Plant Science Exam 4: Bioactive Plant Properties
1/228
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 16, 19, 20, and 21
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
229 Terms
Chapter 16
Stimulating Beverages
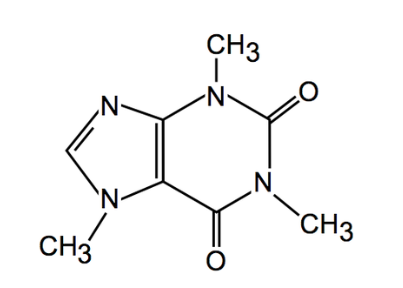
What is this structure?
Caffeine
What are the effects of Caffeine on the body?
alkaloid that stimulates the CNS
increases HR, BP, and respiration
vasoconstrictor (makes blood vessels smaller)
What are 2 common medications Caffeine is added to?
Aspirin and Acetaminophen
Is Caffeine addictive?
Yes. It can create nervousness and irritability and other withdrawal symptoms without it.
What are the effects of high levels of Caffeine in a pregnant woman?
May lower fetal growth of the child. Mothers have to limit the amounts that they consume
What are the health benefits of caffeine in some studies?
Decrease Type 2 Diabetes, Parkinson’s and some cancers
Caffeine is produced only by plants, yet is has profound effects on the CNS of animals.
Why would plants, which do not possess a nervous system, have evolved neurologically active compounds?
As a defense mechanism, caffeine helps reduce herbivores consuming the plant. It deters pests and animals by making the plant taste unpleasant or causing negative effects, so they avoid eating it.
What plant is coffee primarily from? Where is it native to?
Caffea arabica plant
Native to Ethiopia but spread through Europe and eventually the Americas
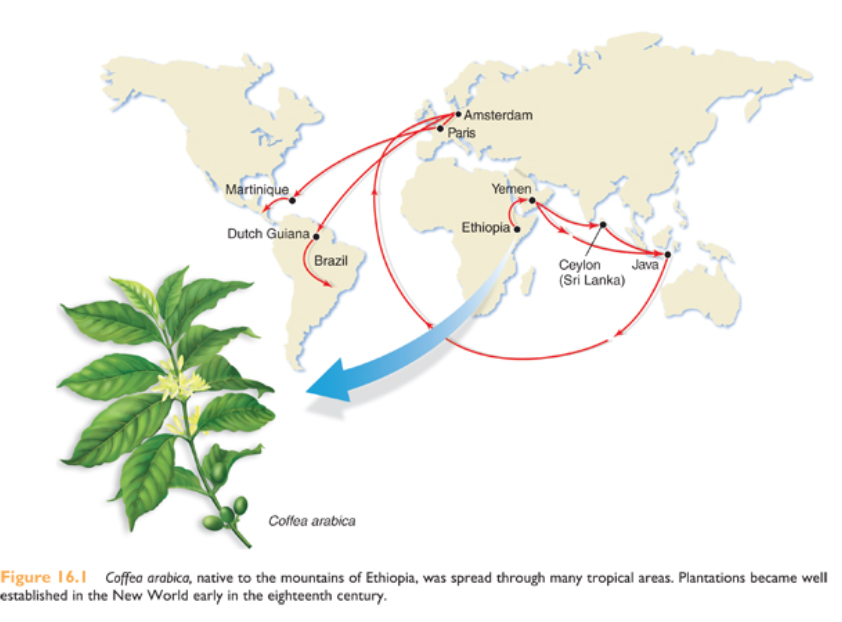
Who is the leading producer of the coffee plant now
Brazil
Irony - not where it originated from
How is coffee cultivated?
from an evergreen shrub
berries of it are harvested
beans are roasted (roasting affects the flavor)
Traditionally coffee plants are grown in the shade but sun-trees have higher yield.
What is the ecological concern?
Deforestation and loss of biodiversity.
Sun-grown trees have to replace other trees in the tropical rain forest. There is a push to do shade-grown trees to maintain the tropical rain forest diversity
What is the world’s most consumed beverage after water?
Tea
What plant does tea usually come from? Where is it native to?
Camellia sinensis
Native to Southeast Asia
Which 2 countries have ancient ancestry with the tea plant?
India and China
How are tea leaves cultivated?
Small tree/shrub pruned for hand harvest by plucking the leaves
Leaves are fermented which results in the differences in type/taste
Describe Green tea fermentation
Describe Oolong tea fermentation
oolong = partial fermentation
Describe Black tea fermentation
black = full fermentation
Describe White tea fermentation
white = no fermentation or steaming (have dense trichomes)
Describe Herbal tea
herbal = not from the tea plant (Camellia sinensis) , usually from other plant species like rose hips, limes, lemons, oranges, etc.
what is theophylline
bronchial muscle relaxer
roasted, fermented seeds of Theobroma cacao tree
native to the neotropics (South America)
where did the specific name of chocolate come from?
named by Linnaeus
Theobroma came from "food of the gods"
what did the Aztecs used cacao seeds as?
what is Chocolatl made from?
roasted and ground cacao beans with chili peppers and other species
2% theobromine
caffeine
phenethylamine
anandamide
What class of secondary plant compounds does chocolate contain?
Alkaloids: carbon ring with nitrogen
Affects with the neurological system of animals so it’s a way for plant to discourage animals to eat them
describe theobromine
acts as a diuretic and heart stimulant
found in tea leaves and kola tree
can get poisoning from really high levels of it
describe phenethylamine
dopamine releasing-agent that is linked to serotonin-levels in the brain
rapidly metabolized when taken orally
describe anandamide
means bliss and delight
affects cannabinoid neurotransmitter that activates some of the same receptors as THC
what are some possible health benefits of dark chocolate
flavonoids have antioxidant properties
improve insulin sensitivity
reduce blood pressure
more processed chocolate = more flavonoids lost
how is chocolate processed
(seeds) beans are roasted, cracked open to release the cotyledons called nibs
nibs are crushed to produce a chocolate liquor called baking chocolate
cocoa butter is used for soaps and cosmetics
what is the high price of chocolate
half of cocoa worldwide is grown in West Africa that is harvested by 12-16 year olds
40% of chocolate eaten is produced by child slaves
describe how Coca-Cola is made
from seeds of Western African cola tree
contains alkaloids caffeine and kolanin which are both cardiac stimulants
added with coca leaf extracts but the cocaine is removed
Chapter 19
Medicinal Plants
what are some ancient uses of plants as medicine
Neanderthal buried with a medicinal plant 60K years ago
4K years old Sumerian tablet had medicinal plants
ancient Chinese, Indian, Aztecs
snakeroot was as a what in the past…
what is used as now…
past = sedative
now = used for BP and schizophrenia
what did Hippocrates believe that disease came from
natural means rather than supernatural
the gods were not punishing them and plants could be used as treatments
what plant in the Middle East was used as a contraceptive and was collected into extinction
giant fennel, mainly by woman
describe the medicinal practices during the Renaissance
age of herbals
used the Doctrines of Signatures: signature or feature of plant parts corresponded to the human part (no scientific basis) — appearance doesn’t mean correlation
what were bloodwort, liverwort, and snakeroot used for according to the doctrine of signatures
bloodwort = blood red sap so used for blood diseases
liverwort = used for liver disease because it has the shape of a liver
snakeroot = used for snake bites
What is morphine come from?
Opium Poppy
Where does salucylic acid come from?
Willow
what percent of US pharmaceuticals have plant-derived active ingredients? what about if you include fungi?
25%
including fungi, 50%
herbal medicine is an established practice in what other countries
China, India, and some other countries
pharmacists provide plants instead of pills
who wrote a book about the uses of plants by Indians of the Missouri River Region
Melvin Gilmore (1919)
Describe the use of Echinacea plant
plant that was used by Native Americans as the antidote for bites and stings, cure of infectious diseases, toothaches and smoked as a remedy for headaches
list and explain common active compounds in medicinal plants
alkaloids: 3000 identified, dominant in bean, nightshade (tomatoes, tobacco), and coffee family
glycosides: effect heart contraction
saponins: progesterone precursor and cortisone
describe what Foxglove is and what it is used for
digitalis glycosides in it that slow heartbeat with increased blood pumped (stronger contraction)
English remedy for dropsy (fluid accumulation from congestive heart failure)
contains digoxin
what compound comes from the inner bark of a Salix (willow) tree
salicilin (glycoside of salicylic acid)
describe acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin)
anti-inflammatory and analgesic
reduces risk of a second heart attack
first organic compound that was able to be synthesized
easier on stomachs than salicilin is
list and explain the compound that come from the fever bark tree
quinine (alkaloid): first effective treatment for malaria, used with water to make gin and tonics by British colonists
Synthetic is chloroquinine
describe what reserpine is used for
isolated from the root of snakeroot
one of the first tranquilizers for schizophrenia
also a treatment for hypertension
describe what the Aloe plant is used for
used for skin conditions
has soothing properties that may promote dermal cell growth and inhibit bacterial infections
found in many lotions, sunscreens, and bath oils
what compound is from Ephedra
ephedrine
describe what ephedrine is used for
decongestant and CNS stimulant similar to adrenaline
weight control supplements
energy boosters
abuse of products containing Ephedra extracts led to increased concerns about unregulated marketing of herbal remedies. should increased regulation occur
cons- lots of work and money, would cause inflation with the prices for them and people would turn to cheaper and possibly unsafe options
pro- more purity in the herbal supplements, we would know the ingredients, and have more studies and knowledge to decrease deaths from adverse effects of them
what compounds are in madagascar periwinkle
vinblastine
vincristine
what are vinblastine and vincristine used for
treat various leukemias and lymphomas
chemo drug that blocks spindle formation in cells
which compound is in Pacific Yew
chemotherapy drug taxol
isolated from the inner bark of the tree
what are the current herbal medicine regulations
considered a dietary supplement by the FDA
testing and clinical trials are not needed for it like for over-the-counter drugs
what is St. John's wort primarily for treating
treating depression and said to raise serotonin levels
Leading treatment for mild to moderate depression in Germany
what is Gingko primarily used for
improvement of dementia symptoms by increased blood flow
anticoagulant (prevents blood cloats)
increased bleeding risk with high consumption
what comes from the leaves of Mitragyna speciosa tree? where is it native?
Kratom
native to southeast Asia
what is Kratom used for
fight fatigue
is a stimulant
interacts with the opioid receptors in the brain causing reduction of pain and fighting opioid wthdrawal
what advice would you give someone who is choosing to self-medicate using herbs
start with small doses to see how it react with your body
make sure that you look into what it reacts with before you start taking it
how can the educated consumer be assured of the efficacy of herbal preparations
stay with more standard and well-known companies like Walgreens
do not get from a sketchy person or company online
Chapter 20
Psychoactive Plants
what are the most widely used psychoactive substances used in the US
caffeine
alcohol
nicotine
psychoactive drug effects are dependent on what (4 factors)
pharmacology of the drug
biology of the individual
psychology of the individual
cultural setting
What does the Central Nervous System (CNS) do and how do neurons work within it?
CNS = brain + spinal cord; made of neurons that send signals using neurotransmitters (NTs)
Some excite or inhibit brain activity → changes in mood, behavior, perception, and thinking
how do psychoactive drugs usually have an effect on the human body
mimicking, amplifying, or blocking the effects of neurotransmitters
what are the three subcategories of psychoactive drugs
stimulants
depressants
hallucinogens
narcotic
any dangerously addictive psychoactive compound
technically a depressant
most narcotics are usually
alkaloids
(THC is an exception because it is a phenolic)
which neurotransmitter is responsible for pleasure
dopamine, primary component of reward circuit
What do psychoactive drugs do to dopamine levels in the brain?
They raise dopamine levels
In a part of the brain called the nucleus accumbens
This makes you feel good or rewarded
how does cocaine act in the human brain
blocks return of dopamine back to the Ventral Tegmental Area which increase dopamine levels = higher pleasure feeling