Ch. 8: Emotion and Health
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 8 of Garret 6e Brain and Behavior
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
1
New cards
Affective Aggression
Hostile or violent behavior characterized by impulsiveness and emotional arousal.
2
New cards
Aggression
Forceful or assertive behavior intended to harm or control another individual.
3
New cards
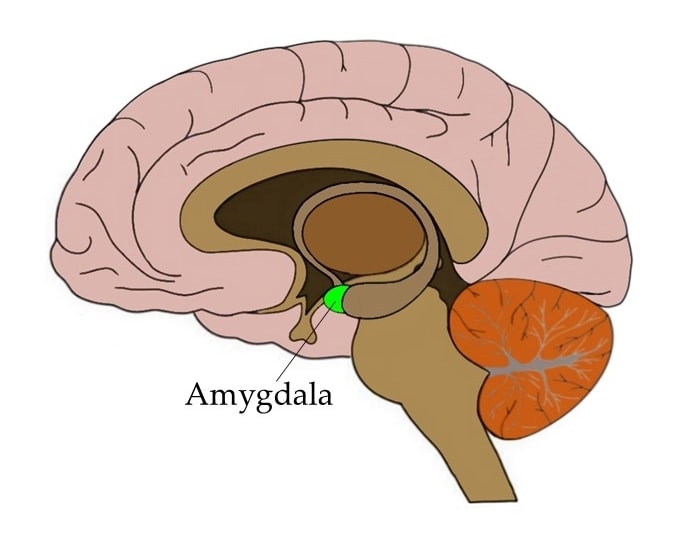
Amygdala
A limbic system structure involved with emotions, especially fear and anxiety, and with sexual behavior, aggression, and learning.
4
New cards
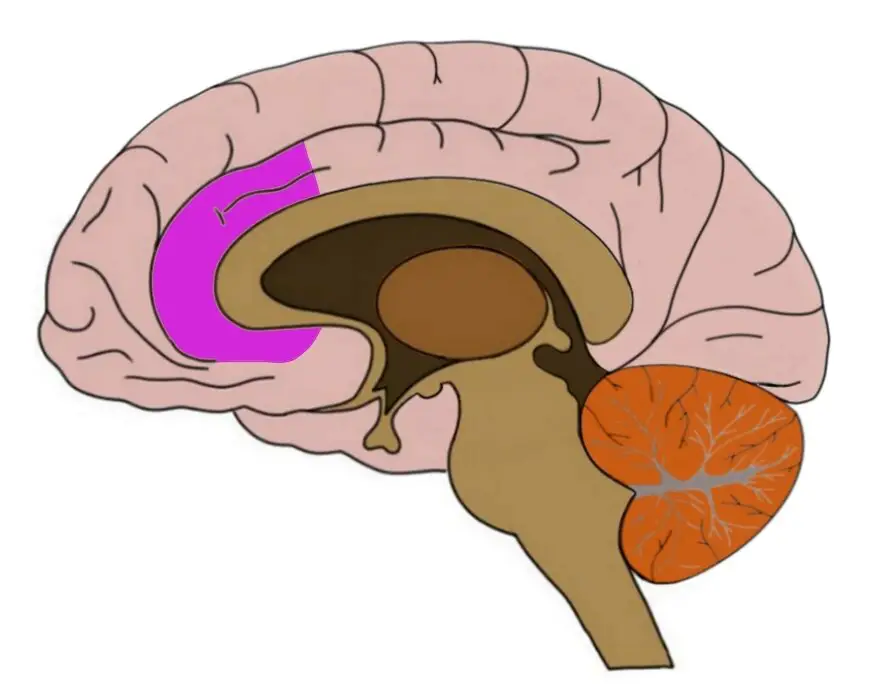
Anterior Cingulate Cortex (ACC)
Part of the limbic system important in attention, decision making, impulse control, emotion, and consciousness.
5
New cards
Autoimmune Disorder
A disorder in which the immune system attacks the body’s own cells.
6
New cards
B Cell
A type of immune cell that fights intruders by producing antibodies.
7
New cards
Cognitive Theory
Theory that states a person identifies an emotion based on a cognitive assessment of the stimulus situation.
8
New cards
Congenital Insensitivity to Pain
A condition present at birth in which the person is insensitive to pain.
9
New cards
Cortisol
A hormone released by the adrenal cortex that produces physiological stress responses.
10
New cards
Emotion
A state of feelings accompanied by physiological activity and often by characteristic facial expression and behavior.
11
New cards
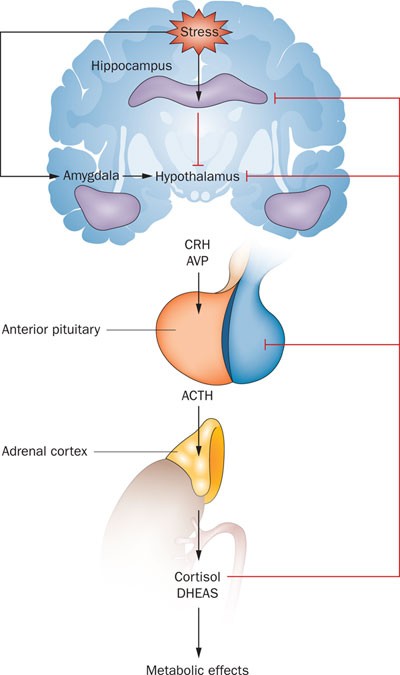
Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
A group of structures that help the body cope with stress.
12
New cards
Immune System
Cells and products that protect the body against foreign substances.
13
New cards
James-Lange Theory
The idea that physiological arousal precedes and causes emotional experience.
14
New cards
Leukocytes
White blood cells, which include macrophages, T cells, and B cells.
15
New cards
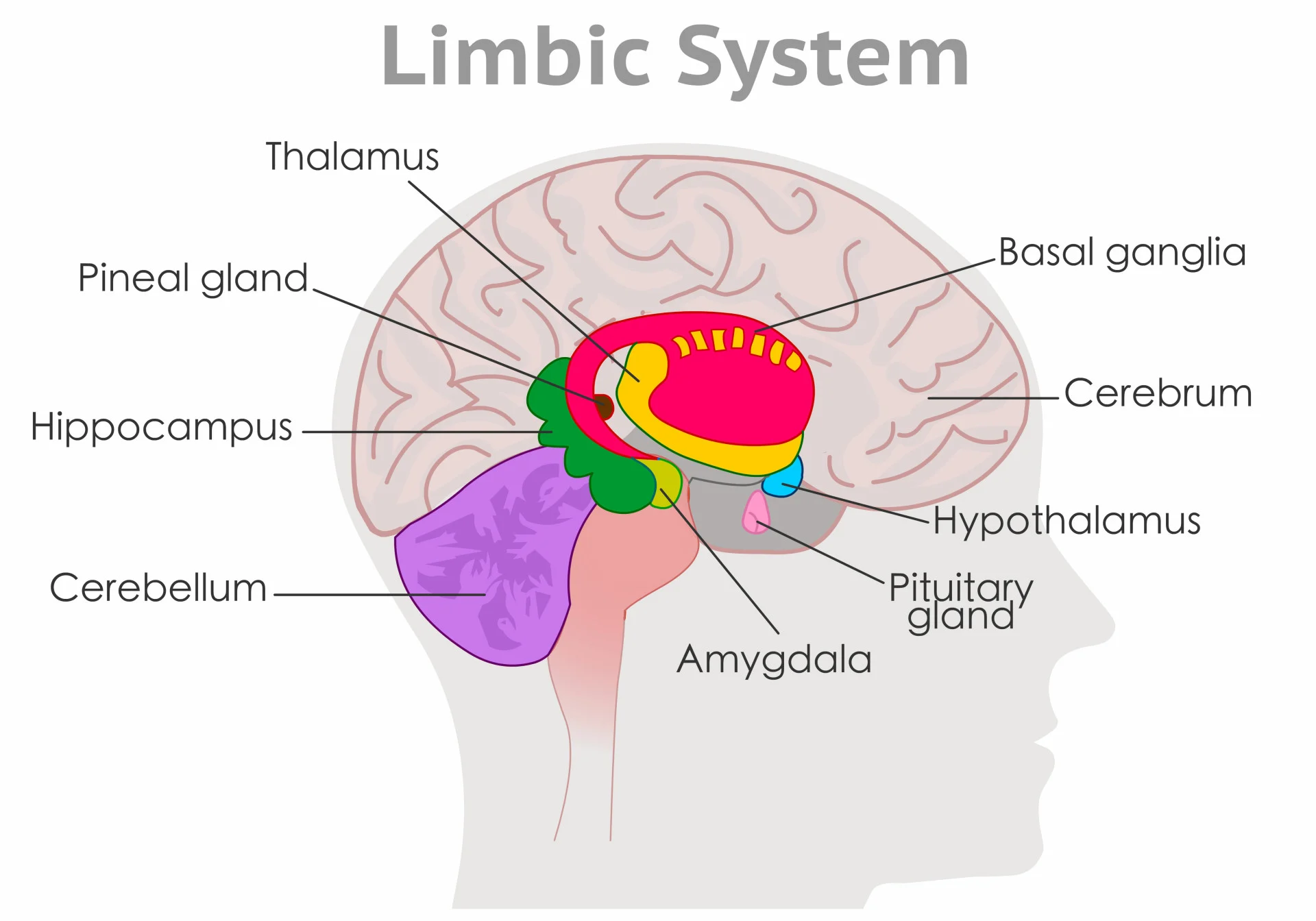
Limbic System
A group of forebrain structures that have roles in emotion, motivated behavior, and learning.
16
New cards
Macrophage
A type of leukocyte that ingests intruders.
17
New cards
Microglia
Glial cells that provide immune protection in the central nervous system.
18
New cards
Mirror Neurons
Cortical neurons that respond to both engaging in and observing an act.
19
New cards
Natural Killer Cell
An immune cell that attacks and destroys certain cancer cells and virus-infected cells.
20
New cards
Predatory Aggression
Hostile behavior in which an animal attacks its prey, or a human engages in a premeditated attack.
21
New cards
Proactive/instrumental Aggression
Emotionless violent behavior intended to gain something for the aggressor.
22
New cards
Reactive/impulsive Aggression
Hostile behavior resulting from a perceived threat, characterized by heightened emotionality.
23
New cards
Skin Conductance Response (SCR)
A measure of sweat gland activation reflecting sympathetic nervous system activity.
24
New cards
Stress
A condition that makes unusual demands on the organism, leading to a negative response.
25
New cards
Sudden Cardiac Death
A fatal event caused by stress leading to excessive sympathetic activity and heart fibrillation.
26
New cards
T Cell
A type of leukocyte that attacks invaders or helps regulate the immune system.