PHYL 141 Exam 3
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
CNS (Central Nervous System)
Consists of the brain and spinal cord, which primarily interpret incoming sensory information and issue instructions based on that information and on past experience
PNS (Peripheral Nervous System)
Consists of the cranial and spinal nerves, ganglia, and sensory receptors
Neuron (Nerve cells)
The basic functional units of nervous tissue. Highly specialized to transmit messages from one part of the body to another in the form of nerve impulses
Ganglia
In the PNS, clusters of neuron cell bodies
Neuroglia
Glial cells, of the CNS include astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglial cells, and ependymal cells. Found in the PNS is Shwann cells, also known as neurolemmocytes, and satellite cells.
Astrocytes
are the most abundant CNS neuroglia
Oligodendrocytes
Have processes that form myelin sheaths around CNS axons
Microglial cells
are defensive cells in the CNS
Ependymal cell
Line cerebrospinal fluid filled cavities
Schwann cells/ Satellite cells
Which form myelin, surround neurons in the PNS
Unipolar Neurons
One very short process, divides into peripheral and Central Processes
Pseudo unipolar neurons
derived from bipolar neurons
Bipolar neurons
two processes attached to the cell body, quite rare
Multipolar neurons
Processes from cell body that are classified as dendrites, carries impulses away from CNS (neurons un brain and spinal cord)
Afferent (Sensory) neurons
Neurons carrying impulses from sensory receptors in viscera to the CNS (towards the Brain)
Efferent (motor) neurons
Neurons carrying impulses from the CNS to the viscera and/or body muscles and glands (away from brain)
Sensory
Contains nerve fibers that conduct impulses from sensory receptors TOWARD CNS
Motor
Contains nerve fibers that conduct impulses AWAY FROM CNS
Interneurons
Which are situated between and contribute to pathways that connect sensory and motor neurons
Mixed nerves
Most nerves of the body, including all spinal nerves, are mixed nerves
Neural tube
The embryonic structure that ultimately forms the brain and spinal cord
Autonomic Reflex (Visceral)
Mediated through the Autonomic nervous system (ANS)
Somatic
Stimulate skeletal muscles by the somatic divisions
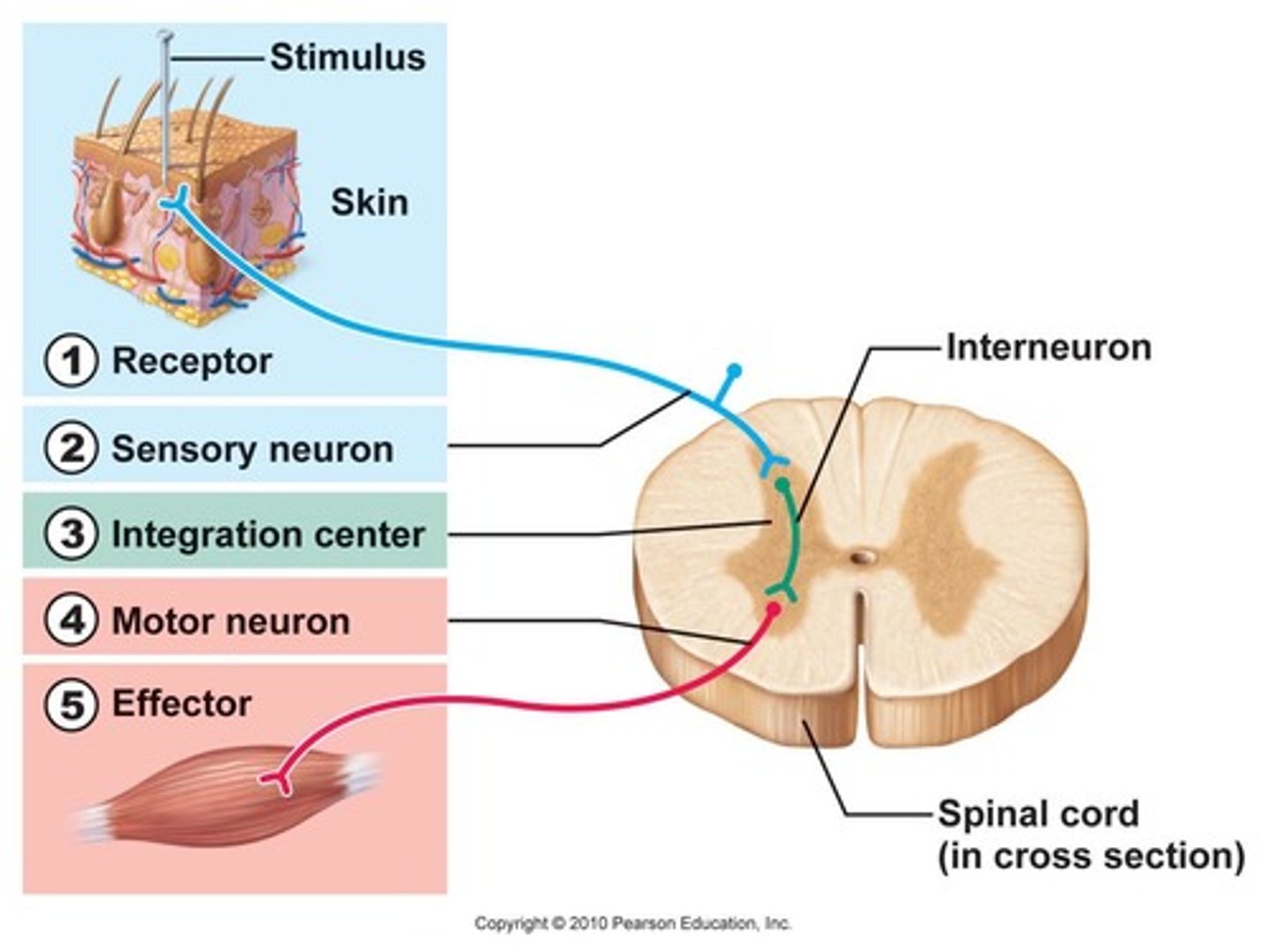
5 components of reflex arc
1. Receptor
2. Sensory Neuron
3. Integration Center
4. Motor Neuron
5. Effector
Stretch reflexes
Deep tendons
Reciprocal Inhibition
Causes them to relax and prevents them from resisting (or reversing) the contraction of the stretched muscle
Monosynaptic Reflex and Polysynaptic Reflex
The integration center is in the spinal cord, and in each example the receptor and effector are in the same limb. The patellar reflex, a two neuron monosynaptic reflex. A flexor reflex, an example of a polysynaptic reflex
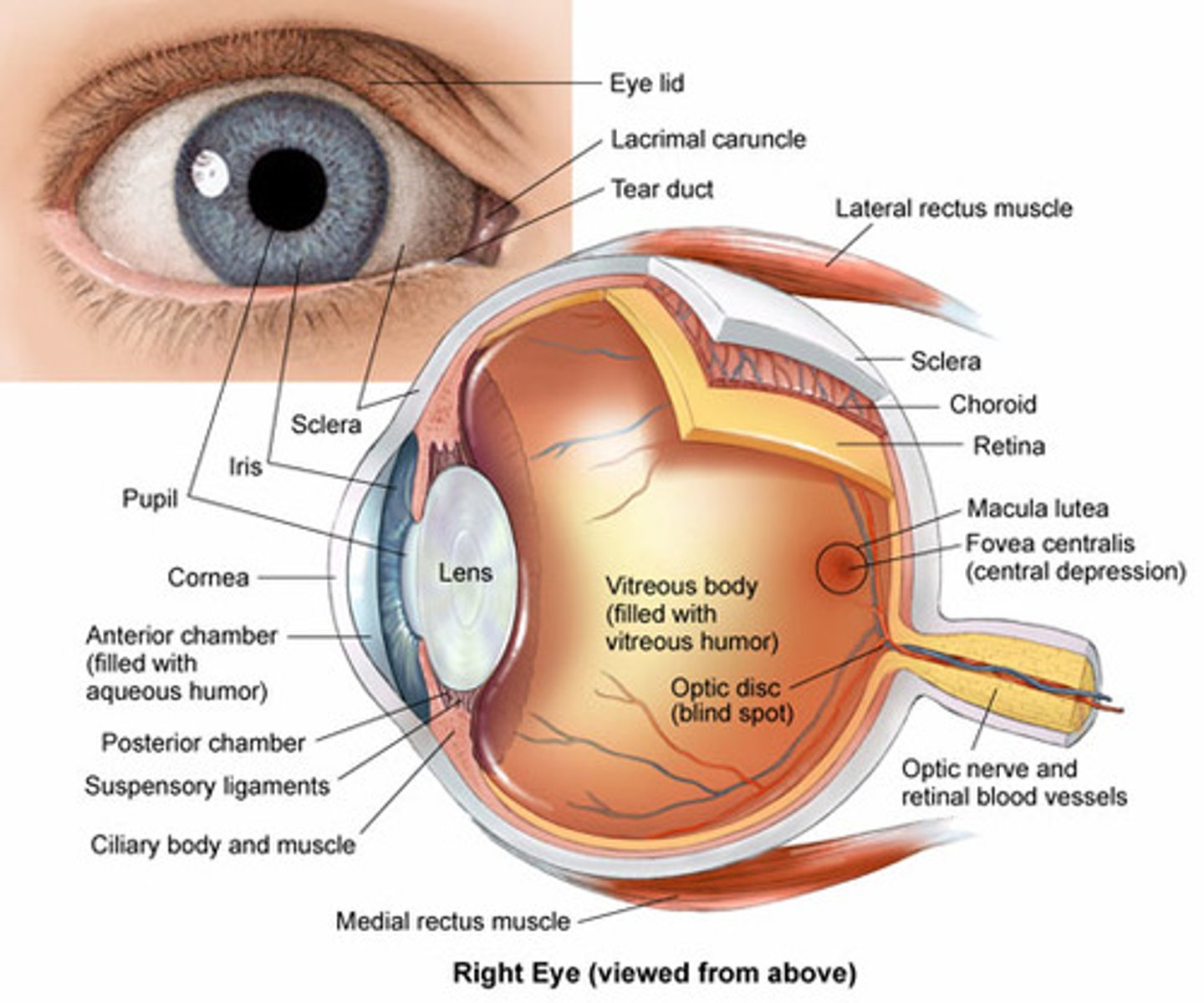
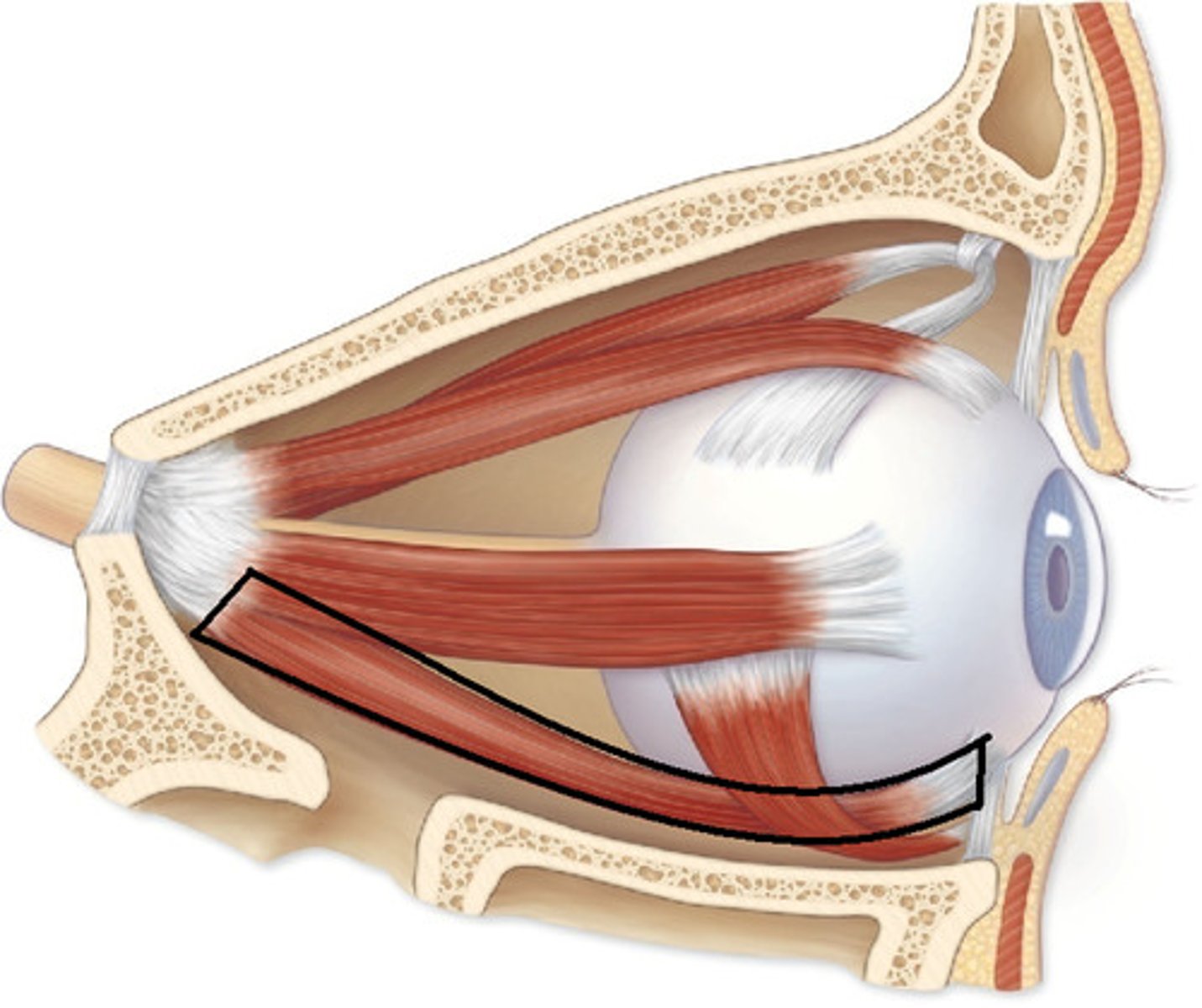
Extrinsic eye muscles
Lateral Rectus
Medial Rectus
Superior Rectus
Inferior Rectus
Inferior Oblique
Superior Oblique
Lateral Rectus
Moves eye laterally
Medial Rectus
Moves eye medially
Superior Rectus
Elevates eye and turns it medially
Inferior Rectus
Depresses eye and turns it laterally
Inferior Oblique
elevates eye and turns it laterally
Superior Oblique
Depresses eye and turns it laterally
Optic Disc (Blind spot)
Site where there are no photoreceptors at fundus
Rods
Specialized photoreceptors for dim light
Cones
Color photoreceptors that operate in high lighting for visual acuity
Optic nerve
Axons leave the retina in the tight bundle of fibers
Sensory Receptors
Respond to outside stimuli
Special Senses
Vision, hearing, Equilibrium, steel and taste
general Senses
React to touch, pressure, pain, heat, cold, stretch, vibration, and changes in body position and are distributed throughout the body
Exteroceptors
React to stimuli in the external environment (EX. cutaneous receptors in skin, receptors in eye)
Interoceptors (Visceroceptors)
Respond to stimuli arising in the body ( EX. Stretch receptors internal organs, chemoreceptors)
Proprioceptors
Respond to internal stimuli from skeletal muscles, joints, and ligaments/tissues covering bones and muscles (similar to interoceptors)
External and middle ear
Sense of hearing
Internal ear
Sense of balance/equilibrium
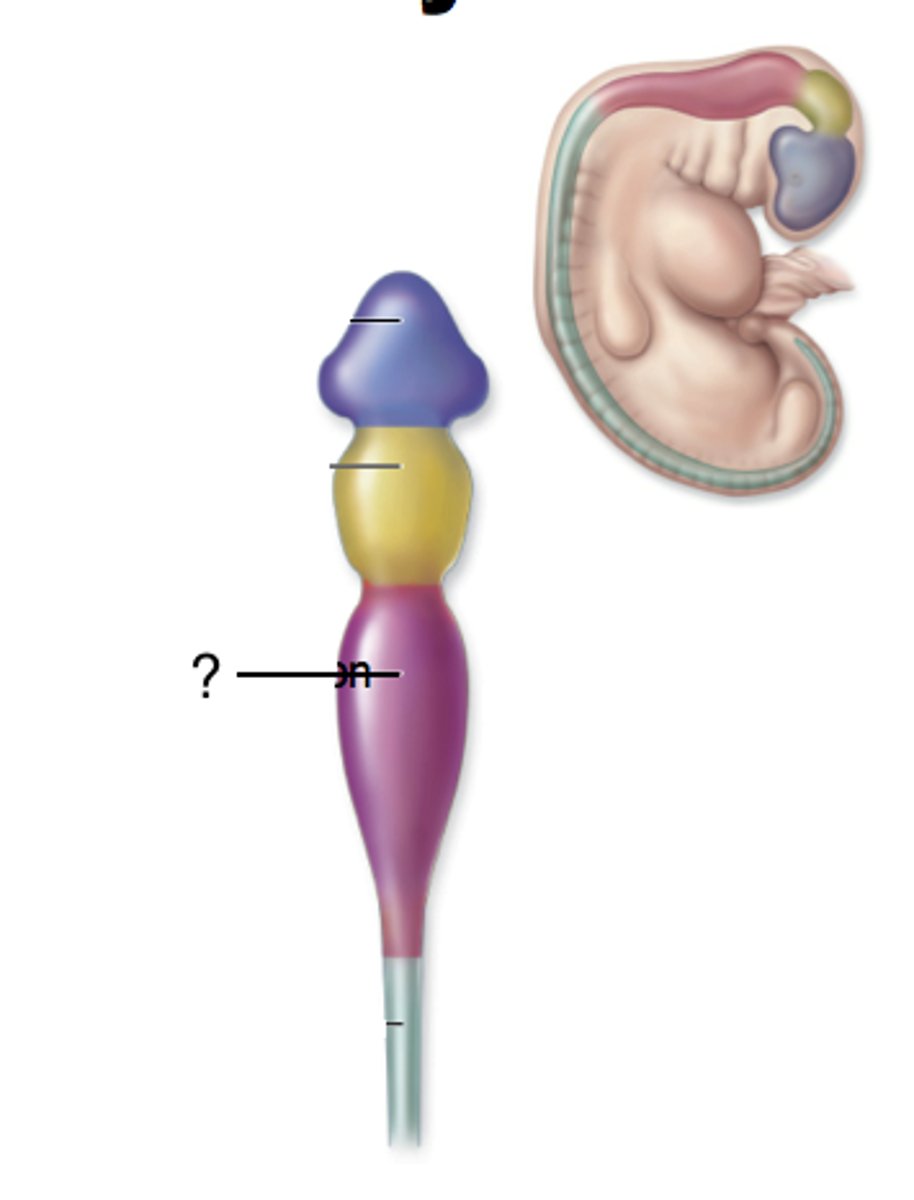
Mesencephalon
2
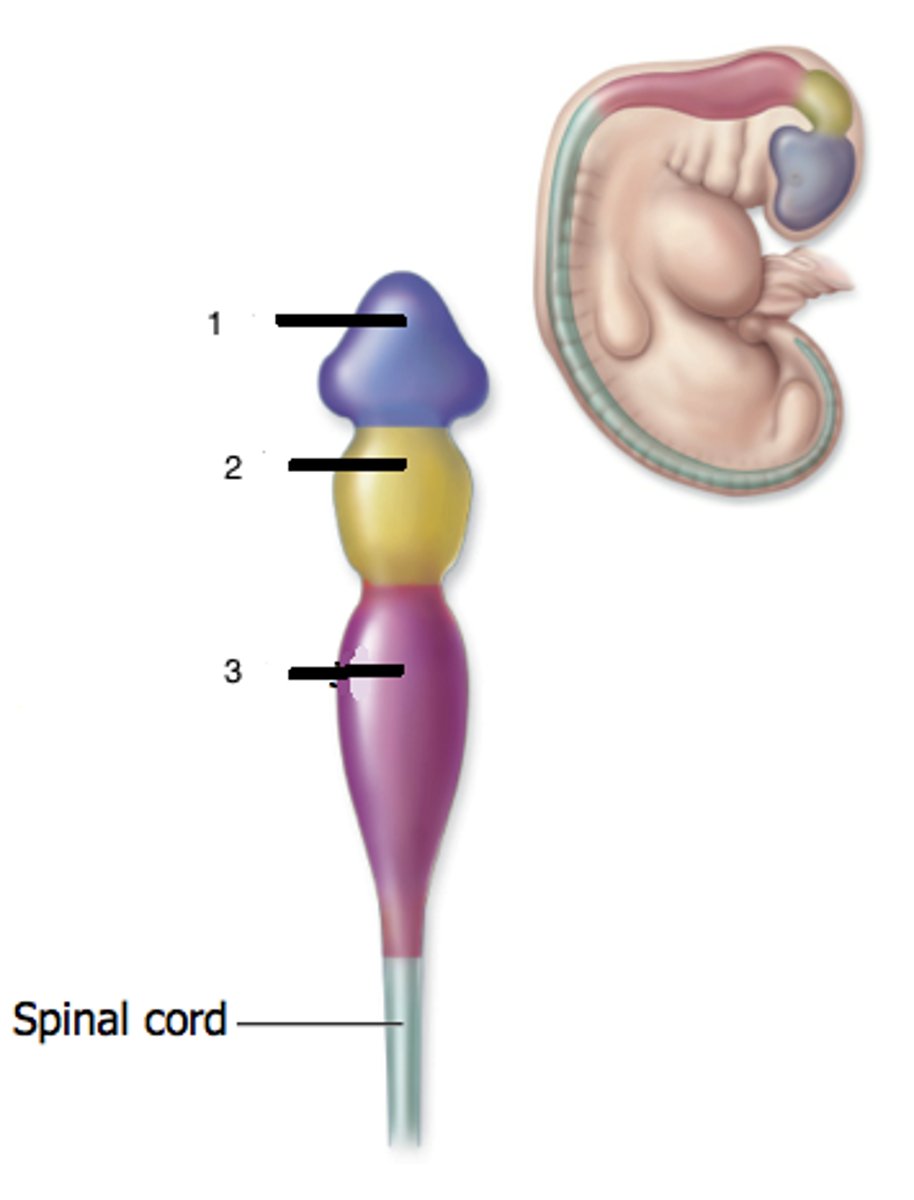
Rhombencephalon
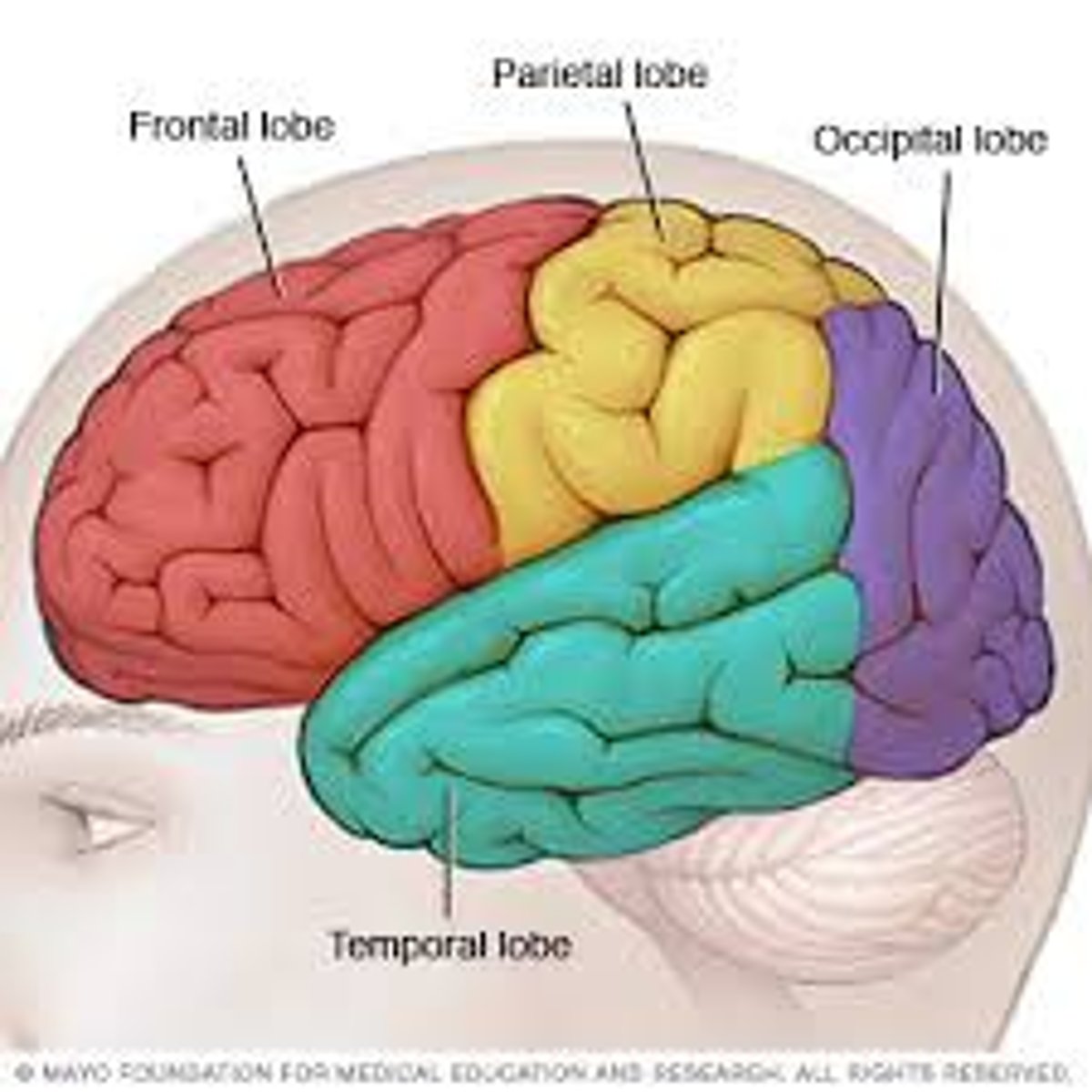
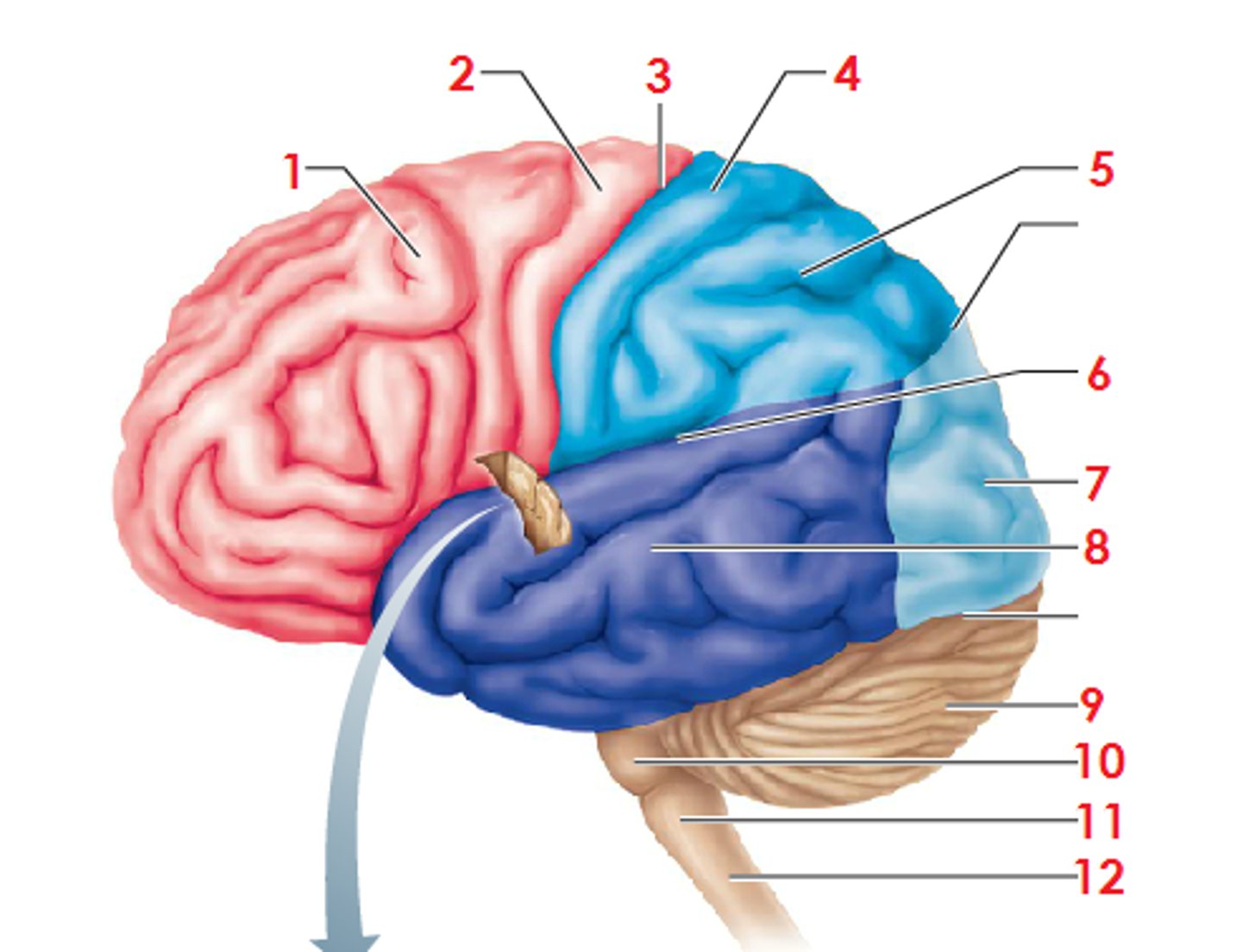
Frontal lobe
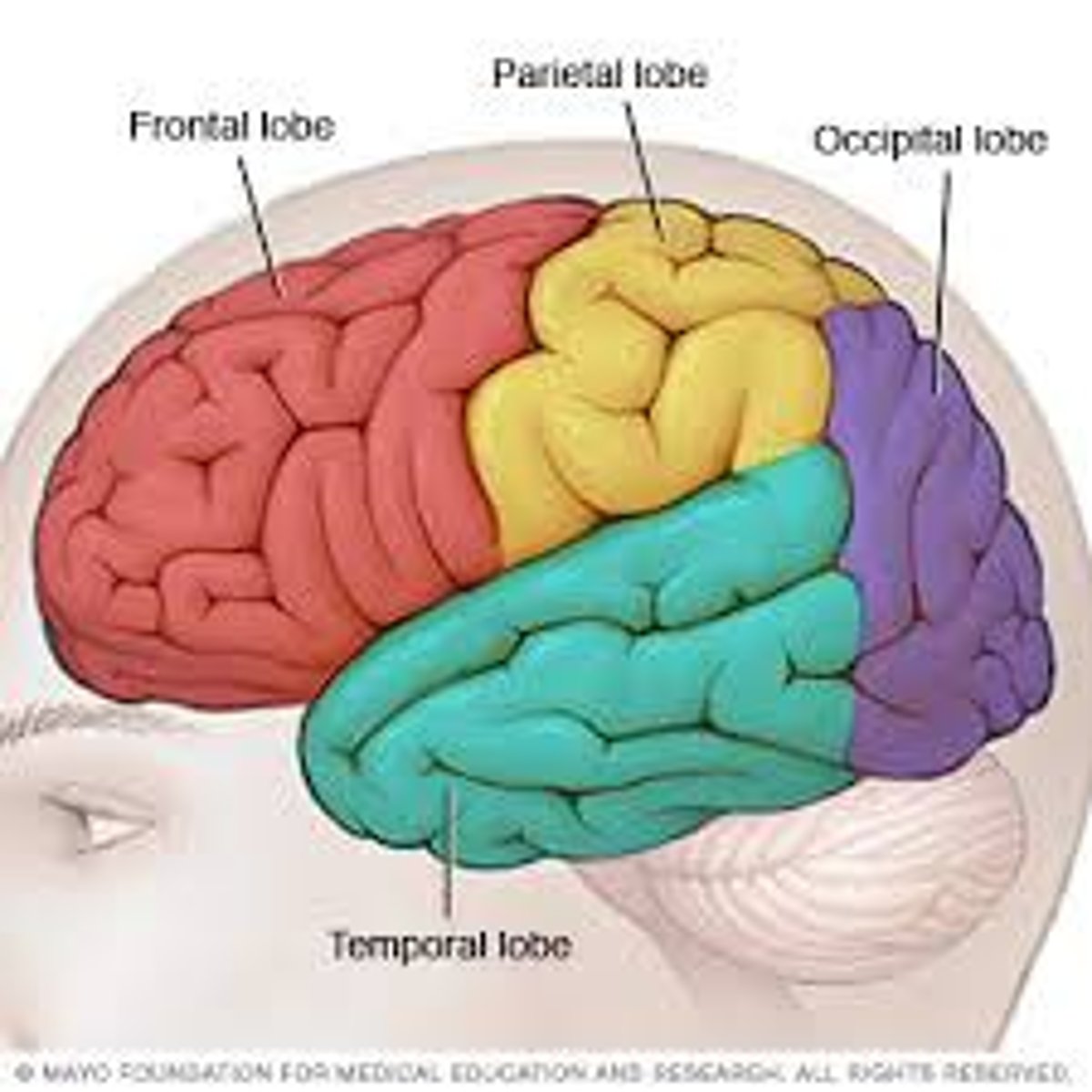
Parietal Lobe
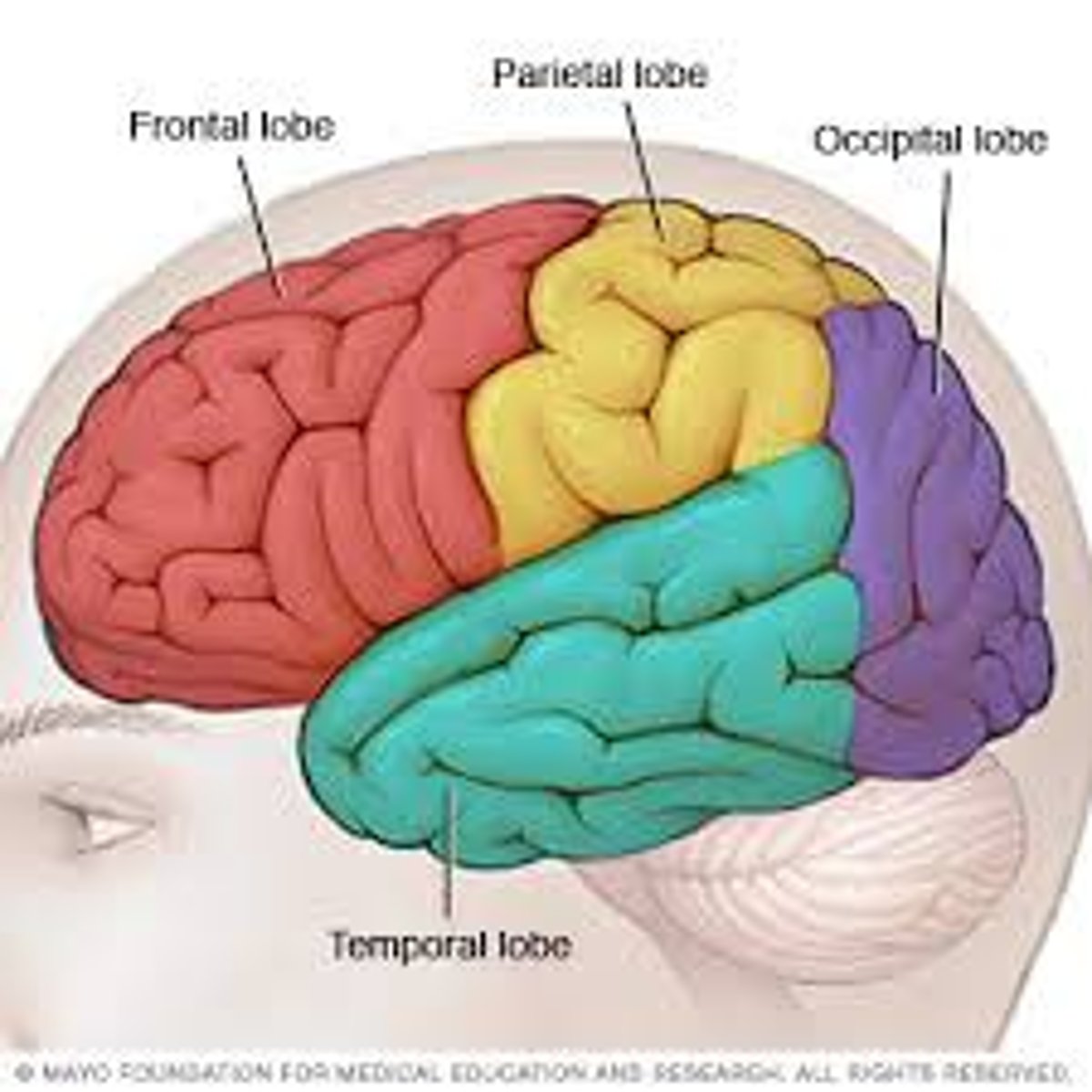
Occipital Lobe
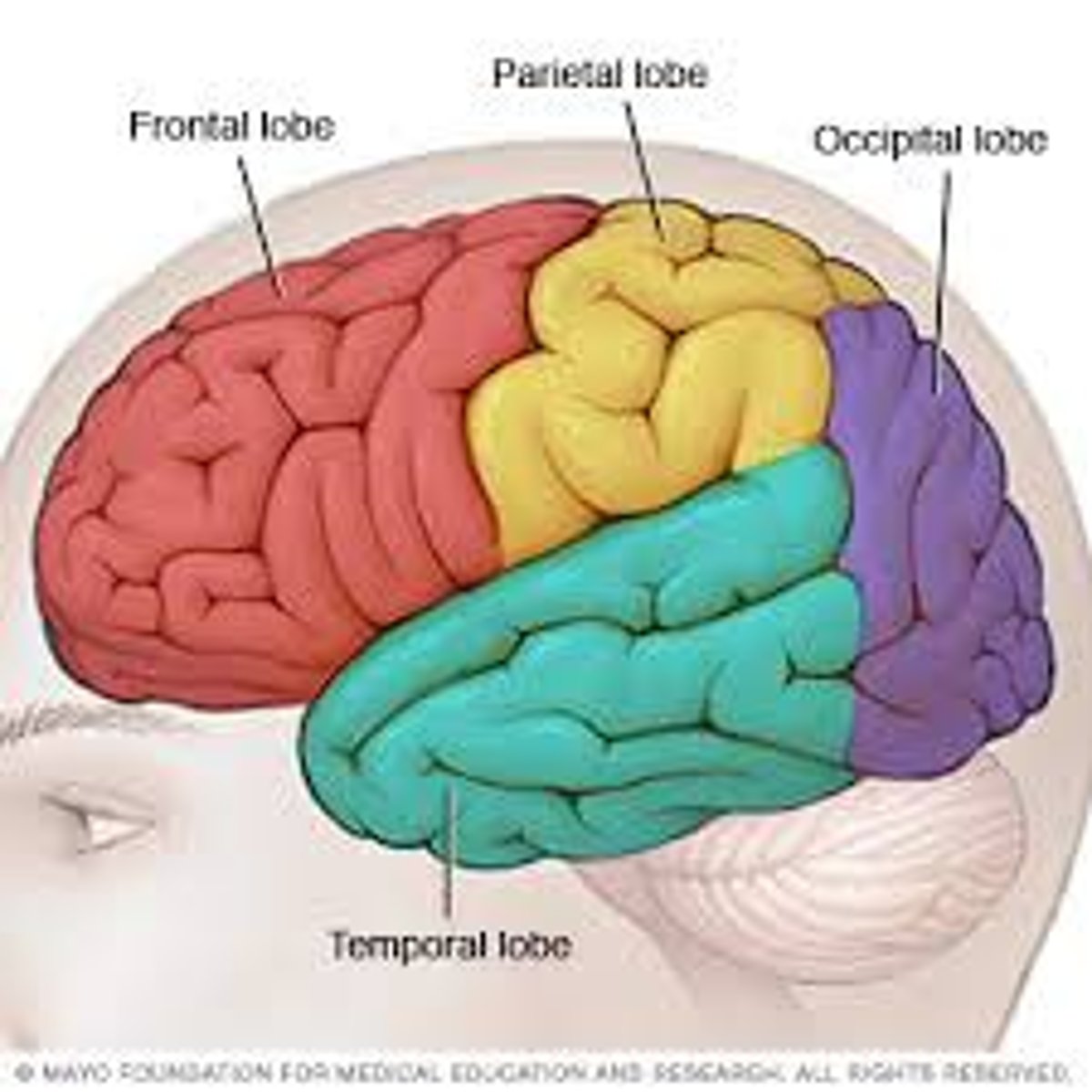
Temporal Lobe
Gyrus
Sulcus
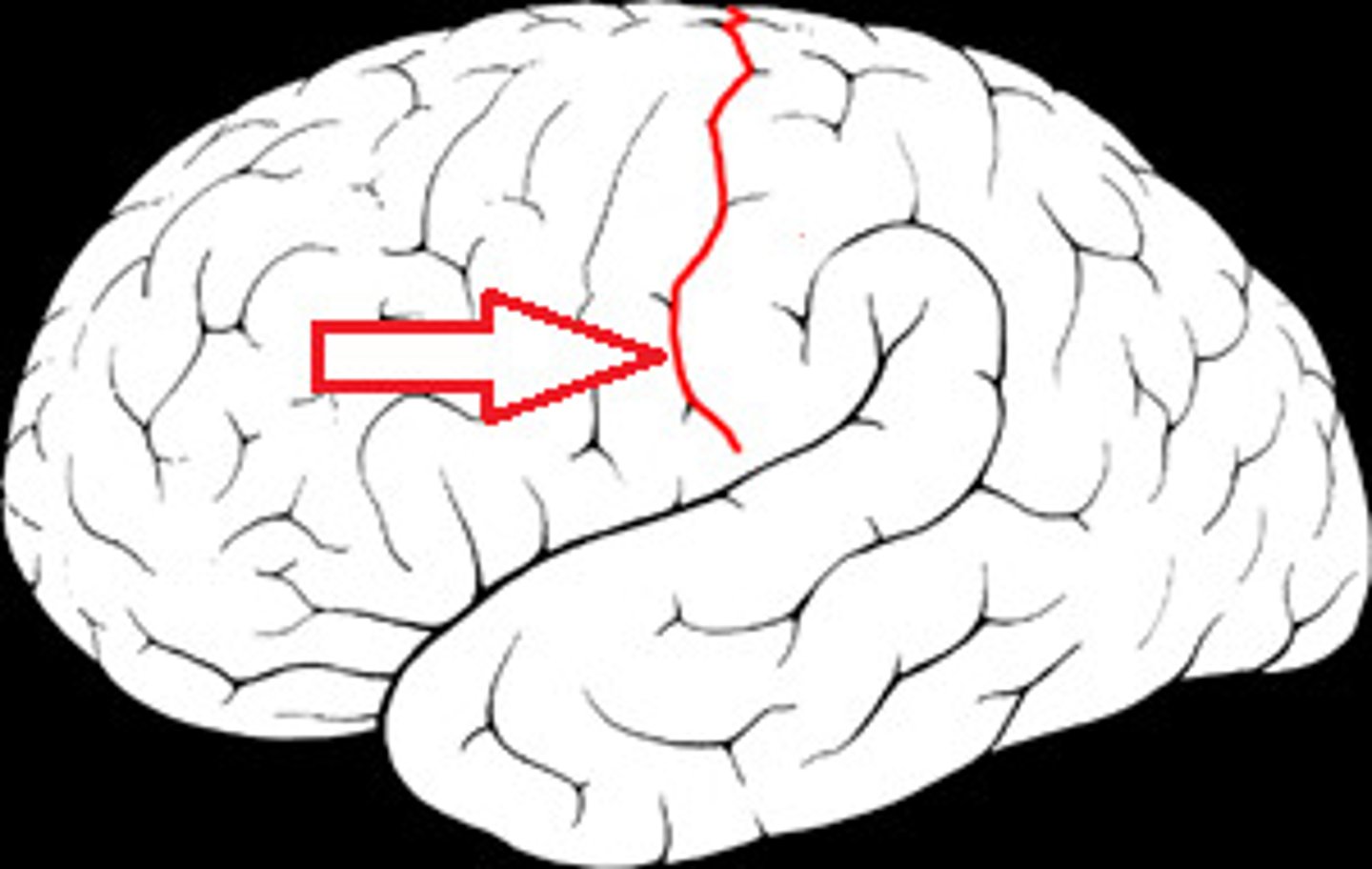
Fissure (a Deep sulcus)
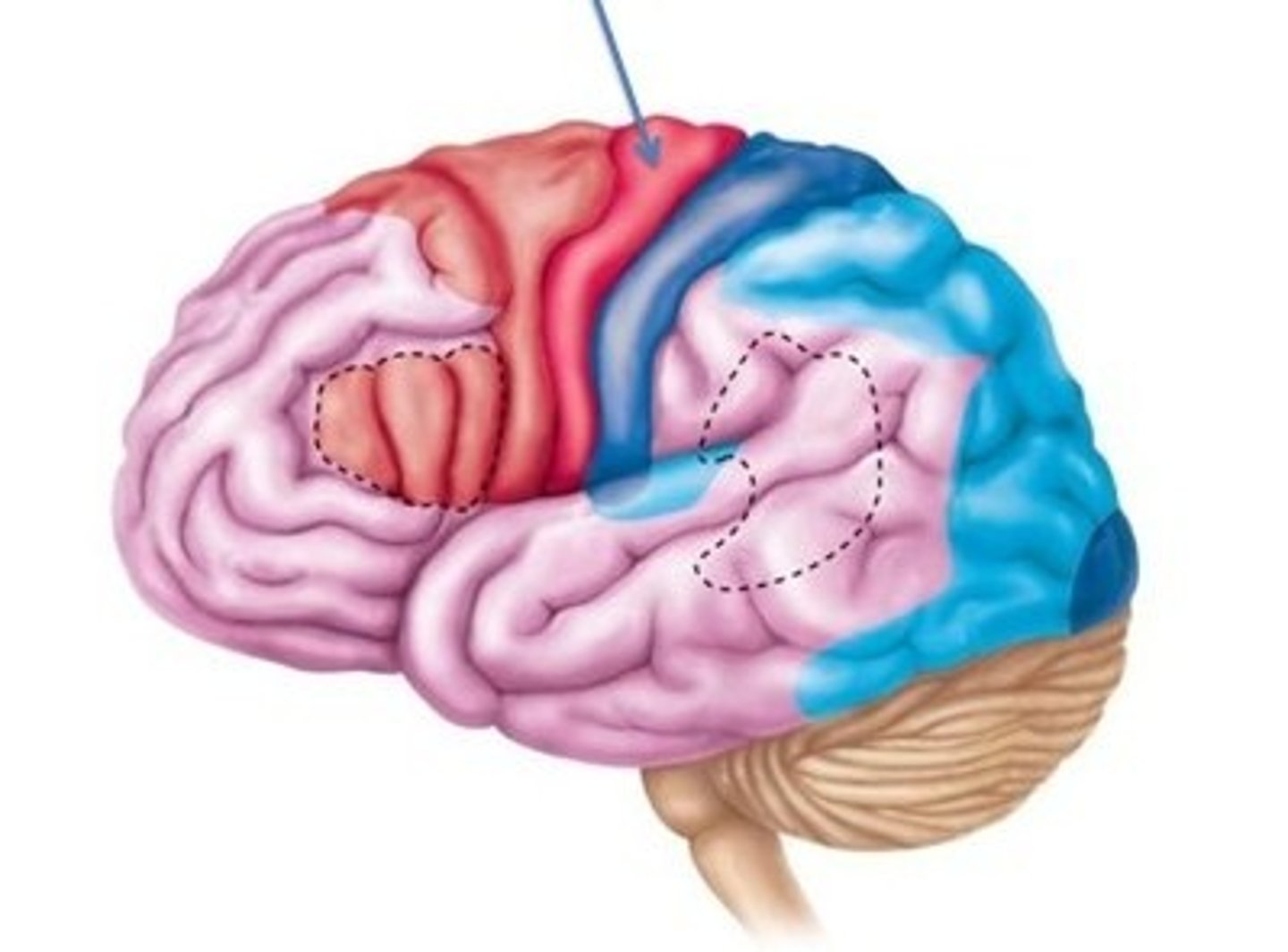
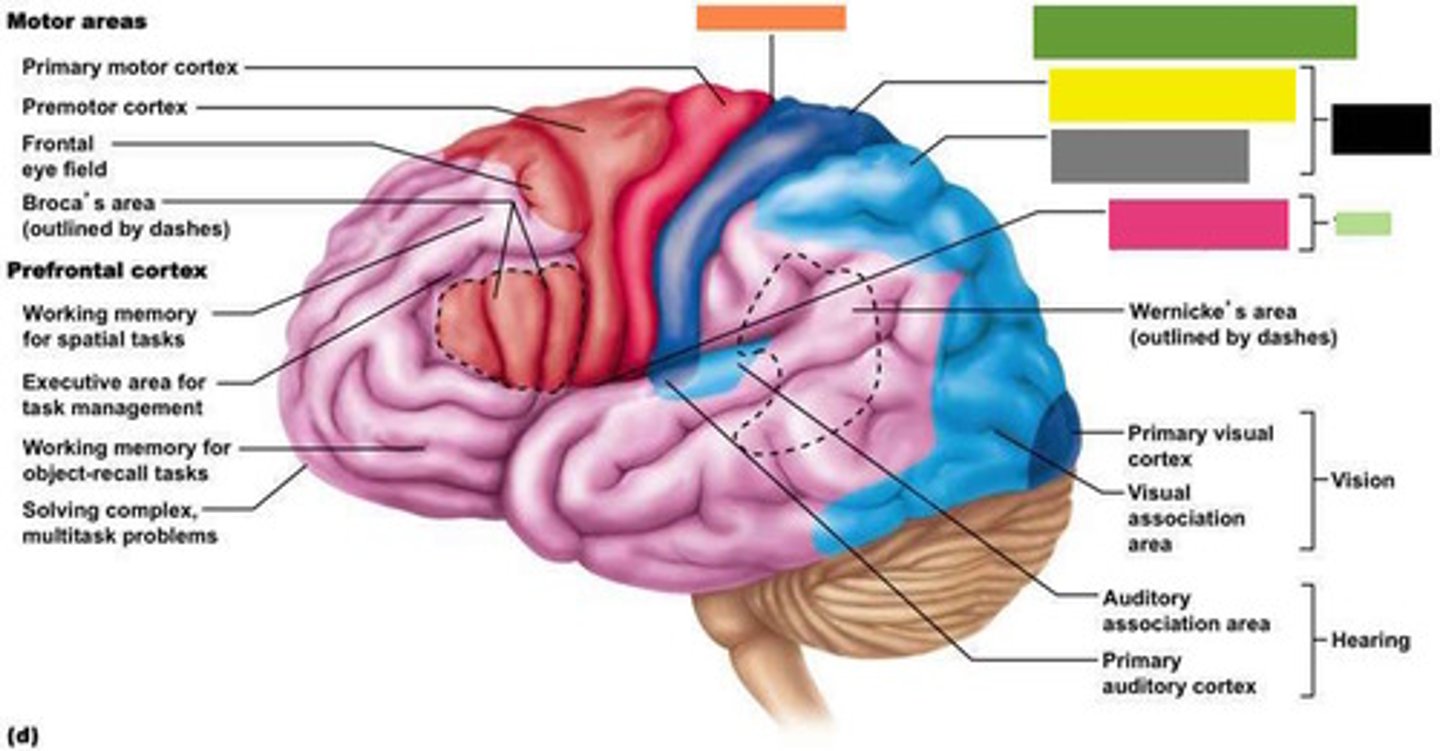
Motor Areas
Primary motor cortex
Premotor cortex
Frontal eye field
Brocas area (outlined by dashes)
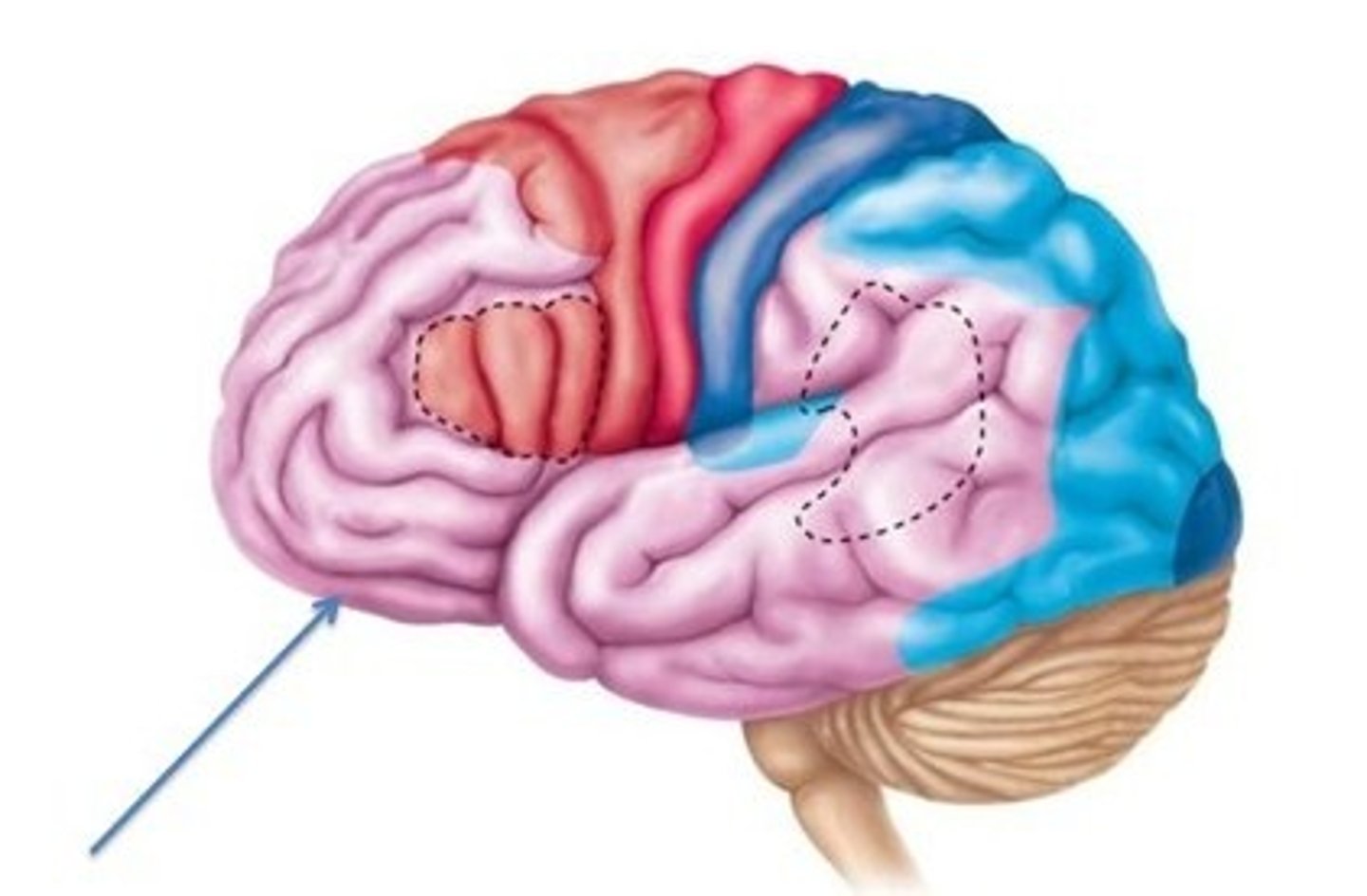
Prefrontal cortex
Working memory for spatial tasks
Executive area for task management
Working memory for object recall tasks
Solving complex, multitask problems
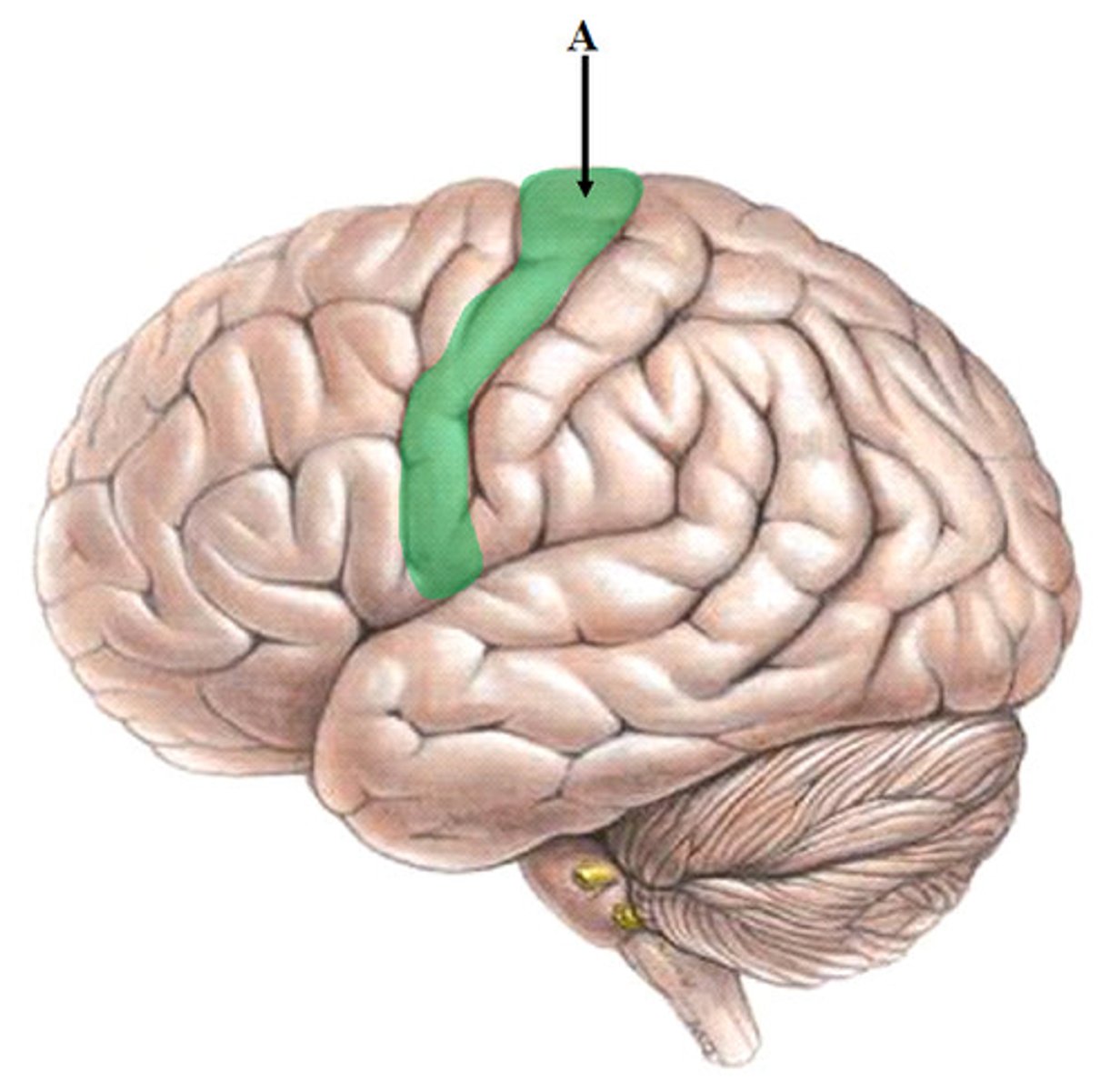
Central Sulcus
3
Sensory areas and related association areas
Primary somatosensory cortex
Somatosensory association cortex
Gustatory cortex (in Insula)
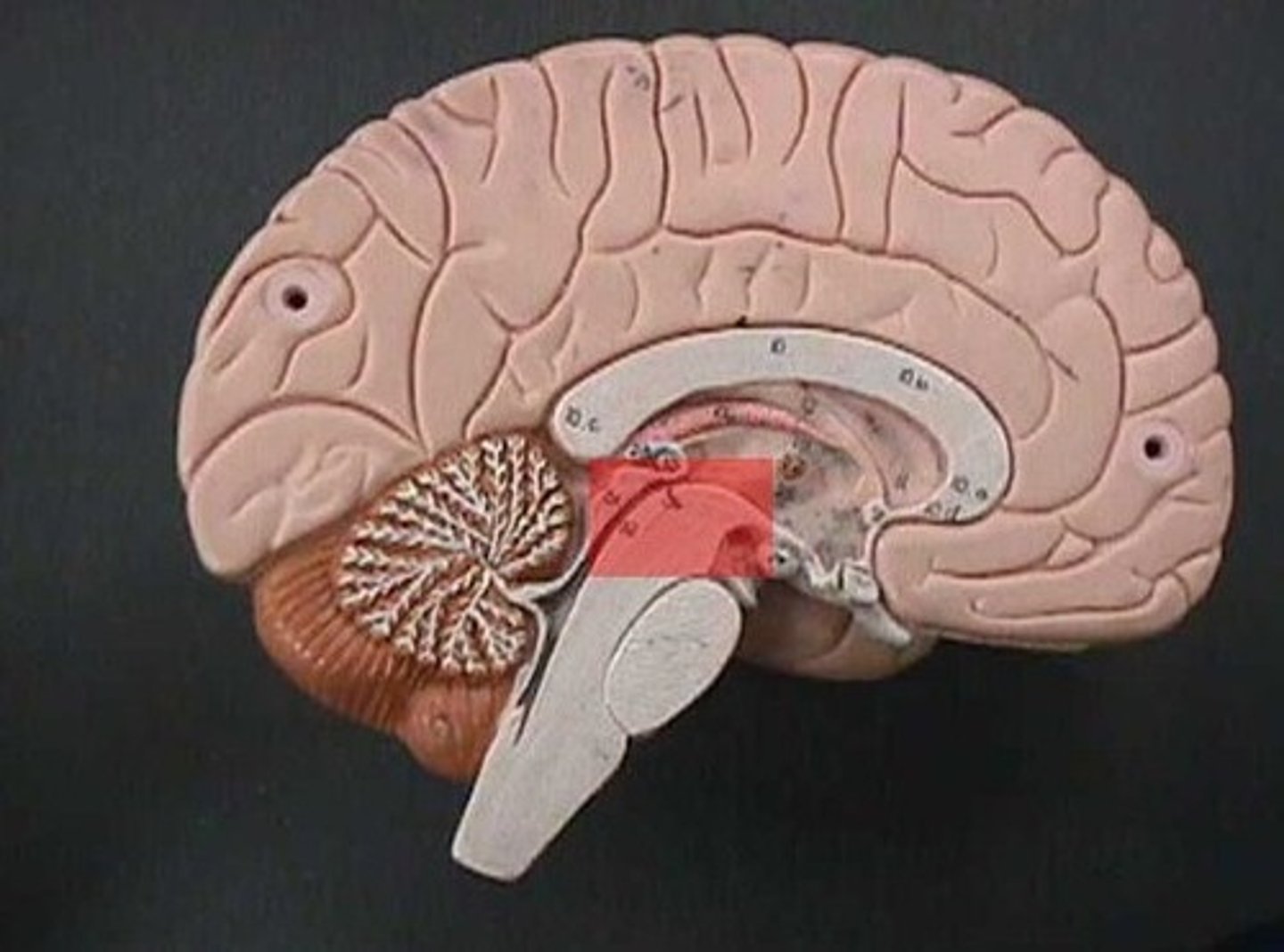
Midbrain
Pons
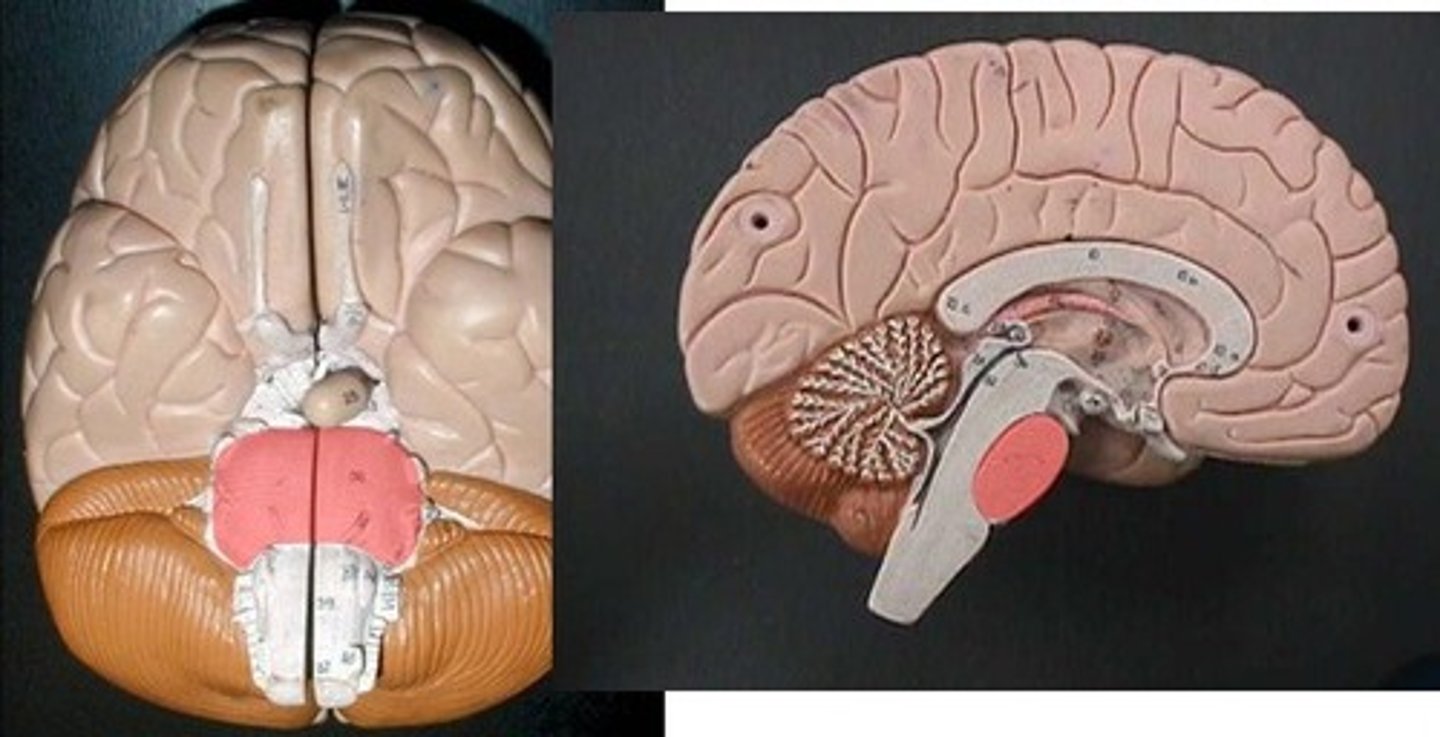
Medulla oblongata
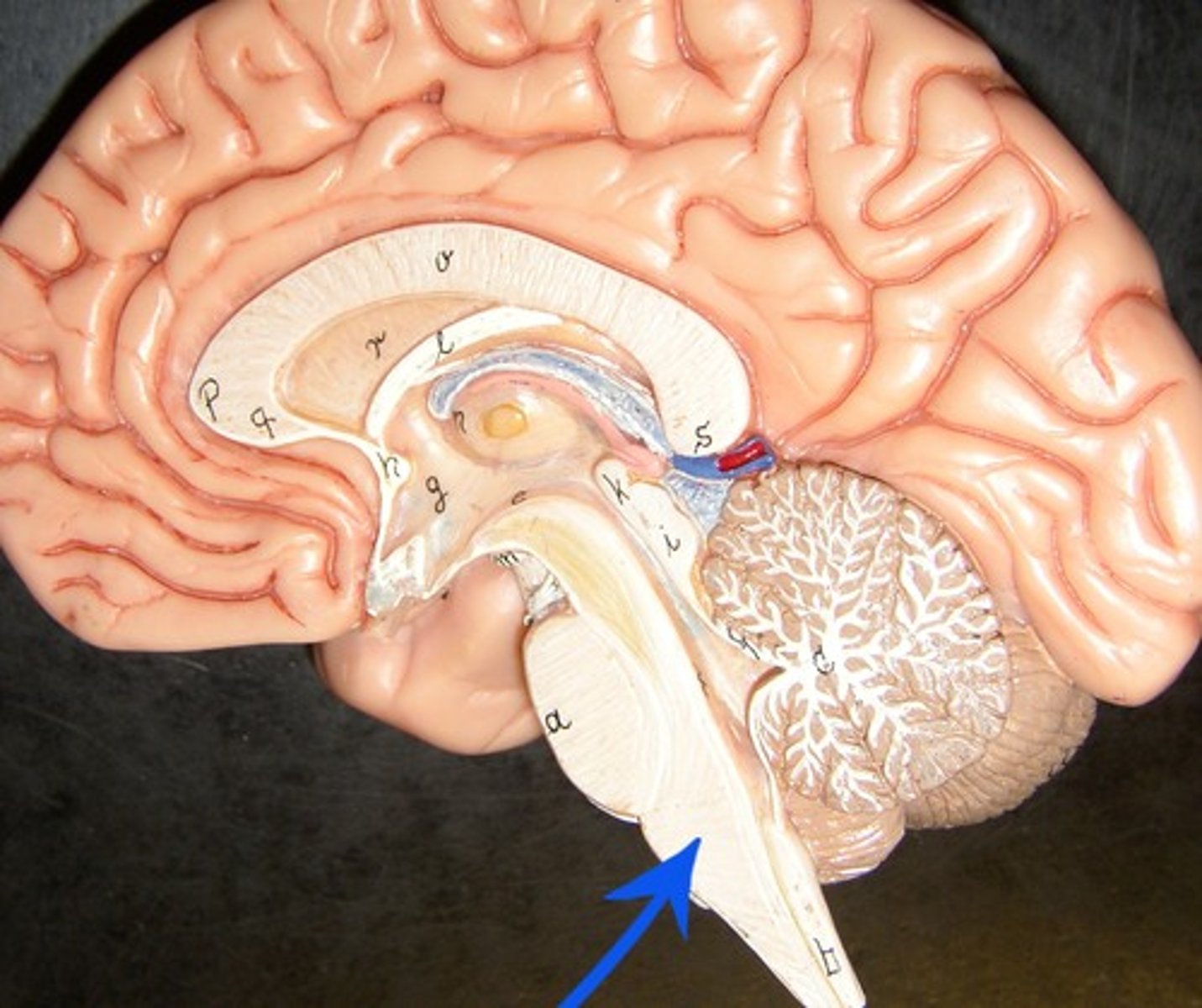
Thalamus
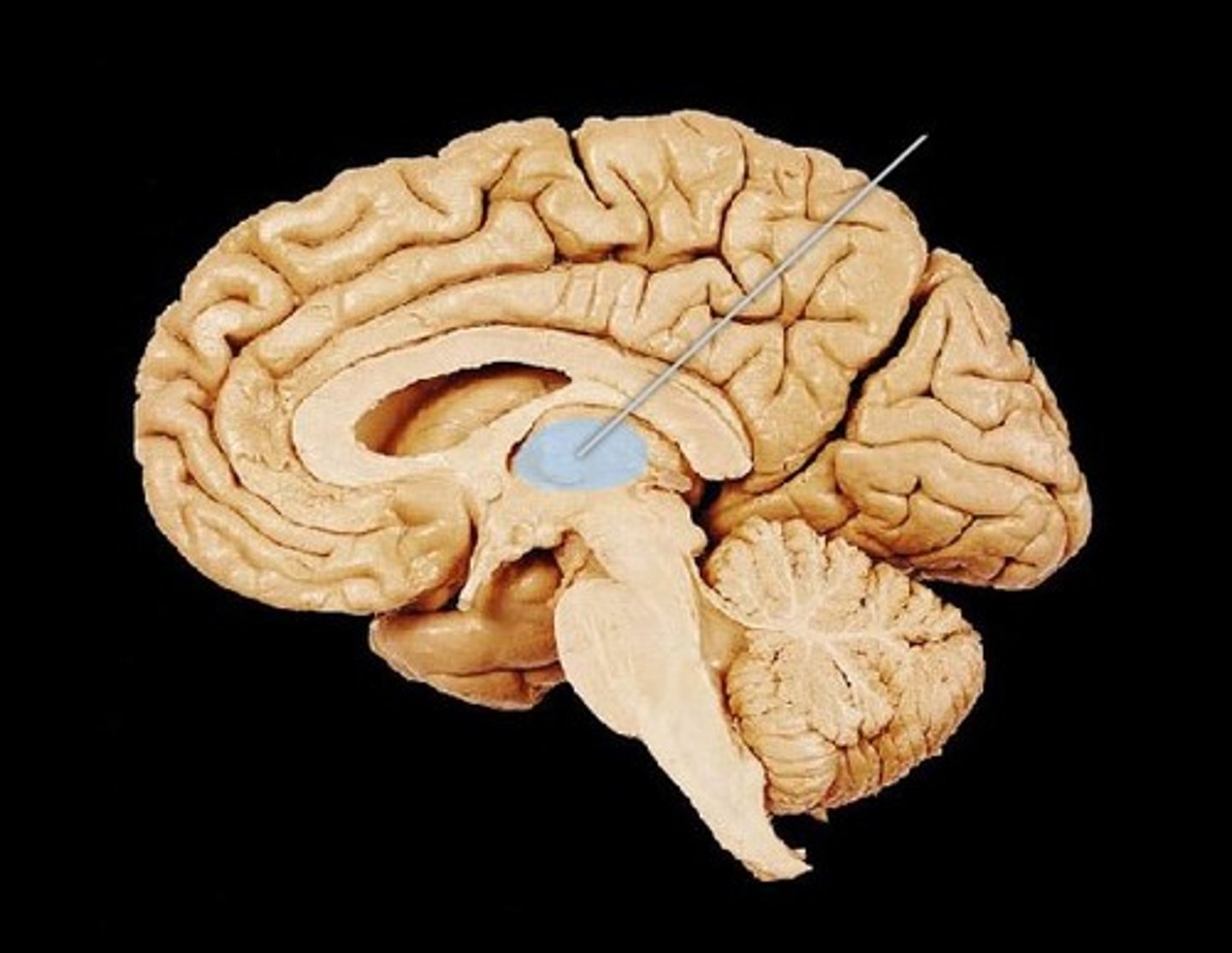
Pineal gland
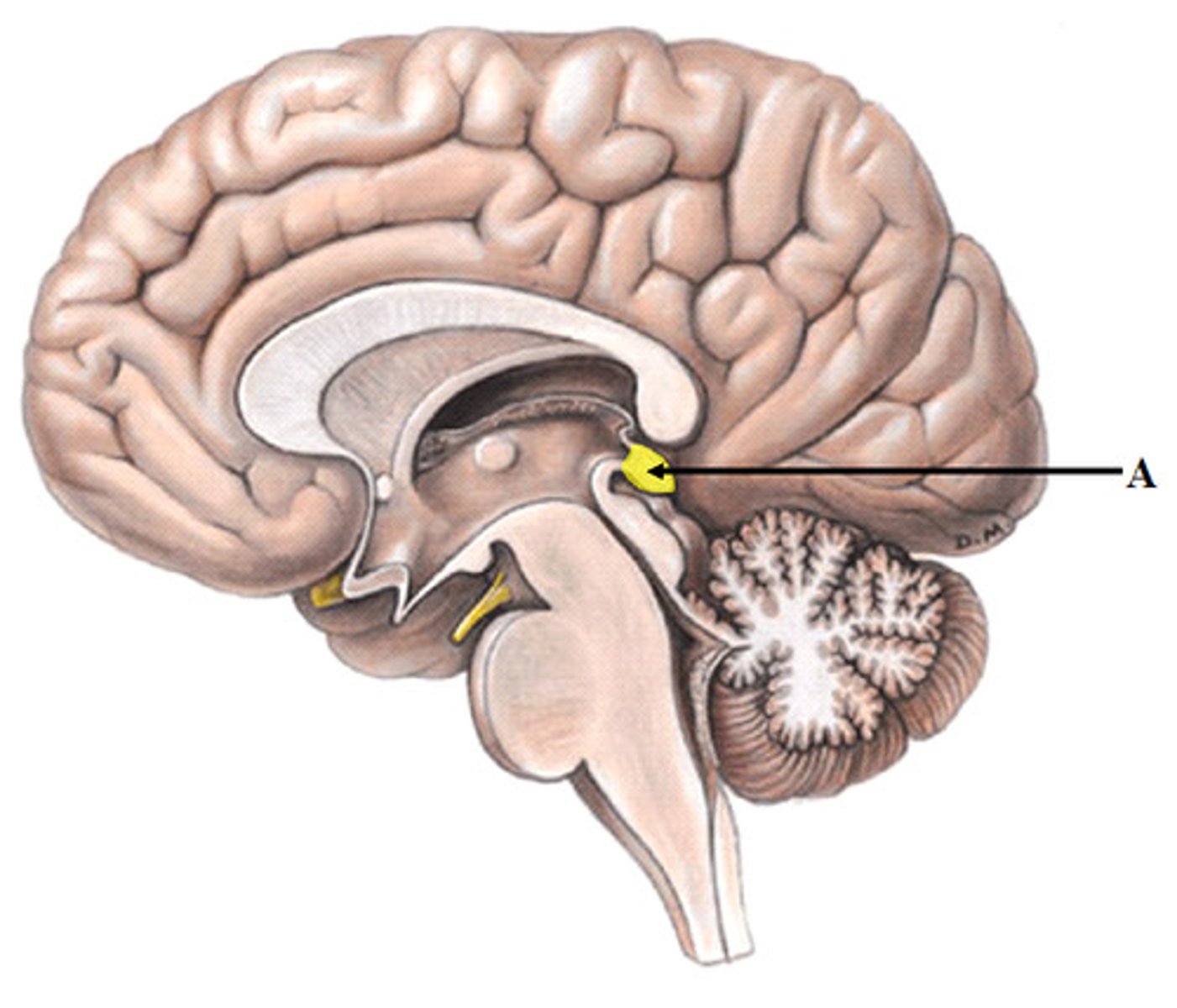
Hypothalamus
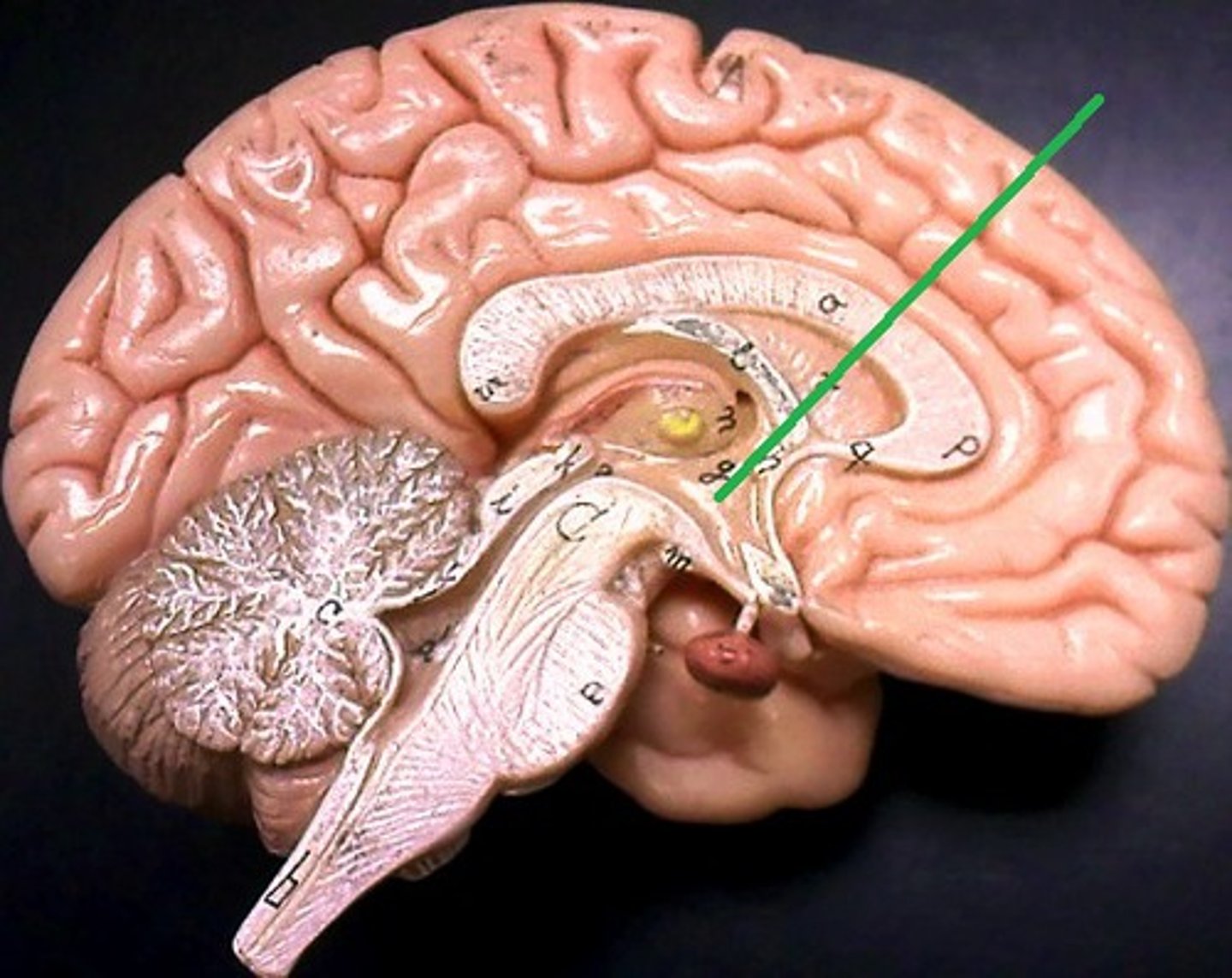
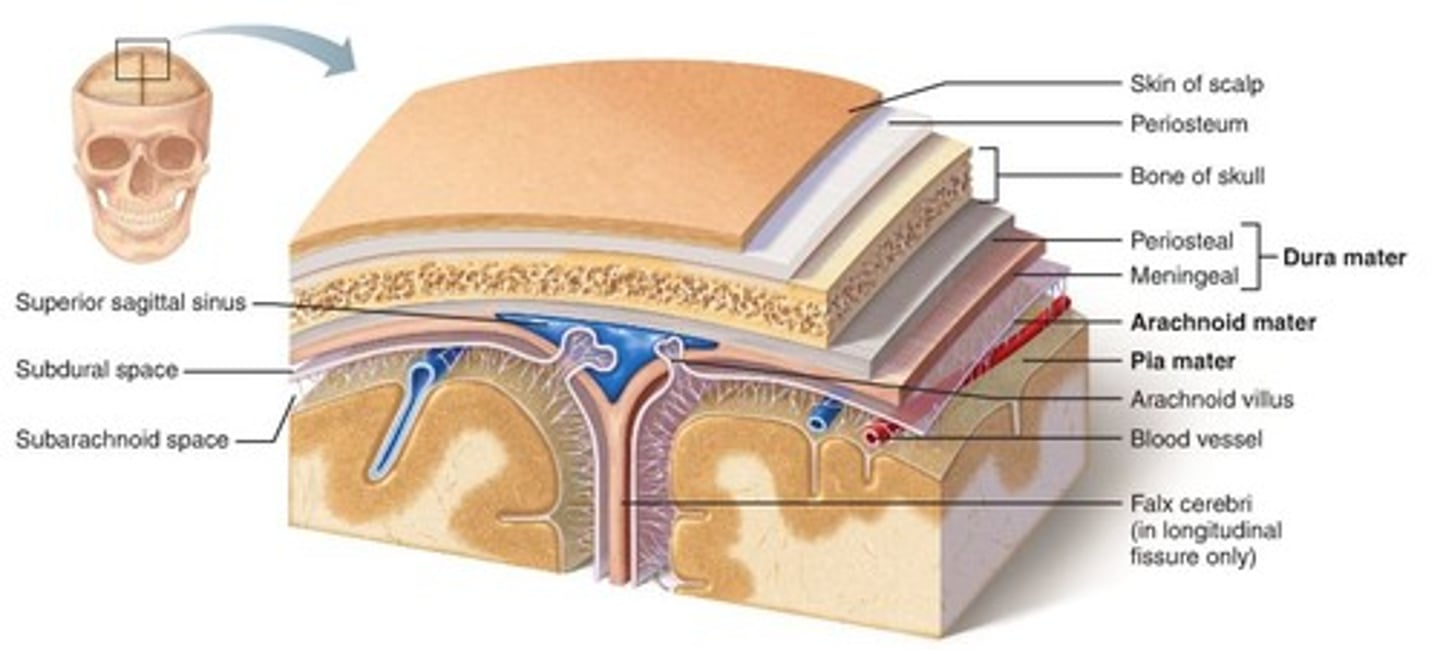
Dura meter
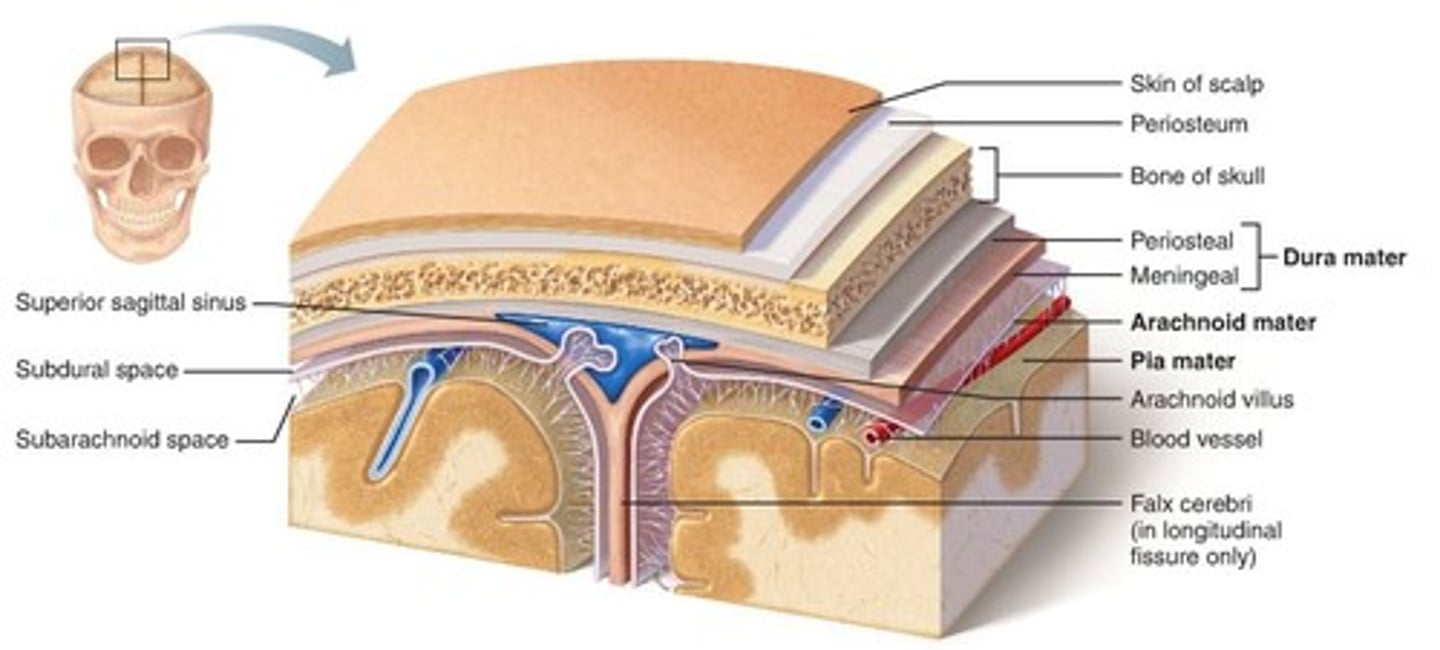
Arachnoid mater
-Periosteal
-Meningeal
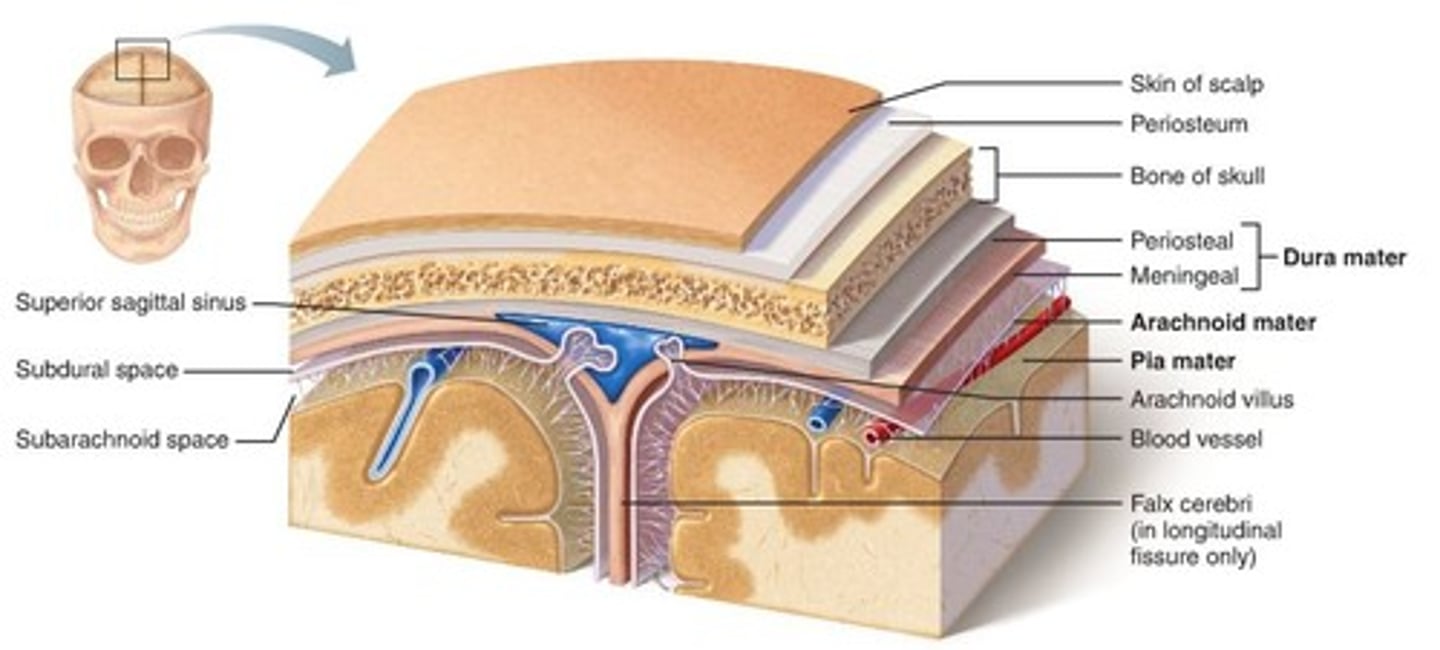
Pia mater
D
A
P
Dura mater
Arachnoid mater
Pia mater
Arachnoid villus
J
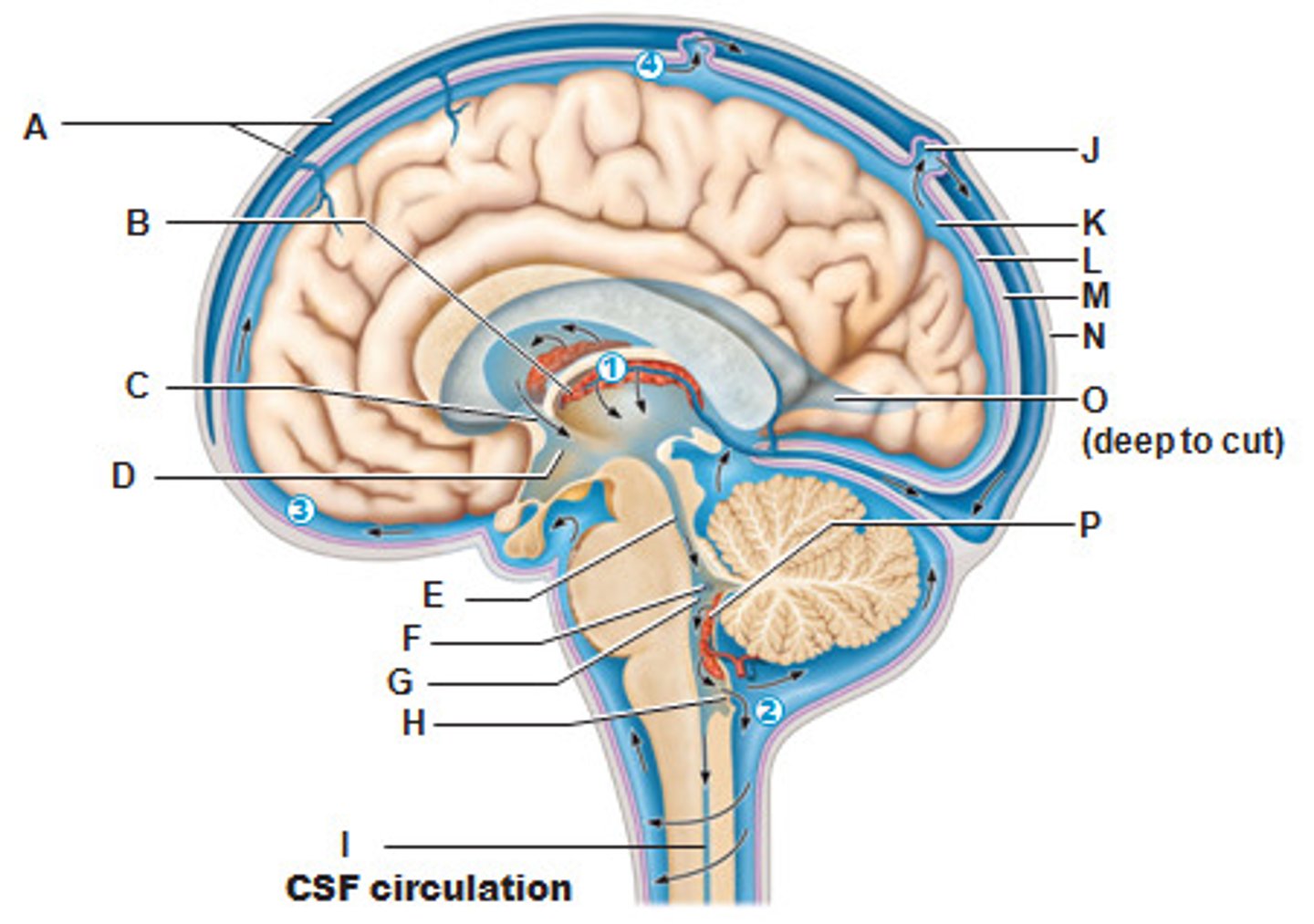
Right Lateral Ventricle (Deep to Cut)
O
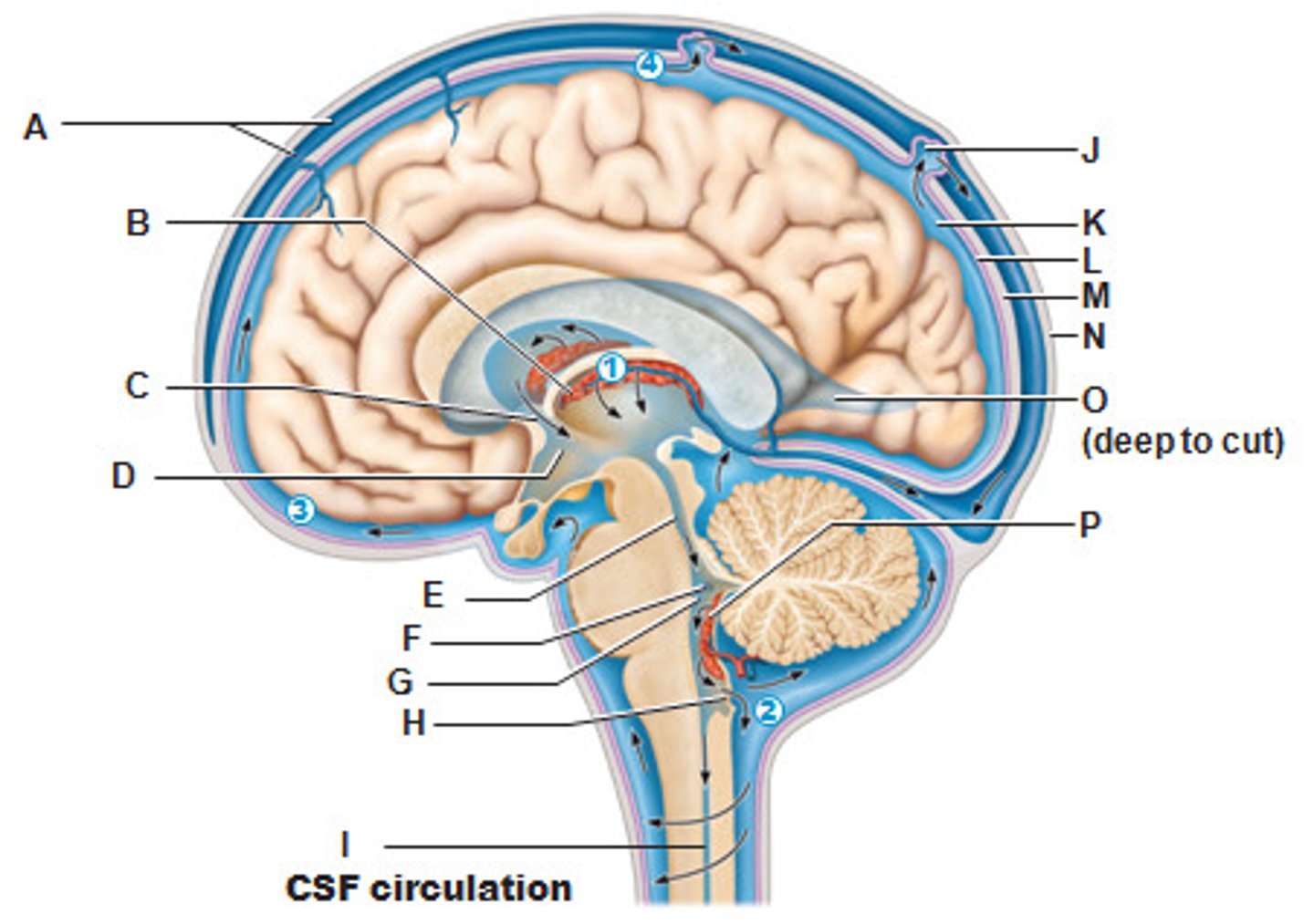
Circulatory Pattern of Cerebrospinal Fluid
START
Lateral Ventricle
Interventricular foramen
Third ventricle
Fourth Ventricle
Subarachnoid space
END
Returns via Arachnoid Villus
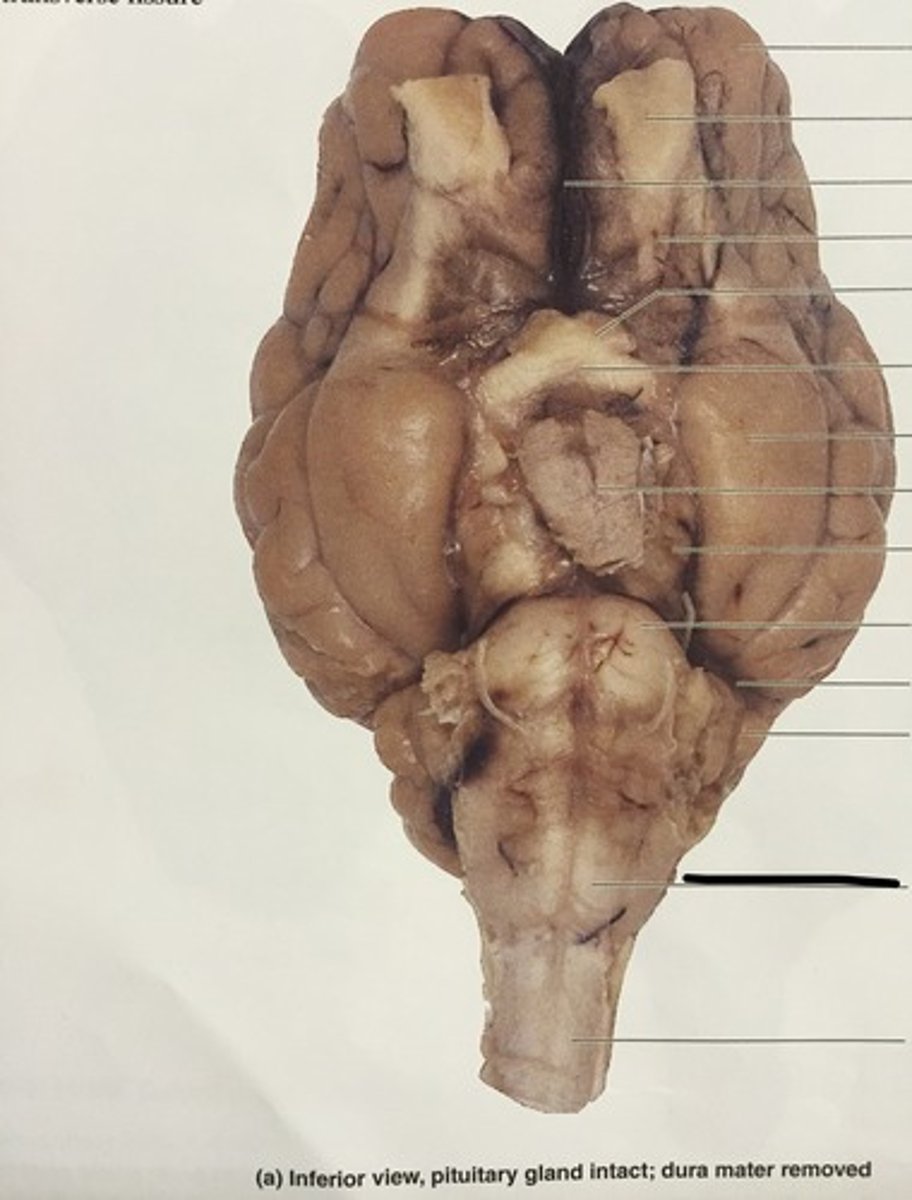
Olfactory Bulb (Sheep brain)
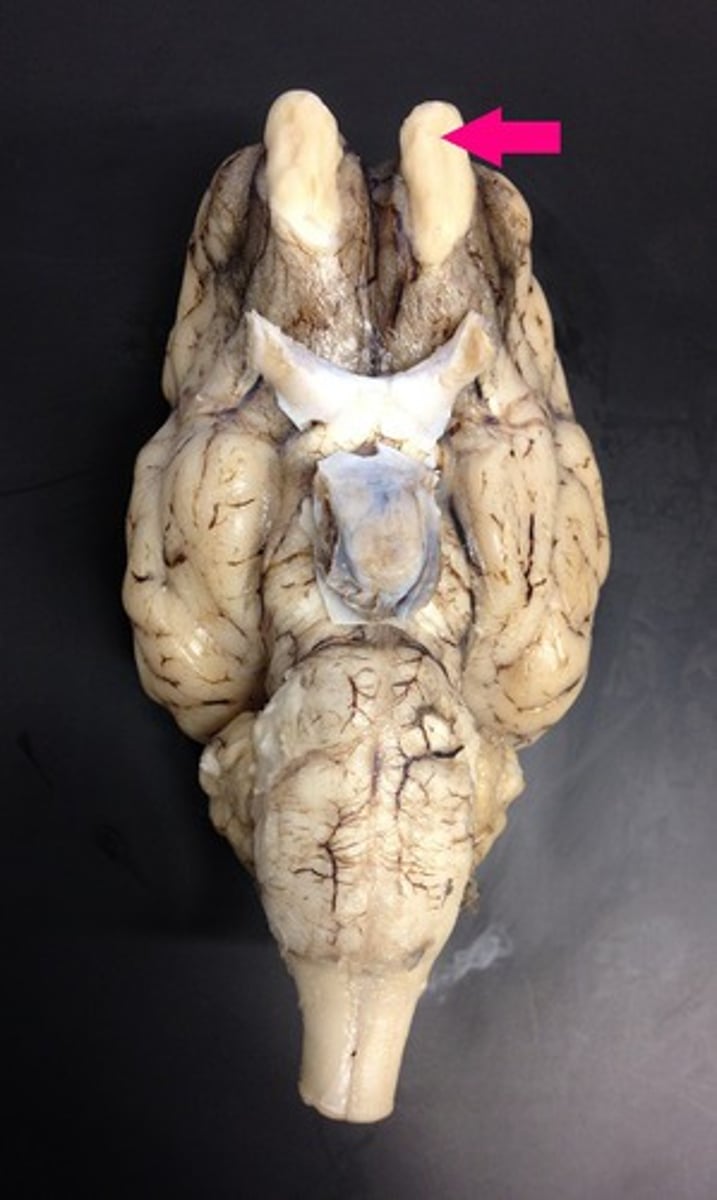
Optic nerve (II) (Sheep Brain)
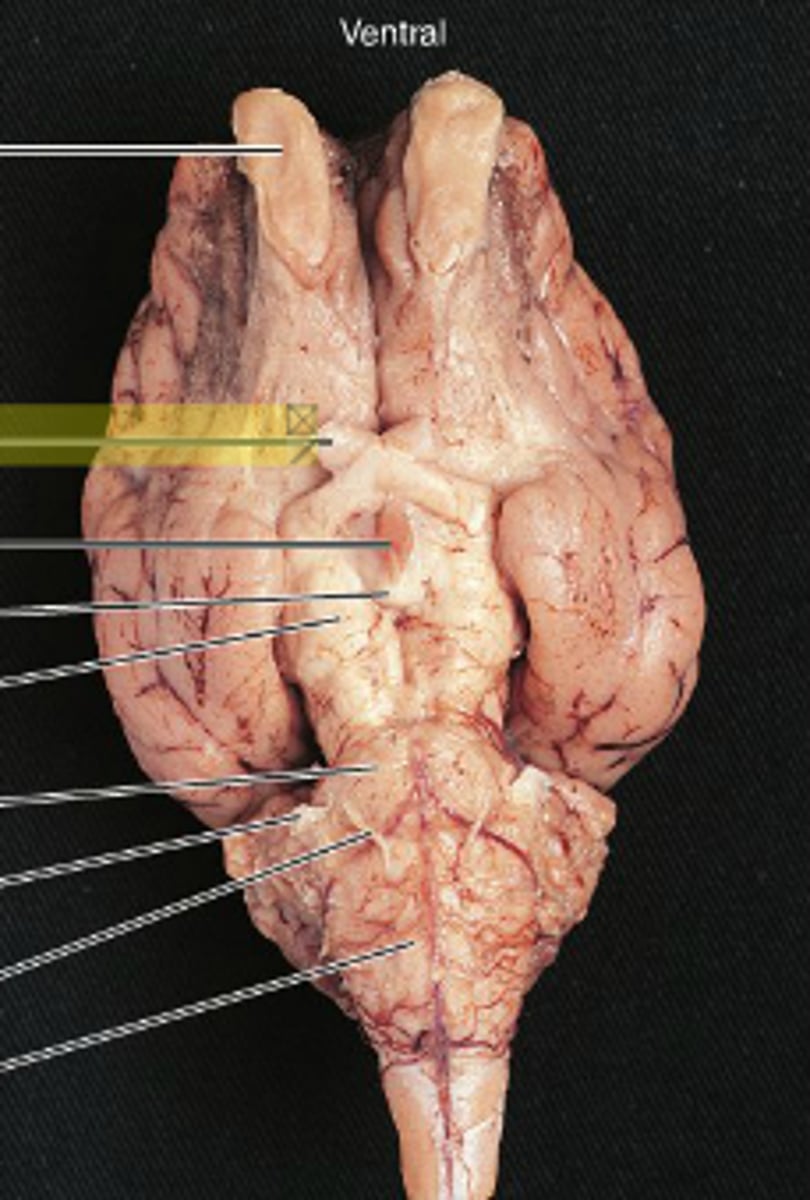
Infundibulum (Sheep Brain)
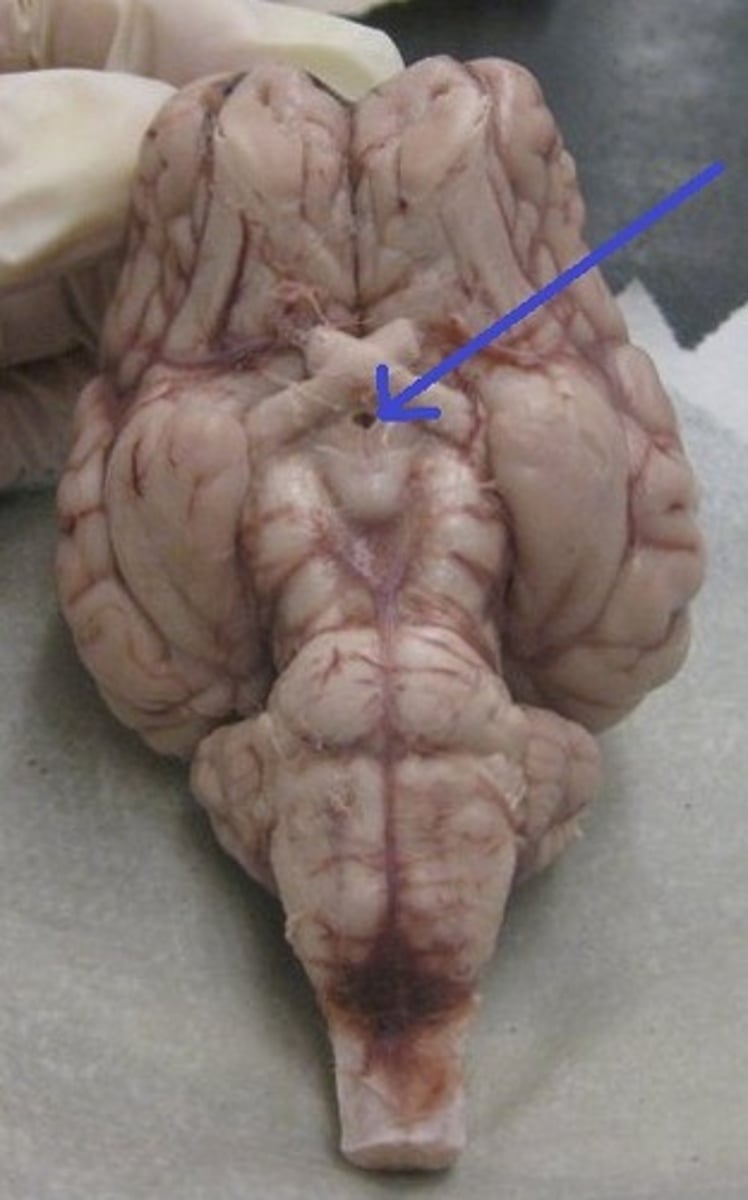
Mammillary body (Sheep Brain)
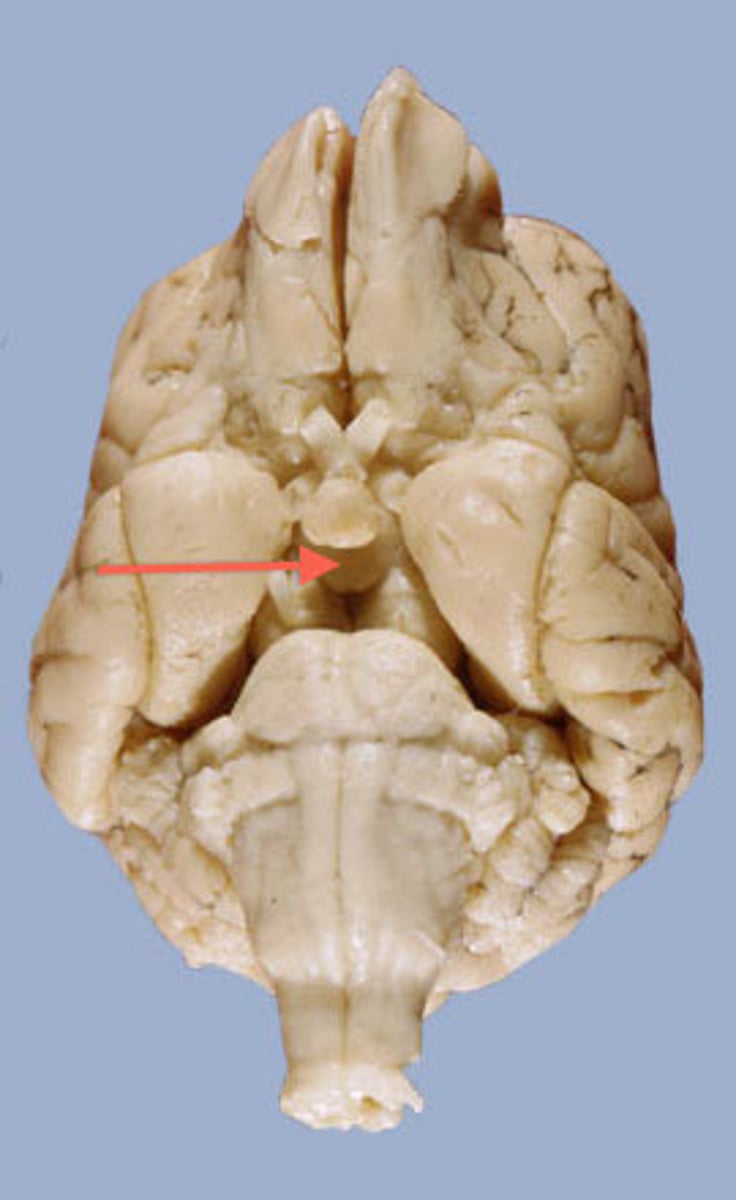
Cerebral Peduncle (Sheep Brain)
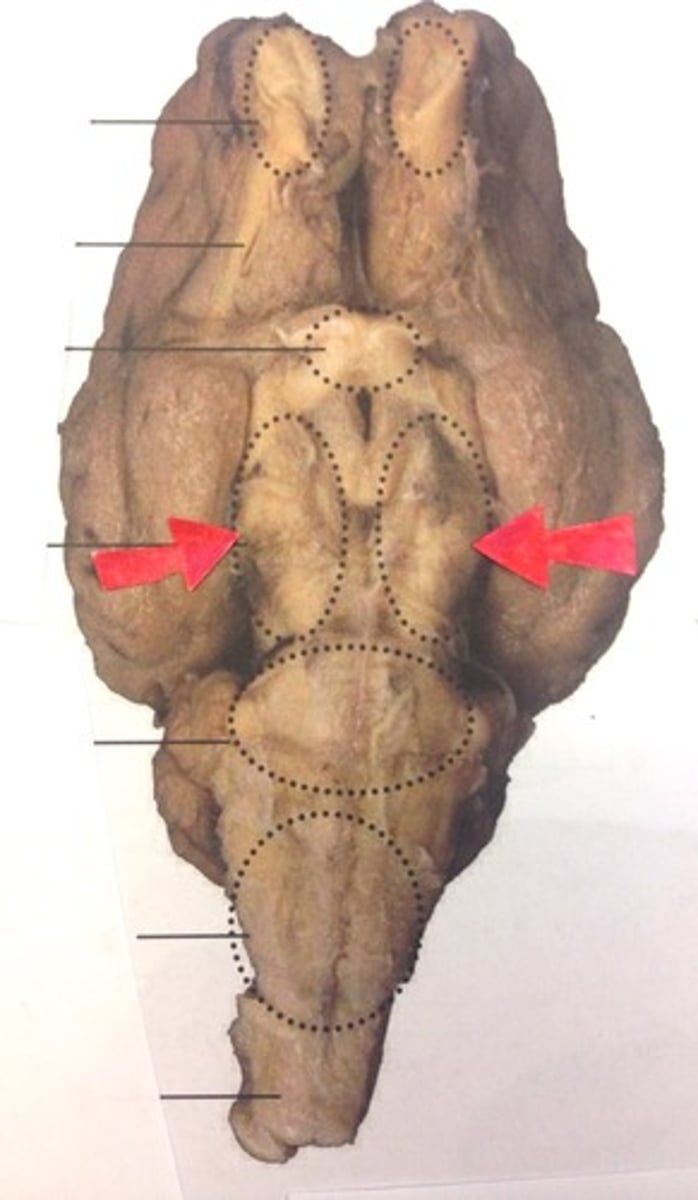
Pons (sheep brain)
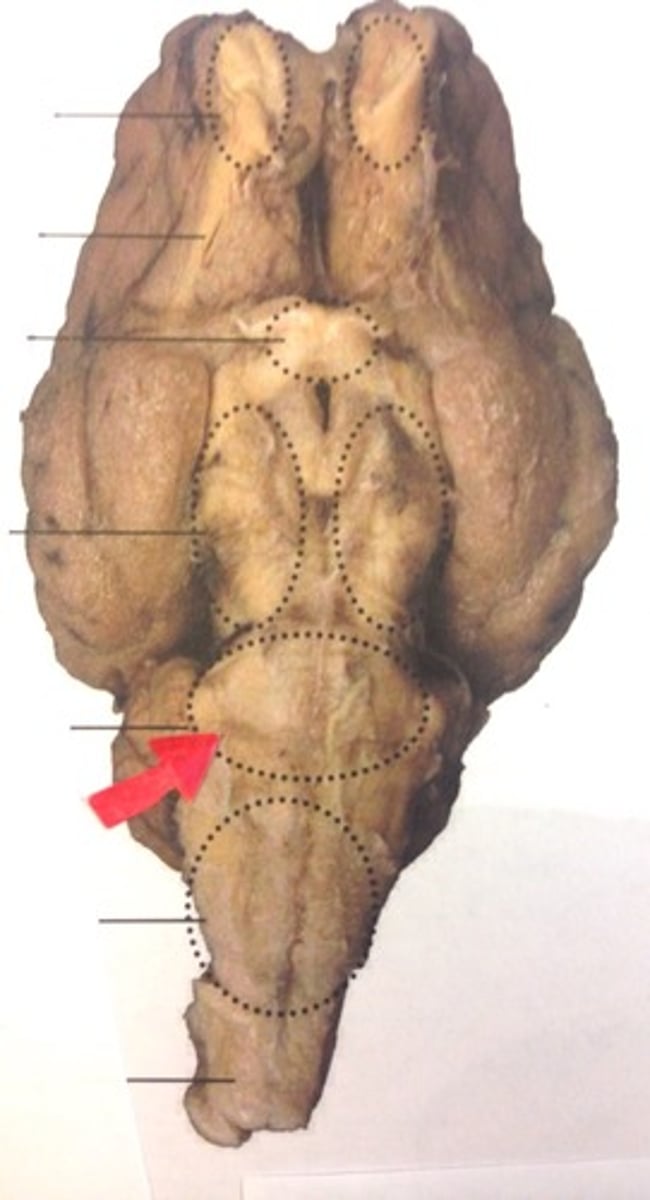
Trigeminal nerve (V) (Sheep brain)
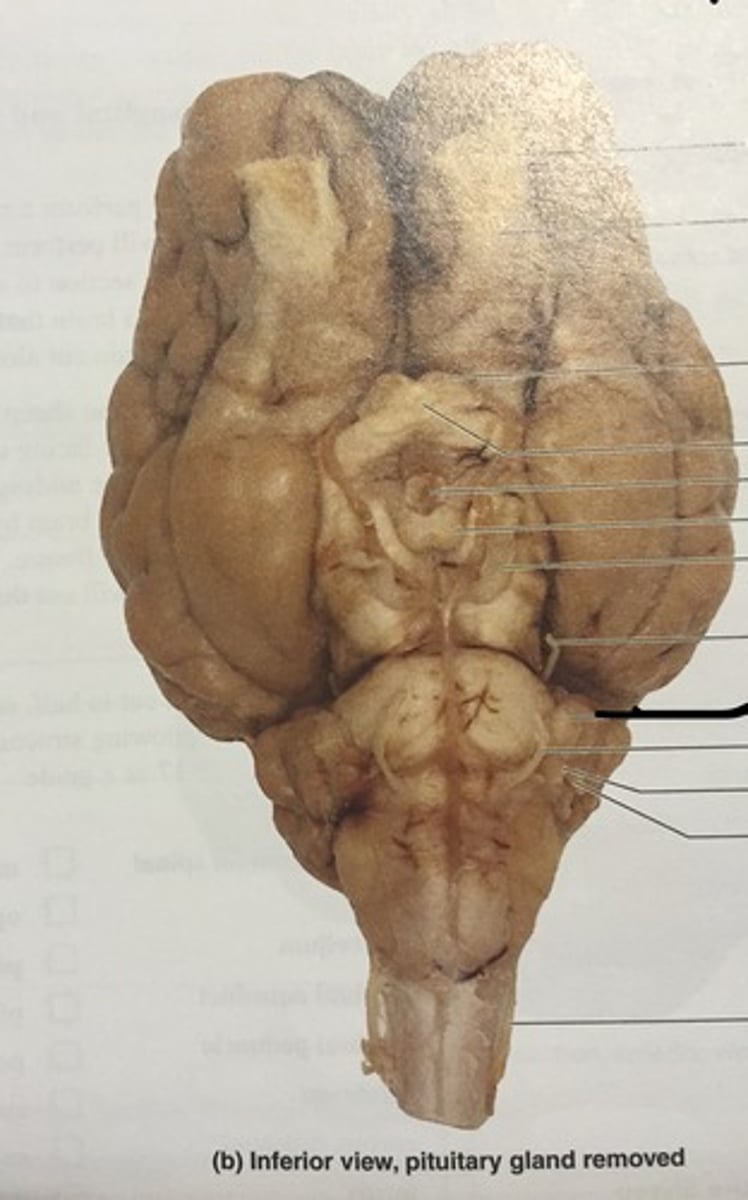
Abducens Nerve (VI) (Sheep Brain)
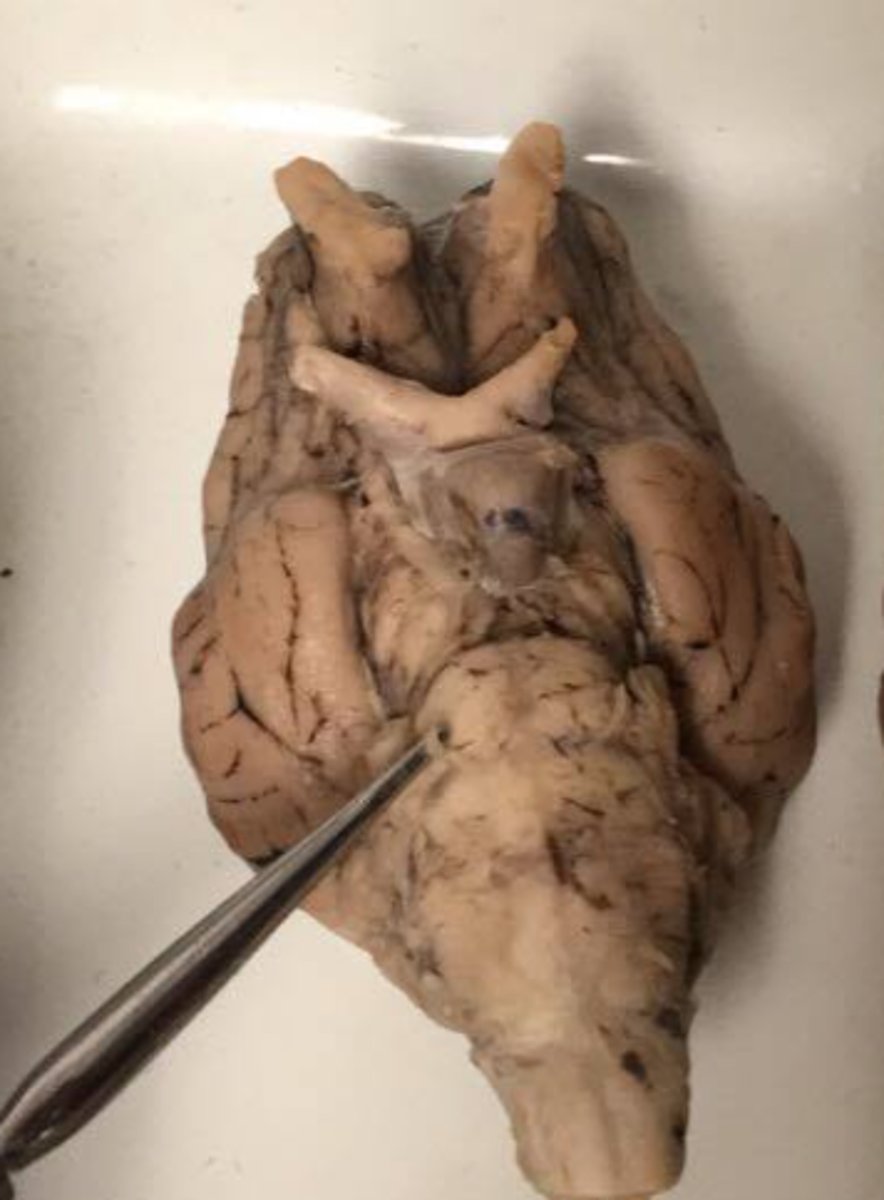
Medulla Oblongata (Sheep Brain)
5 Steps of Reflex Arc
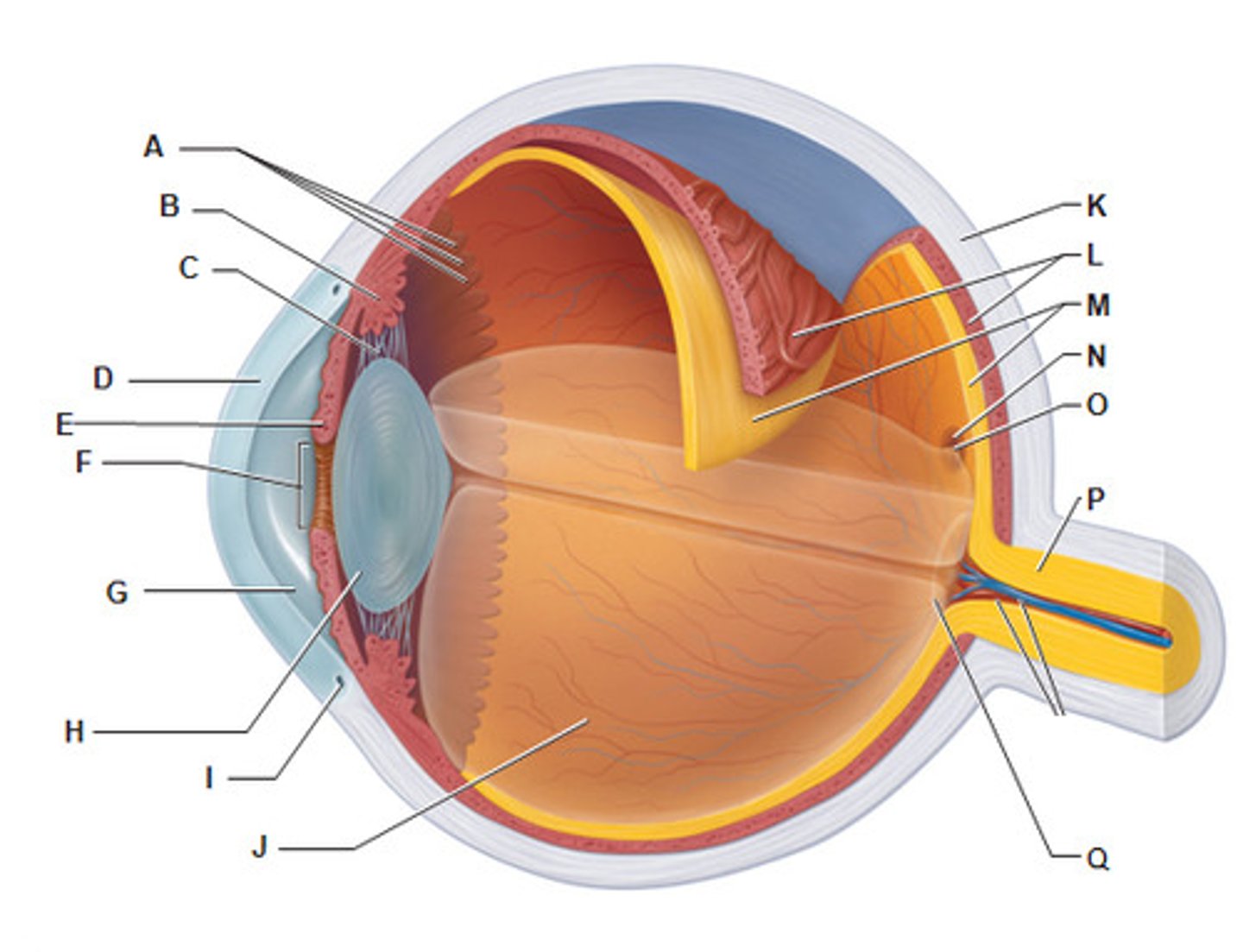
Superior Oblique Muscle
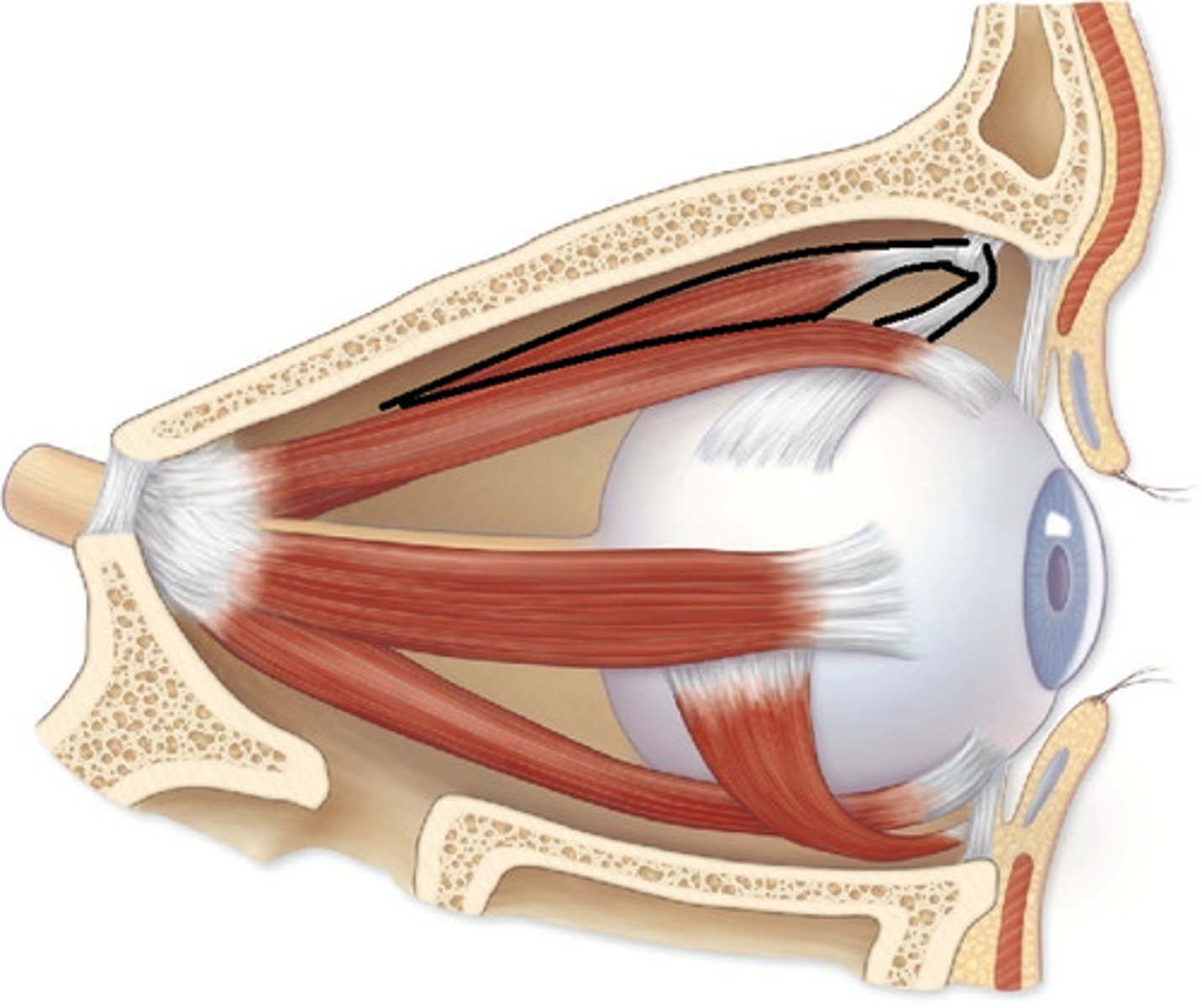
Trochlea
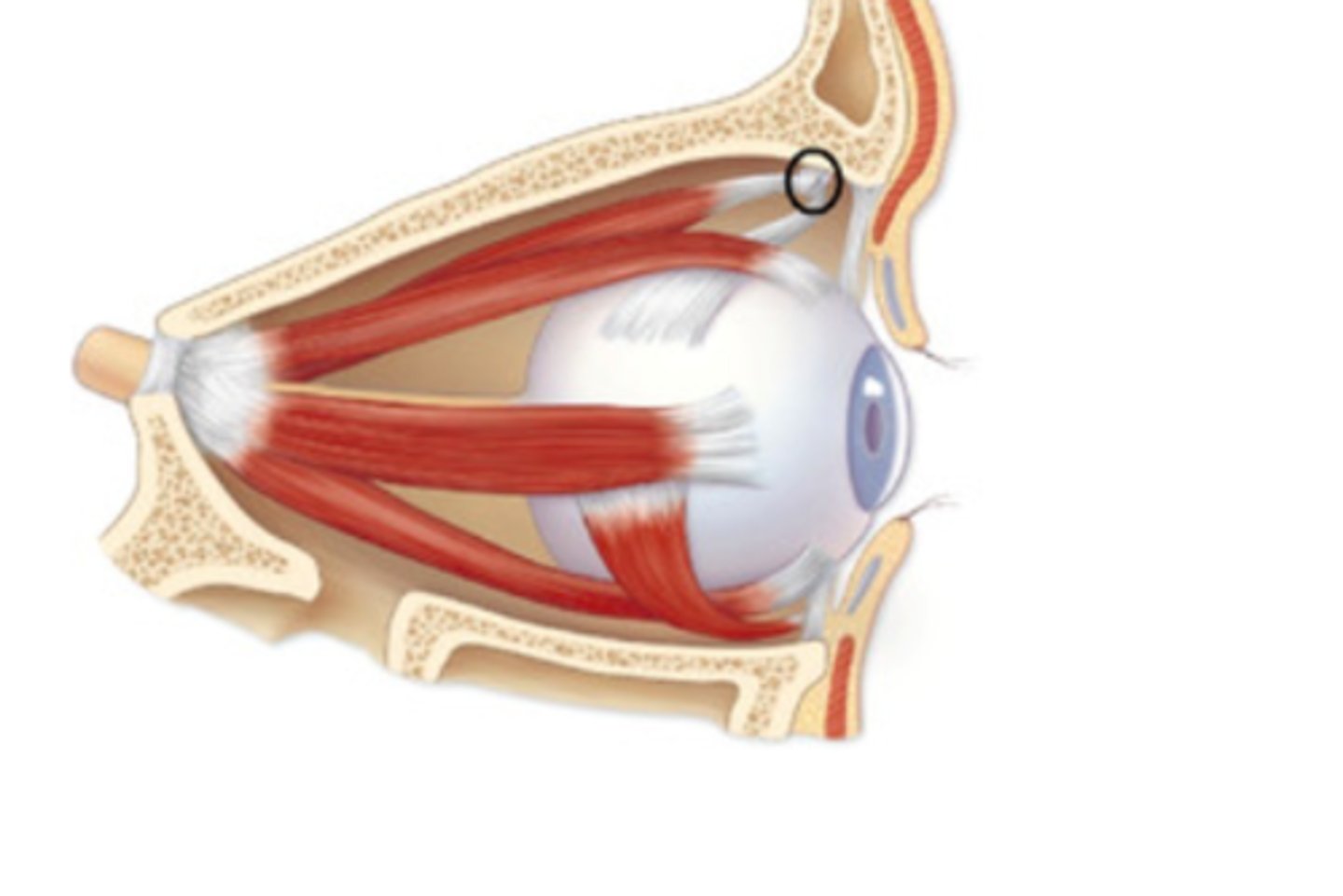
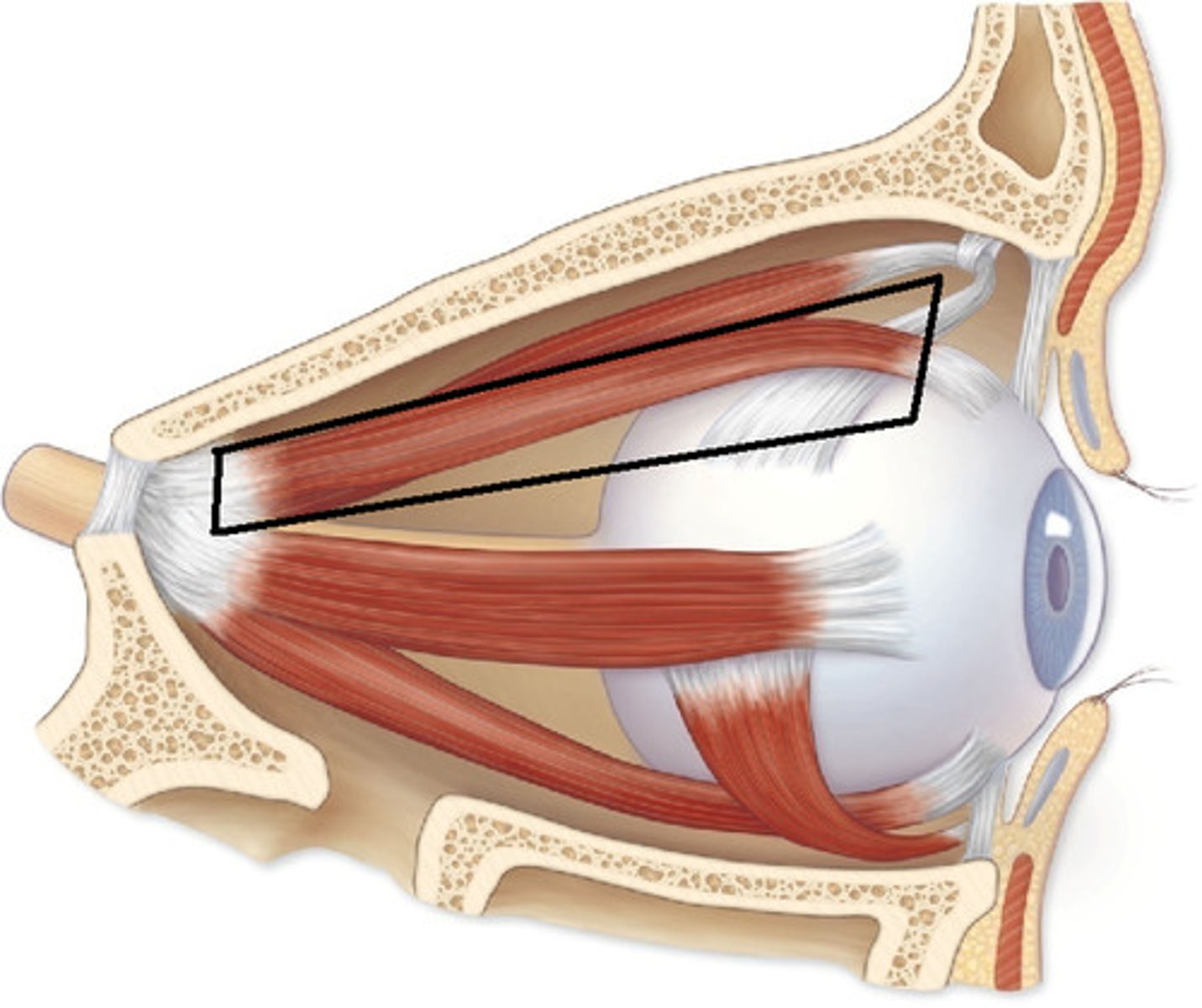
Superior Oblique Tendon
C
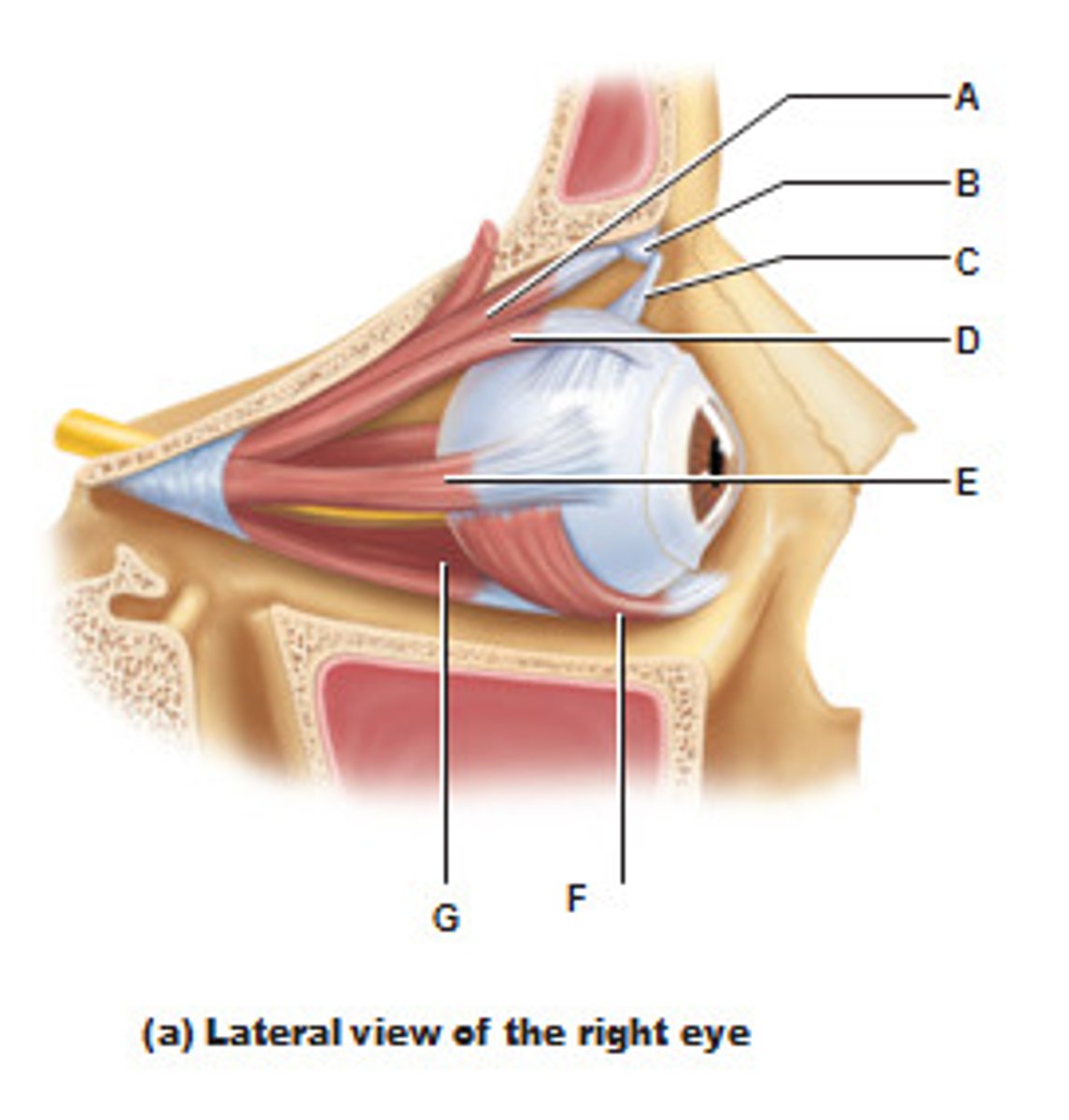
Superior rectus muscles
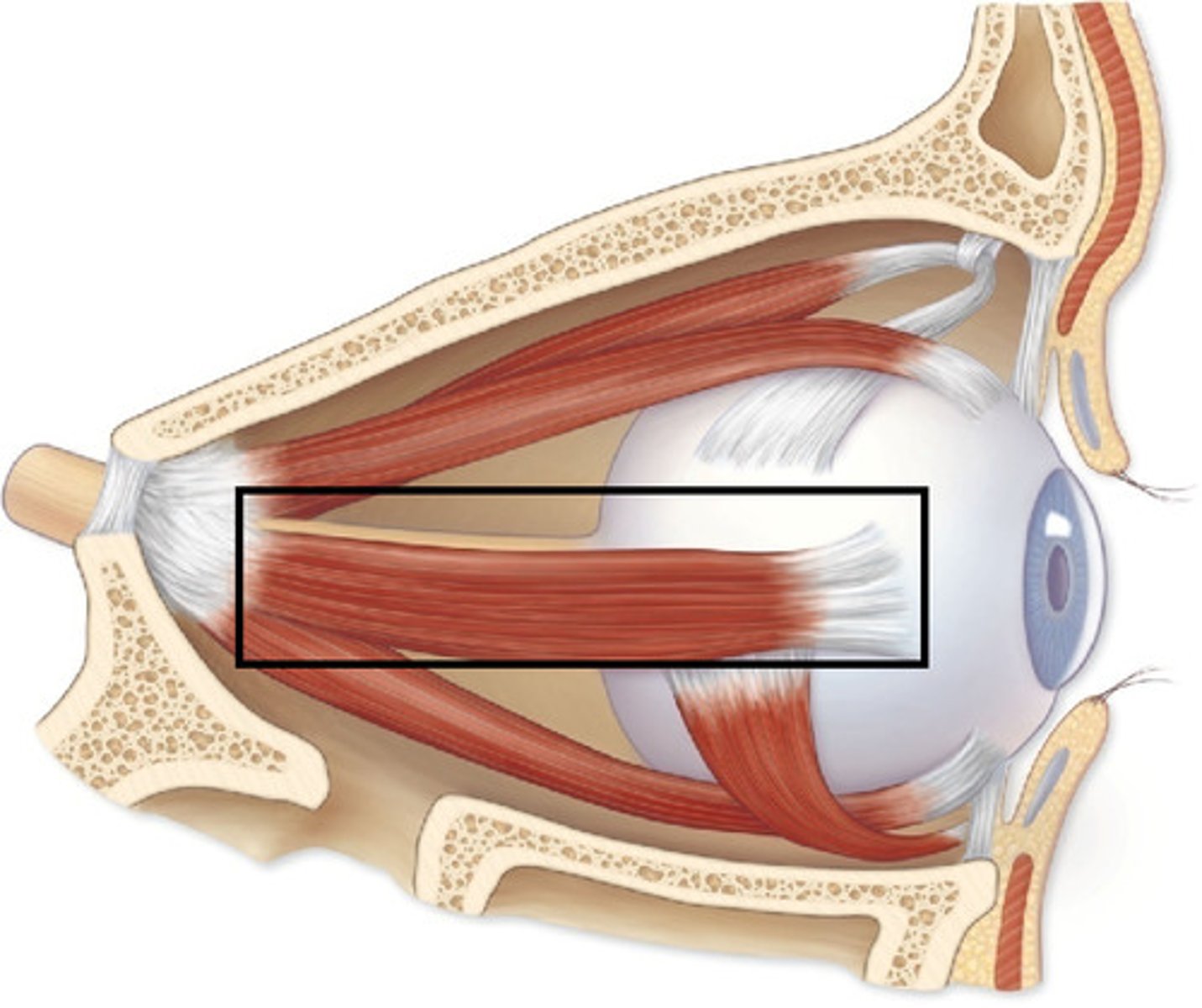
Lateral rectus muscle in eye
Inferior oblique muscle in eye
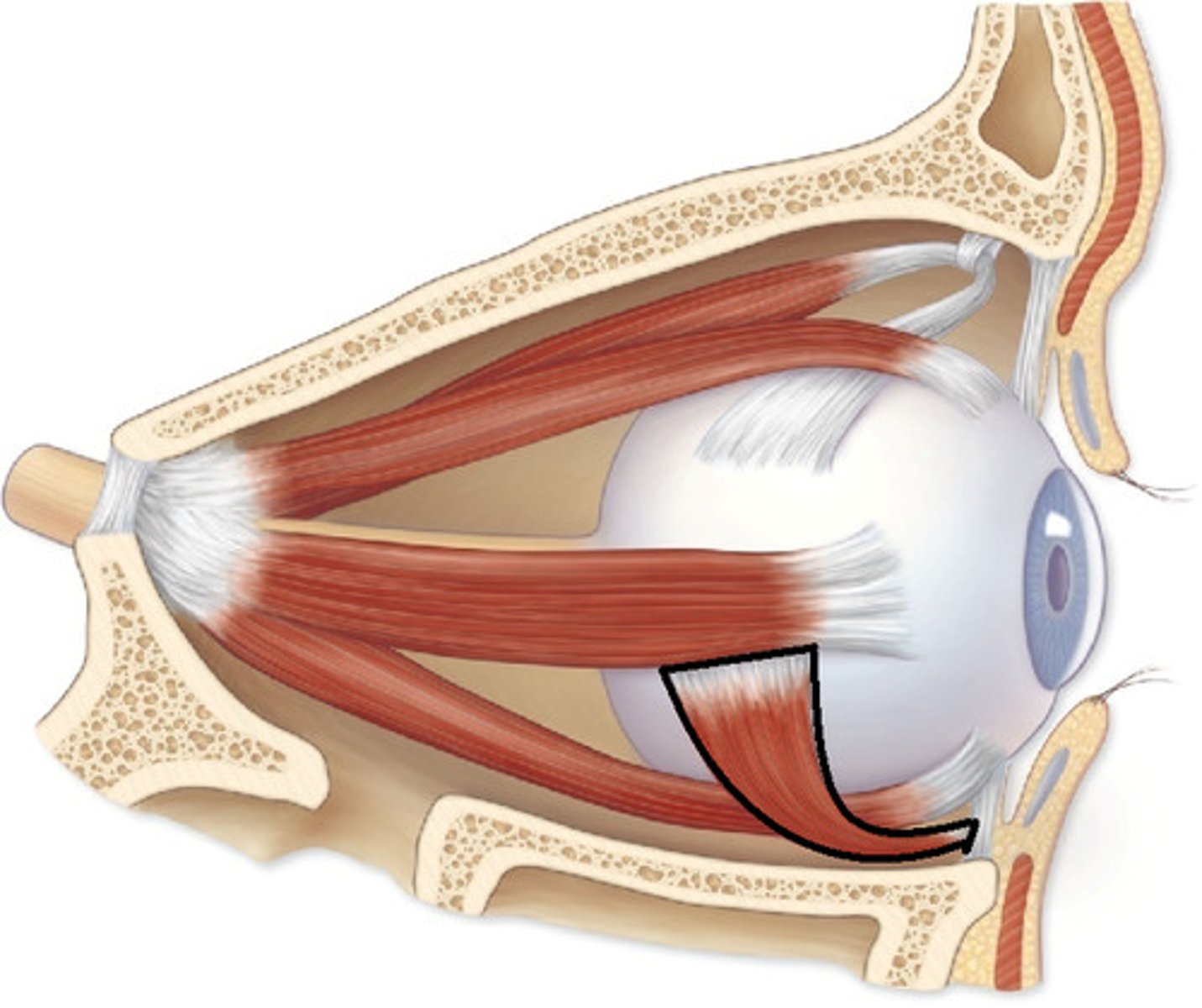
Inferior rectus muscle in eye
Ciliary body
B
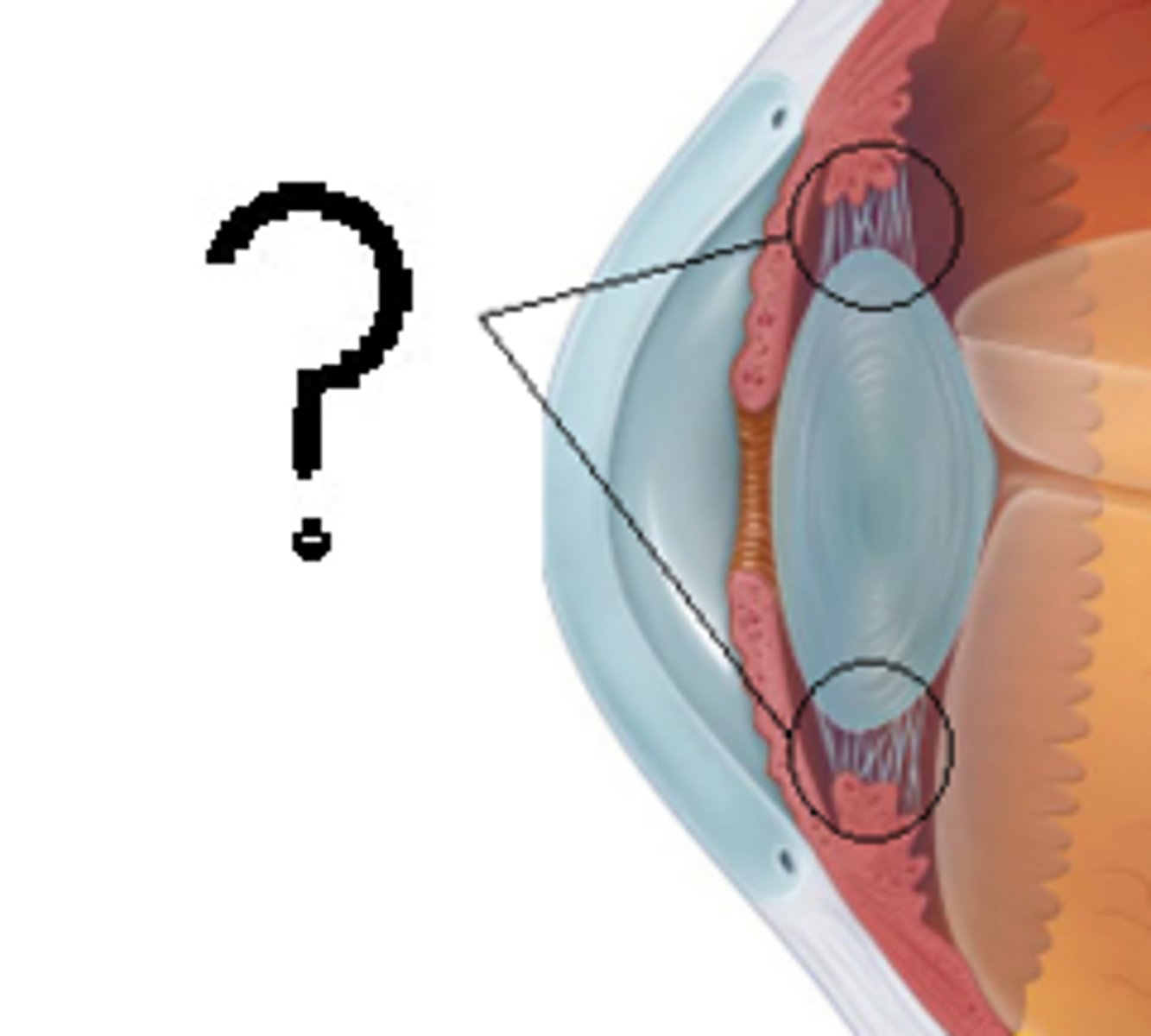
Ciliary Zonule
Cornea
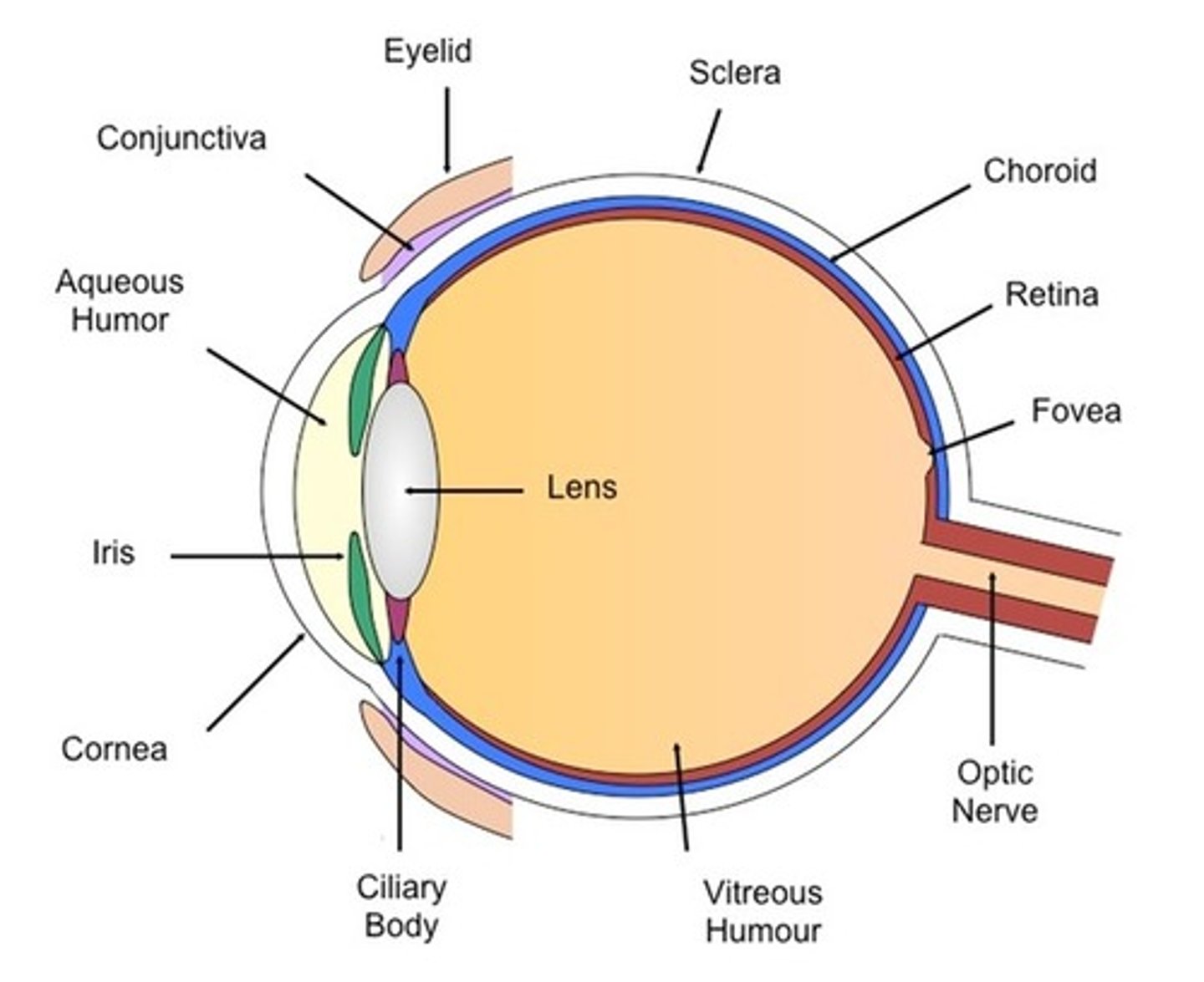
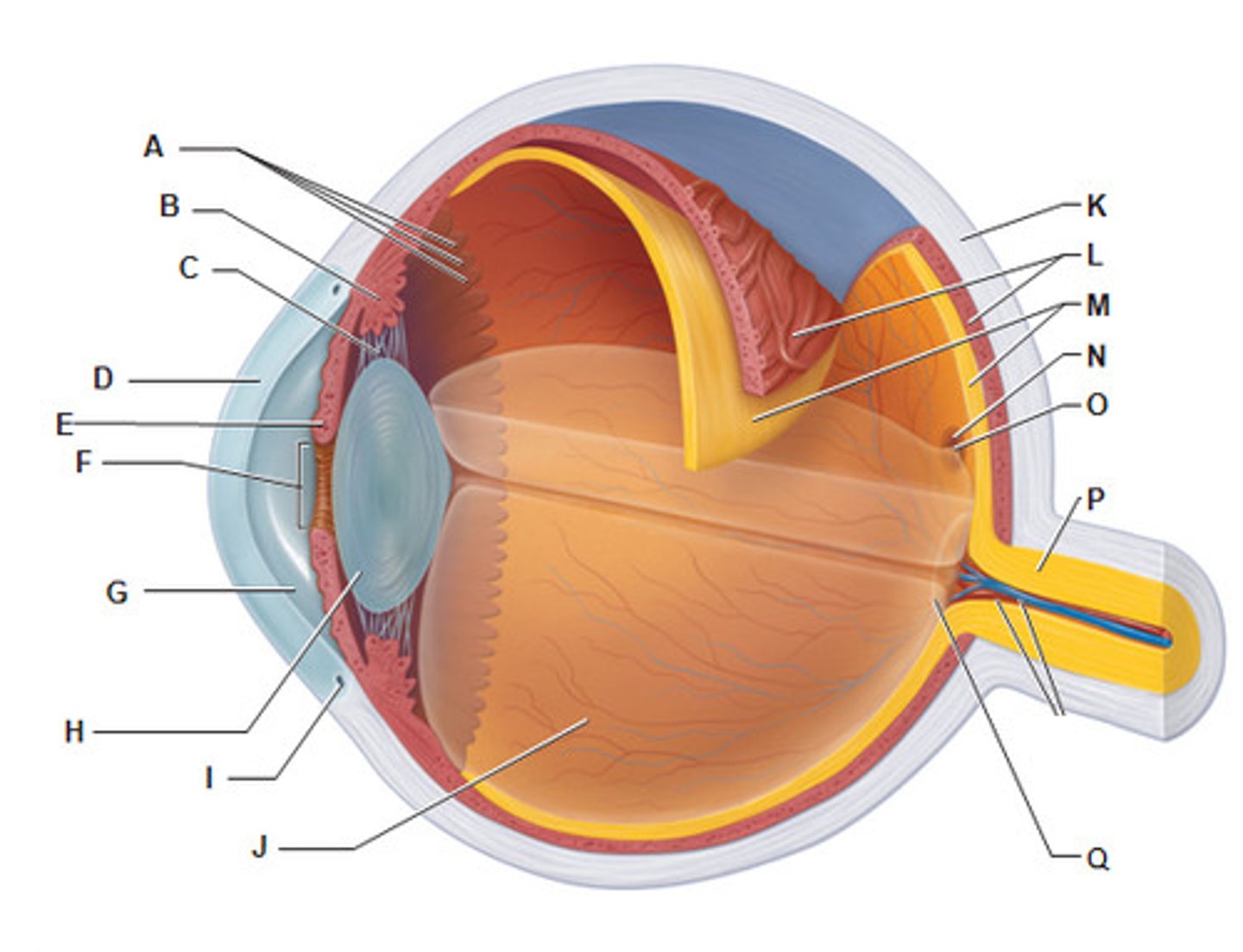
Iris internal eye
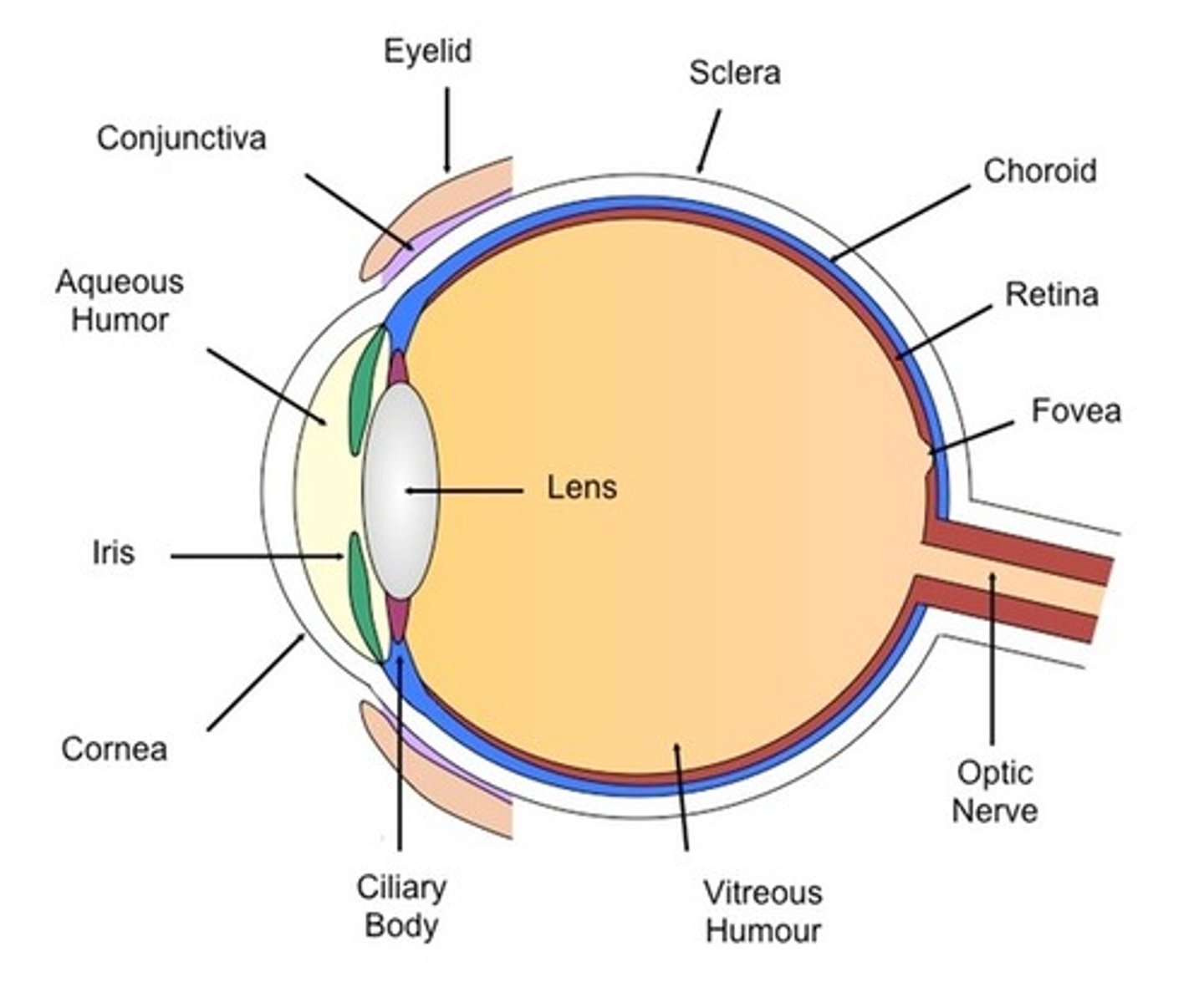
Pupil internal eye
space between the iris
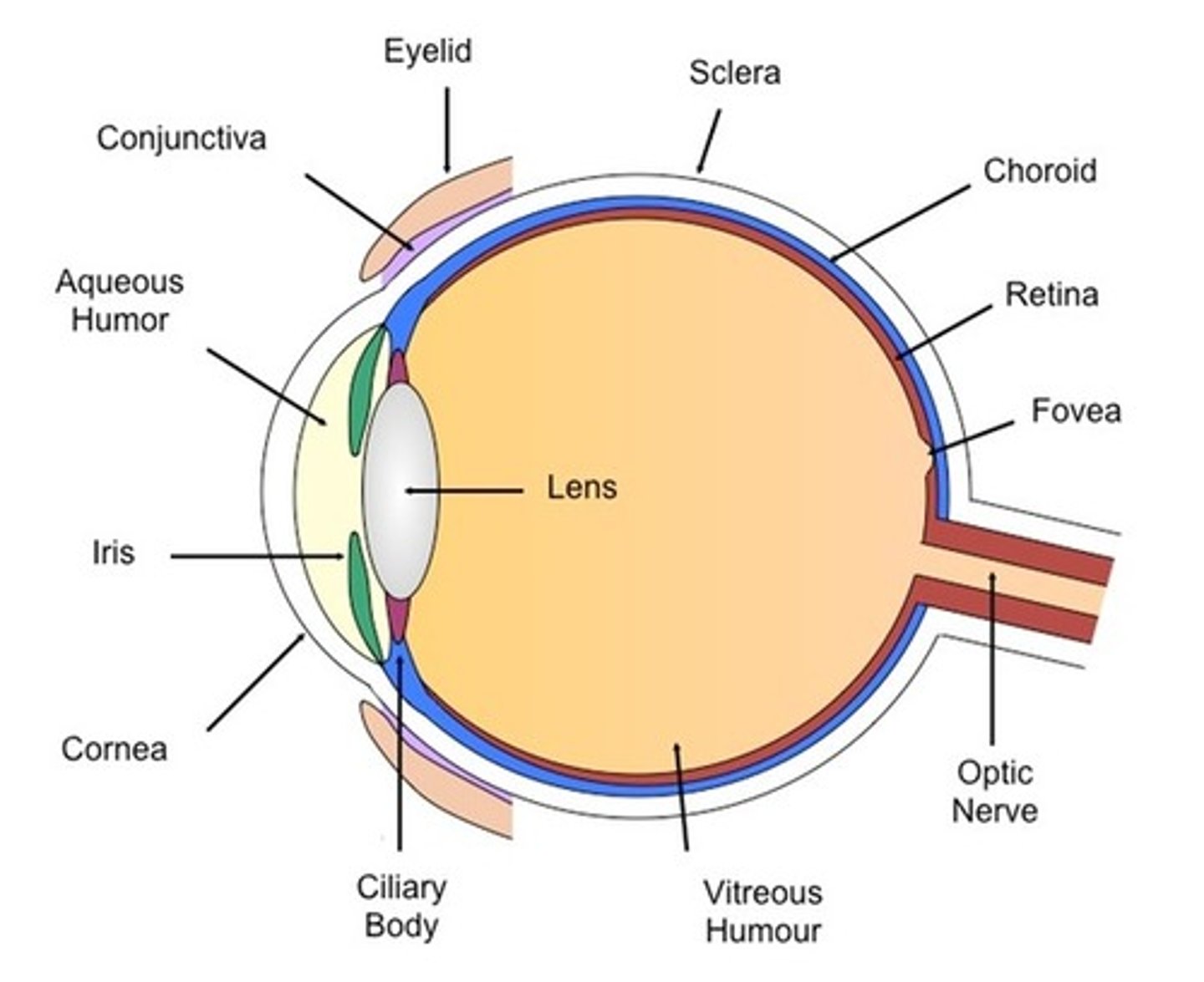
anterior Segment (contains aqueous humor)
G
Lens (internal eye)
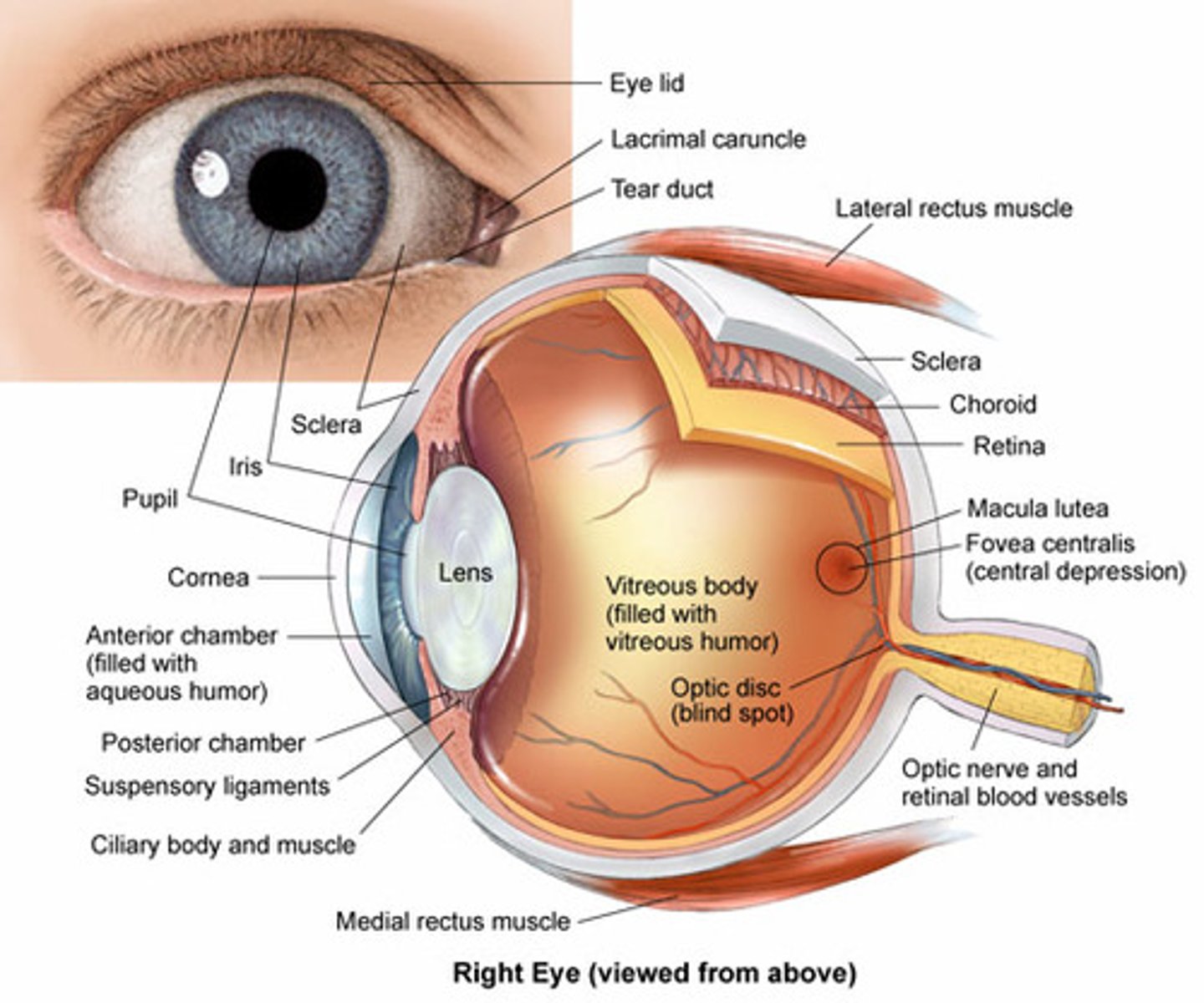
Scleral venous sinus
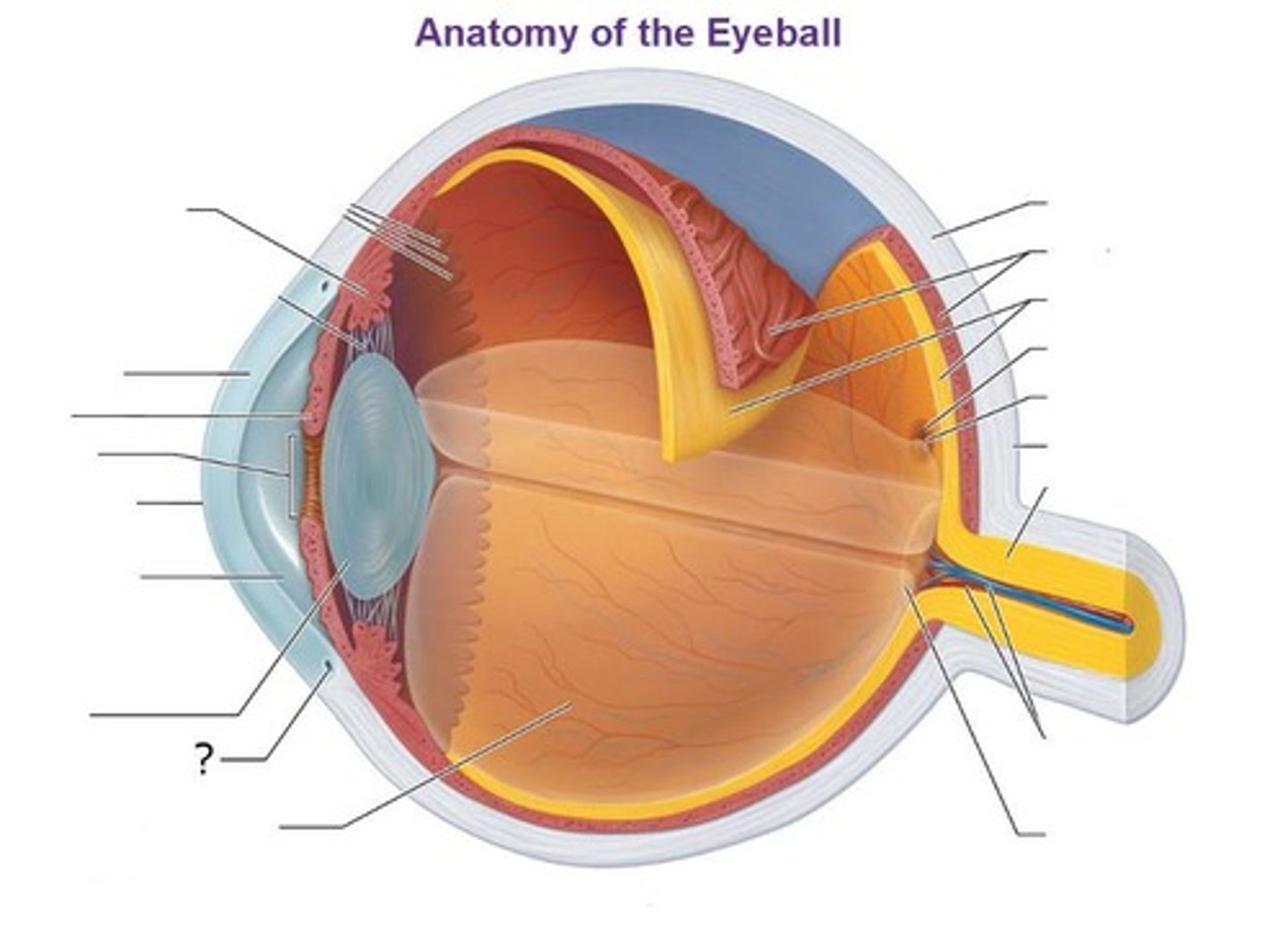
Posterior Segment (Contains vitreous humor)
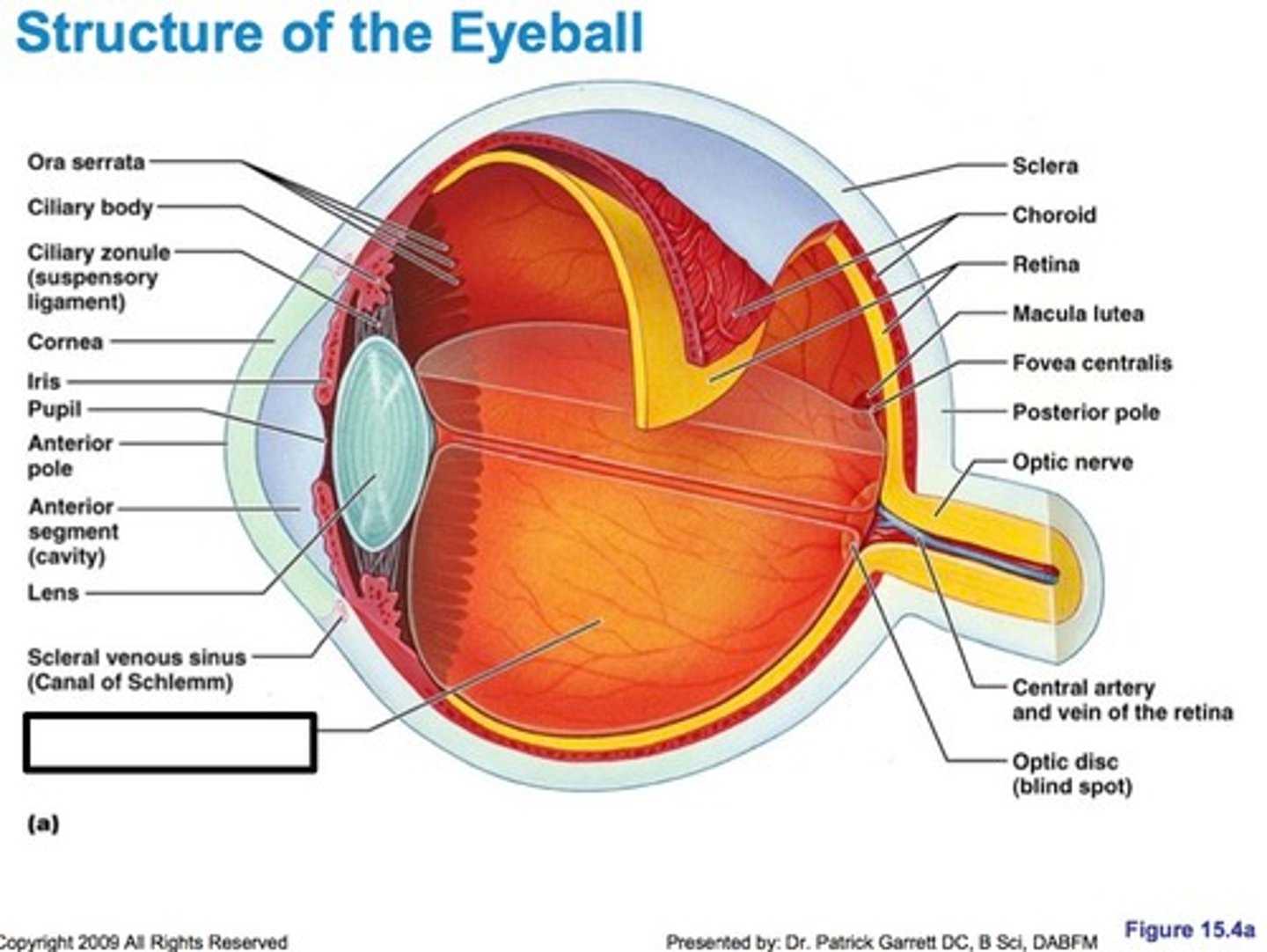
Sclera (Internal eye)
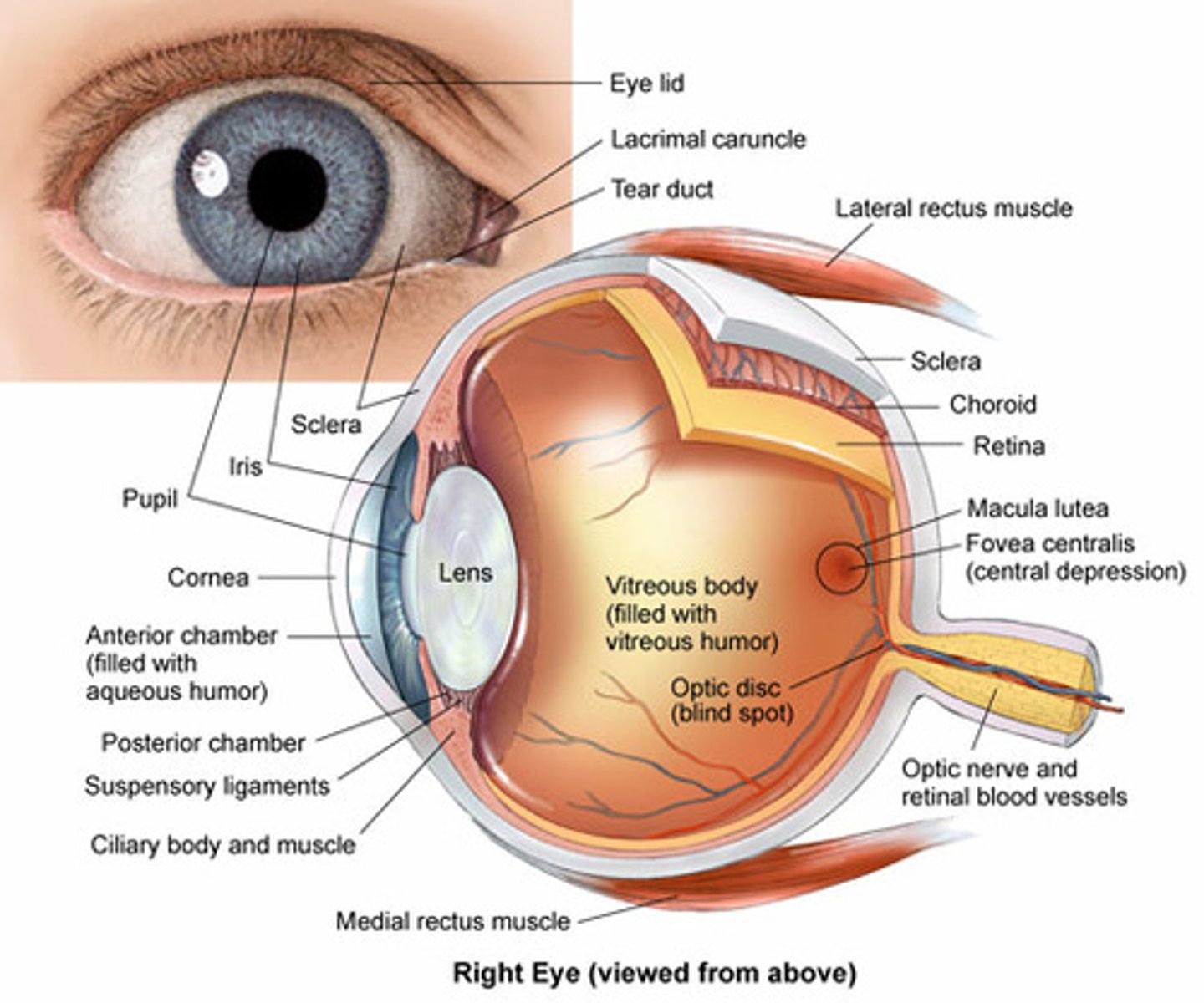
Choroid (Internal eye)