Phyla Molluska & Echinodermata
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Invertebrate Zoology
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Mollusks are ______ and protected by _____
soft bodied; calcareous shell
3 body regions of mollusks
Head
Visceral hump (mantle)
Muscular foot
What secretes the shell?
the mantle
All organs are found in the ______.
visceral hump (mantle)
Mollusks have radula which are
a ribbon of small teeth used for feeding
Reproduction in mollusks
Mono/Dioecious
Many mollusks have larval stages like _____ and ______
trochophore and veliger
What kind of development do mollusks have?
protostomic development (mouth forms first in embryo)
What are the four main classes of mollusks?
Polyplacophora, Gastropoda, Bivalvia, Cephalopoda
What are the key shell and body features of chitons (Class Polyplacophora)?
8 dorsal plates, strong foot, reduced head
Class Polyplacophora
All marine.
Radula used for scraping algae.
Lives mostly in the intertidal zone.
What is the defining shell feature of chitons (Class Polyplacophora)?
8 dorsal plates
Where do chitons live and what do they eat?
marine intertidal zone and graze on algae
Class Gastropoda
Marine, freshwater, land.
Mostly benthic.
Undergo torsion.
Close shell with operculum.
From Class Gastropoda - Cone snail (Conus) has a _________.
radula with deadly toxins which can kill by respiratory paralysis
What major developmental feature defines gastropods?
Torsion - twisting of the visceral mass, shell, and mantle
What is the function of the operculum in many snails?
Acts as a trap door that closes the shell for protection.
For gastropods, what larval type is specific to marine species?
veliger
Bivalves = ______
filter feeders
Cephalopods = _______
predators/carnivores
Odontophore
cartilage structure that supports the radula
Osphradium
sensory organ that checks water for silt + food particles
What are nudibranchs (sea slugs)?
Shell-less, brightly colored gastropods
What are pteropods (“sea butterflies”)?
Pelagic gastropods that swim using wing-like extensions of their foot.
What type of mollusk are sea slugs (nudibranchs)?
shell-less; brightly colored gastropods
What adaptations do nudibranchs have for defense?
Chemical defenses or store stinging cells
Tegula (Black Turban Snail)
Conical, rounded shell.
Dark charcoal to black; top (apex) eroded to gold/white.
Nucella (Whelks)
Heavy, coiled spiral shell.
Color varies.
Eats barnacles.
Littorina (Periwinkles)
Broad/conical shells.
Live in intertidal zones.
Algal grazers.
Haliotis (Abalone)
Low, open spiral shell.
Row of respiratory pores along the shell edge.
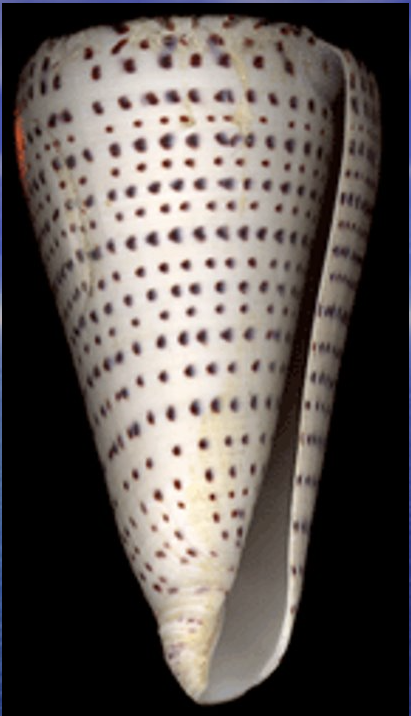
Cone snail
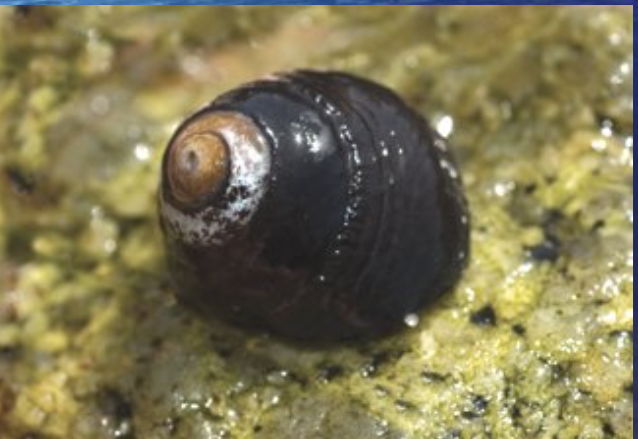

Black Turban Snail

Sea slug (nudibranch)
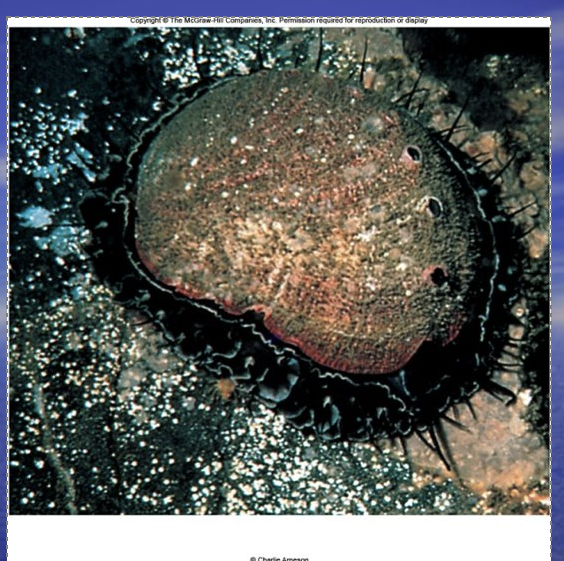
Red Abalone (has row of respiratory pores)
Three layers of bivalve shell:
Periostracum (outer)
Prismatic (middle)
Nacreous (inner)
What major anatomical structures do bivalves lack?
Head and radula. They filter feed with gills.
How do clams, scallops, oysters, and mussels differ in locomotion/attachment?
Clams - dig with hatchet foot
Scallops - swim by clapping valves
Oysters - permanently attached by one valve
Mussels - attach with byssal threads
How do bivalves feed and breathe?
Large gills (filtration/gas exchange) and siphons (water flow)
Marine Bivalve Life Cycle
egg hatches into trochophore, grows into veliger, attaches to substrate on sea floor, becomes adult
How do freshwater bivalve larvae (glochidia) develop?
develops inside female, attach to fish gills/fins as parasites, let go and fall down, become juveniles then adults
How are pearls formed?
When an irritant gets trapped between shell and mantle, causing layers of nacre to be deposited
What major anatomical modification defines cephalopods?
The foot is modified into 8-10 arms and tentacles surrounding the mouth.
What are the two major cephalopod groups and examples of each?
Nautiloids: Nautilus (shell)
Coleoids: Octopus, squid, cuttlefish (no shell)
What structure do male cephalopods use for reproduction?
hectocotylus
What unique shell feature does the Nautilus have, and what is it used for?
A coiled, chambered shell filled with gas to control buoyancy
What is the daily behavior pattern of the Nautilus?
Surface at night, stay benthic during the day in cooler water
For Nautilus: Suckers absent but __________
tentacles are coated with sticky matter to which crabs, shrimps, etc. get stuck
Loligo (Market Squid)
10 appendages.
Seasonally abundant near shore; lay large communal egg masses on sand
Octopus
8 arms.
Body is red-brown, but can change color.
Nocturnal (active at night and hides during the day).
What type of symmetry do echinoderms (starfish) have, and what major structures do they lack?
Radial symmetry; lack head and brain
What is the water vascular system (WVS) used for in echinoderms?
Locomotion, feeding, respiration, and attachment
What type of skeleton do echinoderms have?
Endoskeleton of CaCO3 ossicles
Water Vascular System (WVS)
made of tubes and canals through which seawater circulates
Flow of water in WVS
Madreporite
Stone canal
Ring canal
Radial canal
Tube feet
Seas stars have a ______ at the center of the body and are surrounded by ______.
central disc; 5 arms
What contributes to the spiny skin of sea stars?
CaCO3 plates
What is Sea Star feeding like?
Carnivores; normally consume shellfish and coral
What are the larval stages of sea stars?
Bipinnaria (1st stage)
Brachiolaria (2nd stage)
What feeding strategy do some brittle stars use?
Filter feeding by raising arms and using mucus strands to catch particles.
Do brittle stars use tube feet for movement?
No, their tube feet lack suckers so they instead use them for feeding
Why are brittle stars called “brittle”?
They intentionally break off arms to distract predators and escape; arms regenerate
What unique defensive feature do some brittle stars have?
Bioluminescence
What are the two main groups within Class Echinoidea?
Regular echinoids (sea urchins) and irregular echinoids (sand dollars, heart urchins)
What is the “test” of a sea urchin?
A hard skeleton made of fused ossicles, covered with movable spines.
What structure is used by sea urchins for chewing, and how many teeth does it have?
Aristotle’s lantern, with five teeth
Which echinoid species is dangerous due to long spines that can puncture human skin?
Diadema
Two forms in Class Crinoidea
Sea lilies (attached)
Feather stars (mobile)
How do crinoids obtain food?
They are suspension feeders, using many branched arms to trap particles
What features do sea cucumbers not have that other echinoderms do?
No arms, no spine, and the madreporite is internal
What is evisceration?
A defense where sea cucumbers remove internal organs or sticky tubules to deter predators
What is the body symmetry of sea cucumbers?
Bilateral symmetry
What are the oral tentacles of sea cucumbers derived from?
They are modified tube feet
How do pearlfish interact with sea cucumbers?
They live inside their respiratory trees, entering through the anus (commensal)
Why is there little fossil evidence of early protochordates?
They were soft-bodied, so they did not fossilize well.
Why are early developmental stages (cleavage, blastula, gastrula) important for studying chordate evolution?
These stages are highly conserved, revealing ancestry
What major group do chordates share a common origin with?
Deuterostomes
5 major vertebrate groups of Phylum Chordata
fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and mammals
4 special features of Phylum Chordata
Notochord
Dorsal tubular nerve cord
Pharyngeal gill slits
Post-anal tail
Invert chordates have 3 classes:
Ascidicia (sea squirt), Thaliacea(salps), and Larvacea
Where are sea squirts commonly grown?
on boats, docks, reefs, or other hard substrate
Feeding system of sea squirts
Water enters through incurrent siphon, goes to pharynx, exits through excurrent siphon
Pharynx of sea squirts has many ________ for __________.
pharyngeal slits; filtering plankton
Which chordate features are present in the larval tunicate (sea squirt)?
Notochord, dorsal nerve cord, post anal tail
Reproduction of sea squirts
Monoecious, cross fertilize, zygote hatches as tadpole larva
What material is a tunicate’s outer covering made of?
A tunic made of cellulose
Class Thaliacea (salps)
Free-living/planktonic.
Tunic is transparent and thin.
In/excurrent siphons present.
Pharyngeal gill slits present.
Class Larvacea
Tiny/planktonic
Paedomorphic.
Adult lives in transparent filter house.
Paedomorphic
when sexually mature individuals retain the larval body form