AP Microeconomics - Consumer Choice Unit Review
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
DEF: Subsitution Effect
When a good’s price changes, consumers substitute relatively cheaper goods for more expensive ones.
DEF: Income Effect
A price change affects the purchasing power of a consumer, which alters the demand for goods.
NORMAL GOODS: demand increases with purchasing power increasing.
INFERIOR GOODS: demand decreases with purchasing power increasing.
DEF: Giffen Goods
[probably won’t be on the test, but just in case!]
A type of inferior good for which demand increases as the price rises, due to the strong income effect outweighing the substitution effect.
DEF: Elasticity
measures responsiveness of one variable to changes in another
Price Elasticity of Demand Formula
The formula for calculating the price elasticity of demand, expressed as the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
MIDPOINT METHOD:
(CHANGE IN Quantity) / (AVERAGE OF QUANTITY) divided by (CHANGE IN Price) / (AVERAGE OF PRICE)
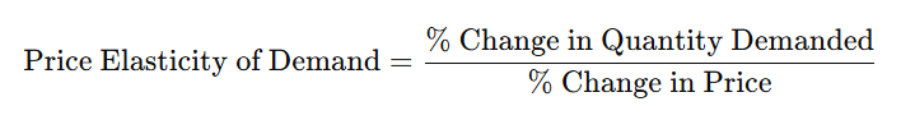
What do you do with the sign for price elasticity of demand?
drop the minus sign - use the absolute value!
price elasticity of demand is ALWAYS positive.
What values determine elastic, inelastic, and unit elastic demand?
elastic: consumers are senstive to price changes; elasticity > 1
inelastic: consumers are less sensitive to price changes; elasticity < 1
unit elastic:consumers are proportionately responsive to price changes; elasticity = 1
DEF: Perfectly Inelastic Demand
Quantity demanded does not change regardless of the price.
VERTICAL demand curve
Elasticity = 0
DEF: Perfectly Elastic Demand
Any price increase eliminates demand entirely
HORIZONTAL demand curve
Elasticity = infinity
How does total revenue react to inelasticity, elasticity, and unit elasticity?
Inelastic: Total revenue increases with price rise.
Elastic: total revenue decreases with price rise.
Unit Elastic: total revenue remainds unchanged with price changes.
DEF: Price Effect
Higher price increases revenue per unit
DEF: Quantity Effect
Higher price reduces quantity sold
What are determinants of price elasticity?
Availability of Substitutes: more substitutes = higher elasticity
Neccessity vs. Luxury: Neccessities = lower elasticity
Share of income: higher share = greater sensitivity
DEF: Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand
Measures how demand for one good changes with the price of another.
FORMULA: Cross-Price Elasticity
% Change in Quantity Demanded of Good A / % Change in Price of Good B
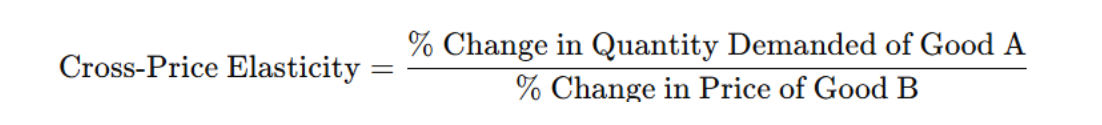
Signs for cross-price elasticity
positive: substitutes
negative: complements
DEF: Income Elasticity of Demand
Measures responsiveness of demand to income changes
FORMULA: Income Elasticity of Demand
% Change in Quantity Demanded / % Change in Income
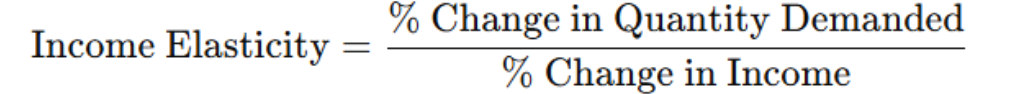
signs for income elasticity of demand
positive: normal goods
negative: inferior goods
DEF: Price Elasticity of Supply
Measures how supply responds to price changes
FORMULA: price elasticity of supply
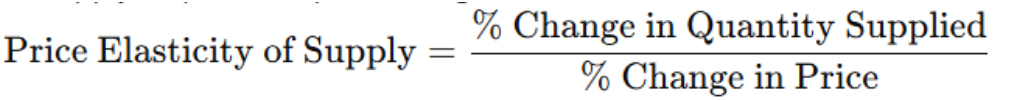
What does it mean to be perfectly inelastic in supply?
elasticity = 0 when it is perfectly inelastic.
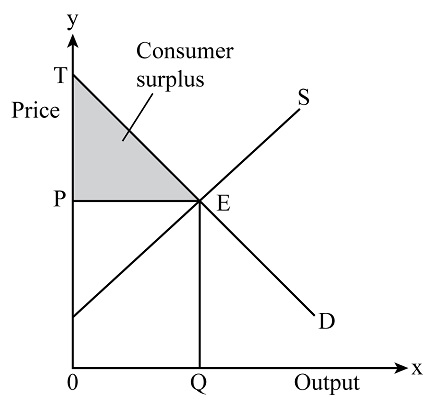
DEF: Consumer Surplus
the net benefit to buyers from purchasing goods at a lower price than their willingness to pay
GRAPHICALLY where is the consumer surplus?
find the area of the triangle to calculate surplus
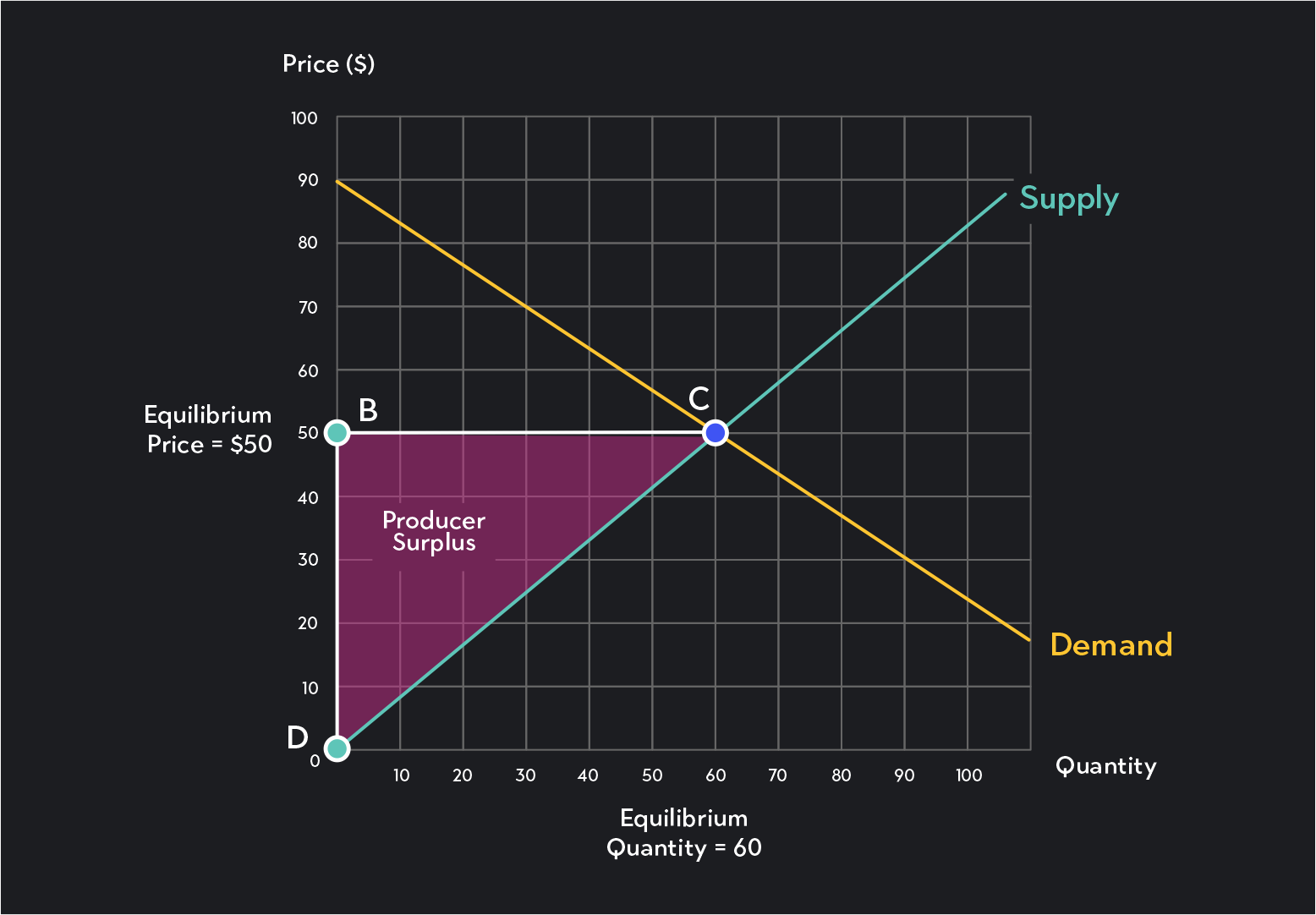
DEF: Producer Surplus
the net benefit to sellers from selling goods at a price higher than their minimum acceptable price
GRAPHICALLY where is the producer surplus?
find the area of the triangle to calculate surplus
DEF: Willingness to Pay
Maximum price a buyer is willing to pay for a good
How do you find total consumer surplus?
the sum of indivdiual surpluses of each consumer is the TOTAL consumer surplus
impact of price increase/decrease on consumer surplus
price drops → increase consumer surplus
price rises → decrease consumer surplus
what determines market effeciency?
when total surplus (consumer + producer surplus) is maximized
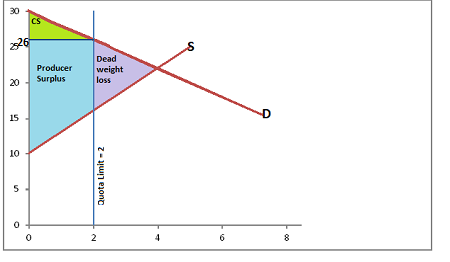
deadweight loss (DWL)
losss of total surplus due to market ineffeciences like TAXES or QUANTITY RESTRICTIONS
MARKET SCENERIOS: What effect does reallocation of goods have on surplus?
shifting goods between consumers or producers reduces surplus.
MARKET SCENERIOS: What effect does change in quantity have?
Deviating from equilbrium quantity results in deadweight loss (DWL).
MARKET SCENERIOS: What effect does excise tax have on the market?
excise taxes create price wedges, reducing quantity trades.
this tax also leads to missed mutually beneficial transcations.
DEF: Tax Incidence
A tax incidence describes a case when buyers and sellers divide a tax burden.
Tax burden depends on price elasticity of supply and demand, not on who officially pays the tax.
DEF: Utility
A measure of satisfaction from consuming goods and services
Expressed in “utils”
DEF: Marginal Utility
Additional satisfaction from consuming one more unit of a good
DEF: Diminishing Marginal Utility
Marginal utility decreases as consumption increases
What is optimal consumption bundle?
the combination of goods that maximizes utility within a budget constraint.