Muscles of the Tongue - Module 7
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Tongue Divisions - Speech Articulation
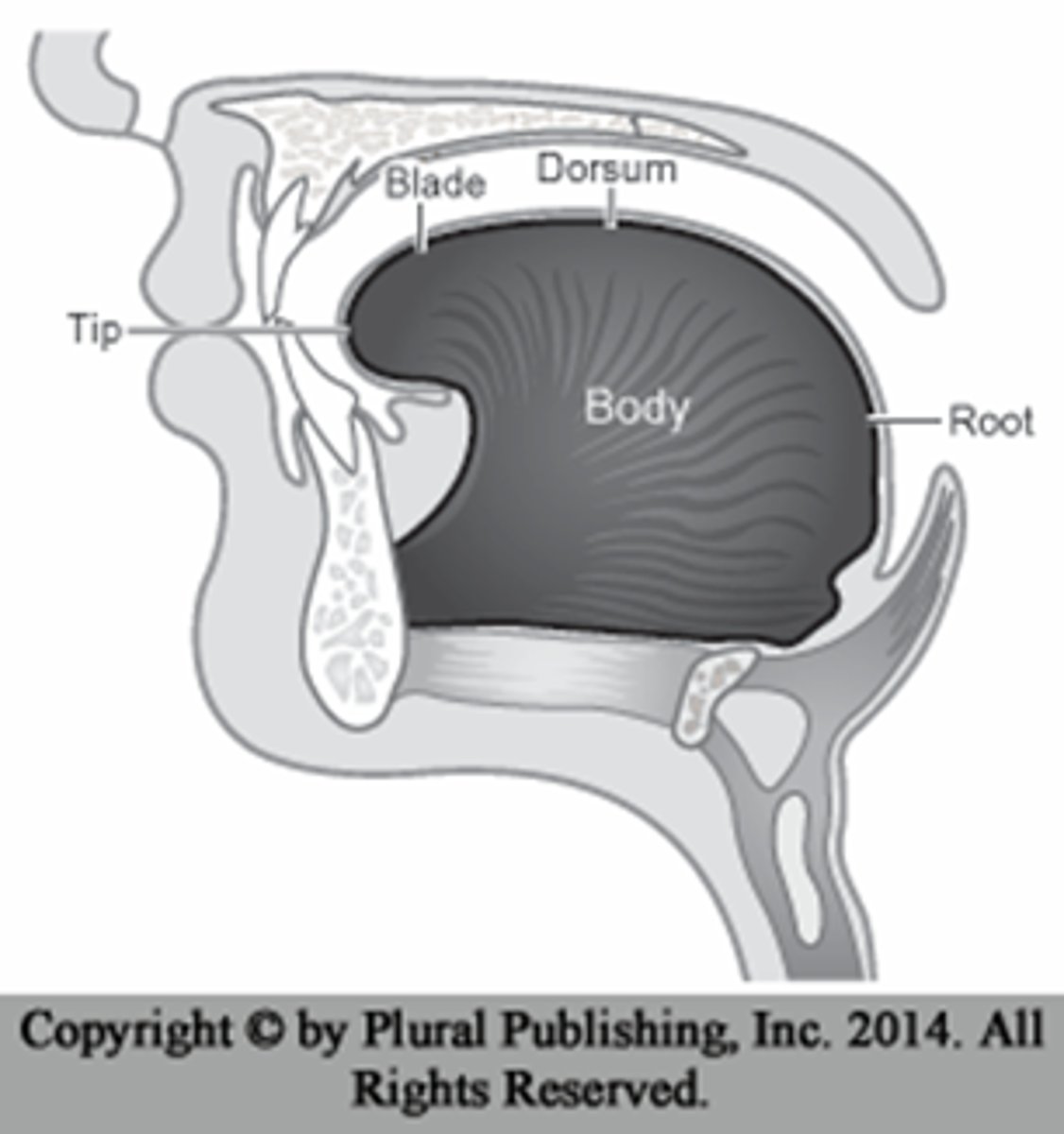
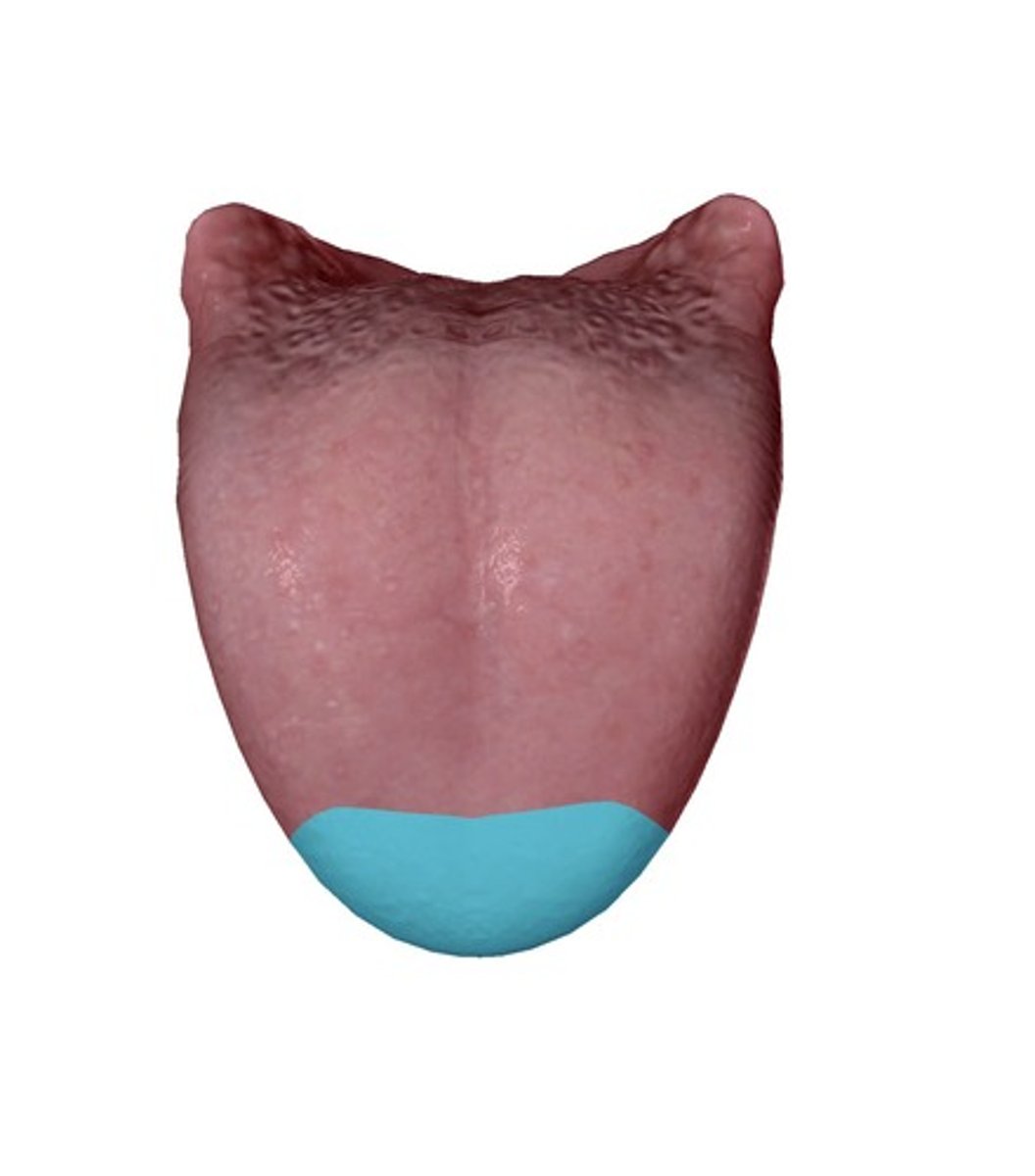
Tip
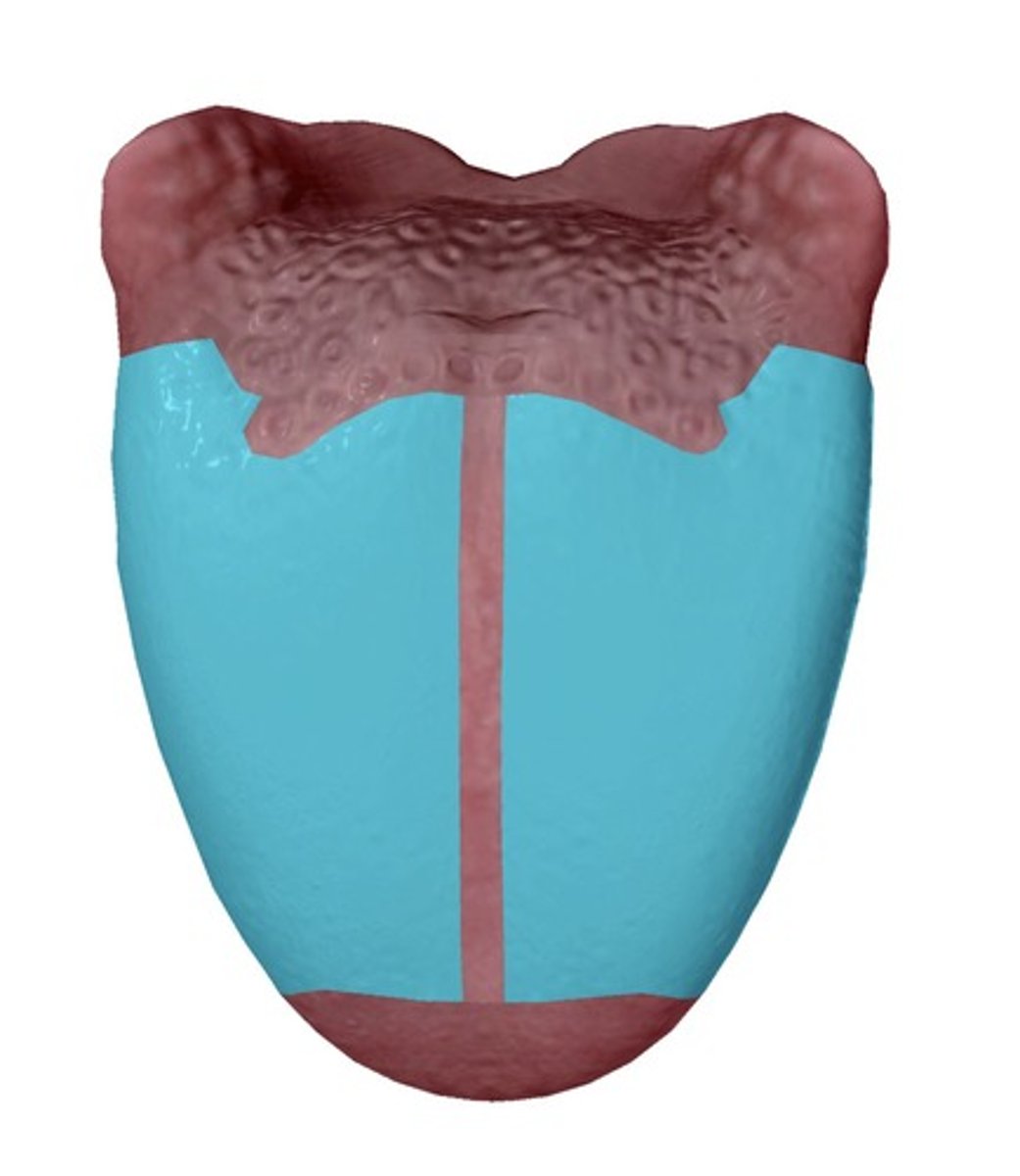
Blade
Dorsum
Root
Body
Tip
Part closest to the front teeth at rest
Blade
Part just posterior to the tip and inferior to the alveolar ridge of the maxilla
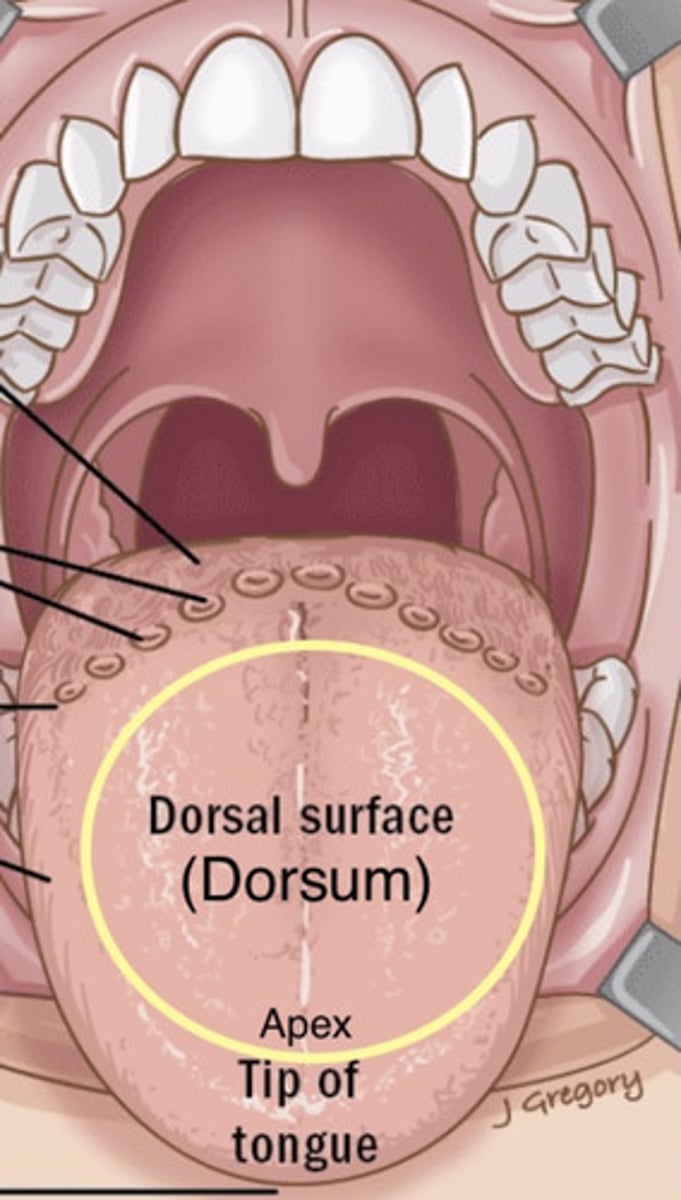
Dorsum
Part posterior to the blade and below the back part of the hard palate
Top surface of the tongue
Root
Part that faces the back of the pharynx and
front of the epiglottis
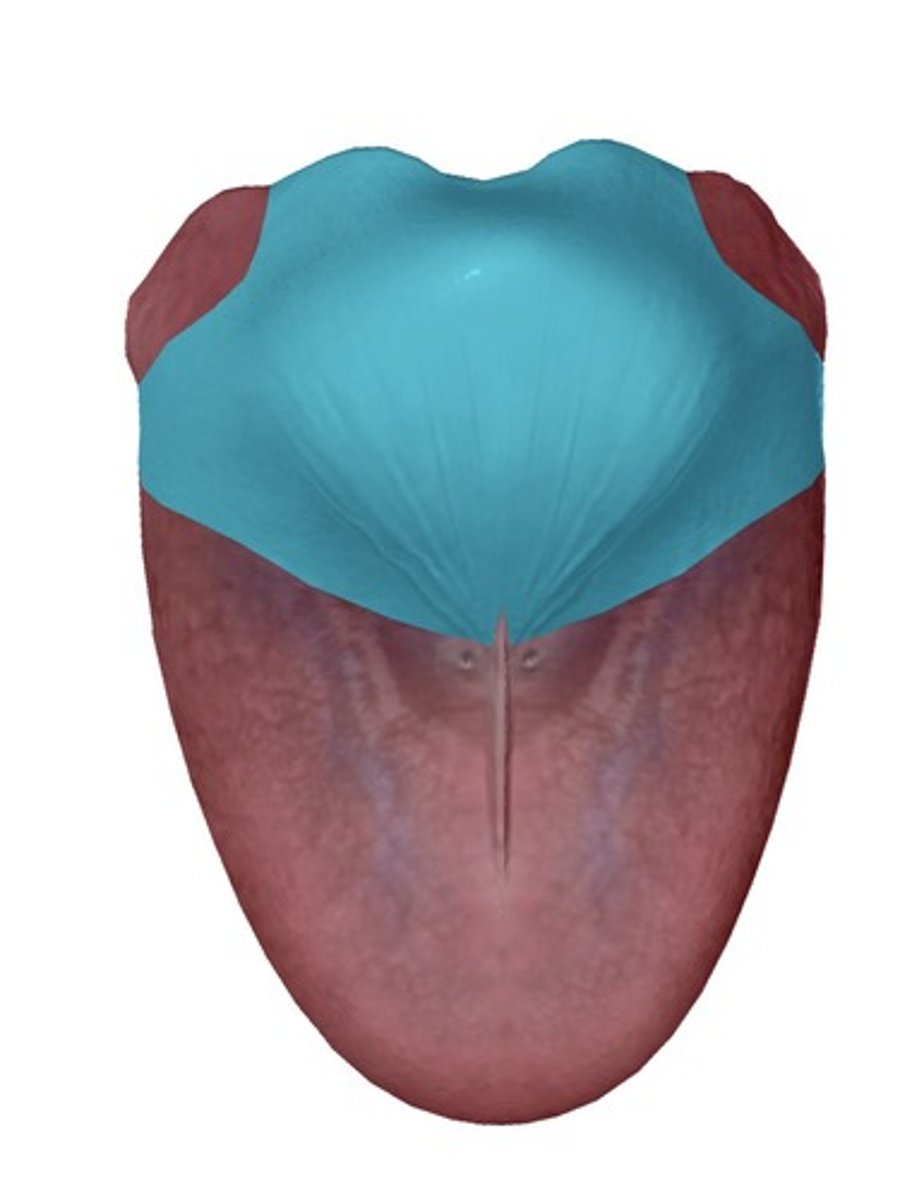
Body
Central mass of the tongue that underlies
the surface features

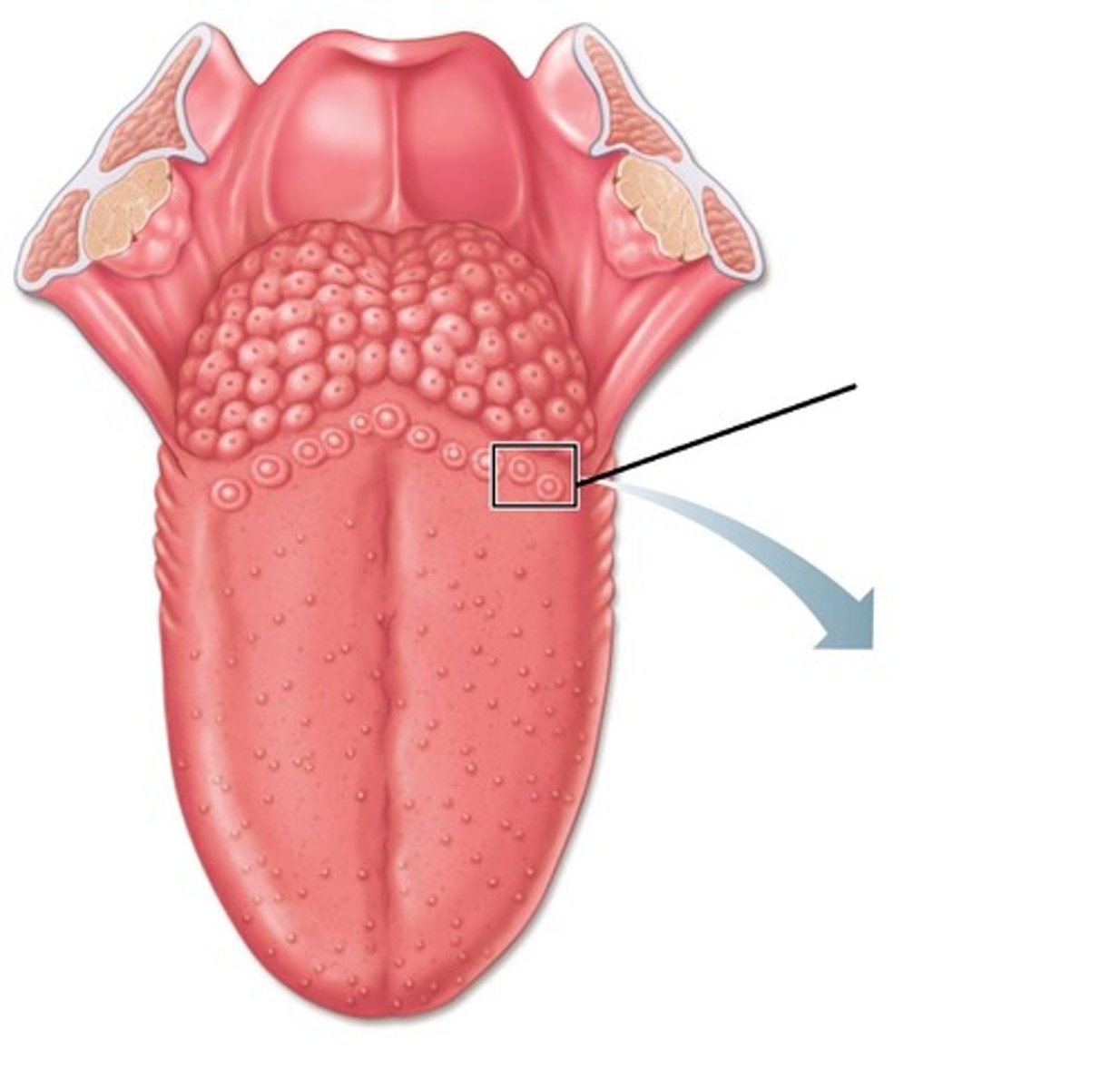
Tongue Structures - Anatomy
Dorsum
Longitudinal median sulcus
Foramen cecum
Papillae
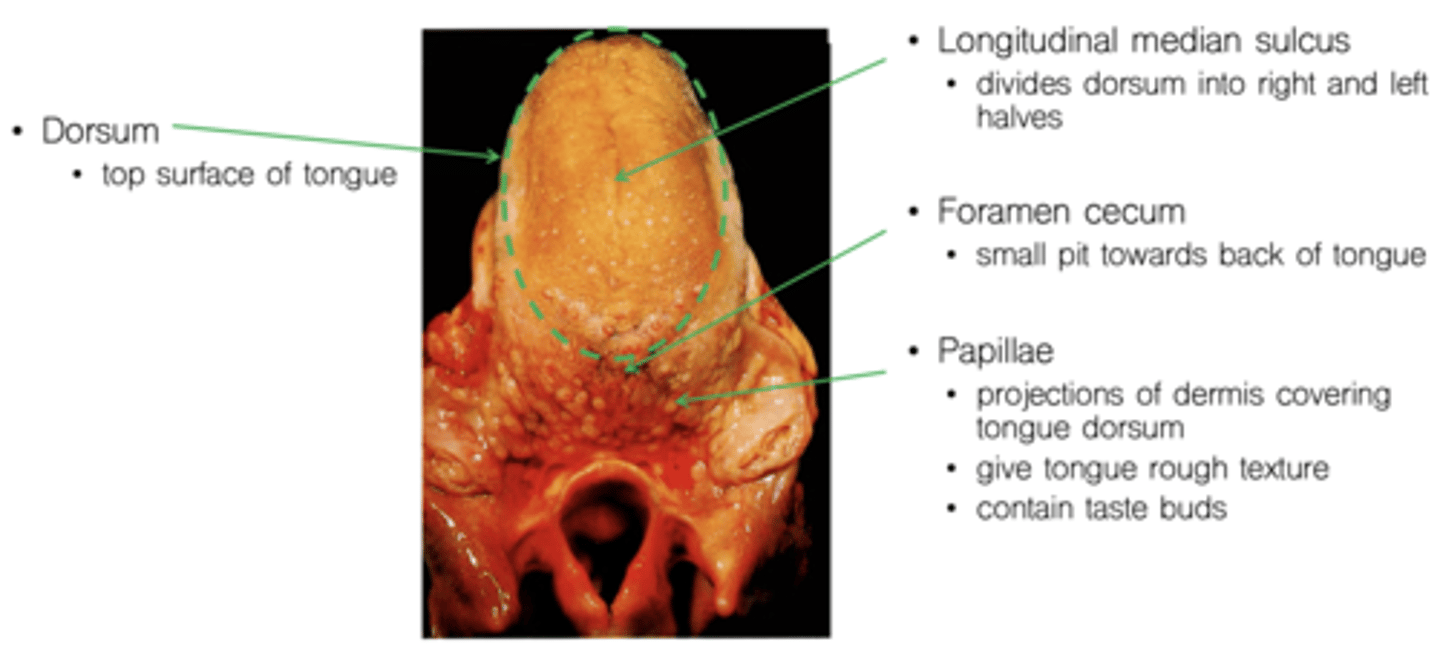
Longitudinal median sulcus
divides dorsum into right and left halves
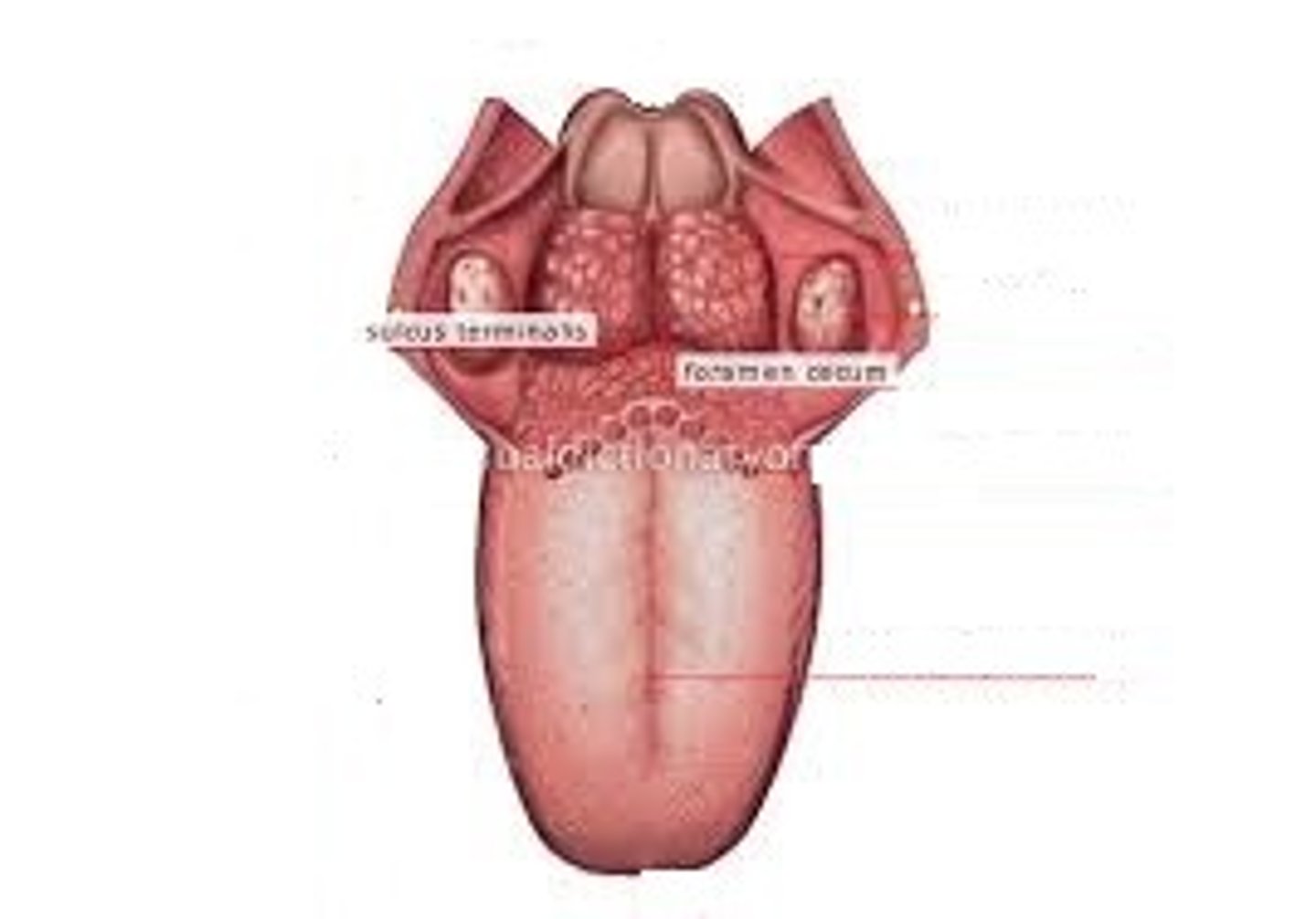
Foramen cecum
small pit towards back of tongue
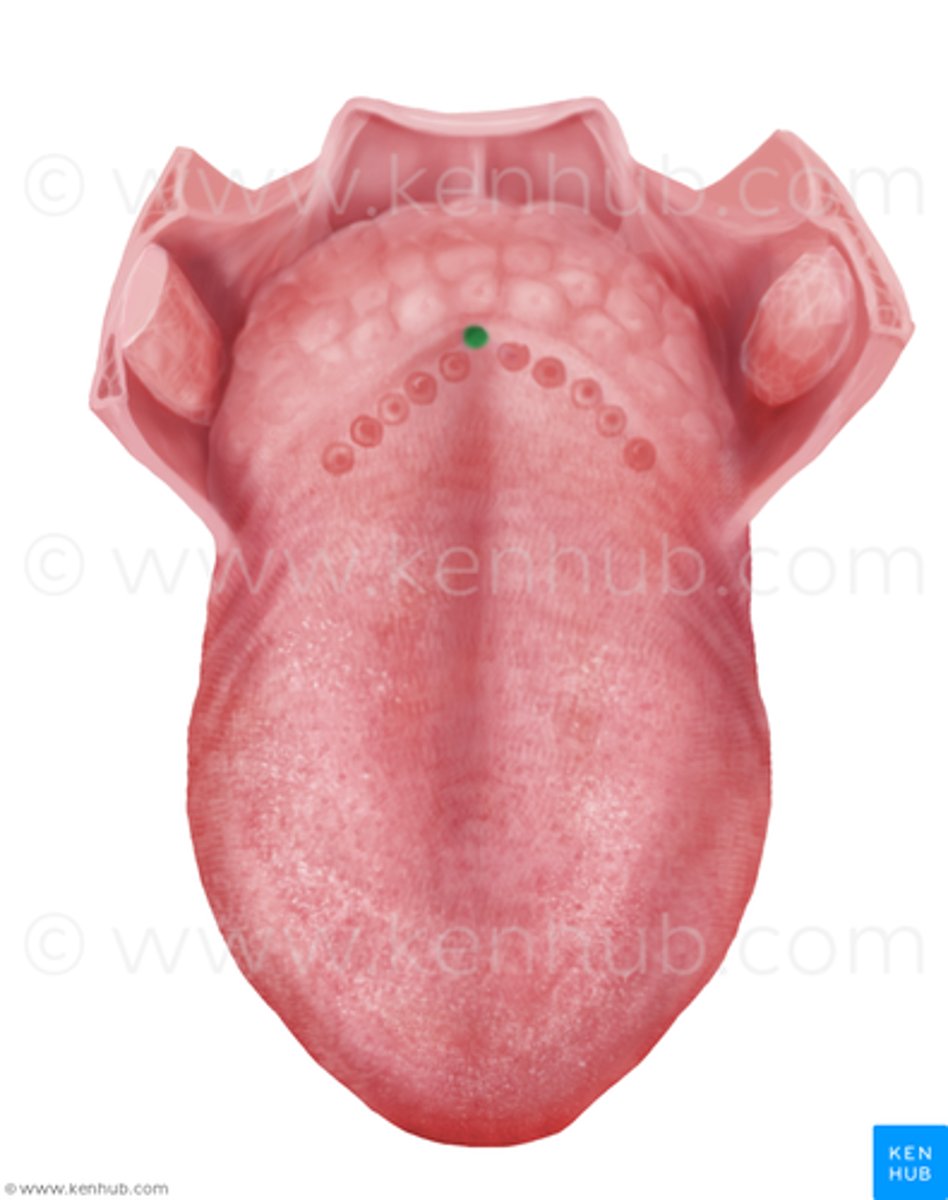
Papillae
projections of dermis covering tongue dorsum
give tongue rough texture
contain taste buds
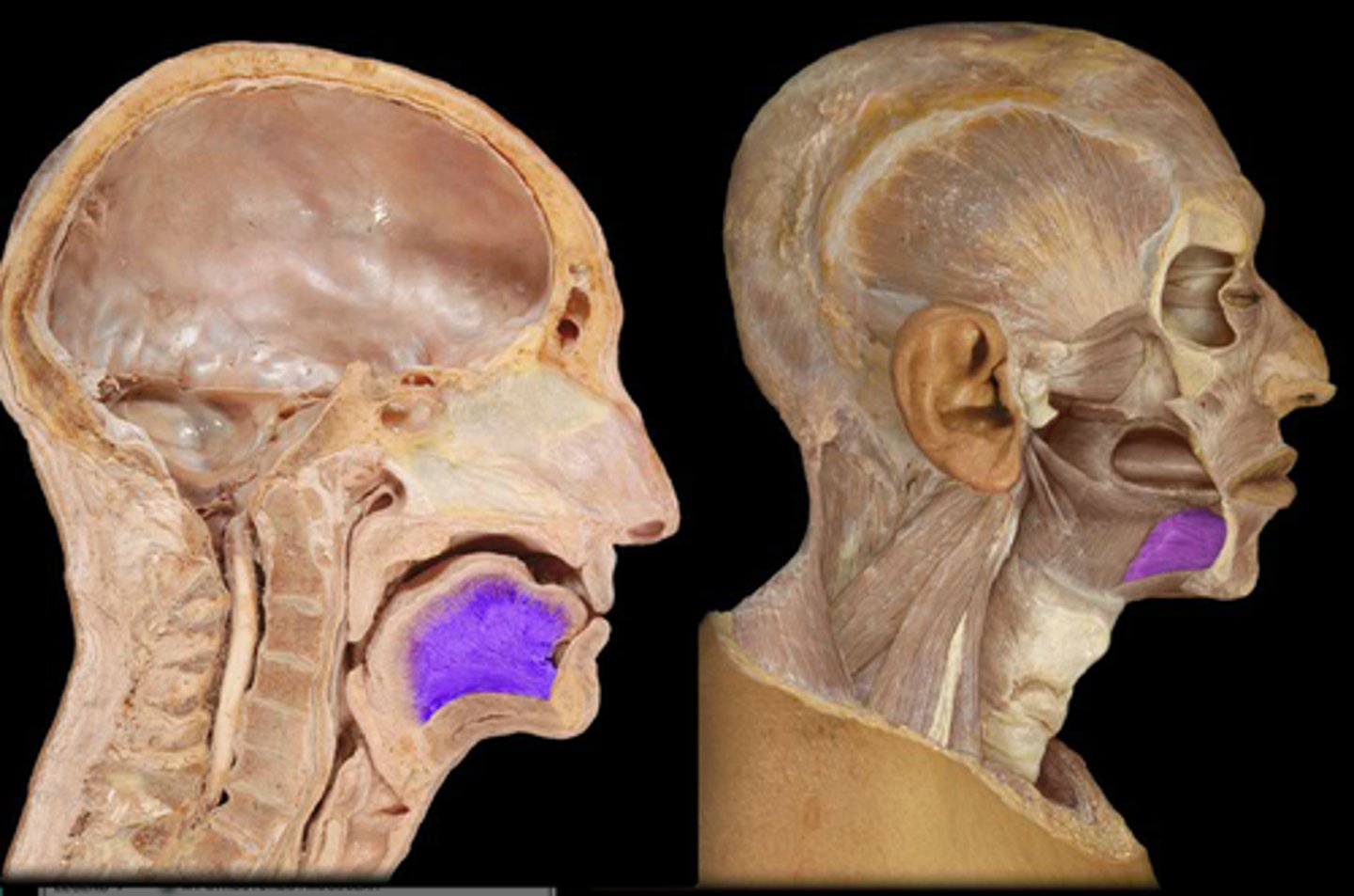
Extrinsic muscles
Serve to anchor tongue, add to its bulk, aid in movement
Perform much of the gross movement of the tongue
Four extrinsic muscles
- Genioglossus
- Styloglossus
- Hyoglossus
- Palatoglossus
Genioglossus
Forms bulk of tongue tissue
Strongest and largest tongue muscle
Origin - mental spines of mandible
Course -
- lower fibers to hyoid bone
- remainder fan out to tongue dorsum
Insertion -
- hyoid
- submucosal fibrous tissue of tongue dorsum
Action -
- posterior fibers alone: draw tongue forward to protrude tip and press tip against teeth
- anterior fibers alone: may retract tongue tip
- all fibers together: pull tongue downward
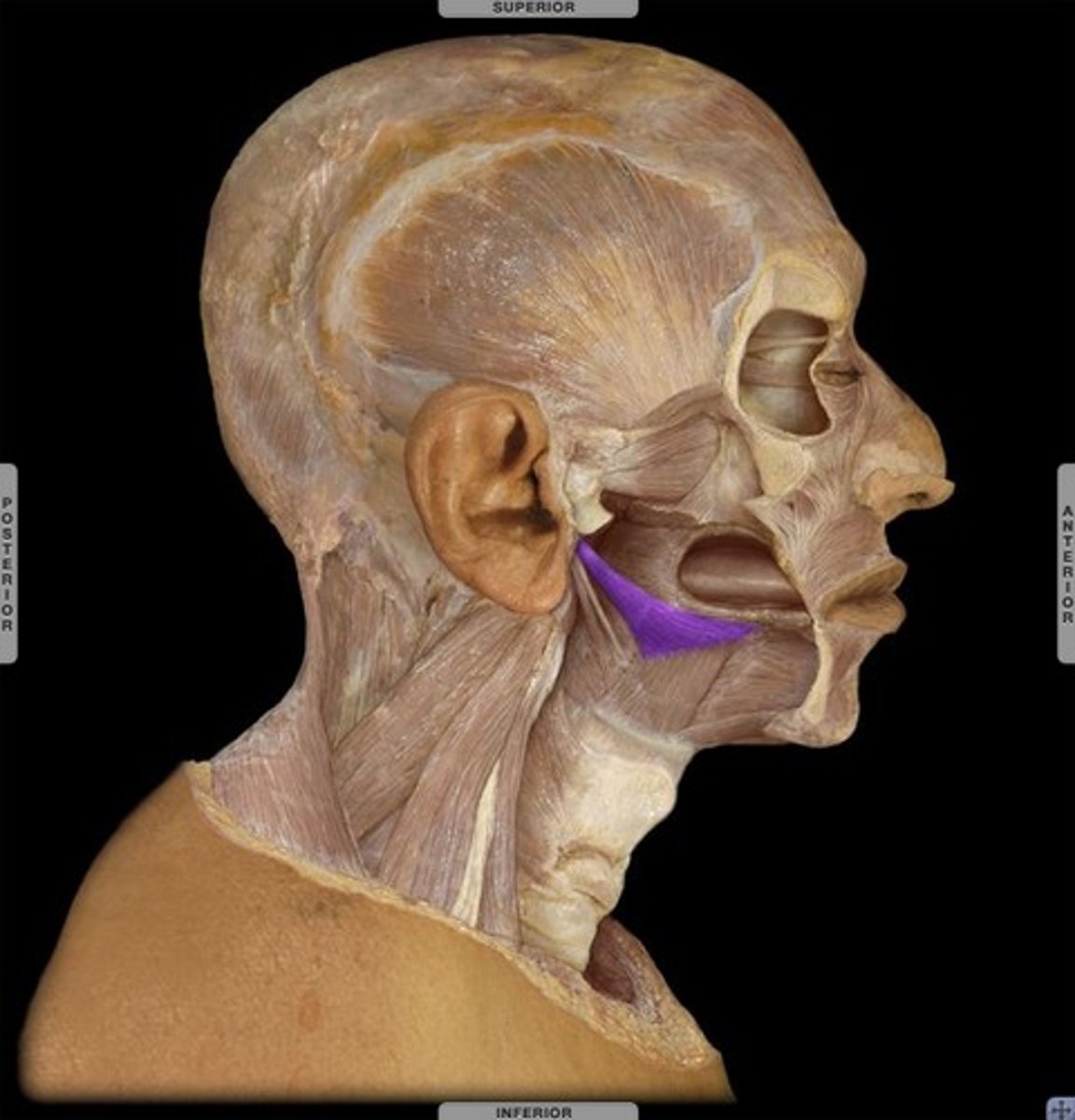
Styloglossus
Small, fan-shaped muscle
Origin - styloid process of temporal bone
Course - inferior and anterior
Insertion -
- sides of tongue near dorsum
- some fibers blending with hyoglossus
Action -
- draw tongue posteriorly and superiorly
- may also create troughing
- antagonist to genioglossus
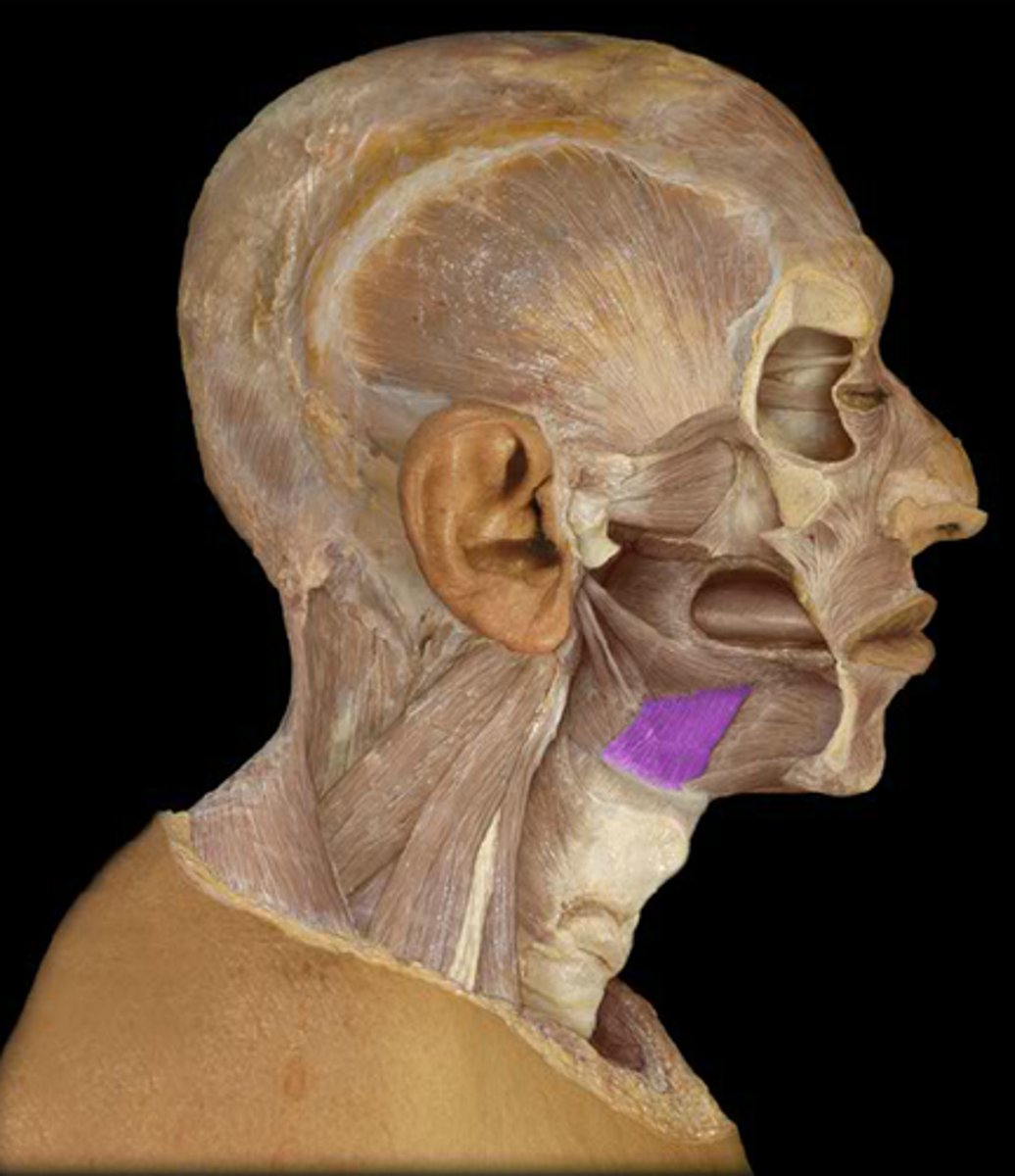
Hyoglossus
Origin - body and greater horn of hyoid bone
Course - vertical, diverging slightly
Insertion -
- lateral submucous tissue of posterior ½ of tongue
- some fibers continue in the palatoglossus
Action - retract and depress tongue
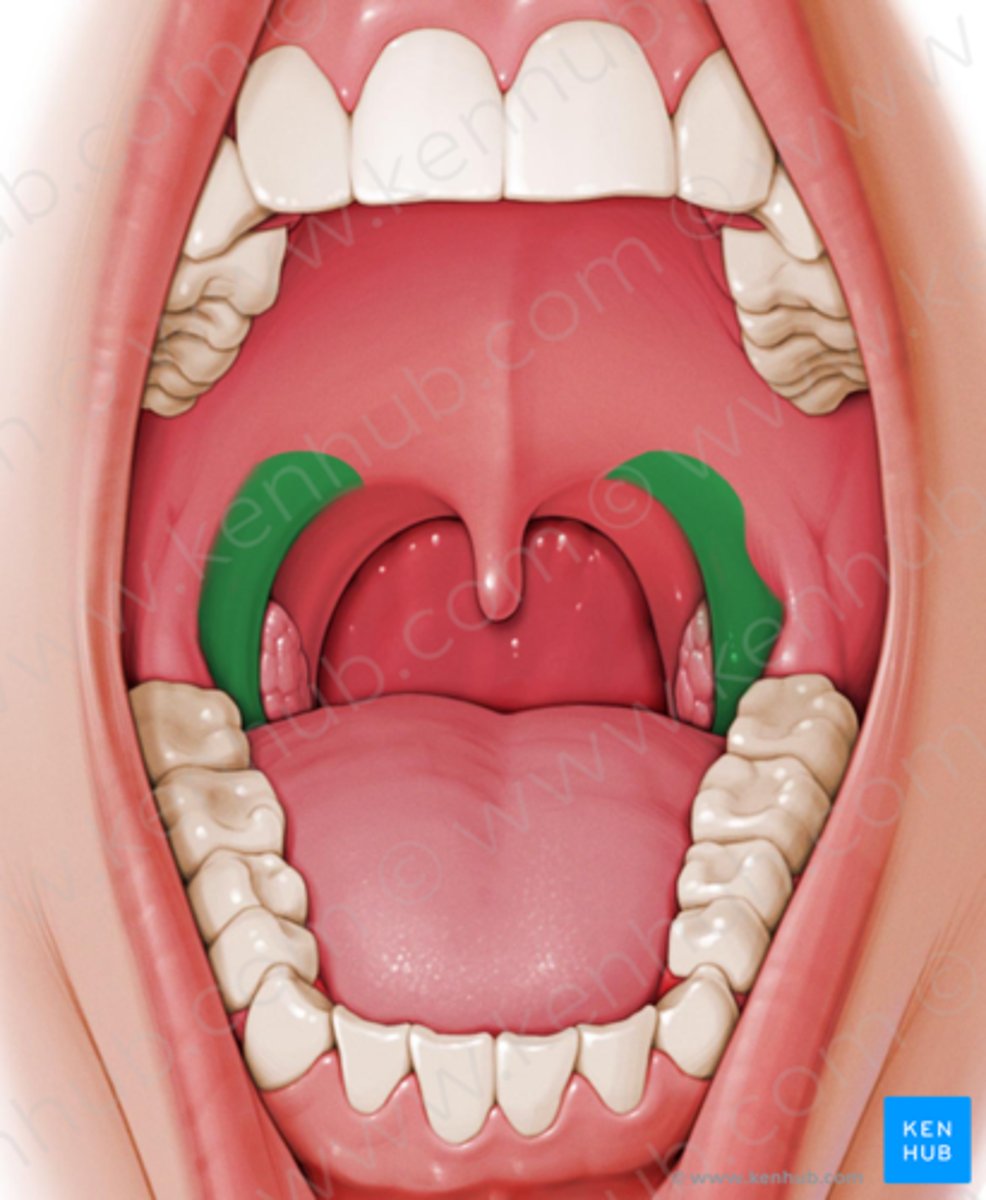
Palatoglossus
Same as Glossopalatine
- Name is reversed to emphasize that palate is fixed instead of tongue
Insertion
- Sides of tongue
Course
- Superior
Origin
- Lower surface of palatal aponeurosis, interdigitating with opposite fibers
Action - may exert upward pull on tongue if velum anchored
Intrinsic muscles
Tongue has two "skeletal" structures
- fibrous midline septum
- connective tissue "bag" just deep to epidermis
- provide attachment points for the intrinsic
muscles
Intrinsic muscles primarily responsible for
fine adjustment of the shape of the tongue
Four intrinsic muscles
- Superior longitudinal
- Inferior longitudinal
- Vertical
- Transverse
Superior Longitudinal
Thin layer of oblique and longitudinal fibers
Just below mucous membrane of dorsum
Origin - submucous fibrous tissue close to
tongue root, median fibrous septum
Course - anterior
Insertion - fibrous membrane at edges of
tongue
Action -
- shorten tongue
- turn tongue tip up
- unilateral: move tongue from side to side
Inferior Longitudinal
fibers lie on undersurface of tongue, lateral to genioglossus
Origin - root of tongue, some perhaps from hyoid bone
Course - anterior
Insertion - blend with other fibers from root to apex
Action -
- shorten tongue
- pull tongue tip down
Vertical
Origin - mucous membrane of tongue dorsum
Course - inferior and slightly lateral
Insertion - sides and inferior surface of tongue
Action - flatten tongue
Transverse
Origin - median fibrous septum
Course - lateral
Insertion - submucous fibrous tissue laterally
Action - narrow and elongate tongue
What are the tongues two "skeletal" structures?
fibrous midline septum
connective tissue "bag" just deep to epidermis
What are the extrinsic tongue muscles purpose?
largely responsible for the gross movement of the tongue (front, back, down)
What are the four extrinsic muscles?
Genioglossus
Styloglossus
Hyoglossus
Palatoglossus
What are the intrinsic tongue muscles purpose?
largely responsible for shaping and elevating the tongue
What are the four intrinsic muscles?
Superior Longitudinal Inferior Longitudinal
Vertical
Transverse