Brain
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
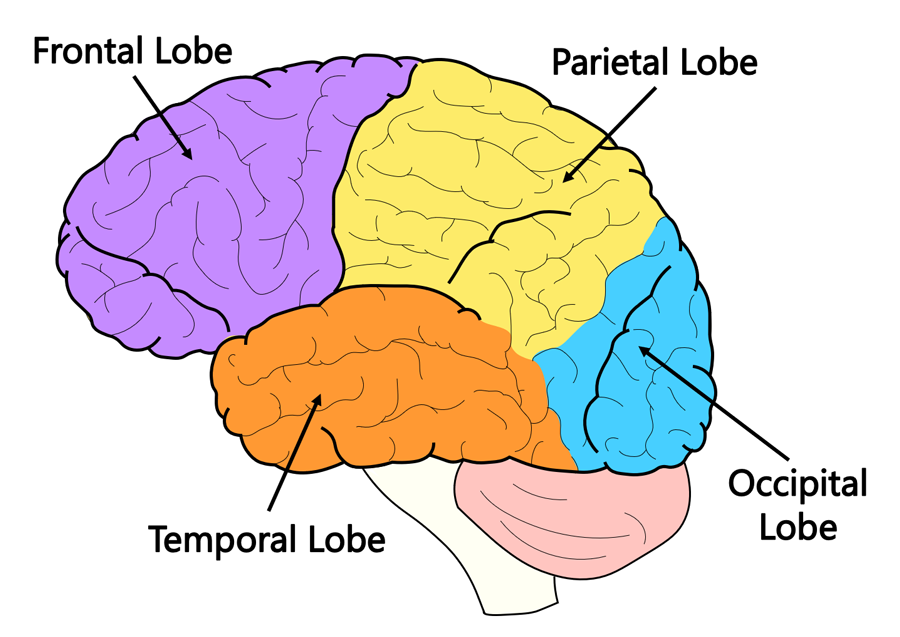
Major Lobes of the Brain
Frontal- thinking/ problem solving
Parietal- perception, numbers
Occipital- Visual
Temporal- audiitory and olfactory, deep and complex memories
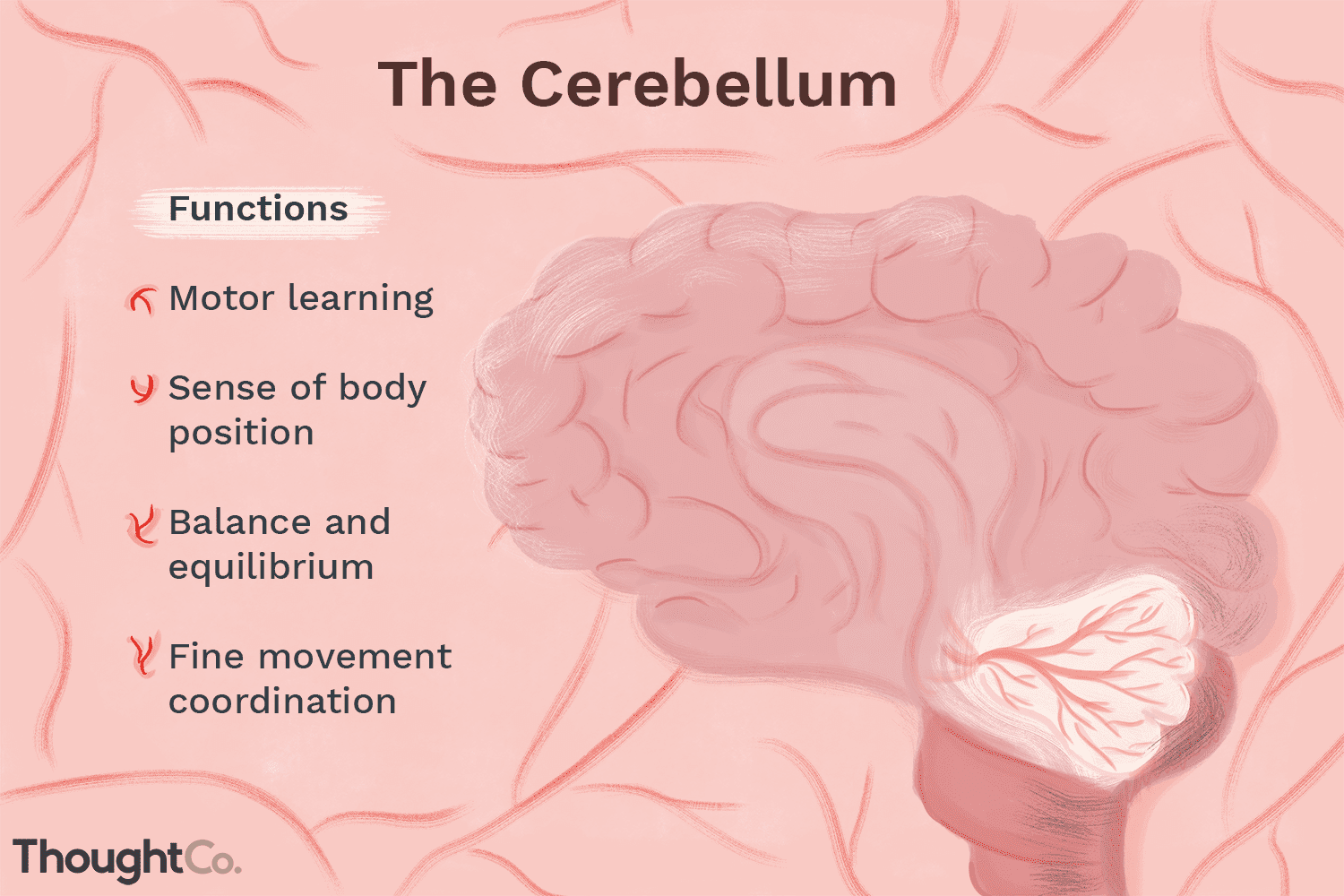
Cerebellum
coordinating movement and balance, processing information for motor control
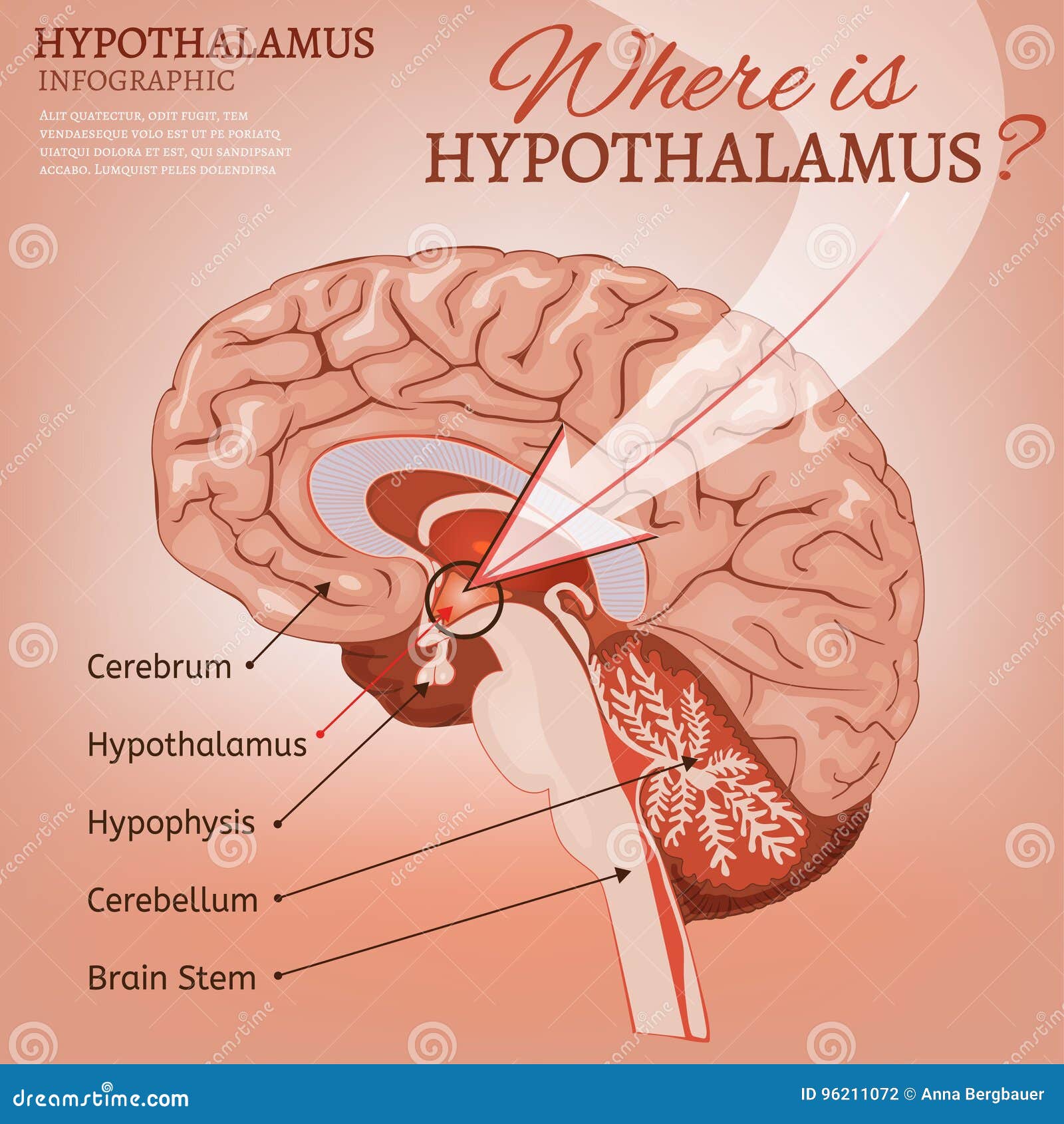
Hypothalamus
Under Thalamus
Autonomic nervous system center, regulates body temp, controls water balance, regulates metabolism, part of limbic system (emotions, tirst, hunger, pain etc)
Diencephalon
Parts: Thalamus Hypothalamus, Epithalamus
Sits on top of brian stem
Enclosed by the cerebral hemisphere
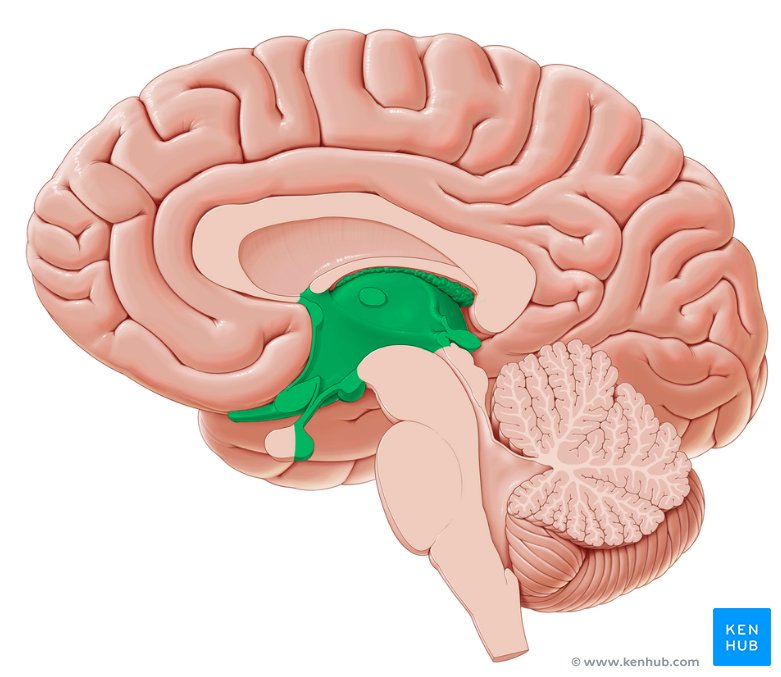
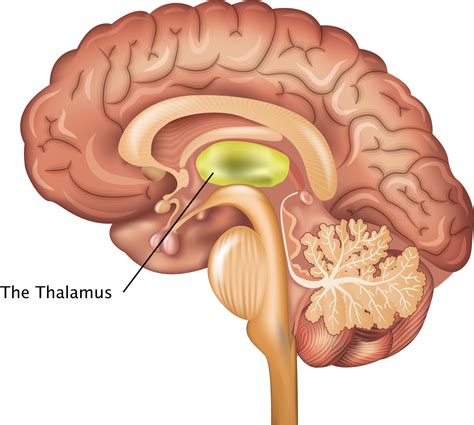
Thalamus
Surrounds third ventricle
Relay station for sensoy impulses
Transfer impulses to the corret par of the cortex for localization and interpretation
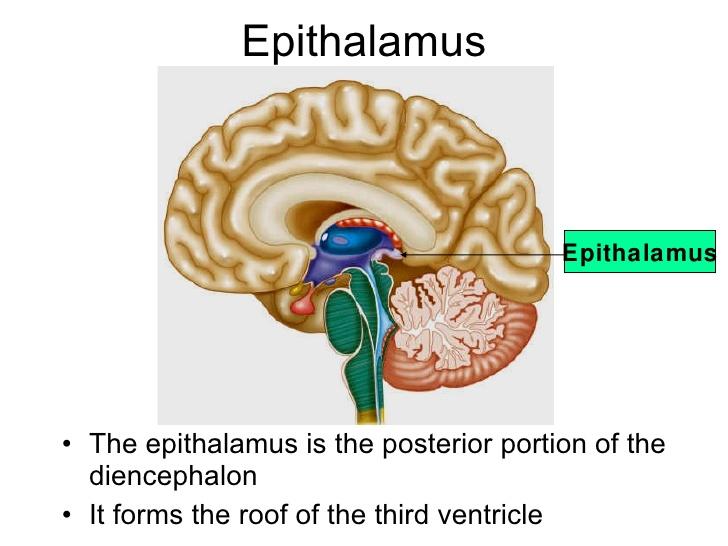
Epithalamus
Forms the roof of the 3rd ventricle
Houses the pineal body (endocrine gland)
Includes the choroid plexus
Forms cerbralspinal fluid
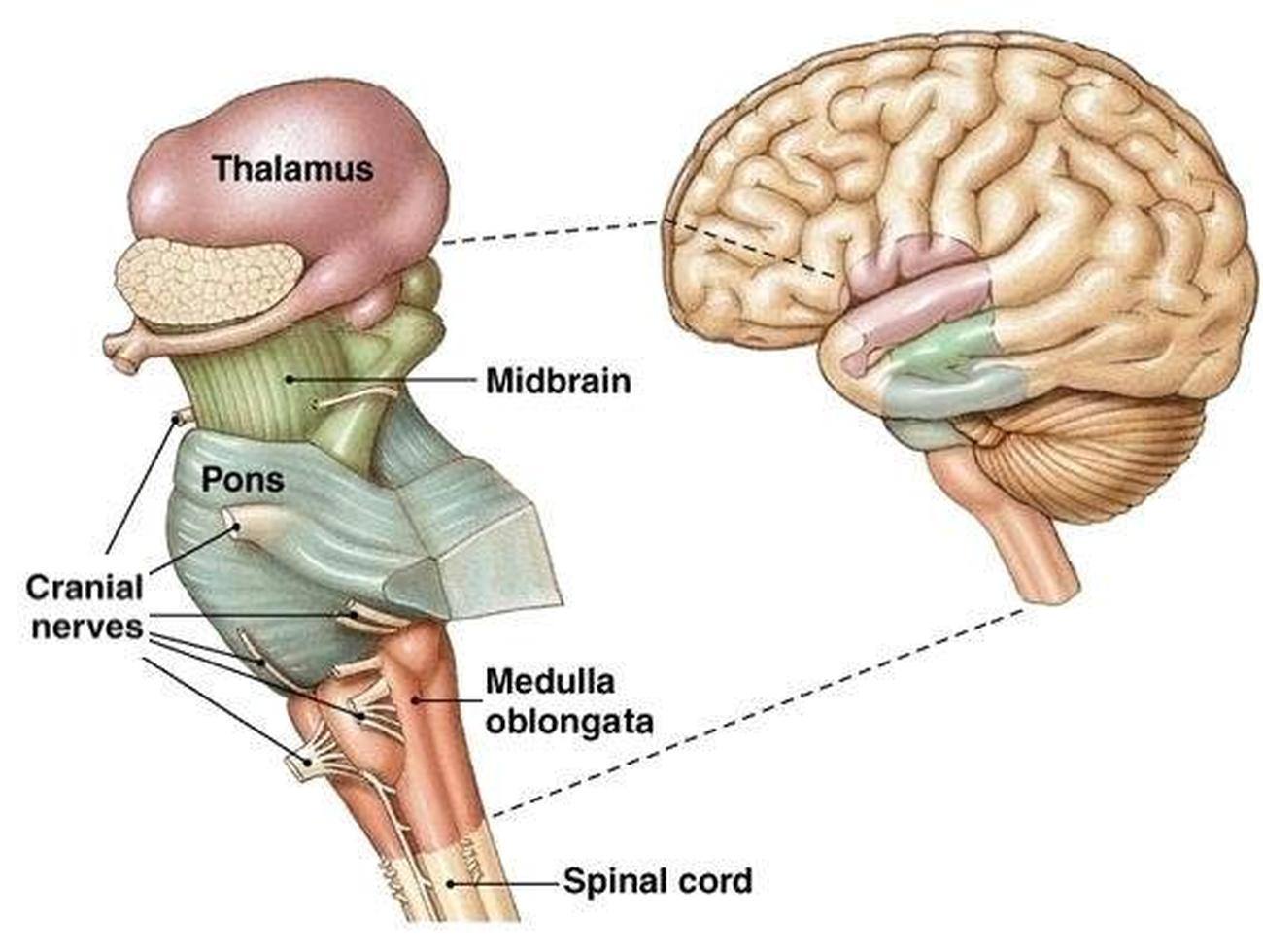
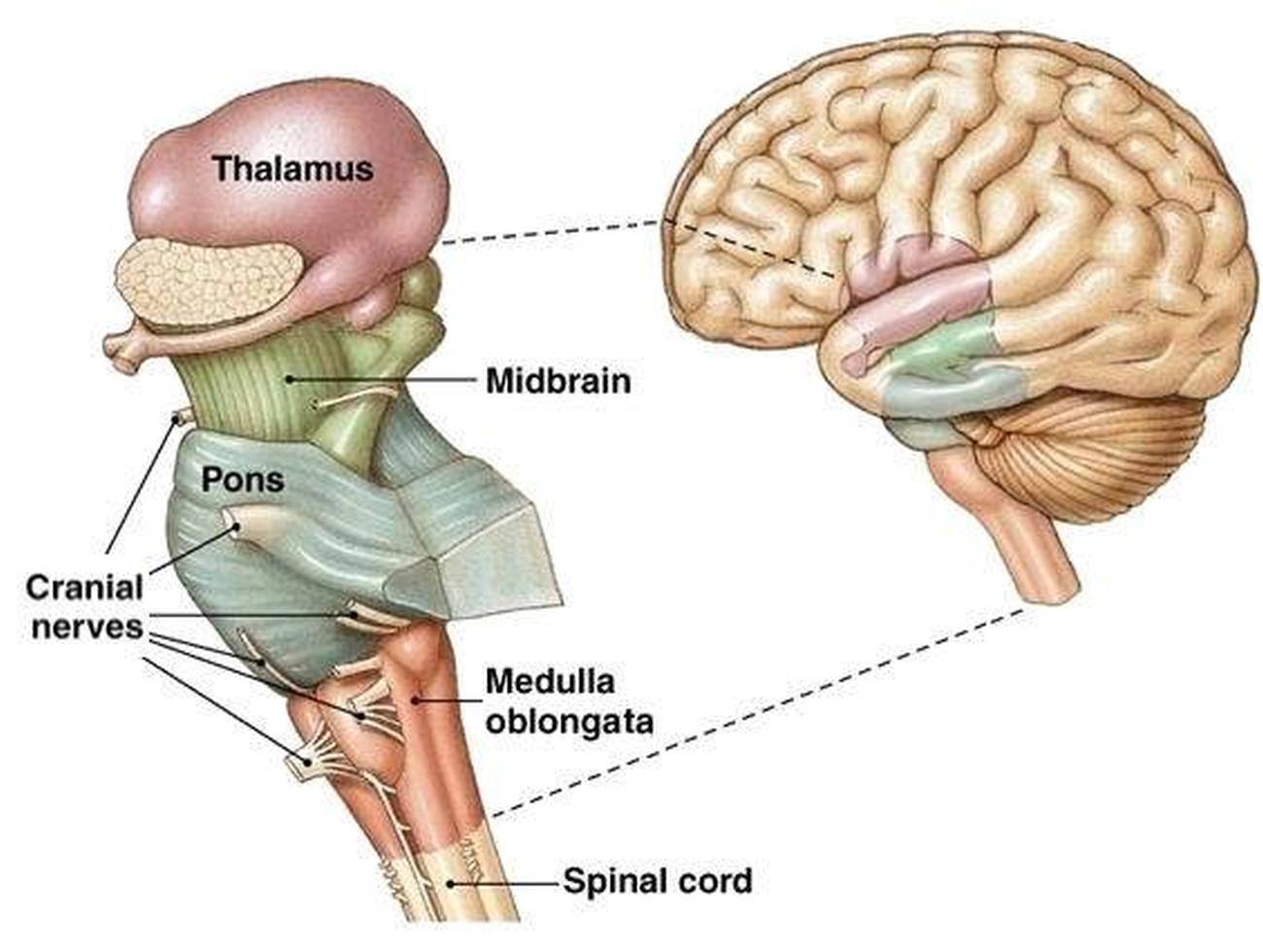
Brain Stem
Parts: Midbrain, Pons, Medulla oblongata
Controls breathing and blood pressure
Midbrain
Reflex centers for vision and hearing
Composed of tracts of nerve fibers
Has two buldging fiber tracts- cerebral peduncles
Has four rounded protrusions-corpora quadrigemina
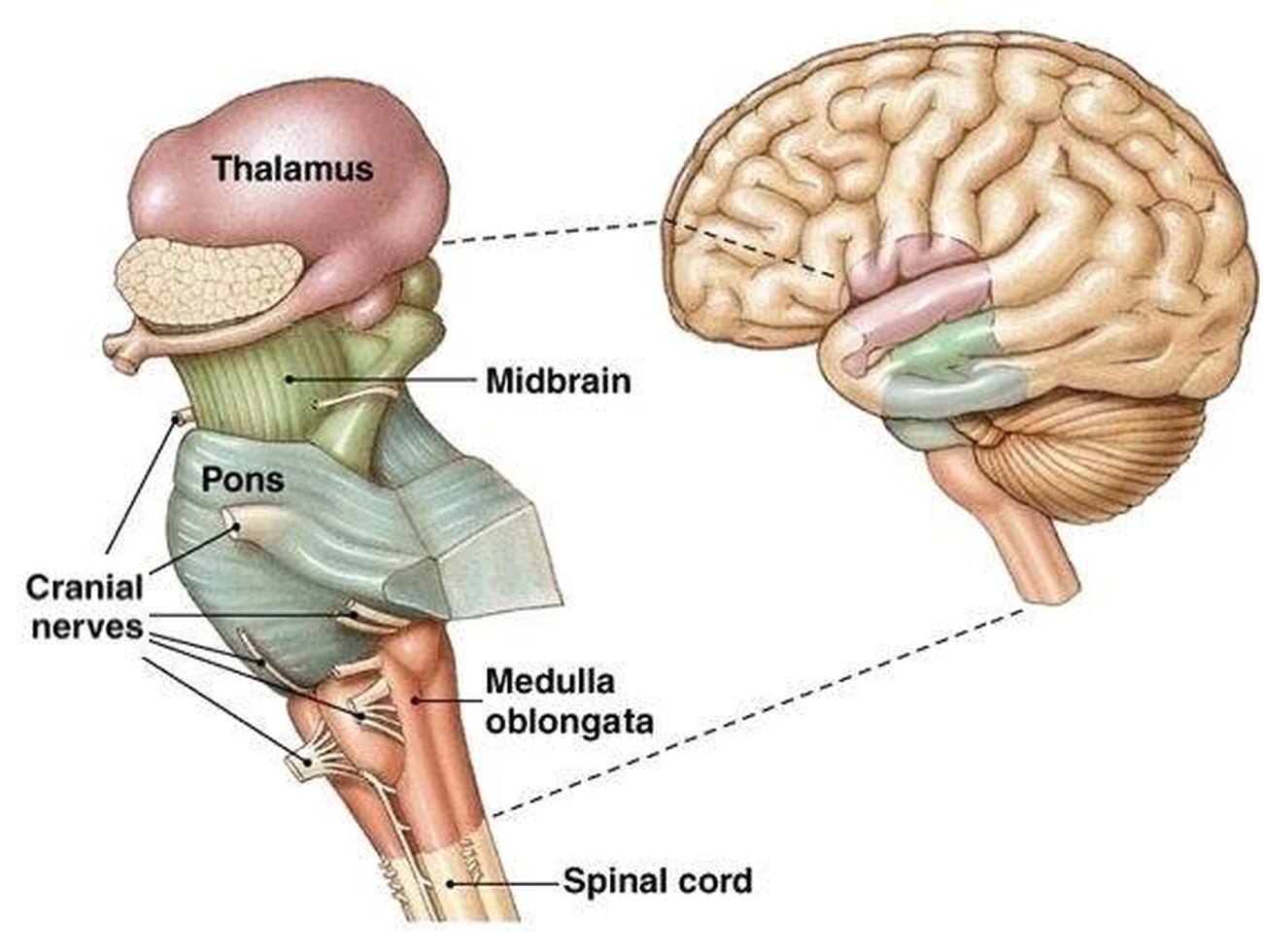
Pons
Nuclei involved in the control of breathing
composed of fiber tracts
buldging center part of brain stem
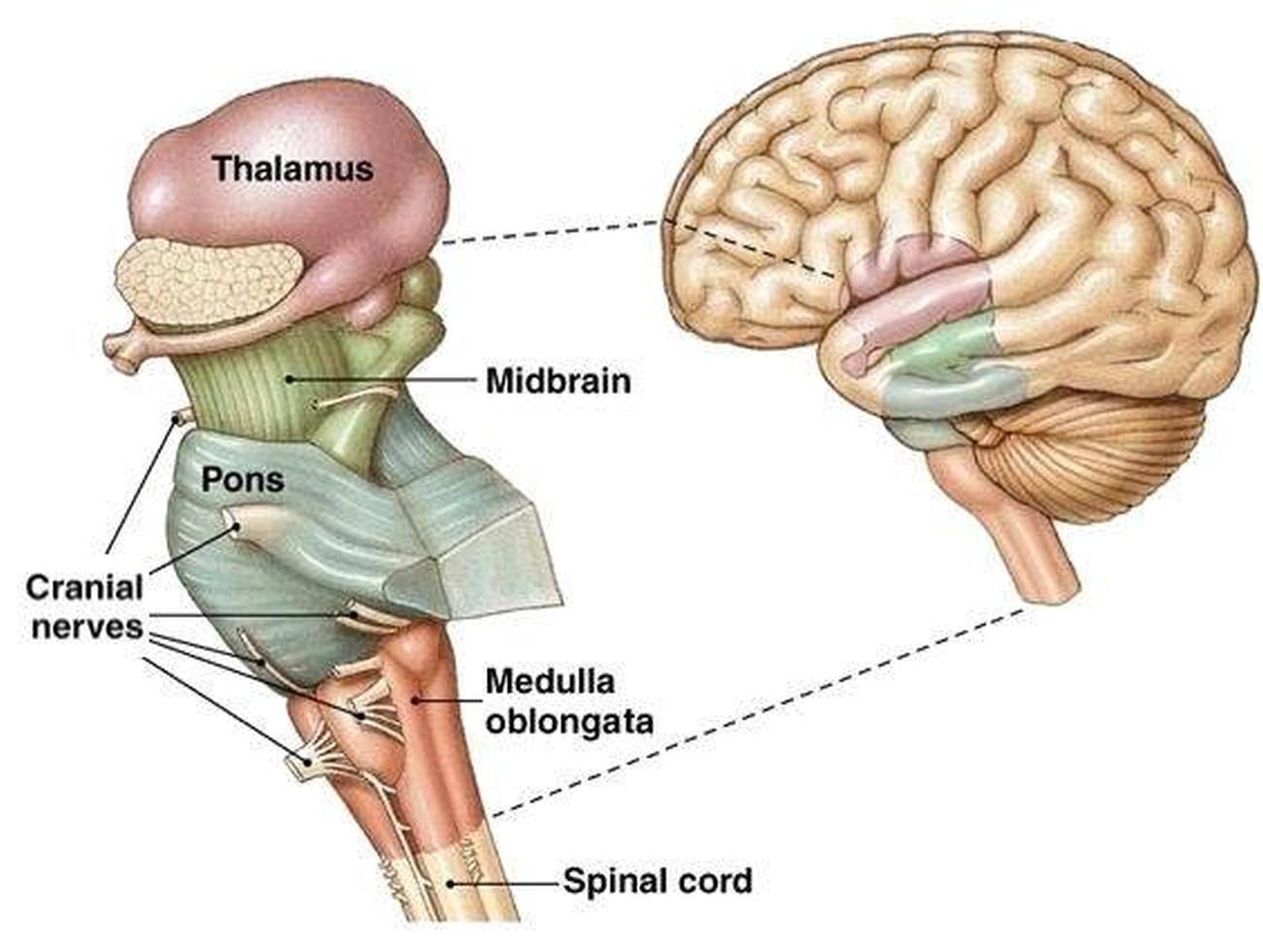
Medulla Oblogata
lowest part of brain stem, merges into spinal cord, fiber tracts
Controls heart rate, blood pressure, breathing, swallowing, vomitting
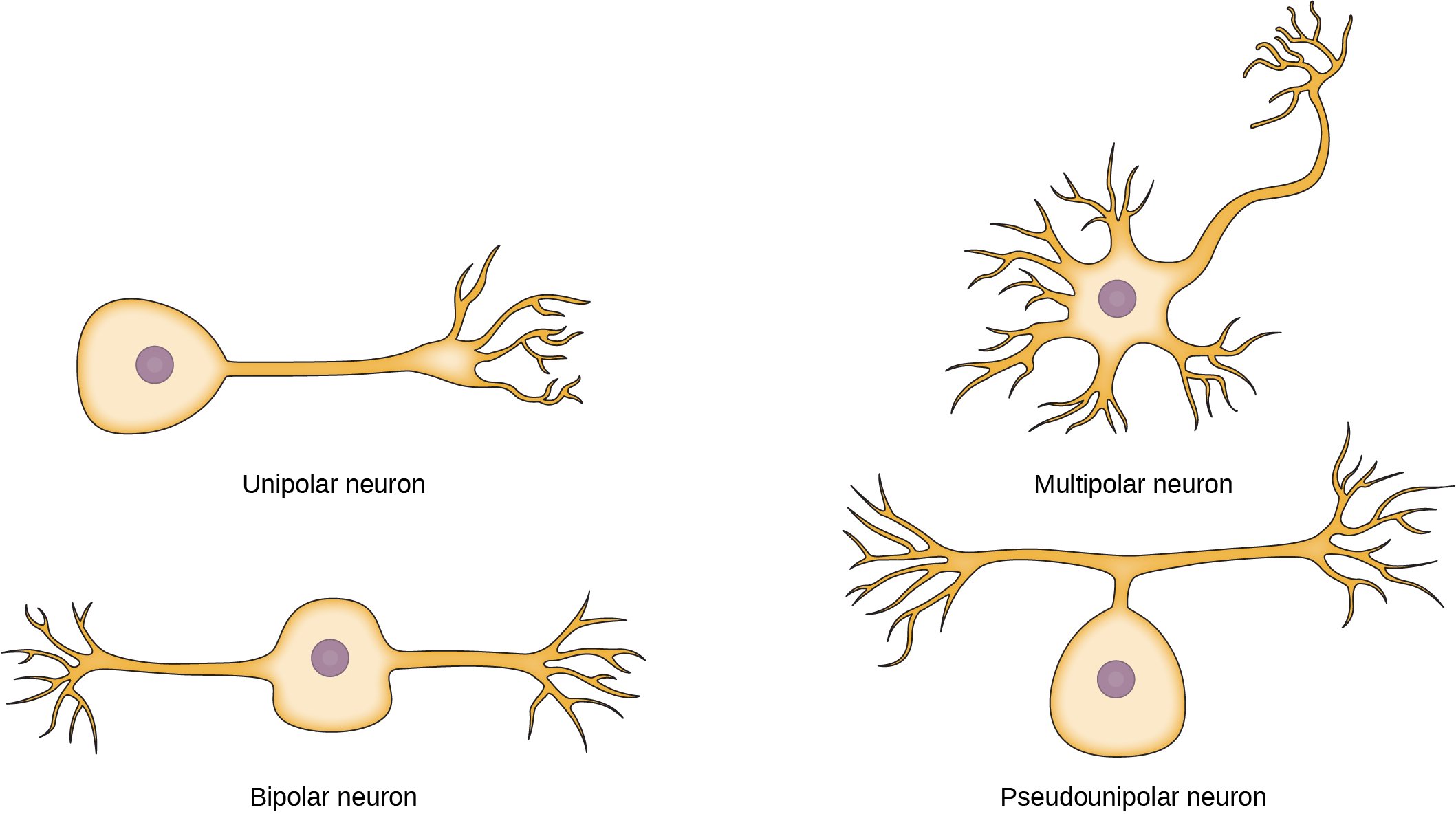
Bipolar neurons
One axon and one dendrite
Eyes and nose
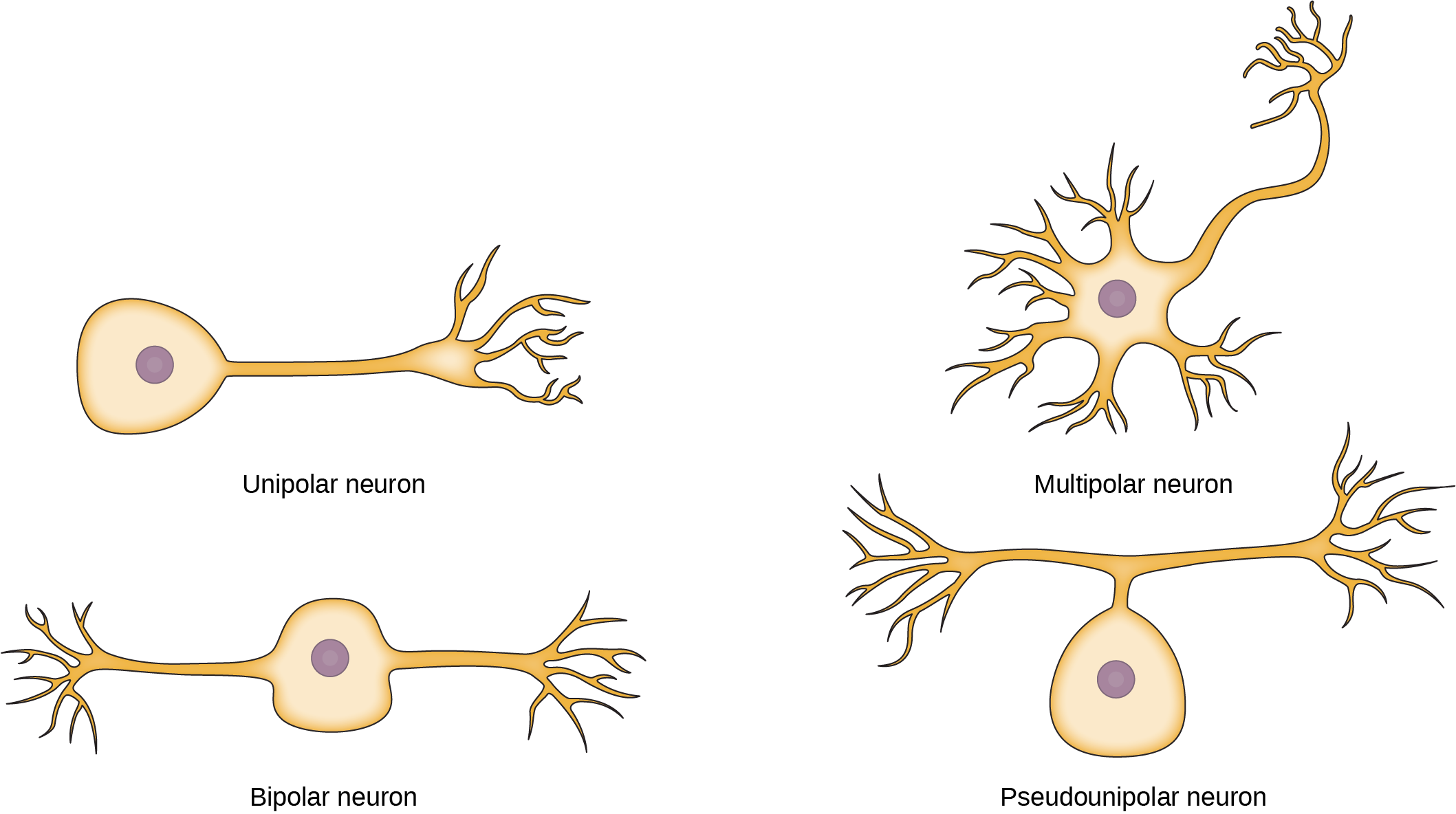
Multipolar neurons
Motor and association
Many extons
brain and spinal cord
Dendrite
conduct impulses toward cell body
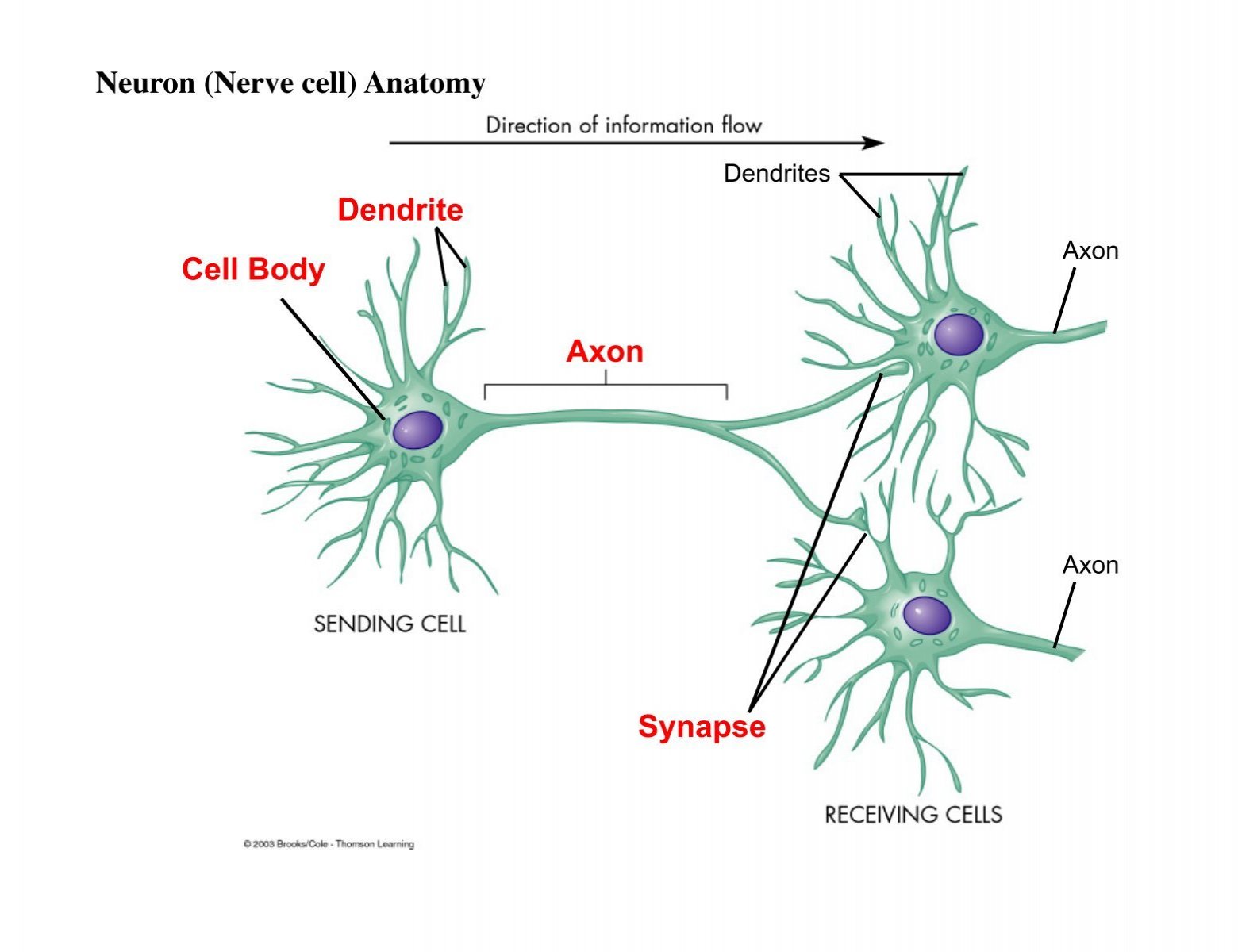
Axon
conduct impulses away from the cell body
only one axon- hill ock
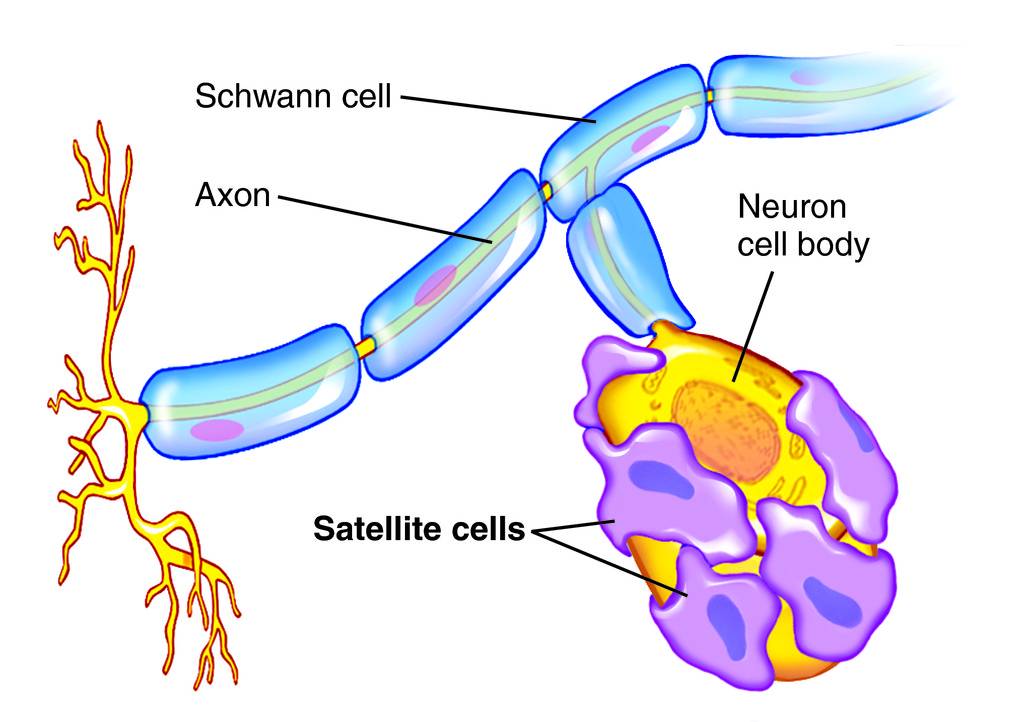
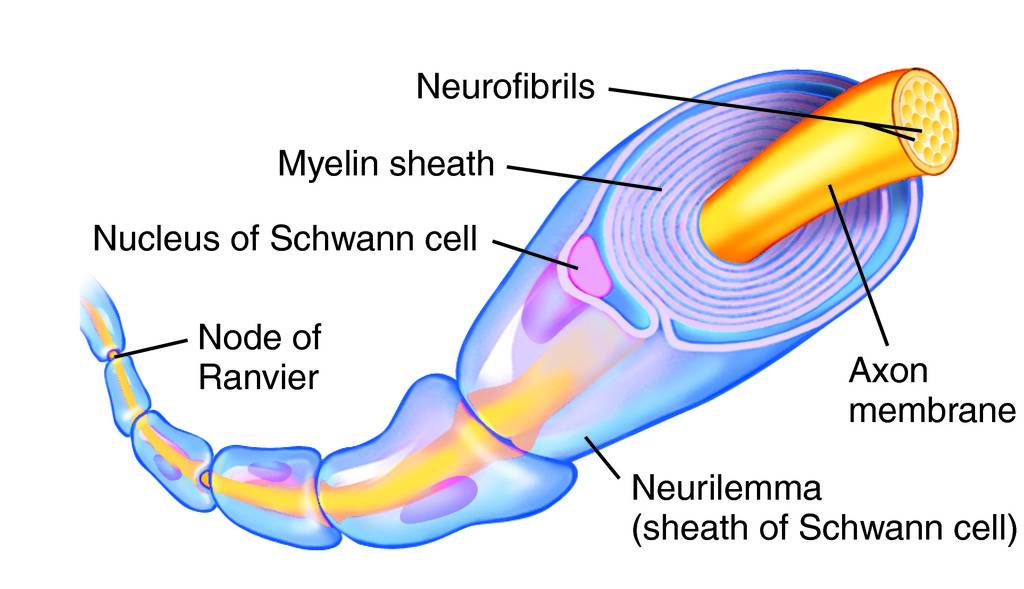
Myelin Sheath
Nerve fiber covering- protects, insulates, increases transmission rate of impulses
Schawnn cells make it
Nodes of ranvier cap it
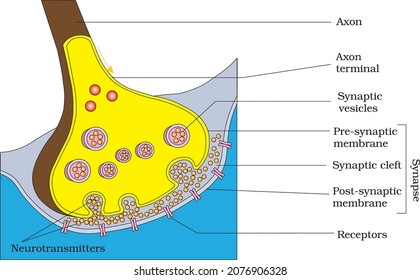
Axon terminal
contain vesicles with neurotransmitters
sepperate from the next neuron by a gap
synaptic cleft
synapse- junction between nerve
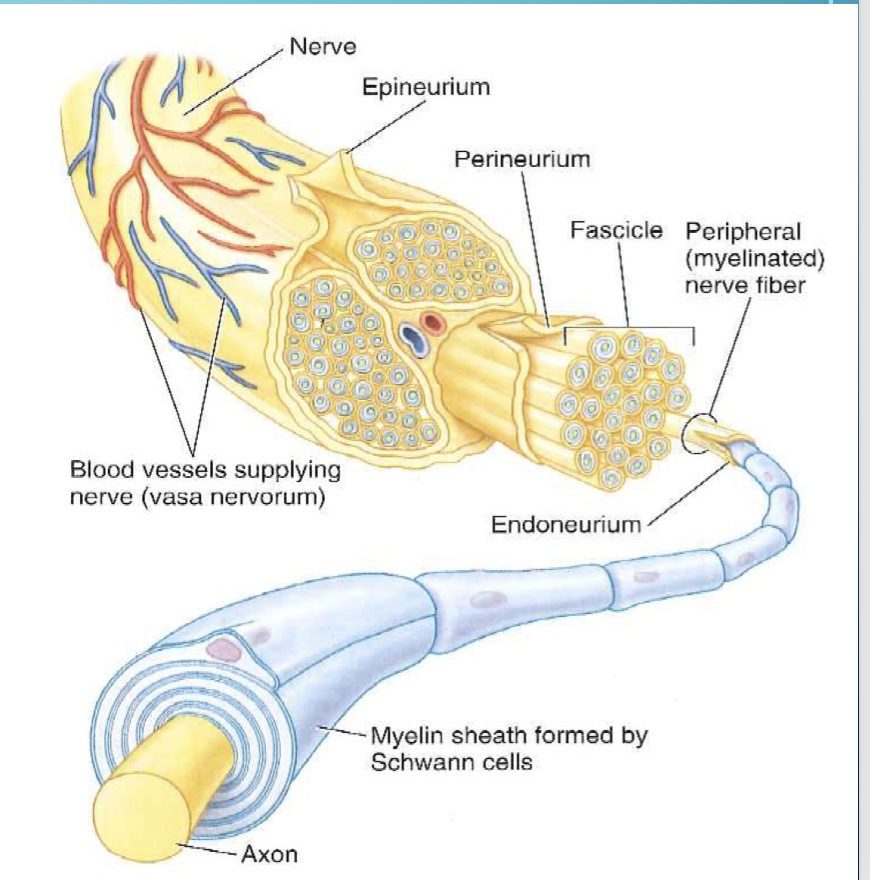
Epineurium
The protective sheath surrounding a nerve fascicle, consisting of several layers of flat cells that provide structural support and maintain the integrity of nerve fascicles.
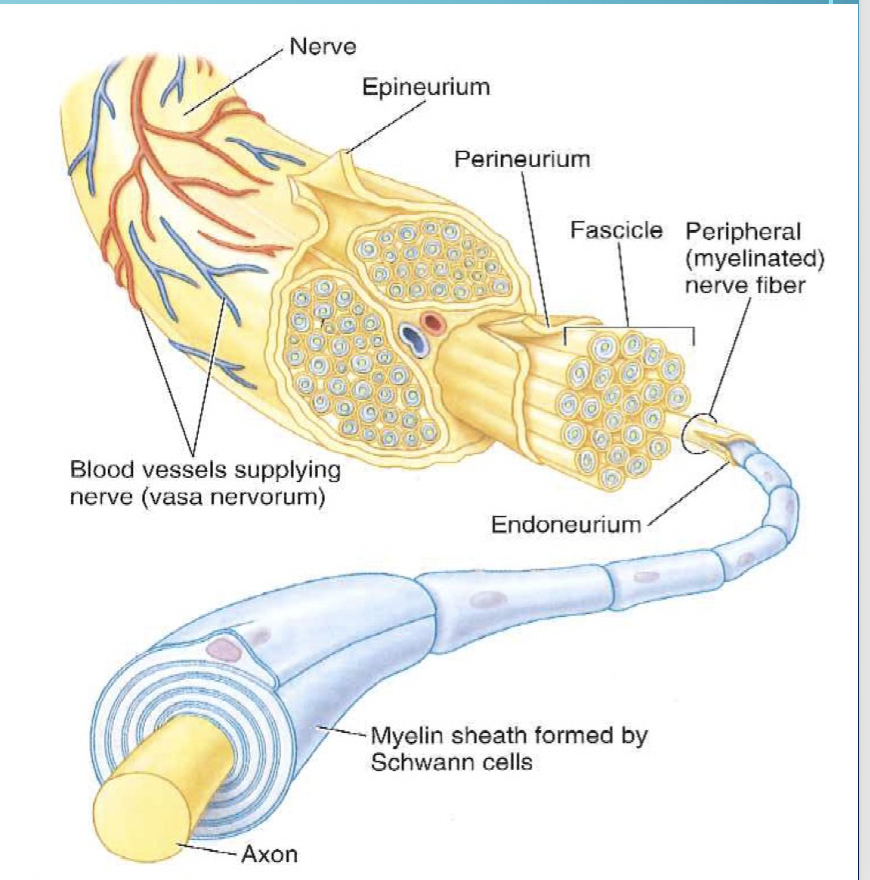
Endoneurium
A delicate layer of connective tissue that surrounds each individual nerve fiber, providing support and protection.
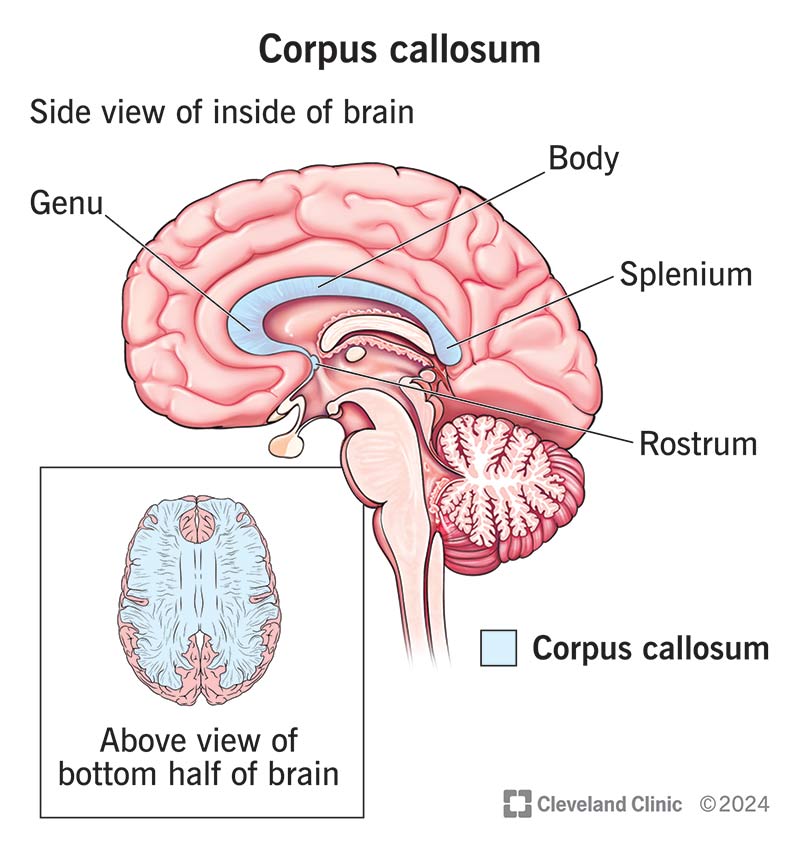
Corpus callosum
connect the left and right hemispheres of your brain
Afferent vs efferent
Sensory (afferent) neurons:
Carries impulses from sensory receptos
vision, hearing, equlibrium, taste and smell, cutanieous (skin), pain, proprioceptors (muscle)
Motor (efferent) neurons:
Carry impulses from the CNS
Interneurons/ Associan neuron
Found in neural pathways of CNS
Connect sensory and motor neurons
Reflex vs. Reflex arc
Reflex- rapid, involuntary, predicatble response to stimuli
Reflex arc- involves CNS and PNS
direct route from senesory neuron to an interneuron and an effector
Gray vs White matter
Gray- myalated, outer layer, composed of neuron cell bodies
White- fiber tracts inside te gray matter
Basal nuclei
internal islands of gray matter
Dorsal horn vs Ventral horn
Dorsal- Afferent, collection of cell bodies outside the CNS, dorsal root ganglia
Ventral- efferent
Layers of cerebrum
gray matter, white matter, basal nuclei
2 subdivisions of nervous system
Central Nervous System(CNS): Brain, spinal cord, dorsal body cavity; interpret incoming sensory information and tissue intructions based on past experience or current conditions
Peripheral Nervous System(PNS): nerves leading to and from the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal Fluid
like blood plasma, made by choroid plexus, water cushion for brain, circulated in arachnoid space, ventricles and central canal of the spinal cord
Protection of CNS
Scalp, skin, skull, meninges, cerebrospinal fuid, blood brain barrier
Meninges
dura matter, double layer
periosteum- surface of skull
Meningeal- outer covering of skull
Folds inward in several areas
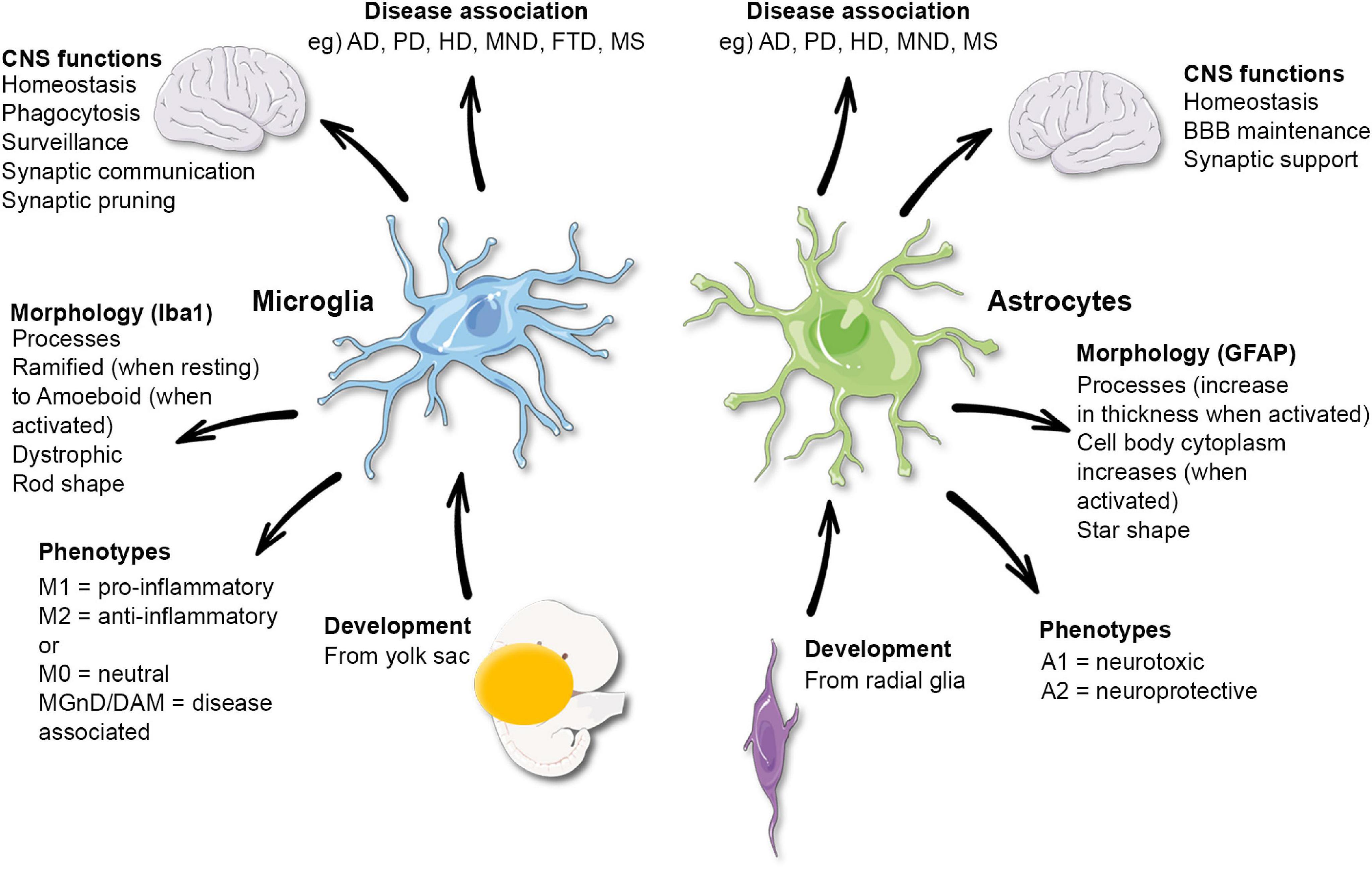
Glial cells
brain cancer
never lose baility to divide
not able to transfer impulses
types: neuroglia, microglia, ependymal, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes
PNS types: staellite, schwann cells
Astrocytes
abundant, star-shaped cells, half of neural tissue
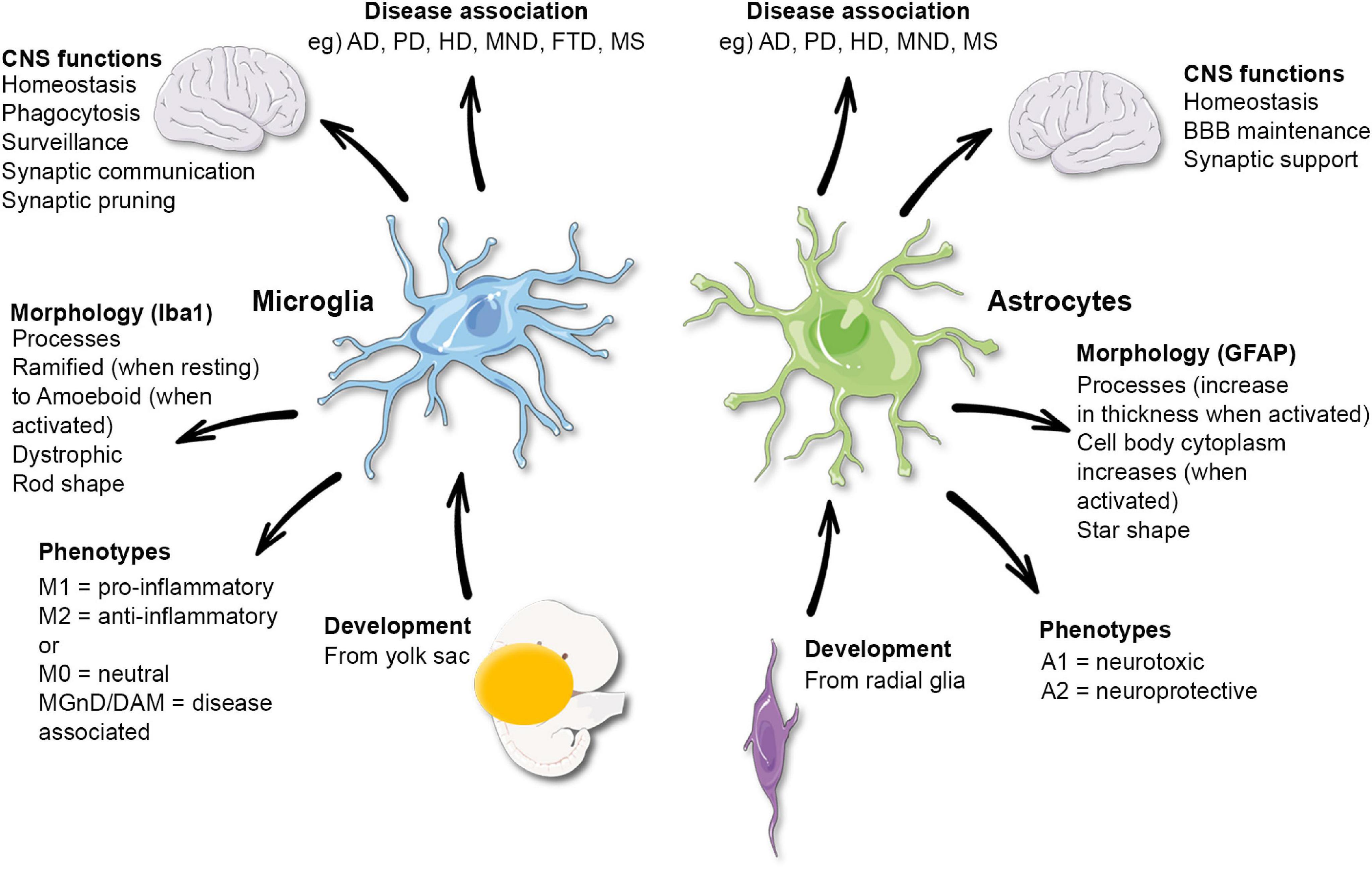
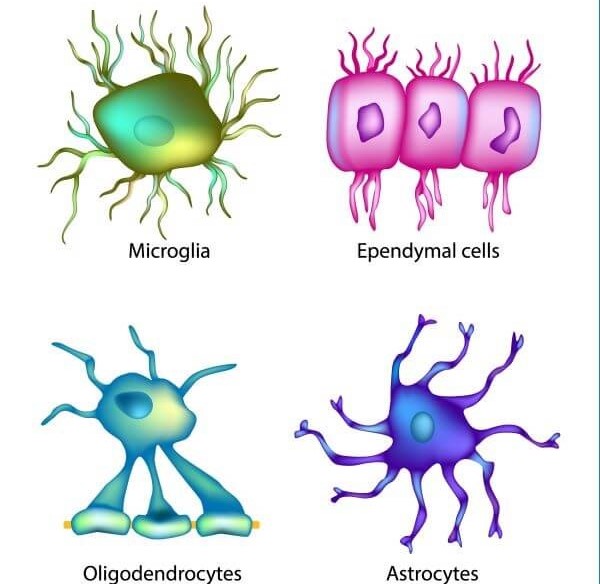
Microglia
spider like phagocytes
Ependymal Cells
lines cavities and brain and spinal cord, beaitng cilia to circulate CS fluid
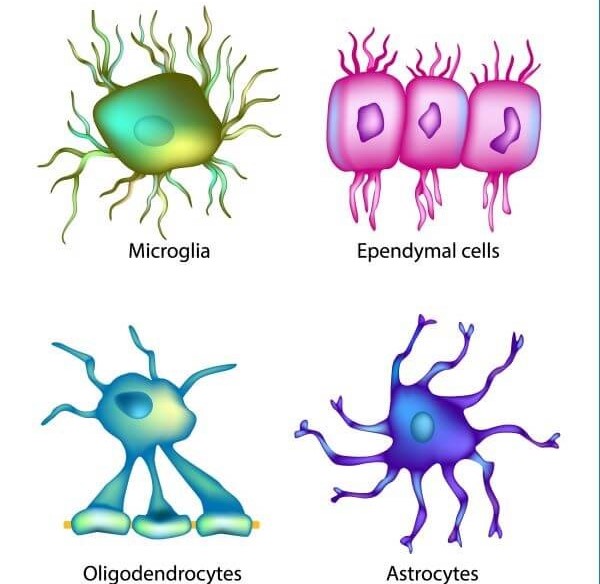
Oligoderdrocytes
myelinated fibers, produce myeline sheath, lacks neurilemma
Satellite cells
protects, cushions neuron cell bodies
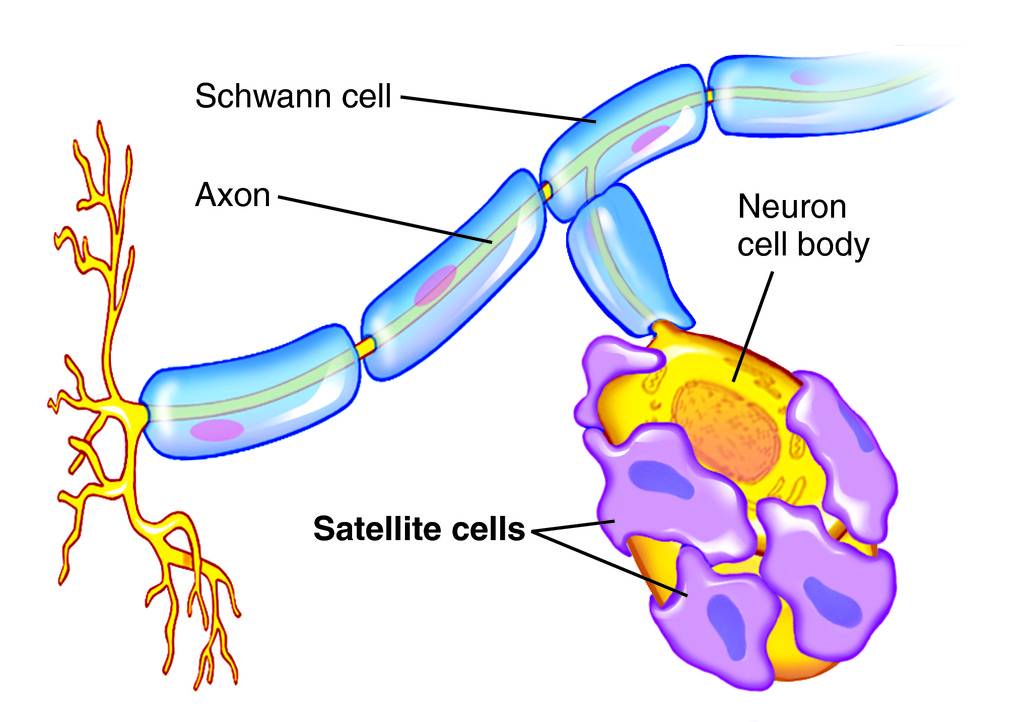
Schwann cells
forms myelin sheath in PNS