Infiltration (Week3)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Infiltration
water in ground surface enters soil
Infiltration Capacity
max rate at which the ground can absorb water
Field Capacity
volume of water the ground can hold
Rate of Infiltration
f = fp when i > or equal to fp
f = i when i > fp
fp - infiltration capacity
f - actual rate of infiltration
i - rainfall intensity
(all in cm/hr units)
Factors Affecting Infiltration Capacity
Characteristics of Soil
Surface of Entry
Fluid Characteristics
Measurement of Infiltration
Flooding-type infiltrometers
tube-type
double-ring type
Tube-type
2-3hrs duration
as infiltration proceeds, the volume is made up by adding water from a burette to keep water level at tip of pointer
Double-ring type
water depths at both rings are kept the same
measurement of water volume is done on inner ring only
Disadvantages of Infiltrometers
raindrop effect us not simulated
driving of the tube or rings disturb the soil structure
results of infiltrometers depend to some extent on their size with larger meters giving less rates than smaller ones
Modelling Inflitration Capacity
focus on the curve as it is an important part on calculation and plotting the graph
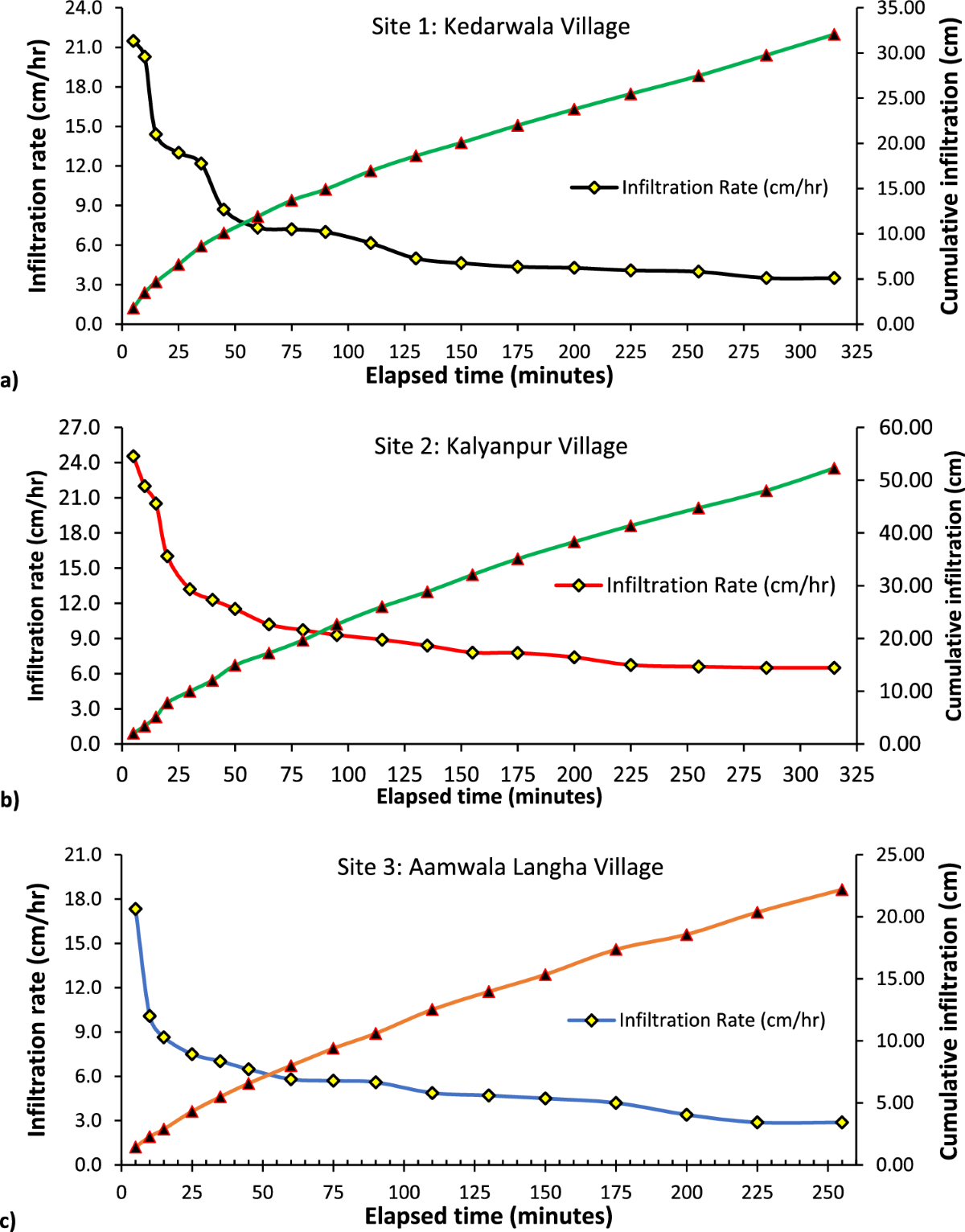
Infiltration rate, fp(t)
rate at which water enters the soil at surface (in/hr or cm/hr)
Cumulative Infiltration, Fp(t)
accumulated depth of water infiltrating during given time period
Cumulative Infiltration Capacity, Fp
accumulation of infiltration over a time period since the start of process
Equations to Express Infiltration Capacities
Horton’s (ONLY ONE DISCUSSED)
Philip’s
Kostiakov
Green-Ampt
Horton’s Equation
fp - infiltration capacity at any time t from start of rainfall
fo - initial infiltration capacity at t = 0
fc - final steady state of infiltration capacity occurring at t = tc, aka constant rate of ultimate infiltration capacity
k - horton’s decay coefficient
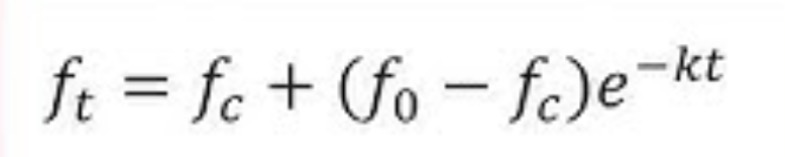
Infiltration Indices
used in hydrological calculations involving floods
constant value of infiltration rate is assumed during the duration of storm
Two types:
Phi Index (Only discussed)
W Index
Phi Index (Φ)
average rainfall above which is the runoff
derived from hyetograph and resulting runoff value
Rainfall excess - amount of rainfall in excess of the index, also called effective rainfall
expressed in length/time (mm/hr, in/hr, etc)
Runoff = Total Rainfall - Infiltration
Runoff = Total Rainfall - Φ(te)
where te = duratiom of rainfall excess values are in terms of depth
Infiltration = Φ(te)