Ochem test 2 hw questions
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
What is the driving force for losing a proton as the last step in electrophilic aromatic substitution?
To rearomatize the ring system
What is the electrophile in aromatic nitration?
NO2+
What is the electrophile in the Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction with tert-butylchloride?
The tert-butyl cation
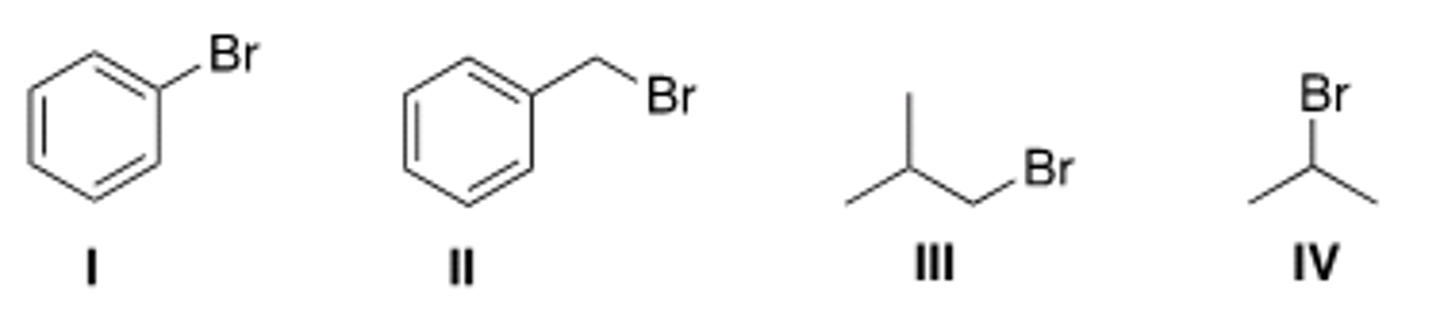
Which of the following halides will not work as an electrophile in a Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction?
I
Why is the nitro group a meta director?
Because it removes more electron density from the ortho and para positions than the meta position, thus deactivating the meta position less.
Which of the following statements about the mechanism of electrophilic aromatic substitution is not true?
All electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions occur via a two-step mechanism.
The transition state of the first step is lower in energy.
The first step is the rate-determining step.
The second step is the fast step.
The transition state of the first step is lower in energy.
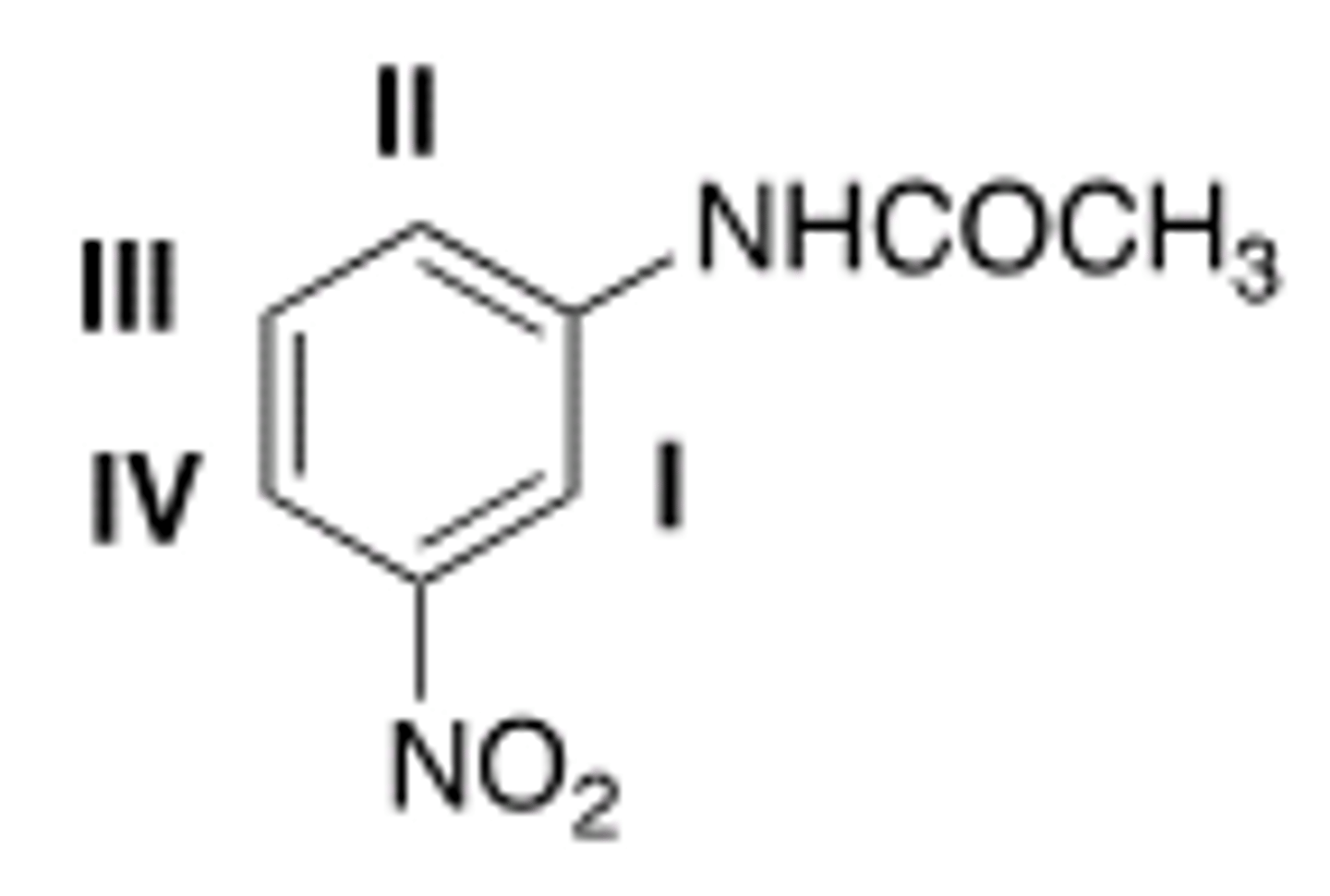
What will be the site that leads to the major mono substitution product for an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction of the following compound?
IV
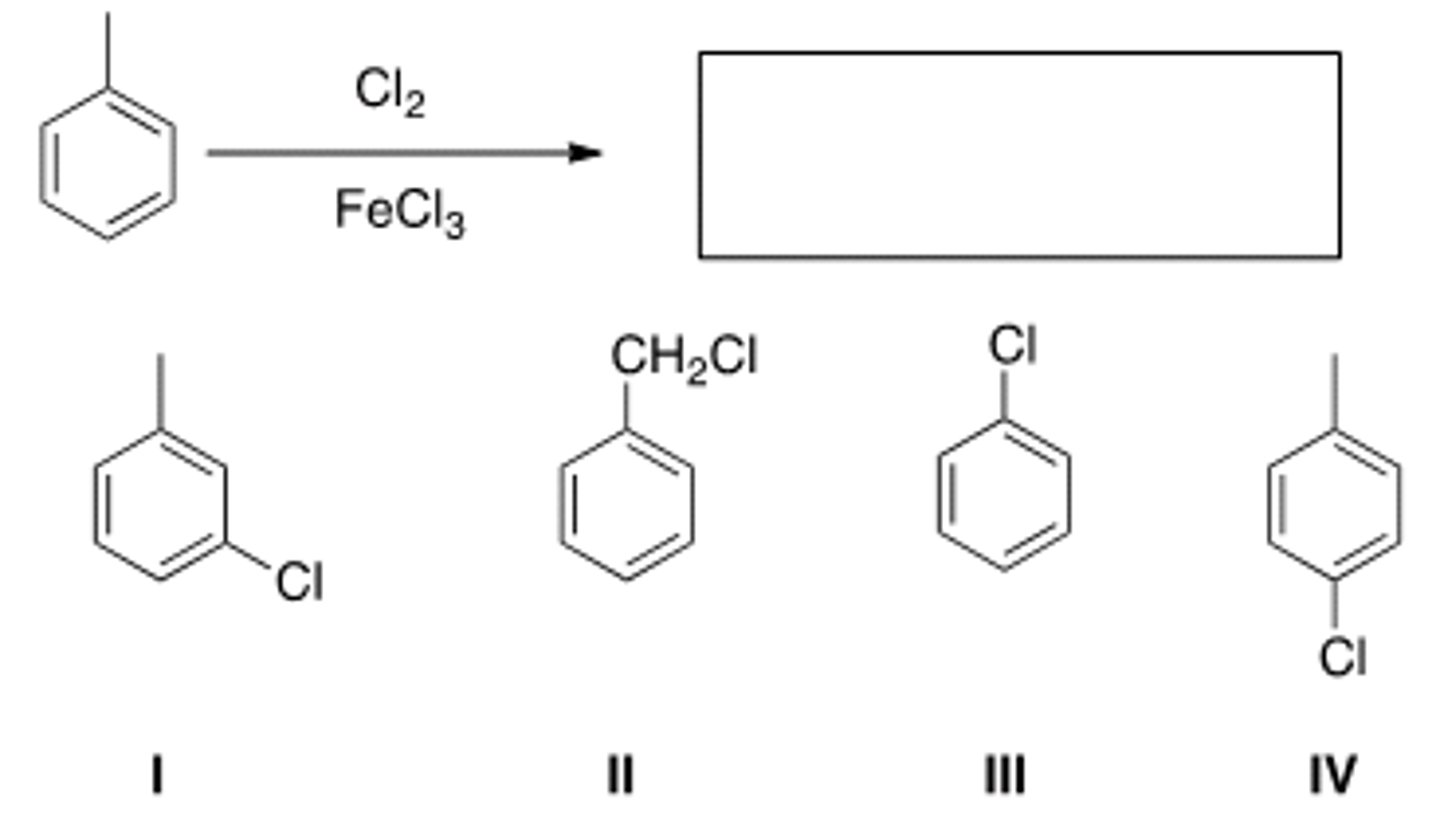
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
IV
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
II
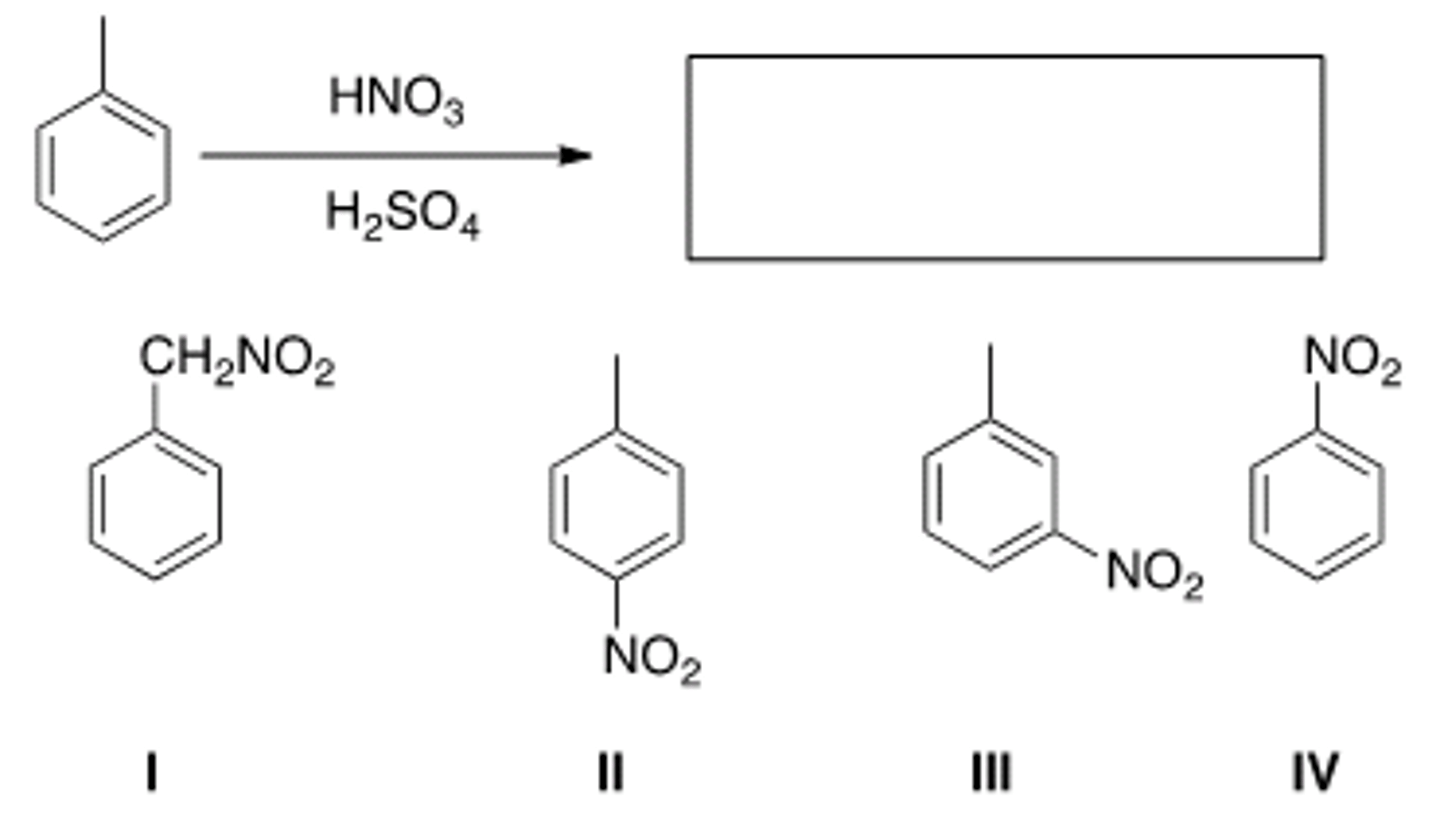
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
I
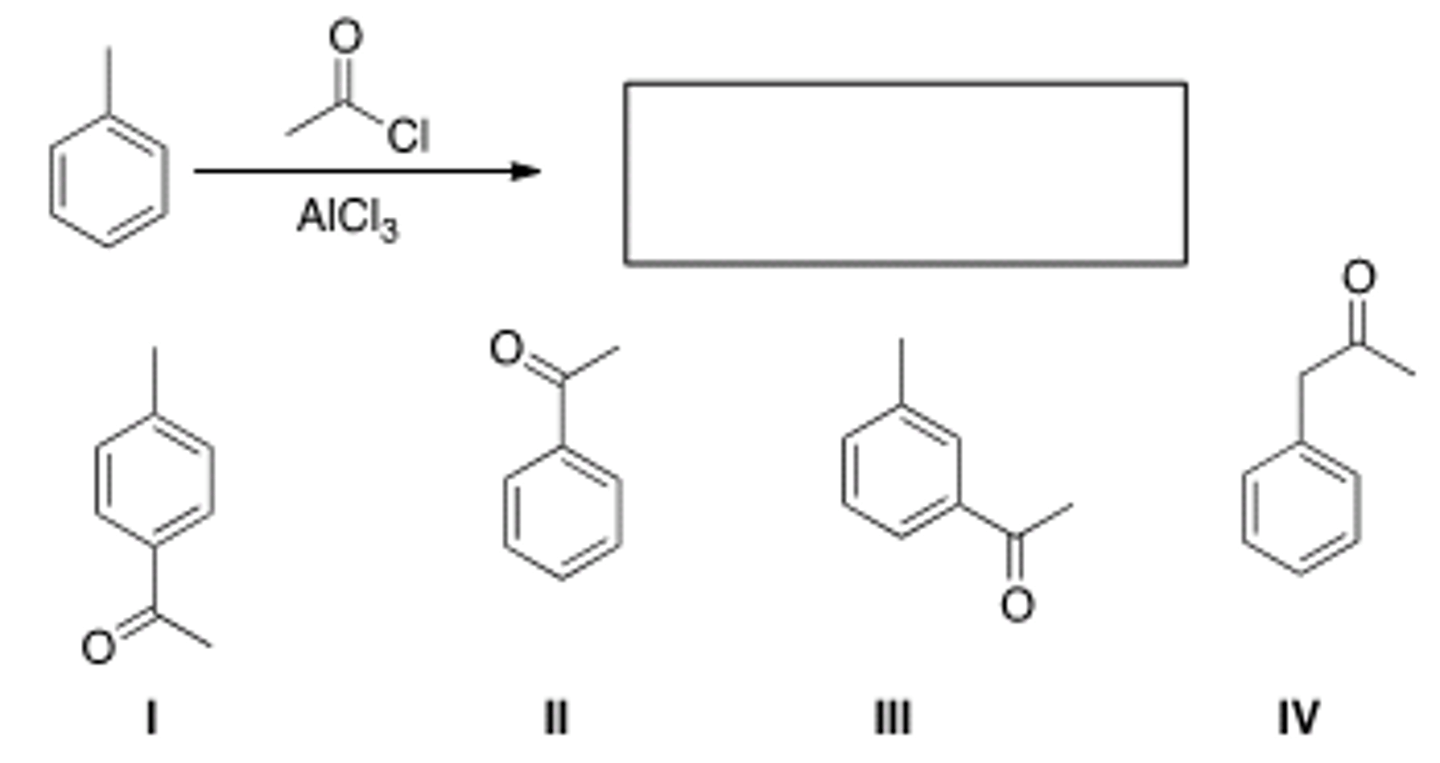
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
II
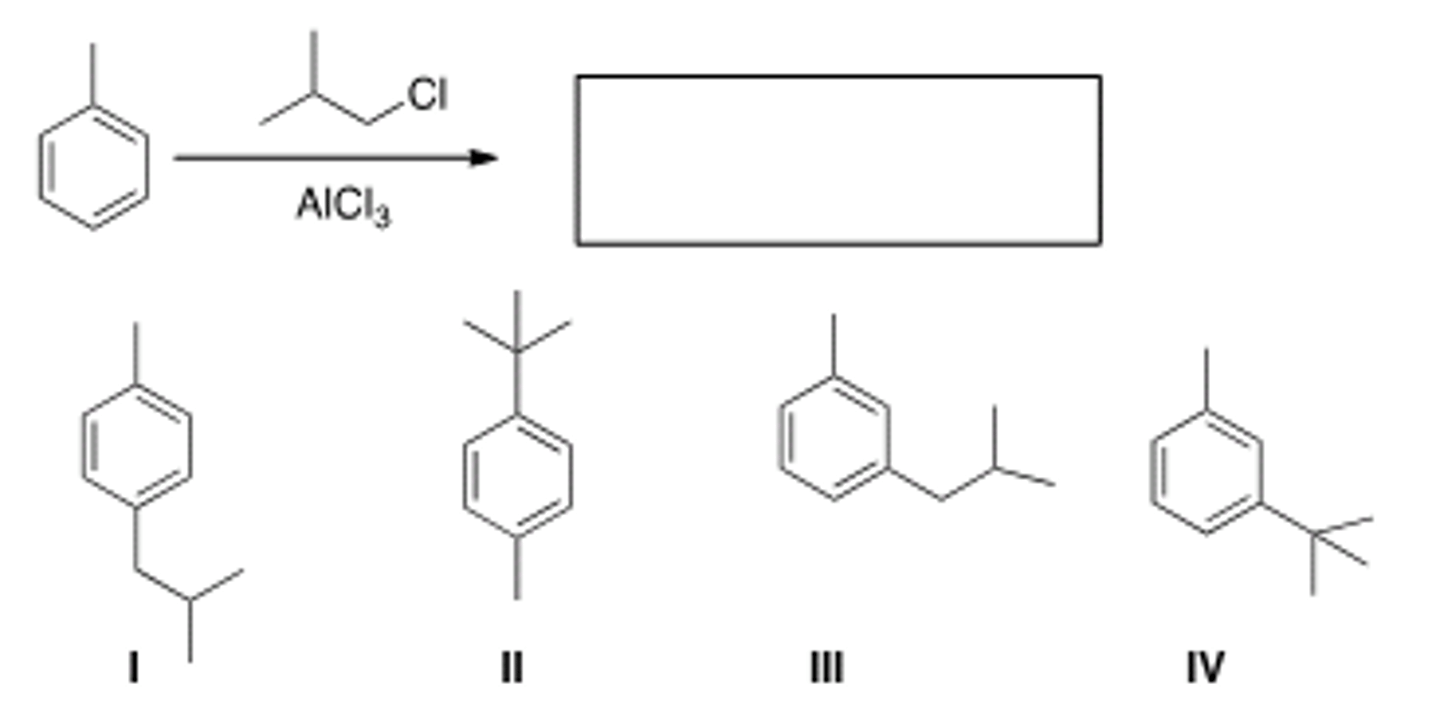
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
III
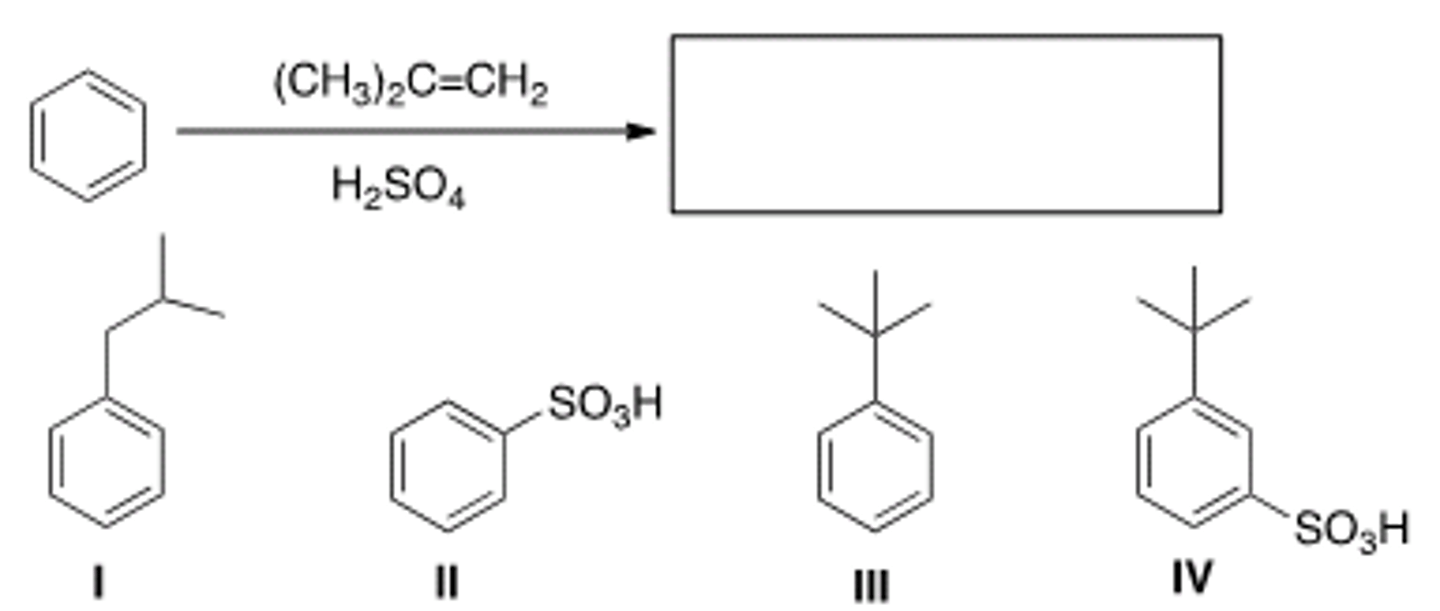
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
II
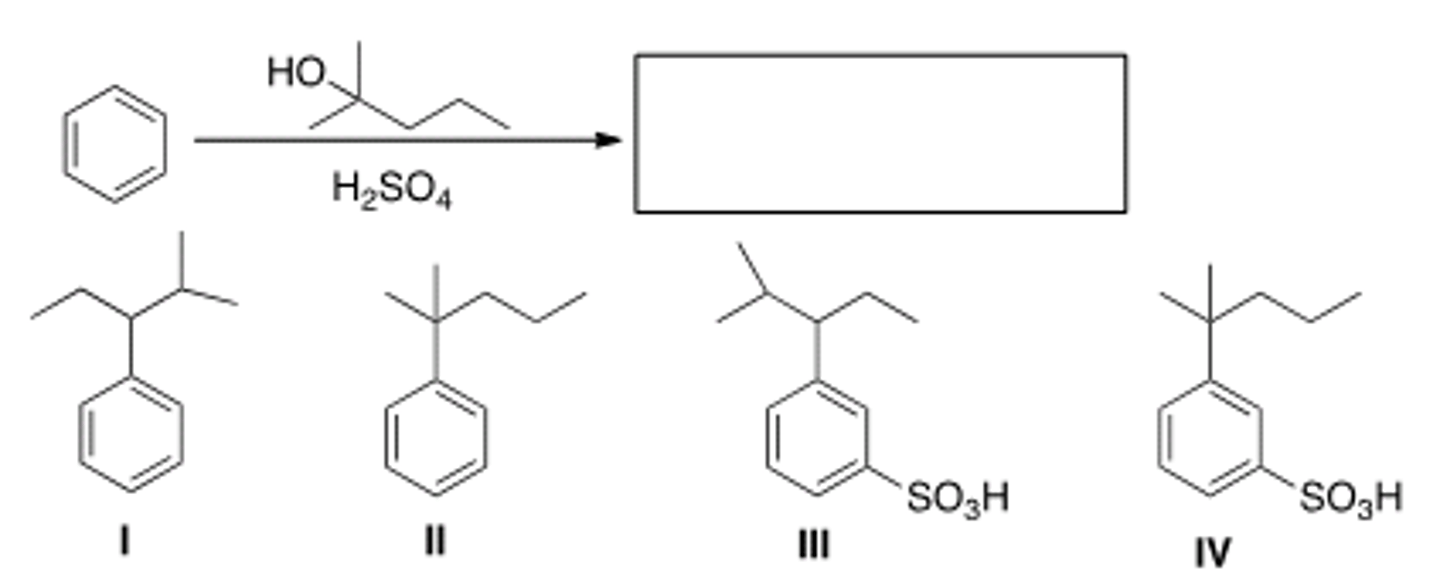
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction?
III
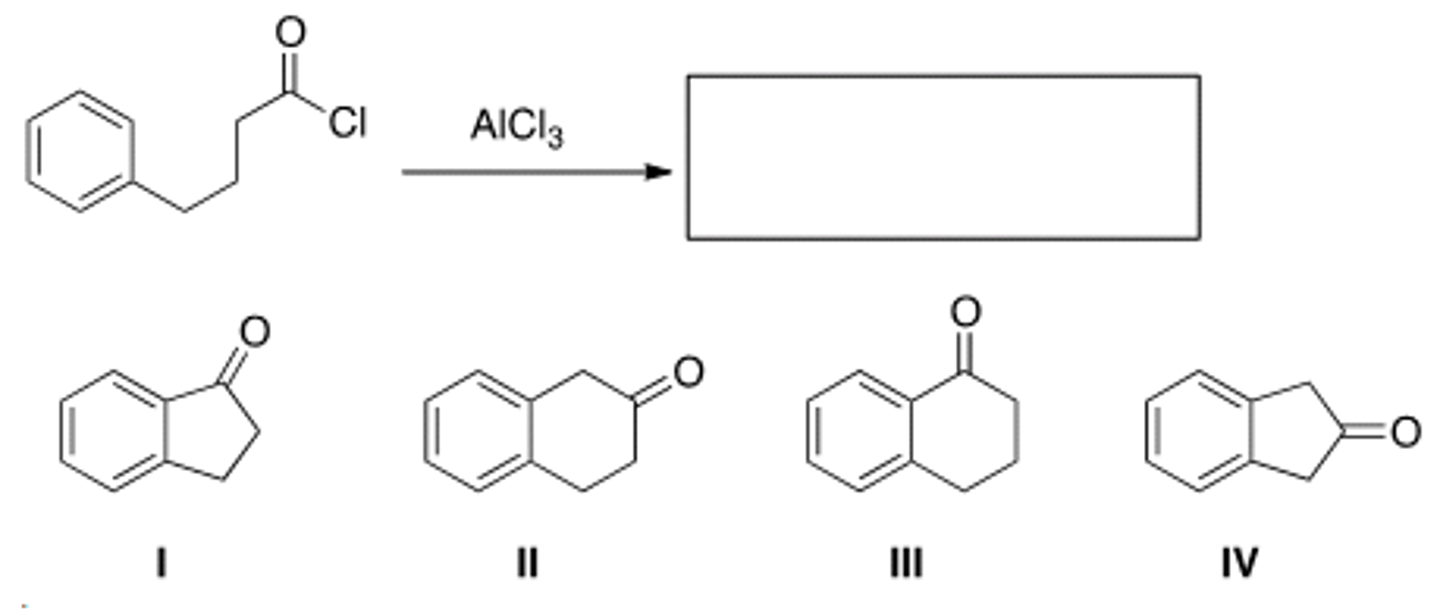
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
only 1 and III
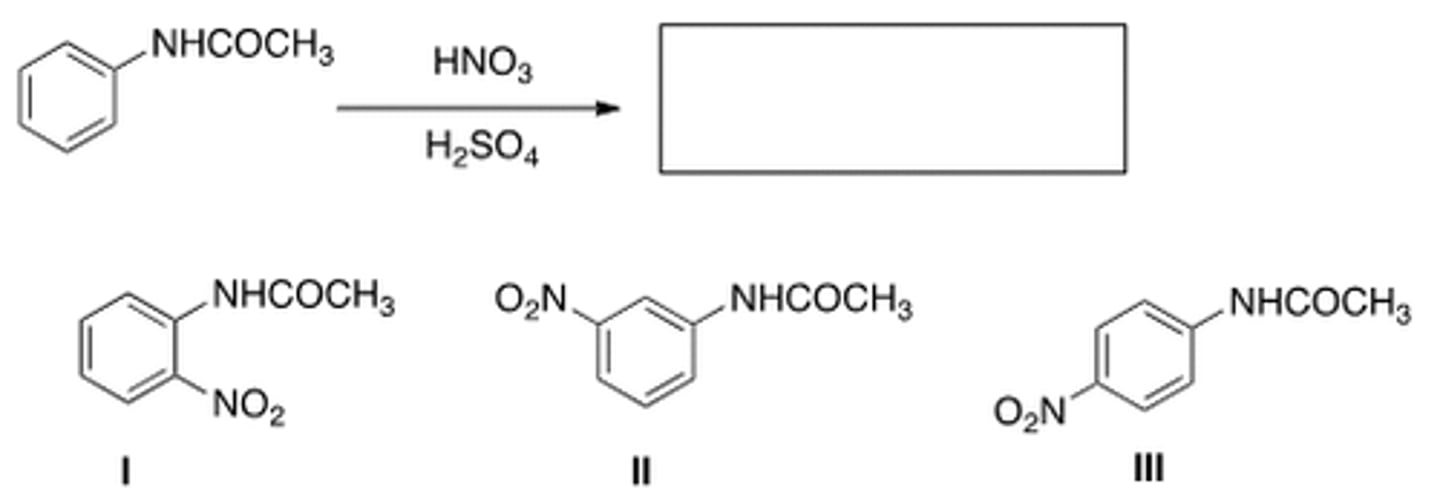
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
only I
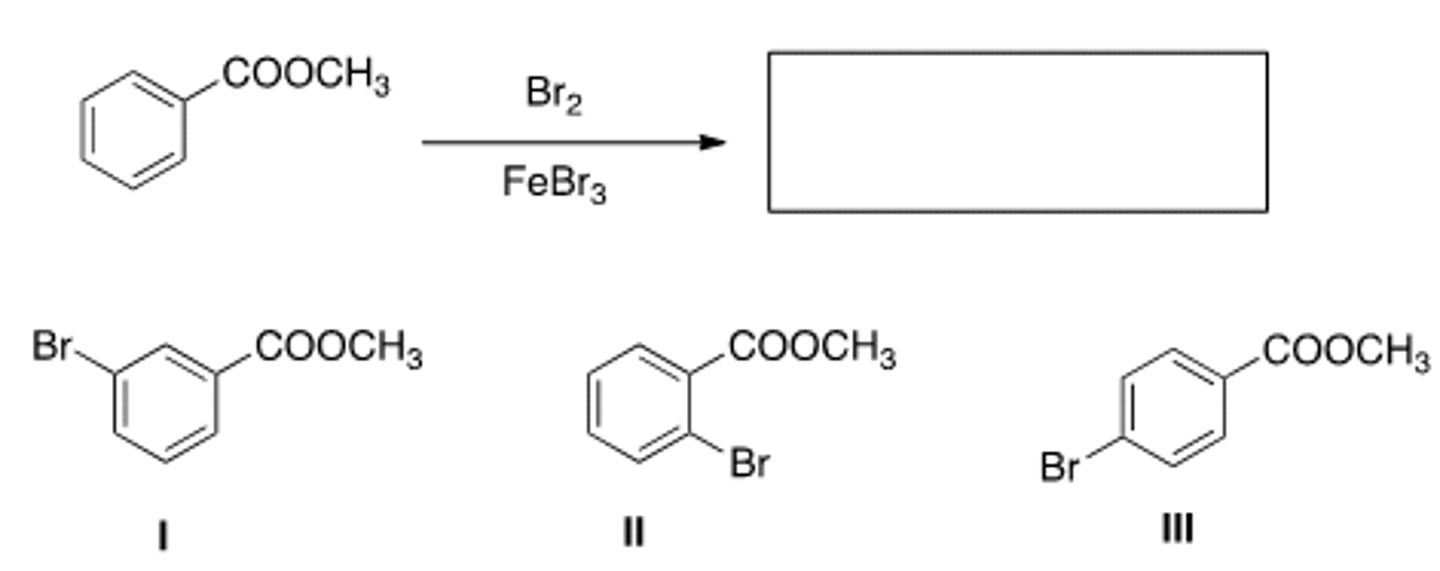
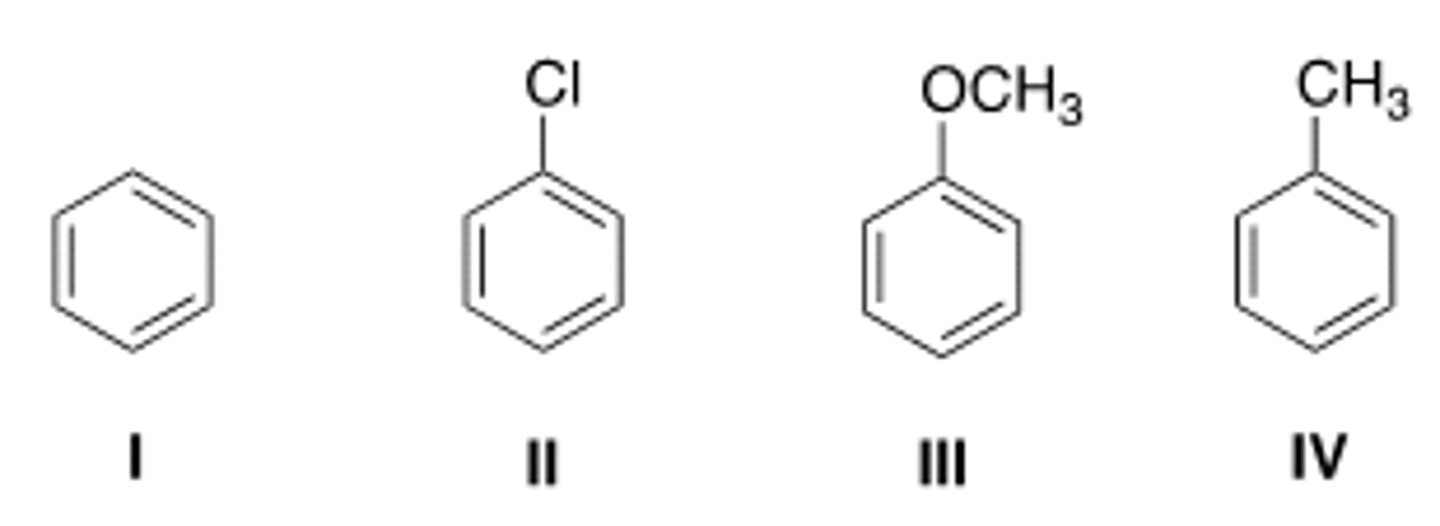
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in electrophilic aromatic substitution.
II < I < IV < III
Rank the following activating groups in order of decreasing strength of activation, listing the most activating first.
II > III > IV > I
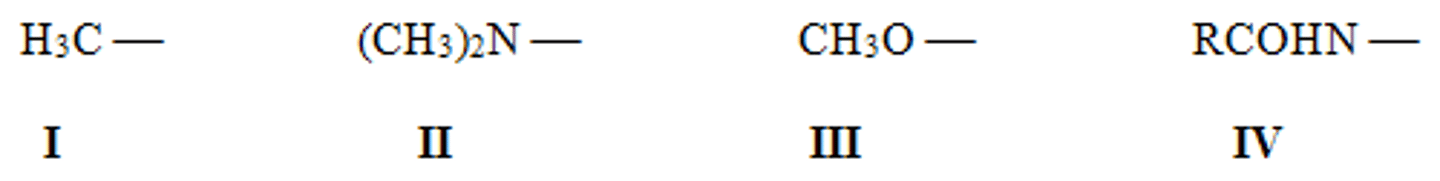
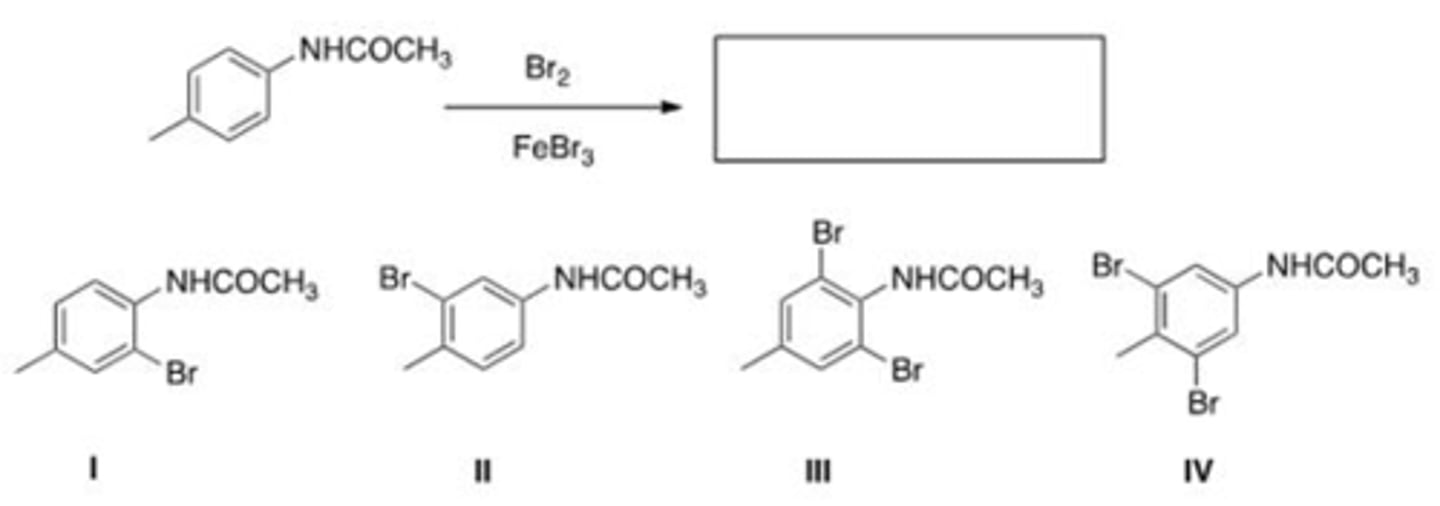
What is the major product of the following reaction?
I
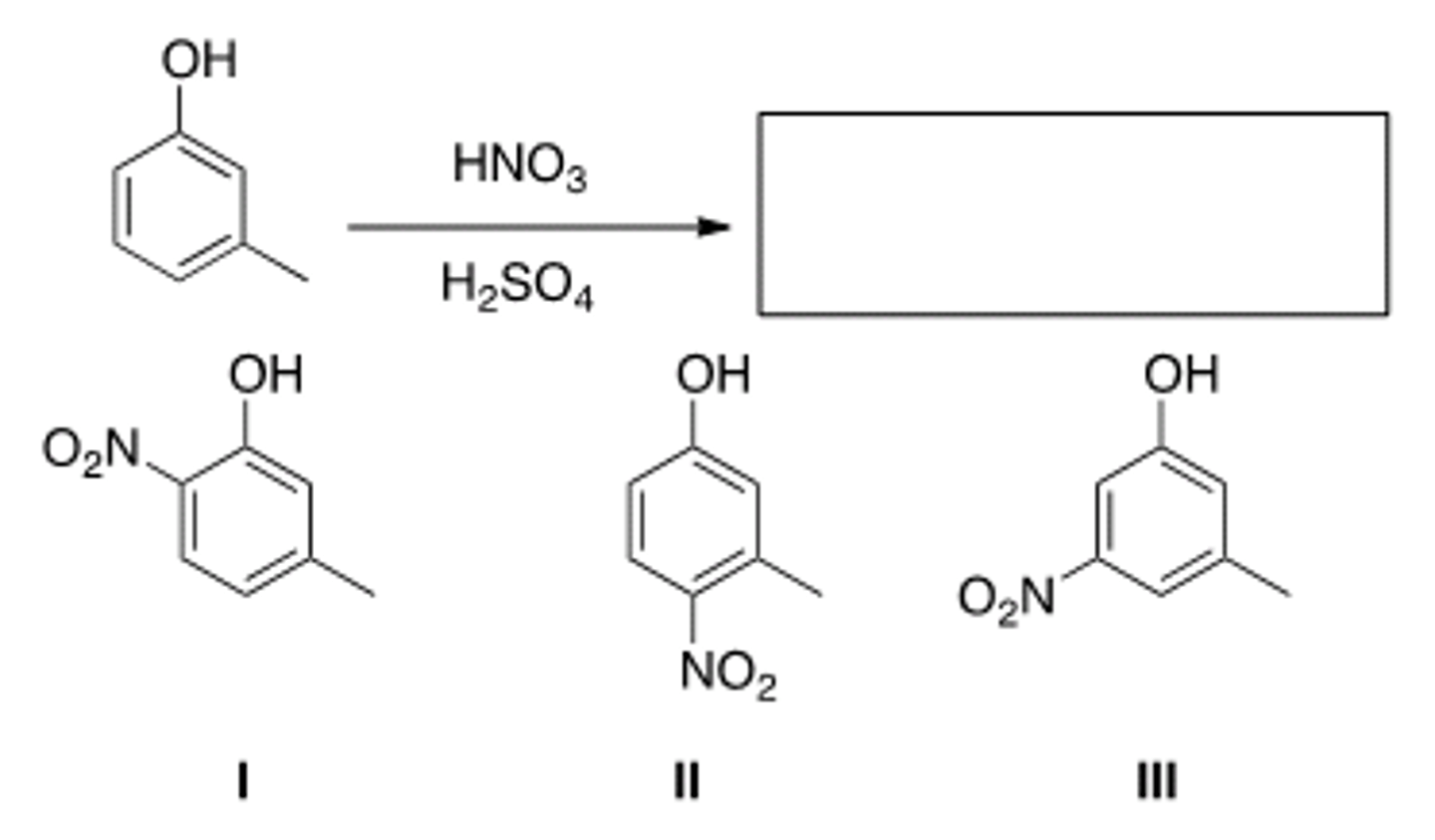
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
only I and II
What are the two distinct pathways for nucleophilic aromatic substitution?
Addition-elimination and elimination-addition
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic aromatic substitution.
I < II < III
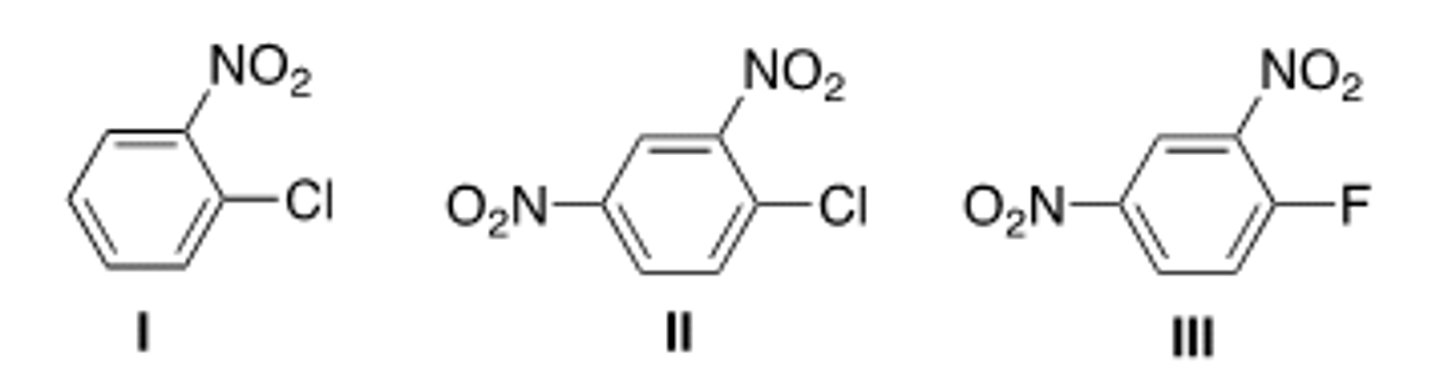
What is the major product of the following reaction?
IV
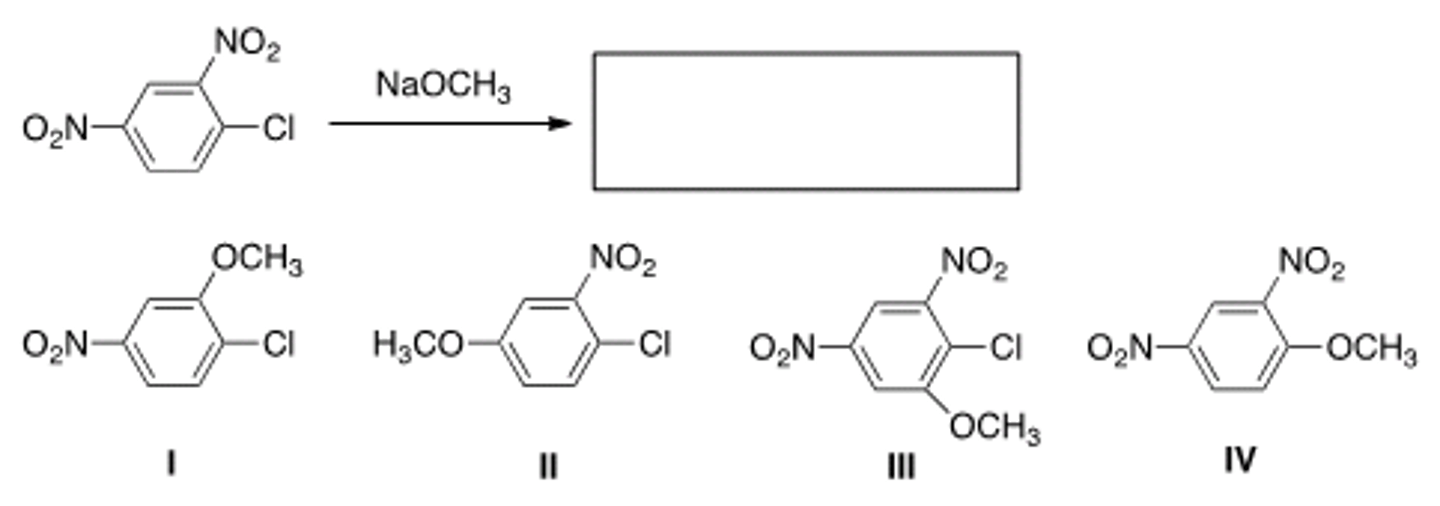
In addition to the product shown, what other product is formed in the following reaction?
IV
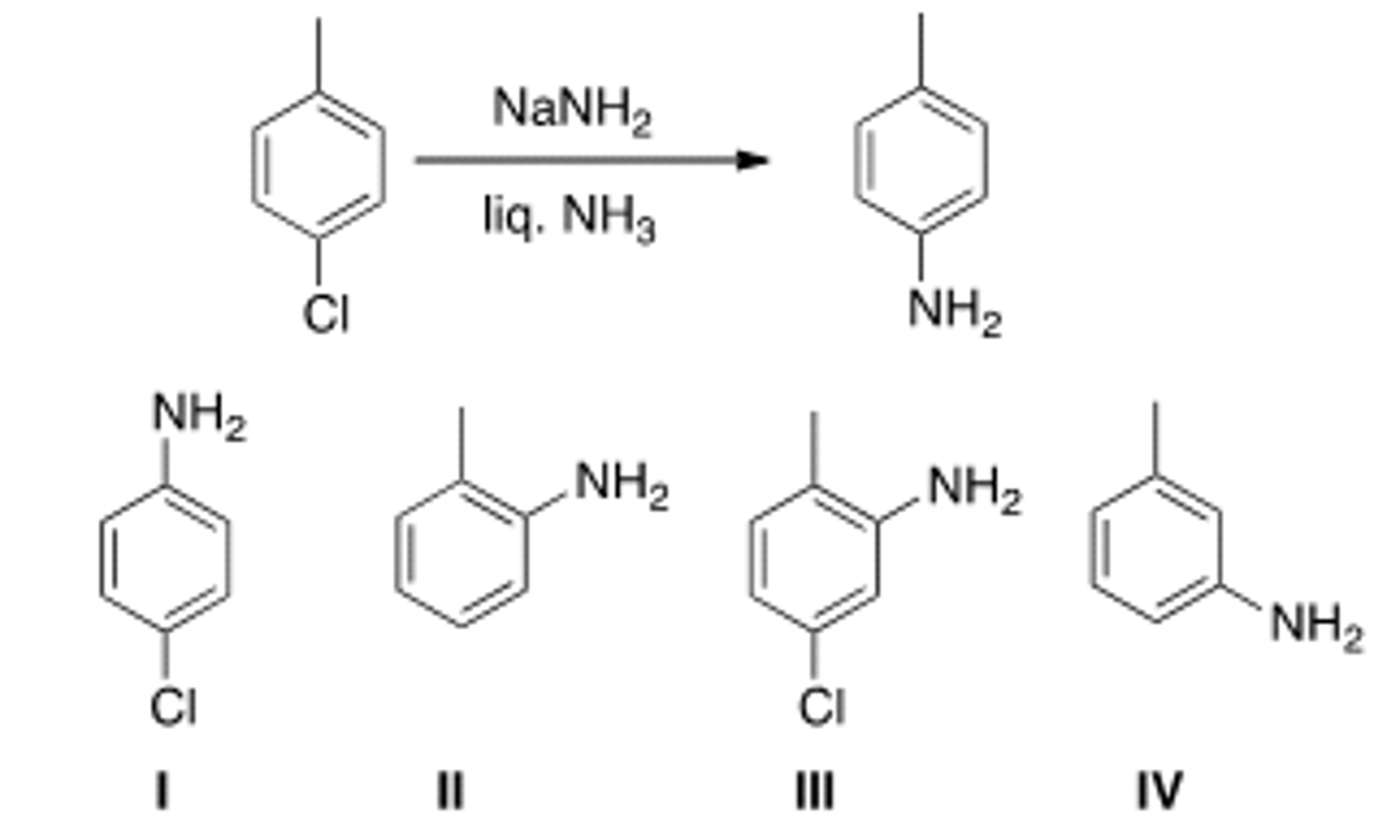
What is the product of the following sequence of reactions?
IV
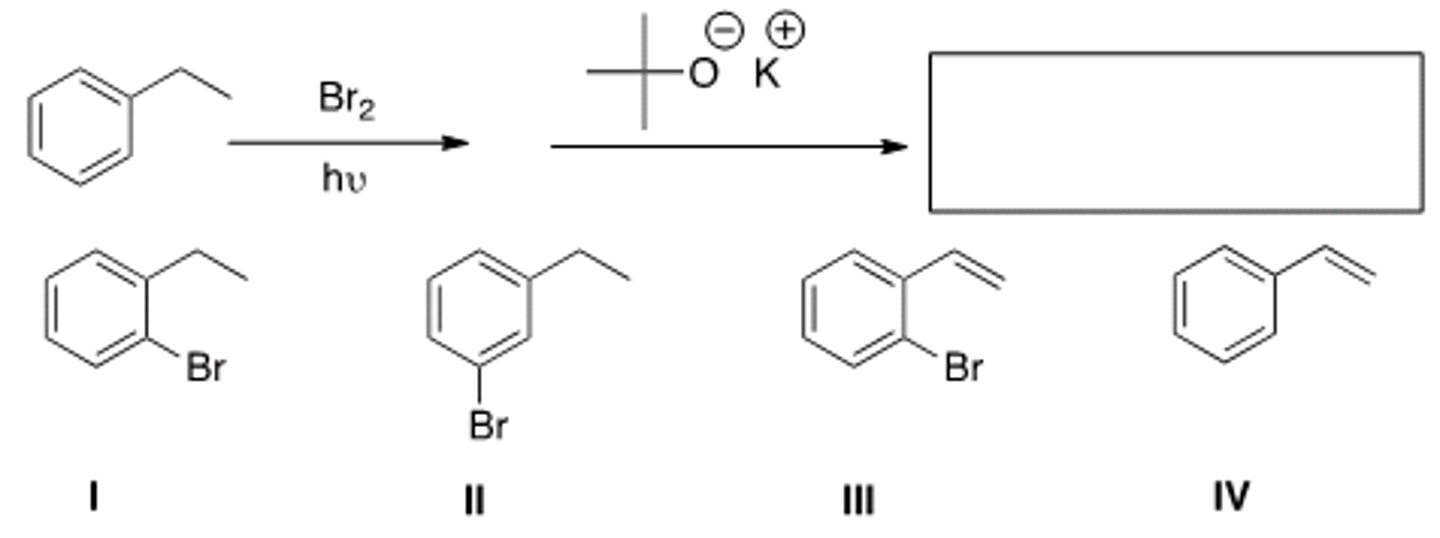
What is the product of the following reaction?
I
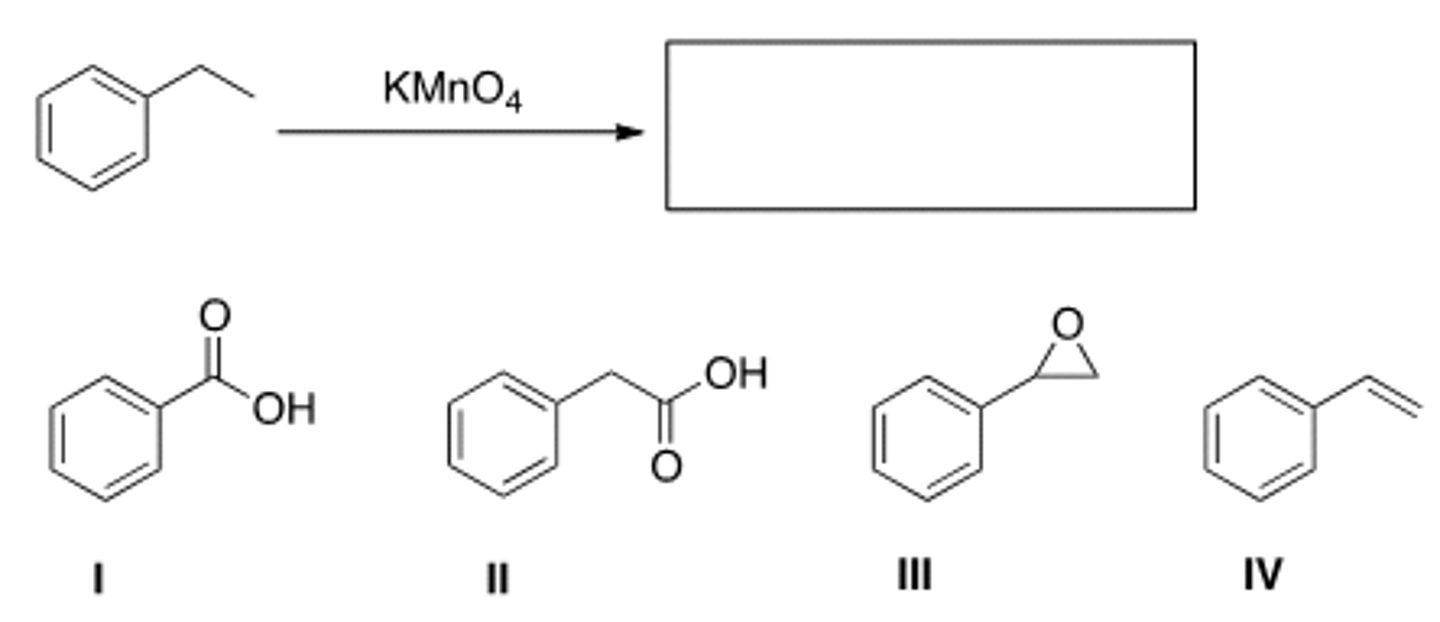
What is the best choice of reagent to bring about the following transformation?
Zn (Hg), HCl
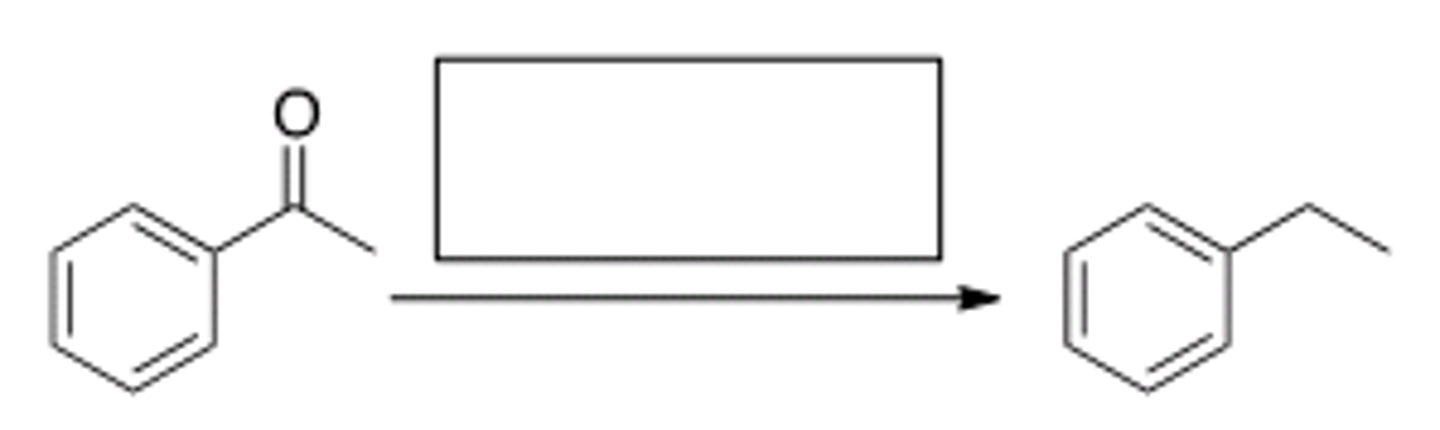

What is the best choice of reagent to bring about the following transformation?
H2, Pd-C

What is the name of the general reaction type that aldehydes and ketones undergo?
Nucleophilic addition
What is the name of the general reaction type that carboxylic acids, esters, and amides undergo?
Nucleophilic acyl substitution
Why are ketones less reactive than aldehydes?
Both (a) Ketones are more sterically hindered and (b) Ketones are less electron deficient due to donation from the two alkyl groups.
Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions, starting with the most reactive compound.
II > IV > I > III
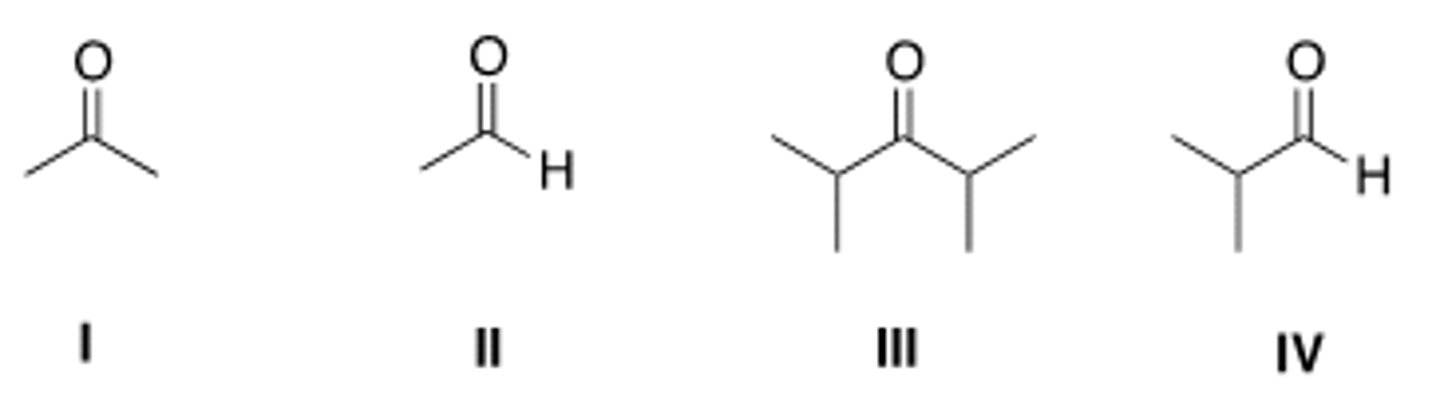
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity in nucleophilic acyl substitution reactions, starting with the least reactive compound.
II < I < III
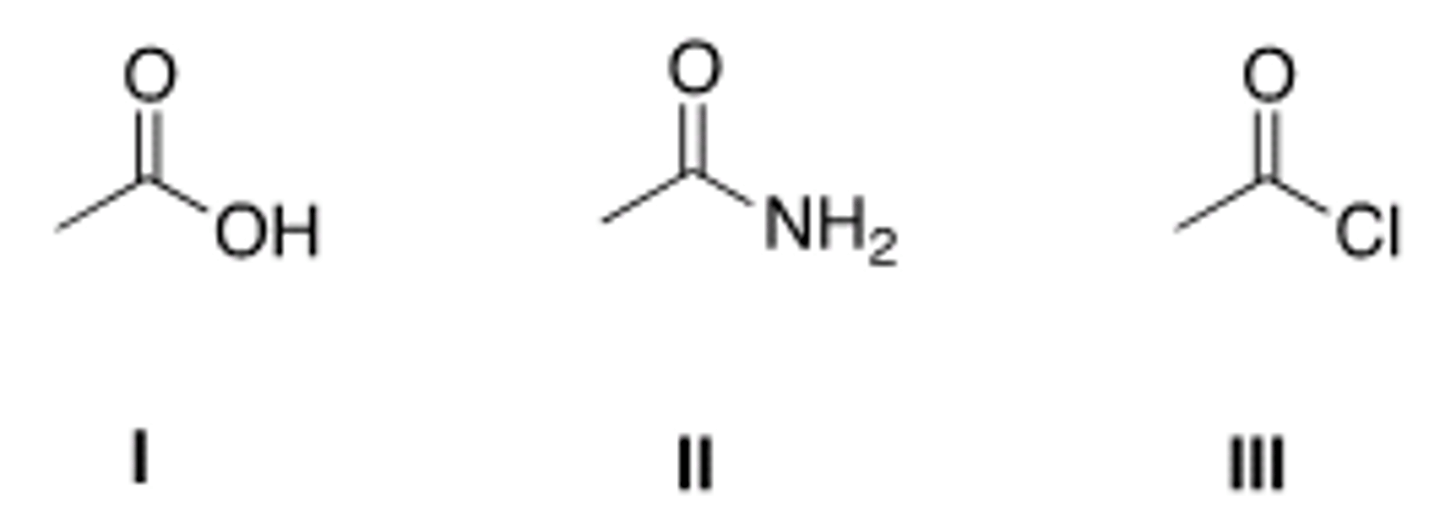
What is the product of the following reaction?
II
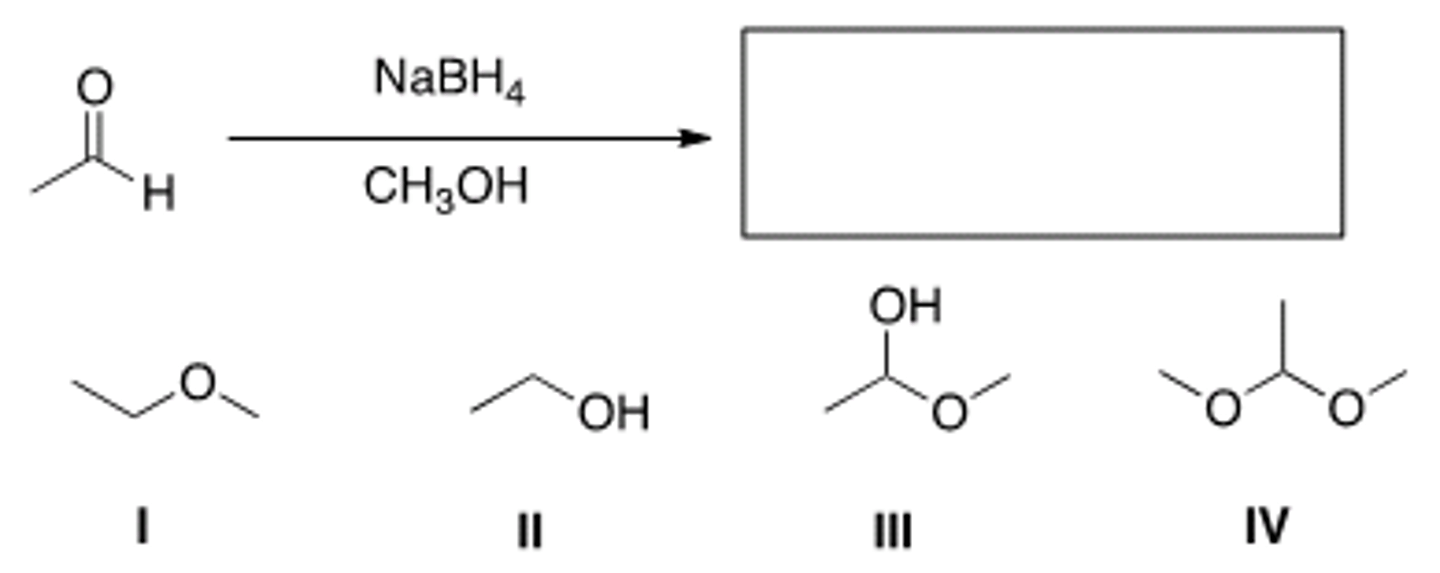
What is the product of the following reaction?
III
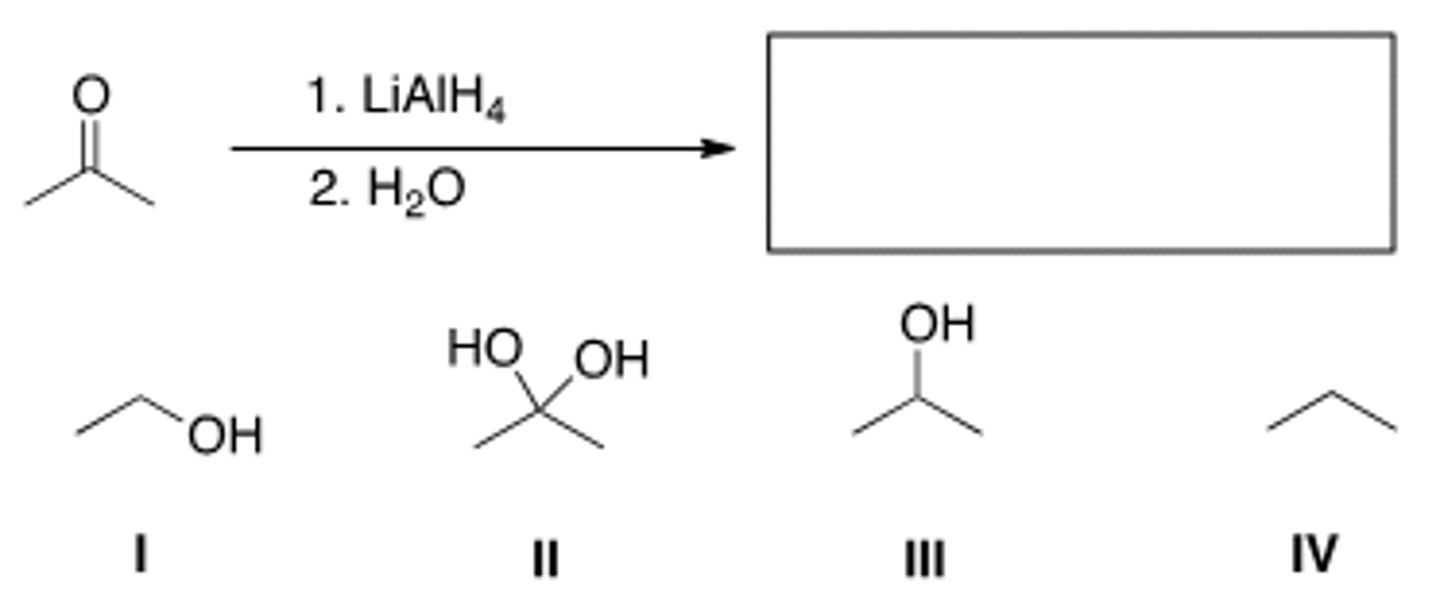
What is the starting material in the following reaction?
IV
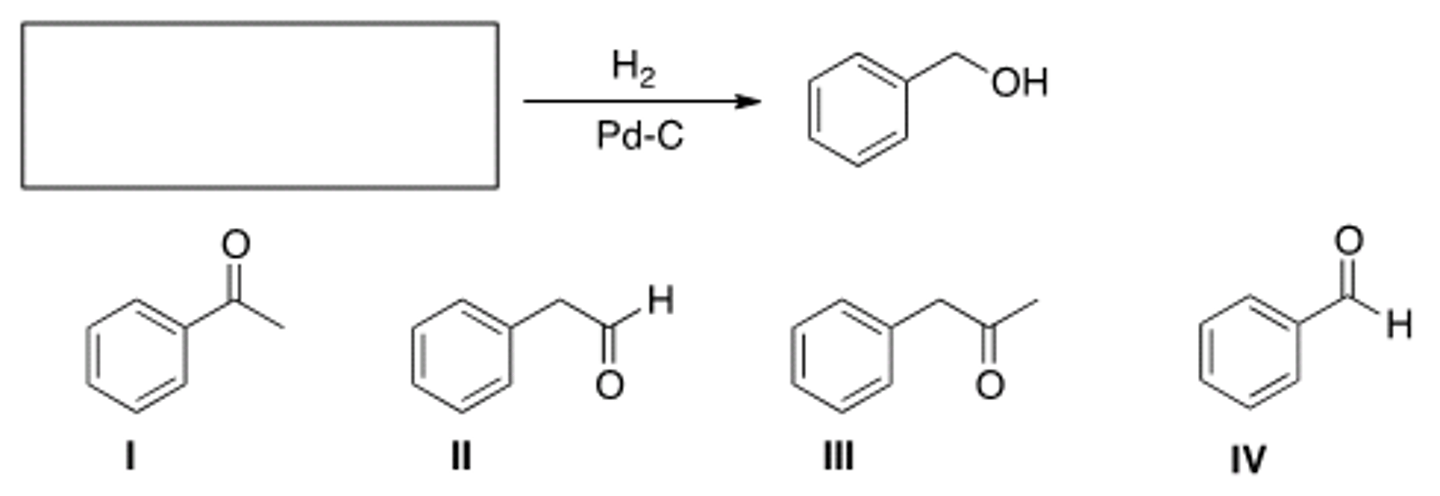
What is the product of the following reaction?
II
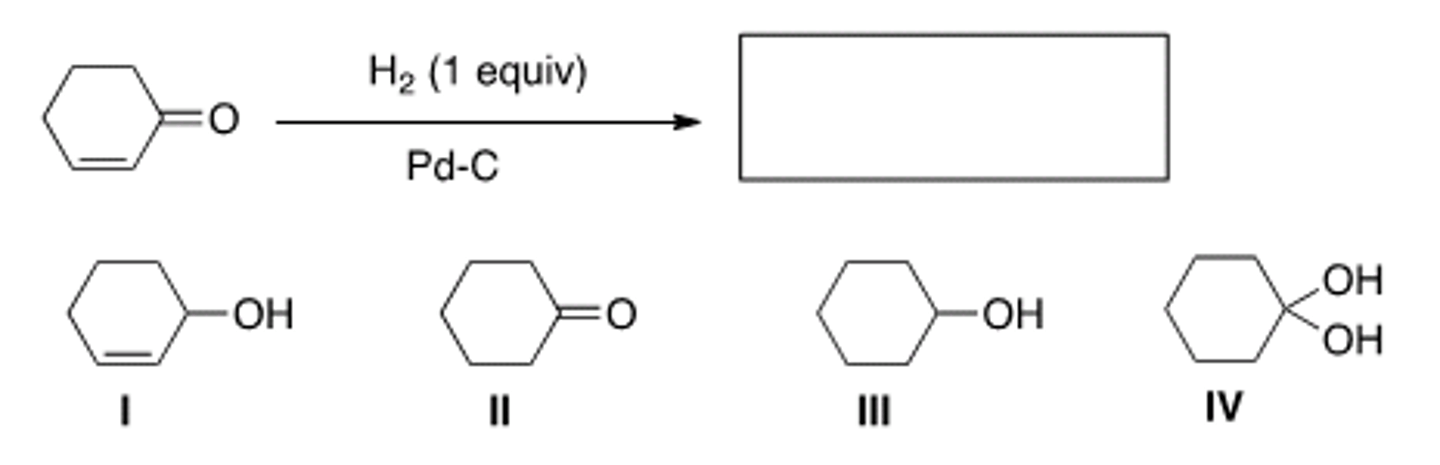
Why would the alcohol in the following compound need to be protected before reaction?
The Grignard reagent will react with the alcohol before the ketone.
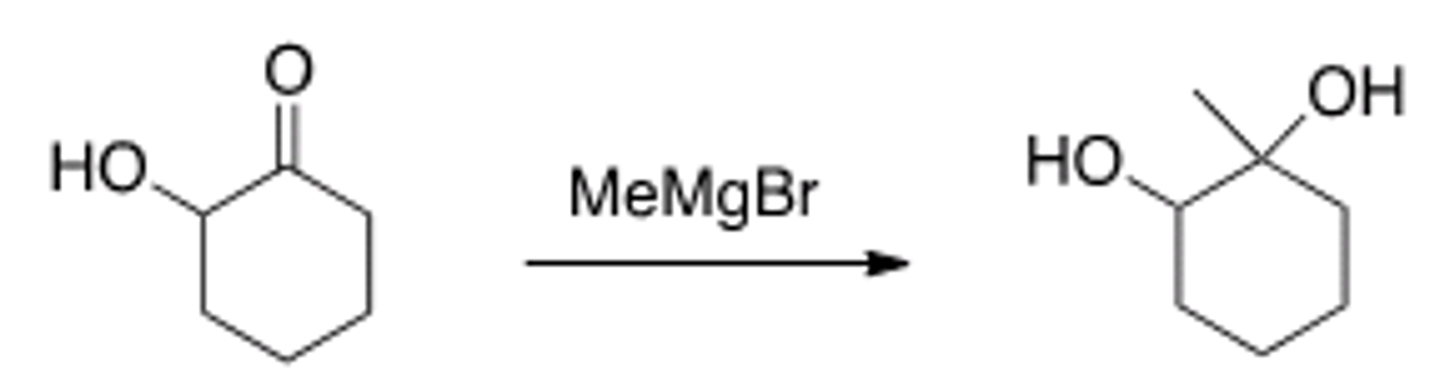
What is the purpose of a silyl ether?
To protect alcohols from organometallic reagents and other reagents
What reagent can be used to cleave a silyl ether protecting group?
Bu4NF
What is the product of the following reaction?
Only I and II
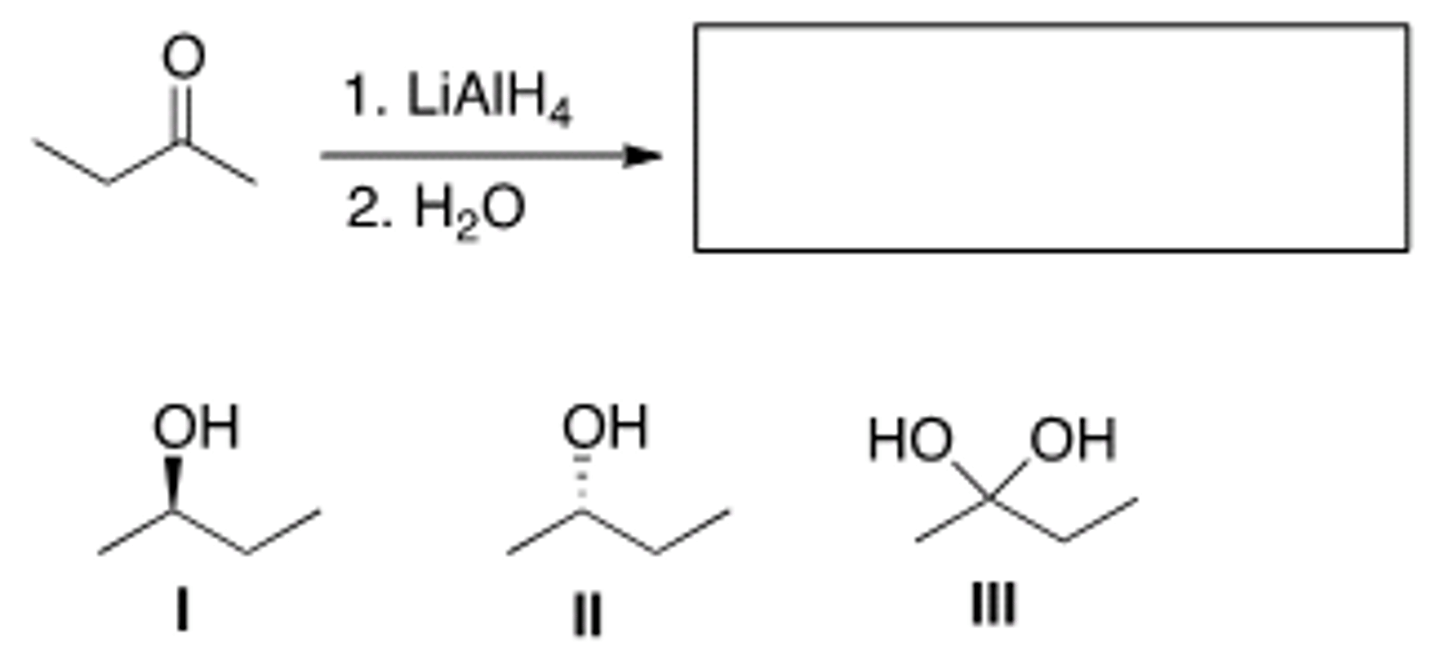
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
II
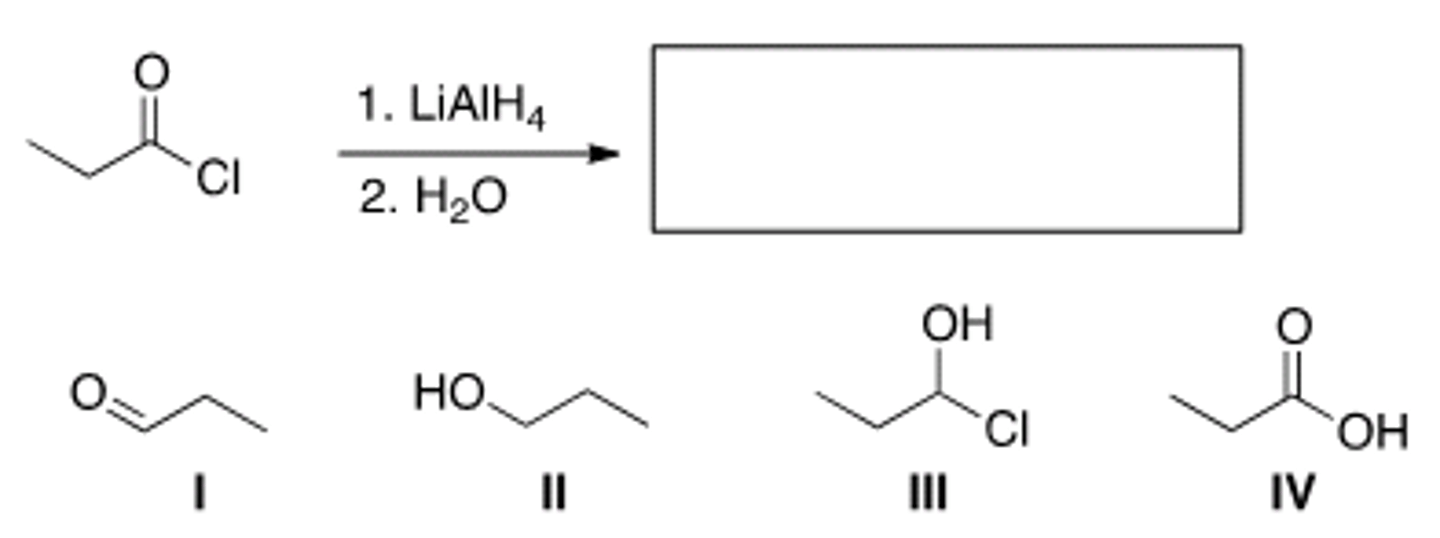
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
I
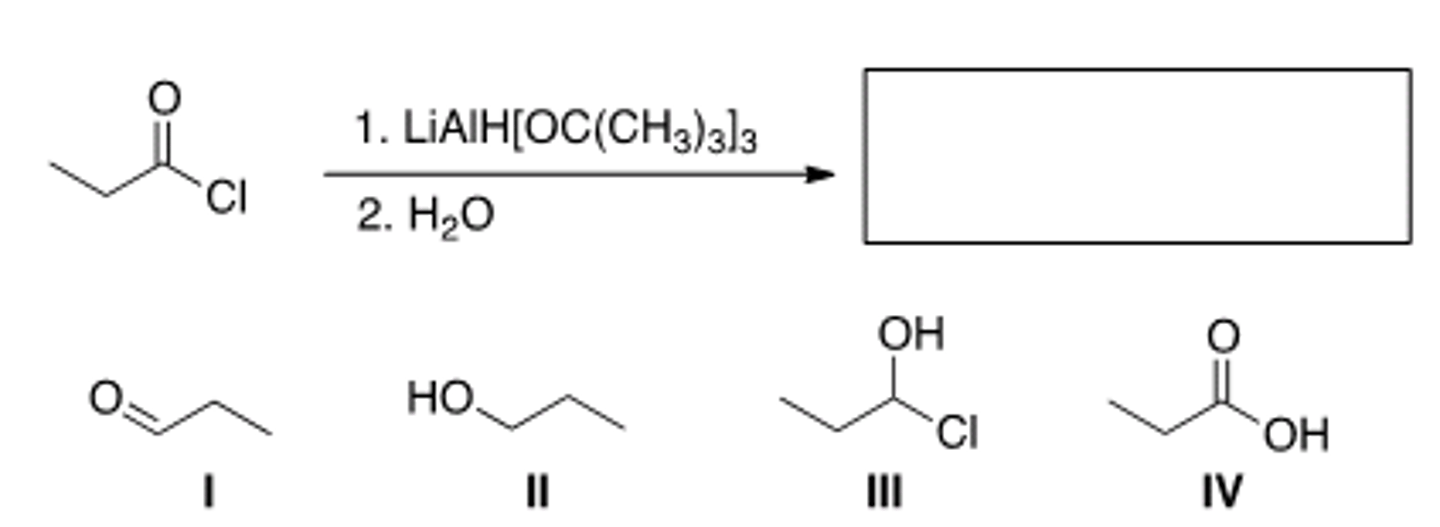
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
IV
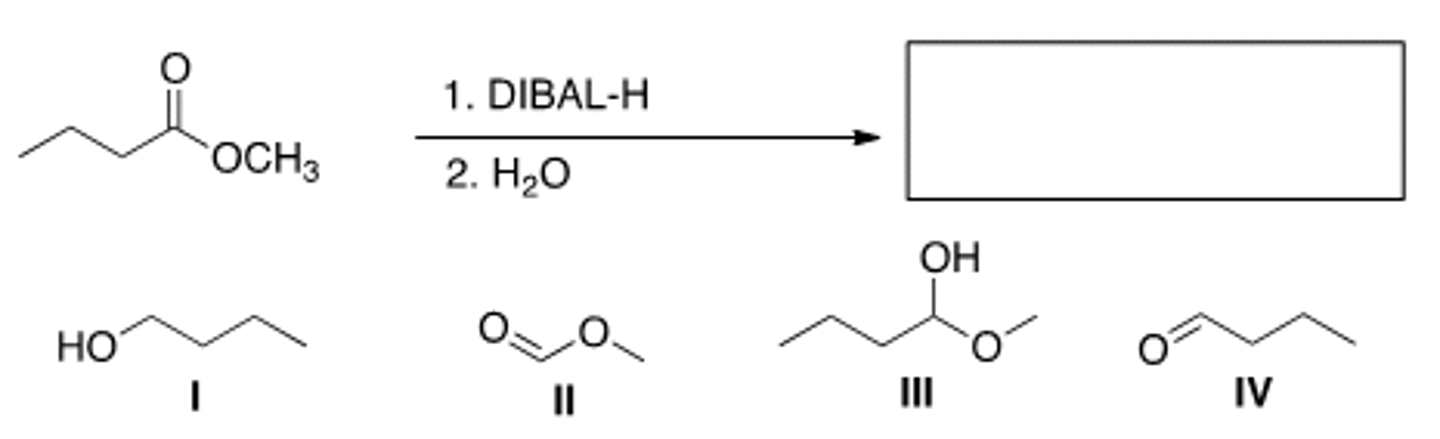
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
III
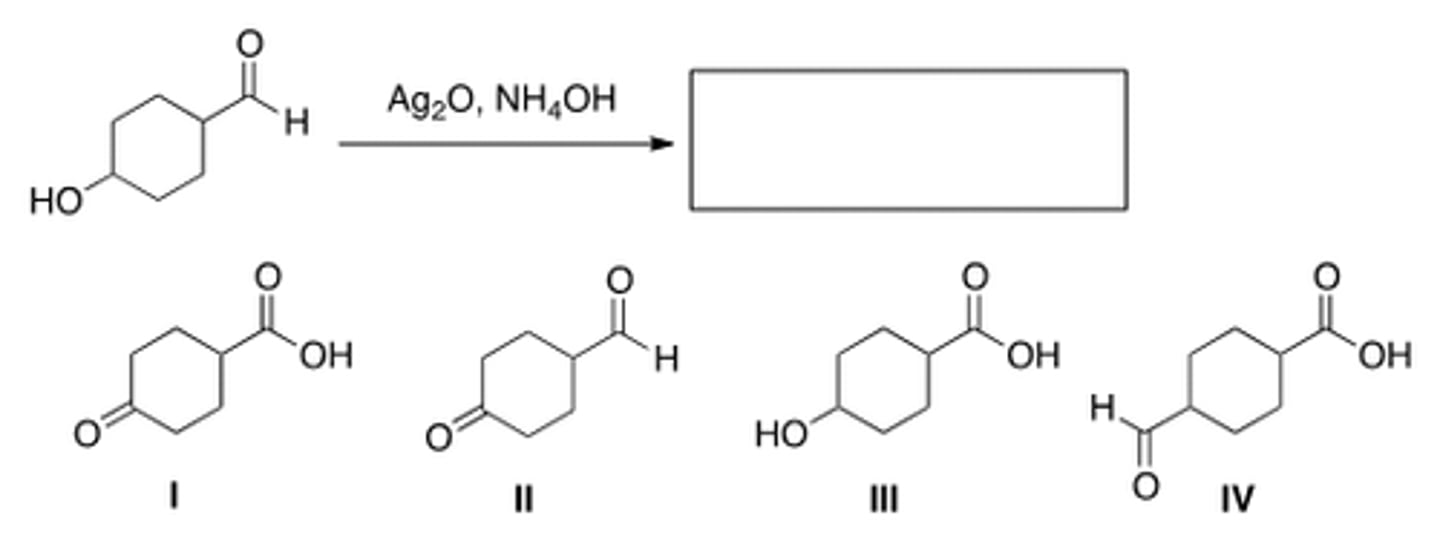
Rank the carbon-metal bond in the following organometallic reagents in order of decreasing polarity, starting with the most polar.
II > I > III
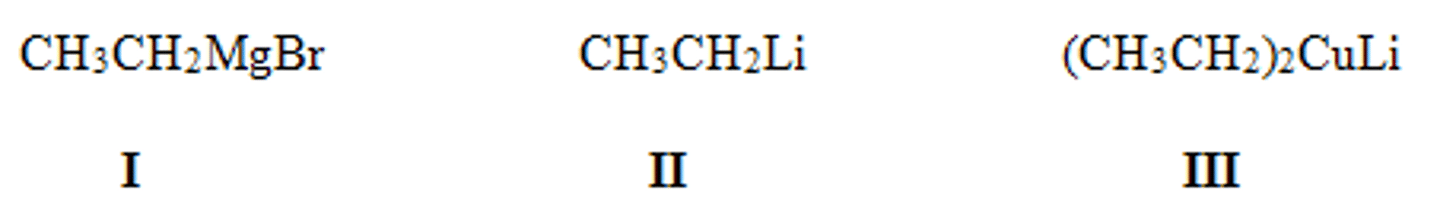
What is the product of the following reaction?
II
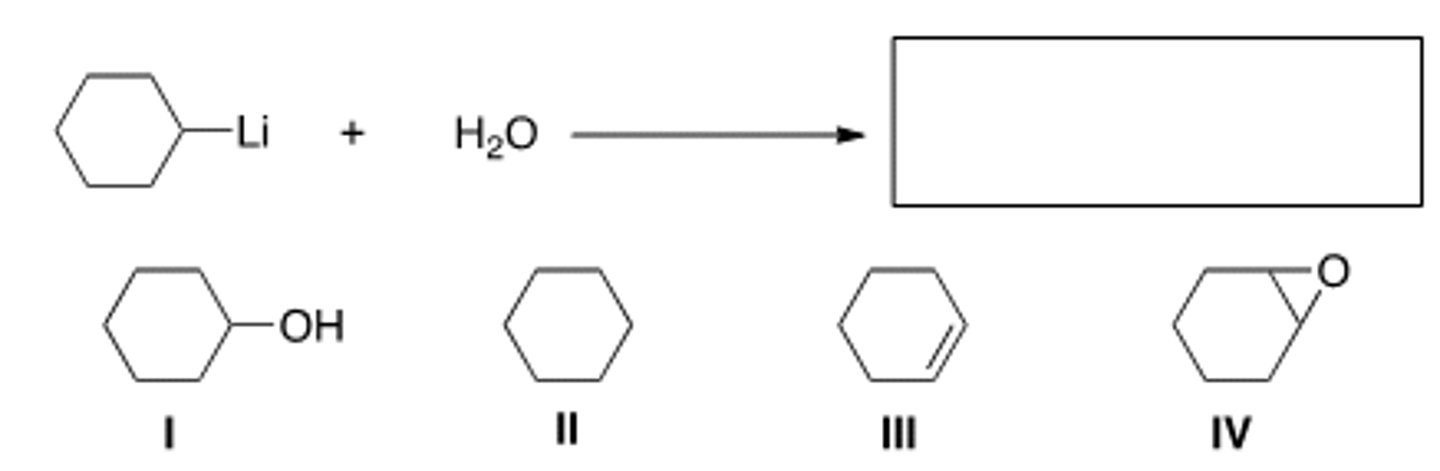
What is the product of the following reaction?
III
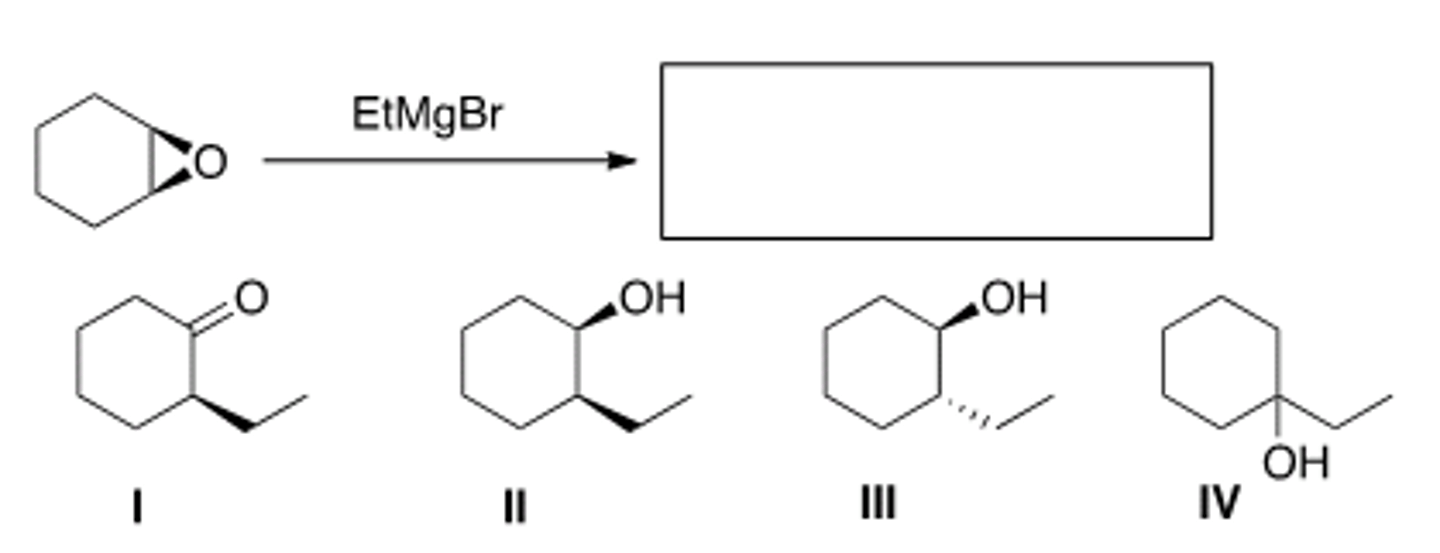
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
Only I and II
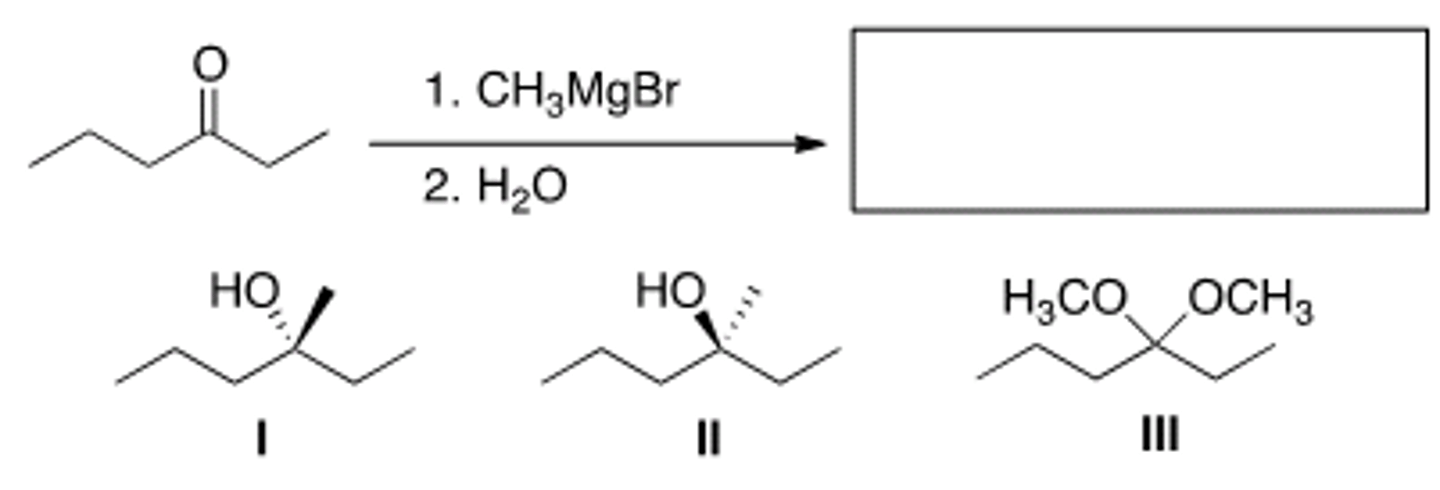
What carbonyl compound and Grignard reagent could be used to prepare 2-butanol?
Only I and II
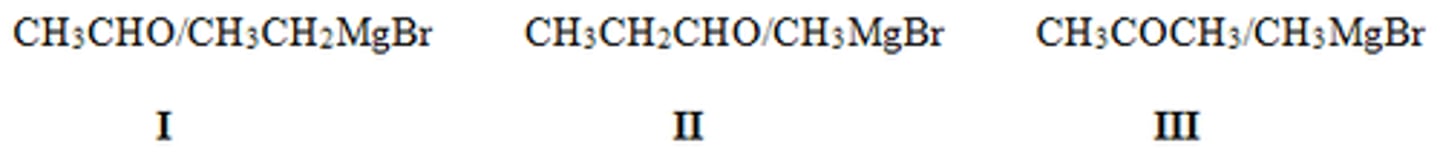
What is the major organic product in the following sequence of reactions?
II
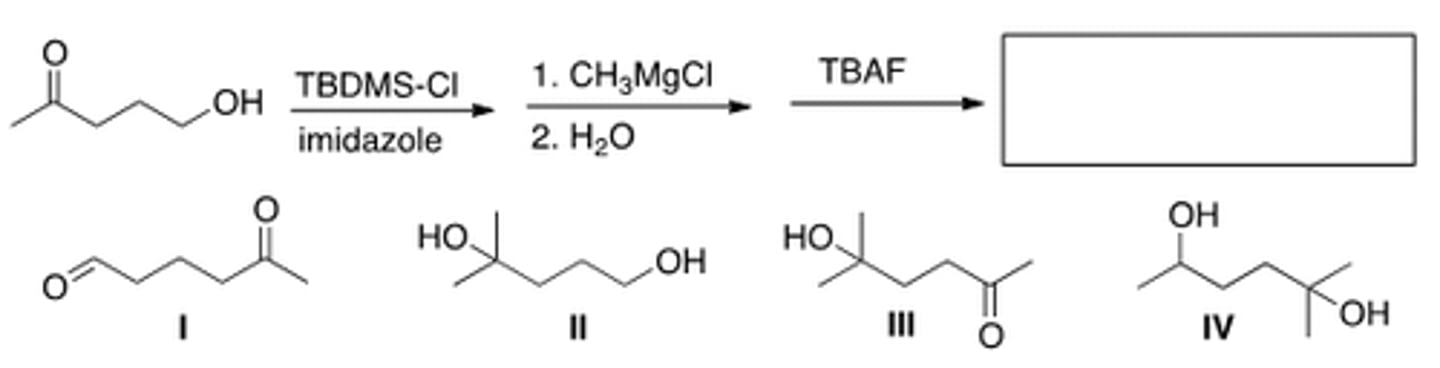
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
I
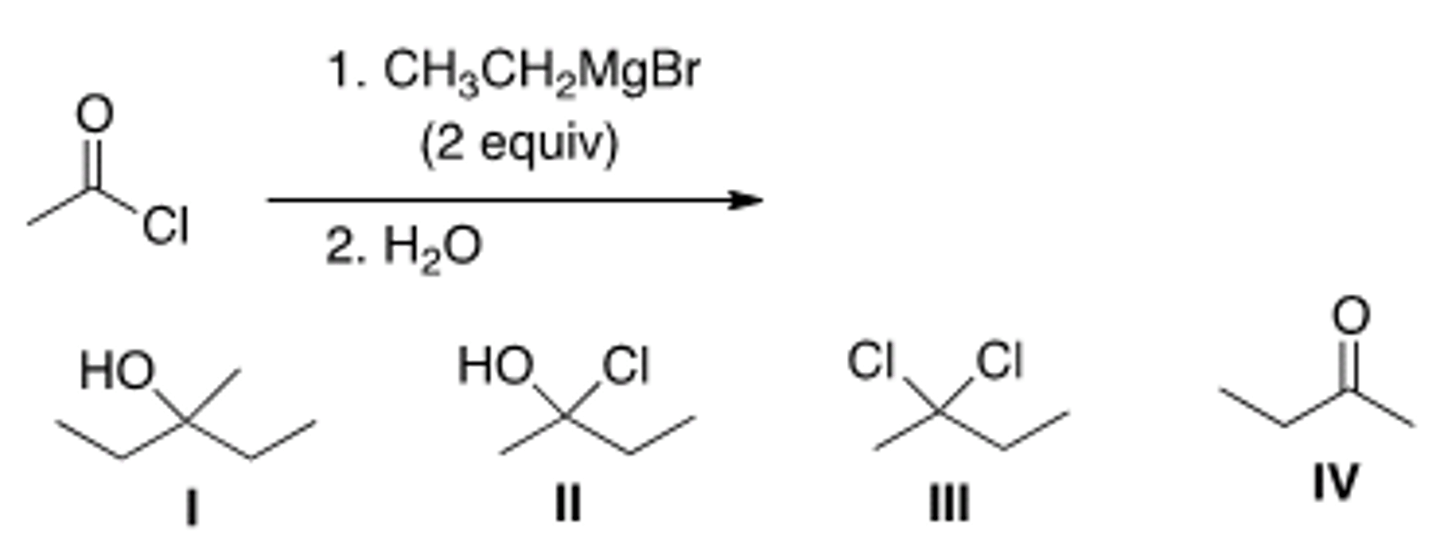
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
II
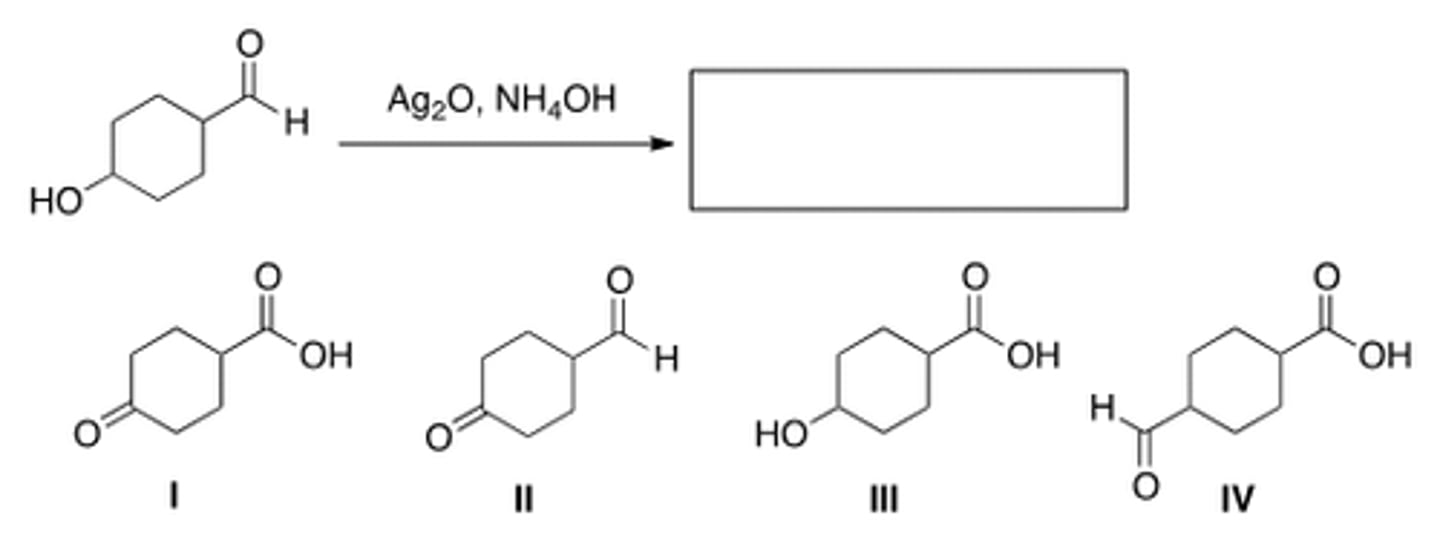
What is the major organic product in the following sequence of reactions?
IV
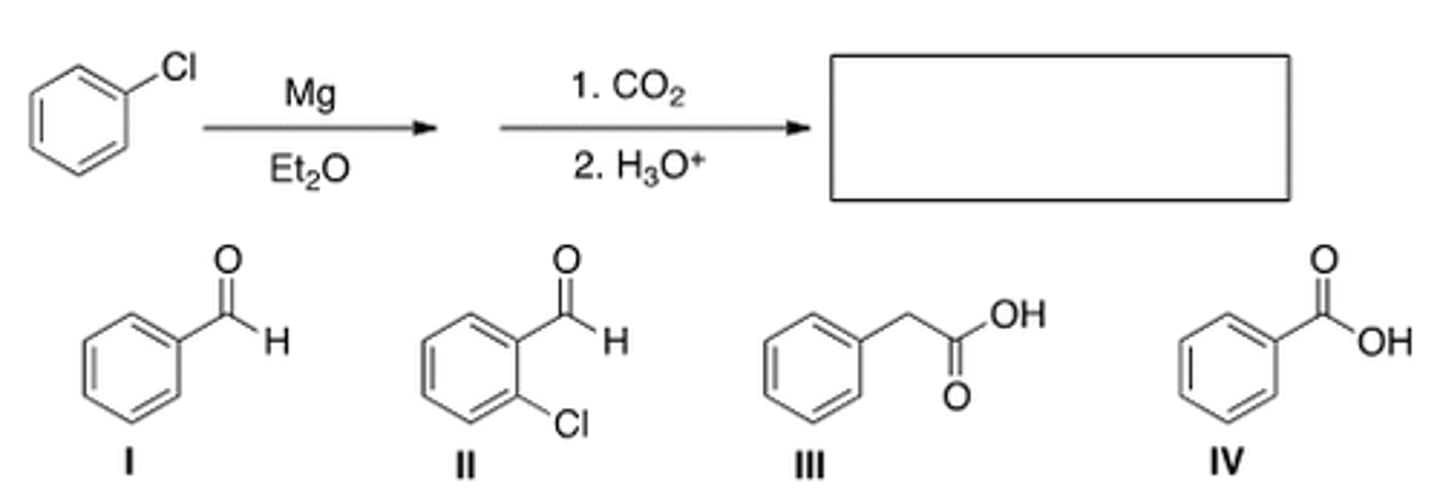
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
[1] Mg, [2] CO2, [3] acidic work-up
![<p>[1] Mg, [2] CO2, [3] acidic work-up</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/0439c702-417a-4994-a6ce-996c2c437502.png)
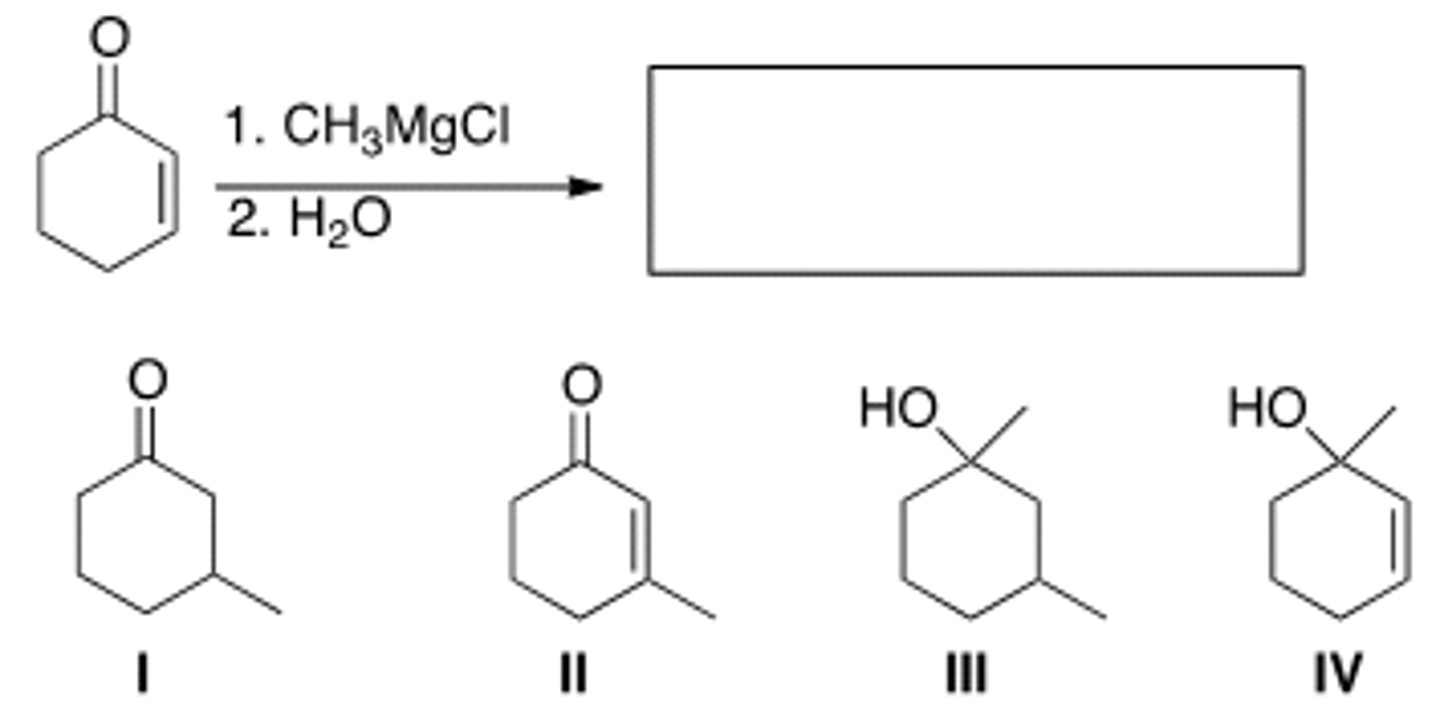
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
IV
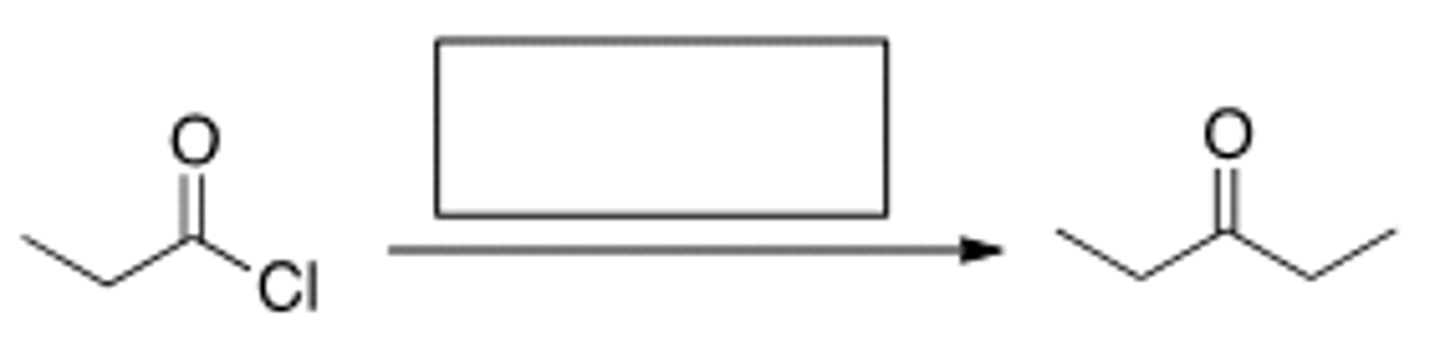
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
Et2CuLi then H2O
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
Ph2CuLi then H2O
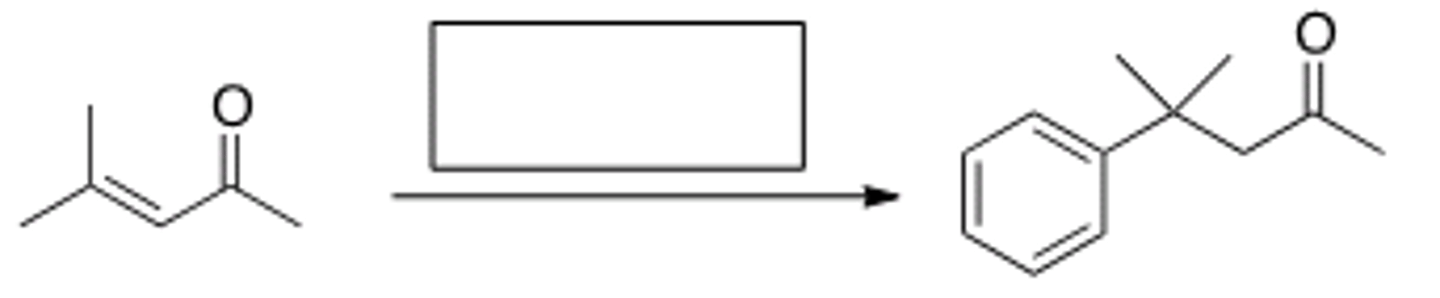
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
LiAlH4 then H2O

Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity toward the nucleophilic hydride reagent, NaBH4.
II < I < III
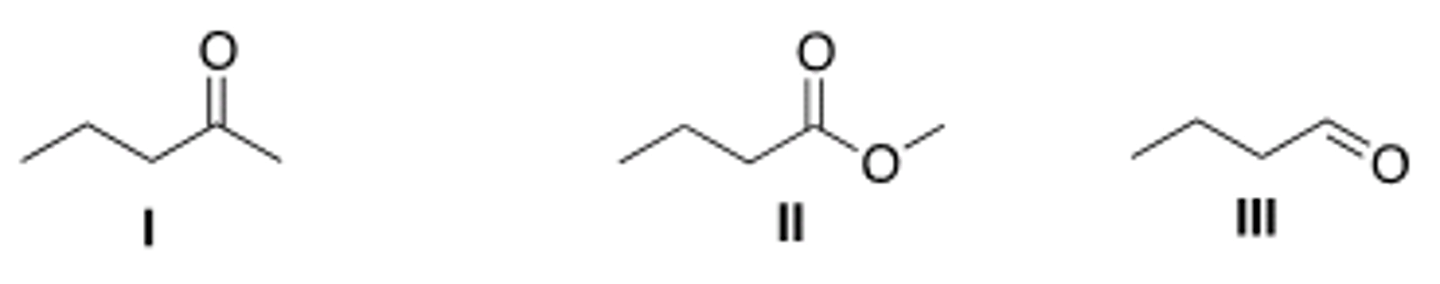
Both LiAlH4 and NaBH4 are reducing agents. Which statement about these reagents is true?
Both reagents contain polar metal-hydrogen bonds. The polarity of the B-H bond is less than the polarity of the Al-H bond, so LiAlH4 is the stronger reducing agent.
Which is the most reactive carbonyl compound?
I
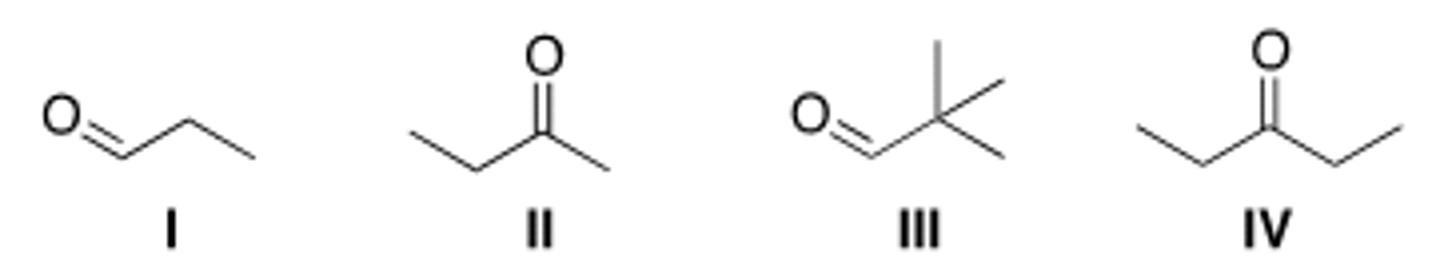
What is the first step in nucleophilic addition under acidic conditions?
Protonation of the carbonyl
Why can't you use acidic conditions (such as aqueous hydrochloric acid) for the addition of a Grignard reagent to a ketone?
Because the Grignard reagent will react with the acid and be quenched
What is the major organic product obtained from the following sequence of reactions?
III
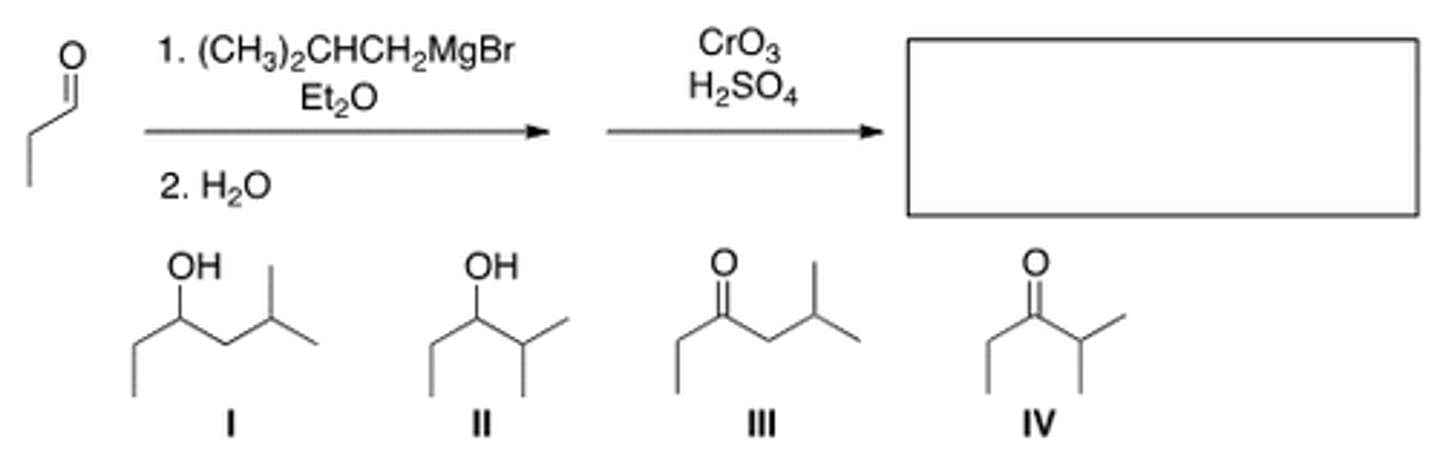
What would you use to prepare the following ylide from the starting phosphonium salt?
Butyl lithium

What is the driving force for the Wittig reaction?
The elimination of triphenylphosphine oxide
Why are strongly acidic conditions not used in the formation of enamines and imines?
The amine will be completely protonated.
What is the product of the following reaction?
IV
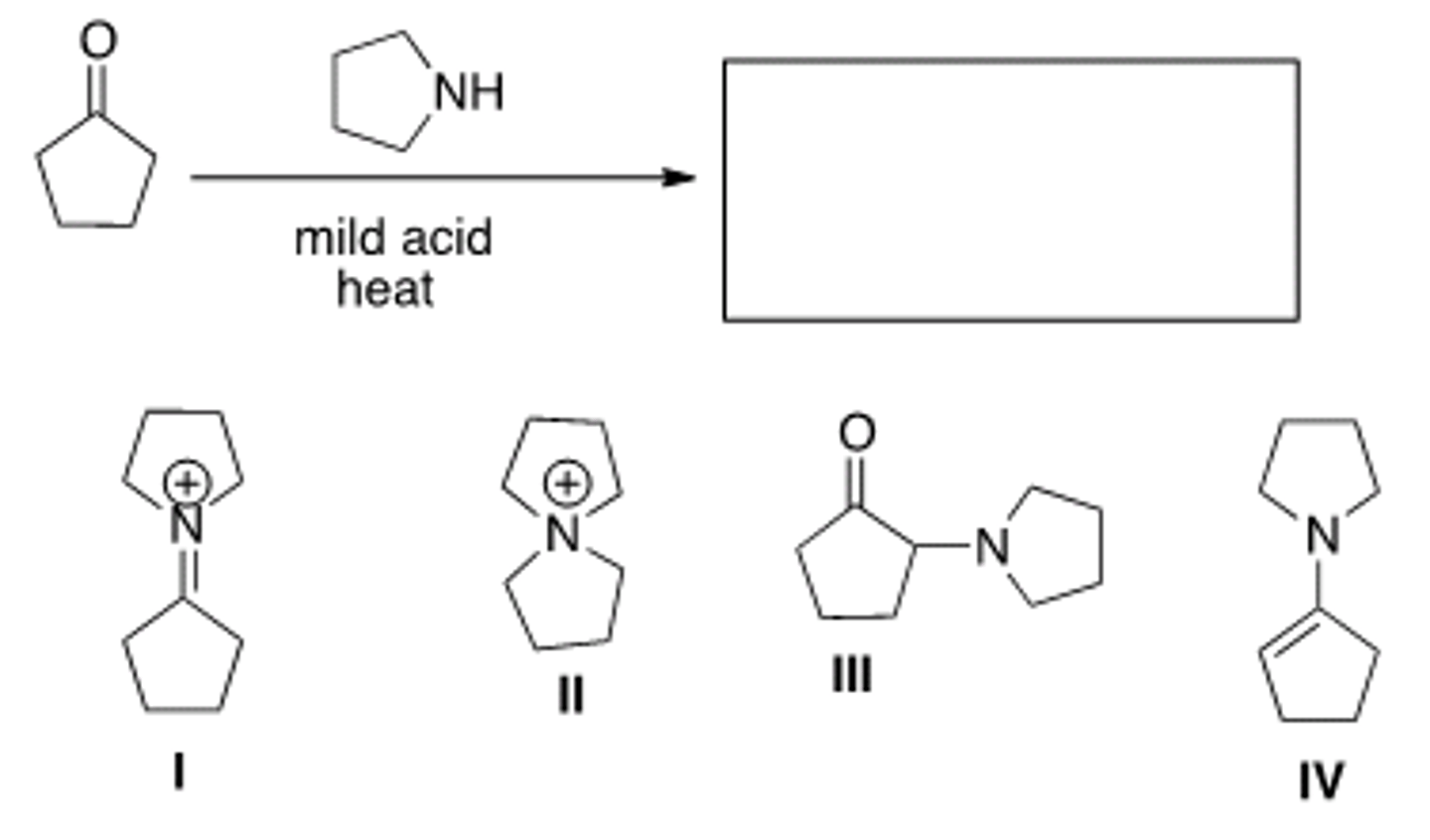
What is the product of the following reaction?
I
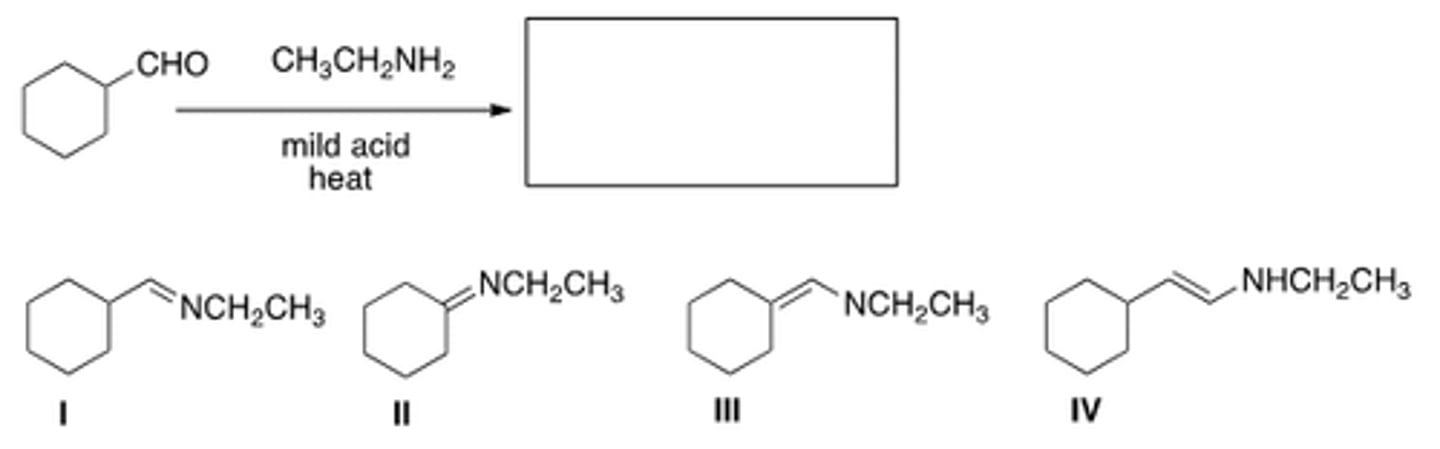
What needs to be done to make the following reaction proceed?
Heat the reaction and add an acid catalyst.
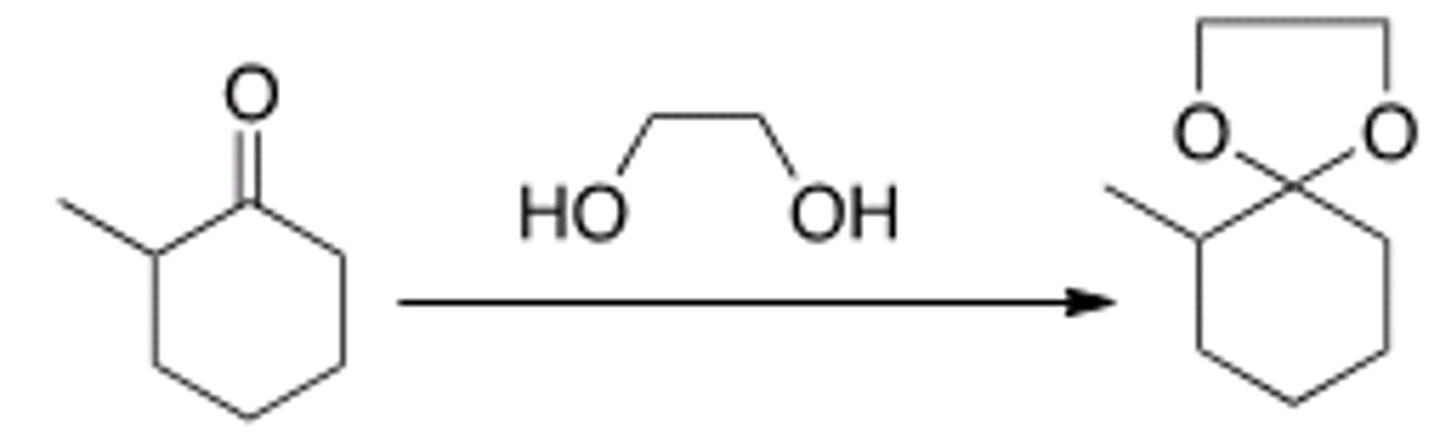
What needs to be done to make the following reaction go to starting materials?
Add aqueous acid.
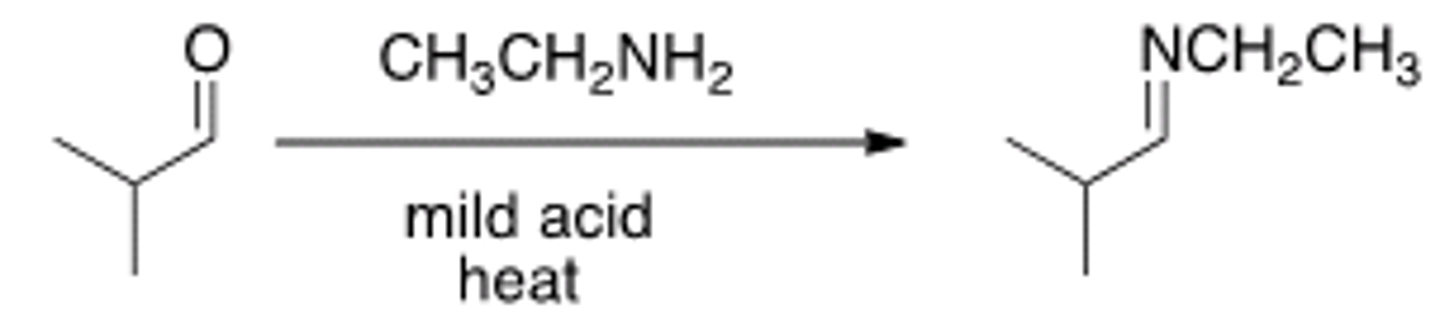
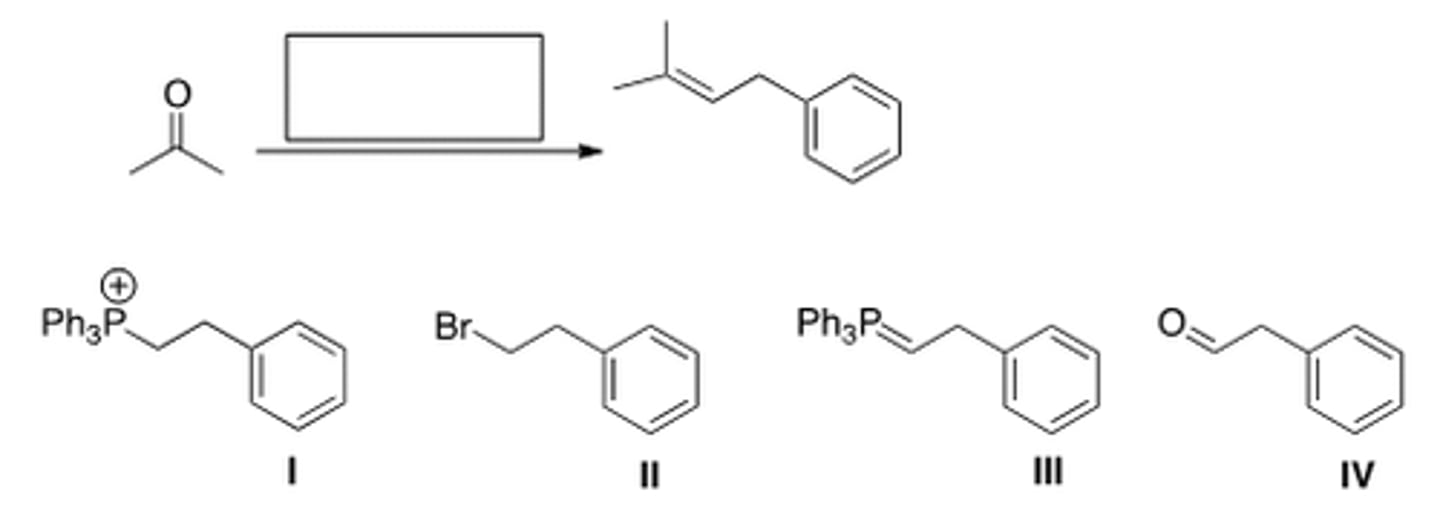
What sequence of reactions is required for the following transformation?
[1] Ph3P, [2] KOtBu, [3] acetone
![<p>[1] Ph3P, [2] KOtBu, [3] acetone</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dfeaafd0-f3fc-4b10-a871-7878c2b312e5.png)
What is the product of the following reaction?
I
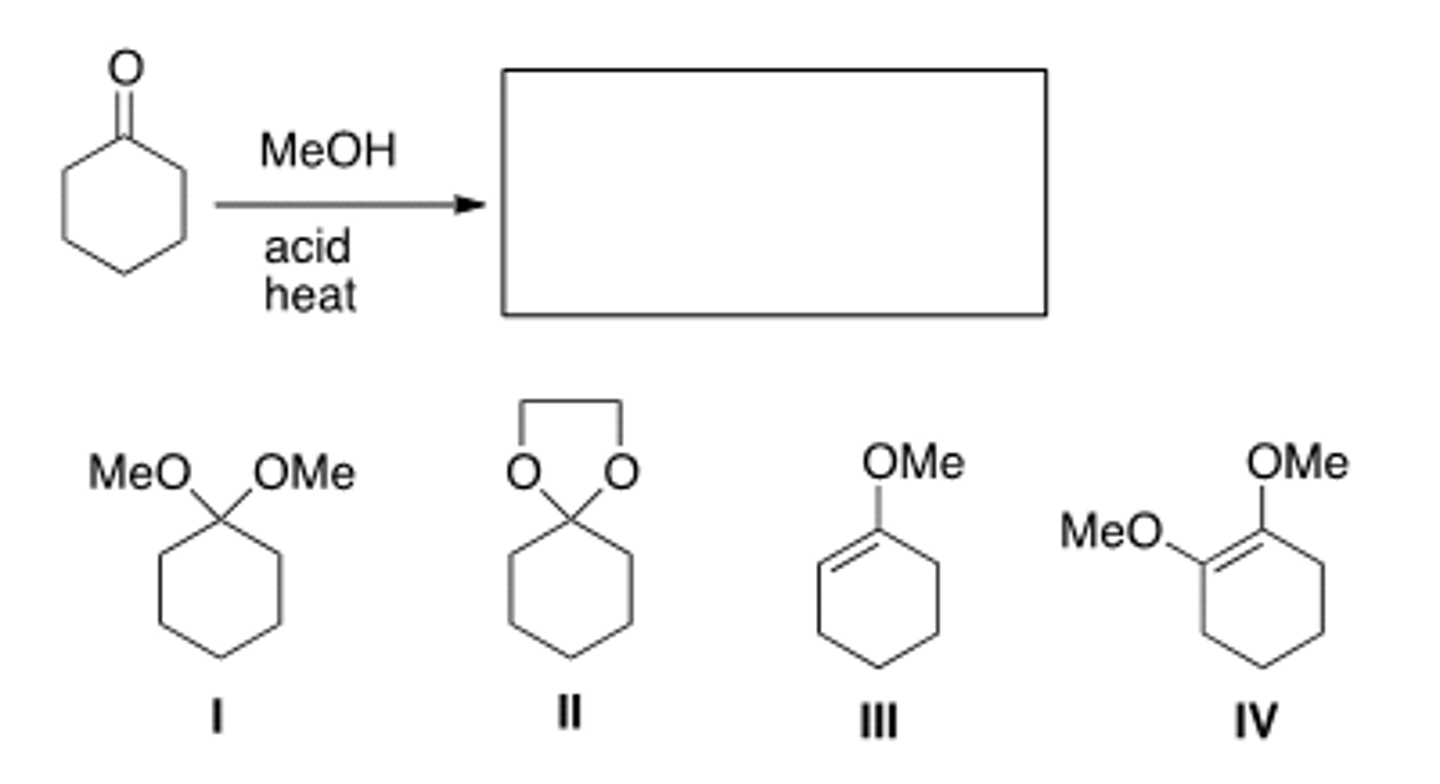
What is (are) the product(s) of the following reaction?
II and III
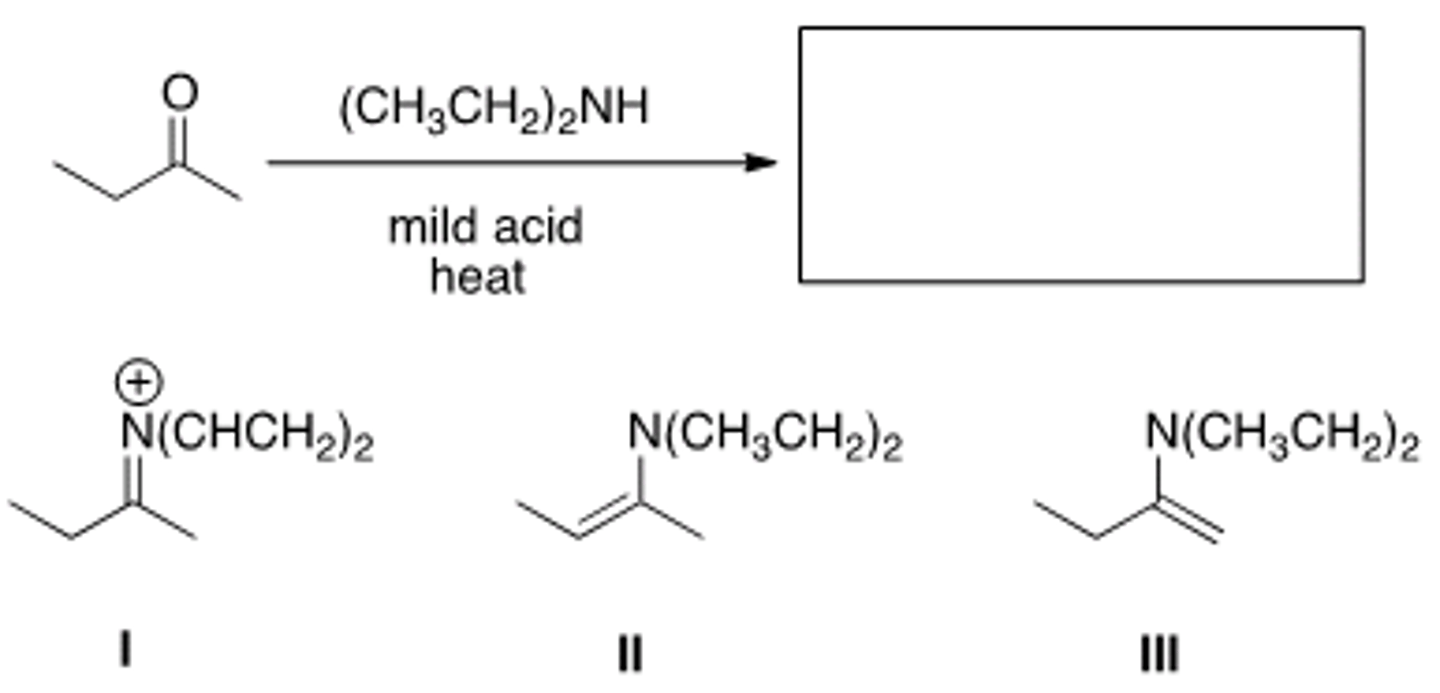
What is the product of the following reaction?
III
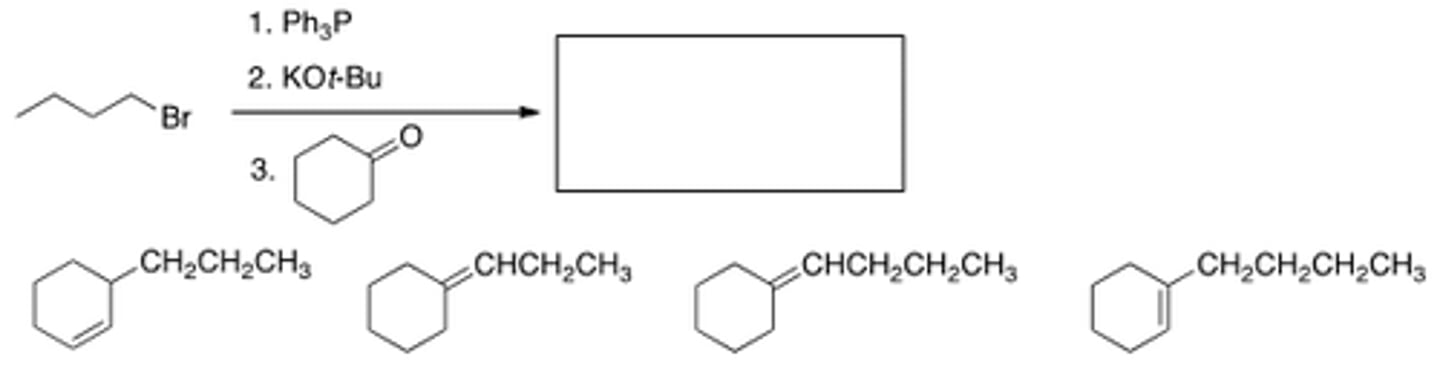
What is the product of the following sequence of reactions?
I
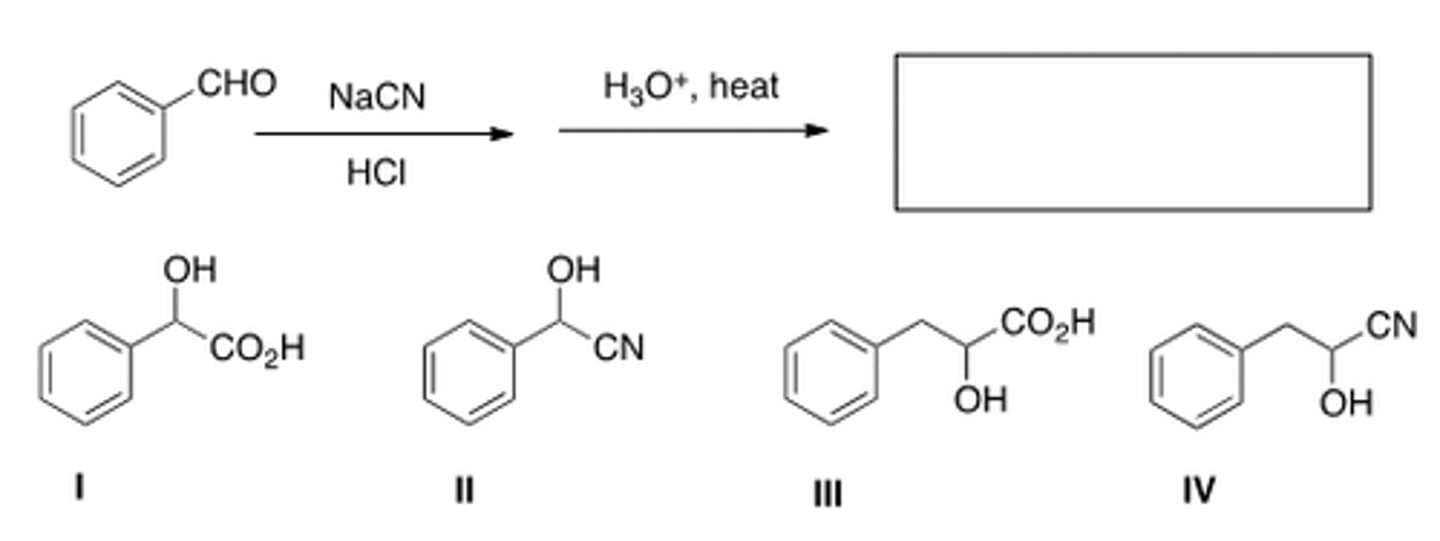
What is the missing reagent in the reaction below?
III
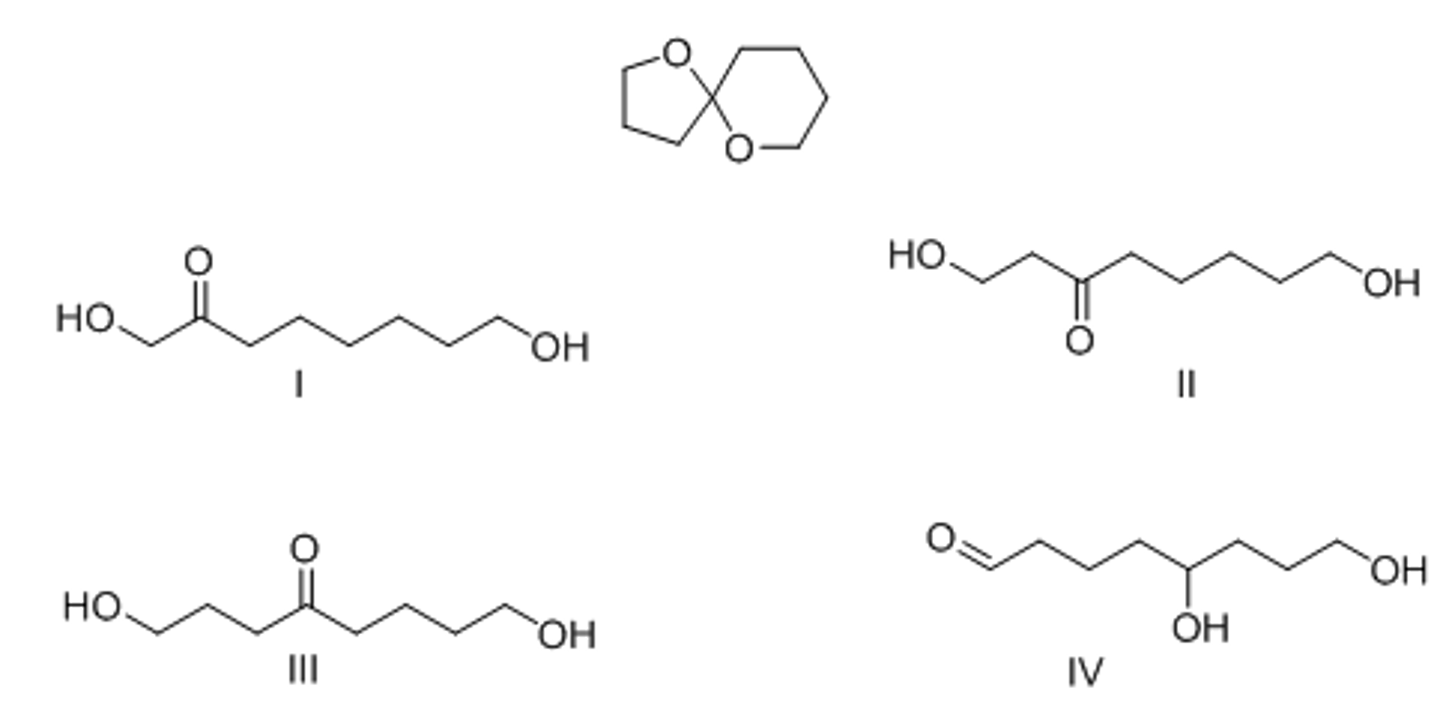
Cyclic acetals are used as protecting groups for ketones or aldehydes because they are inert to all of the following reagents except
aqueous acid.
What is the product of the following reaction?
II
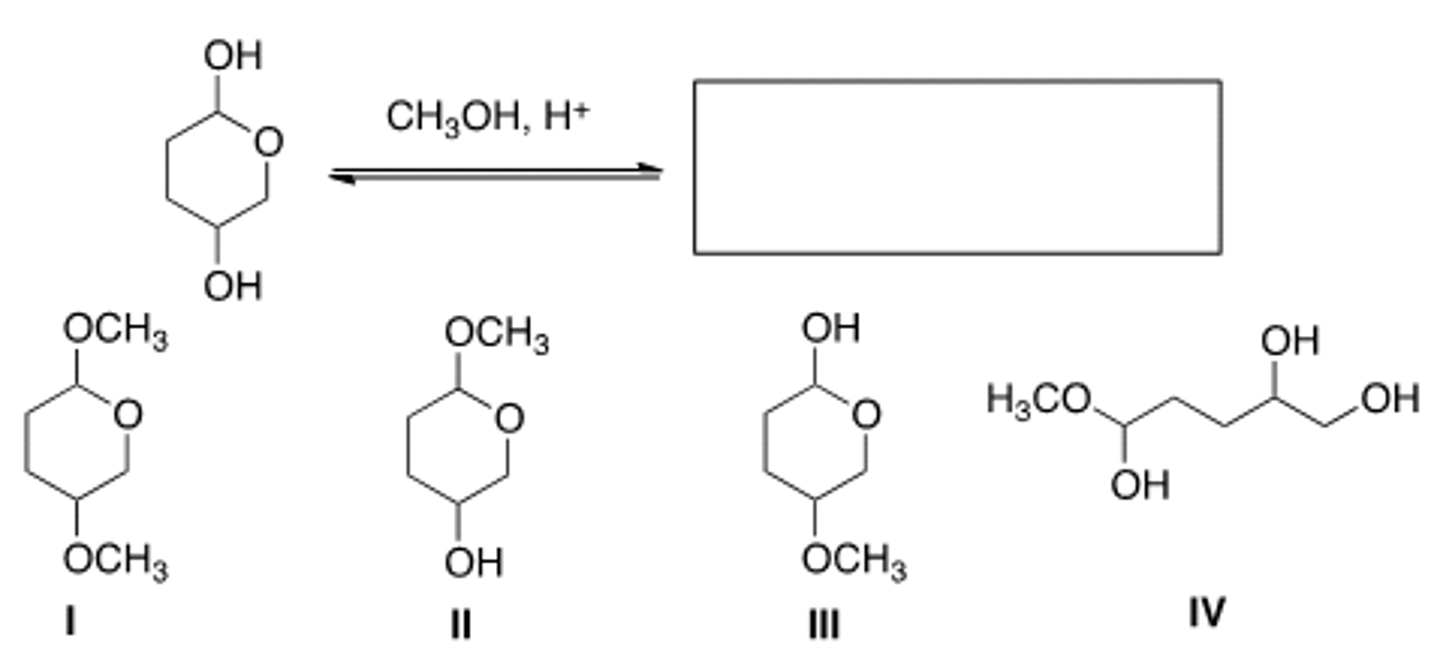
What product is formed when the following acetal is hydrolyzed with aqueous acid?
III