Hematology Exam 1 Study Guide
1/154
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
155 Terms
What are the 7 formed elements found in the blood?
RBCs
Neutrophils
Basophils
Eosinophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Platelets (thrombocytes)
What are the three parts that blood separates into when centrifuged?
Plasma (top)
Buffy Coat (middle)
RBCs (bottom)
What elements make up the buffy coat?
white blood cells and platelets
What color tube do you need for a CBC?
purple
What color tube do you need for a serum chemistry?
red
____ - the fluid portion of blood, which still contains clotting factors?
plasma
____ - the fluid portion of blood which remains after the sample is allowed to form a clot
serum
_____ - the most common WBC in all domestic species except ruminants. Single nucleus with three to five lobes. Faintly blue or pink cytoplasm with pink granules in the cytoplasm.
segmented neutrophil
____ - raerly seen in normal blood smears, most commonly seen in equine blood smears. Nucleus is elongated to slightly indented, and the cytoplasm is light purple with few to numerous small, round purple granlues.
basophils
____ - Nucleus is very similar to neutrophils, but segments are less defined. The cytoplasm is faint blue with mutiple red to red-orange granules.
Eosinophils
____ - largest of all WBCs. The cytoplasm is abundant, bluish-gray, foamy, or ground glass in appearance, often containing multiple small to large vacuoles.
Monocytes
_____ - most common WBC seen in ruminants and lab animals. Smallest of the WBCs. The nucleus is round or oval and slightly indented, and the cytoplasm is a small amount of light blue
Lymphocytes
_____ - cells are biconcave disk shapes, non-nucleated, and pink to salmon to red in color
mammalian RBCs
____ - RBCs are oval and nucleated
Fish, bird, reptile, and amphibian RBCs
____ - RBCs are oval and non-nucleated
camelid RBCs
_____ - fragments of the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow. Small, anucleated, and discoid-shaped. Cytoplasm is light blue with multiple, fine, pink to purple granules.
Platelets
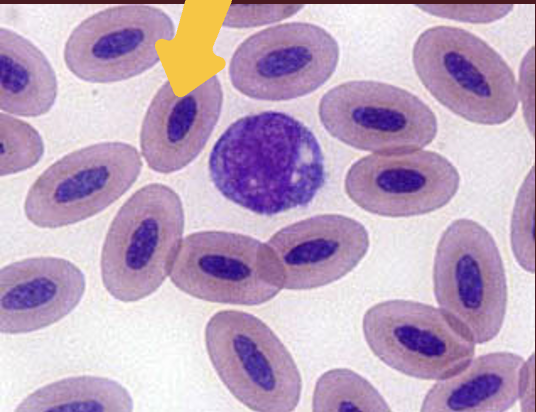
What species do these red blood cells belong to?
birds, fish, reptiles, amphibians
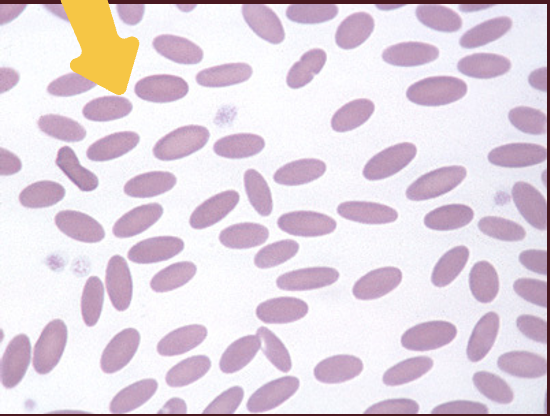
What species do these RBCs belong to?
camelids
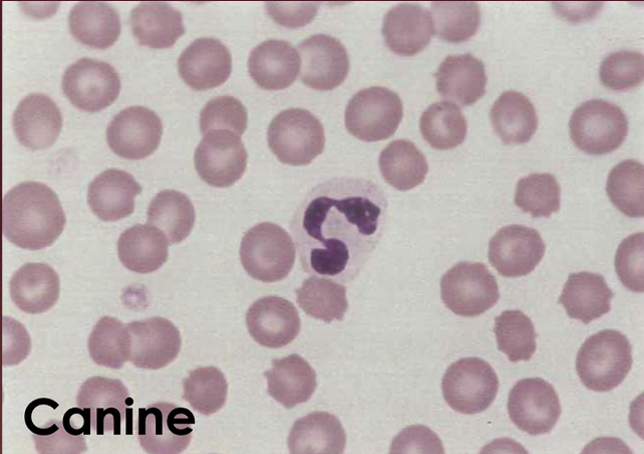
What type of WBC is this?
Neutrophil
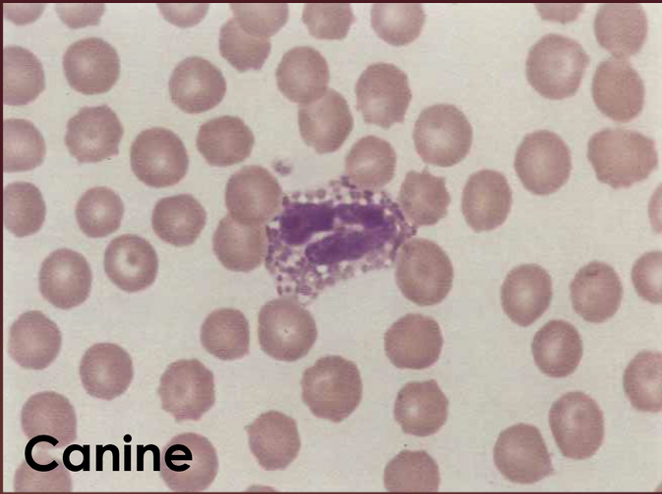
What type of WBC is this?
Eosinophil
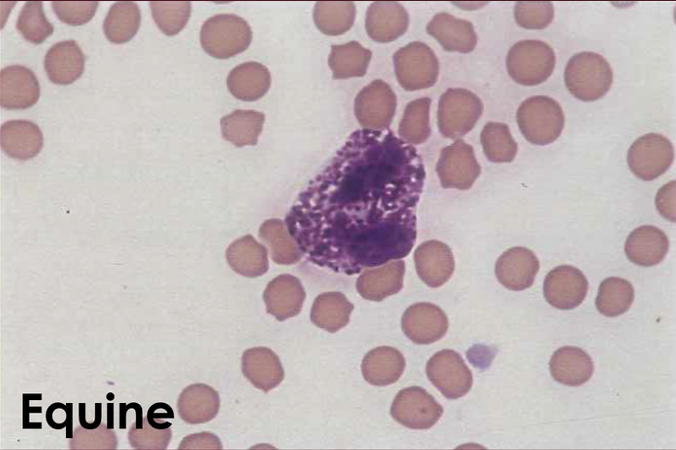
What type of WBC is this?
Basophil
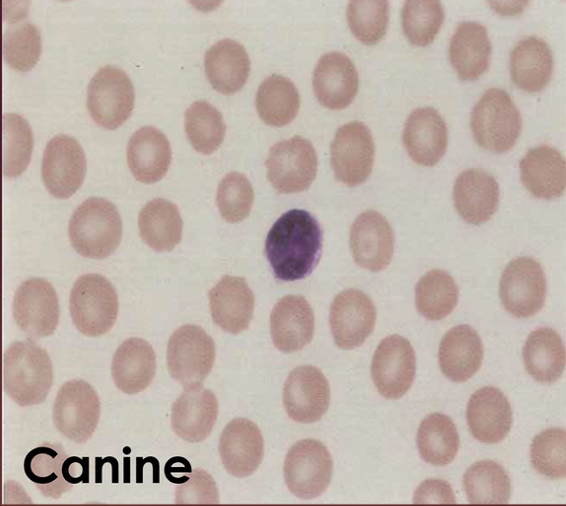
What type of WBC is this?
lymphocyte
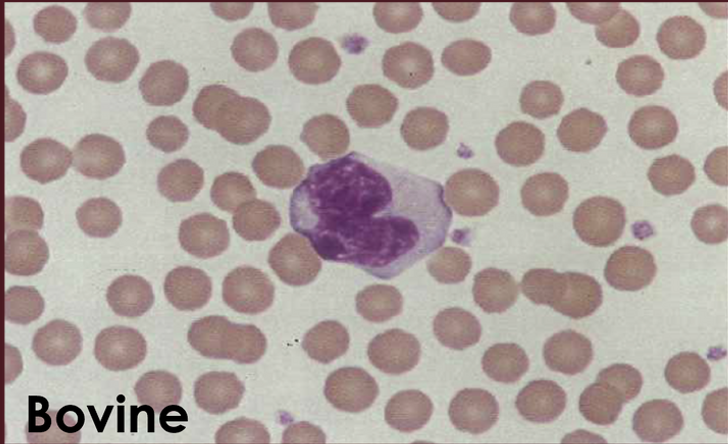
What type of WBC is this?
Monocyte
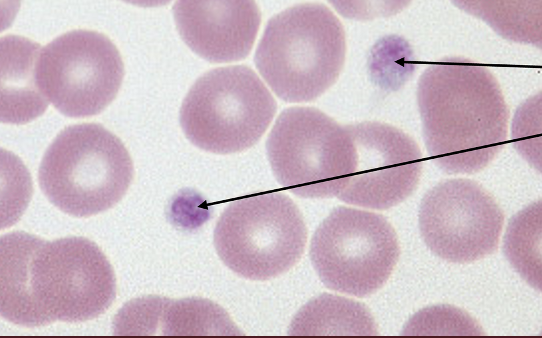
What type of cells are these?
platelets
What is the monolayer?
ideal zone for microscopic examination where red blood cells are distributed in a single layer, barely touching or slightly separated
Which species have nucleated RBCs?
birds
fish
reptiles
amphibians
Which WBC is the most common in domestic species except for in ruminants and rats/mice?
neutrophils
Which WBC is most common in ruminants, rats, and mice?
lymphocytes
Which WBC is the largest?
monocyte
Which WBC can become a plasma cell and produce antibodies?
B lymphocyte
____ - fragments of the cytoplasm of megakaryocytes in the bone marrow
thrombocyte
____ - functions to transport oxygen to tissue and remove CO2 and other waste
erythrocyte
____ - functions in counteracting foreign substances
leukocyte
What is the maximum amount of blood you can collect from small companion animals?
1% of the animal’s total body weight
What is the maximum amount of blood you can collect from birds?
1% of the animal’s total body weight
What is the maximum amount of blood you can collect from reptiles?
0.8% of the animal’s total body weight
What is the maximum amount of blood you can collect from pocket pets?
0.8 of the animal’s total body weight
What is the maximum amount of blood you can collect from large animals?
Animal’s weight (kgs) x 1000g/kg x 0.06 (6% total body weight) x .10 (10% of total blood volume to be collected within a 2-week time period.)
How much blood can you collect from any animal that is not considered healthy (sick or unstable)?
you should only take half of the calculated maximum volume
What is anisocytosis?
variation in RBC size
____ - RBCs are larger than normal
macrocytes
_____ - RBCs are smaller than normal
microcytes
_____ - RBCs are normal size
normacytic
Which RBC index assesses RBC size?
MCV = Mean Corpuscular Volume
High MCV =
macrocytic
Low MCV =
microcytic
Normal MCV =
normocytic
What is poikilocytosis?
Variation is RBC shape
When is poikilocytosis commonly seen?
in healthy goats and ruminant neonates
What is polychromasia?
variation is RBC color (RBCs with faint to obvious blue color)
What is hypochromasia?
RBCs have increased central pallor and less heme (pale in color)
What is hyperchromasia?
RBCs have decreased central pallor with “more” heme (darker in color)
Which RBC index evaluates hemoglobin concentration?
MCHC = Mean Corpuscular Hemoglobin Concentration
Low MCHC =
hypo chromic
High MCHC =
hyperchromic
Normal MCHC =
normochromic
Can we ever have a cell that is truly hyper chromic?
No, there is a limit for how much heme an RBC can have; they can’t be over-pigmented. It is simply a mistake in over-staining
What is the difference between rouleaux and agglutination?
Rouleaux = arrangement of RBCs in columns or stacks like coins.
Agglutination = antibody coats the RBC surface, causing clumping
Where is rouleaux most commonly seen?
in horses
What are some causes of rouleaux?
delay between time of collection and making the blood smear
refrigeration
inflammation
What test can you perform to differentiate between rouleaux and agglutination?
add a drop of saline to the slide, rouleaux will disperse and agglutination will remain clumped
Which RBC inclusions stain well with diff quik?
Basophilic stippling
Howell-Jolly bodies
Which RBC inclusions stain well only with New Methylene Blue?
Heinz bodies
Reticulocytes
Why might RBCs be macrocytic and polychromic on a blood smear?
If the RBCs are immature (Reticulocytes)
Why might RBCs be microcytic?
If the patient is suffering from autoimmune diseases or splenic disorders
What is an RBC shape that is typically described as microcytic and hyperchomic?
spherocytes
Why might poikilocytosis be present on a blood smear?
The most common form of poikilocytosis is echinocytes. They are an artifact of the preparation of the blood film due to the slow drying of the blood
The most commonly seen shape variation among RBCs are what?
echinocytes
What might be the reason for mammalian RBCs to be nucleated?
Nucleated RBCs appear when they are prematurely released from the bone marrow. This can be caued by extreme demand, such as anemia
What is significant about Howell-jolly bodies?
the nucleus is single, round, and randomly located within the cell
What is significant about heinz bodies?
Nucleus is a small, round to irregular, refractile denatured hemoglobin that can be single or multiple within the cell or on the surface.
Which cell type is associated with oxidative damage?
Heinz bodies
Heinz bodies are commonly seen where?
in healthy cats
When might you expect to see basophilic stippling?
With heavy metal toxicity, particularly lead poisoning
What does a reticulocyte look like when stained with diff quik?
cells will stain bluish with diff quik but the clumps of dark staining material will not be visible
What does a reticulocyte look like when stained with New Methylene Blue?
Clumps of dark staining material can be seen in the RBC cytoplasm
____ - general term for any thin or flattened RBC
leptocyte
What causes leptocytes to be present on a blood smear?
leptocytes are usually seen with anemia
____ - aka target cells - contains a thicker darker staining center surrounded by a lighter staining area and a darker periphery
codocytes
_____ - bar cells - darker staining central area which extends across the cell with a pale are on either side
Knizocytes
_____ - Elongated, often curved, central pale area often resembling a mouth or smiley face
stomatocytes
____ - crenated RBCs (RBCs that have shrunk)
echinocytes
_____ - aka burr cells
acanthocytes
What is the primary difference between echinocytes and acanthocytes?
Echinocytes = characterized by blunt projections evenly distributed around the periphery of the cell
Acanthocytes = multiple irregularly spaced, rounded or club-like projections over the entire surface of the RBC
Acanthocytes are associated/seen with what?
liver and kidney diseases and rattlesnake bites in dogs
after exercise in horses
lymphosarcoma in dogs
____ - irregular RBC fragment due to mechanical damage to the cell membrane
schistocyte
_____ - aka helmet cell
Keratocyte
_____ - teardrop shaped RBC. Due to failure of the normal RBC to resume its shape after passage through the capillaries
Dacryocyte
____ - sickle cell
Drepanocyte
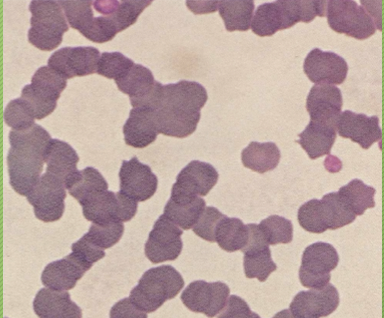
What cell arrangement is this?
Rouleaux
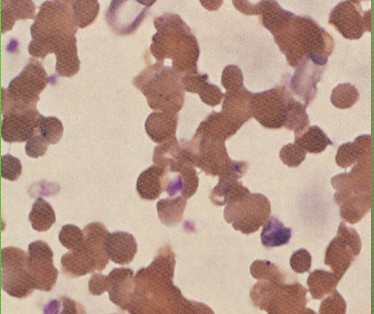
What cell arrangement is this?
Agglutination
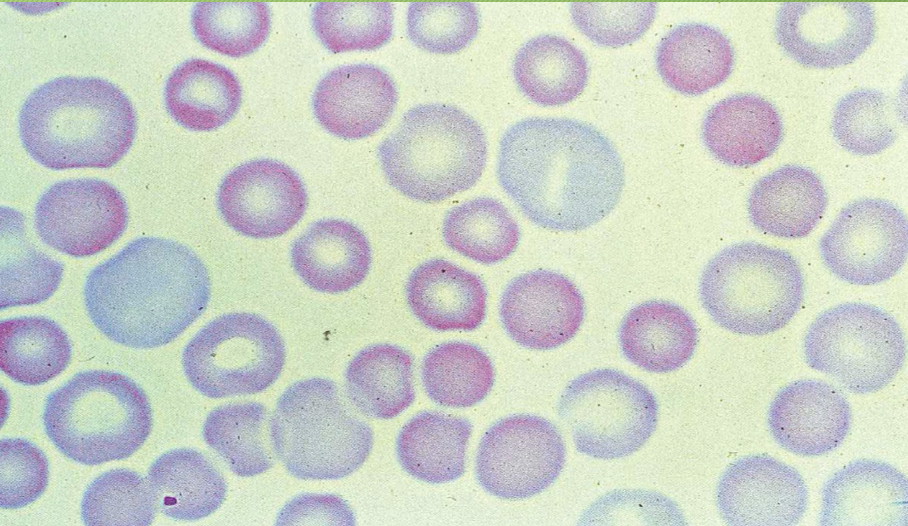
This is an example of what kind of cell abnormality?
anisocytosis
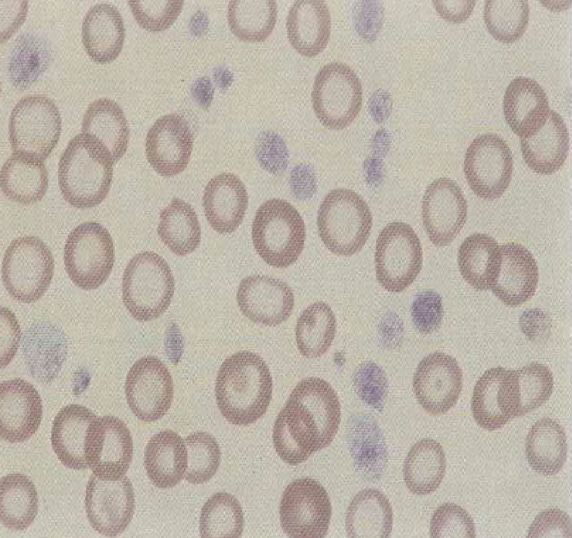
What type of cell abnormality is this?
Hypochromic
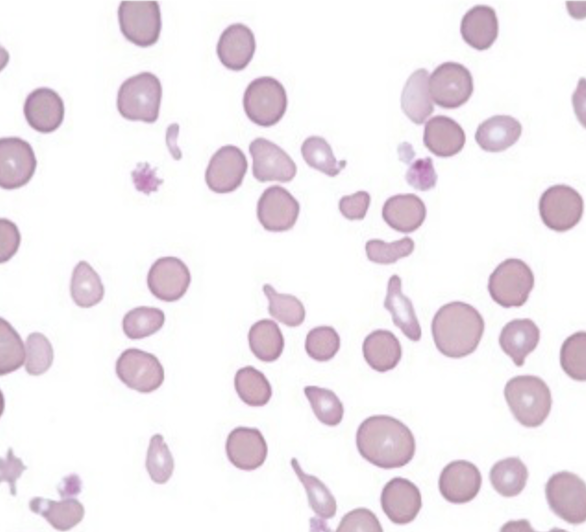
What type of cell abnormality is this?
Poikilocytosis
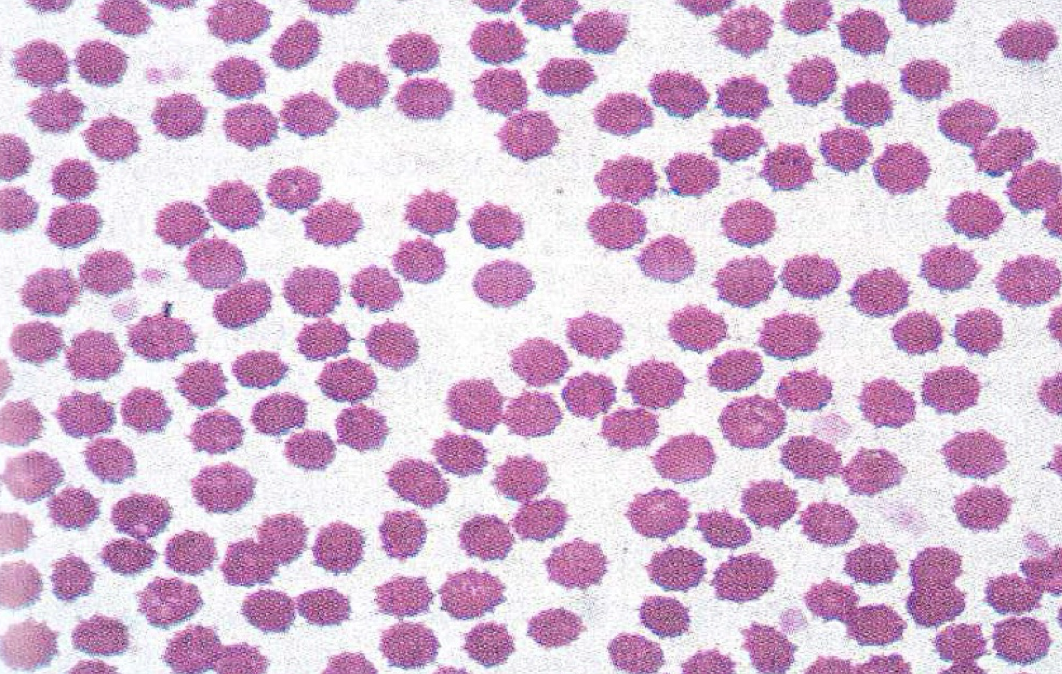
What type of cell is this?
Echinocytes
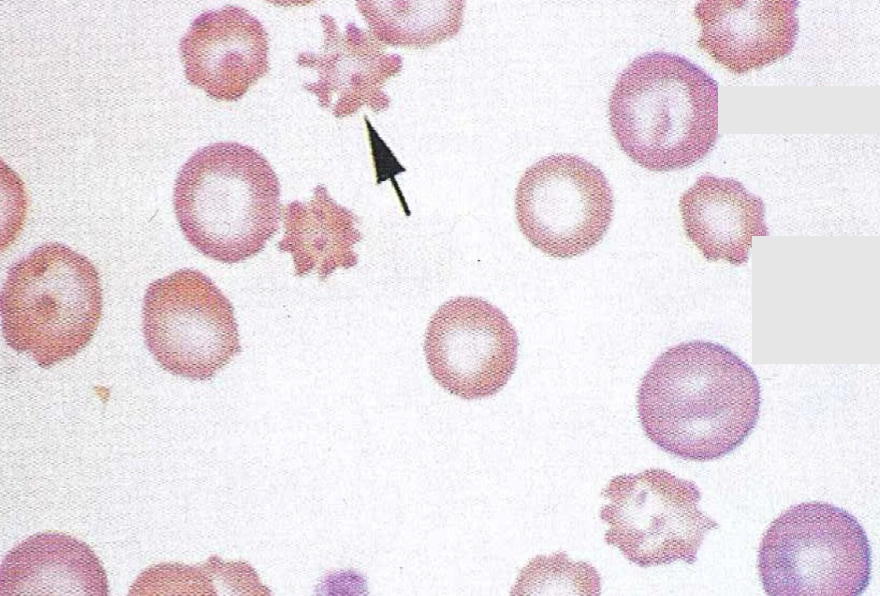
What type of cell is this?
Acanthocyte
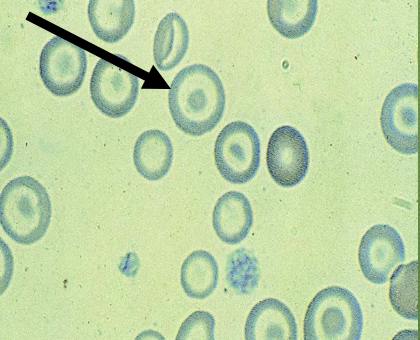
What type of cell?
Codocyte (target cell)
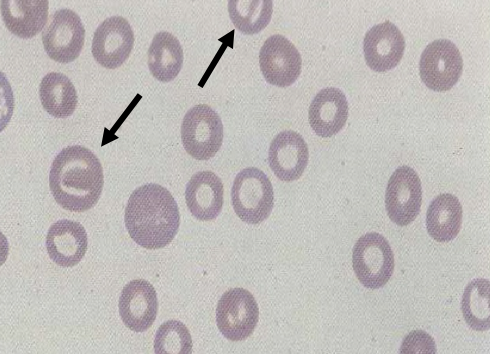
What type of cell?
Knizocytes (bar cells)
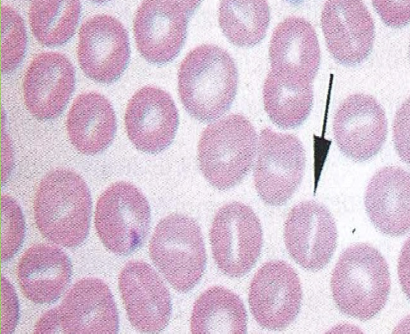
What type of cell?
Stomatocytes
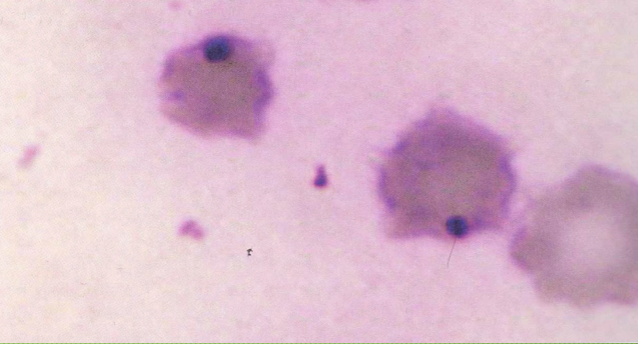
What type of cell?
Howell-Jolly bodies (diff quik stain)