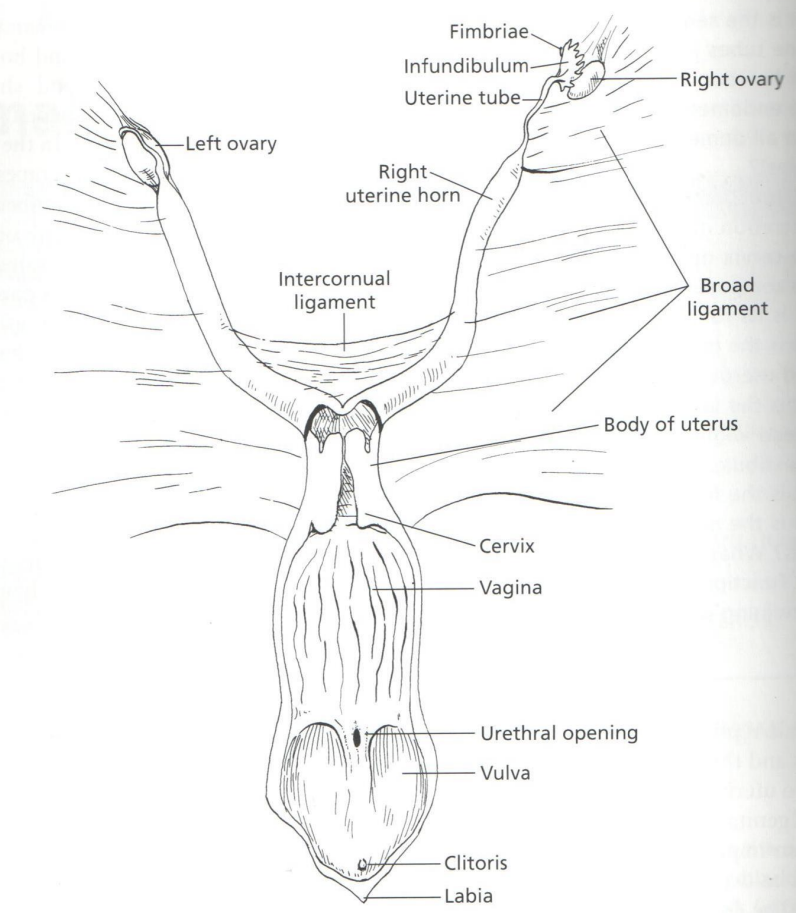
Ovaries and Follicles
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What are ovaries?
Paired glands that provide for the development of oocytes and production of hormones
What is ovulation?
The release of mature oocytes
Where are the ovaries located?
To its respective right or left kidney and is suspended form the dorsal wall of abdomen
Parts of the Ovary
What covers the ovary
What is the periphery of ovary called
Function
What is the middle of ovary called
Function
What covers the ovary: Tunica albuginea
What is the periphery of ovary called: Cortex (functional part)
Function: Contains large mass of follicles in various stages of development
What is the middle of ovary called: Medulla (supportive part)
Function: Contains loose connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves
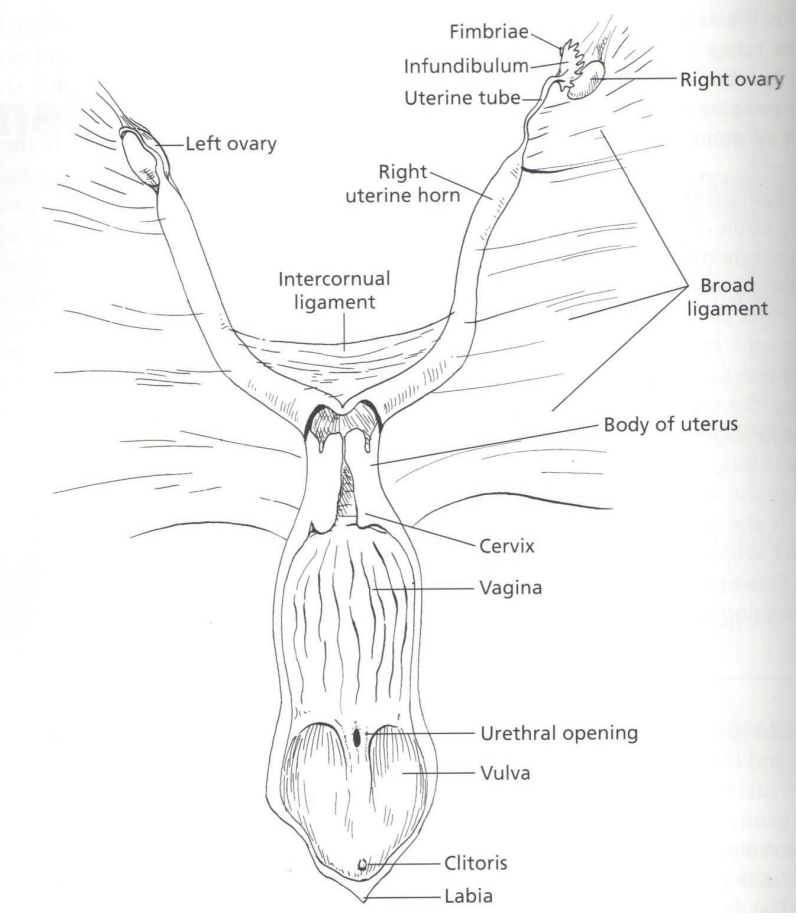
Picture of
What are the 3 types of follicles in oocyte?
Primordial follicle #ffb3c6
Growing follicle #ff8fab
Graafian follicle #fb6f92
Primordial Follicle #ffb3c6
What does it contain
Where do the oocyte in primordial follicle come from?
What does it contain: A single oocyte surrounded by.a single layer of granulosa cells
Where do the oocyte in primordial follicle come from:
Derived from mitosis of oogonia in the embryonic genital ridge
Which then migrates to the ovary
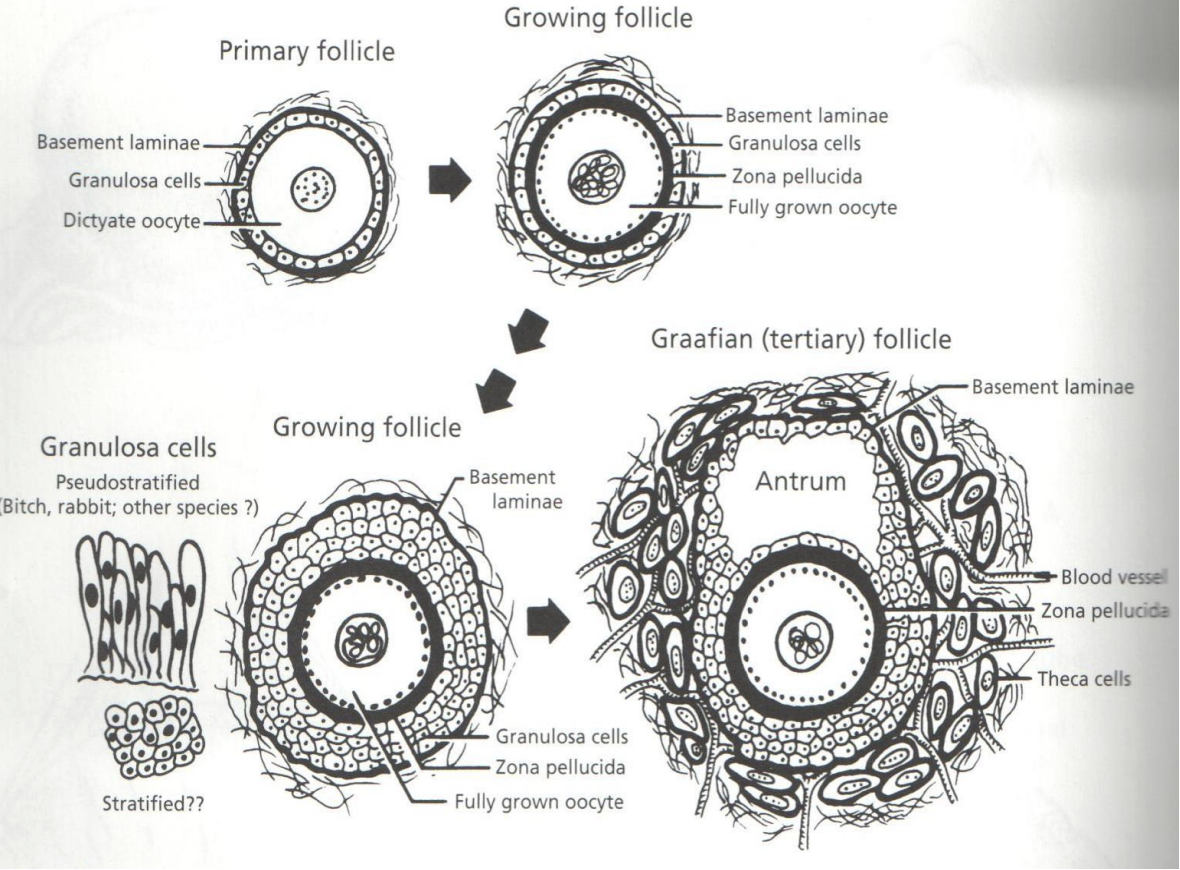
Growing Follicle #ff8fab
What
What structures are absent in a growing follicle
What: A follicle that has begun developing from the primordial stage but not yet formed thecal layer or antrum
Structures absent: Thecal layer or antrum
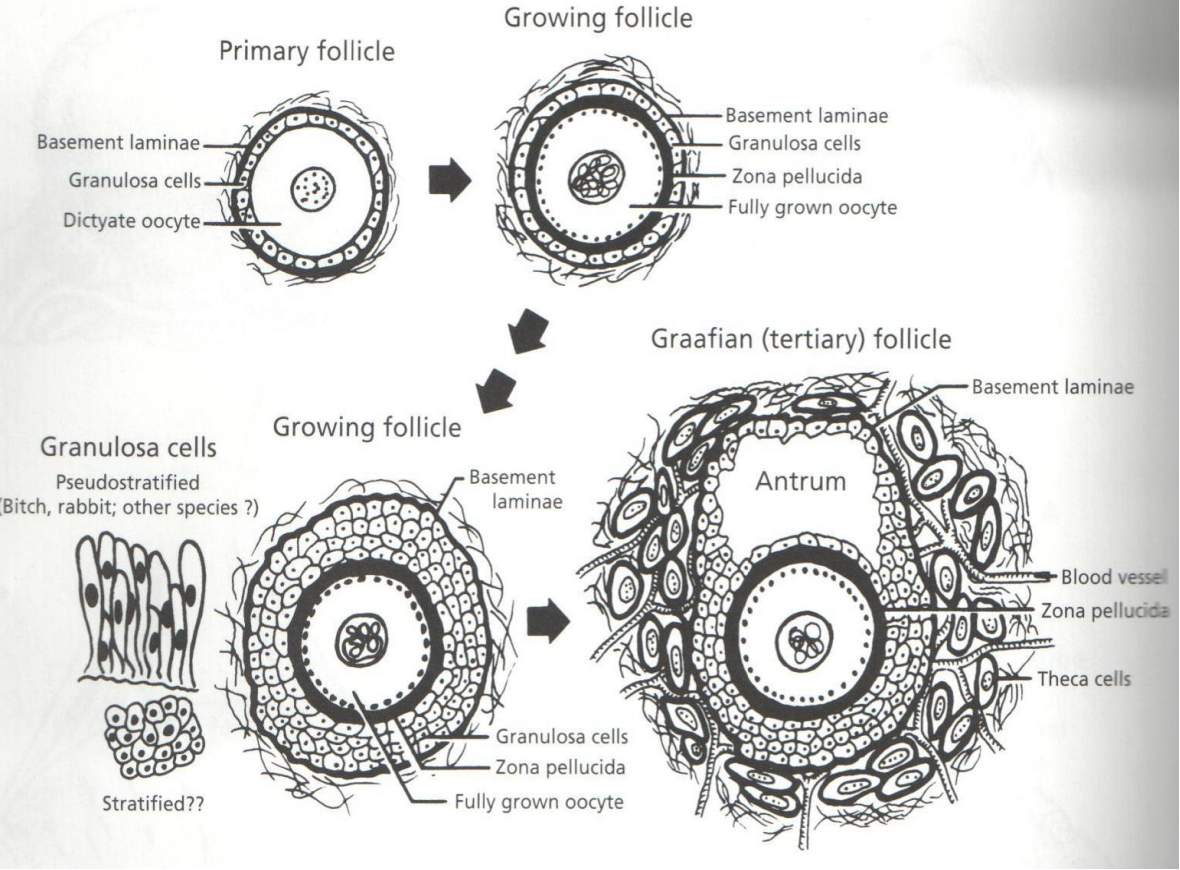
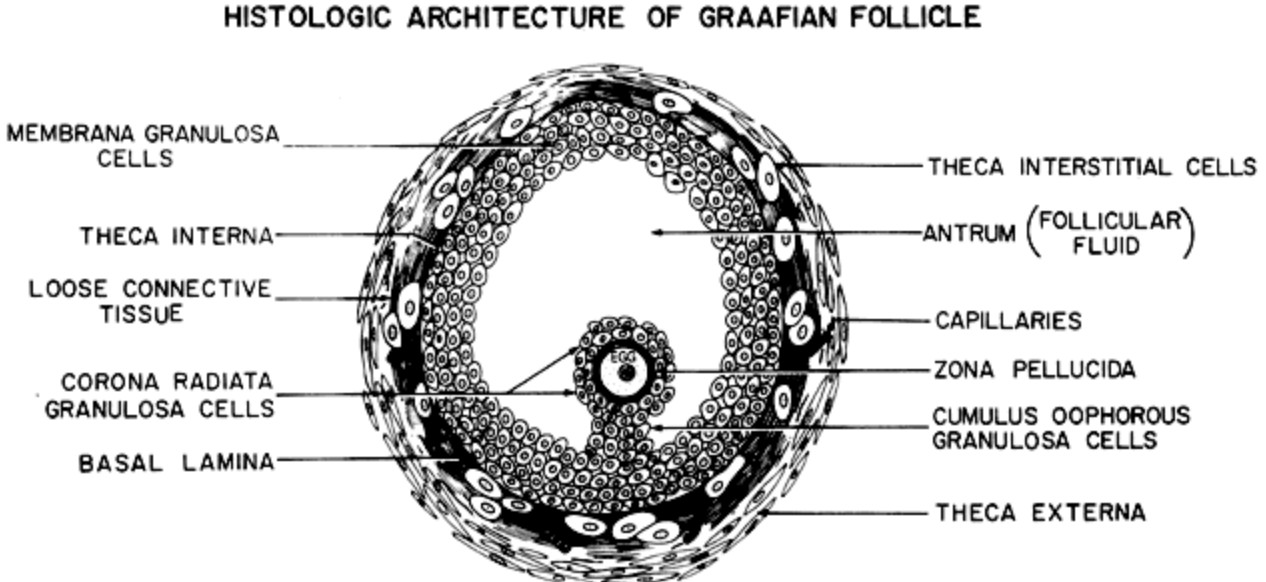
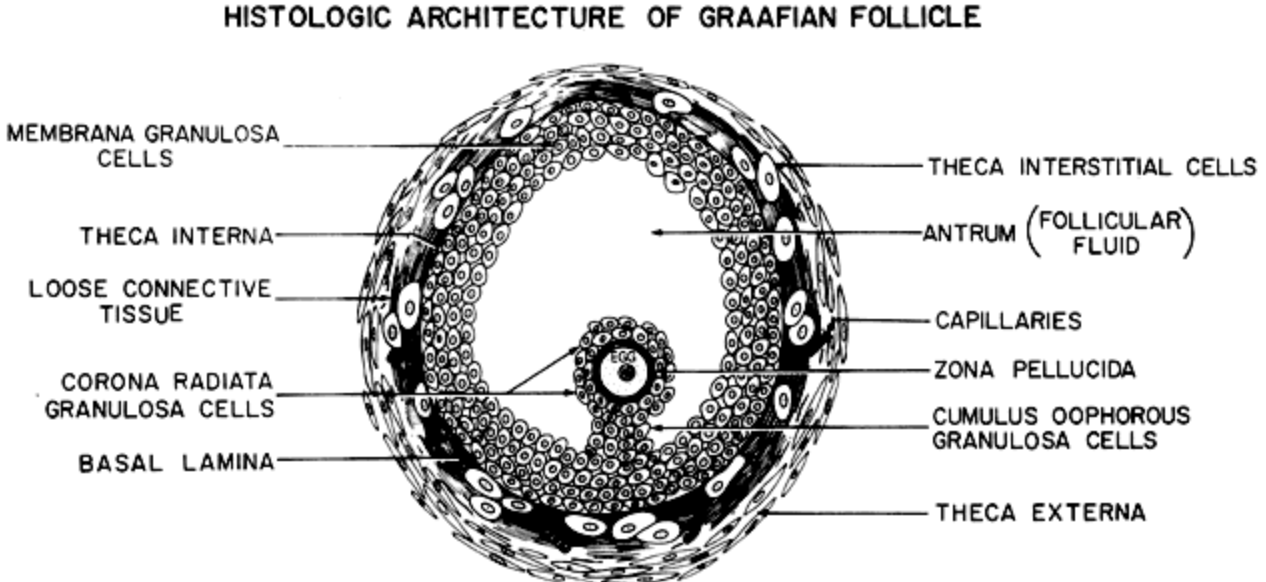
Graafin Follicle? #fb6f92
What
What controls the formation of Graafian follicles
When does the formation start
What: A mature follicle with a visible antrum and 2 thecal layers
Theca interna
Theca extera
What controls the formation of Graafian follicles:
Its hormone dependent
Formation starts: At puberty when LH and FSH levels start to rise and fall with each estrous cycle
Zona pellucida
What
Its function to fertilisation
What: A glycoprotein layer surrounding the oocyte
Function to fertilisation: Sperm must recoginse, bind and travel through zona pellucida to reach oocyte plasma membrane
What is follicle regression?
The periodic process in which immature ovarian follicles degenerate
And are re-absorbed during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle
What happens to the multiple follicles that mature each month?
Only 1 follicle is ovulated
Remaining undergo atresia
What happens to the single dominant follicle after ovulation?
It becomes corpus luteum