7) fx healing and ortho infections
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
fx definition
any structural break in continuity of bone
fx are accomplished by
significant soft tissue injury
soft tissue injury determines
severity of injury and speed of rehab
bones are much stronger in ________ than _______
- compression than tension
bone mineral is strongest in
compression
bone matrix is strongest in
tension
fx description
open or closed
site
Configuration
displacement
open fx
any break in the skin that extends down to bone
more soft tissue damage, takes longer to heal
open fx are more or less at risk for injection
more at risk for infection
closed fx
skin is intact
less infection risk, less soft tissue damage
fx site description
which bone
proximal, middle, distal
diaphyseal, metaphyseal, epiphyseal
intra- or extra-articular
fracture-dislocation
intra-articular fx
fx involving joint surface and surrounding area
fx configuration
incomplete
transverse
oblique
spiral
comminuted
comminuted fx
has more than two parts
more vascular and soft tissue injury
spiral fx is caused by what type of motion
plant and twist
Undisplaced fracture
buckle, hairline
impacted
displaced fx
lateral shift
angulation
lengthening or shortening
pediatric fx - type 1
fx through growth plate
pediatric fx - type 2
fx exits through metaphysis
Pediatric fx - type 3
fx exits through epiphysis (intra-articular)
Pediatric fx - type 4
Transverse across growth plate (intra-articular)
stages of fx healing
- inflammation
- soft callus
- hard callus
- remodeling
inflammation stage
lasts 1-3 days
- pain, swelling, heat
- fx hematoma clots at fx site
- inflammatory cells migrate into region
soft callus stage
early stage
clinical stability is poor
osteogenic "repair cells" from periosteum infiltrate hematoma
in the soft callus stage, chondroblasts
form cartilage callus
during the soft callus stage, is the callus visible on x-ray?
no
soft callus stage, osteogenic cells differentiate into
osteoblasts
cartilage callus is converted into
woven type bone
later on, at the end of the soft callus stage can the callus be seen on x-ray?
yes
- weeks 2-3
hard callus stage is about ______ weeks
6-12
hard callus stage
fracture sire no longer moves
cartilage is replaced by woven bone
callus is well developed on x-ray
remodeling phase proceeds for
years
wolff's law
bone responds to stress, becoming stronger
- osteoblasts lay down new bone along lines of stress
- osteoclasts resorb poorly located bone
factors that affect fx healing
age
site and configuration
initial displacement
blood supply
factors that affect healing - age
children heal much quicker
adolescents to older adults heal similarly
elderly only heal slower when malnourished or when they have medical conditions
metaphyseal bone heals faster than
diaphyseal bone because metaphyseal bone has better blood supply
comminuted fractures heal
slower
- greater soft tissue injury
- compromised blood supply to the fragments
pediatric growth plate injuries heal in _____ the time
half
- due to the cellular machinery is ready for healing
factors that affect healing - initial displacement
more displaced heals slower
more soft tissue damage
more vascular disruption
factors that affect healing - blood supply
fx need good blood supply to heal
scaphoid in wrist has _____ blood supply
poor
blood supply in tibia for healing
tibia is subcutaneous, not surrounded by muscle and has poorer blood supply
fx treatments
immobilization
closed reduction - immobilization, percutaneous fixation, external fixation
open reduction internal fixation (ORIF)
immobilization alone is used for
non-displaced fx
- cast or brace
displaced fx need to be
reduced (straightened)
closed reductions are performed by
manually realigning the fx without surgically opening the site
some type of anesthesia is typically used
Immobilization after reduction if stable
cast immobilization
immobilization after reduction if unstable
percutaneous or external fixation
percutaneous fixation
running small pins across the fx
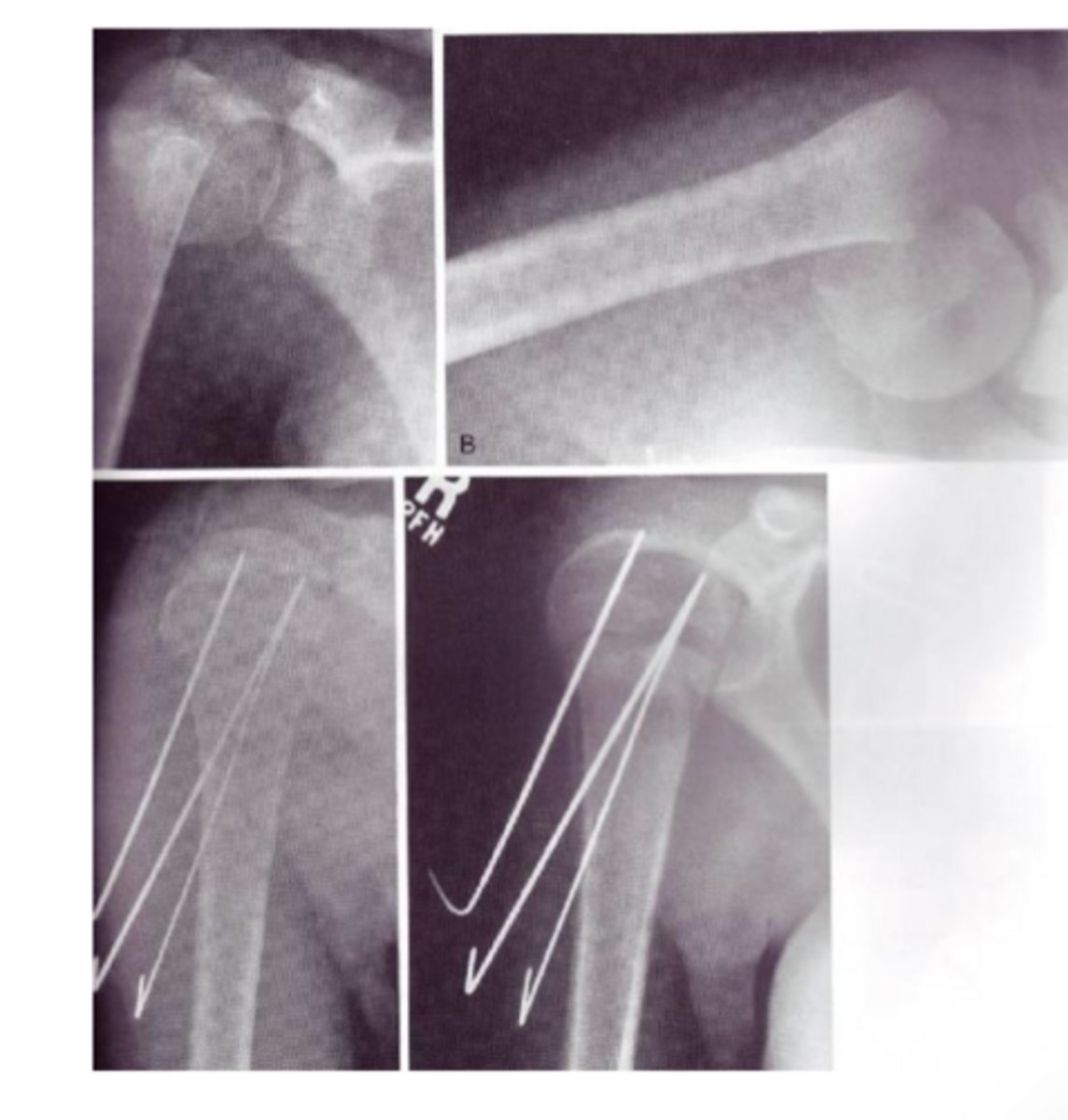
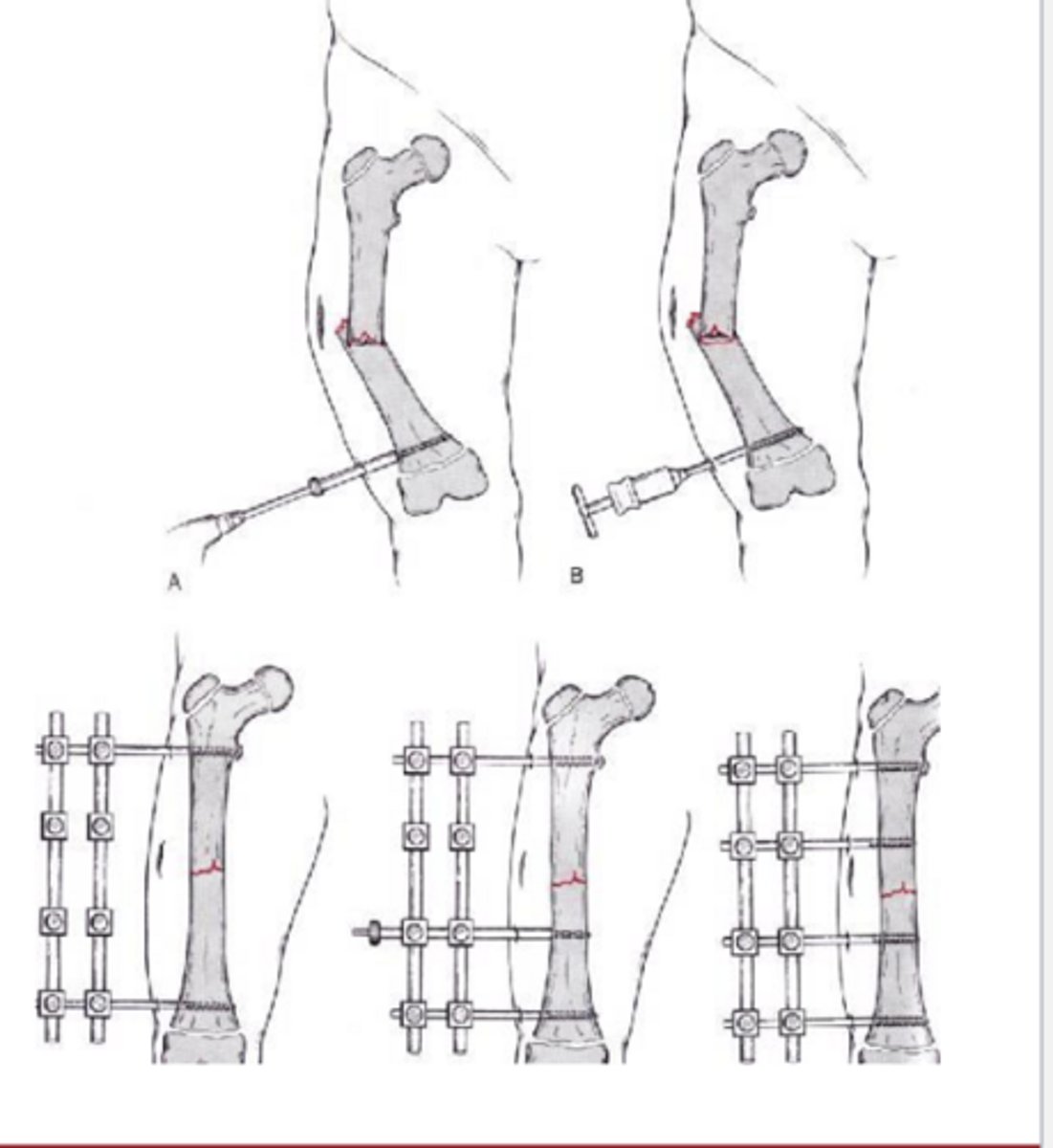
external fixation
place pins on both sides of a fx site and connect them with an external bar
fx that cannot be reduced closed need to be
surgically opened
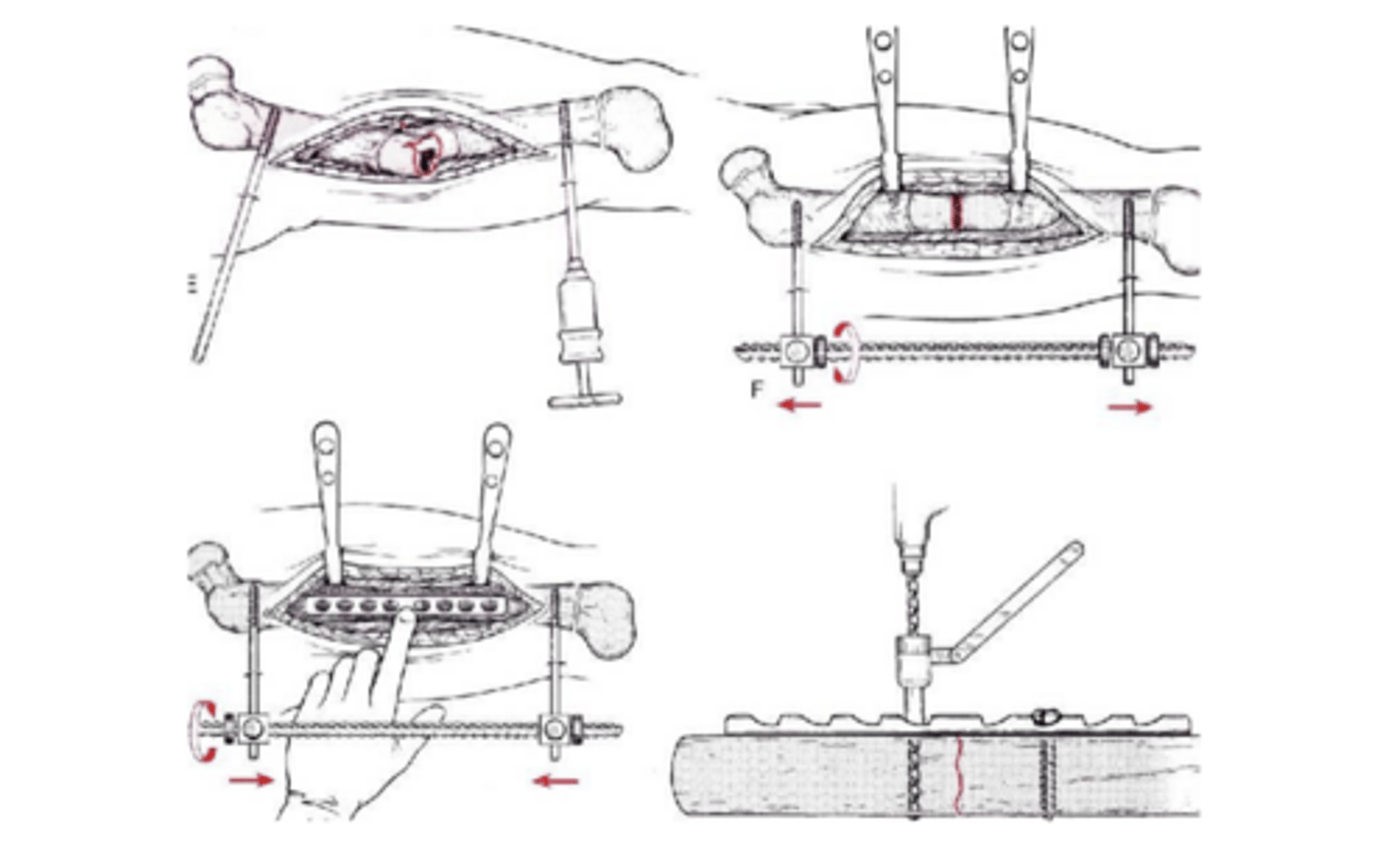
Open Reduction Internal Fixation (ORIF)
surgically procedure using plates and screws to hold fx in place
tissue healing and stress
tissues heal better with stress
stress stimulates osteoblasts and strengthens bones
motion lines up healing collagen fibers in anatomic orientation
common fx
proximal humerus
distal radious
scaphoid
hip
femur
tibia
ankle
proximal humeras fx
metaphyseal, extra-articular
most are stable and heal well
shoulder and elbow stiffness very common
early motion if possible
distal radius fx
metaphyseal, intra-articular
often need fixation to hold reduction
work on finger and elbow ROM early
scaphoid fx
very poor blood supply, artery enters the distal half only
takes 3-4 months to heal
stiffness from immobilization
hip fx
femoral neck - intra-articular, hemiarthroplasty
intertrochanteric - metaphyseal, ORIF
early mobilization, PWB
femur fx
diaphyseal
intra-medullary rod
early mobilization and WB
tibia fx
diaphyseal
closed reduction and casting or IM rod
poor blood supply, takes 3-4 months to heal
early mobilization for IM rod, delayed for casting
ankle fx
lateral malleolus, medial malleolus or bimalleolar fx
if unstable, needs ORIF
WBAT in cast at 2-4 weeks
Ankle stiffness common
complications with fx healing
malunion
nonunion
infection
compartment syndrome
complex regional pain syndrome - reflex sympathetic dystrophy (RSD)
malunion
fracture heals normally
unacceptable alignment
nonunion
fx does not show any sign of healing by 3 months
need to stimulate bone to heal
electrical stimulator
bone graft
improved immobilization
infection
possible after any surgical procedure
more common with open fx and people with diabetes
compartment syndrome
vascular compromised caused by extreme swelling
tissue pressure becomes higher than venous pressure
blood can get in, but it can't get out - blocked circulation
muscle compartment becomes ischemic and muscle dies
complex regional pain syndrome
pain, swelling, and autonomic dysfunction are all hallmarks
early complex regional pain syndrome
constant burning, aching, pain out of
proportion to injury; edema can rapidly
lead to joint stiffness
middle complex regional pain syndrome
cold, glossy skin with decreased ROM
late complex regional pain syndrome
atrophy and contractures
complex regional pain syndrome - stage 1
3-6 months
- Deep burning pain, edema which causes
stiffness, erythema, pallor or cyanosis, tremor,
dystonic posture
complex regional pain syndrome - stage 2
3-6 months
- diffuse severe pain, worsening stiffness, thin glossy skin, loss of hair
complex regional pain syndrome - stage 3
constant severe pain, skin is cool, pale and dry, subcutaneous tissue disappears, and fingers become narrow