1.2 How Markets Work
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are the underlying assumptions of rational economic decision making?
Underlying assumptions of rational economic decision making=
consumers aim to maximise utility(economic welfare)
firms aim to maximise profits
governments aim to maximise social welfare
How do consumers aim to maximise utility (economic welfare)?
Consumers aim to maximise utility (economic welfare)=
rational consumer (Homo Economicus) who makes decisions by calculating the utility gained from each decision and chooses the one that will give them the most satisfaction
How do firms aim to maximise profit?
Firms aim to maximise profit=
Neo-classical theory assumes that the owners of firms want to maximise their reward from ownership and so aim to maximise profit to keep shareholders happy
How do goverments aim to maximise social welfare?
Governments aim to maximise social welfare=
as goverments are voted in by the public and work for the public, so should maximise their satisfaction by taking decisions which increases social welfare
What is demand?
Demand= quantity of a good/service that consumers are willing and able to buy at a given time in a given time period
What is the law of demand?
Law of demand= there is an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded
as prices increases, quantity demanded decreases
as prices decreases. quantity demanded increases
What is the diagram for the demand curve- when there is a change in price?
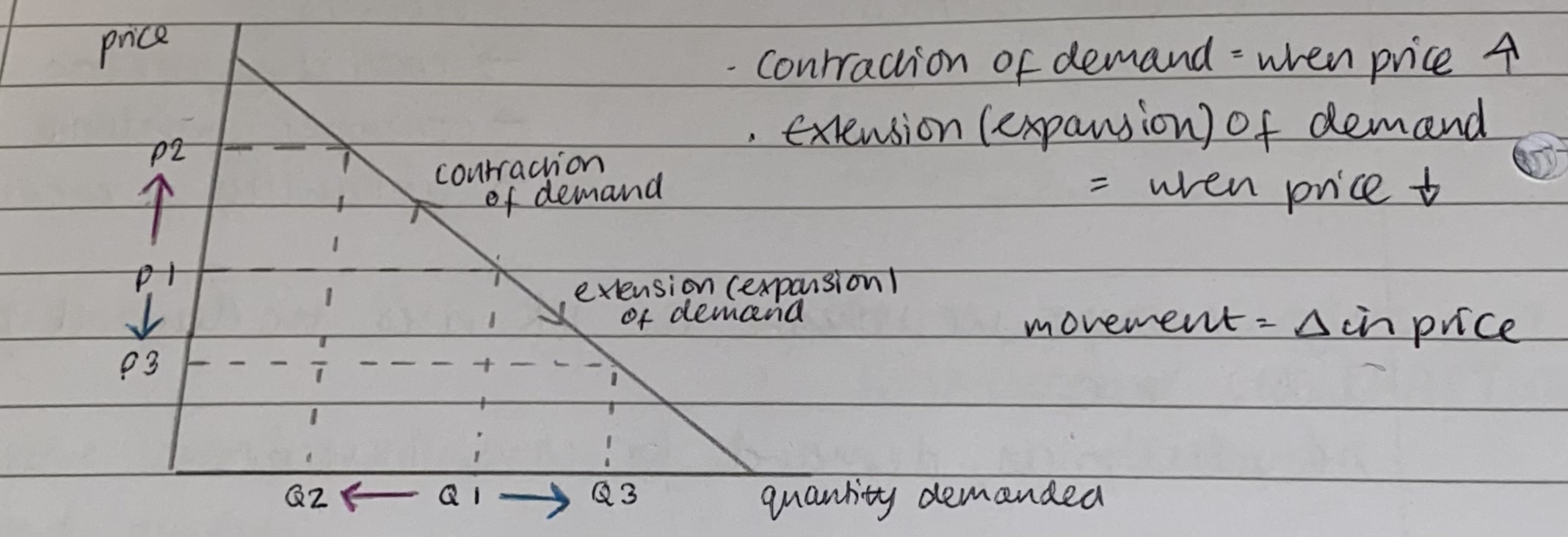
When does contraction of demand happen on the demand curve?
Contraction of demand happens when the price increases
When does extension (expansion) of demand happen on the demand curve?
Extension(expansion) of demand happens when price decreases
Why does the demand curve slope downward?
Demand curve slope downward=
income effect
substitution effect
(law of diminishing marginal utility)
What is the income effect, and how does that affect the demand curve?
Income effect=
as prices rise, purchasing power of income decreases
consumers are less able to buy the same quantity of goods & services
leads to a contraction in demand
What is the substitution effect, and how does that affect the demand curve?
Substitution effect=
as prices rices, other goods and services become relatively price- competitive
consumers switch their consumption towards these alternatives
leads to a contraction in demand for original good or service
What is the diagram for the demand curve, when non-price factor affects demand?
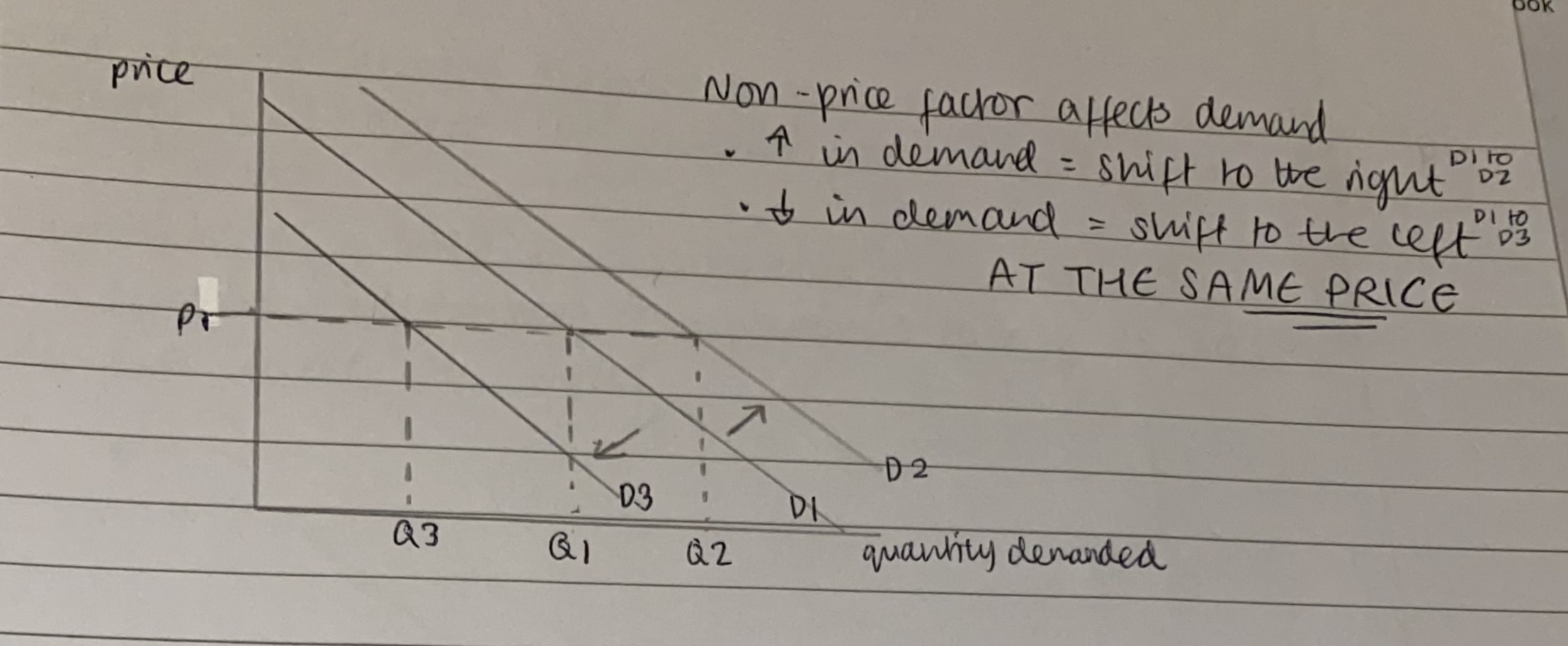
What happens as non- price factor affects demand?
Non- price factor affects demand=
increase in demand= shift to the right
decrease in demand= shift to the left
AT THE SAME PRICE
What are the non-price factors causing shifts in demand curve?
Non-price factors causing shifts in demand curve→
PACSIFIC
Population
Advertising
Substitute’s price
Income
Fashion/tastes
Interest rates
Complement’s price
How does Population (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Population (non-price factor) causes shifts in demand curve=
Increase in population, increase in demand (shift to right)
Decrease in population, decrease in demand (shift to left)
How does Advertising (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Advertising (non-price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
Effective advertising, increases willingness to buy, shift to right
Bad advertising decreases willingness to buy, shift to left
How does Substitute’s price (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Substitute’s price (non-price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
if price of substitute good increases, demand for original good increases (shift to right)
if price of substitute good decreases, demand for original good decreases (shift to left)
How does income (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Income (non- price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
For normal goods, as income increases, demand increases (shift to right)
For normal goods, as income decreases, demand decreases (shift to left)
For inferior goods, as income increases, demand decreases (shift to left)
For inferior goods, as income decreases, demand increases (shift to right)
What are examples of normal and inferior goods?
Examples of=
normal goods= luxury cars, designer clothing
inferior goods= fast food
How does Fashion/tastes (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Fashion/tastes (non-price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
if a good becomes more fashionable, demand increases (shift to right)
if a good becomes less fashionable, demand decreases (shift to left)
How does Interest rates (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Interest rates (non-price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
lower interest rates; borrowing cheaper; demand increases for goods bought with loans (shift to right)
higher interest rates; borrowing more expensive; demand decreases (shift to left)
How does Complement’s price (non-price factor) cause shift in demand curve?
Complement’s price (non-price factor) causes shift in demand curve=
price of complementary good increases, demand decreases for original good
What is the law of diminishing marginal utility?
Diminishing marginal utility= extra benefit gained from consumption of a good- declines as extra units are consumed
(marginal meaning the change in satisfaction)
How does the law of diminishing marginal utility influence the shape of the demand curve?
Law of diminishing marginal utility influence the shape of the demand curve=
Indicates why demand curve slopes downward as if more of a good is consumed, there is less satisfaction derived from the good; consumers are less willing to pay high prices at high quanitities since they are gaining less satisfaction
What is change in quantity demanded?
Change in quantity demanded= change in price → movement ALONG the curve
What is change in demand?
Change in demand= change in non-price factors → SHIFTS curve left or right
What is price(own) elasticity of demand (PED)?
Price elasticity of demand (PED)= responsiveness of quantity demanded given a change in price
What is the equation for price elasticity of demand?
Price elasticity of demand= % change in quantity demand/ % change in price
What is perfectly inelastic?
Perfectly inelastic= QD doesn’t change as price changes, PED=0
What is relatively inelastic?
Relatively inelastic= QD changes by smaller % than price, PED<1
What is unitary elastic?
Unitary elastic= QD changes by same % as price, PED=1
What is relatively elastic?
Relatively elastic= QD changes by larger % than price, PED>1
What is perfectly elastic?
Perfectly elastic= QD falls to 0 at any price increase, PED= infinity
What are the factors affecting PED?
Factors affecting PED=
(no. of) Substitutes
Percentage of income
Luxury/necessity
Addictive/ habit- forming
Time period
SPLAT
How does the number of substitutes affect PED?
(No. of) substitutes affects PED=
more substitutes= more price elastic demand
fewer substitues= more price inelastic demand
How does the percentage of income affect PED?
Percentage of income affects PED=
larger % of income= more price elastic demand
smaller % of income= more price inelastic demand
How does luxury/ necessity affect PED?
Luxury/necessity affects PED=
luxuries= more price elastic demand
necessities= more price inelastic demand
How does addictive/ habit-forming (goods) affect PED?
Addictive/habit-forming (goods) affects PED=
addictive goods= more price inelastic demand
habit-forming goods= more price inelastic demand
How does the time period affect PED?
Time period affect PED=
short-run= more price inelastic demand
long-run= more price elastic demand
What is elasticity?
Elasticity= how much the quantity demanded (QD) will be affected by a change in price/ income/ other factor