Tongue: structure, papillae, muscles
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Tongue is supported caudally by?
Hyoid bone
Tongue consist of?
Striated muscle
CT and adipose tissue
Glands
Thick mucous membrane
Function of tongue
Important tactile organ by mechanical or taste buds (chemical selection of food)
Prehension
Sorting of solid food
Mastication
Deglutition
Delivers insalivated bolus into pharnyx
What are the 5 nerves that innervate the tongue and which is the only motor nerve?
Mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (V)
Facial nerve (VII)
Glossopharyngeal nerve (IX)
Vagus nerve (X)
Hypoglossal nerve (XII, motor nerve)
Structure of Tongue
Dorsum linguae
Apex
Frenulum linguae
Corpus linguae
Radix linguae
Dorsum linguae: Upper surface of tongue
Apex: Tip of tongue
Frenulum linguae: Thin membrane fold under tongue
Corpus linguae: Main body
Radix linguae: Back part of tongue that connects to throat
Where is the tongue located?
Lies in the intermanibular space
How is the tongue anchored to mandible and hyoid apparatus?
Extrinsic lingual muscle
Which animals’ body of tongue has extensive lateral surfaces?
Herbivores and pig
Structure specific to ruminants
Has torus linguae
Raised bump at back of tongue
Fossa linguae
Groove infront of it
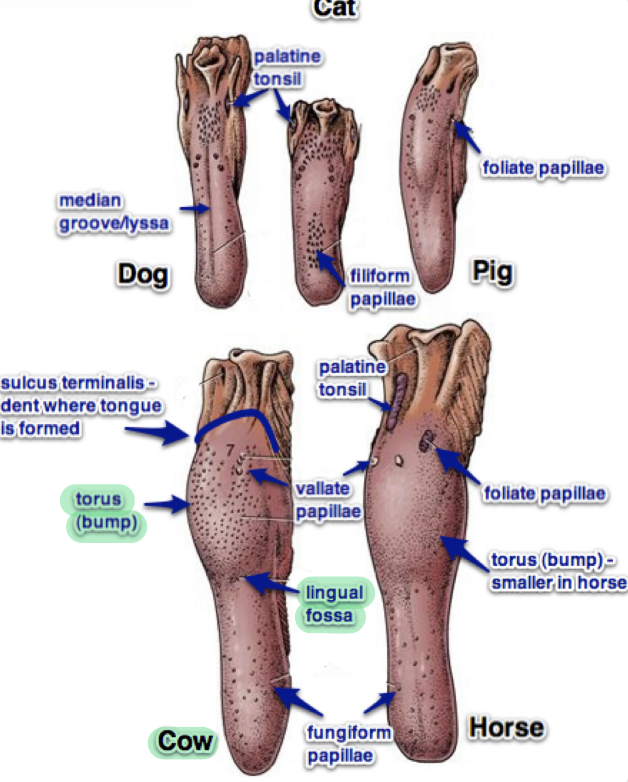
Structure specific to horse
Has cartilage bar in the middle of tongue
Structure specific to dog
Has median groove (dorsum)
Mucous membrane is thin and delicate
Which animals have thick and tough mucosa in their dorsum?
Ruminent and cats
Mucous membrane has numerous?
Papillae
What are the 5 types of tongue papillae?
Filiform papillae
Conical and lenticular papillae #ffca00
Fungiform papillae
Vallate papillae
Folliate papillae
Which papillaes are mechanical?
Filiform papillae
Conical and lenticular papillae
Which papillaes are gustatory?
Fungiform papillae
Vallate papillae
Folliate papillae
Filiform
Shape
Heavily cornified in
Soft and long in
Located in radix (back) in only which species
Shape: Soft and horny
Heavily cornified in: Ox and cats
Soft and long in: Carnivores and pigs
Located in radix (back) in only which species: Carnivores and pigs
Conical & Lenticular Papillae
Location
Location: Scattered among filiform (especially on torus linguae)
Fungiform Papillae
Location
Function
Location: Dorsum (upper surface)
Function: Taste buds
Vallate Papillae
Location
Pairing in
Pigs & house
Carnivores
Ox
Sheep
Goat
Location: Dorsum (upper surface)
Pairing in:
Pigs & house: 1 large pair
Carnivores: 2-3 pairs
Ox: 8-17 pairs
Sheep: 18-24 pairs
Goat: 12-18 pairs
Foliate Papillae
Location
Present in which animals
Absent in
Location: Border of tongue
Present in: Horse, pig and dog
Absent in: Ruminants
Which 3 papillaes are found in all domestic animals
Filiform
Fungiform
Vallate
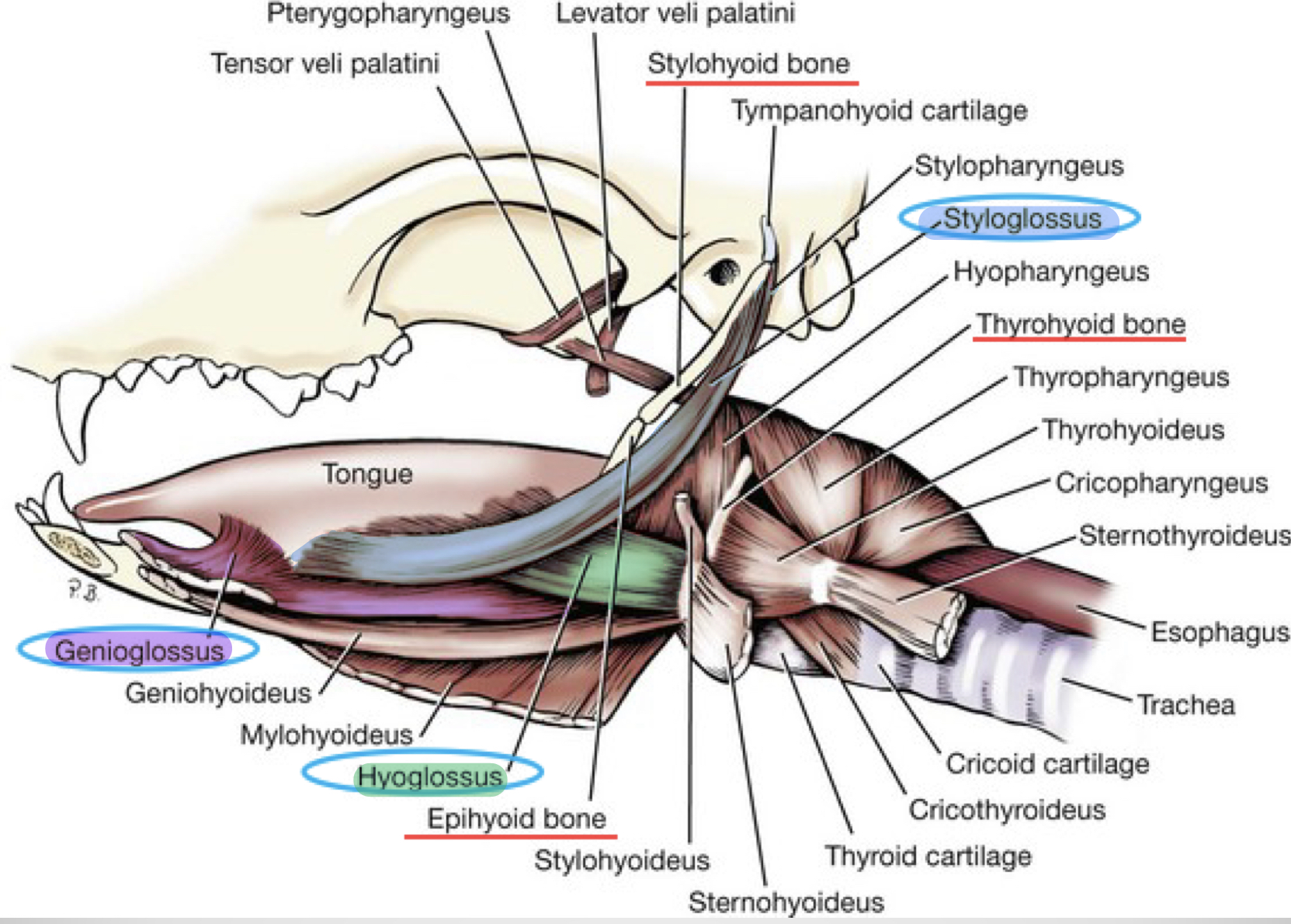
What are the 2 types of lingual muscles found in the tongue?
Intrinsic lingual muscle
Extrinsic lingual muscle
Intrinsic Lingual Muscle
Relationship with tongue
Consist of
Relationship with skeleton
Types of directions
Able to
Relationship with tongue: Bulk of tongue
Consist of: Deep and superficial fibres bundles
Relationship with skeleton: Not attach
Types of directions:
Longitudinal
Perpendicular
Transverse
Able to: Alter shape of tongue
Extrinsic Muscles
Originate from
The 3 types
Originates from: Skeleton
3 types:
Genioglossus:
Fan shaped, lies next to median plane and separated by lingual septum
Hyoglossus:
Ventrolateral to tongue
Styloglossus:
Long, slender muscle originates from ventral end of stylohyoid
Masticatory Apparatus
What are the 3 things that aid in the masticatory aspect of oral cavity
Teeth and gums
Temporomandibular & symphysical joint of jaw
Masticatory muscles
What are the 3 masticatory muscles?
Temporalis
Massester
Pterygoid
Temporalis Muscle
Function
Large in
Function: Pulls mandible upwards
Large in: Dog and cats
Massester Muscle
Function
Small in
Better developed in
Function: Raise mandible and draw it towards active side
Small in: Dogs
Better developed in: Herbivores that make lateral and rotational movements when chewing
Pterygoid Muscle
Location
Function
Location: Medial to mandible
Function: Raise mandible and draws it inward