EFFECT OF TRAUMA ON DENTITION
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
what are common causes of trauma in the primary dentition (3)
falls
bumping into objects
non-accidental
what are common causes of trauma in the secondary dentition (3)
sport
assault
road traffic accidents (RTA)
primary dentition: which teeth are most commonly affected by trauma
maxillary central incisors
primary dentition: what is the prevalence of trauma
17-54%
primary dentition: are males or females more commonly affected
males = females
primary dentition: at which age is trauma most common
2-4 yrs
primary dentition: what type of trauma is most common
luxation: loosening of tooth involving tooth movement
photo: lateral luxation
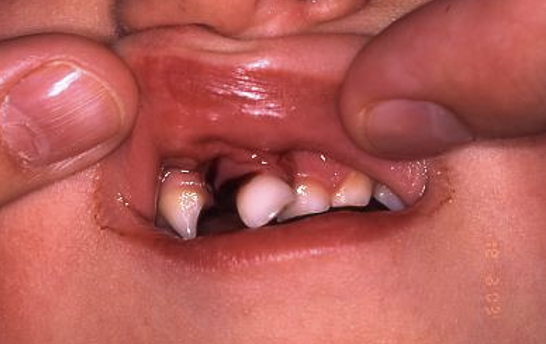
permanent dentition: which teeth are most commonly affected by trauma
maxillary central incisors
permanent dentition: what is the prevalence of trauma
prevalence of trauma in 12yo = 12% (UK)
permanent dentition: are males or females more commonly affected
males > females
sports
violence
crime
permanent dentition: at which age is trauma most common
8-10 years (roots have not fully formed but incisors have erupted so if vitality is compromised then any root treatment is more complex)
permanent dentition: what type of trauma is most common
uncomplicated crown fracture
uncomplicated = not involving pulp
who is the famous author who led the world in dental traumatology research
Andreasen
list the types of tooth fractures in order of increasing severity (6)
enamel infraction
enamel fracture
uncomplicated enamel and dentine fracture
complicated enamel and dentine fracture
crown root fracture - difficult restoration
root fracture - 3 types
diagram of tooth fractures
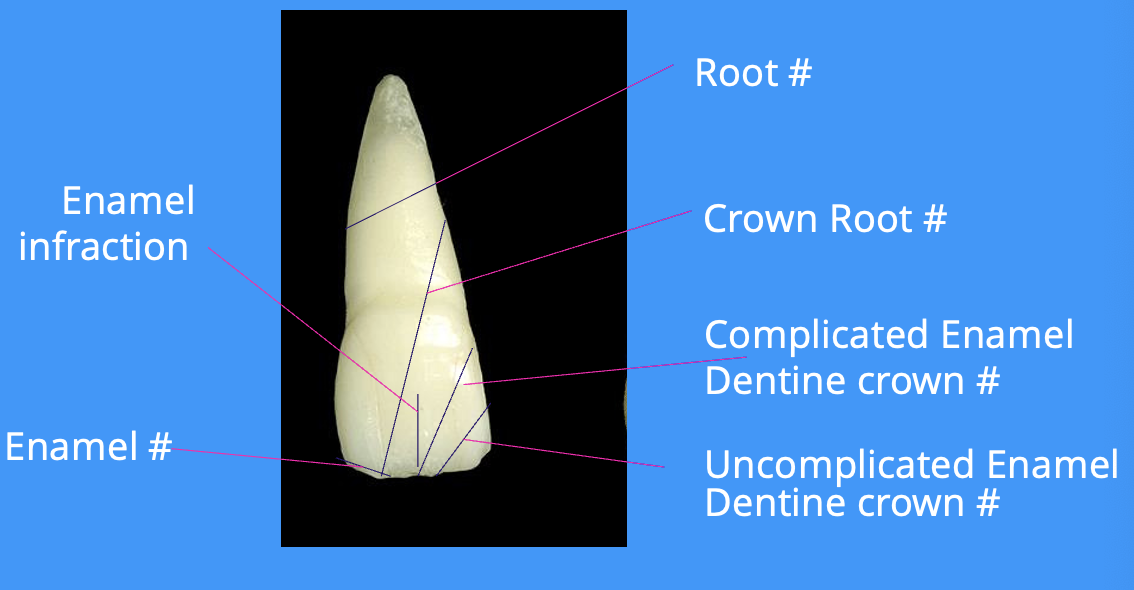
list the types of periodontal tissue injuries (6)
concussion
subluxation
luxation
avulsion
intrusion
extrusion
define the types of periodontal tissue injuries
concussion: tooth accepts a blow, is not responsive to vitality testing
subluxation: loosening of tooth without tooth movement (tooth remains in correct positioning)
luxation: loosening of tooth involving tooth movement
avulsion: tooth has been knocked out of mouth
intrusion: tooth has been pushed inwards
extrusion: tooth has been pulled outwards - almost knocked out
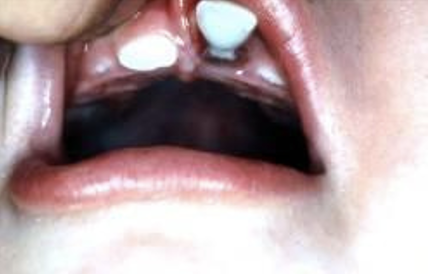
what type of periodontal tissue injury is this
labial luxation
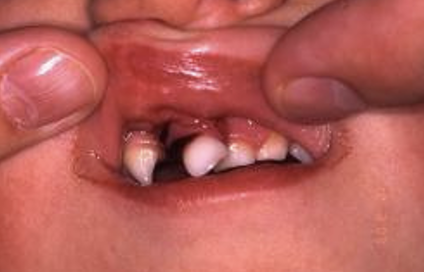
what types of periodontal tissue injury is this
lateral luxation of 51 and avulsion of 52
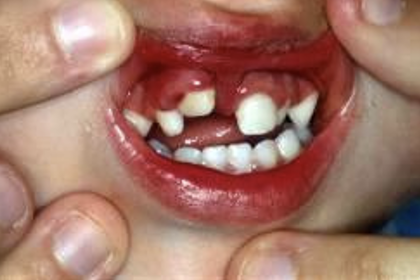
what type of periodontal tissue injury is this
intrusion
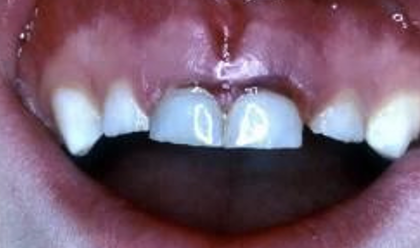
what type of periodontal tissue injury is this
subluxation of 51 and 61

what type of periodontal tissue injury is this
extrusion
list the types of soft tissue injuries (3)
laceration
contusion
abrasion
define the types of soft tissue injuries
laceration: tear in the mucosa
usually caused by a sharp object
contusion: bruise
usually caused by a blunt object
abrasion: rubbing or scraping injury
e.g. face sliding along ground during a fall
what are long term effects of trauma to 1° teeth on 1° teeth (4)
discolouration - can be permanent or can resolve (due to blood seeping into dentinal tubules)
discolouration and infection
resorption and early exfoliation - can happen faster if there is an infection
delayed exfoliation
what are long term effects of trauma to 1° teeth on 2° teeth (3)
enamel defects
abnormal tooth/ root morphology
delayed eruption
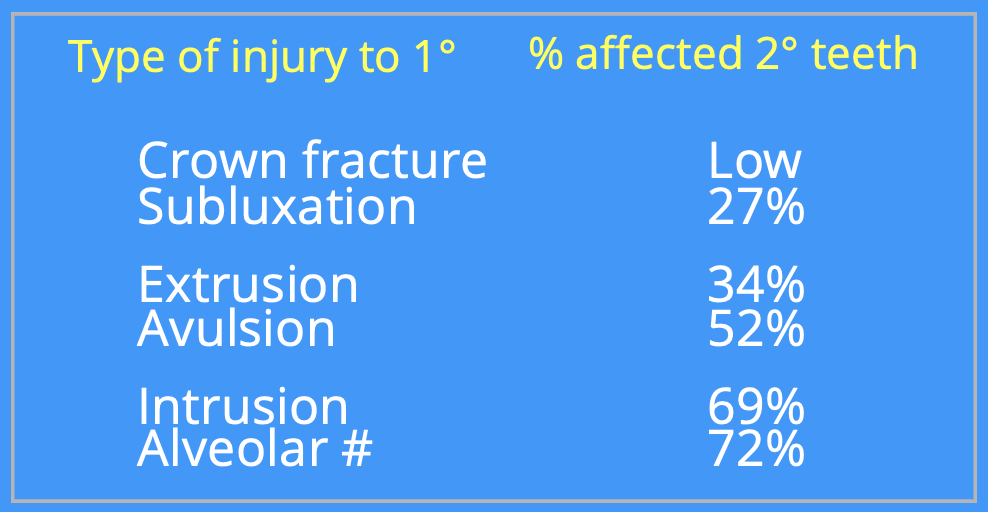
what type of periodontal tissue injury to 1° has the greatest effect on 2° teeth
intrusion
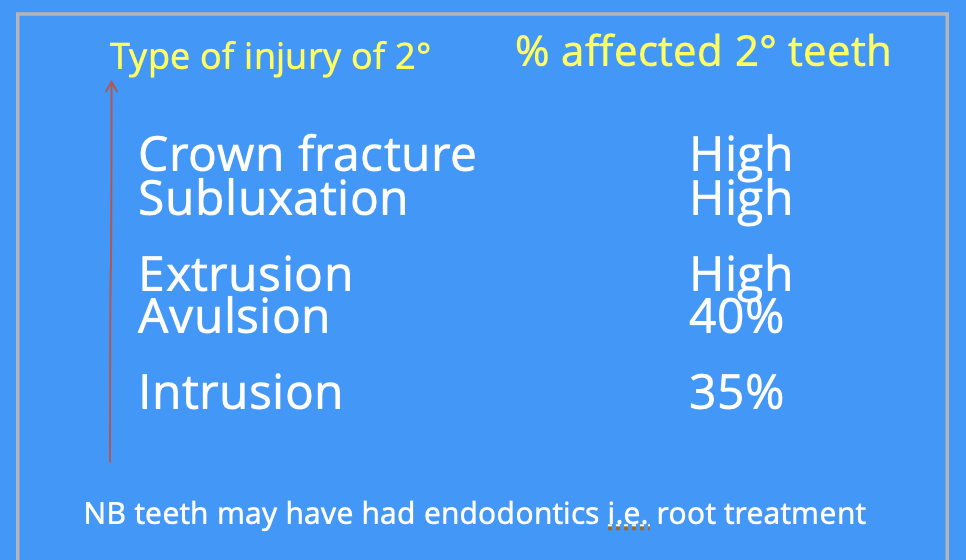
table showing type of injury to 1° and % of affected 2° as a consequence
what do these images show
discolouration due to trauma
no infection indicated in radiograph
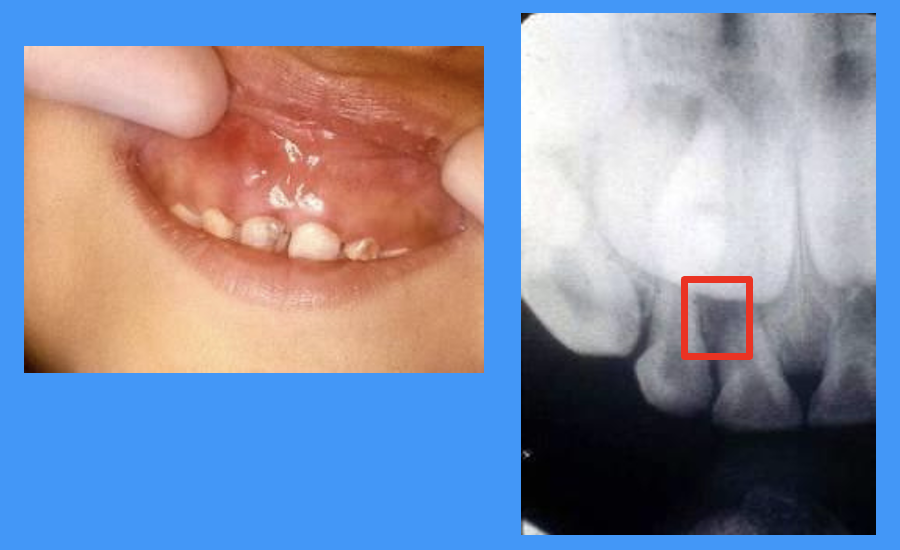
what do these images show
trauma to discoloured tooth with an abscess above
red square = abscess in radiograph
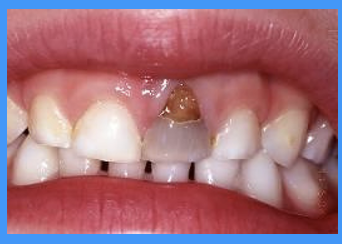
what does this image show
tooth has darkened
non-vital tooth
laceration of gingiva
caries present where the root has been exposed
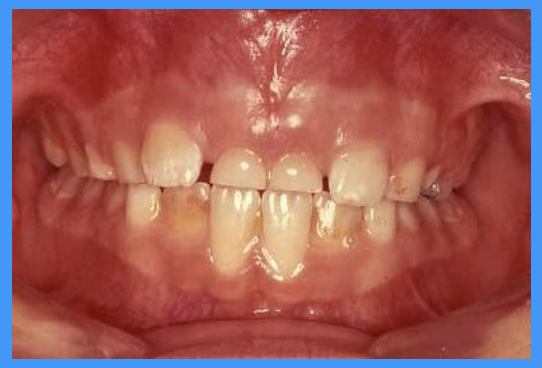
what is discolouration NOT an indication of
discolouration ≠ a non-vital tooth
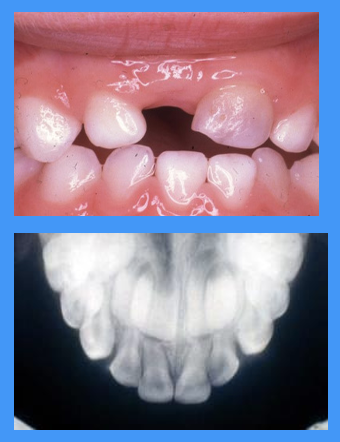
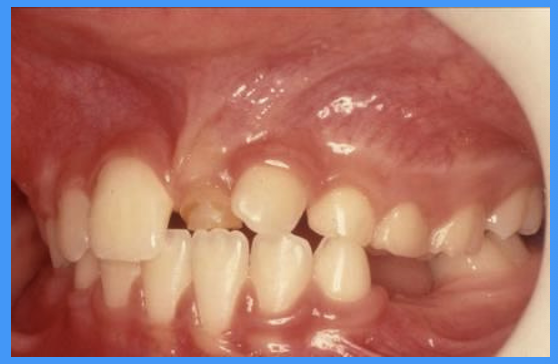
what does this clinical image show
delayed exfoliation
retention of upper central incisors due to trauma
upper lateral, lower central + lateral incisors are all 2°
what does this clinical image show
delayed exfoliation
retention of UL1 due to trauma
what is the solution to retained teeth due to trauma
extract 1° so 2° can erupt
find reason behind why permanent teeth have not erupted
what are other effects of 1° trauma (3)
enamel opacity/ enamel hypoplasia
dilaceration
odontome
outline enamel opacity/ enamel hypoplasia
enamel opacity: enamel is less translucent than normal - visible colour change
enamel hypoplasia: thin/ missing enamel
images of enamel opacity and enamel hypoplasia
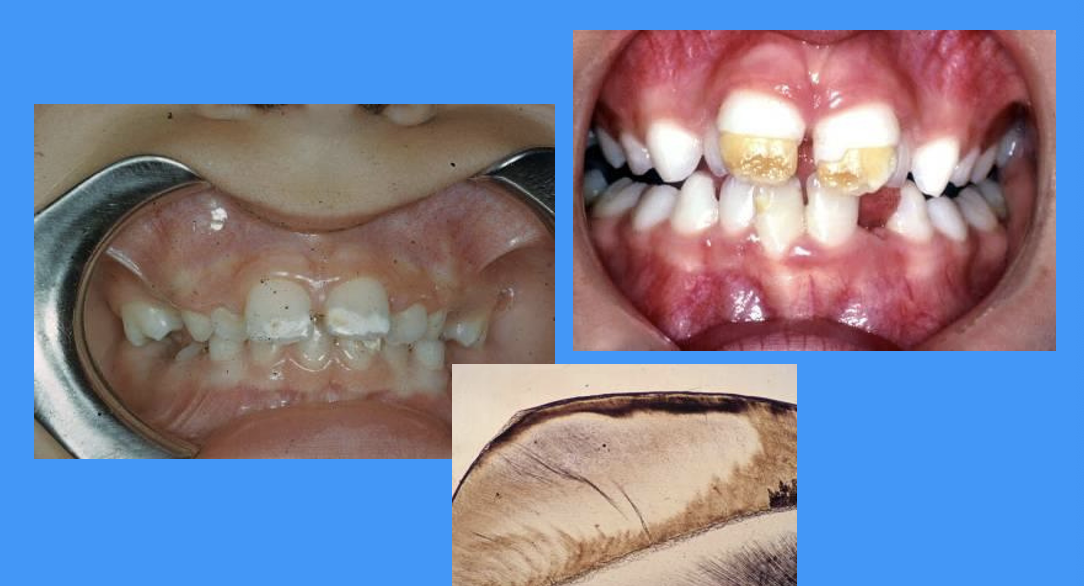
radiograph of enamel hypoplasia
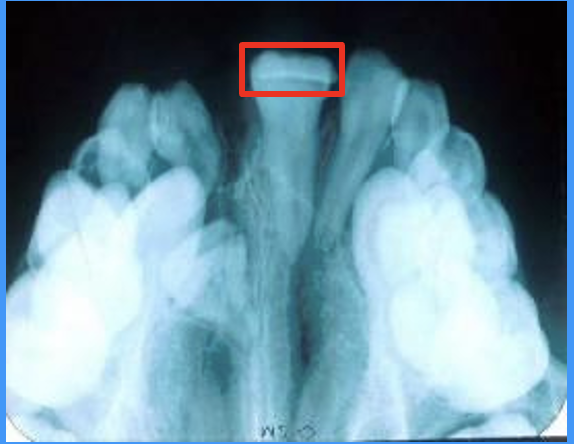
outline dilaceration
dilaceration: abnormal angulation/ bend in the root
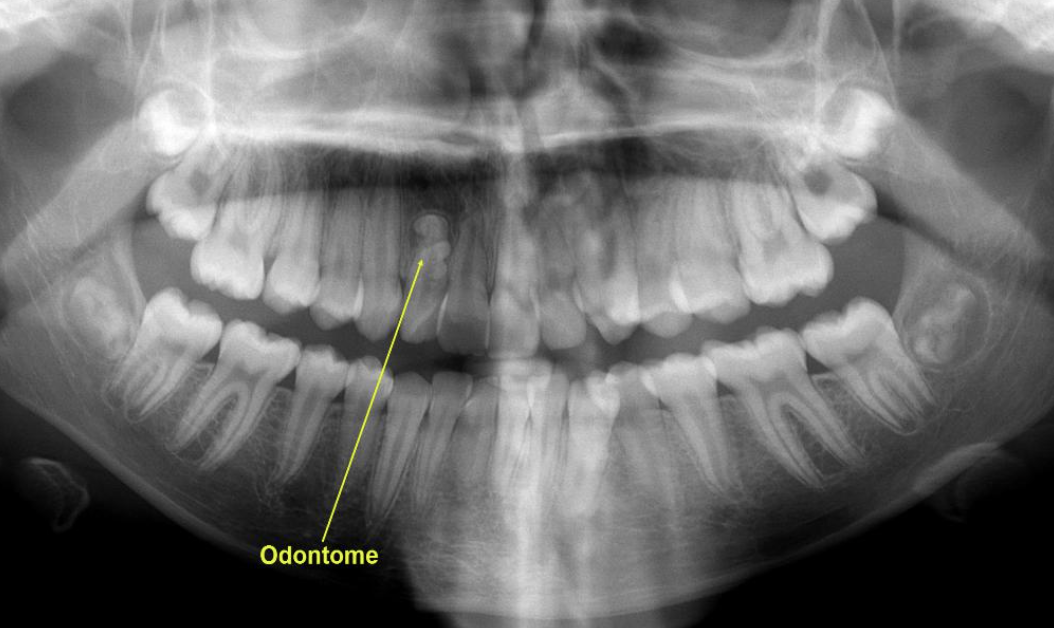
outline odontome
odontome: a benign tooth structure consisting of normal dental tissues that is not actually a tooth
how does the risk of severe damage change with age
the risk of severe damage decreases with age because the older you are the more developed the 2° tooth is
dependent on injury though
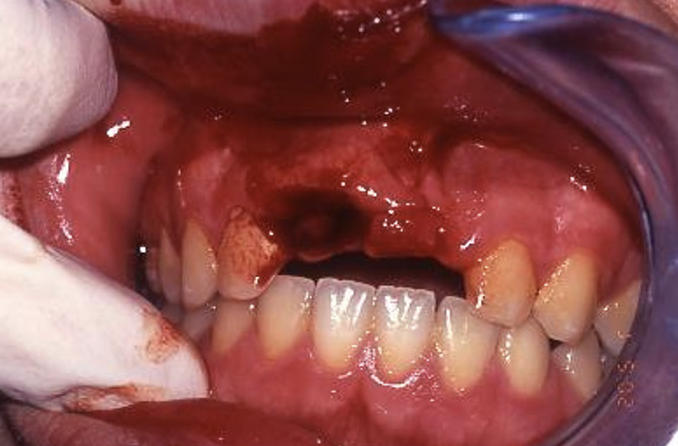
which periodontal tissue injury does this image show
avulsion: tooth has been knocked out of mouth
what are the consequences of trauma to 2° teeth
pulp death » RCT
inflammatory resorption
replacement resorption - bone is laid down
pulpal obliteration
tooth fracture
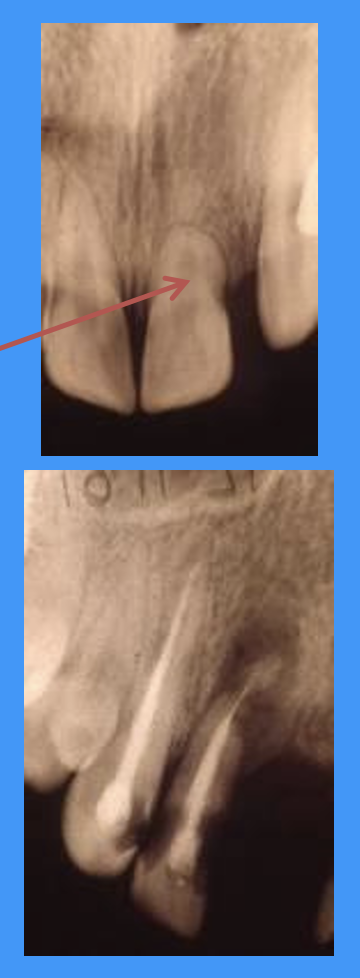
what does the red arrow and bottom radiograph show
red arrow = area of replacement resorption
bottom radiograph = inflammatory resorption (dark area = no bone)
table showing type of injury to 2° and the % of affected 2° teeth as a consequence
what are some implications of dental trauma (4)
pain
distress
costs to patients
money for treatment
time off school/ work
self-esteem
costs to health service
how should an avulsed 2° be managed
emergency management of an avulsed 2° tooth
check if there is another more urgent injury apart from avulsion e.g. head injury characterised by confusion, unconsciousness, nausea, vomiting
tetanus vaccination needed
clean dirt and debris on tooth carefully under running water - DO NOT REMOVE PERIODONTAL TISSUE
re-implant tooth
OR
store in milk until re-implanted
if no milk, use water or get person to dribble over their tooth
DO NOT LET TOOTH DRY OUT
what is the best treatment for dental trauma
PREVENTION!
e.g. wear gum shield during sports