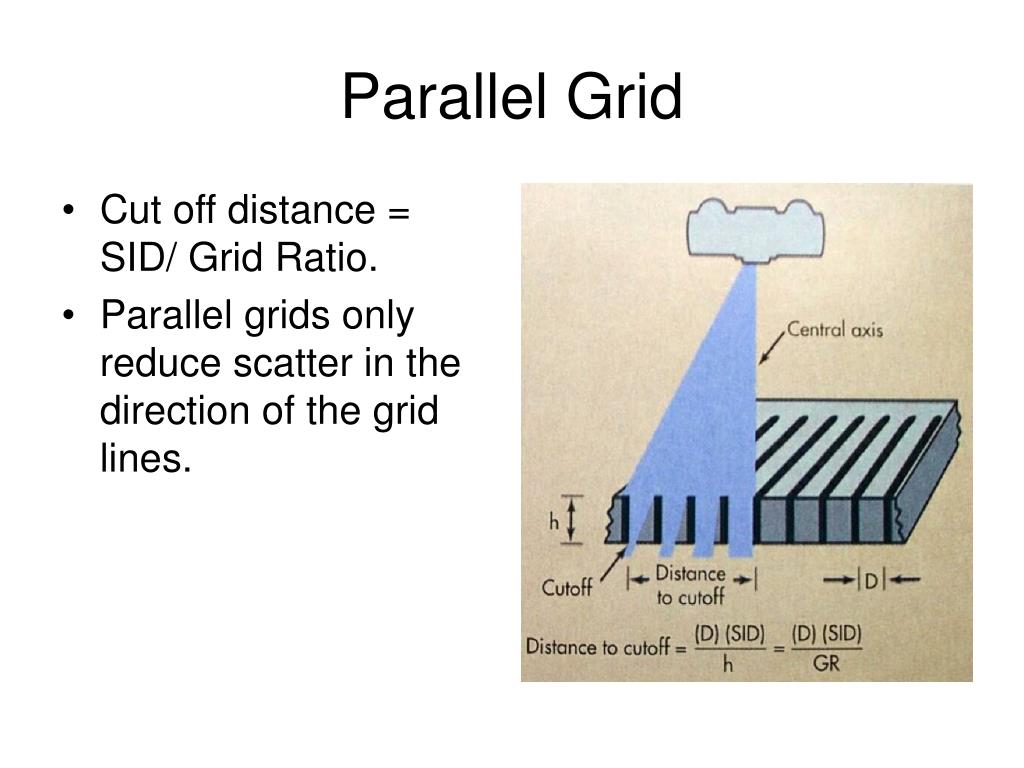
What kind is Parallel Grid? how dose it affect scatter
Simplest type of grid
Cleans up scatter in only one direction
How is Parallel Grid normally used?
Used primarily with short SID or large area image receptor
Crossed Grids aka
Cross Hatch grid
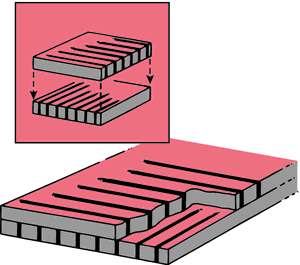
Compared to linear grid
more effective
What does Cross grid consist of?
Consist of two linear grids placed perpendicular to one another
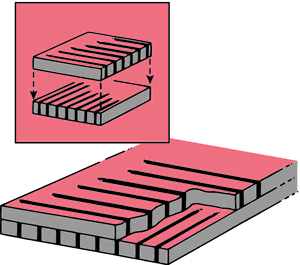
Advantage of Cross Grid ?
Advantage - better with use of higher kVp
Disadvantage of Cross Grid?
grid cut off
What is Focused Grid designed to do?
minimize grid cut off
How are the lead strips for Focused Grid?
Angled to match the imaginary divergent x-ray beam
Focused Grid: high ratio to low ratio
High ratio grids have less positioning latitude than low ratio
When can Focused grid be used?
Can only be used at SID specified on grid by the manufacturer (or grid cut off will occur)
Most often are moving grids
Moving Grids AKA
Potter-bucky diaphragm, bucky diaphragm or bucky grid
What is Moving grid?
Mechanism that is moved at the time of an x-ray exposure
Advantage of Moving Grid
Removes grid lines by motion (blurring)
2 types of Moving Grid
Reciprocating and Oscillating
Reciprocating
Most common type
Motor driven back and forth several tines during an exposure
Oscillating
Powered by an electromagnet
Grid moves in a circular pattern
Virtual Grid: what does each x-ray have?
Each incident x-ray on a digital IR has measurable energy and frequency
Virtual Grid: TECHNIQUE
Technique to identify each xray and assign it to an energy or frequency bin
Results from Virtual Grid
digitally reconstructed radiograph produced with fewer scatter interactions
Virtual Grid helps to?
Reduce patient dose
Imrpve image contrast
Eliminate artifacts
Grid Problems
off level grid
off center grid
off focus grid
upside down grid
Off-level Grid
Occurs by having the tube improperly positioned
Off-Center Grid AKA
Lateral decentering
Off Center Grid positioning
Center of grid myst be positioned directly under tube so beam passes through the centermost interspace of grid
Any lateral shift =
Grid Cut off
Off Focus Grid needs
Proper SID - important so grid cut off does not occur
What is Off Focus Gris most important for?
Most important for high ratio grids
What do Low Ratio gids have?
Have more positioning latitude
Upside Down Grids
Will cause severe grid cutoff
Grid Selection: when using high kVp
high ratio grids should be used
As grid ratio increase =
so does scatter radiation
What is the ratio often employed
8:1
Grid Selection: Rule of Thumb
8:1 grids for technique below 90 kVp
Above 90 kVp = use higher grid ratios
What is a major disadvantage to grids
Increased patient dose
Air-Gap Technique
Alternative method of decreasing scatter radiation in place of grid
Air Gap Technique: where is the IR placed?
10 to 15 cm from patient, so fewer scattered x-ray interactions with image receptor and enhance contrast
How is technique changed for Air Gap Tehcnique
mAs is increased about 10% for every cm
Disadvantage of Air Gap Technique
image magnification