2.2 Phishing
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
6 Terms
Phishing
A type of social engineering that uses various communication methods, like email or text, to trick individuals into believing something is legitimate when it’s not. It often involves spoofing and aims to steal private information, such as usernames, passwords, or personal details.
Always check the URL to ensure the link directs to a trusted site.
Often have subtle flaws, such as incorrect spelling, unusual fonts, or poor graphics, that can give them away.
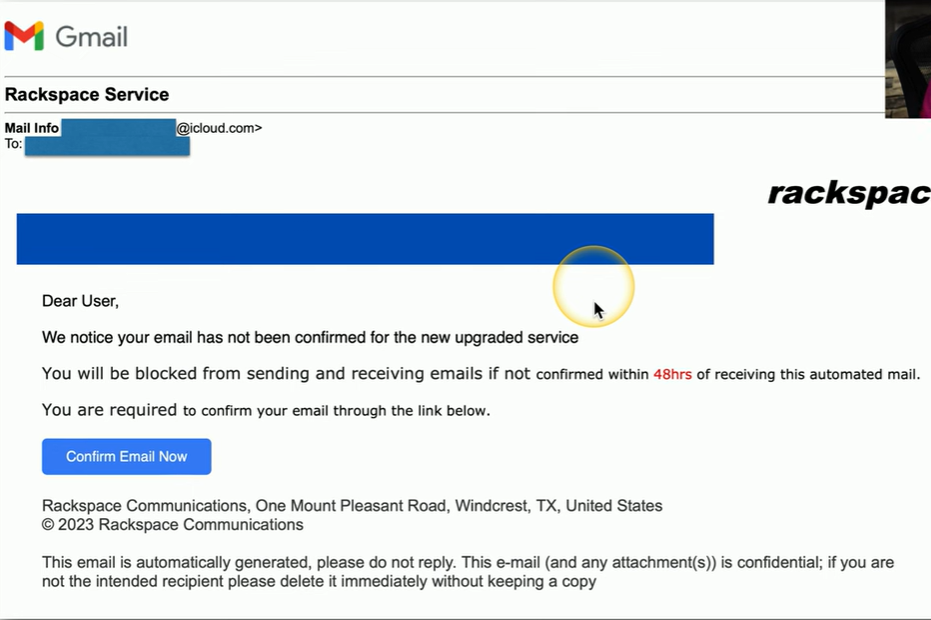
Phishing Example
A message with a deadline urging you to click a "Confirm Email Now" link.
Appears to be from an iCloud.com address, which is associated with Apple, the message is actually intended for someone using a Rackspace email service.
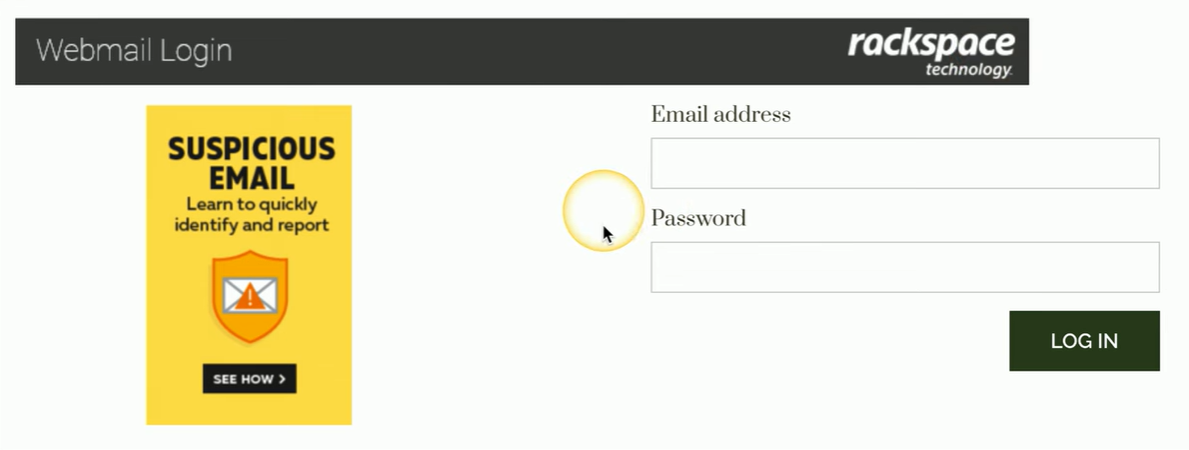
Upon clicking the link, you're directed to a login page that resembles the Rackspace site, but closer inspection reveals subtle differences
Business Email Compromise (BEC)
The scammer uses email to trick someone into sending money or divulging confidential company info. The culprit poses as a trusted figure, then asks for a fake bill to be paid or for sensitive data they can use in another scam.
Attackers may spoof an official email address or use one that's very similar to the real domain.
For instance, an email might appear to come from "Professor@professormessor.com," but a closer look reveals a subtle misspelling in the domain. (professormesser.com)
Malicious attachments are often included to infect the recipient’s system.
Attacker gains access to your email
Can send phishing messages or search for sensitive information like financial data or login credentials.
May even use password reset features to take control of accounts.
Malicious attachments are often included to infect the recipient’s system.
Tricks & Misdirection
Make cyberattacks successful by using digital sleight of hand to deceive users
One common tactic is typosquatting, where attackers register domain names that are slight misspellings of popular websites or brands. This tricks users who mistype URLs into visiting malicious sites.
Another method is pretexting, where attackers create false scenarios and impersonate trustworthy entities. For example, they might call claiming to be from Visa, asking for personal information under the guise of handling an automated payment.
Phishing With Different Bait
Phishing can take various forms, each with different bait.
Vishing, or voice phishing, occurs when attackers spoof a caller ID to impersonate a trusted entity, like a bank, to steal personal account information.
Smishing, or SMS phishing, involves similar tactics but through text messages, often with spoofed numbers, and may ask for personal details or contain malicious links.